Luster (textiles) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
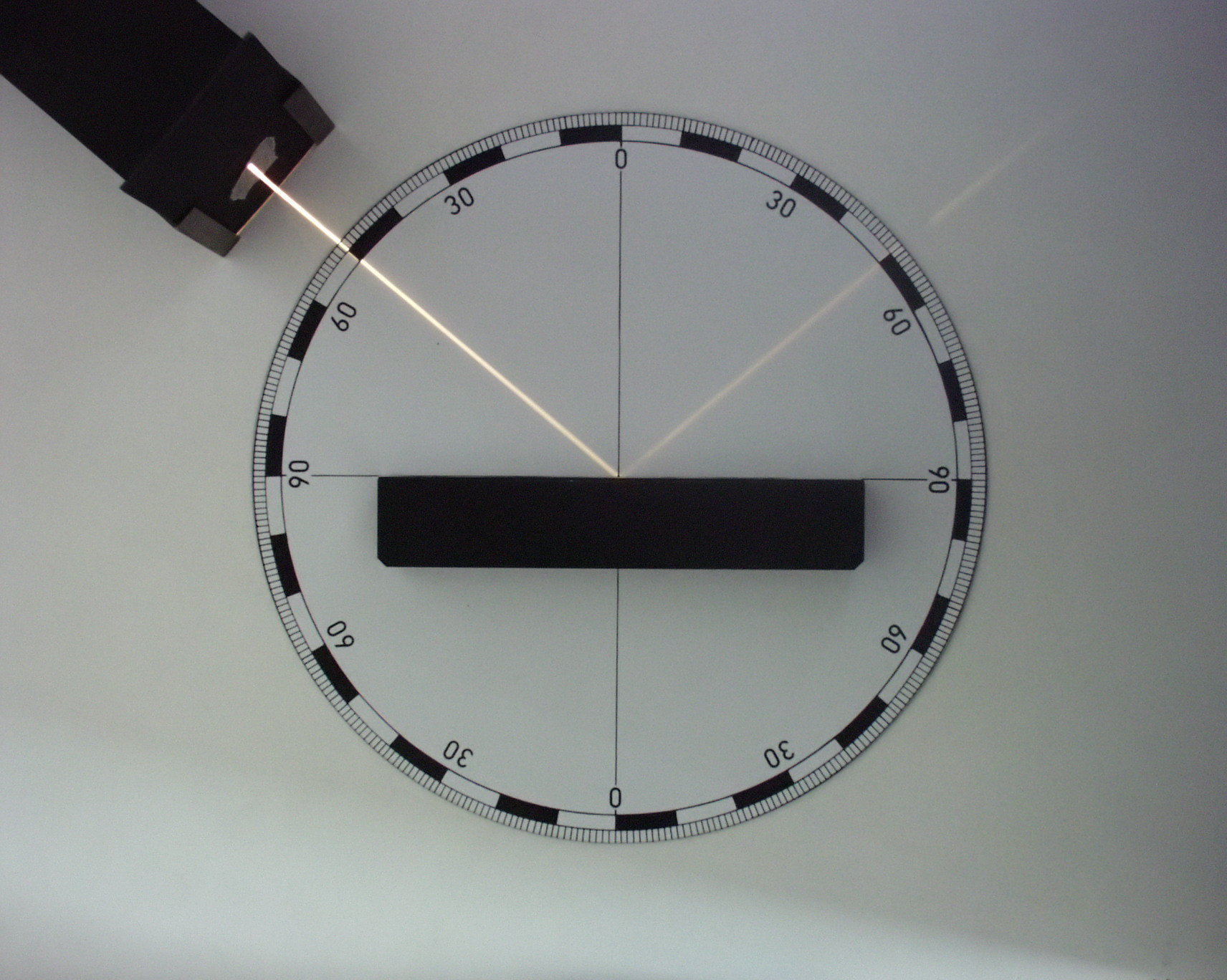 Factors affecting
Factors affecting '' '' lie with fiber properties, but various processes can also alter the surface of textiles and transform the fabric luster. Surface manipulation has a significant impact on light reflection. Rough surfaces absorb and scatter light, while neat and clean surfaces reflect more light.
 In
In textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
s, lustre or luster is a physical property
A physical property is any property that is measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momentary states. Physical properties are ...
that makes them appear bright, glossy, and shiny. The amount of light reflected from the surface of a fiber is referred to as its luster.The level of luster is determined by how light reflects off the surface. For example, round surfaced fiber reflects more light and appears shinier than fiber with an irregular surface. Synthetic fiber
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants (like cotton) ...
s with a more regular surface seem brighter than natural fiber
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals.
