|
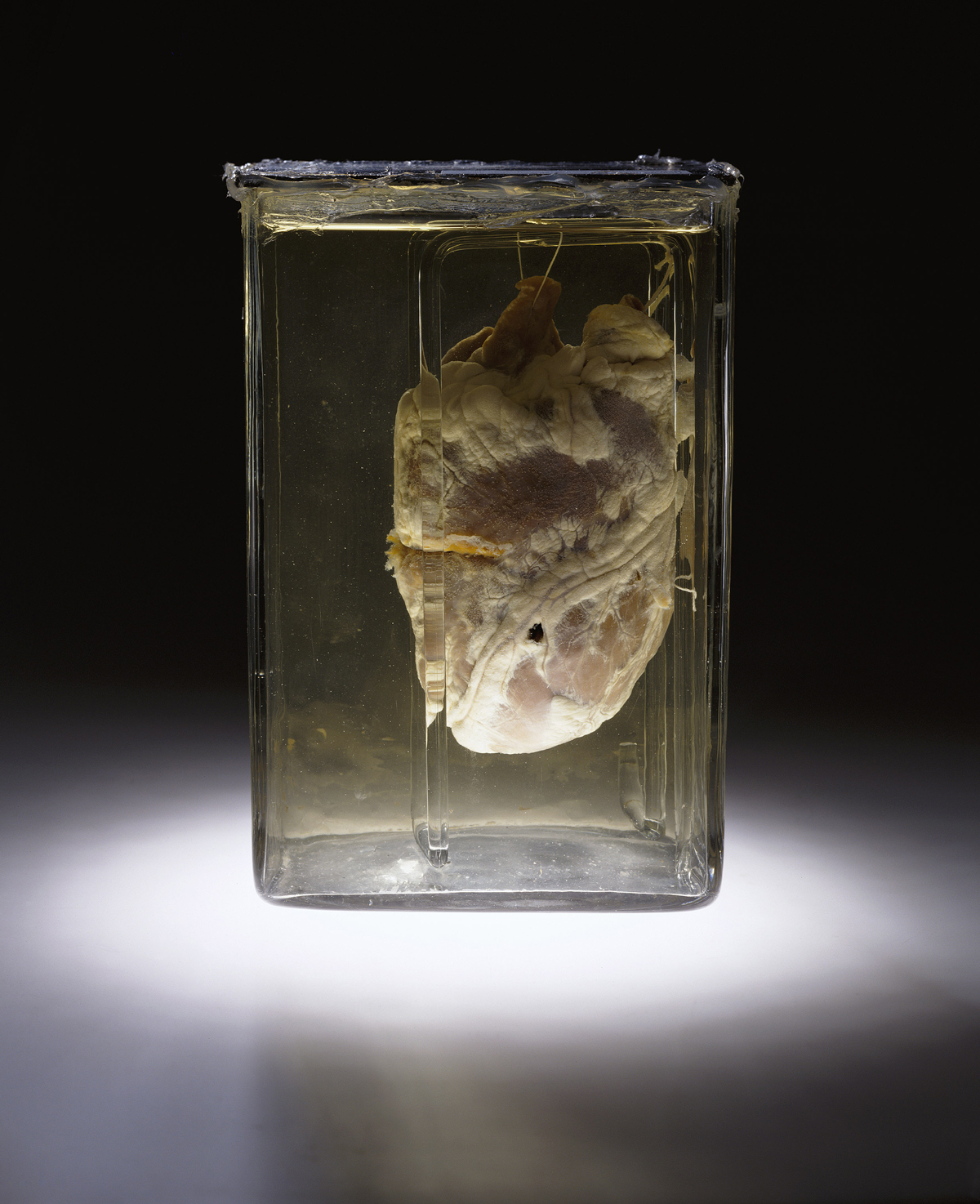
Lung Float Test
The lung float test, also called the hydrostatic test or docimasia, is a controversial autopsy procedure used in determining whether lungs have undergone respiration. It has historically been employed in cases of suspected infanticide to help determine whether or not an infant was stillborn. In the test, lungs that float in water are thought to have been aerated, while those that sink are presumed to indicate an absence of air. The test is not infallible and many factors can cause the test to give false positive or negative results. Decomposition may result in postmortem gas formation, allowing a non-aerated lung to float. During labor, air can be introduced to a deceased infant's lungs while moving through the birth canal. Lungs exposed to air do not always float. Große Ostendorf et al. showed the procedure gave a false result in 2% of cases. In a 1997 paper, J.J. Moar emphasises the risk of misdiagnosing live birth, writing that the "majority of new born infants seen at autopsy sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Autopsy
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death; or the exam may be performed to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. The term ''necropsy'' is generally used for non-human animals. Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist. Only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Manner of death must be determined ** Determine if death was natural or unnatural ** Injury source and extent on the corpse * Pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Breathing
Breathing (spiration or ventilation) is the rhythmical process of moving air into ( inhalation) and out of ( exhalation) the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or external respiration, brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where cellular respiration takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose being the prevention of resources being spent on weak or disabled offspring. Unwanted infants were usually abandoned to die of exposure, but in some societies they were deliberately killed. Infanticide is generally illegal, but in some places the practice is tolerated, or the prohibition is not strictly enforced. Most Stone Age human societies routinely practiced infanticide, and estimates of children killed by infanticide in the Mesolithic and Neolithic eras vary from 15 to 50 percent. Infanticide continued to be common in most societies after the historical era began, including ancient Greece, Roman Empire, ancient Rome, the Phoenicians, ancient China, ancient Japan, Pre-Islamic Arabia, early modern Europe, Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal Australia, Indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetus, fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without vital signs, signs of life. A stillbirth can often result in the feeling of guilt (emotion), guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and sudden infant death syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive. Often the cause is unknown. Causes may include pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and birth complications, problems with the placenta or umbilical cord, birth defects, infections such as malaria and syphilis, and poor health in the mother. Risk factors include a mother's age over 35, smoking, drug use, use of assisted reproductive technology, and first pregnancy. Stillbirth may be suspected when no fetal movement is felt. Confirmation is by ultrasound. Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Childbirth
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy, where one or more Fetus, fetuses exits the Womb, internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section and becomes a newborn to the world. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million human births globally. In Developed country, developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in Developing country, developing countries most are home births. The most common childbirth method worldwide is vaginal delivery. It involves four stages of labour: the cervical effacement, shortening and Cervical dilation, opening of the cervix during the first stage, descent and birth of the baby during the second, the delivery of the placenta during the third, and the recovery of the mother and infant during the fourth stage, which is referred to as the Postpartum period, postpartum. The first stage is characterised by abdominal cramping or also back pain in the case of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus (; September 129 – AD), often Anglicization, anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Ancient Rome, Roman and Greeks, Greek physician, surgeon, and Philosophy, philosopher. Considered to be one of the most accomplished of all medical researchers of Ancient history, antiquity, Galen influenced the development of various scientific disciplines, including anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and neurology, as well as philosophy and logic. The son of Aelius Nicon, a wealthy Greek architect with scholarly interests, Galen received a comprehensive education that prepared him for a successful career as a physician and philosopher. Born in the ancient city of Pergamon (present-day Bergama, Turkey), Galen traveled extensively, exposing himself to a wide variety of medical theories and discoveries before settling in Ancient Rome, Rome, where he served prominent members of Roman society and eventually was given the position of perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Forensic Pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases and civil law cases in some jurisdictions. Coroners and medical examiners are also frequently asked to confirm the identity of remains. Duties Forensic pathology is an application of medical jurisprudence. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who has completed training in anatomical pathology and has subsequently specialized in forensic pathology. The requirements for becoming a "fully qualified" forensic pathologist vary from country to country. Some of the different requirements are discussed below (see ''§ Education''). The forensic pathologist performs autopsies/postmortem examinations with the goal of determining the cause of death as well as the possible manner of death. The autopsy report contains conclusions made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Born Alive Rule
The born alive rule is a common law legal principle that holds that various criminal laws, such as homicide and assault, apply only to a child that is " born alive". U.S. courts have overturned this rule, citing recent advances in science and medicine, and in several states feticide statutes have been explicitly framed or amended to include fetuses in utero. Abortion in Canada is still governed by the born alive rule, as courts continue to hold to its foundational principles. In 1996, the Law Lords confirmed that the rule applied in English law but that alternative charges existed in lieu, such as a charge of unlawful or negligent manslaughter instead of murder.''Attorney General's Reference No 3 of 1994'' History The born alive rule was originally a principle at common law in England that was carried to the United States and other former colonies of the British Empire. First formulated by William Staunford, it was later set down by Edward Coke in his Institutes of the Laws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neonaticide
Neonaticide is the deliberate act of a parent murdering their own child during the first 24 hours of life. As a noun, the word "neonaticide" may also refer to anyone who practices or who has practiced this. Neonaticide is relatively rare in developed countries, but most of these murders remain secret: Neonaticide is considerably more commonly committed by mothers than fathers; infanticide is also more likely to be committed by mothers than fathers. A 1999 United States Department of Justice study concluded that between 1976 and 1997 in the United States, mothers were responsible for a higher share of children killed during infancy, while fathers were more likely to have been responsible for the murders of children age eight or older. Statistics 90% of neonaticidal mothers are 25 years of age or younger. Less than 20% are married. Less than 30% are seen as psychotic or depressed. They have typically denied or concealed the pregnancy since conception. 45% of all child murder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Forensic Pathology
Forensic pathology is pathology that focuses on determining the cause of death by examining a corpse. A post mortem examination is performed by a medical examiner or forensic pathologist, usually during the investigation of criminal law cases and civil law cases in some jurisdictions. Coroners and medical examiners are also frequently asked to confirm the identity of remains. Duties Forensic pathology is an application of medical jurisprudence. A forensic pathologist is a medical doctor who has completed training in anatomical pathology and has subsequently specialized in forensic pathology. The requirements for becoming a "fully qualified" forensic pathologist vary from country to country. Some of the different requirements are discussed below (see ''§ Education''). The forensic pathologist performs autopsies/postmortem examinations with the goal of determining the cause of death as well as the possible manner of death. The autopsy report contains conclusions made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose being the prevention of resources being spent on weak or disabled offspring. Unwanted infants were usually abandoned to die of exposure, but in some societies they were deliberately killed. Infanticide is generally illegal, but in some places the practice is tolerated, or the prohibition is not strictly enforced. Most Stone Age human societies routinely practiced infanticide, and estimates of children killed by infanticide in the Mesolithic and Neolithic eras vary from 15 to 50 percent. Infanticide continued to be common in most societies after the historical era began, including ancient Greece, Roman Empire, ancient Rome, the Phoenicians, ancient China, ancient Japan, Pre-Islamic Arabia, early modern Europe, Aboriginal Australians, Aboriginal Australia, Indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |