List Of Ikshvaku Dynasty Kings In Hinduism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to
According to

 The genealogy of the
The genealogy of the 
 #
#
 After the Samadhi of Lord Ramachandra and his brothers; their sons had inherited their lands. From Rama, his sons;
After the Samadhi of Lord Ramachandra and his brothers; their sons had inherited their lands. From Rama, his sons;
 #Brihatkshaya (or Bruhadrunam)
#Urukriya (or Gurukshep)
#Vatsavyuha
#Prativyoma
#Bhaanu
#Divakara (or Divak)
#Veer Sahadeva
#Brihadashva-2
#Bhanuratha (or Bhanumaan)
#Pratitashva
#Supratika
#Marudeva
#Sunakshatra
#Pushkara (or Kinnara)
#Antariksha
#Suvarna (or Sutapaa)
#Sumitra (or Amitrajit)
#Bruhadaraaj (Okkaka)
#Rudraksh
Descendants through the
#Brihatkshaya (or Bruhadrunam)
#Urukriya (or Gurukshep)
#Vatsavyuha
#Prativyoma
#Bhaanu
#Divakara (or Divak)
#Veer Sahadeva
#Brihadashva-2
#Bhanuratha (or Bhanumaan)
#Pratitashva
#Supratika
#Marudeva
#Sunakshatra
#Pushkara (or Kinnara)
#Antariksha
#Suvarna (or Sutapaa)
#Sumitra (or Amitrajit)
#Bruhadaraaj (Okkaka)
#Rudraksh
Descendants through the  #Kritanjaya (Sivisamjaya)
#Ranajjaya (Sihassara)
#Jayasena (Mahakoshala or Sanjaya)
#
#Kritanjaya (Sivisamjaya)
#Ranajjaya (Sihassara)
#Jayasena (Mahakoshala or Sanjaya)
#
 According to
According to Hindu traditions
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Shraddhadeva Manu
Vaivasvata Manu (), also referred to as Shraddhadeva and Satyavrata, is the current Manu—the progenitor of the human race in Hindu mythology. He is the seventh of the 14 Manus of the current kalpa (aeon) of Hindu cosmology.
Forewarned abou ...
(Sanskrit manuśraddhādeva) is the current Manu
Manu may refer to:
Geography
* Manú Province, a province of Peru, in the Madre de Dios Region
**Manú National Park, Peru
** Manú River, in southeastern Peru
* Manu River (Tripura), which originates in India and flows into Bangladesh
*Manu Tem ...
and the progenitor of the current ''manvantara
A ''manvantara'', in Hindu cosmology, is a cyclic period of time identifying the duration, reign, or age of a Manu (Hinduism), Manu, the progenitor of mankind. In each ''manvantara'', seven Rishis, certain deities, an Indra, a Manu (Hinduism), Ma ...
''. He is considered as the seventh of the fourteen Manus of the current ''kalpa (aeon)
A ''kalpa'' is a long period of time (aeon) in Hindu and Buddhist cosmology, generally between the creation and recreation of a world or universe.
Etymology
''Kalpa'' ( sa, कल्प, , a formation or creation) in this context, means "a lon ...
''.
Shraddhadeva was the king of the Dravida Kingdom
Dravida is mentioned as one of the kingdoms in the southern part of present-day mainland India during the time of the Mahabharata.
Dravida in the Mahabharata
Dravida is listed among the ancient Indian (Bharata Varsha) kingdoms:
"In the south, ...
before Pralaya
Pralaya ( sa, प्रलय, , Apocalypse or the Annihilation of the Universe, translit=Pralaya) is a concept in Hindu eschatology. Generally referring to four different phenomena, it is most commonly used to indicate the event of the dissol ...
