|
BASICA
The IBM Personal Computer Basic, commonly shortened to IBM BASIC, is a programming language first released by IBM with the IBM Personal Computer, Model 5150 (IBM PC) in 1981. IBM released four different versions of the Microsoft BASIC interpreter, licensed from Microsoft for the PC and PCjr. They are known as Cassette BASIC, Disk BASIC, Advanced BASIC (BASICA), and Cartridge BASIC. Versions of Disk BASIC and Advanced BASIC were included with IBM PC DOS up to PC DOS 4. In addition to the features of an ANSI standard BASIC, the IBM versions offered support for the graphics and sound hardware of the IBM PC line. Source code could be typed in with a full-screen editor, and very limited facilities were provided for rudimentary program debugging. IBM also released a version of the Microsoft BASIC compiler for the PC, concurrently with the release of PC DOS 1.10 in 1982. Background IBM licensed Microsoft BASIC for the IBM Personal Computer, despite already having its own version of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GW-BASIC
GW-BASIC is a dialect of the BASIC programming language developed by Microsoft from IBM BASICA. Functionally identical to BASICA, its BASIC interpreter is a fully self-contained executable and does not need the Cassette BASIC ROM found in the original IBM PC. It was bundled with MS-DOS operating systems on IBM PC compatibles by Microsoft. The language is suitable for simple games, business programs and the like. Since it was included with most versions of MS-DOS, it was also a low-cost way for many aspiring programmers to learn the fundamentals of computer programming. Microsoft also sold a BASIC compiler, BASCOM, compatible with GW-BASIC, for programs needing more speed. According to Mark Jones Lorenzo, given the scope of the language, "GW-BASIC is arguably the ''List_of_Latin_phrases_(N)#ne_plus_ultra, ne plus ultra'' of Microsoft's family of line-numbered BASICs stretching back to Altair BASIC and perhaps even of line-numbered BASIC in general." With the release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft BASIC
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer. During the home computer craze during the late-1970s and early-1980s, BASIC was ported to and supplied with many home computer designs. Slight variations to add support for machine-specific functions, especially graphics, led to a profusion of related designs like Commodore BASIC and Atari Microsoft BASIC. As the early home computers gave way to newer designs like the IBM Personal Computer and Apple Macintosh, BASIC was no longer as widely used, although it retained a strong following. The release of Visual Basic reboosted its popularity and it remains in wide use on Microsoft Windows platforms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
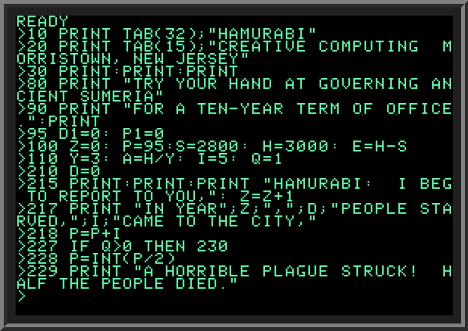
BASIC
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College in 1963. They wanted to enable students in non-scientific fields to use computers. At the time, nearly all computers required writing custom software, which only scientists and mathematicians tended to learn. In addition to the program language, Kemeny and Kurtz developed the Dartmouth Time Sharing System (DTSS), which allowed multiple users to edit and run BASIC programs simultaneously on remote terminals. This general model became very popular on minicomputer systems like the PDP-11 and Data General Nova in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Hewlett-Packard produced an entire computer line for this method of operation, introducing the HP2000 series in the late 1960s and continuing sales into the 1980s. Many early video games trace their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC Interpreter
A BASIC interpreter is an interpreter that enables users to enter and run programs in the BASIC language and was, for the first part of the microcomputer era, the default application that computers would launch. Users were expected to use the BASIC interpreter to type in programs or to load programs from storage (initially cassette tapes then floppy disks). BASIC interpreters are of historical importance. Microsoft's first product for sale was a BASIC interpreter (Altair BASIC), which paved the way for the company's success. Before Altair BASIC, microcomputers were sold as kits that needed to be programmed in machine code (for instance, the Apple I). During the Altair period, BASIC interpreters were sold separately, becoming the first software sold to individuals rather than to organizations; Apple BASIC was Apple's first software product. After the MITS Altair 8800, microcomputers were expected to ship bundled with BASIC interpreters of their own (e.g., the Apple II, which had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Personal Computer XT
