MBASIC Programming Language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
MBASIC is the Microsoft BASIC implementation of
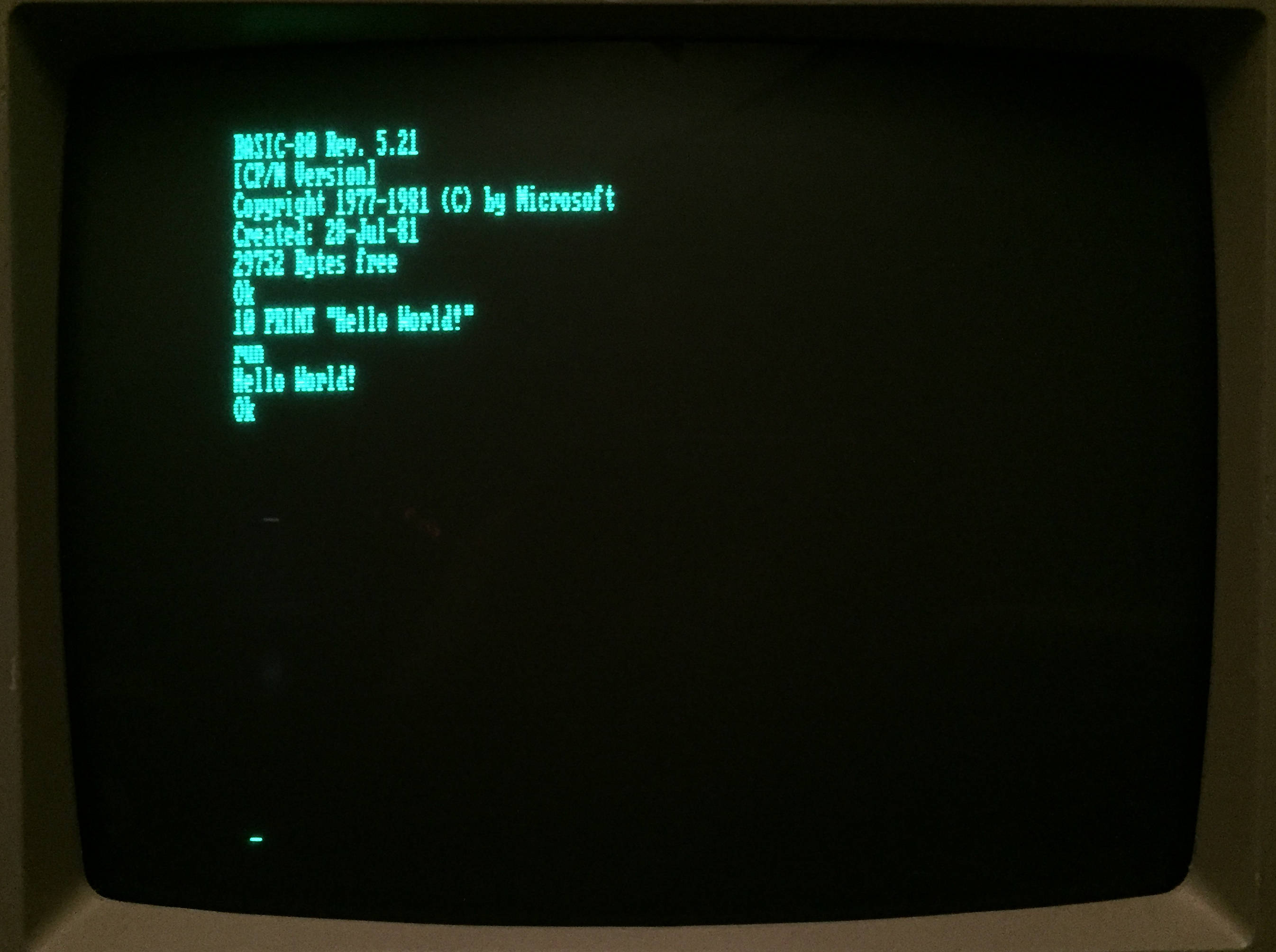 MBASIC version 5 required a CP/M system with at least 28 KB of
MBASIC version 5 required a CP/M system with at least 28 KB of
BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
for the CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/Intel 8085, 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Dig ...
operating system. MBASIC is a descendant of the original Altair BASIC
Altair BASIC is a discontinued interpreter for the BASIC programming language that ran on the MITS Altair 8800 and subsequent S-100 bus computers. It was Microsoft's first product (as Micro-Soft), distributed by MITS under a contract. Altair B ...
interpreters that were among Microsoft's first products. MBASIC was one of the two versions of BASIC bundled with the Osborne 1
The Osborne 1 is the first commercially successful portable computer, released on April 3, 1981 by Osborne Computer Corporation. It weighs , cost US$1,795, and runs the CP/M 2.2 operating system. It is powered from a wall socket, as it has no ...
computer. The name "MBASIC" is derived from the disk file name MBASIC.COM of the BASIC interpreter. MBASIC, like its predecessor family of 8-bit interpreters Microsoft BASIC
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first v ...
