Lucía Martínez Valdivia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Reed College is a private
 The Reed Institute (the legal name of the college) was founded in 1908 and held its first classes in 1911. Reed is named for Oregon pioneers Simeon Gannett Reed (1830–1895) and Amanda Reed (died 1904). Simeon was an entrepreneur involved in several enterprises, including trade on the Willamette and
The Reed Institute (the legal name of the college) was founded in 1908 and held its first classes in 1911. Reed is named for Oregon pioneers Simeon Gannett Reed (1830–1895) and Amanda Reed (died 1904). Simeon was an entrepreneur involved in several enterprises, including trade on the Willamette and
 According to sociologist Burton Clark, Reed is one of the most unusual institutions of higher learning in the United States, featuring a traditional liberal arts and natural sciences curriculum. It requires freshmen to take Humanities 110, an intensive introduction to multidisciplinary inquiry, covering ancient Greece and Rome, the Hebrew Bible and ancient Jewish history, and as of 2019, Ancient Mesoamerica and the Harlem Renaissance. Reed also has a TRIGA research reactor on campus, making it the only school in the United States to have a nuclear reactor operated primarily by undergraduates. Reed also requires all students to complete a thesis (a two-semester-long research project conducted under the guidance of professors) during the senior year as a prerequisite of graduation. Upon completion of the senior thesis, students must also pass an oral defense of ninety minutes related to the thesis topic and how the thesis relates to the larger context of the student's studies.
Reed maintains a 9:1 student-to-faculty ratio, and its small classes emphasize a "conference" style where the professor often acts as a mediator for discussion rather than a lecturer. While large lecture-style classes exist, Reed emphasizes its smaller lab and conference sections.
According to sociologist Burton Clark, Reed is one of the most unusual institutions of higher learning in the United States, featuring a traditional liberal arts and natural sciences curriculum. It requires freshmen to take Humanities 110, an intensive introduction to multidisciplinary inquiry, covering ancient Greece and Rome, the Hebrew Bible and ancient Jewish history, and as of 2019, Ancient Mesoamerica and the Harlem Renaissance. Reed also has a TRIGA research reactor on campus, making it the only school in the United States to have a nuclear reactor operated primarily by undergraduates. Reed also requires all students to complete a thesis (a two-semester-long research project conducted under the guidance of professors) during the senior year as a prerequisite of graduation. Upon completion of the senior thesis, students must also pass an oral defense of ninety minutes related to the thesis topic and how the thesis relates to the larger context of the student's studies.
Reed maintains a 9:1 student-to-faculty ratio, and its small classes emphasize a "conference" style where the professor often acts as a mediator for discussion rather than a lecturer. While large lecture-style classes exist, Reed emphasizes its smaller lab and conference sections.
 Although letter grades are given to students, grades are de-emphasized at Reed and focus is placed on a narrative evaluation. According to the school, "a conventional letter grade for each course is recorded for every student, but the registrar's office does not distribute grades to students, provided that work continues at satisfactory (C or higher) levels. Unsatisfactory grades are reported directly to the student and the student's adviser. Papers and exams are generally returned to students with lengthy comments but without grades affixed." Students can request copies of their official transcript from the registrar. There is no dean's list or honor roll ''per se'', but students who maintain a GPA of 3.5 or above for an academic year receive academic commendations at the end of the spring semester which are noted on their transcripts. Many Reed students graduate without knowing their cumulative GPA or their grades in individual classes. Reed is singled out as having little to no grade inflation over the years; only ten students graduated with a perfect 4.0 GPA in the period from 1983 to 2012. (Transcripts are accompanied by a card contextualizing Reed's grading approach so as not to penalize students' graduate school applications.) Although Reed does not award Latin honors to graduates, it confers several awards for academic achievement at commencement, including naming students to Phi Beta Kappa.
Reed has no fraternities or sororities and few NCAA sports teams although physical education classes (which range from
Although letter grades are given to students, grades are de-emphasized at Reed and focus is placed on a narrative evaluation. According to the school, "a conventional letter grade for each course is recorded for every student, but the registrar's office does not distribute grades to students, provided that work continues at satisfactory (C or higher) levels. Unsatisfactory grades are reported directly to the student and the student's adviser. Papers and exams are generally returned to students with lengthy comments but without grades affixed." Students can request copies of their official transcript from the registrar. There is no dean's list or honor roll ''per se'', but students who maintain a GPA of 3.5 or above for an academic year receive academic commendations at the end of the spring semester which are noted on their transcripts. Many Reed students graduate without knowing their cumulative GPA or their grades in individual classes. Reed is singled out as having little to no grade inflation over the years; only ten students graduated with a perfect 4.0 GPA in the period from 1983 to 2012. (Transcripts are accompanied by a card contextualizing Reed's grading approach so as not to penalize students' graduate school applications.) Although Reed does not award Latin honors to graduates, it confers several awards for academic achievement at commencement, including naming students to Phi Beta Kappa.
Reed has no fraternities or sororities and few NCAA sports teams although physical education classes (which range from
 *Division of Arts: includes the Art (Art History and Studio Art), Dance, Music, and Theatre Departments;
*Division of History and Social Sciences: includes the History, Anthropology, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology Departments, as well as the International and Comparative Policy Studies Program;
*Division of Literature and Languages: includes the Classics, Chinese, English, French, German, Russian, and Spanish Departments, as well as the Creative Writing and General Literature Programs;
*Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: includes the Mathematics, Biology, Chemistry, and Physics Departments, and
*Division of Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics: includes the Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics Departments.
*Division of Arts: includes the Art (Art History and Studio Art), Dance, Music, and Theatre Departments;
*Division of History and Social Sciences: includes the History, Anthropology, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology Departments, as well as the International and Comparative Policy Studies Program;
*Division of Literature and Languages: includes the Classics, Chinese, English, French, German, Russian, and Spanish Departments, as well as the Creative Writing and General Literature Programs;
*Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: includes the Mathematics, Biology, Chemistry, and Physics Departments, and
*Division of Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics: includes the Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics Departments.
 For Fall 2016, the freshman class had 357 students. 10% were valedictorians of their high school classes and another 2% were salutatorians. 32% ranked in the top 5% of their class. The median scores on their SAT tests were 680 math, 710 verbal, and 680 writing, which puts them at the 96th percentile. The class was drawn from the largest pool ever—5,705 applicants—and was the most selective in Reed's history, with an admittance rate of 31%. , to increase student enrollment from historically underrepresented minorities, Reed encourages they apply for the college's "Discover Reed Fly-In Program", an all-inclusive, all-expenses-paid, multi-day campus tour and open to all high school seniors who are US citizens or permanent residents, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
