 Lothal () was one of the southernmost sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation, located in the Bhāl region of the modern state of
Lothal () was one of the southernmost sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation, located in the Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth- ...
. Construction of the city is believed to have begun around 2200 BCE.
Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), the official Indian government agency for preservation of ancient monuments, discovered Lothal in 1954. Excavation work in Lothal commenced on 13 February 1955 and continued till 19 May 1960. According to the ASI, Lothal had the world's earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over bodies of water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a sin ...
. This trade route stretched between Harappan cities in Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
and the peninsula of Saurashtra where the surrounding Kutch desert of today was a part of the Arabian Sea. However, this interpretation has been challenged by other archaeologists, who argue Khufu's Red Sea harbour at Wadi al-Jarf is older, dating its construction to between 2580 to 2550 BC and that Lothal was a comparatively small town, and that the "dock" was primarily an irrigation tank.
The National Institute of Oceanography in Goa discovered foraminifera (marine microfossils) and salt, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and dr ...
crystals in the rectangular structure clearly indicating that sea water once filled the structure and it was definitely a dockyard.
Lothal was a vital and thriving trade centre in ancient times, with its trade of beads, gems and valuable ornaments reaching the far corners of West Asia and Africa. The techniques and tools they pioneered for bead-making and in metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
have stood the test of time for over 4000 years.
Lothal is situated near the village of Saragwala in the Dholka Taluka of Ahmedabad district. It is six kilometres south-east of the Lothal- Bhurkhi railway station on the Ahmedabad-Bhavnagar
Bhavnagar is a city in the Bhavnagar district of the Saurashtra region of Gujarat, a state of India. It was founded in 1723 by Bhavsinhji Takhtasinhji Gohil (1703–1764). It was the capital of Bhavnagar State, which was a princely state befo ...
railway line. It is also connected by all-weather roads to the cities of Ahmedabad (85 km/53 mi), Bhavnagar, Rajkot and Dholka
Dholka is a city and municipality in the Ahmedabad District of the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the headquarters of Dholka Taluka, and is 48 km by road via National Highway 8A southwest of the city of Ahmedabad. Dholka has an average e ...
. The nearest cities are Dholka and Bagodara. Resuming excavation in 1961, archaeologists unearthed trenches sunk on the northern, eastern and western flanks of the mound, bringing to light the inlet channels and ''nullah'' ("ravine", or "gully") connecting the dock with the river. The findings consist of a mound
A mound is a heaped pile of earth, gravel, sand, rocks, or debris. Most commonly, mounds are earthen formations such as hills and mountains, particularly if they appear artificial. A mound may be any rounded area of topographically higher ...
, a township, a marketplace, and the dock. Adjacent to the excavated areas stands the Archaeological Museum, where some of the most prominent collections of Indus-era antiquities in India are displayed.
The Lothal site was nominated, in April 2014, as a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, and its application is pending on the tentative list of UNESCO.
Archaeology
 When British India was partitioned in 1947, most Indus sites, including Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, became part of
When British India was partitioned in 1947, most Indus sites, including Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, became part of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
. The Archaeological Survey of India undertook a new program of exploration, and excavation. Many sites were discovered across northwestern India. Between 1954 and 1958, more than 50 sites were excavated in the Kutch (notably Dholavira), and Saurashtra peninsulas, extending the limits of Harappan civilisation by to the river Kim, where the Bhagatrav site accesses the valley of the rivers Narmada and Tapti. Lothal stands from Mohenjo-daro, which is in Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
.
The meaning of Lothal (a combination of ''Loth'' and ''(s) thal'') in Gujarati is "the mound of the dead". This is not unusual, as the name of the city of Mohenjo-daro in Sindhi translates to the same. People in villages neighbouring to Lothal had known of the presence of an ancient town and human remains. As recently as 1850, boats could sail up to the mound. In 1942, timber was shipped from Broach to Saragwala via the mound. A silted creek connecting modern Bholad with Lothal and Saragwala represents the ancient flow channel of a river or creek.
Speculation suggests that owing to the comparatively small dimensions of the main city (), Lothal was not a large settlement at all, and its "dock" was perhaps an irrigation tank. However, the ASI and other contemporary archaeologists assert that the city was a part of a major river system on the trade route of the ancient peoples from Sindh to Saurashtra in Gujarat. Lothal provides with the largest collection of antiquities in the archaeology of modern India. It is essentially a single culture site—the Harappan culture in all its variances is evidenced. An indigenous micaceous Red Ware culture also existed, which is believed to be autochthonous and pre-Harappan. Two sub-periods of Harappan culture are distinguished: the same period (between 2400 and 1900 BCE) is identical to the exuberant culture of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro.
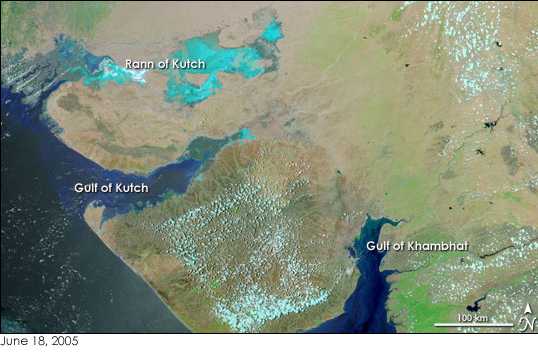 After the core of the Indus civilisation had decayed in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, Lothal seems not only to have survived but to have thrived for many years. Its constant threats – tropical storms and floods – caused immense destruction, which destabilised the culture and ultimately caused its end. Topographical analysis also shows signs that at about the time of its demise, the region suffered from
After the core of the Indus civilisation had decayed in Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, Lothal seems not only to have survived but to have thrived for many years. Its constant threats – tropical storms and floods – caused immense destruction, which destabilised the culture and ultimately caused its end. Topographical analysis also shows signs that at about the time of its demise, the region suffered from aridity
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
or weakened monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
rainfall. Thus the cause for the abandonment of the city may have been changes in the climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologica ...
as well as natural disasters, as suggested by environmental magnetic records. Lothal is based upon a mound that was a salt marsh inundated by tide. Remote sensing and topographical studies published by Indian scientists in the ''Journal of the Indian Geophysicists Union'' in 2004 revealed an ancient, meandering river adjacent to Lothal, in length according to satellite imagery— an ancient extension of the northern river channel bed of a tributary of the Bhogavo river. Small channel widths () when compared to the lower reaches () suggest the presence of a strong tidal influence upon the city—tidal waters ingressed up to and beyond the city. Upstream elements of this river provided a suitable source of fresh water for the inhabitants.