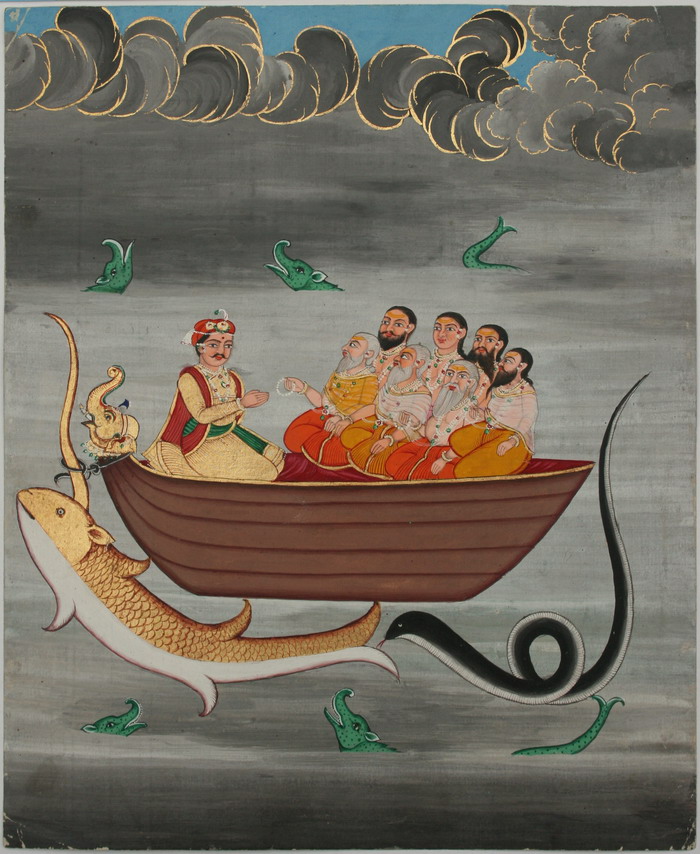
, the great flood. Forewarned about the flood by the Matsya
Matsya ( sa, मत्स्य, lit. ''fish'') is the fish avatar of the Hindu god Vishnu. Often described as the first of Vishnu's ten primary avatars, Matsya is described to have rescued the first man, Manu, from a great deluge. Matsya m ...
Avatar
Avatar (, ; ), is a concept within Hinduism that in Sanskrit literally means "descent". It signifies the material appearance or incarnation of a powerful deity, goddess or spirit on Earth. The relative verb to "alight, to make one's appearanc ...
of Lord Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
, he saved humanity by building a boat that carried his family and the saptarishi to safety. He is the son of Vivasvana and is therefore also known as Vaivasvata Manu, and his dynasty as the Suryavaṃśa. He is also called Satyavrata (always truthful).
Ikshvaku
Ikshvaku (Sanskrit ; Pāli: ) is a legendary king in Hindu mythology. He is described to be the first king of the Kosala kingdom, and was one of the ten sons of Shraddhadeva Manu, the first man on the earth. He was the founder and first king of ...
(Sanskrit; ikṣvāku, from Sanskrit ikṣu; Pali: Okkāka), is one of the ten sons of Shraddhadeva Manu, and is credited to be the founder of the Ikshvaku Dynasty.
Suryavanshi kings

 The genealogy of the
The genealogy of the Ikshvaku dynasty
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is ...
to Rama is mentioned in the Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
in two lists. The only difference between the two lists is that, Kukshi is mentioned only in the second list. In the first list, Vikukshi is mentioned as the son of Ikshavaku. The descendants of Vikukshi are known as Vikauwa.

 #
# Vaivasvata Manu
Vaivasvata Manu (), also referred to as Shraddhadeva and Satyavrata, is the current Manu—the progenitor of the human race in Hindu mythology. He is the seventh of the 14 Manus of the current kalpa (aeon) of Hindu cosmology.
Forewarned about ...
or Satyavarta (Known as Nabhi
King Nabhi or Nabhi Rai was the 14th or the last '' Kulakara'' of '' avasarpini'' (the descending half of the cosmic time cycle in Jainism and the one in which the world is said to be at present). He was the father of Rishabhanatha, the first ' ...
in the Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' ( sa, भागवतपुराण; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' or simply ''Bhagavata'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen great Puranas (''Mahapuranas''). Composed in Sa ...
).