For Fall 2016, the freshman class had 357 students. 10% were valedictorians of their high school classes and another 2% were salutatorians. 32% ranked in the top 5% of their class. The median scores on their SAT tests were 680 math, 710 verbal, and 680 writing, which puts them at the 96th percentile. The class was drawn from the largest pool ever—5,705 applicants—and was the most selective in Reed's history, with an admittance rate of 31%. , to increase student enrollment from historically underrepresented minorities, Reed encourages they apply for the college's "Discover Reed Fly-In Program", an all-inclusive, all-expenses-paid, multi-day campus tour and open to all high school seniors who are US citizens or permanent residents, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
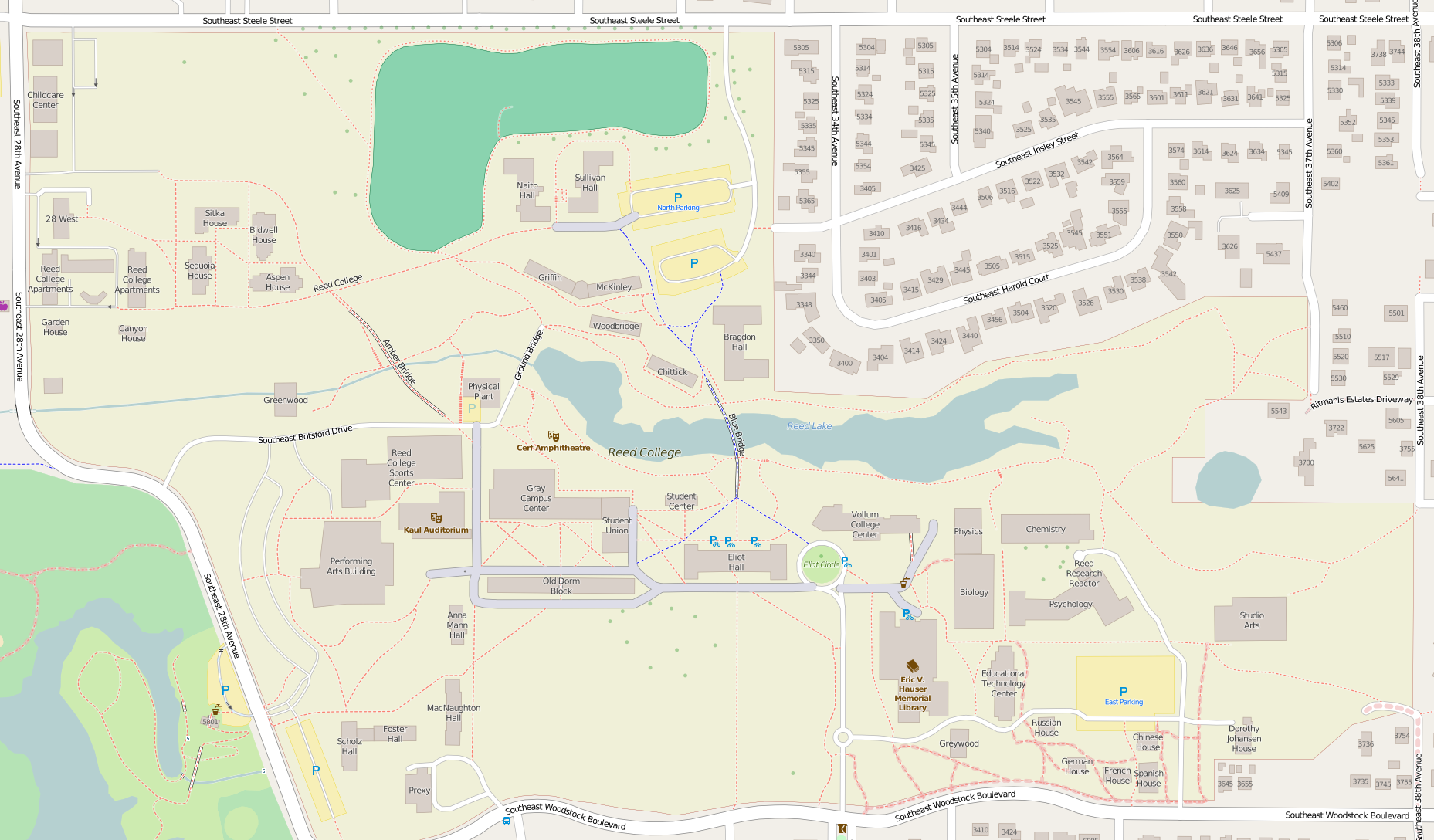
 The Reed College campus was established on a tract of land in southeast
The Reed College campus was established on a tract of land in southeast
 Reed houses 945 students in 18 residence halls on campus and several college-owned houses and apartment buildings on or adjacent to campus. Residence halls on campus range from the traditional (i.e., Gothic Old Dorm Block, referred to as "ODB") to the eclectic (e.g., Anna Mann, a Tudor-style cottage built in the 1920s by Reed's founding architect A. E. Doyle, originally used as a women's hallRomel Hernandez, "This New House"
Reed houses 945 students in 18 residence halls on campus and several college-owned houses and apartment buildings on or adjacent to campus. Residence halls on campus range from the traditional (i.e., Gothic Old Dorm Block, referred to as "ODB") to the eclectic (e.g., Anna Mann, a Tudor-style cottage built in the 1920s by Reed's founding architect A. E. Doyle, originally used as a women's hallRomel Hernandez, "This New House"
''Reed''
(Spring 2007), p. 15.), language houses (Spanish, Russian, French, German, and Chinese), "temporary" housing, built in the 1960s (Cross Canyon – Chittick, Woodbridge, McKinley, Griffin), to more recently built dorms (Bragdon, Naito, Sullivan). There are also theme residence halls including everything from substance-free living to Japanese culture to music to a dorm for students interested in outdoors activities (hiking, climbing, bicycling, kayaking, skiing, etc.). The college's least-loved complex (as measured by applications to the college's housing lottery), MacNaughton and Foster-Scholz, is known on campus as "Asylum Block" because of its post-World War II modernist architecture and interior spaces dominated by long, straight corridors lined with identical doors, said by students to resemble that of an insane asylum. Until 2006, it was thought that these residence halls had been designed by architect Pietro Belluschi. Under the 10-year Campus Master Plan adopted in 2006, Foster-Scholz is scheduled to be demolished and replaced, and MacNaughton to be remodeled. According to the master plan, "The College's goal is to provide housing on or adjacent to the campus that accommodates 75% of the ull-timestudent population. At present, the College provides on-campus housing for 838 students". In Spring 2007, the college broke ground on the construction of a new quadrangle called the Grove with four new Leed certified residence halls (Aspen, Sequoia, Sitka, Bidwell) on the northwest side of the campus, which opened in Fall 2008. A new Spanish House residence was completed. Together, the five new residences added 142 new beds. Reed also has off-campus housing. Many houses in the Woodstock and Eastmoreland Portland neighborhoods are traditionally rented to Reed students. On February 21, 2018, Reed announced the construction of the "largest residence hall in its history". Completed in Fall 2019, Trillium houses an additional 180 students, boosting Reed's housing capacity to nearly 80% of the student body, up from 68%. The addition of Trillium guarantees housing for both freshman and sophomores, as students were formerly subjected to a housing lottery after freshman year. The new building is also designed to meet "LEED Platinum standards", and Reed is currently evaluating proposals to put solar panels on the roof.
 The Reed College Canyon, a natural area and national wildlife preserve, bisects the campus, separating the academic buildings from many of the residence halls (the so-called ''cross-canyon halls''). The canyon is filled by Crystal Creek Springs, a natural spring that drains into Johnson Creek.
Canyon Day, a tradition dating back to 1915, is held twice a year. On Canyon Day students and Reed neighbors join canyon crew workers to spend a day helping with restoration efforts.
A landmark of the campus, the Blue Bridge, spans the canyon. This bridge replaced the unique cantilevered bridge that served in that spot between 1959 and 1991, which "featured stressed plywood girders – the first time this construction had been used on a span of this size: a straight bridge long and high. It attracted great architectural interest during its lifetime".
A new pedestrian and bicycle bridge spanning the canyon was opened in Fall 2008. This bridge, dubbed the "Bouncy Bridge", "Orange Bridge", and in some cases the "Amber Bridge" by students, is long, about a third longer than the Blue Bridge, and "connect the new north campus quad to Gray Campus Center, the student union, the library, and academic buildings on the south side of campus".
The Reed College Canyon, a natural area and national wildlife preserve, bisects the campus, separating the academic buildings from many of the residence halls (the so-called ''cross-canyon halls''). The canyon is filled by Crystal Creek Springs, a natural spring that drains into Johnson Creek.
Canyon Day, a tradition dating back to 1915, is held twice a year. On Canyon Day students and Reed neighbors join canyon crew workers to spend a day helping with restoration efforts.
A landmark of the campus, the Blue Bridge, spans the canyon. This bridge replaced the unique cantilevered bridge that served in that spot between 1959 and 1991, which "featured stressed plywood girders – the first time this construction had been used on a span of this size: a straight bridge long and high. It attracted great architectural interest during its lifetime".
A new pedestrian and bicycle bridge spanning the canyon was opened in Fall 2008. This bridge, dubbed the "Bouncy Bridge", "Orange Bridge", and in some cases the "Amber Bridge" by students, is long, about a third longer than the Blue Bridge, and "connect the new north campus quad to Gray Campus Center, the student union, the library, and academic buildings on the south side of campus".
 The Paradox ("Est. in the 80s") is a student-run coffee shop located on campus. In 2003 the Paradox opened a second coffee shop, dubbing it the "Paradox Lost" (an allusion to
The Paradox ("Est. in the 80s") is a student-run coffee shop located on campus. In 2003 the Paradox opened a second coffee shop, dubbing it the "Paradox Lost" (an allusion to

File:Steve Jobs Headshot 2010-CROP.jpg, Notable Reed alumni include Tektronix co-founder Howard Vollum (1936), businessman John Sperling (1948), linguistic anthropologist
liberal arts college
A liberal arts college or liberal arts institution of higher education is a college with an emphasis on undergraduate study in liberal arts and sciences. Such colleges aim to impart a broad general knowledge and develop general intellectual capac ...
in Portland, Oregon. Founded in 1908, Reed is a residential college with a campus in the Eastmoreland neighborhood, with Tudor-Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
style architecture, and a forested canyon nature preserve at its center.
Referred to as one of "the most intellectual colleges in the country", Reed is known for its mandatory first-year humanities program, senior thesis, progressive politics, de-emphasis on grades, academic rigor, grade deflation, and unusually high proportion of graduates who go on to earn doctorates and other postgraduate degrees. The college has many prominent alumni, including over a hundred Fulbright Scholars, 67 Watson Fellows
Watson may refer to:
Companies
* Actavis, a pharmaceutical company formerly known as Watson Pharmaceuticals
* A.S. Watson Group, retail division of Hutchison Whampoa
* Thomas J. Watson Research Center, IBM research center
* Watson Systems, maker ...
, and three Churchill Scholars; its 32 Rhodes Scholars
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
are the second-highest count for a liberal arts college. Reed is ranked fourth in the United States for all postsecondary institutions for the percentage of its graduates who go on to earn a Ph.D., after Caltech, Harvey Mudd, and Swarthmore College
Swarthmore College ( , ) is a Private college, private Liberal arts colleges in the United States, liberal arts college in Swarthmore, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1864, with its first classes held in 1869, Swarthmore is one of the earliest coeduca ...