Town planning
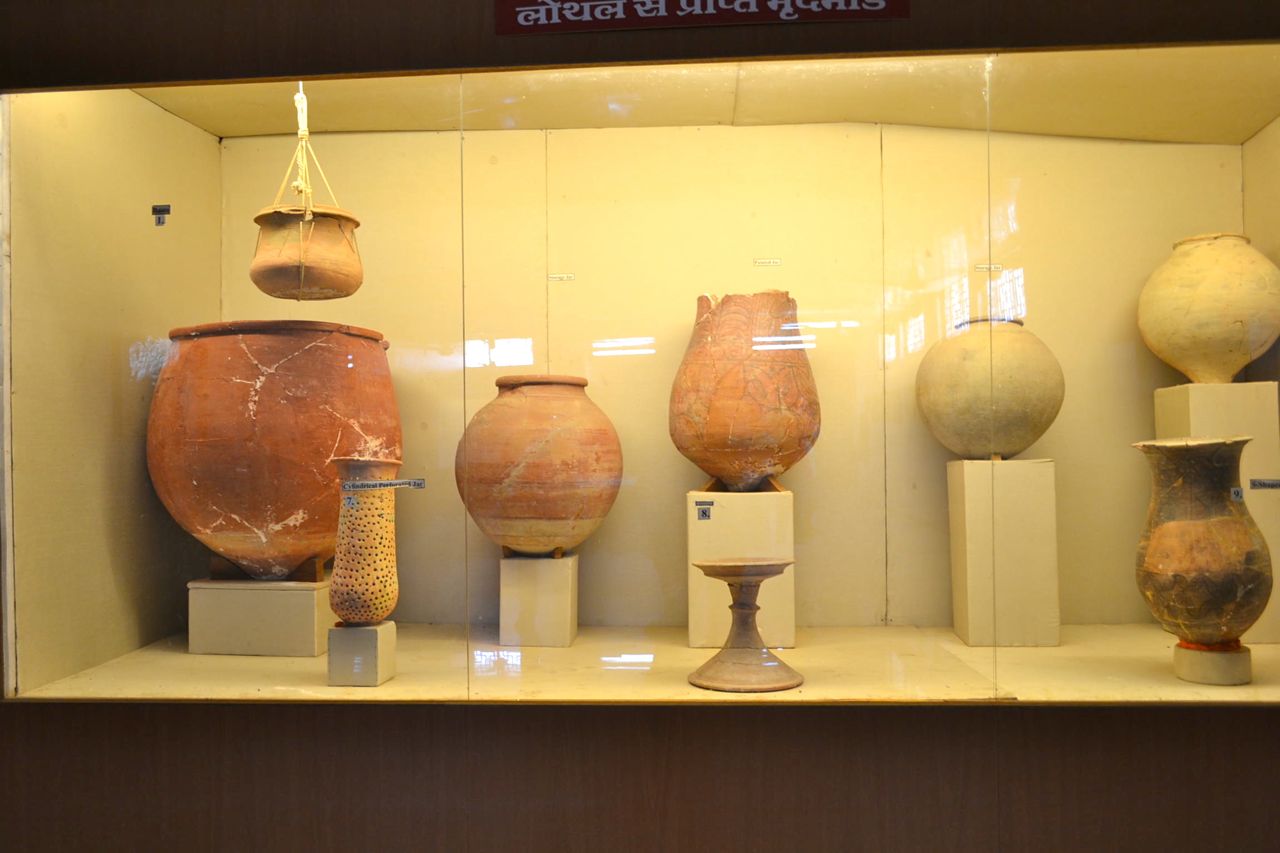 All the construction were made of fire dried bricks, lime and sand mortar and not by sun-dried bricks as bricks are still intact after 4000 years and still bonded together with each other with the mortar bond.
All the construction were made of fire dried bricks, lime and sand mortar and not by sun-dried bricks as bricks are still intact after 4000 years and still bonded together with each other with the mortar bond.
Economy and urban culture

 The uniform organization of the town and its institutions make it evident that the Harappans were very disciplined people. Commerce and administrative duties were performed according to standards laid out. Municipal administration was strict – the width of most streets remained the same over a long time, and no encroached structures were built. Householders possessed a sump, or collection chamber to deposit solid waste in order to prevent the clogging of city drains. Drains, manholes, and cesspools deposited the waste in the river which was washed out during high tide maintaining the cleanliness of the city. A new provincial style of Harappan art and painting was pioneered. The new approaches included realistic portrayals of animals in their natural surroundings. Metalware, gold and jewellery and tastefully decorated ornaments attest to the culture and prosperity of the people of Lothal.
Most of their equipment: metal tools, weights, measures, seals, earthenware and ornaments were of the uniform standard and quality found across the Indus civilization. Lothal was a major trade centre, importing ''en masse'' raw materials like copper, chert and semi-precious stones from Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, and mass distributing to inner villages and towns. It also produced large quantities of bronze
The uniform organization of the town and its institutions make it evident that the Harappans were very disciplined people. Commerce and administrative duties were performed according to standards laid out. Municipal administration was strict – the width of most streets remained the same over a long time, and no encroached structures were built. Householders possessed a sump, or collection chamber to deposit solid waste in order to prevent the clogging of city drains. Drains, manholes, and cesspools deposited the waste in the river which was washed out during high tide maintaining the cleanliness of the city. A new provincial style of Harappan art and painting was pioneered. The new approaches included realistic portrayals of animals in their natural surroundings. Metalware, gold and jewellery and tastefully decorated ornaments attest to the culture and prosperity of the people of Lothal.
Most of their equipment: metal tools, weights, measures, seals, earthenware and ornaments were of the uniform standard and quality found across the Indus civilization. Lothal was a major trade centre, importing ''en masse'' raw materials like copper, chert and semi-precious stones from Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, and mass distributing to inner villages and towns. It also produced large quantities of bronze celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, fish-hooks, chisels, spears and ornaments. Lothal exported its beads, gemstones, ivory and shells. The stone blade industry catered to domestic needs—fine chert was imported from the Larkana valley or from Bijapur in modern Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Kar ...
. Bhagatrav supplied semi-precious stones while ''chank'' shell came from Dholavira and Bet Dwarka. An intensive trade network gave the inhabitants great prosperity. The network stretched across the frontiers to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, Bahrain and Sumer. One of the evidence of trade in Lothal is the discovery of typical Persian gulf seals, a circular button seal
Architectural development
 While the wider debate over the end of Indus civilisation continues, archaeological evidence gathered by the ASI appears to point to natural catastrophes, specifically floods and storms as the source of Lothal's downfall. A powerful flood submerged the town and destroyed most of the houses, with the walls and platforms heavily damaged. The acropolis was levelled (2000–1900 BCE), and inhabited by common tradesmen and newly built makeshift houses. The worst consequence was the shift in the course of the river, cutting off access to the ships and dock. The people built a new but shallow inlet to connect the flow channel to the dock for sluicing small ships into the basin. Large ships were moored away. Houses were rebuilt, yet without removal of flood debris, which made them poor-quality and susceptible to further damage. Public drains were replaced by soakage jars. The citizens did not undertake encroachments, and rebuilt public baths. However, with a poorly organised government, and no outside agency or central government, the public works could not be properly repaired or maintained. The heavily damaged warehouse was never repaired properly, and stocks were stored in wooden canopies, exposed to floods and fire. The economy of the city was transformed. Trade volumes reduced greatly, though not catastrophically, and resources were available in lesser quantities. Independent businesses caved, allowing a merchant-centric system of factories to develop where hundreds of craftsmen worked for the same supplier and financier. The bead factory had ten living rooms and a large workplace courtyard. The coppersmith's workshop had five furnaces and paved sinks to enable multiple artisans to work.
The declining prosperity of the town, paucity of resources and poor administration increased the woes of a people pressured by consistent floods and storms. Increased salinity of soil made the land inhospitable to life, including crops. This is evidenced in adjacent cities of Rangpur, Rojdi, Rupar and Harappa in
While the wider debate over the end of Indus civilisation continues, archaeological evidence gathered by the ASI appears to point to natural catastrophes, specifically floods and storms as the source of Lothal's downfall. A powerful flood submerged the town and destroyed most of the houses, with the walls and platforms heavily damaged. The acropolis was levelled (2000–1900 BCE), and inhabited by common tradesmen and newly built makeshift houses. The worst consequence was the shift in the course of the river, cutting off access to the ships and dock. The people built a new but shallow inlet to connect the flow channel to the dock for sluicing small ships into the basin. Large ships were moored away. Houses were rebuilt, yet without removal of flood debris, which made them poor-quality and susceptible to further damage. Public drains were replaced by soakage jars. The citizens did not undertake encroachments, and rebuilt public baths. However, with a poorly organised government, and no outside agency or central government, the public works could not be properly repaired or maintained. The heavily damaged warehouse was never repaired properly, and stocks were stored in wooden canopies, exposed to floods and fire. The economy of the city was transformed. Trade volumes reduced greatly, though not catastrophically, and resources were available in lesser quantities. Independent businesses caved, allowing a merchant-centric system of factories to develop where hundreds of craftsmen worked for the same supplier and financier. The bead factory had ten living rooms and a large workplace courtyard. The coppersmith's workshop had five furnaces and paved sinks to enable multiple artisans to work.
The declining prosperity of the town, paucity of resources and poor administration increased the woes of a people pressured by consistent floods and storms. Increased salinity of soil made the land inhospitable to life, including crops. This is evidenced in adjacent cities of Rangpur, Rojdi, Rupar and Harappa in Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
, Mohenjo-daro and Chanhudaro in Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
. A massive flood (c. 1900 BCE) completely destroyed the flagging township in a single stroke. Archaeological analysis shows that the basin and dock were sealed with silt and debris, and the buildings razed to the ground. The flood affected the entire region of Saurashtra, Sindh and south Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
, and affected the upper reaches of the Indus and Sutlej, where scores of villages and townships were washed away. The population fled to inner regions.
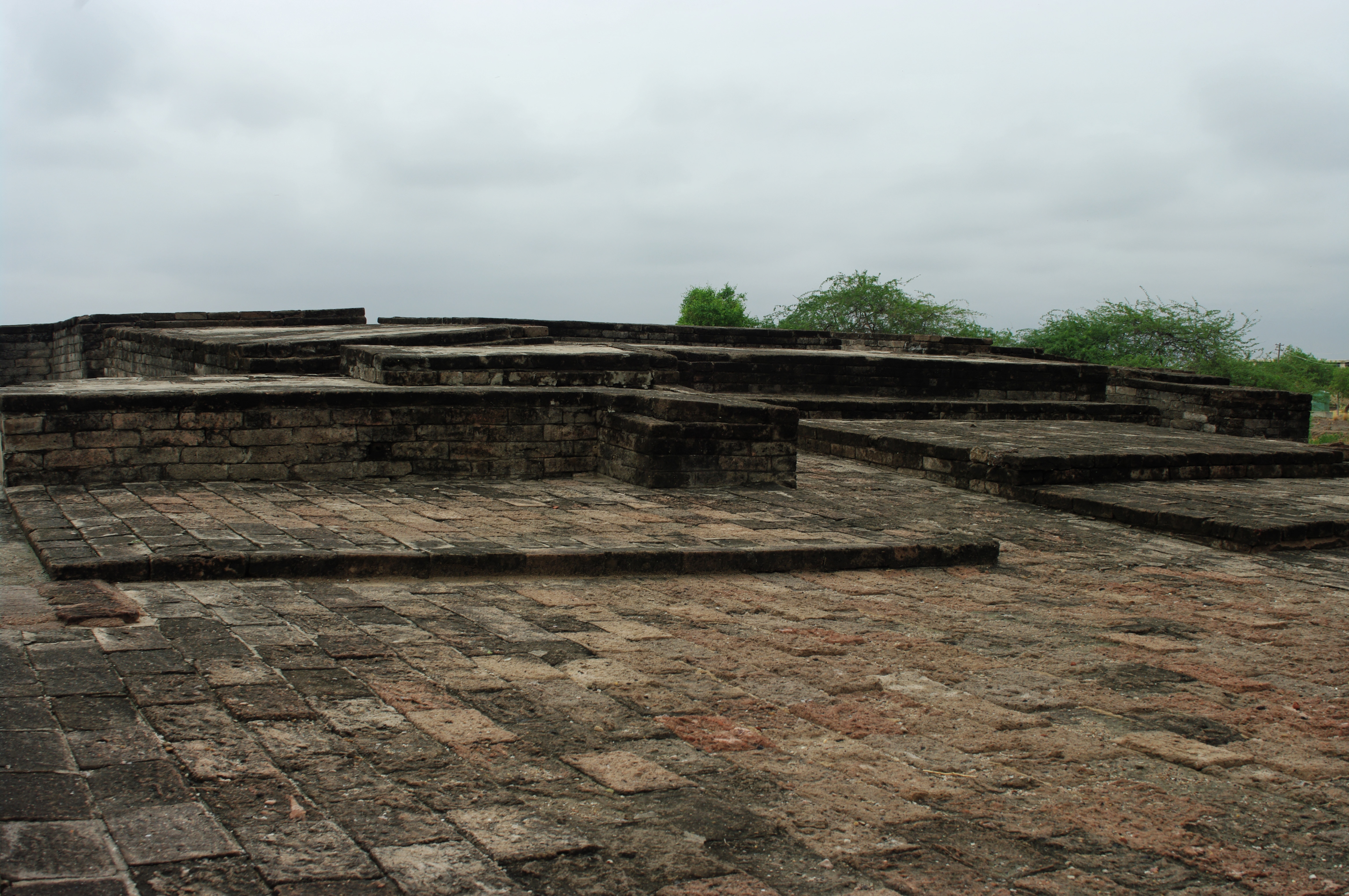

Later Harappan culture
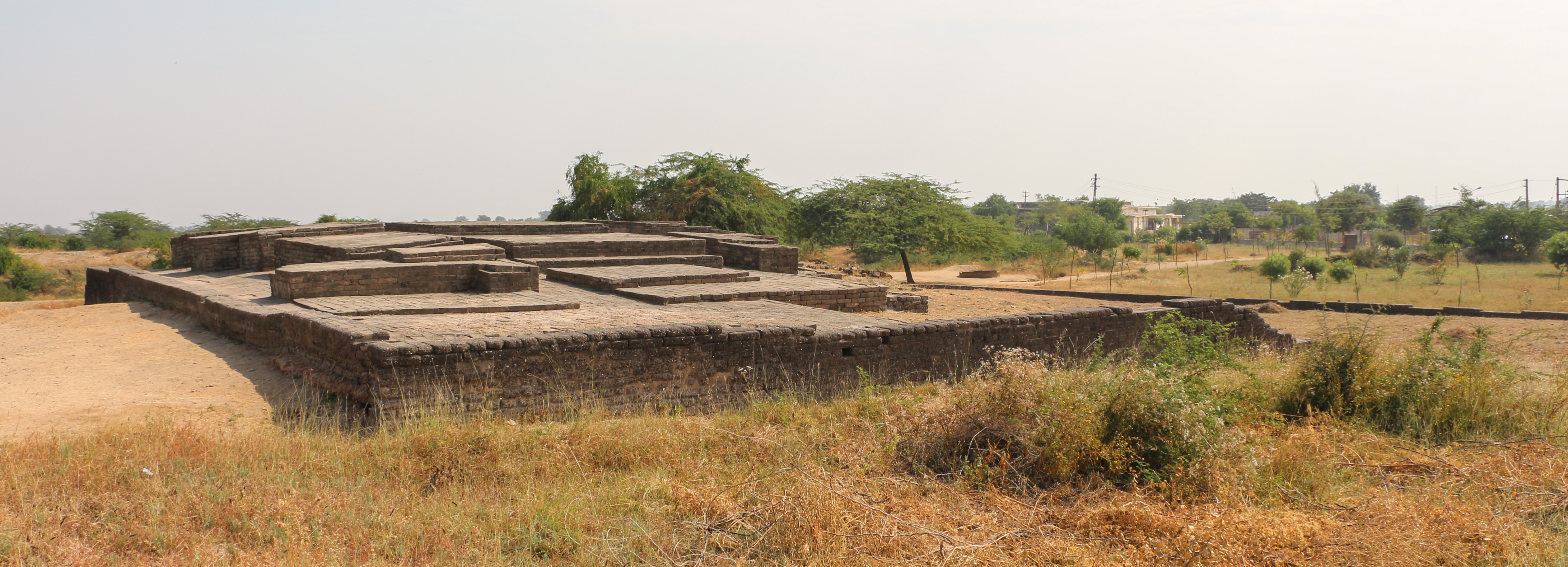 Archaeological evidence shows that the site continued to be inhabited, albeit by a much smaller population devoid of urban influences. The few people who returned to Lothal could not reconstruct and repair their city, but surprisingly continued to stay and preserved religious traditions, living in poorly built houses and reed huts. That they were the Harappan peoples is evidenced by the analyses of their remains in the cemetery. While the trade and resources of the city were almost entirely gone, the people retained several Harappan ways in writing, pottery, and utensils. About this time ASI archaeologists record a mass movement of refugees from Punjab and Sindh into Saurashtra and to the valley of Sarasvati (1900–1700 BCE). Hundreds of ill-equipped settlements have been attributed to this people as ''Late Harappans'' a completely de-urbanised culture characterised by rising illiteracy, less complex economy, unsophisticated administration and poverty. Though Indus seals went out of use, the system of weights with an 8.573 gram (0.3024 oz avoirdupois
Archaeological evidence shows that the site continued to be inhabited, albeit by a much smaller population devoid of urban influences. The few people who returned to Lothal could not reconstruct and repair their city, but surprisingly continued to stay and preserved religious traditions, living in poorly built houses and reed huts. That they were the Harappan peoples is evidenced by the analyses of their remains in the cemetery. While the trade and resources of the city were almost entirely gone, the people retained several Harappan ways in writing, pottery, and utensils. About this time ASI archaeologists record a mass movement of refugees from Punjab and Sindh into Saurashtra and to the valley of Sarasvati (1900–1700 BCE). Hundreds of ill-equipped settlements have been attributed to this people as ''Late Harappans'' a completely de-urbanised culture characterised by rising illiteracy, less complex economy, unsophisticated administration and poverty. Though Indus seals went out of use, the system of weights with an 8.573 gram (0.3024 oz avoirdupois
Civilization
The people of Lothal made significant and often unique contributions to human civilisation in the Indus era, in the fields of city planning, art, architecture, science, engineering, pottery, and religion. Their work inmetallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
, seals, beads and jewellery was the basis of their prosperity.
