|
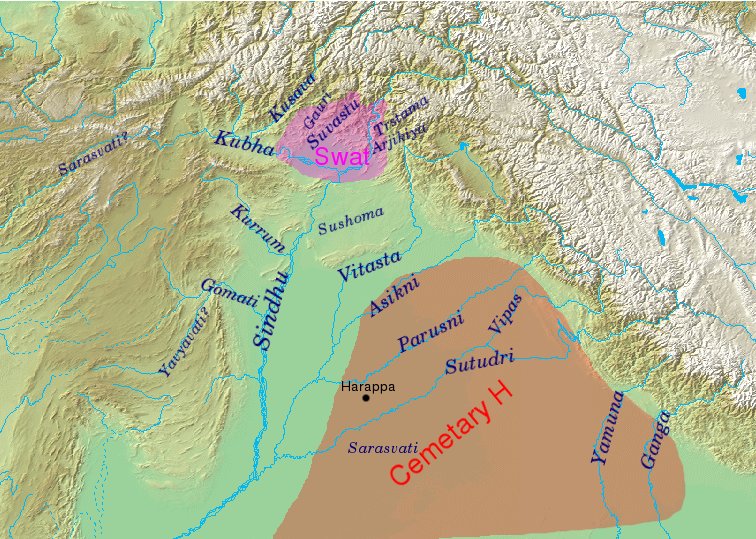
Cemetery H Culture
The Cemetery H culture was a Bronze Age culture in the Punjab region in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, from about 1900 BC until about 1300 BC. It is regarded as a regional form of the late phase of the Harappan (Indus Valley) civilisation (alongside the Jhukar culture of Sindh and Rangpur culture of Gujarat), but also as the manifestation of a first wave of Indo-Aryan migrations, predating the migrations of the proto-Rig Vedic people. Origins The Cemetery H culture was located in and around the Punjab region in present-day India and Pakistan. It was named after a cemetery found in "area H" at Harappa. Remains of the culture have been dated from about 1900 BC until about 1300 BC. According to Rafique Mughal, the Cemetery H culture developed out of the northern part of the Indus Valley civilization around 1700 BC, being part of the Punjab Phase, one of three cultural phases that developed in the Localization Era or "Late Harappan phase" of the Indus Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swat Culture
In the United States, a SWAT team (special weapons and tactics, originally special weapons assault team) is a police tactical unit that uses specialized or military equipment and tactics. Although they were first created in the 1960s to handle riot control or violent confrontations with criminals, the number and usage of SWAT teams increased in the 1980s and 1990s during the War on Drugs and later in the aftermath of the September 11 attacks. In the United States by 2005, SWAT teams were deployed 50,000 times every year, almost 80% of the time to serve search warrants, most often for narcotics. By 2015 that number had increased to nearly 80,000 times a year. SWAT teams are increasingly equipped with military-type hardware and trained to deploy against threats of terrorism, for crowd control, hostage taking, and in situations beyond the capabilities of ordinary law enforcement, sometimes deemed "high-risk". SWAT units are often equipped with Automatic rifle, automatic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangpur, Gujarat
Rangpur is an ancient archaeological site near Vanala on Saurashtra peninsula in Gujarat, western India. Lying on the tip between the Gulf of Khambhat and Gulf of Kutch, it belongs to the period of the Indus Valley civilization, and lies to the northwest of the larger site of Lothal. It is the type site for the Rangpur culture, a regional form of the late phase of the Indus Valley Civilization that existed in Gujarat during the 2nd millennium BCE. Excavation Rangpur culture: Based on the distinct pottery excavated here, it was identified as a separate culture or subculture. See also * Bet Dwarka * Chronological dating ** Phases in archaeology ** Pottery in the Indian subcontinent * List of Indus Valley Civilization sites * Periodisation of the Indus Valley Civilisation ** Ahar-Banas culture ** Late Harappan Phase of IVC (1900 - 1500 BCE) *** Cemetery H culture The Cemetery H culture was a Bronze Age culture in the Punjab region in the northern part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima ''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown in West Africa around 3,000 years ago. In agriculture, it has largely been replaced by higher-yielding Asian r ...'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera ''Zizania (genus), Zizania'' and ''Porteresia'', both wild and domesticated, although the term may also be used for primitive or uncultivated varieties of ''Oryza''. As a cereal, cereal grain, domesticated rice is the most widely consumed staple food for over half of the world's World population, human population,Abstract, "Rice feeds more than half the world's population." especially in Asia and Africa. It is the agricultural commodity with the third-highest worldwide production, after sugarcane and maize. Since sizable portions of sugarcane and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sky, night, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed stars, fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterism (astronomy), asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper names. Astronomers have assembled star catalogues that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designations. The observable universe contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way galaxy. A star's life star formation, begins with the gravitational collapse of a gaseous nebula of material composed primarily of hydrogen, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peacock
Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera ''Pavo (genus), Pavo'' and ''Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens, although peafowl of either sex are often referred to colloquialism, colloquially as "peacocks." The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally of the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl of Southeast Asia; the one African species is the Congo peafowl, native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual. The functions of the elaborate iridescent Animal coloration, colouration and large "train" of peacocks have been the subject of extensive scientific debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia. Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammals belonging to the family Bovidae of the order Artiodactyla. A stricter definition, also known as the "true antelopes," includes only the genera ''Gazella'', ''Nanger'', ''Eudorcas'' and ''Antilope''. One North American species, the pronghorn, is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope," but it belongs to a different family from the African and Eurasian antelopes. A group of antelope is called a herd. Unlike deer antlers, which are shed and grown annually, antelope horns grow continuously. Etymology The English word "antelope" first appeared in 1417 and is derived from the Old French ''antelop'', itself derived from Medieval Latin ''ant(h)alopus'', which in turn comes from the Byzantine Greek word ἀνθόλοψ, ''anthó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Civilization
