List Of Constituencies Of The Lok Sabha on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The




































Members of the Lok SabhaLok Sabha elections results live 2019Lok Sabha ElectionsLIST OF CONTESTING CANDIDATES IN ASSEMBLY CONSTITUENCIES OF PHASE-1Candidate Affidavits for Lok Sabha 2009 ElectionList of all Lok Sabha Constituencies in India
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Constituencies Of The Lok Sabha *
 The
The Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-p ...
, the lower house of the Parliament of India
The Parliament of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of ...
, is made up of Members of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
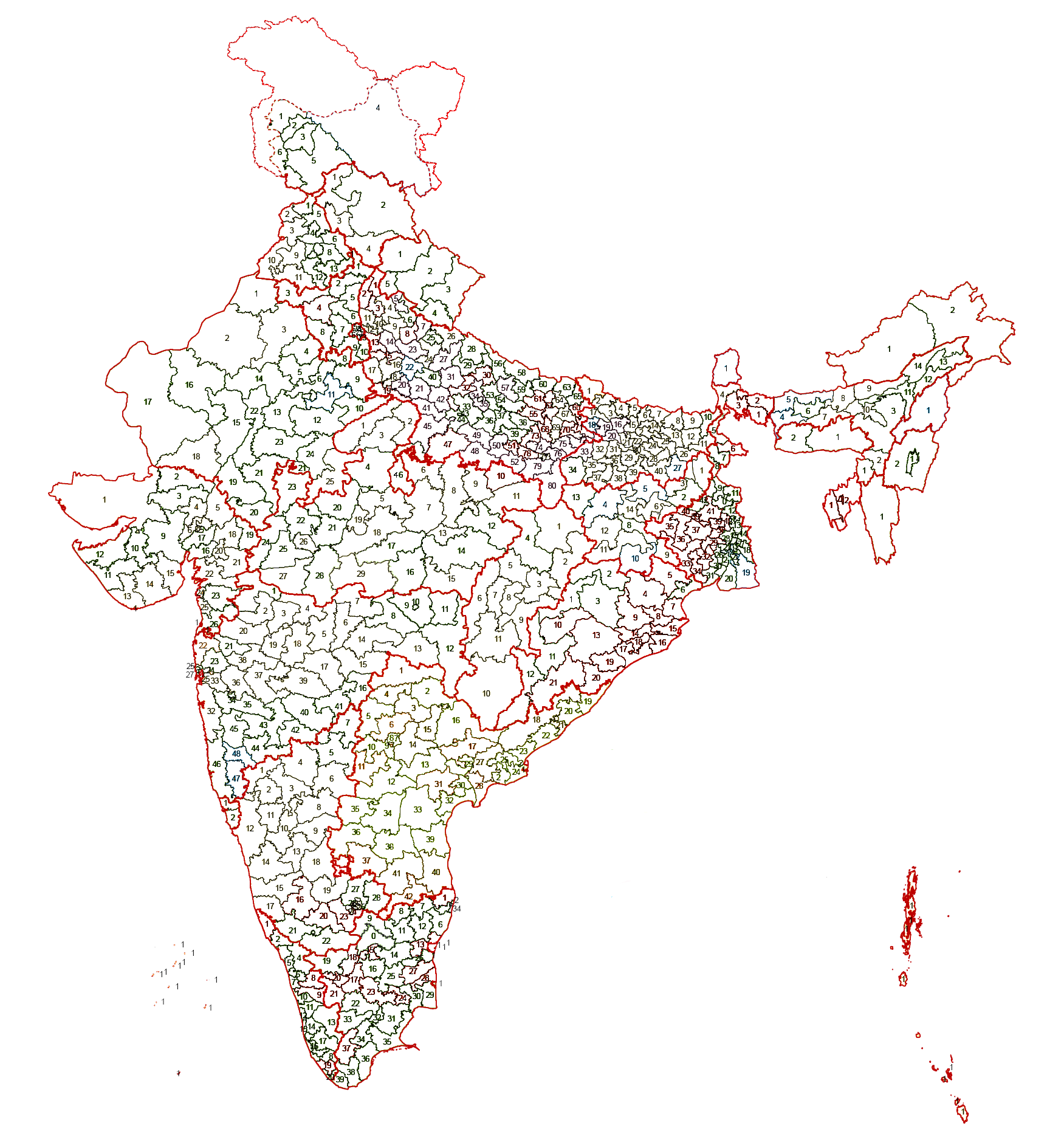
( MPs). Each MP, represents a single geographic constituency. There are currently 543 constituencies while maximum seats will fill up to 550 (after article 331- 2 seats reserved for Anglo Indian but by 104th Constitution Amendment article 331 is null by parliament , before this amendment maximum seat will 552)
The maximum size of the Lok Sabha as outlined in the Constitution of India
The Constitution of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental ...
is 552 members, made up of up to 524 members representing people of 28 states and 19 members representing people of 8 Union territories on the basis of their population.
