Leishmaniasis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by
 The symptoms of leishmaniasis are
The symptoms of leishmaniasis are
 Leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of infected female phlebotomine sandflies which can transmit the
Leishmaniasis is transmitted by the bite of infected female phlebotomine sandflies which can transmit the
 Leishmaniasis is diagnosed in the hematology laboratory by direct visualization of the
Leishmaniasis is diagnosed in the hematology laboratory by direct visualization of the
 The treatment is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of ''Leishmania'', and the type of infection.
For visceral leishmaniasis in India, South America, and the Mediterranean,
The treatment is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of ''Leishmania'', and the type of infection.
For visceral leishmaniasis in India, South America, and the Mediterranean,
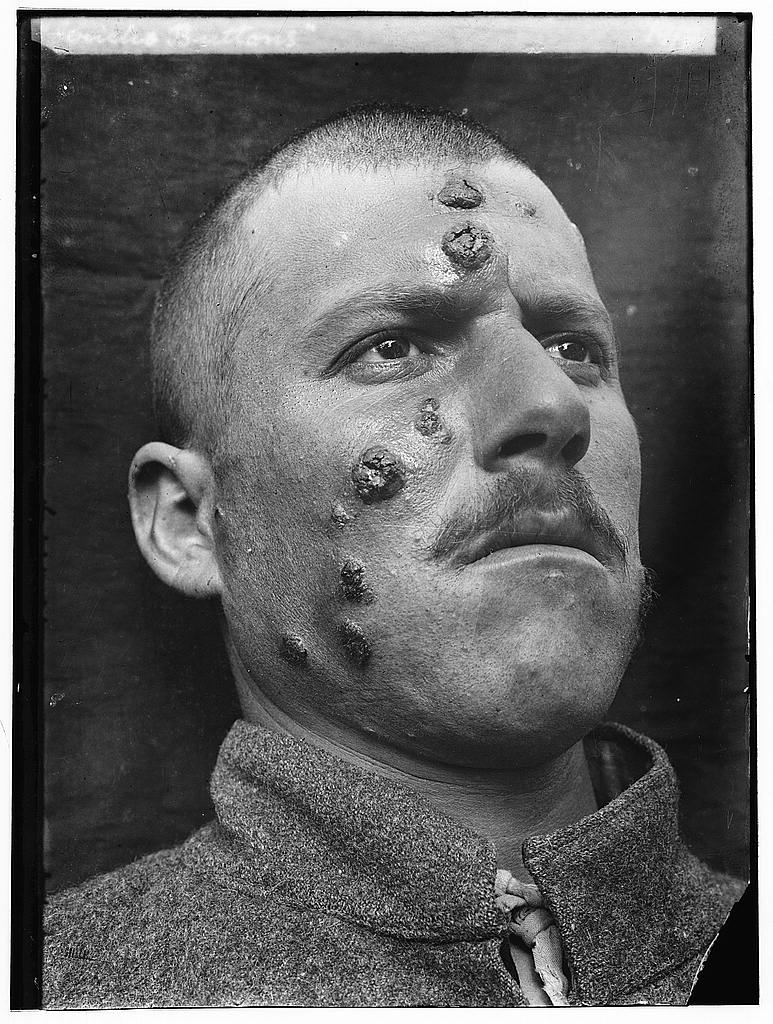 Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis appear on tablets from King
Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis appear on tablets from King
parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
s of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania
''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...
''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies
Sandfly (or sand fly) is a colloquial name for any species or genus of flying, biting, blood-sucking dipteran (fly) encountered in sandy areas. In the United States, ''sandfly'' may refer to certain horse flies that are also known as "greenhe ...
, ''Phlebotomus
''Phlebotomus'' is a genus of " sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance.
...
'' and ''Lutzomyia
''Lutzomyia'' is a genus of phlebotomine sand flies consisting of nearly 400 species, at least 33 of which have medical importance as vectors of human disease. Species of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' are found only in the New World, distributed in ...
'', and occurs most frequently in the tropics and sub-tropics of Africa, Asia, the Americas, and southern Europe. The disease can present in three main ways: cutaneous
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different d ...
, mucocutaneous, or visceral
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a ...