# Ikshvaku
Ikshvaku (Sanskrit ; Pāli: ) is a legendary king in Hindu mythology. He is described to be the first king of the Kosala kingdom, and was one of the ten sons of Shraddhadeva Manu, the first man on the earth. He was the founder and first king of ...
(Known as Okkāka in Buddhist literature, as Rishabhanatha
Rishabhanatha, also ( sa, ऋषभदेव), Rishabhadeva, or Ikshvaku is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism and establisher of Ikshvaku dynasty. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain c ...
in Jain texts, and thus possibly an Avatar of Vishnu)
# Bharata (Chakravarti-Samrat, son of Rishabha
Rishabhanatha, also ( sa, ऋषभदेव), Rishabhadeva, or Ikshvaku is the first (Supreme preacher) of Jainism and establisher of Ikshvaku dynasty. He was the first of twenty-four teachers in the present half-cycle of time in Jain c ...
).
# Kukshi
Kukshi is a town in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh state, India. Kukshi has population of around 37,482 making it a Tier-3 city and a Semi-Urban centre. It is a Nagar Parishad. Kukshi is famous for the business of cotton, mirchi, gold and silv ...
or Vikukshi or Shashad.
# Bān or Shakuni (Son of Kukshi)
# Kakutstha
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is ...
or Puranjaya or Anaranya I
# Anena
# Prithu
Prithu (Sanskrit: पृथु, ''Pṛthu'', lit. "large, great, important, abundant") is a sovereign ( chakravarti), featured in the Puranas. According to Hinduism, he is an avatar (incarnation) of the preserver god—Vishnu. He is also called ...
# Vishtarashva
# Chandra
Chandra ( sa, चन्द्र, Candra, shining' or 'moon), also known as Soma ( sa, सोम), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and ...
# Yuvanashva I
# Shravasta
# Brihadashva
# Dhundumār or Kuvalayashva
# Dhreedhashva or Kapilashva or Bhadrashva
# Pramoda
# Haryashva I or Pramodak (Married Mādhavī, daughter of Chakravarti Yayati
Yayāti ( sa, ययाति, translit=Yayāti), is a king in Hindu tradition. He is described to be a Chandravamsha king. He is regarded to be the progenitor of the races of the Yadavas and the Pandavas.
He is considered in some texts to ...
)
# Nikumbha
Nikumbha () is the name of multiple beings in Hindu mythology, a rakshasa and a danava.
Legend
Rakshasa Nikumbha
Nikumbha, the rakshasa, is the son of Kumbhakarna and Vajramala. He is instructed by Kubera to watch over the Pisacas (a t ...
# Baharnashva
# Giritashva
# Amitashva
# Krishashva or Akrutashva
# Prasenajit I
# Yuvanashva II
# Mandhata
Mandhata, also called Shivapuri or Mahismati, Capital of Awanti Mahajanpad Omkareshwar, is a riverine island in the Narmada river in Khandwa district, Madhya Pradesh, India. Omkareshwar Jyotirlinga is situated on the southern part of the i ...
(Chakravarti-Samrat)
# Purukutsa I (or Vasud) and Muchukunda
In Hindu history, Muchukunda (), the son of King Mandhata, and brother of Ambarisha, is an Ikshvaku (Suryavamsha) king.
Battle with the asuras
Once, in a battle, the devas were defeated by the asuras. Tormented by arrows, they sought help from ...
# Ambarisha
In Hindu mythology, Ambarisha ( sa, अम्बरीषः, ) is an Ikshvaku king, and the son of Mandhata.Pargiter, F.E. (1972) 922 ''Ancient Indian Historical Tradition'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, p.92. He is believed to have conquered th ...