.
History
 The Reed Institute (the legal name of the college) was founded in 1908 and held its first classes in 1911. Reed is named for Oregon pioneers Simeon Gannett Reed (1830–1895) and Amanda Reed (died 1904). Simeon was an entrepreneur involved in several enterprises, including trade on the Willamette and
The Reed Institute (the legal name of the college) was founded in 1908 and held its first classes in 1911. Reed is named for Oregon pioneers Simeon Gannett Reed (1830–1895) and Amanda Reed (died 1904). Simeon was an entrepreneur involved in several enterprises, including trade on the Willamette and Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
s with his close friend and associate, former Portland Mayor William S. Ladd (for whom Ladd's Addition
Ladd's Addition is an inner southeast historic district of Portland, Oregon, United States. It is Portland's oldest planned residential development, and one of the oldest in the western United States. The district is known in Portland for a di ...
is named). Unitarian minister Thomas Lamb Eliot
Thomas Lamb Eliot ( – ) was an Oregon pioneer, minister of one of the first churches on the west coast of the U.S., president of the Portland Children's Home, president of the Oregon Humane Society, a director of the Art Association, director o ...
, who knew the Reeds from the church choir, is credited with convincing Reed of the need for "a lasting legacy, a 'Reed Institute of Lectures,' and joked it would 'need a mine to run it.'" Reed's will suggested his wife could "devote some portion of my estate to benevolent objects, or to the cultivation, illustration, or development of the fine arts in the city of Portland, or to some other suitable purpose, which shall be of permanent value and contribute to the beauty of the city and to the intelligence, prosperity, and happiness of the inhabitants". Ladd's son, William Mead Ladd, donated 40 acres from the Ladd Estate Company to build the new college. Reed's first president (1910–1919) was William Trufant Foster, a former professor at Bates College and Bowdoin College
Bowdoin College ( ) is a private liberal arts college in Brunswick, Maine. When Bowdoin was chartered in 1794, Maine was still a part of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The college offers 34 majors and 36 minors, as well as several joint eng ...
in Maine. Prior to coming to Reed, Foster wrote that his ideal college would be one that "combats laziness, superficiality, dissipation, excessive indulgence in college life, by making the moral and intellectual requirements an honest, sustained, and adequate challenge to the best powers of the best American youth."
Contrary to popular belief, the college did not grow out of student revolts and experimentation, but out of a desire to provide a "more flexible, individualized approach to a rigorous liberal arts education". Founded explicitly in reaction to the "prevailing model of East Coast, Ivy League education", the college's lack of varsity athletics, fraternities, and exclusive social clubs– as well as its coeducational, nonsectarian, and egalitarian status—gave way to an intensely academic and intellectual college whose purpose was to devote itself to "the life of the mind"—the academic life— rather than a social or fraternal one.
During the 1930s, President Dexter Keezer
Dexter Merriam Keezer (24 August 1895 – June 24, 1991) was an American economist who served as president of Reed College from 1934 to 1942.
Biography
Dexter Merriam Keezer was born Aug. 24, 1895, in Acton, Massachusetts. He graduated from Amh ...
became very concerned about what he considered to be dishonorable behavior at Reed, primarily the fraternization among male and female students and the consumption of alcohol by students. A large portion of the Student Council even took the position that Oregon's liquor laws did not apply to Reed's campus. Policies restricting the ability of students from visiting the dormitories of the opposite sex were fiercely resisted.
After World War II the college saw its enrollment numbers dramatically increase as veterans began enrolling in the college.
The college has developed a reputation for the political progressivism of its student body.
Distinguishing features
 According to sociologist Burton Clark, Reed is one of the most unusual institutions of higher learning in the United States, featuring a traditional liberal arts and natural sciences curriculum. It requires freshmen to take Humanities 110, an intensive introduction to multidisciplinary inquiry, covering ancient Greece and Rome, the Hebrew Bible and ancient Jewish history, and as of 2019, Ancient Mesoamerica and the Harlem Renaissance. Reed also has a TRIGA research reactor on campus, making it the only school in the United States to have a nuclear reactor operated primarily by undergraduates. Reed also requires all students to complete a thesis (a two-semester-long research project conducted under the guidance of professors) during the senior year as a prerequisite of graduation. Upon completion of the senior thesis, students must also pass an oral defense of ninety minutes related to the thesis topic and how the thesis relates to the larger context of the student's studies.
Reed maintains a 9:1 student-to-faculty ratio, and its small classes emphasize a "conference" style where the professor often acts as a mediator for discussion rather than a lecturer. While large lecture-style classes exist, Reed emphasizes its smaller lab and conference sections.
According to sociologist Burton Clark, Reed is one of the most unusual institutions of higher learning in the United States, featuring a traditional liberal arts and natural sciences curriculum. It requires freshmen to take Humanities 110, an intensive introduction to multidisciplinary inquiry, covering ancient Greece and Rome, the Hebrew Bible and ancient Jewish history, and as of 2019, Ancient Mesoamerica and the Harlem Renaissance. Reed also has a TRIGA research reactor on campus, making it the only school in the United States to have a nuclear reactor operated primarily by undergraduates. Reed also requires all students to complete a thesis (a two-semester-long research project conducted under the guidance of professors) during the senior year as a prerequisite of graduation. Upon completion of the senior thesis, students must also pass an oral defense of ninety minutes related to the thesis topic and how the thesis relates to the larger context of the student's studies.
Reed maintains a 9:1 student-to-faculty ratio, and its small classes emphasize a "conference" style where the professor often acts as a mediator for discussion rather than a lecturer. While large lecture-style classes exist, Reed emphasizes its smaller lab and conference sections.
 Although letter grades are given to students, grades are de-emphasized at Reed and focus is placed on a narrative evaluation. According to the school, "a conventional letter grade for each course is recorded for every student, but the registrar's office does not distribute grades to students, provided that work continues at satisfactory (C or higher) levels. Unsatisfactory grades are reported directly to the student and the student's adviser. Papers and exams are generally returned to students with lengthy comments but without grades affixed." Students can request copies of their official transcript from the registrar. There is no dean's list or honor roll ''per se'', but students who maintain a GPA of 3.5 or above for an academic year receive academic commendations at the end of the spring semester which are noted on their transcripts. Many Reed students graduate without knowing their cumulative GPA or their grades in individual classes. Reed is singled out as having little to no grade inflation over the years; only ten students graduated with a perfect 4.0 GPA in the period from 1983 to 2012. (Transcripts are accompanied by a card contextualizing Reed's grading approach so as not to penalize students' graduate school applications.) Although Reed does not award Latin honors to graduates, it confers several awards for academic achievement at commencement, including naming students to Phi Beta Kappa.
Reed has no fraternities or sororities and few NCAA sports teams although physical education classes (which range from
Although letter grades are given to students, grades are de-emphasized at Reed and focus is placed on a narrative evaluation. According to the school, "a conventional letter grade for each course is recorded for every student, but the registrar's office does not distribute grades to students, provided that work continues at satisfactory (C or higher) levels. Unsatisfactory grades are reported directly to the student and the student's adviser. Papers and exams are generally returned to students with lengthy comments but without grades affixed." Students can request copies of their official transcript from the registrar. There is no dean's list or honor roll ''per se'', but students who maintain a GPA of 3.5 or above for an academic year receive academic commendations at the end of the spring semester which are noted on their transcripts. Many Reed students graduate without knowing their cumulative GPA or their grades in individual classes. Reed is singled out as having little to no grade inflation over the years; only ten students graduated with a perfect 4.0 GPA in the period from 1983 to 2012. (Transcripts are accompanied by a card contextualizing Reed's grading approach so as not to penalize students' graduate school applications.) Although Reed does not award Latin honors to graduates, it confers several awards for academic achievement at commencement, including naming students to Phi Beta Kappa.
Reed has no fraternities or sororities and few NCAA sports teams although physical education classes (which range from kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits fac ...
to juggling to capoeira) are required for graduation. Reed also has several intercollegiate athletic clubs, notably the basketball, rugby, Ultimate Frisbee, and soccer teams.
Reed students and faculty are expected to abide by an ethical code known as "The Honor Principle". First introduced as an agreement to promote ethical academic behavior with the explicit end of relieving the faculty of policing student behavior, the Honor Principle was extended to cover all aspects of student life. While inspired by traditional honor systems, Reed's Honor Principle differs from those in that it is a guide for ethical standards themselves, and provides no codified rules governing behavior. Rather, the onus is on students individually and as a community to define which behaviors are acceptable and which are not.
Discrete cases of grievance, known as "Honor Cases", are adjudicated by a Judicial Board of twelve full-time students. There is also an "Honor Council" of students, faculty, and staff who educate the community on the Honor Principle and mediate conflict between individuals.