. The cutaneous form presents with skin ulcers, while the mucocutaneous form presents with ulcers of the skin, mouth, and nose. The visceral form starts with skin ulcers and later presents with fever, low red blood cell count, and enlarged spleen and liver.
Infections in humans are caused by more than 20 species of ''Leishmania''. Risk factors include poverty
Poverty is the state of having few material possessions or little income. Poverty can have diverse social, economic, and political causes and effects. When evaluating poverty in ...
, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
, and urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
. All three types can be diagnosed by seeing the parasites under microscopy. Additionally, visceral disease can be diagnosed by blood tests.
Leishmaniasis can be partly prevented by sleeping under nets treated with insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
. Other measures include spraying insecticides to kill sandflies and treating people with the disease early to prevent further spread. The treatment needed is determined by where the disease is acquired, the species of ''Leishmania'', and the type of infection. Some possible medications used for visceral disease include liposomal amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. ...
, a combination of pentavalent antimonials and paromomycin
Paromomycin is an antimicrobial used to treat a number of parasitic infections including amebiasis, giardiasis, leishmaniasis, and tapeworm infection. It is a first-line treatment for amebiasis or giardiasis during pregnancy. Otherwise it is g ...
, and miltefosine
Miltefosine, sold under the trade name Impavido among others, is a medication mainly used to treat leishmaniasis and free-living amoeba infections such as ''Naegleria fowleri'' and '' Balamuthia mandrillaris''. This includes the three forms of l ...
. For cutaneous disease, paromomycin, fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prevent ...
, or pentamidine may be effective.
About 4 to 12 million people are currently infected in some 98 countries. About 2 million new cases and between 20 and 50 thousand deaths occur each year. About 200 million people in Asia, Africa, South and Central America, and southern Europe live in areas where the disease is common. The World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
has obtained discounts on some medications to treat the disease. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical disease, tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in Developing country, developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety ...
. The disease may occur in a number of other animals, including dogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Do ...
and rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are na ...
s.
Signs and symptoms
 The symptoms of leishmaniasis are
The symptoms of leishmaniasis are skin sores
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves lacerated or punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force trauma or compression. In pathology, a ''wound'' is an acute injury that damages the epiderm ...
which erupt weeks to months after the person is bitten by infected sand flies.
Leishmaniasis may be divided into the following types:
* Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Cutaneous leishmaniasis is the most common form of leishmaniasis affecting humans. It is a skin infection caused by a single-celled parasite that is transmitted by the bite of a phlebotomine sand fly. There are about thirty species of ''Leishm ...
is the most common form, which causes an open sore at the bite sites, which heals in a few months to a year and half, leaving an unpleasant-looking scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a na ...
. Diffuse cutaneous leishmaniasis produces widespread skin lesions which resemble leprosy
Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria ''Mycobacterium leprae'' or ''Mycobacterium lepromatosis''. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damag ...
, and may not heal on its own.
* Mucocutaneous leishmaniasis causes both skin and mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
l ulcers with damage primarily of the nose and mouth.
* Visceral leishmaniasis
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), also known as kala-azar (Hindi: kālā āzār, "black sickness") or "black fever", is the most severe form of leishmaniasis and, without proper diagnosis and treatment, is associated with high fatality. Leishmaniasi ...
or ''kala-azar'' ('black fever') is the most serious form, and is generally fatal if untreated. Other consequences, which can occur a few months to years after infection, include fever
Fever, also referred to as pyrexia, is defined as having a body temperature, temperature above the human body temperature, normal range due to an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point. There is not a single ...
, damage to the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
and liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
, and anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
.
Leishmaniasis is considered one of the classic causes of a markedly enlarged (and therefore palpable) spleen; the organ, which is not normally felt during examination of the abdomen, may even become larger than the liver in severe cases.
Cause
protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
''Leishmania
''Leishmania'' is a parasitic protozoan, a single-celled organism of the genus '' Leishmania'' that are responsible for the disease leishmaniasis. They are spread by sandflies of the genus ''Phlebotomus'' in the Old World, and of the genus '' ...