Science and engineering
 A thick ring-like shell object found with four slits each in two margins served as a
A thick ring-like shell object found with four slits each in two margins served as a compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
to measure angles on plane surfaces such as housing alignments, roads or land surveys. S.R. Rao also suggested that it could have functioned as an instrument for measuring angles and perhaps the position of stars and thus for navigation like a sextant. Lothal contributes one of three measurement scales that are integrated and linear (others found in Harappa and Mohenjodaro). An ivory scale from Lothal has the smallest-known decimal divisions in Indus civilisation. The scale is 6 millimetres (0.2 inches) thick, broad and the available length is , but only 27 graduations are visible over , the distance between graduation lines being (the small size indicates use for fine purposes). The sum total of ten graduations from Lothal is approximate to the ''angula'' in the '' Arthashastra''. The Lothal craftsmen took care to ensure durability and accuracy of stone weights by blunting edges before polishing.
For their renowned draining system, Lothal engineers provided corbelled roofs, and an apron of kiln-fired bricks over the brick face of the platform where the sewerage entered the cesspool. Wooden screens inserted in grooves in the side drain walls held back solid waste. The well is built of radial bricks, in diameter and deep. It had an immaculate network of underground drains, silting chambers and cesspools, and inspection chambers for solid waste. The extent of drains provided archaeologists with many clues regarding the layout of streets, organisation of housing and baths. On average, the main sewer is in depth, with outer dimensions of 86 × 68 × 33 cm (34 × 27 × 13 in). Lothal brick-makers used a logical approach in manufacture of bricks, designed with care in regards to thickness of structures. They were used as headers and stretchers in same and alternate layers. Archaeologists estimate that in most cases, the bricks were in ratio 1:0.5:0.25 on three sides, in dimensions which were integral multiples of large graduations of Lothal scale of .
Religion and disposal of the dead
 The people of Lothal worshipped a fire god who is speculated to be the horned deity depicted on seals. The presence of private and public fire-altars where religious ceremonies were hosted further testifies to their spiritual beliefs. Archaeologists have discovered gold pendants, charred ashes of terra-cotta cakes and pottery, bovine remains, beads and other signs that may indicate the practice of the Gavamayana sacrifice, associated with the ancient Vedic religion. Animal worship is also evidenced, but not the worship of the
The people of Lothal worshipped a fire god who is speculated to be the horned deity depicted on seals. The presence of private and public fire-altars where religious ceremonies were hosted further testifies to their spiritual beliefs. Archaeologists have discovered gold pendants, charred ashes of terra-cotta cakes and pottery, bovine remains, beads and other signs that may indicate the practice of the Gavamayana sacrifice, associated with the ancient Vedic religion. Animal worship is also evidenced, but not the worship of the Mother Goddess
A mother goddess is a goddess who represents a personified deification of motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction, or the earth goddess who embodies the bounty of the earth or nature. When equated with the earth or the natural world, ...
that is evidenced in other Harappan cities—experts consider this a sign of the existence of diversity in religious traditions. However, it is believed that a sea goddess, perhaps cognate with the general Indus-era Mother Goddess, was worshipped. Today, the local villagers likewise worship a sea goddess, ''Vanuvati Sikotarimata'', suggesting a connection with the ancient port's traditions and historical past as an access to the sea. But the archaeologists also discovered that the practice had been given up by 2000 BCE (determined by the difference in burial times of the carbon-dated remains). It is suggested that the practice occurred only on occasion. It is also considered that given the small number of graves discovered—only 17 in an estimated population of 15,000—the citizens of Lothal also practised cremation
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre ...
of the dead. Post-cremation burials have been noted in other Indus sites like Harappa, Mehi and Damb-Bhuti.
Metallurgy and jewellery
 Lothal copper is unusually pure, lacking the
Lothal copper is unusually pure, lacking the arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, bu ...
typically used by coppersmiths across the rest of the Indus valley. The city imported ingots from probable sources in the Arabian peninsula. Workers mixed tin with copper for the manufacture of celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, arrowheads, fishhooks, chisels, bangles, rings, drills, and spearheads, although weapon manufacturing was minor. They also employed advanced metallurgy in following the ''cire perdue'' technique of casting, and used more than one-piece moulds for casting birds and animals. They also invented new tools such as curved saws and twisted drills unknown to other civilisations at the time.
Lothal was one of the most important centres of production for shell-working, owing to the abundance of chank shell of high quality found in the Gulf of Kutch and near the Kathiawar coast. Gamesmen, beads, unguent vessels, chank shells, ladles and inlays were made for export and local consumption. Components of stringed musical instruments like the plectrum and the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually somethi ...
were made of shell. An ivory workshop was operated under strict official supervision, and the domestication of elephants has been suggested. An ivory seal, and sawn pieces for boxes, combs, rods, inlays and ear-studs were found during excavations. Lothal produced a large quantity of gold ornaments—the most attractive item being microbeads of gold in five strands in necklaces, unique for being less than 0.25 millimetres (0.010 inches) in diameter. Cylindrical, globular and jasper beads of gold with edges at right angles resemble modern pendants used by women in Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
in plaits of hair. A large disc with holes recovered from a sacrificial altar is compared to the ''rukma'' worn by Vedic priests. Studs, cogwheel and heart-shaped ornaments of faience
Faience or faïence (; ) is the general English language term for fine tin-glazed pottery. The invention of a white pottery glaze suitable for painted decoration, by the addition of an oxide of tin to the slip of a lead glaze, was a major ad ...
and steatite were popular in Lothal. A ring of thin copper wire turned into double spirals resembles the gold-wire rings used by modern Hindus for weddings.