, were heavily inspired by Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until ...
PDP-10
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especi ...
's BASIC-PLUS
BASIC-PLUS is an extended dialect of the BASIC programming language that was developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) for use on its RSTS/E time-sharing operating system for the PDP-11 series of 16-bit minicomputers in the early 1970s thro ...
.
Environment
 MBASIC version 5 required a CP/M system with at least 28 KB of
MBASIC version 5 required a CP/M system with at least 28 KB of random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows ...
(RAM) and at least one diskette drive.
Unlike versions of Microsoft BASIC-80
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first ve ...
that were customized by home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers that entered the market in 1977 and became common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a s ...
manufacturers to use the particular hardware features of the computer, MBASIC relied only on the CP/M operating system calls for all input and output. Only the CP/M console (screen and keyboard), line printer
A line printer Printer (computing), prints one entire line of text before advancing to another line. Most early line printers were
printer (computing)#Impact printers, impact printers.
Line printers are mostly associated with unit record eq ...
, and disk devices were available.
MBASIC in the uncustomized form had no functions for graphics
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of the data, as in design and manufa ...
, color, joysticks, mice, serial communications
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits ar ...
, networking, sound, or even a real-time clock
A real-time clock (RTC) is an electronic device (most often in the form of an integrated circuit) that measures the passage of time.
Although the term often refers to the devices in personal computers, server (computing), servers and embedded ...
function. MBASIC did not fully support the features of the host CP/M operating system, for example, it did not support CP/M's user areas for organizing files on a diskette. Since CP/M systems were typically single-user and stand alone, there was no provision for file or record locking, or any form of multitasking. Apart from these limitations, MBASIC was considered at the time to be a powerful and useful implementation of BASIC.
Features
Language system
MBASIC is aninterpreter
Interpreting is translation from a spoken or signed language into another language, usually in real time to facilitate live communication. It is distinguished from the translation of a written text, which can be more deliberative and make use o ...
. Program source text was stored in memory in tokenized form, with BASIC keywords replaced by one-byte tokens which saved memory space and speeded execution. Any line prefixed with a line number was stored as program text; BASIC statements not prefixed with a line number were executed immediately as commands. Programs could be listed on the screen for editing, or saved to disk in either a compressed binary format or as plain ASCII
ASCII ( ), an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for representing a particular set of 95 (English language focused) printable character, printable and 33 control character, control c ...
text. Every source line was identified with a number, which could be used as the target of a GOTO or GOSUB
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
transfer. Only line editing commands were provided.CP/M products providing full-screen editing support required their own installation routines to customize the software for the specific computer terminal
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. Most early computers only had a front panel to input or display ...
used as the system console. No support was provided within CP/M to standardize terminal capabilities. It was often beneficial to save a program as plain text and edit it with a full featured editor.
Program text, variables
Variable may refer to:
Computer science
* Variable (computer science), a symbolic name associated with a value and whose associated value may be changed
Mathematics
* Variable (mathematics), a symbol that represents a quantity in a mathemat ...
, disk buffer
In computer storage, a disk buffer (often ambiguously called a disk cache or a cache buffer) is the embedded memory in a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD) acting as a buffer (computer science), buffer between the rest of the com ...
s and the CP/M operating system itself all had to share the 64 kilobyte address space of the 8080
The Intel 8080 is Intel's second 8-bit microprocessor. Introduced in April 1974, the 8080 was an enhanced successor to the earlier Intel 8008 microprocessor, although without binary compatibility.'' Electronic News'' was a weekly trade newspa ...
processor. Typically when first starting MBASIC there would be less than 32 kB memory available for programs and data, even on a machine equipped with a full 64 kilobytes of RAM. Comment lines, prefixed with the REM keyword or an apostrophe, could be placed in the program text but took up valuable memory space, which discouraged BASIC users from fully documenting their code. To allow larger and more complex programs to be run, later versions of MBASIC supported functions that allowed portions of program text to be read in and executed under program control (the " CHAIN " and MERGE statements). No support for "shell" command execution was provided, though this functionality could be duplicated by a determined programmer.
A particular advantage of MBASIC was the full-text error messages provided for syntax and run-time errors. MBASIC also had a "trace" function that displayed line numbers as they were executed. While this occupied the same screen space as normal program output, it was useful for detecting conditions such as endless loop
In computer programming, an infinite loop (or endless loop) is a sequence of instructions that, as written, will continue endlessly, unless an external intervention occurs, such as turning off power via a switch or pulling a plug. It may be inte ...
s.