Delimitation of constituencies
Under theDelimitation Act of 2002
The Delimitation commission or Boundary commission of India is a commission established by the Government of India under the provisions of the Delimitation Commission Act. The main task of the commission is Boundary delimitation, redrawing the ...
, the Delimitation Commission of India has redefined the list of parliamentary constituencies, their constituent assembly segments and reservation status (whether reserved for Scheduled castes (SC) candidates or Scheduled tribes (ST) candidates or unreserved). 2008 Karnataka Legislative Assembly election, which took place in May 2008, was the first state election to use newly demarcated assembly constituencies.
Consequently, all assembly elections scheduled in 2008, viz. in the states of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, NCT of Delhi, Mizoram and Rajasthan were based on newly defined assembly constituencies.
The size and shape of the Parliamentary and Assembly Constituencies are determined, according to section 4 of the Representation of the People Act, 1950, by an independent Delimitation Commission. Under a constitutional amendment of 1976, delimitation was suspended until after the census of 2001. However, certain amendments to the Constitution made in 2001 and 2003 have, while putting a freeze on the total number of existing seats as allocated to various States in the House of the People and the State Legislative Assemblies on the basis of 1971 census until the first census to be taken after the year 2026,http://elections.tn.nic.in/delimitation.html provided that each State shall be delimited into territorial Parliamentary and Assembly Constituencies on the basis of 2001 census and the extent of such constituencies as delimited shall remain frozen until the first census to be taken after the year 2026. The number of seats to be reserved for SC/ ST shall be re-worked out on the basis of 2001 census. The constituency shall be delimited in a manner that the population of each Parliamentary and Assembly Constituency in a State so far as practicable be the same throughout the State.
Summary
The Delimitation Commission, set up under the Delimitation Act, 2002, was entrusted with the task of readjusting all parliamentary and assembly constituencies in the country in all the states of India, except the state of Jammu and Kashmir, on the basis of population ascertained in 2001 Census. Government of India promulgated an Ordinance amending the Delimitation Act, 2002 nullifies the Final Order of the Delimitation Commission for the state of Jharkhand. Later on, the Government have passed four separate Orders under Sec 10 A of the Delimitation Act, 2002, deferring the delimitation exercise in the four North Eastern states of Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur and Nagaland. Following table indicates the total number of seats and number of seats reserved for SC and ST statewise. Between 1952 and 2020, two seats were reserved in theLok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-p ...
for members of the Anglo-Indian
Anglo-Indian people fall into two different groups: those with mixed Indian and British ancestry, and people of British descent born or residing in India. The latter sense is now mainly historical, but confusions can arise. The '' Oxford English ...
community. They were nominated by the President of India
The president of India ( IAST: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Indian Armed Forces. Droupadi Murm ...
on the advice of the Government of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, ...
. In 2020, it was abolished under the 104th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2019.
Andhra Pradesh (25)
Arunachal Pradesh (2)
Assam (14)
Bihar (40)
Chhattisgarh (11)
Goa (2)
Gujarat (26)
Haryana (10)
Himachal Pradesh (4)
Jharkhand (14)
Karnataka (28)
Kerala (20)
Madhya Pradesh (29)
Maharashtra (48)
Manipur (2)
Meghalaya (2)
Mizoram (1)
Nagaland (1)
Odisha (21)
Punjab (13)

Rajasthan (25)
Sikkim (1)
Tamil Nadu (39)
Telangana (17)
Tripura (2)
Uttar Pradesh (80)
Uttarakhand (5)
West Bengal (42)
Union territories (19)
Andaman and Nicobar Islands (1)
Chandigarh (1)
Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu (2)
Delhi (7)
Jammu and Kashmir (5)
Ladakh (1)
Lakshadweep (1)
Puducherry (1)
See also
* List of former constituencies of the Lok Sabha * State governments of IndiaReferences
External links
Members of the Lok Sabha
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Constituencies Of The Lok Sabha *