The IBM Personal Computer XT (model 5160, often shortened to PC/XT) is the second computer in the IBM Personal Computer line, released on March 8, 1983. Except for the addition of a built-in hard drive and extra expansion slots, it is very similar to the original IBM PC model 5150 from 1981. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of "XT" on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some publications expanded the term as "''eXtended Technology''" or just "''eXTended''". Features The XT was regarded as an incremental improvement over the PC and a disappointment compared to the next-generation successor that some had anticipated. Compared to the original IBM PC, the XT has the following major differences: * The number of expansion slots is increased from five to eight * Base RAM is increased to at least 128 KB * 2x32KB ROM ICs replace the previous 6x8KB ROM ICs * A 10 MB hard drive is included as standard equipment * PC DOS 2.0 is included * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Personal System/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM PC, XT, AT, and PC Convertible in IBM's lineup. Many of the PS/2's innovations, such as the 16550 UART (serial port), 1440 KB 3.5-inch floppy disk format, 72-pin SIMMs, the PS/2 port, and the VGA video standard, went on to become standards in the broader PC market. The PS/2 line was created by IBM partly in an attempt to recapture control of the PC market by introducing the advanced yet proprietary Micro Channel architecture (MCA) on higher-end models. These models were in the strange position of being incompatible with the IBM-compatible hardware standards previously established by IBM and adopted in the PC industry. However, IBM's initial PS/2 computers were popular with target market corporate buyers, and by September 1988 IBM reported that it had sold 3 million PS/2 machines. This was only 18 months after the new range had been introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Cassette Tape
The original IBM Personal Computer and IBM PCjr included support for storing data and programs on compact cassette tape. It was common for home computers of the time, such as the Apple II, Commodore 64 and BBC Micro, to use cassette tapes for storage due to the lower cost of hardware and media compared to floppy disks. A wide range of commercial home computer software was available on tape throughout the 80s. The IBM PC cassette format did not experience the same popularity however, since very few were shipped without at least one floppy disk drive, and apart from one diagnostic tape available from IBM, there seems never to have been any software sold on tape, and the interface was not included on the followup PC XT. Despite this lack of popularity, up until the original PC's discontinuation in 1987, IBM continued to offer a Model 104 which shipped without a floppy disk drive. The IBM PCjr was also seldom sold without a floppy disk drive, but it also had two ROM cartridge sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks, CD-RWs, DVD-RWs and the older magnetic tapes and drum memory), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. RAM contains multiplexing and demultiplexing circuitry, to connect the data lines to the addressed storage for reading or writing the entry. Usually more than one bit of storage is accessed by the same address, and RAM devices often have multiple data lines and are said to be "8-bit" or "16-bit", etc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compaq Portable
The Compaq Portable was an early portable computer which was one of the first IBM PC compatible systems. It was Compaq Computer Corporation's first product, to be followed by others in the Compaq Portable series and later Compaq Deskpro series. It was not simply an 8088-CPU computer that ran a Microsoft DOS as a PC "work-alike", but contained a reverse-engineered BIOS, and a version of MS-DOS that was so similar to IBM's PC DOS that it ran nearly all its application software. The computer was also an early variation on the idea of an " all-in-one". It became available two years after the similar, but CP/M-based, Osborne 1 and Kaypro II. Columbia Data Products' MPC 1600 "Multi Personal Computer" had come out in June 1982. Other "work-alikes" included the MS-DOS and 8088-based, but not entirely IBM PC software compatible, Dynalogic Hyperion, Eagle Computer's Eagle 1600 series, including the Eagle Spirit portable, and the Corona personal computer The latter two compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC Compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones. The term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, since IBM no longer sells personal computers after it sold its personal computer division in 2005 to Chinese technology company Lenovo. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "personal computer" generally, but rather an x86 computer capable of running the same software that a contemporary IBM PC could. The term was initially in contrast to the variety of home computer systems available in the early 1980s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore 64. Later, the term was primarily used in contrast to Apple's Macintosh computers. These "clones" duplicated almost all the significant features of the original IBM PC architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a button or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system. Restarting a computer also is called Reboot (computing), rebooting, which can be "hard", e.g. after electrical power to the CPU is switched from off to on, or "soft", where the power is not cut. On some systems, a soft boot may optionally clear RAM to zero. Both hard and soft booting can be initiated by hardware such as a button press or by a software command. Booting is complete when the operative runtime system, typically the operating system and some applications,Including Daemon (computing), daemons. is attained. The process of returning a computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_b.jpg)