Art

 The discovery of etched
The discovery of etched carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often use ...
beads and non-etched barrel beads in Kish and Ur (modern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
), Jalalabad (Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
) and Susa (Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
) attest to the popularity of the Indus bead industry across West Asia. The lapidaries select stones of variegated colours, producing beads of different shapes and sizes. The methods of Lothal bead-makers were so advanced that no improvements have been noted over 4,000 years—modern makers in the Khambhat area follow the same technique. Double-eye beads of agate and collared or gold-capped beads of jasper and carnelian beads are among those attributed as uniquely from Lothal. It was very famous for micro-cylindrical beads of steatite (chlorite).
The Lothal excavation yielded 213 seals, third in volume amongst all Indus sites. Seal-cutters preferred short-horned bulls, mountain goats, tigers and composite animals like the elephant-bull for engravings. There is a short inscription of intaglio in almost every seal. Stamp seals with inserted copper rings in a perforated button were used to seal the cargo with impressions of packing materials like mats, twisted cloth, and cords. These seals were only verified at Lothal. Quantitative descriptions along with seals of rulers and owners were stamped on goods. A unique seal found here is from Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
—circular, with motif of a dragon flanked by jumping gazelles.
Lothal offers two new types of pottery, a convex bowl with or without stud handle and a small jar with flaring rim, both of which were found in the micaceous Red Ware period and not in contemporary Indus cultures. Lothal artists introduced a new form of realistic painting. Paintings depict animals in their natural surroundings. On one large vessel, the artist depicts birds with fish in their beaks, resting in a tree, while a fox-like animal stands below. This scene bears resemblance to the story of The Fox and the Crow in the '' Panchatantra''. Artistic imagination is also suggested via careful portrayals—for example, several birds with legs aloft in the sky suggest flight, while half-opened wings suggest imminent flight. On a miniature jar, the story of the thirsty crow and deer is depicted – of how the deer could not drink from the narrow-mouth of the jar, while the crow succeeded by dropping stones in the jar. The features of the animals are clear and graceful. Movements and emotions are suggested by the positioning of limbs and facial features—in a jar without overcrowding.
A complete set of terra-cotta gamesmen, has been found in Lothal—animal figures, pyramids with ivory handles and castle-like objects (similar to the chess set of Queen Hatshepsut in Egypt). The realistic portrayal of human beings and animals suggests a careful study of anatomical and natural features. The bust of a male with slit eyes, sharp nose, and square-cut beard is reminiscent of Sumerian figures, especially stone sculptures from Mari. In images of men and women, muscular and physical features are sharp, prominently marked. Terra-cotta models also identify the differences between species of dogs and bulls, including those of horses. Animal figures with wheels and a movable head may have been utilised as toys.
Excavated Lothal
 On plan, Lothal stands north-to-south and east-to-west. At the height of its habitation, it covered a wider area since remains have been found south of the mound. Due to the fragile nature of unbaked bricks and frequent floods, the superstructures of all buildings have receded. However, the dwarfed walls, platforms, two wells, drains, and paved bathing platforms are visible. The dock walls were also preserved beyond the great deluge (c.1900 BCE) due to the loam that was deposited by persistent floods. Erosion and brick robbery are responsible for the absence of high standing walls as well as the ancient nullah, inlet channel, and riverbed. The flood-damaged peripheral wall of mud-bricks is visible near the warehouse area. The remnants of the north–south sewer are burnt bricks in the cesspool. Cubical blocks of the warehouse on a high platform are also visible.
The ASI has covered the peripheral walls, the wharf, and many houses of the early phase with earth to protect from natural phenomena, but the entire archaeological site is nevertheless facing grave concerns about necessary preservation. Salinity ingress and prolonged exposure to the rain and sun are gradually eating away the remains of the site. Heavy rain in the region has damaged the remains of the sun-dried mud brick constructions. Stagnant rain water has lathered the brick and mud work with layers of moss. Due to
On plan, Lothal stands north-to-south and east-to-west. At the height of its habitation, it covered a wider area since remains have been found south of the mound. Due to the fragile nature of unbaked bricks and frequent floods, the superstructures of all buildings have receded. However, the dwarfed walls, platforms, two wells, drains, and paved bathing platforms are visible. The dock walls were also preserved beyond the great deluge (c.1900 BCE) due to the loam that was deposited by persistent floods. Erosion and brick robbery are responsible for the absence of high standing walls as well as the ancient nullah, inlet channel, and riverbed. The flood-damaged peripheral wall of mud-bricks is visible near the warehouse area. The remnants of the north–south sewer are burnt bricks in the cesspool. Cubical blocks of the warehouse on a high platform are also visible.
The ASI has covered the peripheral walls, the wharf, and many houses of the early phase with earth to protect from natural phenomena, but the entire archaeological site is nevertheless facing grave concerns about necessary preservation. Salinity ingress and prolonged exposure to the rain and sun are gradually eating away the remains of the site. Heavy rain in the region has damaged the remains of the sun-dried mud brick constructions. Stagnant rain water has lathered the brick and mud work with layers of moss. Due to silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel wh ...
ation, the dockyard's draft has been reduced by and saline deposits are decaying the bricks. Officials blame the salinity on capillary action and point out that cracks are emerging and foundations weakening even as restoration work slowly progresses.
Dockyard
wharf
A wharf, quay (, also ), staith, or staithe is a structure on the shore of a harbour or on the bank of a river or canal where ships may dock to load and unload cargo or passengers. Such a structure includes one or more Berth (moorings), berths ...