Academics
Reed categorizes its academic program into five Divisions and the Humanities program. Overall, Reed offers five Humanities courses, twenty-six department majors, twelve interdisciplinary majors, six dual-degree programs with other colleges and universities, and programs for pre-medical and pre-veterinary students.Divisions
 *Division of Arts: includes the Art (Art History and Studio Art), Dance, Music, and Theatre Departments;
*Division of History and Social Sciences: includes the History, Anthropology, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology Departments, as well as the International and Comparative Policy Studies Program;
*Division of Literature and Languages: includes the Classics, Chinese, English, French, German, Russian, and Spanish Departments, as well as the Creative Writing and General Literature Programs;
*Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: includes the Mathematics, Biology, Chemistry, and Physics Departments, and
*Division of Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics: includes the Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics Departments.
*Division of Arts: includes the Art (Art History and Studio Art), Dance, Music, and Theatre Departments;
*Division of History and Social Sciences: includes the History, Anthropology, Economics, Political Science, and Sociology Departments, as well as the International and Comparative Policy Studies Program;
*Division of Literature and Languages: includes the Classics, Chinese, English, French, German, Russian, and Spanish Departments, as well as the Creative Writing and General Literature Programs;
*Division of Mathematics and Natural Sciences: includes the Mathematics, Biology, Chemistry, and Physics Departments, and
*Division of Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics: includes the Philosophy, Religion, Psychology, and Linguistics Departments.
Humanities program
Reed President Richard Scholz in 1922 called the educational program as a whole "an honest effort to disregard old historic rivalries and hostilities between the sciences and the arts, between professional and cultural subjects, and,... the formal chronological cleavage between the graduate and the undergraduate attitude of mind". The Humanities program, which came into being in 1943 (as the union of two year-long courses, one in "world" literature, the other in "world" history) is one manifestation of this effort. One change to the program was the addition of a course in Chinese Civilization in 1995. The faculty has also recently approved several significant changes to the introductory syllabus. These changes include expanding the parameters of the course to include more material regarding urban and cultural environments. Reed's Humanities program includes the mandatory freshman course ''Introduction to Western Humanities'' covering ancient Greek and Roman literature, history, art, religion, and philosophy. Sophomores, juniors, and seniors may take ''Early Modern Europe'' covering Renaissance thought and literature; ''Modern Humanities'' covering theEnlightenment
Enlightenment or enlighten may refer to:
Age of Enlightenment
* Age of Enlightenment, period in Western intellectual history from the late 17th to late 18th century, centered in France but also encompassing (alphabetically by country or culture): ...
, the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, and Modernism, and/or ''Foundations of Chinese Civilization''. There is also a Humanities Senior Symposium.
Interdisciplinary and dual-degree programs
Reed also offers interdisciplinary programs in American studies, Environmental Studies, Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Chemistry-Physics, Classics-Religion, Dance/Theatre, History-Literature, International and Comparative Policy Studies (ICPS), Literature-Theatre, Mathematics-Economics, and Mathematics-Physics. Reed offers dual-degree programs in Computer Science (with University of Washington), Engineering (with Caltech, Columbia University, andRensselaer Polytechnic Institute
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute () (RPI) is a private research university in Troy, New York, with an additional campus in Hartford, Connecticut. A third campus in Groton, Connecticut closed in 2018. RPI was established in 1824 by Stephen Van ...
), Forestry or Environmental Management (with Duke University
Duke University is a private research university in Durham, North Carolina. Founded by Methodists and Quakers in the present-day city of Trinity in 1838, the school moved to Durham in 1892. In 1924, tobacco and electric power industrialist James ...
), and Fine Art (with the Pacific Northwest College of Art).
Rankings
In 1995, Reed College refused to participate in the '' U.S. News & World Report'' "best colleges" rankings, making it the first educational institution in the United States to refuse to participate in college rankings. According to Reed's Office of Admissions the school's refusal to participate is based in 1994 disclosures by '' The Wall Street Journal'' about institutions flagrantly manipulating data in order to move up in the rankings in ''U.S. News'' and other popular college guides. ''U.S. News'' maintains that their rankings are "a very legitimate tool for getting at a certain level of knowledge about colleges." In 2019, a team of statistics students recreated the formula used by ''U.S. News'' and were able to identify and quantify the penalty imposed on Reed. The students found the college to be ranked an estimated 52 places below an unbiased application of the U.S. News scoring rubric. '' Money'' magazine ranked Reed 551st in the U.S. out of 739 schools evaluated for its 2020 "Best Colleges for Your Money" edition. Reed is ranked as tied for the 63rd best liberal arts college by '' U.S. News & World Report'' in its 2021 rankings, and tied for 16th in "Best Undergraduate Teaching", tied for 18th in "Most Innovative Schools", and tied for 199th in "Top Performers on Social Mobility". In 2006, '' Newsweek'' magazine named Reed as one of twenty-five "New Ivies", listing it among "the nation's elite colleges". In 2012, ''Newsweek'' ranked Reed the 15th "most rigorous" college in the nation. Reed College ranked in the bottom 6% of four year colleges nationwide in the Brookings Institute's rating of U.S. colleges by incremental impact on alumni earnings 10 years post-enrollment. An episode of Malcolm Gladwell's podcast Revisionist History examines the flaws in the U.S. News system of university rankings. The episode features a project done by a Reed professor of statistics and her students to investigate the mechanics of the ranking algorithm, attempting to see if Reed's ranking had been purposefully devalued because the school refused to submit its information to U.S. News. Previous investigations by Reed students to re-create U.S. News's statistical ranking algorithm found that Reed's correct 2019 rank was #38 instead of its assigned rank of #90.Admissions
Admissions
 For Fall 2016, the freshman class had 357 students. 10% were valedictorians of their high school classes and another 2% were salutatorians. 32% ranked in the top 5% of their class. The median scores on their SAT tests were 680 math, 710 verbal, and 680 writing, which puts them at the 96th percentile. The class was drawn from the largest pool ever—5,705 applicants—and was the most selective in Reed's history, with an admittance rate of 31%. , to increase student enrollment from historically underrepresented minorities, Reed encourages they apply for the college's "Discover Reed Fly-In Program", an all-inclusive, all-expenses-paid, multi-day campus tour and open to all high school seniors who are US citizens or permanent residents, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
For Fall 2016, the freshman class had 357 students. 10% were valedictorians of their high school classes and another 2% were salutatorians. 32% ranked in the top 5% of their class. The median scores on their SAT tests were 680 math, 710 verbal, and 680 writing, which puts them at the 96th percentile. The class was drawn from the largest pool ever—5,705 applicants—and was the most selective in Reed's history, with an admittance rate of 31%. , to increase student enrollment from historically underrepresented minorities, Reed encourages they apply for the college's "Discover Reed Fly-In Program", an all-inclusive, all-expenses-paid, multi-day campus tour and open to all high school seniors who are US citizens or permanent residents, regardless of their race or ethnicity.
Tuition and finances
The total direct cost for the 2018–19 academic year, including tuition, fees and room-and-board, was $70,550. Indirect costs (books, supplies, transportation, personal expenses) can tack on another $3,950. For the 2017–18 academic year, the average financial aid package – including grants, loans, and work opportunities – was approximately $45,325". In 2017–18 about half of students received financial aid from the college. In 2004, 1.4% of Reed graduates defaulted on their student loans – below the national Cohort Default Rate average of 5.1%. Reed's endowment as of June 30, 2021, was $779 million. In the economic downturn that began in late 2007, Reed's total endowment had declined from $455 million in June 2007 to $311 million in June 2009. By the end of 2013, however, the endowment surpassed the $500 million mark.Academic honors
Reed has produced the second-highest number ofRhodes scholars
The Rhodes Scholarship is an international postgraduate award for students to study at the University of Oxford, in the United Kingdom.
Established in 1902, it is the oldest graduate scholarship in the world. It is considered among the world' ...
for any liberal arts college—32—as well as over fifty Fulbright Scholars, over sixty Watson Fellow
The Thomas J. Watson Foundation is a charitable trust formed 1961 in honor of former chairman and CEO of IBM, Thomas J. Watson. The Foundation's stated vision is to empower students “to expand their vision, test and develop their potential, a ...
s, and two MacArthur ("Genius") Award winners. A very high proportion of Reed graduates go on to earn PhDs, particularly in the natural sciences, history, political science, and philosophy. Reed is ranked third in the percentage of graduates who go on to earn PhDs in all disciplines, after only Caltech and Harvey Mudd. In 1961, '' Scientific American'' declared that second only to Caltech, "This small college in Oregon has been far and away more productive of future scientists than any other institution in the U.S." Reed is ranked first in producing PhDs in biology, second in chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
and humanities, third in history, foreign languages, and political science, fourth in science and mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, fifth in physics and social sciences, sixth in anthropology, seventh in area and ethnic studies and linguistics, and eighth in English literature
English literature is literature written in the English language from United Kingdom, its crown dependencies, the Republic of Ireland, the United States, and the countries of the former British Empire. ''The Encyclopaedia Britannica'' defines E ...
and medicine.
Reed's debating team, which had existed for only two years at the time, was awarded the first place sweepstakes trophy for Division II schools at the final tournament of the Northwest Forensics Conference in February 2004.
Loren Pope, former education editor for '' The New York Times,'' writes about Reed in ''Colleges That Change Lives
''Colleges That Change Lives'' began as a college educational guide first published in 1996 by Loren Pope. Colleges That Change Lives (CTCL) was founded in 1998 is a non-profit, 501(c)(3) based on Pope's book.