Files and input/output
Data could be read and stored to disk as either sequential files (delimited by the CP/M convention of CR/ LF at the end of each line) or else as fixed-record-length random access files, which, given a sufficiently determined programmer, could be used to perform database-type record manipulation. TheMicrosoft Binary Format
In computing, Microsoft Binary Format (MBF) is a format for floating-point numbers which was used in Microsoft's BASIC languages, including MBASIC, GW-BASIC and QuickBASIC prior to version 4.00.
There are two main versions of the format. The or ...
for floating point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some base) multiplied by an integer power of that base.
Numbers of this form ...
numbers was proprietary to the implementation, which meant that data could only be interchanged with other programs using ASCII text representation or else with extensive programming to convert the binary format.
Variables and data types
MBASIC supported the following data types: * 8-bit character data, in strings of length 0 to 255 characters; * 16-bitinteger
An integer is the number zero (0), a positive natural number (1, 2, 3, ...), or the negation of a positive natural number (−1, −2, −3, ...). The negations or additive inverses of the positive natural numbers are referred to as negative in ...
s;
* 32-bit floating point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some base) multiplied by an integer power of that base.
Numbers of this form ...
(single precision), equivalent to six decimal digits, with a two-digit exponent;
* 64-bit floating point (double precision), equivalent to sixteen decimal digits, with a two-digit exponent.
String operators included substring selection, concatenation, assignment, and testing for equality.
Arrays of the above types were allowed with up to 7 dimensions, but no functions or operators worked on arrays; for example, there was no assignment of arrays. Unlike some other BASIC implementations of the time, MBASIC did not provide support for matrix
Matrix (: matrices or matrixes) or MATRIX may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Matrix (mathematics), a rectangular array of numbers, symbols or expressions
* Matrix (logic), part of a formula in prenex normal form
* Matrix (biology), the m ...
operations, complex number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the for ...
s, or a decimal (BCD) data type for financial calculations. All floating point operations were carried out in software since typical CP/M systems did not have floating point hardware. The built-in mathematics functions ( sine, cosine, tangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points o ...
, natural log
The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant , which is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to . The natural logarithm of is generally written as , , or sometimes, if ...
, exponential
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including:
* Exponential function, also:
**Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above
*Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value
* Ex ...
, square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number is a number such that y^2 = x; in other words, a number whose ''square'' (the result of multiplying the number by itself, or y \cdot y) is . For example, 4 and −4 are square roots of 16 because 4 ...
) only gave single precision results. A software pseudorandom number generator
A pseudorandom number generator (PRNG), also known as a deterministic random bit generator (DRBG), is an algorithm for generating a sequence of numbers whose properties approximate the properties of sequences of random number generation, random n ...
was provided; this relied on the user to key in a seed number to obtain a sequence of numbers useful for games and some simulations. MBASIC permitted but did not require the LET keyword for assignment statements.
Early versions of BASIC on microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (P ...
s were infamous for one- or two-character variable names, which made the meanings of variables difficult to recall in complex programs. MBASIC version 5 allowed identifiers up to 40 characters long, which permitted programmers to give variables readable names.
Program flow control
Program flow control in MBASIC was controlled by IF...THEN...ELSE... conditional tests, WHILE...WEND loops, and GOTO and GOSUB instructions. No CASE statement was available, although an ON...GOTO... (computed GOTO) provided multi-way branches. Subroutines had no parameters and all variables were global. MBASIC did not make structured programming Structured programming is a programming paradigm aimed at improving the clarity, quality, and development time of a computer program by making specific disciplined use of the structured control flow constructs of selection ( if/then/else) and repet ...
mandatory for programmers and it was easy to write spaghetti code
Spaghetti code is a pejorative phrase for difficult-to- maintain and unstructured computer source code. Code being developed with poor structure can be due to any of several factors, such as volatile project requirements, lack of programming style ...
.
PEEKs, POKEs, and user functions
No discussion of BASICs on the8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data bu ...
computers of the late '70s and early '80s would be complete without mentioning the importance of the PEEK and POKE
In computing, PEEK and POKE are commands used in some high-level programming languages for accessing the contents of a specific Memory cell (computing), memory cell referenced by its memory address. PEEK gets the byte located at the specified m ...
functions for directly reading and writing to memory. Since these systems typically had no memory protection
Memory protection is a way to control memory access rights on a computer, and is a part of most modern instruction set architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that h ...