, long, built on the western arm of the dock, with a ramp leading to the warehouse and acropolis, built on a packed mud platform, original in height (Now it is .) on the south westen flank of the basin. The warehouse was originally built on sixty-four cubical blocks, square, with passages, and based on a mud-brick podium. The pedestal was very high to provide maximum protection from floods. Brick-paved passages between blocks served as vents, and a direct ramp led to the dock to facilitate loading. The warehouse was located close to the acropolis, to allow tight supervision by ruling authorities. Despite elaborate precautions, the major floods that brought the city's decline destroyed all but twelve blocks, which became the makeshift storehouse.
Rao's identification of basin as a dock was challenged by Leshnik in 1968 and later Yule in 1982,
who offered an alternative assessment of the feature as primarily an irrigation tank. In their assessment the dimensions of the "inlet" are not large enough to accommodate the draft of ocean going vessels, with inland craft having to be used to ferry goods to ocean going vessels birthed elsewhere. The identification of just two wells in the town, one on the southern edge of the dock and the other on the acropolis, were also offered to support the alternative primary purpose, as a tank to irrigate vegetables in the adjoining fields, a place to bathe, and a quay to unload river boats.
The National Institute of Oceanography, Goa discovered foraminifera (marine microfossils) and salt, gypsum crystals (due to evapouration of seawater) in the rectangular structure clearly indicating that sea water once filled the structure, though Leshnik argued these could have been left through flood events.
The purpose of the 5 stone weights found around the basin, as to whether they were anchors or Shadoof weights has also been debated, as have the source of the estuarine shells from the dock, 5 terracotta models of boats and a circular Persian Gulf seal from Bahrain.
It is speculated that Lothal engineers studied tidal movements, and their effects on brick-built structures, since the walls are of kiln-burnt bricks. This knowledge also enabled them to select Lothal's location in the first place, as the Gulf of Khambhat has the highest tidal amplitude and ships can be sluiced through flow tides in the river estuary.
The main inlet is wide, and another is provided on the opposite side. To counter the thrust of water, offsets were provided on the outer wall faces.
At high tide flow of of water would have allowed ships to enter. Provision was made for the escape of excess water through the outlet channel, wide and high in the southern arm.
There was an important public building opposite to the warehouse whose superstructure has completely disappeared. Throughout their time, the city had to brace itself through multiple floods and storms. Dock and city peripheral walls were maintained efficiently. The town's zealous rebuilding ensured the growth and prosperity of the trade. However, with rising prosperity, Lothal's people failed to upkeep their walls and dock facilities, possibly as a result of over-confidence in their systems. A flood of moderate intensity in 2050 BCE exposed some serious weaknesses in the structure, but the problems were not addressed properly.
Acropolis and lower town
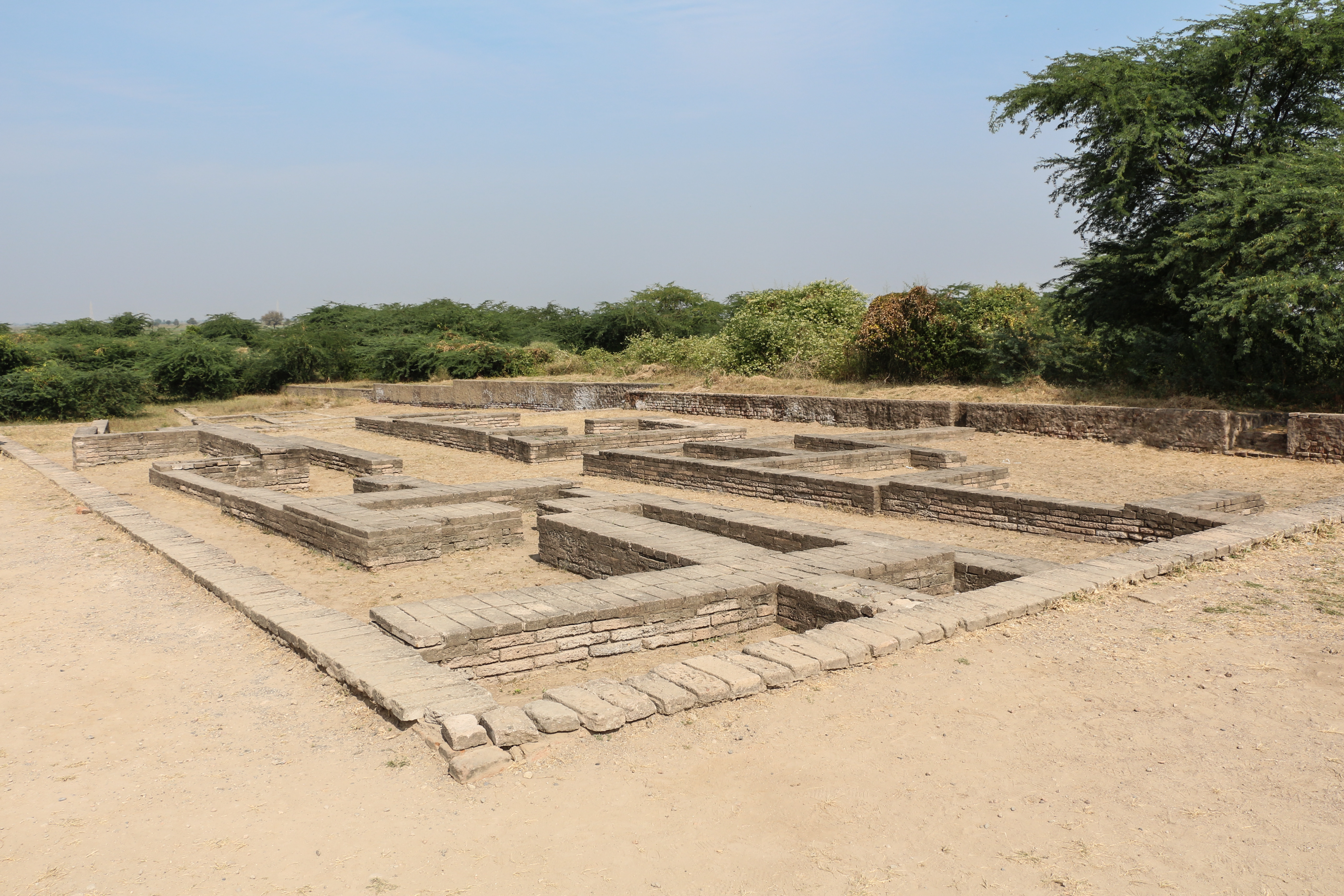 The town center of Acropolis was the political and commercial heart of Lothal measuring at east-to-west by north-to-south. There were three streets and two lanes running east–west, and two streets running north–south. The four sides of the rectangular platform on which houses were built are formed by mud-brick structures of thickness and high. The identified bathing platforms are located in the acropolis, and part of mostly two-roomed houses with open courtyards. The bricks used for paving the bathing platforms were polished to prevent seepage. The pavements were lime-plastered, and edges were wainscoted (wooden panels) by thin walls. The ruler's residence was and hosted a bathing platform with contiguous squat latrine which was also connected to an outside drain that discharged into the dock. The lower town marketplace was on the main north–south street wide. Built in straight rows on either side of the street are residences and workshops, although brick-built drains and early period housing has now disappeared. The street maintained a uniform width and did not undergo encroachment during the reconstructive periods after deluges. There are multiple two-roomed shops and workplaces of coppersmiths and blacksmiths.