The book
''Colleges That Change Liv ...
,'' saying, "If you're a genuine intellectual, love the life of the mind, and want to learn for the sake of learning, the place most likely to empower you is not Harvard, Yale, Princeton, Chicago, or Stanford. It is the most intellectual college in the country — Reed in Portland, Oregon."
Drug use
Since the 1960s, Reed has had a reputation for tolerating open drug use among its students. ''The Insider's Guide to the Colleges
The ''Yale Daily News'' is an independent student newspaper published by Yale University students in New Haven, Connecticut since January 28, 1878. It is the oldest college daily newspaper in the United States. The ''Yale Daily News'' has con ...
'', written by the staff of ''Yale Daily News
The ''Yale Daily News'' is an independent student newspaper published by Yale University students in New Haven, Connecticut since January 28, 1878. It is the oldest college daily newspaper in the United States. The ''Yale Daily News'' has consis ...
'', notes an impression among students of institutional permissiveness: "According to students, the school does not bust students for drug or alcohol use unless they cause harm or embarrassment to another student."
In April 2008, student Alex Lluch died of a heroin overdose in his on-campus dorm room. His death prompted revelations of several previous incidents, including the near-death heroin overdose of another student only months earlier. College President Colin Diver said "I don't honestly know" whether the drug death was an isolated incident or part of a larger problem. "When you say Reed," Diver said, "two words often come to mind. One is brains. One is drugs." Local reporter James Pitkin of the newspaper '' Willamette Week'' editorialized that "Reed College, a private school with one of the most prestigious academic programs in the U.S., is one of the last schools in the country where students enjoy almost unlimited freedom to experiment openly with drugs, with little or no hassles from authorities", though ''Willamette Week'' stated the following week concerning Pitkin's editorial: "As of press time, almost 500 responses, many expressing harsh criticism of ''Willamette Week'', had been posted on our website."
In March 2010, another student died of drug-related causes in his off-campus residence. This led '' The New York Times'' to conclude that "Reed... has long been known almost as much for its unusually permissive atmosphere as for its impressively rigorous academics." Law enforcement authorities promised to take action, including sending undercover agents to Reed's annual Renn Fayre
Renn Fayre is an annual three-day campus-wide celebration that occurs at Reed College, a liberal arts college located in Portland, Oregon, Portland, Oregon, United States. The festival began as a one-day Renaissance Fayre, held during the spring ...
celebration.
In February 2012, the Reed administration chose to call the police following the discovery of "two to three pounds of marijuana and a small amount of ecstasy and LSD in the on-campus apartment of two juniors." Following campus debate, Reed's president at the time, Colin Diver, issued a letter to students and staff, saying the college would not tolerate illegal drug use on campus: "Such behavior endangers the health and welfare of the entire community, attracts potentially dangerous criminal activity on campus, undermines the academic mission of the college, and violates the college's obligations under state and federal law."
Political and social activism
Reed has a reputation for being politically left-of-center. During the McCarthy era of the 1950s, then-President Duncan Ballantine fired Marxist philosopher Stanley Moore, a tenured professor, for his failure to cooperate with theHouse Un-American Activities Committee
The House Committee on Un-American Activities (HCUA), popularly dubbed the House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC), was an investigative committee of the United States House of Representatives, created in 1938 to investigate alleged disloy ...
(HUAC) investigation. According to an article in the college's alumni magazine, "because of the decisive support expressed by Reed's faculty, students, and alumni for the three besieged teachers and for the principle of academic freedom, Reed College's experience with McCarthyism stands apart from that of most other American colleges and universities. Elsewhere in the academic world both tenured and nontenured professors with alleged or admitted communist party ties were fired with relatively little fuss or protest. At Reed, however, opposition to the political interrogations of the teachers was so strong that some believed the campus was in danger of closure." A statement of "regret" by the Reed administration and Board of Trustees was published in 1981, formally revising the judgment of the 1954 trustees. In 1993, then-President Steve Koblik invited Moore to visit the college, and in 1995 the last surviving member of the Board that fired Moore expressed his regret and apologized to him.
Reedies Against Racism
On September 26, 2016, students organized a boycott of all college operations in participation with the National Day of Boycott, a national day of protest which was proposed by actorIsaiah Washington
Isaiah Washington IV is an American actor and media personality. Following a series of film appearances, he came to prominence for portraying Dr. Preston Burke in the first three seasons of the series ''Grey's Anatomy'' from 2005 to 2007.
Wash ...
on Twitter in response to the issue of police brutality against African-Americans. Following the boycott, students created an activist group called Reedies Against Racism (RAR) and presented a list of demands for the college purportedly on behalf of students from marginalized backgrounds. The primary demand concerned Reed's mandatory freshman Humanities course, proposing that the course either be changed to be more inclusive of world literature and classics or to be made not mandatory. One element of the class deemed racist by the protestors was the use of the 1978 Steve Martin song "King Tut" in a discussion about cultural appropriation
Cultural appropriation is the inappropriate or unacknowledged adoption of an element or elements of one culture or identity by members of another culture or identity. This can be controversial when members of a dominant culture appropriate from ...
. Students began a protest campaign against the curriculum by sitting in during lectures with signs with quotations from various African-American and non-white academics. Other protests separate from the Humanities course also included efforts to shout down speakers, including Kimberly Peirce after she was accused of profiting from transphobia while making the film '' Boys Don't Cry''. The group eventually focused on Reed's banking relationship with Wells Fargo, based on allegations that the bank had invested in the Dakota Access Pipeline
The Dakota Access Pipeline (DAPL) or Bakken pipeline is a underground pipeline in the United States that has the ability to transport up to 750,000 barrels of light sweet crude oil per day. It begins in the shale oil fields of the Bakken Forma ...
project and the private prison industry, and staged an occupation of Reed's Eliot Hall.
There was some opposition to the lecture protests, notably by Reed professor of English Lucía Martínez Valdivia, who stated that a protest during her lecture on Sappho
Sappho (; el, Σαπφώ ''Sapphō'' ; Aeolic Greek ''Psápphō''; c. 630 – c. 570 BC) was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her Greek lyric, lyric poetry, written to be sung while ...
would amplify her pre-existing case of PTSD. In November 2017, Chris Bodenner of '' The Atlantic'' wrote about growing student resentment toward the tactics of RAR. In response to protests the faculty decided to undergo the decennial review process a year early, as well as to complete the process in three months instead of the usual year. In January 2018, Humanities 110 Chair professor Libby Drumm announced in a campus-wide email that the course curriculum would be restructured after years of faculty discussion and in response to student feedback as well as input from an external review committee composed of humanities faculty from other institutes, adopting a "four-module structure" that would include texts from the Americas and allow greater flexibility in the curriculum which would be integrated beginning fall 2018. The external review had not in fact been completed nor reviewed at the time of the announcement.
Following "a contentious year of protests, including an anti-racism sit-in in Kroger's office", college president John Kroger resigned, effective June 2018.
Campus

 The Reed College campus was established on a tract of land in southeast
The Reed College campus was established on a tract of land in southeast Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
known in 1910 as Crystal Springs Farm, a part of the Ladd Estate, formed in the 1870s from original land claims. The college's grounds include of contiguous land, including a wooded wetland known as Reed Canyon.
Portland architect A. E. Doyle
Albert Ernest Doyle (July 27, 1877 – January 23, 1928) was a prolific architect in the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington. He is most often credited for his works as A.E. Doyle. He opened his own architectural practice in 1907. From ...