''. (1) The sandflies inject the infective stage, metacyclic promastigote
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid excavates distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. ...
s, during blood meals. (2) Metacyclic promastigotes in the puncture wound are phagocytized by macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, and (3) transform into amastigote
An amastigote is a protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryot ...
s. (4) Amastigotes multiply in infected cells and affect different tissues, depending in part on the host, and in part on which ''Leishmania'' species is involved. These differing tissue specificities cause the differing clinical manifestations of the various forms of leishmaniasis. (5,6) Sandflies become infected during blood meals on infected hosts when they ingest macrophages infected with amastigotes. (7) In the sandfly's midgut, the parasites differentiate into promastigotes, (8) which multiply, differentiate into metacyclic promastigotes, and migrate to the proboscis.
The genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
s of three ''Leishmania'' species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
(''L. major'', ''L. infantum'', and ''L. braziliensis'') have been sequenced, and this has provided much information about the biology of the parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
. For example, in ''Leishmania'', protein-coding genes are understood to be organized as large polycistronic
A cistron is an alternative term for "gene". The word cistron is used to emphasize that genes exhibit a specific behavior in a cis-trans test; distinct positions (or loci) within a genome are cistronic.
History
The words ''cistron'' and ''gene ...
units in a head-to-head or tail-to-tail manner; RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
II transcribes long polycistronic messages in the absence of defined RNA pol II promoters, and ''Leishmania'' has unique features with respect to the regulation of gene expression in response to changes in the environment. The new knowledge from these studies may help identify new targets for urgently needed drugs and aid the development of vaccines.
Vector
Although most of the literature mentions only one genus transmitting ''Leishmania'' to humans (''Lutzomyia
''Lutzomyia'' is a genus of phlebotomine sand flies consisting of nearly 400 species, at least 33 of which have medical importance as vectors of human disease. Species of the genus ''Lutzomyia'' are found only in the New World, distributed in ...
'') in the New World, a 2003 study by Galati suggested a new classification for New World sand flies, elevating several subgenera to the genus level. Elsewhere in the world, the genus ''Phlebotomus
''Phlebotomus'' is a genus of " sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance.
...
'' is considered the vector of leishmaniasis.
Possible non-human reservoirs
Some cases of infection of non-human animals of human-infecting species of Leishmania have been observed. In one study, ''L. major'' was identified in twelve out of ninety-one wildwestern lowland gorilla
The western lowland gorilla (''Gorilla gorilla gorilla'') is one of two Critically Endangered subspecies of the western gorilla (''Gorilla gorilla'') that lives in Montane ecosystems#Montane forests, montane, Old-growth forest, primary and sec ...
fecal samples and in a study of fifty-two captive non-human primates under zoo captivity in a leishmaniasis endemic area, eight (all three chimpanzees
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative the ...
, three golden lion tamarins
The golden lion tamarin (''Leontopithecus rosalia'', pt, mico-leão-dourado , ), also known as the golden marmoset, is a small New World monkey of the family Callitrichidae. Native to the Atlantic coastal forests of Brazil, the golden lion ta ...
, a tufted capuchin
The tufted capuchin (''Sapajus apella''), also known as brown capuchin, black-capped capuchin, or pin monkey is a New World primate from South America and the Caribbean islands of Trinidad and Margarita. As traditionally defined, it is one of th ...
, and an Angolan talapoin
The Angolan talapoin (''Miopithecus talapoin''), also known as the southern talapoin, is a species of primate in the family Cercopithecidae. Talapoins are the smallest species of Old-World monkeys.
Description
The fur of the Angolan talapoin is ...
), were found to be infected with L. infantum and capable of infecting ''Lutzomyia longipalpis'' sand flies, although "parasite loads in infected sand flies observed in this study were considered low".
Organisms
Visceral disease is usually caused by ''Leishmania donovani
''Leishmania donovani'' is a species of intracellular parasites belonging to the genus ''Leishmania'', a group of haemoflagellate kinetoplastids that cause the disease leishmaniasis. It is a human blood parasite responsible for visceral leishmani ...
'', ''L. infantum'', or ''L. chagasi'', but occasionally these species may cause other forms of disease. The cutaneous form of the disease is caused by more than 15 species of ''Leishmania''.
Risk factors
Risk factors include malnutrition, deforestation, lack of sanitation, suppressed immune system and urbanization.Diagnosis
amastigotes
An amastigote is a protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryot ...
