|
Cross Section (fiber)
The cross section depicts the shape of the various textile fibers. Each textile fiber offers a distinct cross sectional appearance when seen under a microscope. The shapes vary from round to oval and flat, different shapes determines certain characteristics of the textiles. Though the majority of synthetic fibers have a circular cross section, but the shape could be altered or engineered during the manufacturing process. The cross-sectional shape is responsible for certain physical properties of textile fibers such as the luster of textiles. Significance The cross-section of a fiber has an effect on the appearance, hand, drape, flexibility, and moisture wicking properties.The cross sectional shape or form of the fibers specifies their texture. Numerous physical characteristics such as hand, bulkiness, and luster are associated with cross sectional shape. Synthetic fibers with a more regular surface seem brighter than natural fibers with an irregular surface, with the exception ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns. Textiles are divided into two groups: Domestic purposes onsumer textilesand technical textiles. In consumer textiles, aesthetics and comfort are the most important factors, but in technical textiles, functional properties are the priority. Geotextiles, industrial textiles, medical textiles, and many other areas are examples of technical textiles, whereas clot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Crop
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope. Fiber crops are characterized by having a large concentration of cellulose, which is what gives them their strength. The fibers may be chemically modified, like in viscose (used to make rayon and cellophane). In recent years, materials scientists have begun exploring further use of these fibers in composite materials. Due to cellulose being the main factor of a plant fiber's strength, this is what scientists are looking to manipulate to create different types of fibers. Fiber crops are generally harvestable after a single growing season, as distinct from trees, which are typically grown for many years before being harvested for such materials as wood pulp fiber or lacebark. In specific circumstances, fiber crops can be superior to wood pulp fiber in terms of technical performance, environmental impact or cost. There are a number of issues regarding the use of fiber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Contour (fiber)
The surface contour of the fiber characterizes its outer surface along its shaft and may be rough, smooth, scaly, serrated, convoluted, or striated, all of which contribute to the friction, softness, and texture. The property is important for the texture and feel of the fabric that is made. Natural fibers, like cotton and wool, have a staple length and irregular, void-filled surface contours. The rough surface aids in the capture of fine particles. Due to the fact that they are not completely solid, they are more compressible. The fiber's microstructures include its cross section shape and surface contour. Shapes of fibers Fiber contour is defined by the fiber's longitudinal surface form. The surface shape of the fiber varies from fiber to fiber which is inherent in natural fibers and may be altered and controlled at the manufacturing stage of synthetic fibers. The fiber shape of synthetic fibers is controlled with a device spinneret during manufacturing (extrusion) process, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Textile Performance
Textile performance, also known as fitness for purpose, is a textile's capacity to withstand various conditions, environments, and hazards, qualifying it for particular uses. The performance of textile products influences their appearance, comfort, durability, and protection. Different textile applications ( automotive, clothing, sleepwear, workwear, sportswear, upholstery, and PPE) require a different set of performance parameters. As a result, the specifications determine the level of performance of a textile product. Textile testing certifies the product's conformity to buying specification. It describes product manufactured for non-aesthetic purposes, where fitness for purpose is the primary criterion. Engineering of high performance fabrics presents a unique set of challenges. The fitness for purpose of textile products is an important consideration for both producers and buyers. Producers, distributors and retailers favor the expectations of the target market, and fash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aesthetics (textile)
Aesthetics in textiles is one of the basic concepts of serviceability of textiles. It is determined by the perception of touch and sight. Aesthetics imply the appearance and attraction of textile products; it includes the color and texture of the material. It is a statement about the end user (consumer) and the target market. When combined with fabric construction, the finish of the clothing material, garment fit, style, and fashion compatibility, colours create an aesthetic comfort. All of these elements work together to satisfy our visual perception. Aesthetics incorporates the role of evaluation (analysing and judging) also. There are various arts and applications that imparts aesthetic properties in textiles. Additionally, the use of LEDs and optical fibres enables the creation of aesthetic properties such as illuminated textiles. History From antiquity until the eighteenth century, the majority of textiles were crafted and decorated by hand. Human ingenuity and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