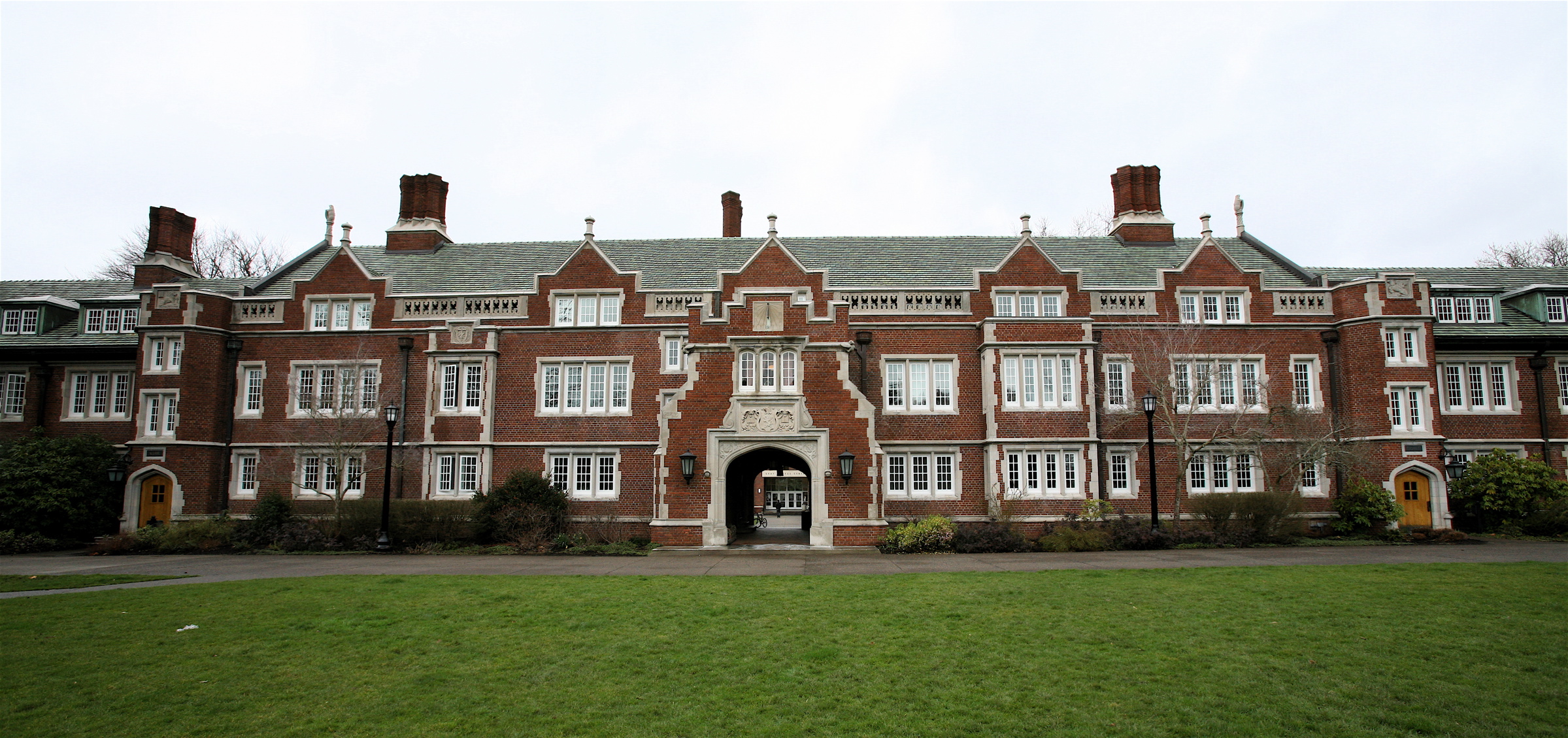
developed a plan, never implemented in full, modeled on the University of Oxford's St. John's College. The original campus buildings (including the Library, the Old Dorm Block
Old Dorm Block is a building on the Reed College campus in Portland, Oregon
Portland (, ) is a port city in the Pacific Northwest and the largest city in the U.S. state of Oregon. Situated at the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia ...
, and what is now the primary administration building, Eliot Hall) are brick Tudor Gothic buildings in a style similar to Ivy League campuses. In contrast, the science section of campus, including the physics, biology, and psychology (originally chemistry) buildings, were designed in the Modernist style. The Psychology Building, completed in 1949, was designed by Modernist architect Pietro Belluschi at the same time as his celebrated Equitable Building in downtown Portland.
The campus and buildings have undergone several phases of growth, and there are now 21 academic and administrative buildings and 18 residence halls. Since 2004, Reed's campus has expanded to include adjacent properties beyond its historic boundaries, such as the Birchwood Apartments complex and former medical administrative offices on either side of SE 28th Avenue, and the Parker House, across SE Woodstock from Prexy. At the same time the Willard House (donated to Reed in 1964), across from the college's main entrance at SE Woodstock and SE Reed College Place, was converted from faculty housing to administrative use. Reed announced on July 13, 2007, that it had purchased the Rivelli farm, a tract of land south of the Garden House and west of Botsford Drive. Reed's "immediate plans for the acquired property include housing a small number of students in the former Rivelli home during the 2007–08 academic year. Longer term, the college anticipates that it may seek to develop the northern portion of the property for additional student housing".
Residence halls
 Reed houses 945 students in 18 residence halls on campus and several college-owned houses and apartment buildings on or adjacent to campus. Residence halls on campus range from the traditional (i.e., Gothic Old Dorm Block, referred to as "ODB") to the eclectic (e.g., Anna Mann, a Tudor-style cottage built in the 1920s by Reed's founding architect A. E. Doyle, originally used as a women's hallRomel Hernandez, "This New House"
Reed houses 945 students in 18 residence halls on campus and several college-owned houses and apartment buildings on or adjacent to campus. Residence halls on campus range from the traditional (i.e., Gothic Old Dorm Block, referred to as "ODB") to the eclectic (e.g., Anna Mann, a Tudor-style cottage built in the 1920s by Reed's founding architect A. E. Doyle, originally used as a women's hallRomel Hernandez, "This New House"''Reed''
(Spring 2007), p. 15.), language houses (Spanish, Russian, French, German, and Chinese), "temporary" housing, built in the 1960s (Cross Canyon – Chittick, Woodbridge, McKinley, Griffin), to more recently built dorms (Bragdon, Naito, Sullivan). There are also theme residence halls including everything from substance-free living to Japanese culture to music to a dorm for students interested in outdoors activities (hiking, climbing, bicycling, kayaking, skiing, etc.). The college's least-loved complex (as measured by applications to the college's housing lottery), MacNaughton and Foster-Scholz, is known on campus as "Asylum Block" because of its post-World War II modernist architecture and interior spaces dominated by long, straight corridors lined with identical doors, said by students to resemble that of an insane asylum. Until 2006, it was thought that these residence halls had been designed by architect Pietro Belluschi. Under the 10-year Campus Master Plan adopted in 2006, Foster-Scholz is scheduled to be demolished and replaced, and MacNaughton to be remodeled. According to the master plan, "The College's goal is to provide housing on or adjacent to the campus that accommodates 75% of the ull-timestudent population. At present, the College provides on-campus housing for 838 students". In Spring 2007, the college broke ground on the construction of a new quadrangle called the Grove with four new Leed certified residence halls (Aspen, Sequoia, Sitka, Bidwell) on the northwest side of the campus, which opened in Fall 2008. A new Spanish House residence was completed. Together, the five new residences added 142 new beds. Reed also has off-campus housing. Many houses in the Woodstock and Eastmoreland Portland neighborhoods are traditionally rented to Reed students. On February 21, 2018, Reed announced the construction of the "largest residence hall in its history". Completed in Fall 2019, Trillium houses an additional 180 students, boosting Reed's housing capacity to nearly 80% of the student body, up from 68%. The addition of Trillium guarantees housing for both freshman and sophomores, as students were formerly subjected to a housing lottery after freshman year. The new building is also designed to meet "LEED Platinum standards", and Reed is currently evaluating proposals to put solar panels on the roof.
Reed Canyon
Douglas F. Cooley Gallery
Reed's Cooley Gallery is an internationally recognized contemporary art space located at the entrance to theEric V. Hauser Memorial Library
The Eric V. Hauser Memorial Library is a library located on the Reed College campus in southeast Portland, Oregon, in the United States.
History
The library was constructed in 1930 and named for Eric V. Hauser, who provided the endowment for ...
. It was established in 1988 as the result of a gift from Susan and Edward Cooley in honor of their late son. The Cooley Gallery has exhibited international artists such as Mona Hatoum, Al Held, David Reed and Gregory Crewdson as well as the contemporary art collection of Michael Ovitz. In pursuit of its mission to support the curriculum of the art, art history, and humanities programs at Reed, the gallery produces three or four exhibitions each year, along with lectures, colloquia, and artist visits. The gallery is currently under the directorship of Stephanie Snyder, who succeeded founding director Susan Fillin-Yeh in 2004.
Food services
The cafeteria, known simply as "Commons", has a reputation for ecologicallysustainable food
A sustainable food system is a type of food system that provides healthy food to people and creates sustainable environmental, economic and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of sustainable agr ...
services. The commons dining hall is operated by Bon Appétit
''Bon Appétit'' is a monthly American food and entertaining magazine, that typically contains recipes, entertaining ideas, restaurant recommendations, and wine reviews. Owned by Condé Nast, it is headquartered at the One World Trade Center i ...
, and food is purchased on an item-by-item basis. Suiting the student body, vegan and vegetarian dishes feature heavily on the menu. It is currently the only cafeteria on the small campus, with the exception of Canyon Cafe (formerly Caffe Circo and Caffe Paradiso), a small cafe on the other side of campus which also operated by board points. Scrounging is a long tradition at Reed College allowing students to offer unfinished Commons' food to students without board points from their trays as they are returned to be washed.
The Reed College Co-ops are a theme community that reside in the Farm and Garden Houses, after many years on the first floor of MacNaughton Hall. These are the only campus dorms that are independent of the school's board plan. They traditionally throw an alternative "Thanksgiving" celebration that has sometimes included a square-dance. The Co-ops house students who purchase and prepare food together, sharing chores and conducting weekly, consensus-based meetings. It is a close community valuing sustainability, organic food, consensus-based decisions, self-government, music, and plants.