(Leishman–Donovan bodies). Buffy-coat preparations of peripheral blood or aspirates from marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, or skin lesions should be spread on a slide to make a thin smear and stained with Leishman stain
Leishman stain, also known as Leishman's stain, is used in microscopy for staining blood smears. It is generally used to differentiate between and identify white blood cells, malaria parasites, and trypanosomas. It is based on a methanolic mixture ...
or Giemsa stain
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups of ...
( pH 7.2) for 20 minutes. Amastigotes are seen within blood and spleen monocytes or, less commonly, in circulating neutrophils and in aspirated tissue macrophages. They are small, round bodies 2–4 μm in diameter with indistinct cytoplasm, a nucleus, and a small, rod-shaped kinetoplast
A kinetoplast is a network of circular DNA (called kDNA) inside a large mitochondrion that contains many copies of the mitochondrial genome. The most common kinetoplast structure is a disk, but they have been observed in other arrangements. Kinet ...
. Occasionally, amastigotes may be seen lying free between cells. However, the retrieval of tissue samples is often painful for the patient and identification of the infected cells can be difficult. So, other indirect immunological methods of diagnosis are developed, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antigen-coated dipsticks, and direct agglutination test. Although these tests are readily available, they are not the standard diagnostic tests due to their insufficient sensitivity and specificity.
Several different polymerase chain reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) t ...
(PCR) tests are available for the detection of ''Leishmania'' DNA. With this assay, a specific and sensitive diagnostic procedure is finally possible. The most sensitive PCR tests use minicircle kinetoplast DNA found in the parasite. Kinetoplast DNA contains sequences for mitochondrial proteins in its maxicircles(~25-50 per parasite), and guide RNA in its minicircles(~10'000 per parasite) of the kinetoplast. With this specific method, one can still detect Leishmania even with a very low parasite load. When needing to diagnose a specific species of Leishmania, as opposed to only detection, other PCR methods have been superior.
Most forms of the disease are transmitted only from nonhuman animals, but some can be spread between humans. Infections in humans are caused by about 21 of 30 species that infect mammals; the different species look the same, but they can be differentiated by isoenzyme In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. dif ...
analysis, DNA sequence analysis
In bioinformatics, sequence analysis is the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alig ...
, or monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ca ...
.
Prevention
* Using insect repellent to exposed skin and under the ends of sleeves and pant legs. Follow the instructions on the label of the repellent. The most effective repellents generally are those that contain the chemical DEET (N,N-diethylmetatoluamide) * Leishmaniasis can be partly prevented by using nets treated withinsecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
or insect repellent while sleeping. To provide good protection against sandflies, fine mesh sizes of 0.6 mm or less are required, but a mosquito net
A mosquito net is a type of meshed curtain that is circumferentially draped over a bed or a sleeping area, to offer the sleeper barrier protection against bites and stings from mosquitos, flies, and other pest insects, and thus against the di ...
with 1.2mm mesh will provide a limited reduction in the number of sandfly bites. Finer mesh sizes have the downside of higher cost and reduced air circulation which can cause overheating. Many Phlebotomine sandfly attacks occur at sunset rather than at night, so it may also be useful to put nets over doors and windows or to use insect repellents
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray") is a substance applied to skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and cont ...
.
* Use of insecticide-impregnated dog collars and treatment or culling of infected dogs.
* Spraying houses and animal shelters with insecticides.*
Treatment
liposomal amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. ...
is the recommended treatment and is often used as a single dose. Rates of cure with a single dose of amphotericin
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious mycosis, fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candida infections, candidiasis, coccidioidomy ...
have been reported as 95%. In India, almost all infections are resistant to pentavalent antimonials. In Africa, a combination of pentavalent antimonials and paromomycin is recommended. These, however, can have significant side effects. Miltefosine
Miltefosine, sold under the trade name Impavido among others, is a medication mainly used to treat leishmaniasis and free-living amoeba infections such as ''Naegleria fowleri'' and '' Balamuthia mandrillaris''. This includes the three forms of l ...
, an oral medication, is effective against both visceral and cutaneous leishmaniasis. Side effects are generally mild, though it can cause birth defects
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
if taken within 3 months of getting pregnant. It does not appear to work for ''L. major'' or ''L. braziliensis''.
The evidence around the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis is poor. A number of topical treatments may be used for cutaneous leishmaniasis. Which treatments are effective depends on the strain, with topical paromomycin effective for ''L. major'', ''L. tropica'', ''L. mexicana'', ''L. panamensis'', and ''L. braziliensis''. Pentamidine is effective for ''L. guyanensis''. Oral fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prevent ...
or itraconazole
Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mouth ...
appears effective in ''L. major'' and ''L. tropica''. There is limited evidence to support the use of heat therapy
Heat therapy, also called thermotherapy, is the use of heat in therapy, such as for pain relief and health. It can take the form of a hot cloth, hot water bottle, ultrasound, heating pad, hydrocollator packs, whirlpool baths, cordless Far infrar ...
in cutaneous leishmaniasis as of 2015.
There are no studies determining the effect of oral nutritional supplements on visceral leishmaniasis being treated with anti-leishmanial drug therapy.
Epidemiology
Out of 200 countries and territories reporting to WHO, 97 countries and territories are endemic for leishmaniasis. The settings in which leishmaniasis is found range from rainforests in Central and South America to deserts in western Asia and the Middle East. It affects as many as 12 million people worldwide, with 1.5–2.0 million new cases each year. The visceral form of leishmaniasis has an estimated incidence of 500,000 new cases. In 2014, more than 90% of new cases reported to WHO occurred in six countries: Brazil, Ethiopia, India, Somalia, South Sudan and Sudan. As of 2010, it caused about 52,000 deaths, down from 87,000 in 1990. Different types of the disease occur in different regions of the world. Cutaneous disease is most common in Afghanistan, Algeria, Brazil, Colombia, and Iran, while mucocutaneous disease is most common in Bolivia, Brazil, and Peru, and visceral disease is most common in Bangladesh, Brazil, Ethiopia, India, and Sudan. Leishmaniasis is found through much of theAmericas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
from northern Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
to South Texas
South Texas is a region of the U.S. state of Texas that lies roughly south of—and includes—San Antonio. The southern and western boundary is the Rio Grande, and to the east it is the Gulf of Mexico. The population of this region is about 4.96 ...
, though not in Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
or Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
, and has recently been shown to be spreading to North Texas
North Texas (also commonly called North Central Texas) is a term used primarily by residents of Dallas, Fort Worth, and surrounding areas to describe much of the north central portion of the U.S. state of Texas. Residents of the Dallas–Fort Wor ...
and Oklahoma, and further expansion to the north may be facilitated by climate change as more habitat becomes suitable for vector and reservoir species for leishmaniasis. Leishmaniasis is also known as ''papalomoyo'', ''papa lo moyo,'' ''úlcera de los chicleros'', and ''chiclera'' in Latin America. During 2004, an estimated 3,400 troops from the Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
n army, operating in the jungles near the south of the country (in particular around the Meta and Guaviare departments), were infected with leishmaniasis. Allegedly, a contributing factor was that many of the affected soldiers did not use the officially provided insect repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray") is a substance applied to skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and cont ...
because of its disturbing odor. Nearly 13,000 cases of the disease were recorded in all of Colombia throughout 2004, and about 360 new instances of the disease among soldiers had been reported in February 2005.
The disease is found across much of Asia, and in the Middle East. Within Afghanistan, leishmaniasis occurs commonly in Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, partly due to bad sanitation and waste left uncollected in streets, allowing parasite-spreading sand flies an environment they find favorable. In Kabul, the number of people infected was estimated to be at least 200,000, and in three other towns (Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safēd ...
, Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a List of cities in Afghanistan, city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population ...
, and Mazar-i-Sharif
, official_name =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, pushpin_map = Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_label = Mazar-i-Sharif
, pushpin ...
) about 70,000 more occurred, according to WHO figures from 2002. Kabul is estimated as the largest center of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the world, with around 67,500 cases as of 2004. Africa, in particular the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
and North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
, is also home to cases of leishmaniasis. Leishmaniasis is considered endemic also in some parts of southern parts of western Europe and spreading towards north in recent years. For example, an outbreak of cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis was reported from Madrid, Spain, between 2010 and 2012.
Leishmaniasis is mostly a disease of the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
, and is rarely known in the developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
outside a small number of cases, mostly in instances where troops are stationed away from their home countries. Leishmaniasis has been reported by U.S. troops stationed in Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
since the Gulf War of 1990, including visceral leishmaniasis.
In September 2005, the disease was contracted by at least four Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
marines
Marines, or naval infantry, are typically a military force trained to operate in littoral zones in support of naval operations. Historically, tasks undertaken by marines have included helping maintain discipline and order aboard the ship (refle ...
who were stationed in Mazar-i-Sharif, Afghanistan, and subsequently repatriated for treatment.
History
 Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis appear on tablets from King
Descriptions of conspicuous lesions similar to cutaneous leishmaniasis appear on tablets from King Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal (Neo-Assyrian language, Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "Ashur (god), Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king o ...
from the seventh century BCE, some of which may have derived from even earlier texts from 1500 to 2500 BCE. Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
n physicians, including Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
in the 10th century CE, gave detailed descriptions of what was called ''balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
'' sore. In 1756, Alexander Russell, after examining a Turkish patient, gave one of the most detailed clinical descriptions of the disease. Physicians in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
would describe it as ''kala-azar'' (pronounced ''kālā āzār'', the Urdu
Urdu (;"Urdu"
''
 As of 2017, no
As of 2017, no
Doctors Without Borders' Leishmaniasis Information Page
CDC Leishmaniasis Page
{{Authority control Dog diseases Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Tropical diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Zoonoses
''
Hindi
Hindi (Devanāgarī: or , ), or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi (Devanagari: ), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been de ...
, and Hindustani phrase for "black fever", ''kālā'' meaning black and ''āzār'' meaning fever or disease). In the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, evidence of the cutaneous form of the disease in Ecuador
Ecuador ( ; ; Quechua: ''Ikwayur''; Shuar: ''Ecuador'' or ''Ekuatur''), officially the Republic of Ecuador ( es, República del Ecuador, which literally translates as "Republic of the Equator"; Quechua: ''Ikwadur Ripuwlika''; Shuar: ''Eku ...
and Peru appears in pre-Inca pottery depicting skin lesions and deformed faces dating back to the first century CE. Some 15th- and 16th-century texts from the Inca
The Inca Empire (also known as the Incan Empire and the Inka Empire), called ''Tawantinsuyu'' by its subjects, (Quechua for the "Realm of the Four Parts", "four parts together" ) was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The admin ...
period and from Spanish colonials mention "valley sickness", "Andean sickness", or "white leprosy", which are likely to be the cutaneous form.
It remains unclear who first discovered the organism. David Douglas Cunningham
David Douglas Cunningham (29 September 1843 – 31 December 1914) was a Scottish doctor and researcher who worked extensively in India on various aspects of public health and medicine. He studied the spread of bacteria and the spores of fungi t ...
, Surgeon Major of the British Indian army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
, may have seen it in 1885 without being able to relate it to the disease. Peter Borovsky
Pyotr Fokich Borovsky (russian: Пётр Фоки́ч Боро́вский, 8 June 1863 – 15 December 1932) was Russian and Soviet surgeon and public health administrator of who worked in Tashkent, professor of surgery in Tashkent Medical In ...
, a Russian military surgeon working in Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of ...
, conducted research into the etiology of "oriental sore", locally known as ''sart'' sore, and in 1898 published the first accurate description of the causative agent, correctly described the parasite's relation to host tissues and correctly referred it to the protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...
. However, because his results were published in Russian in a journal with low circulation, his results were not internationally acknowledged during his lifetime. In 1901, William Boog Leishman
Lieutenant-General Sir William Boog Leishman, (, 6 November 1865 – 2 June 1926) was a Scottish pathologist and British Army medical officer. He was Director-General of Army Medical Services from 1923 to 1926.
Biography
Leishman was born in ...
identified certain organisms in smears taken from the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
of a patient who had died from "dum-dum fever" (Dum Dum
Dum Dum is a city and a municipality of Kolkata district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of Kolkata urban area and also a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority (KMDA).
Etymology
During the 19th ...
is an area close to Calcutta
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , List of renamed places in India#West Bengal, the official name until 2001) is the Capital city, capital of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal, on the eastern ba ...
