Luigi Barzini Sr. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Luigi Barzini Sr. (February 7, 1874 – September 6, 1947) in ''BARZINI Luigi''
in: Historic Archives of the Senate, open source, retrieved: 2022-10-28
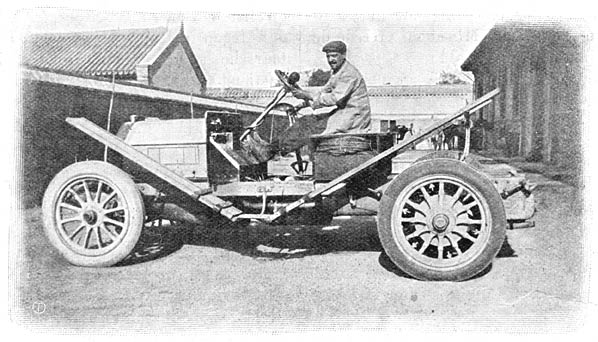 As a journalist of the ''Corriere della Sera'', in 1907 he accompanied
As a journalist of the ''Corriere della Sera'', in 1907 he accompanied
Italy: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present
', Infobase Publishing,
{{DEFAULTSORT:Barzini, Luigi sr 1874 births 1947 deaths People from Orvieto Italian journalists Italian male journalists Italian anti-communists People of the Italian Social Republic War correspondents of the Russo-Japanese War Chevaliers of the Légion d'honneur 20th-century Italian writers 20th-century Italian male writers
Orvieto
Orvieto () is a city and ''comune'' in the Province of Terni, southwestern Umbria, Italy, situated on the flat summit of a large butte of volcanic tuff. The city rises dramatically above the almost-vertical faces of tuff cliffs that are compl ...
, son of Ettore Barzini and Maria Bartoccini, was an Italian Senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
and the most noted journalist
A journalist is an individual that collects/gathers information in form of text, audio, or pictures, processes them into a news-worthy form, and disseminates it to the public. The act or process mainly done by the journalist is called journalism ...
and war correspondent of the second half of the Italian Belle Époque
The Belle Époque or La Belle Époque (; French for "Beautiful Epoch") is a period of French and European history, usually considered to begin around 1871–1880 and to end with the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era ...
.in: Historic Archives of the Senate, open source, retrieved: 2022-10-28
Work Life
Barzini started his career as a journalist in 1898, working for minor Italian magazines and was almost immediately noticed and hired byLuigi Albertini
Luigi Albertini (19 October 1871–29 December 1941) was an influential Italian newspaper editor, member of the Parliament, and historian of the First World War.
As editor of one of Italy's best-known newspapers, ''Corriere della Sera'' of Mila ...
, then director of the ''Corriere della Sera
The ''Corriere della Sera'' (; en, "Evening Courier") is an Italian daily newspaper published in Milan with an average daily circulation of 410,242 copies in December 2015.
First published on 5 March 1876, ''Corriere della Sera'' is one of It ...
'', the most prestigious Italian newspaper. In 1900, he was sent as war correspondent to Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, where he witnessed and reported about the Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
, distinguishing himself for his ability to get first hand information. During the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905, he was embedded within the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
, and covered its campaigns in Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manc ...
.
 As a journalist of the ''Corriere della Sera'', in 1907 he accompanied
As a journalist of the ''Corriere della Sera'', in 1907 he accompanied Prince Scipione Borghese
Prince Luigi Marcantonio Francesco Rodolfo Scipione Borghese, commonly known as Scipione Borghese (11 September 1871, Migliarino – 18 November 1927, Florence), was an Italian aristocrat, industrialist, politician, explorer, mountain climber an ...
in the famous Peking to Paris motor race
The Peking to Paris motor race was an automobile race, originally held in 1907, between Peking (now Beijing), then Qing China (now the People's Republic of China) and Paris, France (then the Third French Republic), a distance of .
The idea f ...
, winning it after a journey of two months in an Itala
Itala was a car manufacturer based in Turin, Italy, from 1904 to 1934, started by Matteo Ceirano and five partners in 1903.
Ceirano family background
The Ceirano brothers, Giovanni Battista, Giovanni, Ernesto and Matteo, were influential in the ...
car across China and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, traveling amongst regions and people that had never seen a car before. Of this adventure, he left a wonderful memoir, filled with hundreds of photographs, in his book ''Peking to Paris'', that was published in 1908 in eleven different languages: a "publishing raid", as his proud Italian editor noted in the preface of the book.
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Barzini was the official correspondent with the Italian Army
"The safeguard of the republic shall be the supreme law"
, colors =
, colors_labels =
, march = ''Parata d'Eroi'' ("Heroes's parade") by Francesco Pellegrino, ''4 Maggio'' (May 4) ...
; an account of his experiences was published in ''The War Illustrated
''The War Illustrated'' was a British war magazine published in London by William Berry (later Viscount Camrose and owner of ''The Daily Telegraph''). It was first released on 22 August 1914, eighteen days after the United Kingdom declared war o ...
''. In 1921, Barzini left the ''Corriere della Sera'' and moved to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, where he directed the Italian-American newspaper '' Corriere d'America ''from 1923 until his return to Italy in 1931. In 1932 he became director of the ''Il Mattino
''Il Mattino'' (meaning ''The Morning'' in English) is an Italian daily newspaper published in Naples, Italy.