 The Paradox ("Est. in the 80s") is a student-run coffee shop located on campus. In 2003 the Paradox opened a second coffee shop, dubbing it the "Paradox Lost" (an allusion to
The Paradox ("Est. in the 80s") is a student-run coffee shop located on campus. In 2003 the Paradox opened a second coffee shop, dubbing it the "Paradox Lost" (an allusion to John Milton
John Milton (9 December 1608 – 8 November 1674) was an English poet and intellectual. His 1667 epic poem '' Paradise Lost'', written in blank verse and including over ten chapters, was written in a time of immense religious flux and political ...
's ''Paradise Lost
''Paradise Lost'' is an epic poem in blank verse by the 17th-century English poet John Milton (1608–1674). The first version, published in 1667, consists of ten books with over ten thousand lines of verse (poetry), verse. A second edition fo ...
,'') at the southern end of the biology building, in the space commonly called the "Bio Fishbowl". The new north-campus dorms, which opened in Fall 2008, feature yet another small cafe, originally dubbed "Cafe Paradiso", thereby providing three coffee shops within a campus. The recent addition of a circus-themed mural to the cafe prompted a name change, and it now operates as Caffe Circo. This third shop is not student-run, but is operated by Bon Appétit
''Bon Appétit'' is a monthly American food and entertaining magazine, that typically contains recipes, entertaining ideas, restaurant recommendations, and wine reviews. Owned by Condé Nast, it is headquartered at the One World Trade Center i ...
. Bon Appétit
''Bon Appétit'' is a monthly American food and entertaining magazine, that typically contains recipes, entertaining ideas, restaurant recommendations, and wine reviews. Owned by Condé Nast, it is headquartered at the One World Trade Center i ...
has a monopoly on the food services at Reed as they are the only ones who accept board points; written into their contract is the prohibition of food carts on campus.
2021 Collapse of the Aubrey R. Watzek Sports Center
On February 15, 2021, theAubrey R. Watzek Sports Center
The Reed College campus includes academic buildings, dormitories and houses, administration and service buildings, student centers and other buildings. Academic buildings include the A. A. Knowlton Laboratory of Physics, Arthur F. Scott Labor ...
, collapsed during Winter Storm Uri. Both gyms that were part of the sports center collapsed. The collapse was attributed to excess snow piling up on the roof of the building causing a support truss to fracture, and strained several others, causing the roof to collapse. The sports center was serving as a COVID-19 testing center, and the destruction of the testing center resulted in the loss of testing kits and other medical supplies needed for COVID-19 testing
COVID-19 testing involves analyzing samples to assess the current or past presence of SARS-CoV-2. The two main types of tests detect either the presence of the virus or antibodies produced in response to infection. Molecular tests for viral ...
.
Icons and student life
Griffin
The official mascot of Reed is thegriffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (Ancient Greek: , ''gryps''; Classical Latin: ''grȳps'' or ''grȳpus''; Late Latin, Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a legendary creature with the body, tail ...
. In mythology, the griffin often pulled the chariot of the sun; in canto 32 of Dante's '' Commedia'' the griffin is associated with the Tree of Knowledge. The griffin was featured on the coat-of-arms of founder Simeon Reed and is now on the official seal of Reed College. Though the school does not have varsity sports, the mascot features prominently throughout campus iconography outside of an athletic context.
School color
The official school color of Reed is Richmond Rose. Over the years, institutional memory of this fact has faded and the color appearing on the school's publications and merchandise has darkened to a shade of maroon. The most common examples of "Richmond Rose" are the satin tapes securing the degree certificate inside a Reed College diploma.School song
The school song, "Fair Reed", is sung to the tune of the 1912 popular song " Believe Me, if All Those Endearing Young Charms". It may be imitative of the Harvard anthem "Fair Harvard", which is also sung to the tune of "Believe Me, if All Those Endearing Young Charms". It was composed by former president William Trufant Foster shortly after Reed's founding, and is rarely heard today. An unofficial Reed Alma Mater, " Epistemology Forever", sung to the tune of " The Battle Hymn of the Republic", has been sung by Reed students since the 1950s.Students' nicknames
Reed students and alumni referred to themselves as "Reedites" in the early years of the college. This term faded out in favor of the now ubiquitous "Reedie" after World War II. Around campus, prospective students are called "prospies".Unofficial mottos and folklore
An unofficial motto of Reed is "Communism, Atheism, Free Love", and can be found in the Reed College Bookstore on sweaters, T-shirts, etc. It was a label that the Reed community claimed from critics during the 1920s as a "tongue-in-cheek slogan" in reference to Reed's nonconformism. Reed's founding president William T. Foster's outspoken opposition against the entrance of the United States into World War I, as well as the college's support for feminism, its adherence to academic freedom (i.e., inviting a leader of theSocialist Party of America
The Socialist Party of America (SPA) was a socialist political party in the United States formed in 1901 by a merger between the three-year-old Social Democratic Party of America and disaffected elements of the Socialist Labor Party of Ameri ...
to speak on campus about the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
’s potential effect on militarism, emancipation of women, and ending the persecution of Jews), and its nonsectarian status made the college a natural target for what was originally meant to be a pejorative slur.
The faux Reed Seal has changed over the years. In its original form the griffin was holding a hammer and sickle in its paws. Later versions had the griffin wearing boxing gloves.
One of the unofficial symbols of Reed is the Doyle Owl
The Doyle Owl, or ''Strigidus cementus,'' according ''The New (Olde) Reed Almanac,'' "is the unofficial mascot of Reed College (the official mascot being the griffin)". It is a concrete statue of an owl, roughly three-foot high, and 300 pound ...
, a roughly concrete statue that has been continuously stolen and re-stolen since about 1919. The original Doyle Owl (originally "House F Owl" after the dormitory named House F that later became Doyle dormitory) was a garden sculpture from the neighborhood stolen by House F residents as a prank (there is a photo of House F residents around the original owl that has been made into a T-shirt). The on-campus folklore of events surrounding the Doyle Owl is sufficiently large that, in 1983, a senior thesis was written on the topic of the Owl's oral history
Oral history is the collection and study of historical information about individuals, families, important events, or everyday life using audiotapes, videotapes, or transcriptions of planned interviews. These interviews are conducted with people wh ...
. The original Doyle Owl was destroyed many years ago; the current avatar is Doyle Owl number 13, plus or minus 11. At the present time only one Owl is being shown.
Paideia
Each January, before the beginning of second-semester classes, the campus holds an interim period called Paideia (drawn from the Greek, meaning 'education'). Originally conceived and approved by the faculty in 1968 for unstructured independent study, or "UIS", Paideia ran for the full month of January from 1969 to 1981, supervised by a committee of faculty, staff and students. This festival of learning takes the form of classes and seminars put on by anyone who wishes to teach, including students, professors, staff members, and outside educators invited on-campus by members of the Reed Community. The classes are intended to be informal, yet intellectual activities free of the usual academic pressure endemic to Reed. Many such classes are explicitly trivial (one long-running tradition is to hold an underwater basket weaving class), while others are trivially academic (such as "Giant Concrete Gnome Construction", a class that, incidental to building monolithicgnome
A gnome is a mythological creature and diminutive spirit in Renaissance magic and alchemy, first introduced by Paracelsus in the 16th century and later adopted by more recent authors including those of modern fantasy literature. Its characte ...
s, includes some content relating to the construction of pre-Christian monoliths). More structured classes (such as martial arts seminars and mini-classes on obscure academic topics), tournaments, and film festivals round out the schedule, which is different every year. The objective of Paideia is not only to learn new (possibly non-useful) things, but to turn the tables on students and encourage them to teach.
In his 2005 Stanford commencement lecture, Apple Inc. founder and Reed dropout
Dropout or drop out may refer to:
* Dropping out, prematurely leaving school, college or university
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Dropout'' (film), a 1970 Italian drama
* "The Dropout", a 1970 episode of ''The Brady Bunch'' ...
Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
credited a Reed calligraphy
Calligraphy (from el, link=y, καλλιγραφία) is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "t ...
class taught by Robert Palladino
Robert Joseph Palladino (November 5, 1932 – February 26, 2016) was an American Trappist monk, calligrapher, and academic. He was a professor at Reed College in Portland, Oregon, where he taught Steve Jobs, and replaced Lloyd J. Reynolds as the ...
for his focus on choosing quality typefaces for the Macintosh. While the full calligraphy course is no longer taught at Reed, Paideia usually features a short course on the subject in addition to the informal, weekly gatherings (currently held every Thursday night) of aspiring calligraphy enthusiasts.