(Chakravarti-Samrat, and younger brother of Purukutsa I)
# Trasadasyu (Son of Purukutsa)
# Sambhruta
# Anaranya II
# Preeshadashva
# Haryashva II
# Hastya
# Sumana
# Tridhanva
# Trayyaruni
# Trishanku
Trishanku (त्रिशंकु), born as Satyavrata, was a king who belonged to ''Ikshvaku dynasty''. Trishanku is commonly referred to through mention of "Trishanku's heaven" or "hanging like Trishanku". The word Trishanku has come to deno ...
or Satyavrata II
# Harishchandra
Harishchandra () is a legendary king of the Solar dynasty, who appears in several legends in texts such as the ''Aitareya Brahmana'', ''Mahabharata'', the ''Markandeya Purana'', and the ''Devi Bhagavata Purana''. The most famous of these storie ...
# Rohitashva
Rohitashva or Lohithashva is a mythologicalHenk W Wagenaar and S S Parikh. "Rohitashva" in ''Allied Chambers Transliterated Hindi-Hindi-English Dictionary''. Allied Publishers. 1993Page 1018/ref> prince in Hinduism. His father was Harishchandra
...
# Harita
Harita () is a king in Hindu literature. He is described to be the son of Yauvanāśva, and the grandson of King Ambarisha of the Suryavamsha dynasty.
Harita is believed to have left his kingdom as a symbolic expiation of his sins. After comple ...
# Chanchu (Contemporary of Chandravanshi King Dushyanta
Dushyanta ( sa, दुष्यन्त, translit=Duṣyanta) is a king of the Chandravamsha (Lunar) dynasty featured in Hindu literature. He is the husband of Shakuntala and the father of Bharata. He appears in the Mahabharata and in Kalid ...
)
# Chakshu or Sudeva (Contemporary of Chandravanshi Emperor Bharata)
# Vijaya
Vijaya may refer to:
Places
* Vijaya (Champa), a city-state and former capital of the historic Champa in what is now Vietnam
* Vijayawada, a city in Andhra Pradesh, India
People
* Prince Vijaya of Sri Lanka (fl. 543–505 BC), earliest recorde ...
# Ruruka or Brahuka
# Pratapendra
# Bruk
# Sushandhi
# Bahuk
''Bahuk'' ( gu, બાહુક) is a Gujarati long narrative poem by Chinu Modi. The poem is composed both in metrical and non-metrical verse and centres on Nala, a character from the ''Mahabharata'' who metamorphosed into Bahuka. It is an ...
# Vrika or Bharata II
# Bahu or Asit
# Sagara Sagara may refer to:
People
* Sagara (ethnic group), a people of Tanzania
* Sagara (Vedic king), Ikshvaku dynasty
* Sagara clan, a clan of 16th century Japan
* Sekihotai (Sagara Souzou), a leader of the Sekihotai military unit during the Boshin ...
(Chakravarti-Samrat)
# Anshuman (The son of Sagara's exiled son, Asamanja
Asamanjasa (), also rendered Asamanja, is the eldest son of King King Sagara, Sagara and one of his two queens, Keshini, in Hindu Literature, Hindu literature.
Legend
Ramayana
The birth of Asamanjasa is described in the Ramayana. King Saga ...
)
# Dileepa I
# Bhagiratha
Bhagiratha (Sanskrit: भगीरथ, ''Bhagīratha'') is a legendary king of the Ikshvaku dynasty in Hindu literature. He is best known for his legend of bringing the sacred river Ganges, personified as the Hindu river goddess Ganga, from heav ...
(Chakravarti-Samrat)
# Suhotra
Sahadeva (Sanskrit: सहदेव) was the youngest of the Pandava brothers, the five principal protagonists of the epic ''Mahabharata''. He and his twin brother, Nakula, were blessed to King Pandu and Queen Madri by invoking the twin gods Ash ...
# Shruti
# Kukutsa II
# Raghu I
# Nabhaga
# Ambarisha II
# Shindhudhwip
# Ayutayu
# Pratayu
# Rituparna
Rutuparna (IAST): Rutuparṇa ( hi, ऋतुपर्ण) was a king of Ayodhya, and son of Sarvakama, into whose service king Nala entered after he had lost his kingdom. Rutuparna was a master mathematician and profoundly skilled in dice Kali ...
# Sarvakama I
# Sudaas
# Kalmashapada
In Hindu scriptures, Kalmashapada (Kalmasapada, कल्माषपाद), also known as Saudasa (), Mitrasaha (मित्रसह), Amitrasaha and Kalmashanghri (Kalmasanghri), was a king of the Ikshvaku dynasty (the Solar dynasty), who ...
# Asmaka
Ashmaka (Sanskrit: ) or Assaka (Pali: ) was a Mahajanapada in ancient India which existed between 700 BCE and 425 or 345 BCE according to the Buddhist texts '' Anguttara Nikaya'' and ''Puranas''. It was located around and between the Godavar ...
# Mulaka or Sarvakama/ II
# Dasharatha I
# Ilibil or Ananaranya III
# Vishvamashaha or Nighna (Contemporary to Kuru King Hasthi, who founded Hastinapur
Hastinapur is a city in the Meerut district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. ''Hastinapura'', described in Hindu texts such as the ''Mahabharata'' and the Puranas as the capital of the Kuru Kingdom, is also mentioned in ancient Jain tex ...
)
# Nidhna
# Animitra
# Duliduh or Muluka
# Dileepa II or Deerghabhahu or Khaṭvāṅga
A khaṭvāṅga ( sa, खट्वाङ्ग) is a long, studded club originally created as a weapon. It was adopted as a traditional religious symbol in Indian religions such as Tantric traditions like Shaivism and Vajrayana Buddhism. The kh ...
# Raghu II
# Aja
# Dasaratha
Dasharatha (Sanskrit: दशरथ, IAST: Daśaratha; born Nemi) was the king of the Kosala kingdom and a scion of the Suryavamsha dynasty in Hinduism. He ruled from this capital at Ayodhya. Dasharatha was the son of Aja and Indumati. He had ...
II (Born as Nemi)
# Bharata III (Younger brother of Rama, and ruler of Kosala on his behalf)
# Ramachandra
Rama (; ), Ram, Raman or Ramar, also known as Ramachandra (; , ), is a major deity in Hinduism. He is the seventh and one of the most popular ''avatars'' of Vishnu. In Rama-centric traditions of Hinduism, he is considered the Supreme Being ...
(Avatar of Vishnu
Vishnu ( ; , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism.
Vishnu is known as "The Preserver" within t ...
and Chakravarti-Samrat)
The other sons of Dasharatha; Lakshmana
Lakshmana ( sa, लक्ष्मण, lit=the fortunate one, translit=Lakṣmaṇa), also spelled as Laxmana, is the younger brother of Rama and his loyalist in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He bears the epithets of Saumitra () and Ramanuja (). ...
and Shatrughna
''Shatrughna'' ( sa, text=शत्रुघ्न, translit=śatrughna, lit=killer of enemies) is a prince of Ayodhya, King of Madhupura and Vidisha, and a brother of Prince Rama in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is also known as ''Ripudaman' ...
were said to be the kings of Karupada and Madhupuri (as well as Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from th ...
) respectively.
Suryavanshi kings after Rama
 After the Samadhi of Lord Ramachandra and his brothers; their sons had inherited their lands. From Rama, his sons;
After the Samadhi of Lord Ramachandra and his brothers; their sons had inherited their lands. From Rama, his sons; Kusha
Kusha was a Suryavansha king. He was the father of Kushanaabha
Kushanaabha was the King of Amavasu dynasty and belongs to Chandravamsha clan. He was the son of Kusha. Kushanabha was the founder of the city Mahodaya (now Kannauj).
Life Marria ...
had inherited South Kosala
Dakshina Kosala (IAST: Dakṣiṇa Kosala, "southern Kosala") is a historical region of central India. It was located in what is now Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh along with some parts of Western Odisha. At its greatest extent, it may have al ...
and Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
had inherited North Kosala, while Bharata's children, Taksha and Pushkara had inherited Takshashila
Taxila or Takshashila (; sa, तक्षशिला; pi, ; , ; , ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and ...
and Pushkalavati
Pushkalavati ( ps, پشکلاوتي; Urdu: ; Sanskrit: ; Prākrit: ; grc, Πευκελαῶτις ) or Pushkaravati (Sanskrit: ; Pāli: ), and later Shaikhan Dheri ( ps, شېخان ډېرۍ; ur, ), was the capital of the Gandhara kingdom, ...
respectively. Lakshmana's children, Angada and Chandraketu had inherited Karupada and Malla
Malla may refer to: Places
;Bolivia
*Malla, Bolivia, a locality
*Malla Jawira, a river
* Malla Jaqhi, a mountain
*Malla Municipality
*Malla Qullu, a mountain
;India
* Mallapuram, Tamil Nadu
*Malla (tribe), an ancient republic, one of the sixte ...
respectively, and Shatrughna's children, Subahu and Shatrughati had inherited Madhupuri and Vidisha
Vidisha (विदिशा, formerly known as Bhelsa and known as Besnagar in ancient times) is a city in central Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located 62.5 km northeast of the state capital, Bhopal. The name "Vidisha" is derived from th ...
respectively.
The Puranas provide a genealogical list from Kusha to Brihadbala, who was killed by Abhimanyu in the Mahabharata war. This list is corroborated by the Raghuvamsha till Agnivarna.
# Kusha
Kusha was a Suryavansha king. He was the father of Kushanaabha
Kushanaabha was the King of Amavasu dynasty and belongs to Chandravamsha clan. He was the son of Kusha. Kushanabha was the founder of the city Mahodaya (now Kannauj).
Life Marria ...
(contemporary of Chandravanshi King Kunti) and Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
# Atithi Atithi may refer to:
* ''Atithi Devo Bhava'', meaning the Guest is equal to God as per Hindu scripture
* ''Atithi'' (1965 film), a 1965 Bengali film
* '' Atithee'', a 1978 Hindi film
* ''Atithi'' (2002 film), a 2002 Kannada film
* ''Atithi'' (200 ...
(contemporary of Chandravanshi King Turvasu II, and son of Kusha)
# Nishadha
The Nishadha kingdom
(IAST: Niṣadha) was a tribe of ancient India that lived in a country of the same name
History
Veerasena was a king of the Nishadha kingdom, and the father of Nala. Nala, the son of Veerasena, became the king after his fathe ...
(founded Nishadha Kingdom)
# Nala II
# Nabhas
# Paundrika
# Ksemadhanva
# Devanika
# Ahinagu
# Ruru Ruru may refer to:
Places
*Ruru, Nepal
* Ruru, New Zealand
People
*Rouran, an ancient nomadic race from the Mongolian steppes, also called Juan Juan
*Ruru Madrid, a Filipino teen actor
Others
*Māori name for the morepork owl
*A Kanohi from the L ...
# Pariyatra
# Sala
# Dala
Dala may refer to:
Places
*Dala Airport, Dalarna province, Sweden
*Dala, Angola
*Dala, Bhutan
*Dala, Kano, Nigeria
**Dalla Hill, a hill in Kano, Nigeria
*Đala, Serbia
*Dalas, Khuzestan Province, Iran
*Dala Township, Yangon, Myanmar
People
* Bi ...
# Bala
Bala may refer to:
Places
India
*Bala, India, a village in Allahabad, India
* Bala, Ahor, a village in the Jalore district of Rajasthan
* Bala, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
Romania
* Bala, Mehedinți, a commune in Mehedinţi ...
# Uktha
# Sahasrasva
# Para II
# Chandravaloka
# Rudraksh
''Rudraksha'' (IAST: ') refers to a stonefruit, the dried stones of which are used as prayer beads by Hindus (especially Shaivas), as well as by Buddhists and Sikhs. When they are ripe, ''rudraksha'' stones are covered by an inedible blue out ...
# Chandragiri
Chandragiri is a suburb and neighbourhood of Tirupati and located in Tirupati district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a part of Tirupati urban agglomeration and a major growing residential area in Tirupati It is the mandal headqua ...
# Banuchandra
# Srutayu
# Uluka
The ''Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India; it was composed by the sage Vyasa. The most important characters of ''Mahabharata'' can be said to include: Krishna; the Pand ...
# Unnabha
# Vajranabha
# Sankhana
# Vyusitasva
# Visvasaha
# Hiranyanabha Kausalya
# Para III (Atnara)
# Brahmistha
# Putra
# Pusya
# Arthasidhi
# Dhruvasandhi
# Sudarsana
# Agnivarna
# Sighraga
# Maru
# Parsusruta
# Susandhi
# Amarsana
# Mahasvana
# Sahasvana
# Visrutvana
# Visvabhava
# Visvasahva
# Nagnajit (Father of Satya
''Satya'' (Sanskrit: सत्य; IAST: ''satya)'' is a Sanskrit word loosely translated as truth, essence. A. A. Macdonell, ''Sanskrit English Dictionary'', Asian Educational Services, , pp. 330–331 It also refers to a virtue in Indian relig ...
, the wife of Shri Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one of ...
)
# Taksaka
# Brihadbala
Brihadbala () is a king featured in Hindu mythology. He is a character in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is described to be the last king of the Kosala Kingdom. In the Kurukshetra War, Brihadbala fights for the Kauravas and is killed by Ab ...
Suryavanshi kings after Mahabharata
ThePuranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends an ...
also provide the list of the kings from Brihadbala
Brihadbala () is a king featured in Hindu mythology. He is a character in the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is described to be the last king of the Kosala Kingdom. In the Kurukshetra War, Brihadbala fights for the Kauravas and is killed by Ab ...
to the last ruler Sumitra. But these lists mention Shakya
Shakya (Pali, Pāḷi: ; sa, शाक्य, translit=Śākya) was an ancient eastern Sub-Himalayan Range, sub-Himalayan ethnicity and clan of north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age i ...
as an individual, and incorporate the names of Shakya, Shuddodhana, Siddhartha (Gautama Buddha) and Rahula between Sanjaya and Prasenajit. The names of the kings are:
Successors of Brihadbala #Brihatkshaya (or Bruhadrunam)
#Urukriya (or Gurukshep)
#Vatsavyuha
#Prativyoma
#Bhaanu
#Divakara (or Divak)
#Veer Sahadeva
#Brihadashva-2
#Bhanuratha (or Bhanumaan)
#Pratitashva
#Supratika
#Marudeva
#Sunakshatra
#Pushkara (or Kinnara)
#Antariksha
#Suvarna (or Sutapaa)
#Sumitra (or Amitrajit)
#Bruhadaraaj (Okkaka)
#Rudraksh
Descendants through the
#Brihatkshaya (or Bruhadrunam)
#Urukriya (or Gurukshep)
#Vatsavyuha
#Prativyoma
#Bhaanu
#Divakara (or Divak)
#Veer Sahadeva
#Brihadashva-2
#Bhanuratha (or Bhanumaan)
#Pratitashva
#Supratika
#Marudeva
#Sunakshatra
#Pushkara (or Kinnara)
#Antariksha
#Suvarna (or Sutapaa)
#Sumitra (or Amitrajit)
#Bruhadaraaj (Okkaka)
#Rudraksh
Descendants through the Shakya
Shakya (Pali, Pāḷi: ; sa, शाक्य, translit=Śākya) was an ancient eastern Sub-Himalayan Range, sub-Himalayan ethnicity and clan of north-eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, whose existence is attested during the Iron Age i ...
Lineage #Kritanjaya (Sivisamjaya)
#Ranajjaya (Sihassara)
#Jayasena (Mahakoshala or Sanjaya)
#
#Kritanjaya (Sivisamjaya)
#Ranajjaya (Sihassara)
#Jayasena (Mahakoshala or Sanjaya)
#Sihahanu
King Sihahanu ( Skt:Sīṃhahanu) was an ancient monarch and paternal grandfather of Gautama Buddha. He was one of the ruler of Shakya Clan.
Family
Sihahanu was a son of King Jayasena and brother of Princess Yasodhara.
He married Kaccanā of D ...
(Shakya)
#Śuddhodana
Śuddhodana (; Pali: ''Suddhōdana''), meaning "he who grows pure rice," was the father of Gautama Buddha, Siddhartha Gautama, better known as the Buddha. He was a leader of the Shakya, who lived in an oligarchic republic, with their capital at ...
(ruler of Shakya Republic of Kapilavastu)
#Siddhartha Shakya (or Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lu ...
, son of Śuddhodana)
#Rāhula
, sa, Rāhula-bhadra; 2.
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Kapilavastu
, death_date =
, death_place = Sources differ
, title = Patriarch of the Dharma (East Asian Buddhism)
, predecessor ...
(only son of Gautam Buddha)
Later Ikshvakus, of the Original line and Rulers of Kosala
The Kingdom of Kosala (Sanskrit: ) was an ancient Indian kingdom with a rich culture, corresponding to the area within the region of Awadh in present-day Uttar Pradesh to Western Odisha. It emerged as a janapada, small state during the late Ve ...
#Sanjaya Mahākosala
# Prasenajit (born when Siddhartha age 27)
#Viḍūḍabha
Viḍūḍabha ( pi, विडूडभ ; sa, विरूढक ) was a king of Kosala during the lifetime of the Buddha.
Life
Early life
He was the son of Prasenajit and , the daughter of a Shakyan chief named by a slave girl .K ...
#Kshudraka (or Kuntala)
#Ranaka (or Kulaka)
#Suratha
#Sumitra
King Sumitra was Last ruler of the Suryavanshi Dynasty of Kosala, as he was defeated by the powerful Mahapadma Nanda
Mahapadma Nanda (IAST: ''Mahāpadmānanda''; c. mid 4th century BCE), according to the Puranas, was the first Emperor of the Nanda Empire of ancient India. The Puranas describe him as a son of the last Shaishunaga king Mahanandin and a Shudra w ...
of Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled ...
in 362 BCE. However, he wasn't killed, and fled to Rohtas, located in present-day Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
.
See also
*Solar dynasty
The Solar dynasty (IAST: Suryavaṃśa or Ravivaṃśa in Sanskrit) or the Ikshvaku dynasty was founded by the legendary king Ikshvaku.Geography of Rigvedic India, M.L. Bhargava, Lucknow 1964, pp. 15-18, 46-49, 92-98, 100-/1, 136 The dynasty is ...
* Lunar dynasty
The Lunar dynasty (IAST: Candravaṃśa) is a legendary principal house of the Kshatriyas varna, or warrior–ruling caste mentioned in the ancient Indian texts. This legendary dynasty was said to be descended from moon-related deities (''Som ...
* Vedic science Vedic science may refer to:
Vedic period
* Ayurveda
* Vedanga, the six ancient disciplines (shastra) subservient to the understanding and tradition of the Vedas
# Shiksha ('): phonetics and phonology (sandhi)
# Chandas ('): meter
# Vyakarana ('): ...
* History of India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
* Puranic chronology
The Puranic chronology is a timeline of Hindu history based on the ''Mahabharata'', the ''Ramayana'', and the Puranas. Two central dates are the Mahabharata War, and the start of the ''Kali Yuga''. The Puranic chronology is referred to by propo ...
* History of Hinduism
The history of Hinduism covers a wide variety of related religious traditions native to the Indian subcontinent. It overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its tradition ...
* Puru and Yadu Dynasties
In Hindu texts, the Puru and Yadu Dynasties are the descendants of legendary King Pururavas who was a famous Hindu ruler in the Treta Yuga. Pururavas was the son of Ila and Budha. Some of the dynasties' important members were Yayati, Yadu, King P ...
* List of Hindu Empires and Dynasties
Indian empires rose to power following the birth of Buddhism, Jainism and Hinduism in the Indian subcontinent. The period of the Gupta Empire under Samudragupta is sometimes attributed to as the Golden Age of India.
List
The following list enumera ...
References
; Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Ikshvaku dynasty kings in Hinduism Hinduism-related lists Solar dynasty