History and profile
''Il Mattino'' was first published on 16 March 1892 by the journalists Edoardo Scarfoglio and Matilde Serao. The pa ...
'',Sarti, ''Italy: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present'', p. 142 but in 1933 lost his position when Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
mistakenly thought him to be the author of a critical article appeared in the French press. The misunderstanding was soon cleared but Barzini had no further chances to direct a newspaper. After the nomination as senator, he continued to work as a correspondent for the Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
newspaper ''Il Popolo d'Italia
''Il Popolo d'Italia'' ("The People of Italy") was an Italian newspaper published from 15 November 1914 until 24 July 1943. It was founded by Benito Mussolini as a pro-war newspaper during World War I, and it later became the main newspaper of ...
'', covering the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, lin ...
and the Russian Invasion.
Barzini and Fascism
Barzini had pro-Fascist
Fascism is a far-right, Authoritarianism, authoritarian, ultranationalism, ultra-nationalist political Political ideology, ideology and Political movement, movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and pol ...
sentiments since before Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in 194 ...
's rise to power. He signed his name on the ''Manifesto of the Fascist Intellectuals
The "Manifesto of Fascist Intellectuals" ( it, "Manifesto degli Intellettuali del Fascismo", italics=no ), by the actualist philosopher Giovanni Gentile in 1925, formally established the political and ideologic foundations of Italian Fascism. I ...
'' in 1925, and was made a senator
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
in 1934, serving on the Commission of the Armed Forces (April 17, 1939 – February 11, 1941), the Committee on Foreign Affairs, Trade and Customs legislation (December 31, 1941 – February 12, 1943 and June 16 to August 5, 1943), Affairs Committee of Italian Africa (April 15, 1942 – June 16, 1943) and the Board of Finance (February 12 to June 16, 1943). He continued to collaborate with Mussolini in the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
, where he directed the official press agency Agenzia Stefani Agenzia Stefani was the leading press agency in Italy from the mid-19th century until the end of World War II. It was founded by Guglielmo Stefani on 26 January 1853 in Turin, and was closed on 29 April 1945 in Milan.
History
The beginning
''T ...
. In 1945, he was convicted for his involvement in the Fascist regime and forbidden to practice the profession of journalist.
Death and family
Barzini died destitute inMilan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
in 1947. He had four children: Emma, Luigi Jr., Ettore, and Ugo. His son, Luigi Barzini, Jr.
Luigi Barzini Jr. (21 December 1908 – 30 March 1984) was an Italian journalist, writer and politician most famous for his 1964 book ''The Italians'', delving deeply into the Italian national character and introducing many Anglo-Saxon and Germa ...
was also a journalist and writer and became widely known for his 1964 book "The Italians".
His son Ettore, after joining the communist Patriotic Action Groups, was arrested in 1943 and deported to a concentration camp in Germany where he died in 1945, despite his father's efforts to save his life. Works
*Nell'Estremo Oriente. Milano, Libreria Editrice Nazionale, 1904 *Il Giappone in armi. Milano, Libreria Editrice Lombarda, 1906 *Guerra Russo-Giapponese. La battaglia di Mukden, 1907 *La metà del mondo vista da un automobile – da Pechino a Parigi in 60 giorni, prima edizione. Milano, Ulrico Hoepli Editore, 1908 ** *Scene della grande guerra, 1915 *Al Fronte, 1915 *La guerra d'Italia. Sui monti, nel cielo e nel mare, 1916 *La guerra d'Italia. Dal Trentino al Carso, 1917 *Impressioni boreali, 1921 *Dall'impero del Mikado all'impero dello Zar, 1935 *Sotto la tenda, 1935 *U.R.S.S. L'impero del lavoro forzato, Ulrico Hoepli Editore, 1938 *Evasione in Mongolia, 1939 *Wu Wang ed altre genti, 1941 *Roosevelt e la guerra all'Inghilterra. Commenti e spiegazioni, Mondadori, 1942Awards
*Commander of theOrder of the Crown of Italy
The Order of the Crown of Italy ( it, Ordine della Corona d'Italia, italic=no or OCI) was founded as a national order in 1868 by King Vittorio Emanuele II, to commemorate the unification of Italy in 1861. It was awarded in five degrees for civi ...
, February 17, 1924
*Grand Officer of the Order of the Crown of Italy, April 16, 1925
*Grand Officer of the Colonial Order of the Star of Italy
The Colonial Order of the Star of Italy ( it, Ordine coloniale della Stella d'Italia ) was founded as a colonial order of chivalry on 18 June 1914 by Italian King Victor Emmanuel III, to reward soldiers deployed to the colony of Libya. The order ...
*Knight of the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleon, ...
(France)
*Croce di Guerra
The War Cross for Military Valor ( it, Croce di Guerra al Valor Militare) is an Italian order for military valor. Established in 1922, the cross may be awarded only in time of war.
Appearance
The medal is a Greek cross made of copper. Inscr ...
*Medaglia di bronzo al valor militare
References
*Sarti, Roland (ed.) (2004).Italy: a reference guide from the Renaissance to the present
', Infobase Publishing,
External links
* *{{DEFAULTSORT:Barzini, Luigi sr 1874 births 1947 deaths People from Orvieto Italian journalists Italian male journalists Italian anti-communists People of the Italian Social Republic War correspondents of the Russo-Japanese War Chevaliers of the Légion d'honneur 20th-century Italian writers 20th-century Italian male writers