Renn Fayre
Renn Fayre is an annual three-day celebration with a different theme each year. Born in the 1960s as an actual renaissance fair, it has long since lost all connection to anachronism and the Renaissance, although its name has persisted. The event is initiated by a procession of seniors throwing their thesis notes in a large bonfire after the completed theses are submitted.Reed Arts Week
Reed Arts Week is a week-long celebration of the arts at Reed. It features music, dance, film, creative writing, and the visual arts.Student organizations
According to Reed's website, each semester, a $130 student body fee "is collected from each full-time student by the business office, acting as agent for the student senate. The fee underwrites publication of the student newspaper and extracurricular activities, and partially supports the student union and ski cabin." Student body funds (totaling roughly $370,000 annually) are distributed each semester to groups that place among the top 40 organizations in the semester's funding poll. The funding poll uses a voting system in which each organization provides a description that is ranked by each member of the student body with either 'top six,' 'approve,' 'no opinion,' 'disapprove.' A former 'deep six' was eliminated from the system in 2019. These ranks are then tabulated by assigning numbers to each rank and summing across all voters. Afterwards, the top forty organizations present their budgets to the student body senate during Funding Circus. The following day the senate makes decisions about each budget in a process called Funding Hell. The school's student-run newspaper, ''The Reed College Quest ''or simply the ''Quest,'' has been published since 1913, and its radio station KRRC had been broadcasting, with a few interruptions, from 1955 The station now broadcasts online only at krrc.fm. Although some student organizations partnered with outside groups such asOxfam
Oxfam is a British-founded confederation of 21 independent charitable organizations focusing on the alleviation of global poverty, founded in 1942 and led by Oxfam International.
History
Founded at 17 Broad Street, Oxford, as the Oxford Co ...
or Planned Parenthood
The Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Inc. (PPFA), or simply Planned Parenthood, is a nonprofit organization that provides reproductive health care in the United States and globally. It is a tax-exempt corporation under Internal Reve ...
are more structured, most student organizations are highly informal. There is no formal process for forming a student organization at Reed; a group of students (or a single student) announcing themselves as or just considering themselves a student organization is enough, but groups that desire funding from the school's Student Activities office or Student Body Fees must register with Student Activities or through the Student Senate. The Reed archive of comic books and graphic novels, the MLLL (Comic Book Reading Room), is well into its fourth decade, and Beer Nation, the student group that organizes and manages various beer gardens throughout the year and during Renn Fayre
Renn Fayre is an annual three-day campus-wide celebration that occurs at Reed College, a liberal arts college located in Portland, Oregon, Portland, Oregon, United States. The festival began as a one-day Renaissance Fayre, held during the spring ...
, has existed for many years. Some organizations, such as the Motorized Couch Collective — dedicated to installing motors and wheels into furniture — have become more Reed myth than reality in recent years.
Reed has ample recreational facilities on campus, a ski cabin on Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portlan ...
, recreational clubs such as the Reed Outing Club (ROC), and Club Sports (with college-paid coaches), including ultimate frisbee, co-ed soccer, rugby, basketball, and squash.
Crime
According to a '' Washington Post'' analysis of federal campus safety data from 2014, Reed College had 12.9 reports of rape per 1,000 students, the "highest total of reports of rape" per 1,000 students of any college in the nation on its main campus. In 2012, Reed College had the third highest reported sexual assault rate among U.S. colleges and universities. It is unclear whether this high reporting rate arises from the college and student body fostering an environment that is more supportive of reporting sexual assault or due to a higher offending pattern by students. in 2013 there were 19 reported forcible sexual offenses among the approximately 1,400 students at the college. In 2011, a student member of Reed's Judicial Board resigned over the college's handling of sexual assault cases. An investigation by the Center for Public Integrity found that those found responsible in cases of sexual assault frequently faced few consequences, while the lives of the victims were left in turmoil.Notable people
Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
, founder of Apple Inc.
File:Larry Sanger cropped.jpg, Larry Sanger, co-founder of Wikipedia
File:Gary Snyder, 2007 (cropped).jpg, Gary Snyder
Gary Snyder (born May 8, 1930) is an American poet, essayist, lecturer, and environmental activist. His early poetry has been associated with the Beat Generation and the San Francisco Renaissance and he has been described as the "poet laureate of ...
, poet
File:Richard Danzig, official Navy photo.jpg, Richard Danzig, 71st U.S. Secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the sec ...
File:Suzan DelBene, official portrait, 115th Congress.jpg, Suzan DelBene
Suzan Kay DelBene (née Oliver; ; born February 17, 1962) is an American politician and businesswoman who has been the United States House of Representatives, United States representative from Washington's 1st congressional district since 2012. ...
, U.S. Representative from Washington
File:Richard L. Hanna 113th Congress.jpg, Richard L. Hanna
Richard Louis Hanna (January 25, 1951 – March 15, 2020) was an American politician who served as a United States House of Representatives, U.S. Representative from New York (state), New York from 2011 to 2017. A member of the Republican Party ...
, U.S. Representative from New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
File:Hope Lange 1957.jpg, Hope Lange, Academy Award-nominated actress
File:James Beard.jpg, James Beard, chef and television personality
File:Arlene Blum 1977 003.jpg, Arlene Blum, mountaineer
Dell Hymes
Dell Hathaway Hymes (June 7, 1927 in Portland, Oregon – November 13, 2009 in Charlottesville, Virginia) was a linguist, sociolinguist, anthropologist, and folklorist who established disciplinary foundations for the comparative, ethnographic stu ...
(1950), Pulitzer Prize-winning poet Gary Snyder
Gary Snyder (born May 8, 1930) is an American poet, essayist, lecturer, and environmental activist. His early poetry has been associated with the Beat Generation and the San Francisco Renaissance and he has been described as the "poet laureate of ...
(1951), fantasy author David Eddings (1954), distance learning pioneer John Bear John Bear may refer to:
*John Bear (educator), American author and educator
*John Bear (snooker player)
John Norman Bear (8 August 1944 – 17 March 2007) was a Canadian professional snooker player.
Career
Born in Kinistino, Saskatchewan ...
(1959), socialist and feminist activist and author Barbara Ehrenreich (1963), radio personality Dr. Demento (1963), programmer
A computer programmer, sometimes referred to as a software developer, a software engineer, a programmer or a coder, is a person who creates computer programs — often for larger computer software.
A programmer is someone who writes/creates ...
, software publisher, author, and philanthropist Peter Norton (1965), former U.S. Secretary of the Navy Richard Danzig (1965), alpinist and biophysical chemist Arlene Blum (1966), chemist Mary Jo Ondrechen (1974), computer engineer Daniel Kottke (1976), and Wikipedia co-founder Larry Sanger (1991).
Among those who attended but did not graduate from Reed are Academy Award-nominated actress Hope Lange, chef James Beard, horse rancher and conspiracy theorist Christopher Langan, and Apple co-founder and former CEO Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
.
Notable Reed faculty of the past and present include former U.S. Senator from Illinois Paul Douglas, and physicists Richard Crandall and David Griffiths.
In popular culture
Reed College has been featured prominently in several books and movies. It is often presented as an enigmatic, eccentric institution at which people who do not fit into mainstream society come together to learn.Literature
* '' Blue Like Jazz'' (2003) by Donald Miller is a semi-autobiographical account of the author's life, and details the author's encounters with other Reed students while auditing classes there in the early 1990s. * ''The Other'' (2008) byDavid Guterson
David Guterson ( ; born May 4, 1956) is an American novelist, short story writer, poet, journalist, and essayist. He is best known as the author of the bestselling Japanese American internment novel ''Snow Falling on Cedars''.
Early life
Guter ...
depicts a Reed College student who drops out after his freshman year to live a solitary life in the Olympic Mountains.
* ''Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
'' (2011) by Walter Isaacson is a biography commissioned by Steve Jobs
Steven Paul Jobs (February 24, 1955 – October 5, 2011) was an American entrepreneur, industrial designer, media proprietor, and investor. He was the co-founder, chairman, and CEO of Apple; the chairman and majority shareholder of Pixar; a ...
, a Reed College alumnus, and contains a chapter on Job's experience attending Reed College.
Film
The Reed College campus has been the set of several motion pictures since 1977. * '' The Possessed'' (1977) is a made-for-televisionhorror film
Horror is a film genre that seeks to elicit fear or disgust in its audience for entertainment purposes.
Horror films often explore dark subject matter and may deal with transgressive topics or themes. Broad elements include monsters, apoca ...
that follows an undead priest who fights demonic forces at a women's college in Salem, Oregon
Salem ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Oregon, and the county seat of Marion County, Oregon, Marion County. It is located in the center of the Willamette Valley alongside the Willamette River, which runs north through the city. The river ...
.
* '' First Love'' (1977) depicts a love story between a male college soccer player and an attractive female student who is loved by another man.
* '' Feast of Love'' (2007) depicts the story of a group of friends who live in Portland, Oregon, the film is composed of vignettes, some of which were filmed on the Reed College campus.
* '' Into the Wild'' (2007) is an adaptation of the Jon Krakauer book of the same name published in 1996, Reed College was used as a stand in during some scenes for Emory University.
* ''Blue Like Jazz'' (2012) is the film adaptation of the book by Donald Miller; the film is set and filmed at Reed College and follows the story of a religiously disillusioned Texan native who moves to the progressive Pacific Northwest to attend Reed College.
See also
*List of Reed College people
This page lists prominent, famous, and notable alumni of Reed College, an American institution of liberal arts and sciences, located in Oregon's most populous city, Portland, along with their past and present positions. In addition to famous Reed C ...
* List of Reed College buildings
References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{Authority control 1908 establishments in Oregon Universities and colleges in Portland, Oregon Educational institutions established in 1908 Liberal arts colleges in Oregon Universities and colleges accredited by the Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities Private universities and colleges in Oregon