) and proposed them to be trypanosomes
Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid excavates distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano'' (borer) and ''soma'' (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. ...
, found for the first time in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. A few months later, Captain Charles Donovan
Charles Donovan MD (19 September 1863 – 29 October 1951) was an Irish medical officer in the Indian Medical Service. He is best remembered for his discoveries of ''Leishmania donovani'' as the causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis, and ''Kl ...
(1863–1951) confirmed the finding of what became known as Leishman-Donovan bodies in smears taken from people in Madras
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
in southern India. But it was Ronald Ross
Sir Ronald Ross (13 May 1857 – 16 September 1932) was a British medical doctor who received the Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine in 1902 for his work on the transmission of malaria, becoming the first British Nobel laureate, and the f ...
who proposed that Leishman-Donovan bodies were the intracellular stages of a new parasite, which he named ''Leishmania donovani''. The link with the disease ''kala-azar'' was first suggested by Charles Donovan, and was conclusively demonstrated by Charles Bentley's discovery of ''L. donovani'' in patients with ''kala-azar''. Transmission by the sandfly was hypothesized by Lionel Napier and Ernest Struthers at the School of Tropical Medicine at Calcutta and later proven by his colleagues. The disease became a major problem for Allied troops fighting in Sicily during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
; research by Leonard Goodwin
Leonard George Goodwin CMG FRS (11 July 1915 – 25 November 2008) was a British protozoologist noted for his work on testing the effectiveness of chemical compounds in treating tropical diseases. He was born in London to a shoe shop manager, an ...
then showed pentostam was an effective treatment.
Society and culture
The Institute for OneWorld Health
PATH (formerly known as the Program for Appropriate Technology in Health) is an international, nonprofit global health organization based in Seattle, with 1,600 employees in more than 70 countries around the world. Its president and CEO is Niko ...
has reintroduced the drug paromomycin
Paromomycin is an antimicrobial used to treat a number of parasitic infections including amebiasis, giardiasis, leishmaniasis, and tapeworm infection. It is a first-line treatment for amebiasis or giardiasis during pregnancy. Otherwise it is g ...
for treatment of leishmaniasis, results with which led to its approval as an orphan drug
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent developed to treat medical conditions which, because they are so rare, would not be profitable to produce without government assistance. The conditions are referred to as orphan diseases.
The assignment of ...
. The Drugs for Neglected Diseases Initiative
The Drugs for Neglected Diseases ''initiative'' (DND''i'') is a collaborative, patients' needs-driven, non-profit drug research and development (R&D) organization that is developing new treatments for neglected tropical diseases, neglected diseas ...
is also actively facilitating the search for novel therapeutics. A treatment with paromomycin will cost about US$10. The drug had originally been identified in the 1960s, but had been abandoned because it would not be profitable, as the disease mostly affects poor people. The Indian government
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the Government, national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy lo ...
approved paromomycin for sale in August 2006.
By 2012 the World Health Organization had successfully negotiated with the manufacturers to achieve a reduced cost for liposomal amphotericin B
Amphotericin B is an antifungal medication used for serious fungal infections and leishmaniasis. The fungal infections it is used to treat include mucormycosis, aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, and cryptococcosis. ...
, to US$18 a vial, but a number of vials are needed for treatment and it must be kept at a stable, cool temperature.
Research
 As of 2017, no
As of 2017, no leishmaniasis vaccine
A Leishmaniasis vaccine is a vaccine which would prevent leishmaniasis. As of 2017, no vaccine for humans was available. Currently some effective leishmaniasis vaccines for dogs exist.
The parasite which causes leishmaniasis is '' Leishmania'', w ...
for humans was available. Research to produce a human vaccine is ongoing.
Currently some effective leishmaniasis vaccines for dogs exist. There is also consideration that public health practices can control or eliminate leishmaniasis without a vaccine.
See also
* Canine vector-borne disease *Tropical disease
Tropical diseases are Infectious disease, diseases that are prevalent in or unique to tropics, tropical and subtropics, subtropical regions. The diseases are less prevalent in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, whic ...
References
External links
*Doctors Without Borders' Leishmaniasis Information Page
CDC Leishmaniasis Page
{{Authority control Dog diseases Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin Tropical diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia infectious disease articles ready to translate Zoonoses