Lemuel Gulliver on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
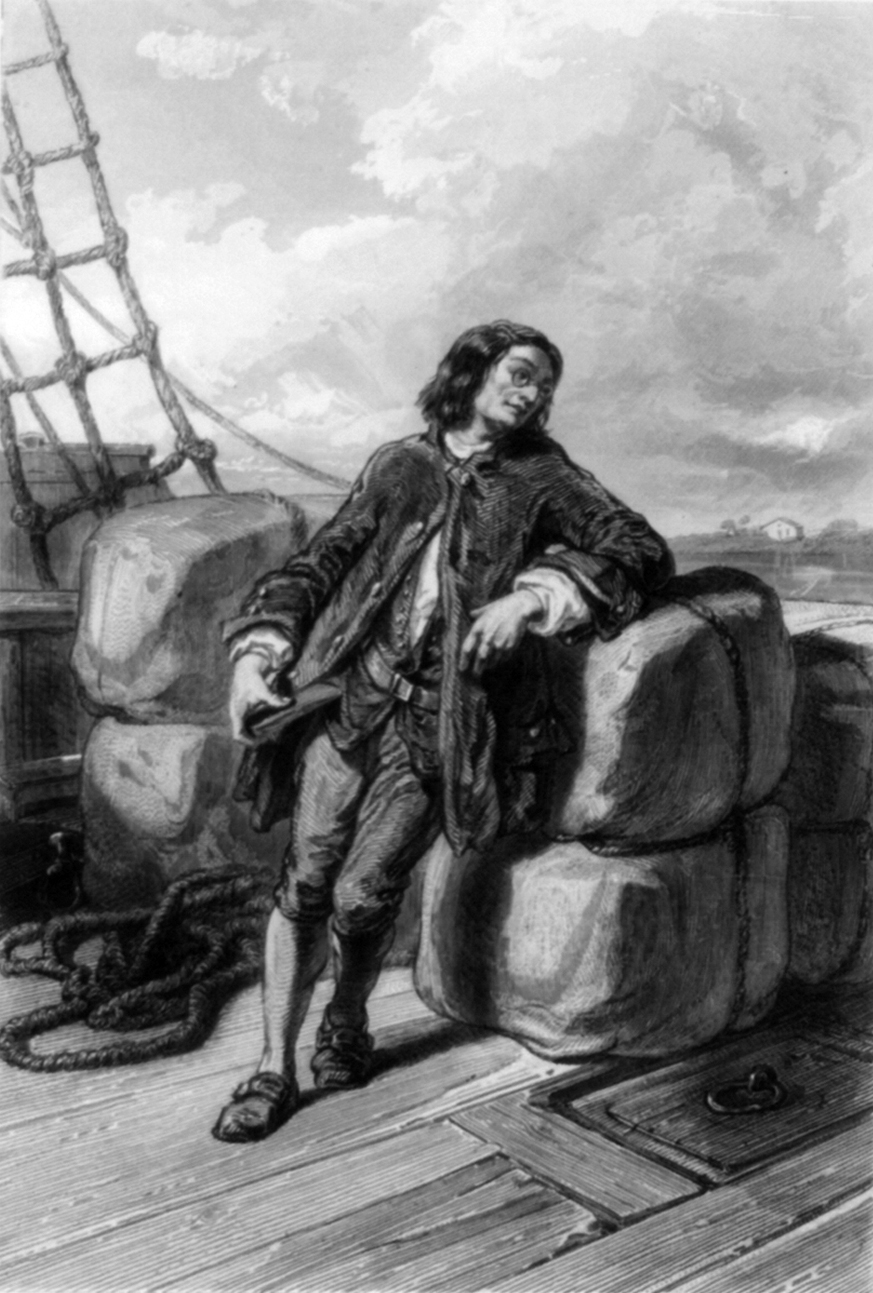
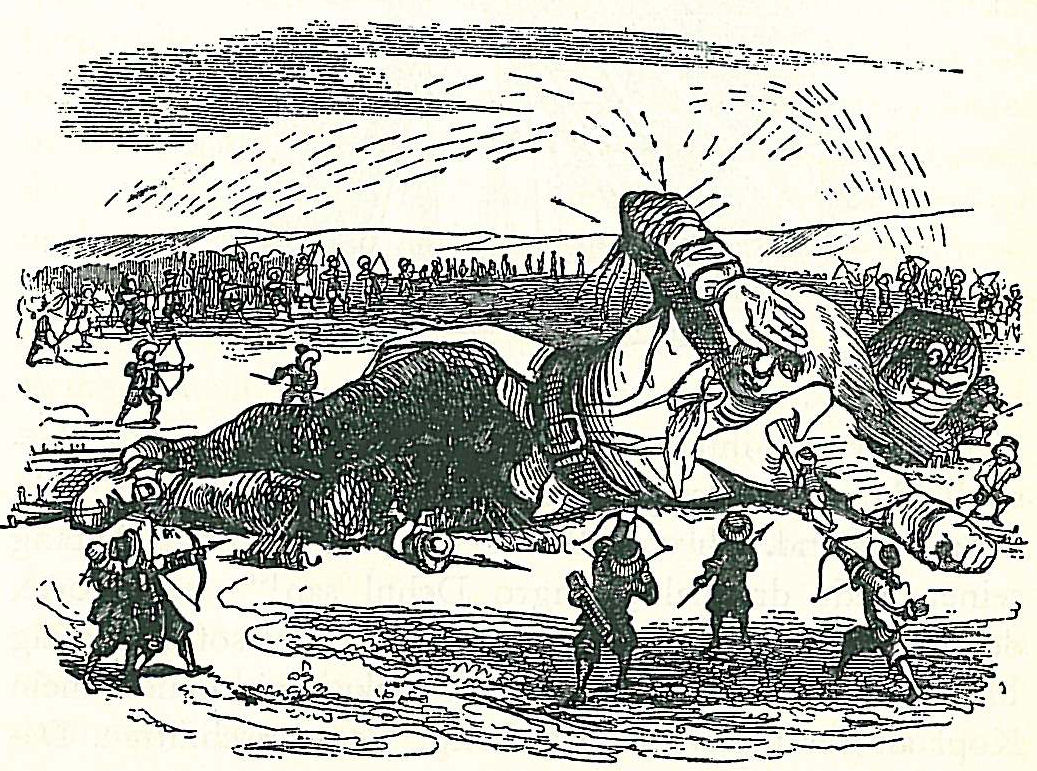
 Lemuel Gulliver () is the fictional protagonist and narrator of ''
Lemuel Gulliver () is the fictional protagonist and narrator of ''


 Lemuel Gulliver () is the fictional protagonist and narrator of ''
Lemuel Gulliver () is the fictional protagonist and narrator of ''Gulliver's Travels
''Gulliver's Travels'', or ''Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships'' is a 1726 prose satire by the Anglo-Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan ...
'', a novel written by Jonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish Satire, satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whig (British political party), Whigs, then for the Tories (British political party), Tories), poe ...
, first published in 1726.
In ''Gulliver's Travels''
According to Swift's novel, Gulliver was born inNottinghamshire
Nottinghamshire (; abbreviated Notts.) is a landlocked county in the East Midlands region of England, bordering South Yorkshire to the north-west, Lincolnshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south, and Derbyshire to the west. The traditi ...
c. 1661, where his father had a small estate; the Gulliver family is said to have originated in Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily ...
, however. He supposedly studied for three years (c. 1675-1678) at Emmanuel College, Cambridge
Emmanuel College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. The college was founded in 1584 by Sir Walter Mildmay, Chancellor of the Exchequer to Elizabeth I. The site on which the college sits was once a priory for Dominican mon ...
, leaving to become an apprentice to an eminent London surgeon; after four years (c. 1678-1682), he left to study at the University of Leiden
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Le ...
, a prominent Dutch university and medical school. He also educated himself in navigation and mathematics, leaving the University around 1685.
Prior to the voyages whose adventures are recounted in the novel, he is described as having travelled less remarkably to the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
(c. 1685-1688) and later to the East Indies
The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Discovery. The Indies refers to various lands in the East or the Eastern hemisphere, particularly the islands and mainlands found in and around t ...
and West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
(c. 1690-1696). In Brobdingnag
Brobdingnag is a fictional land, which is occupied by giants, in Jonathan Swift's 1726 satirical novel ''Gulliver's Travels.'' The story's main character, Lemuel Gulliver, visits the land after the ship on which he is travelling is blown off cou ...
, he compares a loud sound to the Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Falls, ...