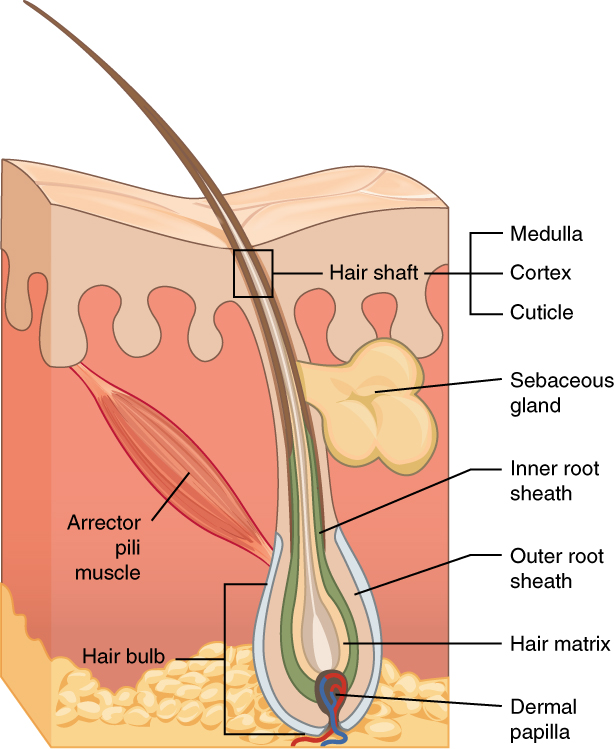
Follicle (anatomy)
A follicle is a small, spherical or vase-like group of cells enclosing a cavity in which some other structure grows or other material is contained. Thyroid follicles make up the thyroid gland. Follicles are best known as the sockets from which hairs grow in humans and other mammals, but the bristles of annelid The annelids (Annelida , from Latin ', "little ring"), also known as the segmented worms, are a large phylum, with over 22,000 extant species including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to various ecol ... worms also grow from such sockets. References {{reflist Skin anatomy Cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Fiber
Animal fibers are natural fibers that consist largely of certain proteins. Examples include silk, hair/ fur (including wool) and feathers. The animal fibers used most commonly both in the manufacturing world as well as by the hand spinners are wool from domestic sheep and silk. Also very popular are alpaca fiber and mohair from Angora goats. Unusual fibers such as Angora wool from rabbits and Chiengora from dogs also exist, but are rarely used for mass production. Not all animal fibers have the same properties, and even within a species the fiber is not consistent. Merino is a very soft, fine wool, while Cotswold is coarser, and yet both Merino and Cotswold are types of sheep. This comparison can be continued on the microscopic level, comparing the diameter and structure of the fiber. With animal fibers, and natural fibers in general, the individual fibers look different, whereas all synthetic fibers look the same. This provides an easy way to differentiate between natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Orifice
A body orifice is any opening in the body of an animal. External In a typical mammalian body such as the human body, the external body orifices are: * The nostrils, for breathing and the associated sense of smell * The mouth, for eating, breathing, and vocalizations such as speech * The ear canals, for the sense of hearing * The nasolacrimal ducts, to carry tears from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity * The anus, for defecation * In males, the urinary meatus, for urination and ejaculation * In females, the urinary meatus, for urination * In females, the vagina, for menstruation, sexual intercourse and childbirth * The nipple orifices Other animals may have some other body orifices: *cloaca, in birds, reptiles, amphibians, and some other animals *siphon in mollusk, arthropods, and some other animals Internal Internal orifices include the orifices of the outflow tracts of the heart, between the heart valves. See also * Internal urethral orifice *Mucosa * Mucocutaneous b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinneret (polymers)
A spinneret is a device used to extrude a polymer solution or polymer melt to form fibers. Streams of viscous polymer exit via the spinneret into air or liquid leading to a phase inversion which allows the polymer to solidify. The individual polymer chains tend to align in the fiber because of viscous flow. This airstream liquid-to-fiber formation process is similar to the production process for cotton candy. The fiber production process is generally referred to as "spinning". Depending on the type of spinneret used, either solid or hollow fibers can be formed. Spinnerets are also used for electrospinning and electrospraying applications. They are sometimes called ''coaxial needles,'' or ''coaxial emitters.'' Spinnerets are usually made of metals with melting points too low to withstand the heating processes employed in industrial metallurgy, and thus are generally not used to form metallic fibers. See also * Electrospinning * Hollow fiber membrane * Spinning (polymers) * Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene. Synthetic fibers can often be produced very cheaply and in large amounts compared to natural fibers, but for clothing natural fibers can give some benefits, such as comfort, over their synthetic counterparts. Natural fibers Natural fibers develop or occur in the fiber shape, and include those produced by plants, animals, and geological processes. They can be classified according to their origin: * Vegetable fibers are generally based on arrangements of cellulose, often with lignin: examples include cotton, hemp, jute, flax, abaca, piña, ramie, sisal, bagasse, and banana. Plant fibers are employed in the manufacture of paper and textile (cloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilobal
In fibers, trilobal is a cross-section shape with three distinct sides. The shape is advantageous for optical reflective properties and is used in textile fibers. Silk fibers' rounded edges and triangular cross section contribute to their luster; in some cases, synthetic fibers are manufactured to mimic this trilobal shape to give them a silk-like appearance. Filaments with a round cross section have less brilliance than trilobal filaments. Etymology is a combination of the words "Tri" for three and "lobal" for sides. Objective Trilobal shape helps in altering hand and increasing the luster. Many synthetic fibres, such as polyester and nylon, are manufactured in Trilobal cross sectional shape for the purpose of enhancing the brilliance and changing the handle. Luster adds aesthetic values in fabrics, contributes to their attractiveness. Occasionally, this adds value to their quality assessment. Use Synthetic fibers are particularly suitable for specific effects such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |