List Of Pacific Hurricane Seasons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A Pacific hurricane is a mature tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E), while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region (90E to 160°E) and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.
A Pacific hurricane is a mature tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E), while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region (90E to 160°E) and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.
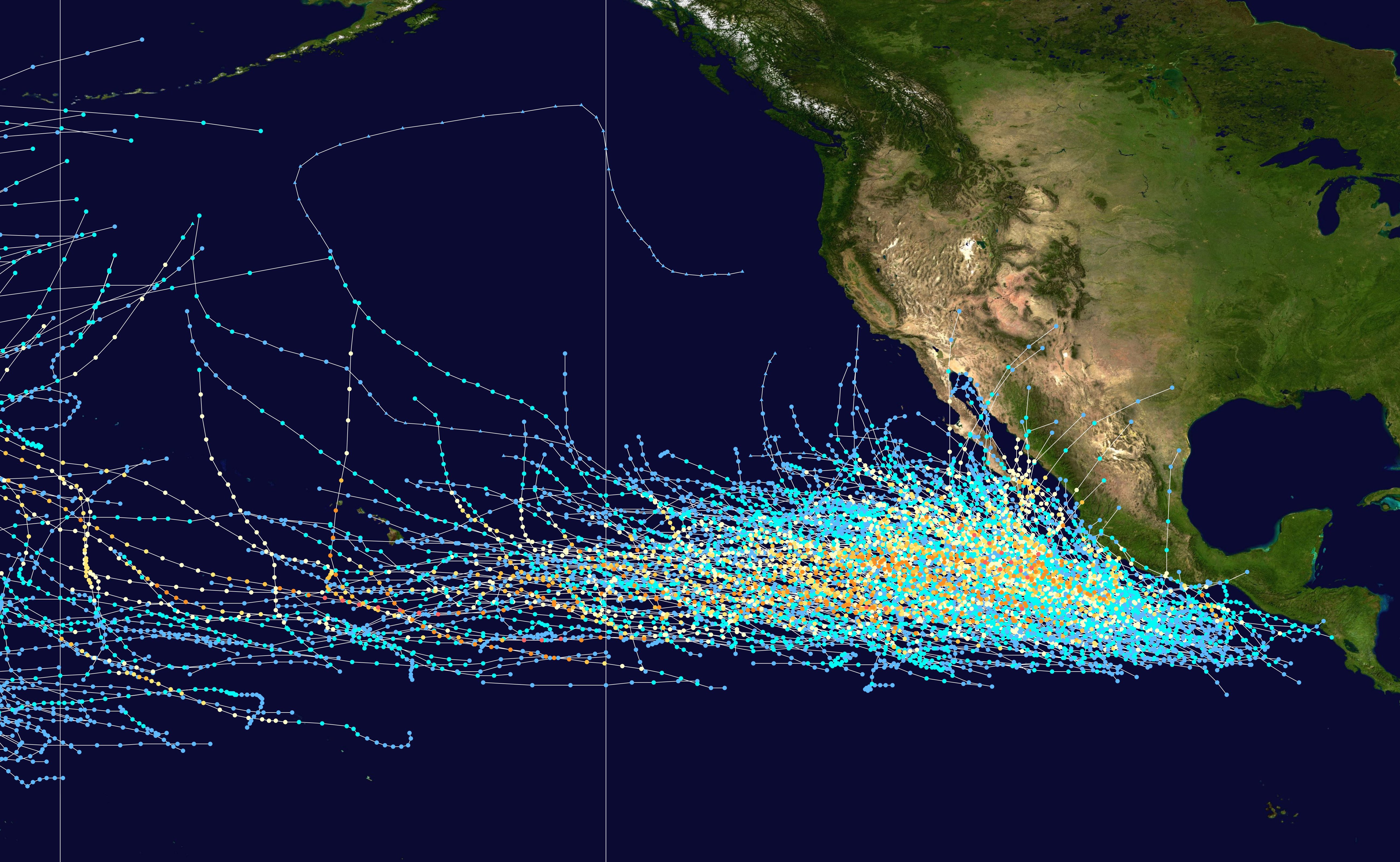 Documentation of Pacific hurricanes dates to the Spanish colonization of Mexico, when the military and missions wrote about "tempestades". In 1730, such accounts indicated an understanding of the storms. After observing the rotating nature of tropical cyclones, meteorologist William Charles Redfield expanded his study to include storms in the eastern North Pacific Ocean in the middle of the 19th century. Between June and October 1850, Redfield observed five tropical cyclones along "the southwestern coast of North America", along with one in each of the three subsequent years. In 1895, Cleveland Abbe reported the presence of many storms between 5° to 15°– N in the eastern Pacific, although many such storms dissipated before affecting the Mexican coast. Two years later, the German Hydrography Office ''Deutsche Seewarte'' documented 45 storms from 1832 to 1892 off the west coast of Mexico.
Despite the documentation of storms in the region, the official position of the United States Weather Bureau denied the existence of such storms. In 1910, the agency reported on global tropical cyclones, noting that "the occurrence of tropical storms is confined to the summer and autumn months of the respective hemispheres and to the western parts of the several oceans." In 1913, the Weather Bureau reinforced their position by excluding Pacific storms among five tropical cyclone basins; however, the agency acknowledged the existence of "certain cyclones that have been traced for a relatively short distance along a northwest course... west of Central America."
After California became a state and the discovery of gold there in 1848, shipping traffic began increasing steadily in the eastern Pacific. Such activity increased further after the Panama Canal opened in 1914, and the shipping lanes moved closer to the coast. By around 1920, Pacific hurricanes were officially recognized due to widespread ship observations, radio service, and a newly created weather network in western Mexico. Within 60 years, further studies of the region's tropical activity indicated that the eastern Pacific is in fact the second most active basin in the world.
During the 1920s, a few documents in the Monthly Weather Review reported additional storms within off the Mexican coastline.
Documentation of Pacific hurricanes dates to the Spanish colonization of Mexico, when the military and missions wrote about "tempestades". In 1730, such accounts indicated an understanding of the storms. After observing the rotating nature of tropical cyclones, meteorologist William Charles Redfield expanded his study to include storms in the eastern North Pacific Ocean in the middle of the 19th century. Between June and October 1850, Redfield observed five tropical cyclones along "the southwestern coast of North America", along with one in each of the three subsequent years. In 1895, Cleveland Abbe reported the presence of many storms between 5° to 15°– N in the eastern Pacific, although many such storms dissipated before affecting the Mexican coast. Two years later, the German Hydrography Office ''Deutsche Seewarte'' documented 45 storms from 1832 to 1892 off the west coast of Mexico.
Despite the documentation of storms in the region, the official position of the United States Weather Bureau denied the existence of such storms. In 1910, the agency reported on global tropical cyclones, noting that "the occurrence of tropical storms is confined to the summer and autumn months of the respective hemispheres and to the western parts of the several oceans." In 1913, the Weather Bureau reinforced their position by excluding Pacific storms among five tropical cyclone basins; however, the agency acknowledged the existence of "certain cyclones that have been traced for a relatively short distance along a northwest course... west of Central America."
After California became a state and the discovery of gold there in 1848, shipping traffic began increasing steadily in the eastern Pacific. Such activity increased further after the Panama Canal opened in 1914, and the shipping lanes moved closer to the coast. By around 1920, Pacific hurricanes were officially recognized due to widespread ship observations, radio service, and a newly created weather network in western Mexico. Within 60 years, further studies of the region's tropical activity indicated that the eastern Pacific is in fact the second most active basin in the world.
During the 1920s, a few documents in the Monthly Weather Review reported additional storms within off the Mexican coastline.
 Hurricane season runs between May 15 and November 30 each year. These dates encompass the vast majority of tropical cyclone activity in this region.
The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for this basin is the United States'
Hurricane season runs between May 15 and November 30 each year. These dates encompass the vast majority of tropical cyclone activity in this region.
The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for this basin is the United States'
The San Diego Hurricane of 2 October 1858.
Retrieved on 2008-04-19. Most east Pacific hurricanes originate from a tropical wave that drifts westward across the intertropical convergence zone, and across northern parts of South America. Once it reaches the Pacific, a surface low begins to develop, however, with only little or no convection. After reaching the Pacific, it starts to move north-westward and eventually west. By that time, it develops convection and thunderstorm activity from the warm ocean temperatures but remains disorganized. Once the tropical wave becomes organized, it becomes a tropical depression. Formation usually occurs from south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec to south of Baja California with a more westerly location earlier in the season. In the eastern Pacific, development is more centered than anywhere else. If wind shear is low, a tropical cyclone can undergo rapid intensification as a result of very warm oceans, becoming a major hurricane. Tropical cyclones weaken once they reach unfavorable areas for a tropical cyclone formation. Their remnants sometimes reach Hawaii and cause showers there. There are a few types of Pacific hurricane tracks: one is a westerly track, another moves north-westward along Baja California and another moves north. Sometimes storms can move north-east either across Central America or mainland Mexico and possibly enter the Caribbean Sea becoming a
 A Pacific hurricane is a mature tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E), while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region (90E to 160°E) and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.
A Pacific hurricane is a mature tropical cyclone that develops within the northeastern and central Pacific Ocean to the east of 180°W, north of the equator. For tropical cyclone warning purposes, the northern Pacific is divided into three regions: the eastern (North America to 140°W), central (140°W to 180°), and western (180° to 100°E), while the southern Pacific is divided into 2 sections, the Australian region (90E to 160°E) and the southern Pacific basin between 160°E and 120°W. Identical phenomena in the western north Pacific are called typhoons. This separation between the two basins has a practical convenience, however, as tropical cyclones rarely form in the central north Pacific due to high vertical wind shear, and few cross the dateline.
List of seasons
1950s
1960s
1970s
1980s
1990s
2000s
2010s
2020s
History
 Documentation of Pacific hurricanes dates to the Spanish colonization of Mexico, when the military and missions wrote about "tempestades". In 1730, such accounts indicated an understanding of the storms. After observing the rotating nature of tropical cyclones, meteorologist William Charles Redfield expanded his study to include storms in the eastern North Pacific Ocean in the middle of the 19th century. Between June and October 1850, Redfield observed five tropical cyclones along "the southwestern coast of North America", along with one in each of the three subsequent years. In 1895, Cleveland Abbe reported the presence of many storms between 5° to 15°– N in the eastern Pacific, although many such storms dissipated before affecting the Mexican coast. Two years later, the German Hydrography Office ''Deutsche Seewarte'' documented 45 storms from 1832 to 1892 off the west coast of Mexico.
Despite the documentation of storms in the region, the official position of the United States Weather Bureau denied the existence of such storms. In 1910, the agency reported on global tropical cyclones, noting that "the occurrence of tropical storms is confined to the summer and autumn months of the respective hemispheres and to the western parts of the several oceans." In 1913, the Weather Bureau reinforced their position by excluding Pacific storms among five tropical cyclone basins; however, the agency acknowledged the existence of "certain cyclones that have been traced for a relatively short distance along a northwest course... west of Central America."
After California became a state and the discovery of gold there in 1848, shipping traffic began increasing steadily in the eastern Pacific. Such activity increased further after the Panama Canal opened in 1914, and the shipping lanes moved closer to the coast. By around 1920, Pacific hurricanes were officially recognized due to widespread ship observations, radio service, and a newly created weather network in western Mexico. Within 60 years, further studies of the region's tropical activity indicated that the eastern Pacific is in fact the second most active basin in the world.
During the 1920s, a few documents in the Monthly Weather Review reported additional storms within off the Mexican coastline.
Documentation of Pacific hurricanes dates to the Spanish colonization of Mexico, when the military and missions wrote about "tempestades". In 1730, such accounts indicated an understanding of the storms. After observing the rotating nature of tropical cyclones, meteorologist William Charles Redfield expanded his study to include storms in the eastern North Pacific Ocean in the middle of the 19th century. Between June and October 1850, Redfield observed five tropical cyclones along "the southwestern coast of North America", along with one in each of the three subsequent years. In 1895, Cleveland Abbe reported the presence of many storms between 5° to 15°– N in the eastern Pacific, although many such storms dissipated before affecting the Mexican coast. Two years later, the German Hydrography Office ''Deutsche Seewarte'' documented 45 storms from 1832 to 1892 off the west coast of Mexico.
Despite the documentation of storms in the region, the official position of the United States Weather Bureau denied the existence of such storms. In 1910, the agency reported on global tropical cyclones, noting that "the occurrence of tropical storms is confined to the summer and autumn months of the respective hemispheres and to the western parts of the several oceans." In 1913, the Weather Bureau reinforced their position by excluding Pacific storms among five tropical cyclone basins; however, the agency acknowledged the existence of "certain cyclones that have been traced for a relatively short distance along a northwest course... west of Central America."
After California became a state and the discovery of gold there in 1848, shipping traffic began increasing steadily in the eastern Pacific. Such activity increased further after the Panama Canal opened in 1914, and the shipping lanes moved closer to the coast. By around 1920, Pacific hurricanes were officially recognized due to widespread ship observations, radio service, and a newly created weather network in western Mexico. Within 60 years, further studies of the region's tropical activity indicated that the eastern Pacific is in fact the second most active basin in the world.
During the 1920s, a few documents in the Monthly Weather Review reported additional storms within off the Mexican coastline.
The Eastern and Central Pacific hurricane database
The Eastern Pacific hurricane best track database was initially compiled onmagnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magne ...
in 1976 for the seasons between 1949 and 1975, at the NHC to help with the development of two tropical cyclone forecast models, which required tracks of past cyclones as a base for its predictions. The database was based on records held by the United States Navy and were interpolated from 12 hourly intervals to 6 hourly intervals based on a scheme devised by Hiroshi Akima in 1970. Initially tracks for the Central Pacific region and tracks for tropical depressions that did not develop into tropical storms or hurricanes were not included within the database. After the database had been created Arthur Pike of the NHC made some internal adjustments, while in 1980 a review was made by Arnold Court under contract from the United States National Weather Service and resulted in additions and/or modifications to 81 tracks in the database. Between 1976–1987, the NHC archived best track data from the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center (EPHC), and in 1982 started including information on Central Pacific tropical storms and hurricanes started to be included in the database based on data from the Joint Typhoon Warning Center and research done by Samuel Shaw of the Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) in 1981.
The format of the database was completely revised by the NHC during 1984, so that the format could resemble the Atlantic database before they took over the warning responsibility from the EPHC for the Eastern Pacific during 1988. During 2008 and 2013 several revisions were made to the database to extend tracks in land, based on reports in the Mariners Weather Log and extrapolation of the tracks since the EPHC stopped issuing advisories on systems before they made landfall. The archives format was significantly changed during 2013 to include non-synoptic best track times, non-developing tropical depressions and wind radii. During February 2016, the NHC released the 1959 Mexico hurricane
The 1959 Mexico hurricane was the deadliest Pacific hurricane on record. First observed south of Mexico on October 23, the cyclone tracked northwestward. It intensified into a Category 3 hurricane on October 25 and reached Categor ...
's reanalysis, which was the first system to be reassessed, using methods developed for the Atlantic reanalysis process.
Climatology
The presence of a semi-permanent high-pressure area known as theNorth Pacific High
The North Pacific High is a semi-permanent, subtropical anticyclone located in the northeastern portion of the Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Hawaii and west of California. It is strongest during the northern hemisphere summer and shifts towa ...
in the eastern Pacific is a dominant factor against the formation of tropical cyclones in the winter, as the Pacific High results in wind shear that causes unfavorable, environmental conditions for tropical cyclone formation. Its effects in the central Pacific basin are usually related to keeping cyclones away from the Hawaiian Islands. Due to westward trade winds, hurricanes in the Pacific rarely head eastward, unless recurved by a trough. A second factor preventing tropical cyclones from forming during the winter is the occupation of a semi-permanent low-pressure area designated the Aleutian Low between January and April. Its presence over western Canada and the northwestern United States contributes to the area's occurrences of precipitation in that duration. In addition, its effects in the central Pacific near 160° W causes tropical waves that form in the area to drift northward into the Gulf of Alaska and dissipate. The retreat of this low allows the Pacific High to also retreat into the central Pacific, leaving a warm and moist environment in its wake. The Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
comes northward into the East Pacific in mid-May permitting the formation of the earliest tropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
s, coinciding with the start of the eastern Pacific hurricane season on May 15.
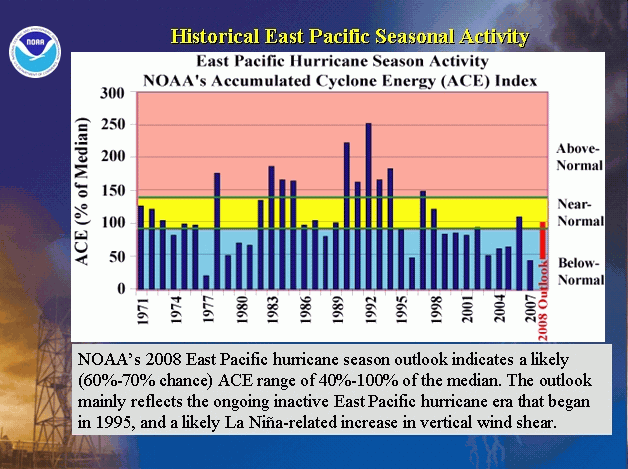
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation also influences the frequency and intensity of hurricanes in the Northeast Pacific basin. During El Niño events, sea surface temperatures increase in the Northeast Pacific and vertical wind shear decreases. Because of this, an increase in tropical cyclone activity occurs; the opposite happens in the Atlantic basin during El Niño, where increased wind shear creates an unfavorable environment for tropical cyclone formation. Contrary to El Niño, La Niña events increase wind shear and decreases sea surface temperatures over the eastern Pacific, while reducing wind shear and increasing sea surface temperatures over the Atlantic.
Eastern North Pacific
 Hurricane season runs between May 15 and November 30 each year. These dates encompass the vast majority of tropical cyclone activity in this region.
The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for this basin is the United States'
Hurricane season runs between May 15 and November 30 each year. These dates encompass the vast majority of tropical cyclone activity in this region.
The Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for this basin is the United States' National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
. Previous forecasters are the Eastern Pacific Hurricane Center and the Joint Hurricane Warning Center. The RSMC monitors the eastern Pacific and issues reports, watches and warnings about tropical weather systems and cyclones as defined by the World Meteorological Organization.
This area is, on average, the second-most active basin in the world. There are an average of 16 tropical storms annually, with 9 becoming hurricanes, and 4 becoming major hurricanes. Tropical cyclones in this region frequently affect mainland Mexico and the Revillagigedo Islands. Less often, a system will affect the Continental United States or Central America. Northbound hurricanes typically reduce to tropical storms or dissipate before reaching the United States: there is only one recorded case of a Pacific system reaching California as a hurricane in almost 200 years of observations—the 1858 San Diego Hurricane
The 1858 San Diego hurricane was a very rare hurricane that impacted Southern California. It is the only known tropical cyclone to directly impact California as a hurricane, although other systems have impacted California as tropical storms. The s ...
.Michael Chenoweth and Chris LandseaThe San Diego Hurricane of 2 October 1858.
Retrieved on 2008-04-19. Most east Pacific hurricanes originate from a tropical wave that drifts westward across the intertropical convergence zone, and across northern parts of South America. Once it reaches the Pacific, a surface low begins to develop, however, with only little or no convection. After reaching the Pacific, it starts to move north-westward and eventually west. By that time, it develops convection and thunderstorm activity from the warm ocean temperatures but remains disorganized. Once the tropical wave becomes organized, it becomes a tropical depression. Formation usually occurs from south of the Gulf of Tehuantepec to south of Baja California with a more westerly location earlier in the season. In the eastern Pacific, development is more centered than anywhere else. If wind shear is low, a tropical cyclone can undergo rapid intensification as a result of very warm oceans, becoming a major hurricane. Tropical cyclones weaken once they reach unfavorable areas for a tropical cyclone formation. Their remnants sometimes reach Hawaii and cause showers there. There are a few types of Pacific hurricane tracks: one is a westerly track, another moves north-westward along Baja California and another moves north. Sometimes storms can move north-east either across Central America or mainland Mexico and possibly enter the Caribbean Sea becoming a
North Atlantic basin tropical cyclone
An Atlantic hurricane, also known as tropical storm or simply hurricane, is a tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean, primarily between the months of June and November. A hurricane differs from a cyclone or typhoon only on the basis ...