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred. The Vedas were composed and orally transmitted with precision by speakers of an Old Indo-Aryan language who had migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ochre Coloured Pottery Culture
The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture (OCP) is a Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain "generally dated 2000–1500 BCE," extending from eastern Punjab to northeastern Rajasthan and western Uttar Pradesh. Artefacts of this culture show similarities with both the Late Harappan culture and the Vedic culture. Archaeologist Akinori Uesugi considers it as an archaeological continuity of the previous Harappan Bara style, while according to Parpola, the find of carts in this culture may reflect an Indo-Iranian migration into the India subcontinent, in contact with Late Harappans. The OCP marked the last stage of the North Indian Bronze Age and was succeeded by the Iron Age black and red ware culture and the Painted Grey Ware culture. Geography and dating The 'Ochre Coloured Pottery culture is "generally dated 2000-1500 BCE," Early specimens of the characteristic ceramics found near Jodhpura, Rajasthan, date from the 3rd millennium (this Jodhpura is located in the district of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gandhara Grave Culture
The Gandhara grave culture, also called Swat culture, or Swat Protohistoric Graveyards Complex, emerged ''c.'' 1400 BCE and lasted until 800 BCE, as recent fieldwork, along with subsequent analyses, have shown there are no burials with these features after 800 BCE. It is found in Middle Swat River course, even though earlier research considered it to be expanded to the Valleys of Dir, Kunar, Chitral, and Peshawar. It has been regarded as a token of the Indo-Aryan migrations, but has also been explained by local cultural continuity. Backwards projections, based on ancient DNA analyses, suggest ancestors of Swat culture people mixed with a population coming from the Inner Asian Mountain Corridor, which carried Steppe ancestry, sometime between 1900 and 1500 BCE. Location and characteristics Relevant finds, artifacts found primarily in graves, were distributed along the banks of the Swat and Dir rivers in the north, Taxila in the southeast, along the Gomal River to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Migration Theory
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Indo-Aryan population movements into the region from Central Asia are considered to have started after 2000 BCE, as a slow diffusion during the Late Harappan period, which led to a language shift in the northern Indian subcontinent. Several hundred years later, the Iranian languages were brought into the Iranian plateau by the Iranians, who were closely related to the Indo-Aryans. The Proto-Indo-Iranian culture, which gave rise to the Indo-Aryans and Iranians, developed on the Central Asian steppes north of the Caspian Sea as the Sintashta culture (2050Lindner, Stephan, (2020)"Chariots in the Eurasian Steppe: a Bayesian approach to the emergence of horse-drawn transport in the early second millennium BC" in Antiquity, V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jonathan Mark Kenoyer
Jonathan Mark Kenoyer (born 28 May 1952, in Shillong, India) is an American archaeologist and ''George F. Dales Jr. & Barbara A. Dales'' Professor of Anthropology at the University of Wisconsin–Madison. He earned his Bachelor of Arts, Master's, and Doctorate degrees at the University of California, Berkeley, finishing in 1983. Kenoyer is president of the Society of Bead Researchers. Being focused on the Indus Valley civilization, Kenoyer is involved in ongoing research on the Indus Civilization in the Indian Subcontinent as well as in adjacent regions such as Oman and Afghanistan. He has also expanded his areas of study into East and Southeast Asia to better understand the long-distance trade linking these regions to the Subcontinent. He was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2011 and is a member of the American Anthropological Association, as well as many other professional associations. He has been involved in numerous institutions that link US acade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indus Valley Tradition
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900 BCE. Together with ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia, it was one of three early civilisations of the Near East and South Asia, and of the three, the most widespread. Its sites spanned an area from much of Pakistan, to northeast Afghanistan, and northwestern India. The civilisation flourished both in the alluvial plain of the Indus River, which flows through the length of Pakistan, and along a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers that once coursed in the vicinity of the Ghaggar-Hakra, a seasonal river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan. The term ''Harappan'' is sometimes applied to the Indus civilisation after its type site Harappa, the first to be excavated early in the 20th century in what was then the Punjab province of B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)