, so presumably, he visited the place at some point. Between his travels, he married Miss Mary Burton (c. 1688), daughter of a London hosier. As of the time of his return from Lilliput, they had a son named Johnny, studying at grammar-school, and a daughter named Betty, married with children by the time Lemuel wrote his memoirs. Mary was pregnant with another child by the time her husband left on his last voyage. In his education and travels, Gulliver acquired some knowledge of "High
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift ...
and Low Dutch, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, French, Spanish, Italian, and Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
"; he later states that he understood some Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and that he "understood (Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
) very well".
Gulliver's remarkable travels begin in 1699 and end in 1715, having changed Gulliver's personality to that of a recluse. He claims to have written his memoirs five years following his last return to England, i.e., in 1720 or 1721. The frontispiece to the 1726 edition of ''Gulliver's Travels'' shows a fictitious engraving of Gulliver at the age of 58 (i.e., c. 1719). An additional preface, attributed to Gulliver, added to a revised version of the work is given the fictional date of April 2, 1727, at which time Gulliver would have been about 65 or 66 years old. The earliest editions of the book credited Gulliver as the author, whom many at the time believed to be a real person. Swift, an Anglican clergyman, had published much of his work anonymously or pseudonymously.
In sequels and spinoffs
* Hungarian writerFrigyes Karinthy
Frigyes Karinthy (; 25 June 1887 – 29 August 1938) was a Hungarian author, playwright, poet, journalist, and translator. He was the first proponent of the six degrees of separation concept, in his 1929 short story, ''Chains'' (''Láncszemek'') ...
reused Gulliver as the protagonist of two novels recounting his further travels, ''Voyage to Faremido
''Voyage to Faremido'' (Hungarian: ''Utazás Faremidóba'', 1916) is a utopian-satirical novel by Frigyes Karinthy. Written as a further adventure of Lemuel Gulliver of '' Gulliver's Travels'', it recounts the story of a World War I pilot who cr ...
'' (1916) and ''Capillaria
''Capillaria'' ( hu, Capillária, 1921) is a fantasy novel by Hungarian author Frigyes Karinthy, which depicts an undersea world inhabited exclusively by women, recounts, in a satirical vein reminiscent of the style of Jonathan Swift, the firs ...
'' (1921). Both stay true to the character as a surgeon with a wife and children, but transpose their plot (and retroactively Gulliver's four earlier travels) to the then-contemporary years leading up to, during, and after World War I.
* In the 2007 comic '' The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen: Black Dossier'' by Alan Moore
Alan Moore (born 18 November 1953) is an English author known primarily for his work in comic books including ''Watchmen'', ''V for Vendetta'', ''The Ballad of Halo Jones'', ''Swamp Thing'', ''Batman:'' ''The Killing Joke'', and ''From Hell' ...
, Gulliver is the leader of the second incarnation of The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen
''The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen'' (''LoEG'') is a comic book series (inspired by the 1960 British film ''The League of Gentlemen'') co-created by writer Alan Moore and artist Kevin O'Neill which began in 1999. The series spans four volum ...
in the 18th century, which then consists of The Scarlet Pimpernel
''The Scarlet Pimpernel'' is the first novel in a series of historical fiction by Baroness Orczy, published in 1905. It was written after her stage play of the same title (co-authored with Montague Barstow) enjoyed a long run in London, having ...
and his wife Lady Blakeney, Fanny Hill
''Memoirs of a Woman of Pleasure''—popularly known as ''Fanny Hill''—is an erotic novel by English novelist John Cleland first published in London in 1748. Written while the author was in debtors' prison in London,Wagner, "Introduction" ...
(with whom Gulliver has been romantically involved), Dr Syn
The Reverend Doctor Christopher Syn is the smuggler hero of a series of novels by Russell Thorndike. The first book, ''Doctor Syn: A Tale of the Romney Marsh'' was published in 1915. The story idea came from smuggling in the 18th-century Romney ...
aka The Scarecrow, Nathaniel Bumppo
Nathaniel "Natty" Bumppo is a fictional character and the protagonist of James Fenimore Cooper's pentalogy of novels known as the '' Leatherstocking Tales''.
Fictional biography
Natty Bumppo, the child of white parents, grew up among Delawar ...
and Orlando. Gulliver leads the League until his death of testicular cancer
Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle, or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.
Risk factors include an u ...
in 1799 and is buried in Lilliput. This version of Gulliver is evidently at least a generation younger than Swift's Gulliver; his dates have evidently been shifted forward in time to allow him to interact with other fictional characters of the later 18th century.