The bead factory, which performs a very important economic function, possesses a central courtyard and eleven rooms, a store, and a guardhouse. There is a cinder dump as well as a double-chambered circular kiln with stoke-holes for fuel supply. Four flues are connected with each other, the upper chamber and the stokehold. The mud plaster of the floors and walls are vitrified owing to intense heat during work. The remnants of raw materials such as reed, cow dung, sawdust, and agate are found, giving archaeologists hints of how the kiln was operated. A large mud-brick building faces the factory, and its significance is noted by its plan. Four large rooms and a hall, with an overall measurement of . The hall has a large doorway and a raised floor in the southern corner of the building.
The town center of Acropolis was the political and commercial heart of Lothal measuring at east-to-west by north-to-south. There were three streets and two lanes running east–west, and two streets running north–south. The four sides of the rectangular platform on which houses were built are formed by mud-brick structures of thickness and high. The identified bathing platforms are located in the acropolis, and part of mostly two-roomed houses with open courtyards. The bricks used for paving the bathing platforms were polished to prevent seepage. The pavements were lime-plastered, and edges were wainscoted (wooden panels) by thin walls. The ruler's residence was and hosted a bathing platform with contiguous squat latrine which was also connected to an outside drain that discharged into the dock. The lower town marketplace was on the main north–south street wide. Built in straight rows on either side of the street are residences and workshops, although brick-built drains and early period housing has now disappeared. The street maintained a uniform width and did not undergo encroachment during the reconstructive periods after deluges. There are multiple two-roomed shops and workplaces of coppersmiths and blacksmiths.
The bead factory, which performs a very important economic function, possesses a central courtyard and eleven rooms, a store, and a guardhouse. There is a cinder dump as well as a double-chambered circular kiln with stoke-holes for fuel supply. Four flues are connected with each other, the upper chamber and the stokehold. The mud plaster of the floors and walls are vitrified owing to intense heat during work. The remnants of raw materials such as reed, cow dung, sawdust, and agate are found, giving archaeologists hints of how the kiln was operated. A large mud-brick building faces the factory, and its significance is noted by its plan. Four large rooms and a hall, with an overall measurement of . The hall has a large doorway and a raised floor in the southern corner of the building.
Coastal trade route
A coastal route may have existed linking sites such as Lothal and Dholavira to Sutkagan Dor on the Makran coast.See also
* List of Indus Valley Civilization sites * Bhagatrav, a small port * Rangpur, Gujarat, a sea portNotes
Harappa Town Planning
(published in "Uttar Pradesh" in November 1961). * S. R. Rao, ''Lothal'' (published by the Director General, Archaeological Survey of India, 1985)
A.S. Khadikar, N. Basaviah, T. K. Gundurao and C. Rajshekhar ''Paleoenvironments around the Harappan port of Lothal, Gujarat, western India, in Journal of the Indian Geophysicists Union''
(2004)
Lawrence S. Leshnik, ''The Harappan "Port" at Lothal: Another View'' American Anthropologist, New Series, Vol. 70, No. 5 (Oct., 1968), pp. 911–922
*S. R. Rao, ''Lothal and the Indus Civilisation'' *S. R. Rao, ''Lothal: A Harappan Port Town (1955–1962) (Memoirs of the Archaeological Survey of India)'
ASIN: B0006E4EAC
*Paul Yule, ''Lothal. Stadt der Harappa-Kultur in Nordwest-Indien''. Materialien zur Allgemeinen und Vergleichenden Archäologie 9, Munich, 1982 = AVA-Materialien, *Sir John Marshall, ''Mohenjo-daro and Indus Civilisation I–III'' (1932) *Dennys Frenez & Maurizio Tosi ''The Lothal Sealings: Records from an Indus Civilization Town at the Eastern End of the Maritime Trade Circuits across the Arabian Sea'', in M. Perna (Ed.), Studi in Onore di Enrica Fiandra. Contributi di archeologia egea e vicinorientale, Naples 2005, pp. 65–103. *
S. P. Gupta
Swaraj Prakash Gupta (S. P. Gupta, 1931–2007) was a prominent Indian archaeologist, art historian authority, Chairman of Indian Archaeological Society, founder of the Indian History and Culture Society, and Director of the Allahabad Museum. H ...
(ed.), ''The Lost Sarasvati and the Indus Civilization'' (1995), Kusumanjali Prakashan, Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the ...
* Jonathan Mark Kenoyer, ''Ancient cities of the Indus Valley Civilization'' (1998) Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print book ...
,
External links
Lothal
*
{{Authority control Archaeological sites in Gujarat Former populated places in India Indian Ocean Indus Valley civilisation sites Port cities in India History of Gujarat 1954 archaeological discoveries 4th-millennium BC establishments Tourist attractions in Ahmedabad district Monuments of National Importance in Gujarat