Löwenstein–Jensen medium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Löwenstein–Jensen medium, more commonly known as LJ medium, is a
 * For diagnosis of mycobacterial infections
* For testing antibiotic susceptibility of isolates
* For differentiating different species of ''Mycobacterium'' (by colony morphology, growth rate, biochemical characteristics, and microscopy)
* For diagnosis of mycobacterial infections
* For testing antibiotic susceptibility of isolates
* For differentiating different species of ''Mycobacterium'' (by colony morphology, growth rate, biochemical characteristics, and microscopy)
growth medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Differe ...
specially used for culture of ''Mycobacterium
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (''Mycobacterium tuberculo ...
'' species, notably ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
''.
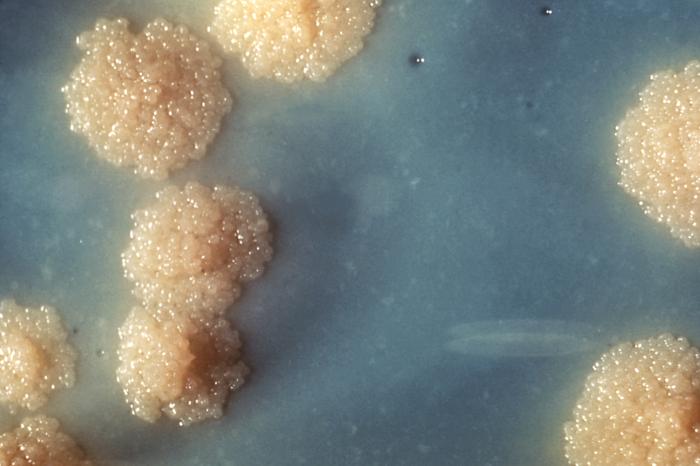
When grown on LJ medium, ''M. tuberculosis'' appears as brown, granular colonies (sometimes called "buff, rough and tough"). The medium must be incubated for a significant length of time, usually four weeks, due to the slow doubling time of ''M. tuberculosis'' (15–20 hours) compared with other bacteria.
The medium is named after the Austrian pathologist Ernst Löwenstein (1878–1950) and the Danish medical doctor Kai Adolf Jensen (16.7.1894-2.5.1971).
Composition
The usual composition as applicable to ''M. tuberculosis'' is: *Malachite green
Malachite green is an organic compound that is used as a dyestuff and controversially as an antimicrobial in aquaculture. Malachite green is traditionally used as a dye for materials such as silk, leather, and paper. Despite its name the dye is ...
* Glycerol
Glycerol () is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, sweet-tasting, viscous liquid. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pha ...
* Asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
* Potato starch
Potato starch is starch extracted from potatoes. The cells of the root tubers of the potato plant contain leucoplasts (starch grains). To extract the starch, the potatoes are crushed, and the starch grains are released from the destroyed cells. Th ...
* Coagulated eggs
* Mineral salt solution
** Potassium dihydrogen phosphate
Monopotassium phosphate (MKP) (also, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, KDP, or monobasic potassium phosphate) is the inorganic compound with the formula KH2PO4. Together with dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4.(H2O)x) it is often used as a fertilizer, ...
** Magnesium sulfate
Magnesium sulfate or magnesium sulphate is a chemical compound, a salt with the formula , consisting of magnesium cations (20.19% by mass) and sulfate anions . It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in water but not in ethanol.
Magnesi ...
** Sodium citrate Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citric acid (though most commonly the third):
* Monosodium citrate
* Disodium citrate
* Trisodium citrate
The three forms of salt are collectively known by the E number E331.
Applications
...
The original formulation included starch, which was later found to be unnecessary, so omitted.
Low levels of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
and nalidixic acid
Nalidixic acid (tradenames Nevigramon, NegGram, Wintomylon and WIN 18,320) is the first of the synthetic quinolone antibiotics.
In a technical sense, it is a naphthyridone, not a quinolone: its ring structure is a 1,8-naphthyridine nucleus that ...
are also present in LJ medium to inhibit growth of Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
and Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
, to limit growth to ''Mycobacterium'' species only. Presence of malachite green in the medium inhibits most other bacteria. It is disinfected and solidified by a process of inspissation. Presence of glycerol enhances the growth of ''M. tuberculosis''.
If the slopes are made on test tubes, they must be stored in cold and used within a month.
For cultivation of '' M. bovis'', glycerol is omitted and sodium pyruvate is added.
The medium appears green, opaque, and opalescent.
Uses
 * For diagnosis of mycobacterial infections
* For testing antibiotic susceptibility of isolates
* For differentiating different species of ''Mycobacterium'' (by colony morphology, growth rate, biochemical characteristics, and microscopy)
* For diagnosis of mycobacterial infections
* For testing antibiotic susceptibility of isolates
* For differentiating different species of ''Mycobacterium'' (by colony morphology, growth rate, biochemical characteristics, and microscopy)
Alternatives
Alternative culture media
While LJ medium is the most popular means of culturing mycobacteria, as recommended by the International Union against Tuberculosis, several alternative media have been investigated.Solid media
* Egg-based – Petragnani medium and Dorset medium *Middlebrook 7H10 agar
Middlebrook 7H10 Agar is a solid growth medium specially used for culture of ''Mycobacterium'', notably ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. It has been reported that the 7H10 medium tends to grow fewer contaminants than the egg-based media commonly use ...
* Middlebrook 7H11 agar
* Blood-based – Tarshis medium
* Serum-based – Loeffler medium
* Potato-based – Pawlowsky medium
Liquid media
* Dubos' medium * Middlebrook 7H9 broth * Proskauer and Beck's medium * Sula's medium * Sauton's mediumRapid detection techniques
The chief limitation of culture-based techniques is the time it takes to culture positivity, which can be several months. Several new molecular technologies have emerged in recent years to secure more speedy confirmation of diagnosis. *Polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed st ...
* GeneXpert MTB/RIF
* Loop-mediated isothermal amplification
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is a single-tube technique for the amplification of DNA for diagnostic purposes and a low-cost alternative to detect certain diseases. LAMP is an isothermal nucleic acid amplification technique. In c ...
See also
*Kinyoun stain
The Kinyoun method or Kinyoun stain (cold method), developed by Joseph J. Kinyoun, is a procedure used to stain acid-fast species of the bacterial genus ''Mycobacterium''. It is a variation of a method developed by Robert Koch in 1882. Certain spe ...
* Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
* Tuberculosis diagnosis
Tuberculosis is diagnosed by finding ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' bacteria in a clinical specimen taken from the patient. While other investigations may strongly suggest tuberculosis as the diagnosis, they cannot confirm it.
A complete medi ...
* Ziehl-Neelsen stain
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lowenstein-Jensen medium Microbiological media