, this allowed a programmer to access portions of the operating system, or functions that would not otherwise be available. This also provided opportunities for user programs to hang the system (by accident, usually). For example, a CP/M programmer might use a POKE function to allow BASIC to switch the console device to the serial port, if the system BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is a type of firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization d ...
supported this. For machines with real-time clocks, a set of PEEK instructions might have been used to access the time.
For more complex operations, MBASIC allowed user-defined functions that could be called from a BASIC program. These were typically placed in a reserved area of memory, or POKEd into string constants, as a series of machine codes ( opcodes). MBASIC also provided hardware INP and OUT instructions that read and wrote directly to the 8080 hardware input/output ports. This could be used to control peripheral devices from a BASIC program if the system hardware permitted.
Any MBASIC programs that made use of PEEK and POKE, and of machine code user functions, were not portable between machines without modifications.
Successors to MBASIC
Besides Microsoft's BASIC-80 for CP/M, a variant of MBASIC was also available as for the ISIS-II operating system. MSX-BASIC is also a well known successor of MBASIC, featuring several extensions specific to theMSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, the director at ASCII Corpo ...
machines.
All the functions of CP/M MBASIC were available in the IBM PC disk-based BASICA or GWBASIC which made migration of programs from CP/M systems to PC-compatibles possible. The tokens used to represent keywords were different, so CP/M programs had to be saved in ASCII source form. Typically screen formatting escape sequences put into the CP/M version would be replaced with the cursor positioning commands found in the PC versions of BASIC, otherwise little rewriting would be needed.
BASCOM
Microsoft sold a CP/M BASICcompiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
(known as BASCOM) which used a similar source language to MBASIC. A program debugged under MBASIC could be compiled with BASCOM. Since program text was no longer in memory and the run-time elements of the compiler were smaller than the interpreter, more memory was available for user data. Speed of real program execution increased about 3 fold.
Developers welcomed BASCOM as an alternative to the popular but slow and clumsy CBASIC. Unlike CBASIC, BASCOM did not need a preprocessor
In computer science, a preprocessor (or precompiler) is a Computer program, program that processes its input data to produce output that is used as input in another program. The output is said to be a preprocessed form of the input data, which i ...
for MBASIC source code so could be debugged interactively. While approving of its superior edit-compile-run-debug loop compared to CBASIC, and stating that binaries ran far faster, Jerry Pournelle
Jerry Eugene Pournelle (; August 7, 1933 – September 8, 2017) was an American scientist in the area of operations research and ergonomics, human factors research, a science fiction writer, essayist, journalist, and one of the first bloggers. ...
in December 1980 denounced Microsoft's requirement of a 9% royalty for each binary copy and $40 for hardware-software combinations. The company also reserved the right to audit developers' financial records. Because authors' typical royalty rates for software was 10-25%, ''InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (''IW'') is an American information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a Web-only publication. Its parent company is International Data Group, and its sister pu ...
'' in 1980 stated that BASCOM's additional 9% royalty rate "could make software development downright unprofitable", concluding that "Microsoft has the technical solution o CBASIC's flaws but not the economic one".
Importance of MBASIC
MBASIC was an important tool during the era of 8-bit CP/M computers. Skilled users could write routines in MBASIC to automate tasks that in modern-day systems would be performed by powerful application program commands or scripting languages. Exchange of useful MBASIC programs was a common function of computerusers' group
A users' group (also user's group or user group) is a type of club focused on the use of a particular technology, usually (but not always) computer-related.
Overview
Users' groups started in the early days of mainframe computers, as a way to sh ...
s. Keying in long BASIC listings from a magazine article was one way of "bootstrapping" software into a new CP/M system. At least one compiler for a high-level language was written in MBASIC, and many small games and utility programs ranging from a few lines to a few thousand lines of code were written.
Other uses
MBASIC is also the name of a commercialBASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to:
Science and technology
* BASIC, a computer programming language
* Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base
* Basic access authentication, in HTTP
Entertainment
* Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film
...
compiler for the Microchip Technology
Microchip Technology Incorporated is a publicly listed American semiconductor corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits.
Its corporate headquarters is located in Chandler, Arizona. ...
PIC microcontroller
PIC (usually pronounced as /pɪk/) is a family of microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1640 originally developed by General Instrument's Microelectronics Division. The name PIC initially referred to ''Peripher ...
family developed by Basic Micro, Inc., unrelated to the CP/M interpreter.
References
* Thom Hogan and Mike Iannamico, ''Osborne 1 User's Reference Guide'',(1982) Osborne Computer Corporation * David A. Lien, ''The BASIC Handbook'', 2nd Edition Encyclopedia of the BASIC Computer Language",(1981), Compusoft Publishing * ''BASIC 80 Reference Manual'', Microsoft Corporation, no date {{BASIC CP/M software Discontinued Microsoft BASICs BASIC programming language family Microsoft programming languages