* Gulliver is mentioned throughout the recent ''Malplaquet'' trilogy of children's novels by Andrew Dalton.Dalton, Andrew. ''The New Empire of Malplaquet''. Lutterworth Press 2009, Taking much of their initial inspiration from T.H. White's '' Mistress Masham's Repose'', the books describe the adventures of a large colony of Lilliputians living secretly in the enormous and mysterious grounds of an English country house
An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a town house. This allowed them to spend time in the country and in the city—hence, for these peopl ...
( Stowe House in Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (), abbreviated Bucks, is a ceremonial county in South East England that borders Greater London to the south-east, Berkshire to the south, Oxfordshire to the west, Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-ea ...
). In ''The Temples of Malplaquet'', for example, Jamie Thompson (their human protector, aged 13) has a dream-like vision of the episode in which Gulliver is first captured by the Lilliputians.
* In the ''Gulliver's Travels
''Gulliver's Travels'', or ''Travels into Several Remote Nations of the World. In Four Parts. By Lemuel Gulliver, First a Surgeon, and then a Captain of Several Ships'' is a 1726 prose satire by the Anglo-Irish writer and clergyman Jonathan ...
'' film released in 2010, Gulliver, played by Jack Black
Thomas Jacob Black (born August 28, 1969) is an American actor, comedian, and musician. He is known for his acting roles in the films '' High Fidelity'' (2000), ''Shallow Hal'' (2001), ''Orange County'' (2002), '' School of Rock'' (2003), ''E ...
, is a mail room worker who fancies himself a writer but plagiarizes most of his work from the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
. After Gulliver is assigned to write a story about the Bermuda Triangle
The Bermuda Triangle, also known as the Devil's Triangle, is an urban legend focused on a loosely defined region in the western part of the North Atlantic Ocean where a number of aircraft and ships are said to have disappeared under mysterio ...
, his ship becomes lost at sea and he finds himself in Lilliput.
In astronomy
OnMars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
's largest moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
, Phobos, the crater Gulliver is named after him, while the crater Grildrig has the name given to Gulliver by the farmer's daughter Glumdalclitch
Glumdalclitch is the name Gulliver gives his "nurse" in Book II of Jonathan Swift's 1726 novel ''Gulliver's Travels''. In Book I, Gulliver travels to the land of Lilliput. Leaving there, he travels to the land of Brobdingnag. In Lilliput, Gulli ...
in Brobdingnag
Brobdingnag is a fictional land, which is occupied by giants, in Jonathan Swift's 1726 satirical novel ''Gulliver's Travels.'' The story's main character, Lemuel Gulliver, visits the land after the ship on which he is travelling is blown off cou ...
, because of Swift's 'prediction' of the two then undiscovered Martian moons, which his Laputan astronomers had discovered.
See also
*Lilliput and Blefuscu
Lilliput and Blefuscu are two fictional island nations that appear in the first part of the 1726 novel ''Gulliver's Travels'' by Jonathan Swift. The two islands are neighbours in the South Indian Ocean, separated by a channel wide. Both are ...
*Brobdingnag
Brobdingnag is a fictional land, which is occupied by giants, in Jonathan Swift's 1726 satirical novel ''Gulliver's Travels.'' The story's main character, Lemuel Gulliver, visits the land after the ship on which he is travelling is blown off cou ...
* Laputa
*Luggnagg
Luggnagg is an island kingdom, one of the imaginary countries visited by Lemuel Gulliver in the 1726 satirical novel '' Gulliver's Travels'' by Anglo-Irish author Jonathan Swift.
Location
The location of Luggnagg is illustrated in both the text ...
* The Engine
References
Sources
*''Gulliver's Travels'' byJonathan Swift
Jonathan Swift (30 November 1667 – 19 October 1745) was an Anglo-Irish Satire, satirist, author, essayist, political pamphleteer (first for the Whig (British political party), Whigs, then for the Tories (British political party), Tories), poe ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gulliver, Lemuel
Characters in British novels of the 18th century
Fictional military captains
Fictional surgeons
Fictional writers
Fictional English people
Gulliver's Travels
Fictional castaways
Fictional sole survivors
Literary characters introduced in 1726
Characters in Irish novels
Male characters in literature
Fictional people from the 18th-century