They can be used as a component of composite materials, where the orientation of fibers ...
s with an irregular surface, with the exception of silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
, which has a regular surface.
Objective
Luster is the degree of gloss or sheen possessed by the fiber or textile surface. Luster addsaesthetic
Aesthetics, or esthetics, is a branch of philosophy that deals with the nature of beauty and taste, as well as the philosophy of art (its own area of philosophy that comes out of aesthetics). It examines aesthetic values, often expressed th ...
values in fabrics, contributes to their attractiveness. Occasionally, this adds value to their quality assessment. In some cases, when lustre is undesirable, fibres are purposefully dulled by the addition of substances.
Factors
 Factors affecting
Factors affecting lustre
Lustre or Luster may refer to:
Places
* Luster, Norway, a municipality in Vestlandet, Norway
** Luster (village), a village in the municipality of Luster
* Lustre, Montana, an unincorporated community in the United States
Entertainment
* '' ...
(the way light reflects)Lustering
Fiber structure
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
line structured fibers possess a higher luster than the amorphous
In condensed matter physics and materials science, an amorphous solid (or non-crystalline solid, glassy solid) is a solid that lacks the long-range order that is characteristic of a crystal.
Etymology
The term comes from the Greek ''a'' ("wi ...
structure. Secondly smooth surface and cross section of the fiber plays a vital role in reflecting the light. The rounded edges and triangular cross section of the silk fiber contribute to its luster properties; in some cases, synthetic fibres mimic this trilobal
In fibers, trilobal is a cross-section shape with three distinct sides. The shape is advantageous for optical reflective properties and is used in textile fibers. Silk fibers' rounded edges and triangular cross section contribute to their luster ...
shape for a silk-like appearance.
Finishes
'Lustering' refers to any process that uses steam, heat, or pressure to enhance the lustre. Other thanfiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
structure, it is chemical orientation and different finishing methods such as singeing
A singe is a slight scorching, burn or treatment with flame. This may be due to an accident, such as scorching one's hair when lighting a gas fire, or a deliberate method of treatment or removal of hair or other fibres.
Hairdressing
A singe is ...
, heat-setting
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very ...
, calendering
Calendering of textiles is a finishing process used to smooth, coat, or thin a material. With textiles, fabric is passed between calender rollers at high temperatures and pressures. Calendering is used on fabrics such as moire to produce its wat ...
, silk surfacing
Silk surfacing was a surface finishing of cotton to obtain an appearance similar to silk.
Process
In contrast to other imitative finishes such as mercerizing, In Silk surfacing, real silk was used in this treatment. Cotton was treated with aci ...
, mercerizing
Mercerisation is a textile finishing treatment for cellulose fabric and yarn, mainly cotton and flax, which improves dye uptake and tear strength, reduces fabric shrinkage, and imparts a silk-like luster.
Development
The process was devi ...
, and bio polishing, etc.
* Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
when mercerized has a round cross-section that appears brighter than untreated cotton (with a bean cut view.)
* Satin
A satin weave is a type of fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves alongside plain weave ...
is a lustrous fabric structure created by the combination of a weave, finish and silk. Satin embraces exceptional brilliance.
Luster describing terms
* When fibers have a high degree of luster, they are described as bright. * The term "matte" refers to something that is relatively dull or not have luster. * Dull that is devoid of luster. * Extra dull fibers are those that lack luster and appear opaque.Delustering
In oppositedelustrant
A delustrant is a substance that reduces the lustre (sheen) of synthetic fibres. The most common delustrant is anatase titanium dioxide.
Synthetic fibres such as nylon are normally extremely shiny and transparent when extruded. Adding powdered ...
, the substances that reduce the luster are added in synthetic fibers. As their names imply, they can be described as "clear," "bright," "dull," "semi-dull," "extra dull," and "super dull" with regards to the amount of luster. Scattering and absorbing light tends to cause the fibre to appear duller because of the delustrating additive, such as titanium dioxide.
Luster index
Earlier, there was ambiguity in the results of luster in textiles. A new approach has been developed to analyze the luster through images. Devices can measure luster in textiles by analyzing the luminance of images taken from various angles.See also
*Hand feel
Hand feel (Hand, Fabric hand, Fabric feel) is the property of fabrics related to the touch that expresses sensory comfort. It refers to the way fabrics feel against the skin or in the hand and conveys information about the cloth's softness and s ...
, the feel of the fabrics.
* Draping
* Shearing (textiles)
Shearing is a kind of mechanical finish in which the appearance of the fabric is enhanced by cutting the loops or raised surface to a uniform and even height. The machine may have a spiral blade similar to a grass cutting machine. A Shearing machi ...
References
{{Reflist Textiles Properties of textiles