, but these are rare.
Central Pacific
Hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30, with a strong peak in August and September. However, tropical cyclones have formed outside those dates. Should a tropical cyclone enter the central north Pacific from the western north Pacific, where they occur year-round, or from the eastern north Pacific, where the season starts in May, it is not known if such a system will be considered out of season or not. The Central Pacific Hurricane Center is the RSMC for this basin and monitors the storms that develop or move into the defined area of responsibility. A previous forecaster was the Joint Hurricane Warning Center. Central Pacific hurricanes are rare and on average 3 or 4 storms form or move in this area per year. Most often, storms that occur in the area are weak and often decline in strength upon entry. The only land masses impacted by tropical cyclones in this region are Hawaii andJohnston Atoll
Johnston Atoll is an Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States, currently administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS). Johnston Atoll is a National Wildlife Refuge and ...
. Due to the small size of the islands in relation to the Pacific Ocean, direct hits and landfalls are rare.
Steering factors
Hurricanes in the Eastern Pacific tend to move westward out to sea, harming no land—unless they cross into the Central Pacific or Western Pacific basins, in which case they might harm land such as Hawaii or Japan. However, hurricanes can recurve to the north or northeast, hitting Central America or Mexico early and late in the hurricane season.Extremes
*The strongest recorded Pacific hurricane was Hurricane Patricia (2015), with 1-minutemaximum sustained winds
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common
indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a distance defined as the radius of maximum wind, or RMW. Unl ...
of 215 mph (345 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 872 mbar (hPa; 25.75 inHg). This ranks Patricia as the strongest tropical cyclone globally in terms of 1-minute sustained winds and the second strongest globally in terms of barometric pressure.
* Hurricane John (1994) was the longest-lived and farthest-travelling tropical cyclone worldwide, traversing 7,165 mi (13,280 km) in 30 days and 18 hours.
*The 1959 Mexico hurricane
The 1959 Mexico hurricane was the deadliest Pacific hurricane on record. First observed south of Mexico on October 23, the cyclone tracked northwestward. It intensified into a Category 3 hurricane on October 25 and reached Categor ...
was the deadliest Pacific hurricane, causing 1,800 fatalities mostly in Colima and Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal En ...
.
See also
*Atlantic hurricane
An Atlantic hurricane, also known as tropical storm or simply hurricane, is a tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean, primarily between the months of June and November. A hurricane differs from a cyclone or typhoon only on the basis of ...
* Cordonazo wind
Cordonazo winds or the Lash of St. Francis ( es, el cordonazo de San Francisco), refers to southerly hurricane winds along the intertropical region (Ecuador, Colombia, Mexico, Panama and Venezuela). In Mexico is associated with tropical cyclones in ...
* Tropical cyclone
* Typhoon
* Atlantic hurricane season
The Atlantic hurricane season is the period in a year from June through November when tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, referred to in North American countries as hurricanes, tropical storms, or tropical depressions. In addition ...
* Pacific typhoon climatology
* Pacific typhoon season
The following is a list of Pacific typhoon seasons. The seasons are limited to the north of the equator between the 100th meridian east and the 180th meridian (aka Prime Antimeridian).
Seasons Pre-1940
1940s
1950s
1960s
1970s
1980s
...
* North Indian Ocean tropical cyclone season
* South-West Indian Ocean tropical cyclone season
* Australian region tropical cyclone season
* South Pacific tropical cyclone season
* South Atlantic tropical cyclone
* Mediterranean tropical-like cyclone
* List of tropical cyclone records
This is a condensed list of worldwide tropical cyclone records set by different storms and seasons.
Major records
See also
* List of weather records
** Tornado records
*List of the most intense tropical cyclones
*List of wettest tropical ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pacific Hurricane Pacific *