Link Bonding on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
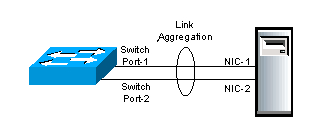 In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundancy in case one of the links should fail, or both. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.
Other umbrella terms used to describe the concept include trunking, bundling, bonding, channeling or teaming.
Implementation may follow vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet, defined in IEEE 802.1AX or the previous
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundancy in case one of the links should fail, or both. A link aggregation group (LAG) is the combined collection of physical ports.
Other umbrella terms used to describe the concept include trunking, bundling, bonding, channeling or teaming.
Implementation may follow vendor-independent standards such as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for Ethernet, defined in IEEE 802.1AX or the previous
provides a method for aggregating multiple network interface controllers (NICs) into a single logical bonded interface of two or more so-called ''(NIC) slaves''. The majority of modern
Windows Management Applications
, visited 8 July 2012
bonded
to give for example 512kbit/s upload bandwidth and 4 megabit/s download bandwidth, in areas that only have access to 2 megabit/s bandwidth.
/ref> * Connectify's Speedify fast bonding VPN - software app for multiple platforms: PC, Mac, iOS and Android Connectify's Speedify Service
/ref> * Peplink's SpeedFusion Bonding Technology Peplink's SpeedFusion Bonding Technology
/ref> * Viprinet's Multichannel VPN Bonding Technology Viprinet's Multichannel VPN Bonding Technology
/ref> * Elsight's Multichannel Secure Data Link Elsight Multichannel Secure Data Link
/ref> * Synopi's Natiply Internet Bonding Technology Synopi's Natiply Internet Bonding Technology
/ref> * ComBOX Networks multi-wan bonding as a service comBOX multi-wan services Broadband bonding
/ref>
Tech Tips - Bonding Modes
Mikrotik link Aggregation / Bonding Guide
* ttp://www.ibm.com/developerworks/aix/library/au-managevlans/index.html?ca=drs Managing VLANs on mission-critical shared Ethernet adapters - IBMbr>Network overview by Rami Rosen (section about bonding)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Link Aggregation Ethernet Link protocols Bonding protocols Network performance Network architecture
IEEE 802.3ad
In computer networking, link aggregation is the combining ( aggregating) of multiple network connections in parallel by any of several methods, in order to increase throughput beyond what a single connection could sustain, to provide redundan ...
, but also proprietary protocols.
Motivation
Link aggregation increases the bandwidth and resilience of Ethernet connections. Bandwidth requirements do not scale linearly. Ethernet bandwidths historically have increased tenfold each generation: 10 megabit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1000 Mbit/s, 10,000 Mbit/s. If one started to bump into bandwidth ceilings, then the only option was to move to the next generation, which could be cost prohibitive. An alternative solution, introduced by many of the network manufacturers in the early 1990s, is to use link aggregation to combine two physical Ethernet links into one logical link. Most of these early solutions required manual configuration and identical equipment on both sides of the connection. There are threesingle points of failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that, if it fails, will stop the entire system from working. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or reliability, be it a business practice, software ap ...
inherent to a typical port-cable-port connection, in either a computer-to-switch or a switch-to-switch configuration: the cable itself or either of the ports the cable is plugged into can fail. Multiple logical connections can be made, but many of the higher level protocols were not designed to fail over completely seamlessly. Combining multiple physical connections into one logical connection using link aggregation provides more resilient communications.
Architecture
Network architects can implement aggregation at any of the lowest three layers of the OSI model. Examples of aggregation at layer 1 (physical layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip.
The ...
) include power line (e.g. IEEE 1901) and wireless (e.g. IEEE 802.11) network devices that combine multiple frequency bands. OSI layer 2 ( data link layer, e.g. Ethernet frame in LANs or multi-link PPP in WANs, Ethernet MAC address) aggregation typically occurs across switch ports, which can be either physical ports or virtual ones managed by an operating system. Aggregation at layer 3 ( network layer) in the OSI model can use round-robin scheduling, hash values computed from fields in the packet header, or a combination of these two methods.
Regardless of the layer on which aggregation occurs, it is possible to balance the network load across all links. However, in order to avoid out-of-order delivery
In computer networking, out-of-order delivery is the delivery of data packets in a different order from which they were sent. Out-of-order delivery can be caused by packets following multiple paths through a network, by lower-layer retransmissio ...
, not all implementations take advantage of this. Most methods provide failover
Failover is switching to a redundant or standby computer server, system, hardware component or network upon the failure or abnormal termination of the previously active application, server, system, hardware component, or network in a computer net ...
as well.
Combining can either occur such that multiple interfaces share one logical address (i.e. IP) or one physical address (i.e. MAC address), or it allows each interface to have its own address. The former requires that both ends of a link use the same aggregation method, but has performance advantages over the latter.
Channel bonding is differentiated from load balancing in that load balancing divides traffic between network interfaces on per network socket (layer 4) basis, while channel bonding implies a division of traffic between physical interfaces at a lower level, either per packet (layer 3) or a data link (layer 2) basis.
IEEE link aggregation
Standardization process
By the mid-1990s, most network switch manufacturers had included aggregation capability as a proprietary extension to increase bandwidth between their switches. Each manufacturer developed its own method, which led to compatibility problems. TheIEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection standards defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC) of wired Ethernet. The standards are produced by the working group of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Eng ...
working group took up a study group to create an interoperable link layer standard (i.e. encompassing the physical and data-link layers both) in a November 1997 meeting. The group quickly agreed to include an automatic configuration feature which would add in redundancy as well. This became known as Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP).
802.3ad
, most gigabit channel-bonding schemes used the IEEE standard of Link Aggregation which was formerly clause 43 of theIEEE 802.3
IEEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection standards defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC) of wired Ethernet. The standards are produced by the working group of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Eng ...
standard added in March 2000 by the IEEE 802.3ad task force. Nearly every network equipment manufacturer quickly adopted this joint standard over their proprietary standards.
802.1AX
The 802.3 maintenance task force report for the 9th revision project in November 2006 noted that certain 802.1 layers (such as 802.1X security) were positioned in the protocol stack below Link Aggregation which was defined as an802.3
IEEE 802.3 is a working group and a collection standards defining the physical layer and data link layer's media access control (MAC) of wired Ethernet. The standards are produced by the working group of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Eng ...
sublayer. To resolve this discrepancy, the 802.3ax (802.1AX) task force was formed, resulting in the formal transfer of the protocol to the 802.1 group with the publication of IEEE 802.1AX-2008 on 3 November 2008.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Within the IEEE Ethernet standards, the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a method to control the bundling of several physical links together to form a single logical link. LACP allows a network device to negotiate an automatic bundling of links by sending LACP packets to their peer, a directly connected device that also implements LACP. LACP Features and practical examples # Maximum number of bundled ports allowed in the port channel: Valid values are usually from 1 to 8. # LACP packets are sent with multicast group MAC address # During LACP detection period #* LACP packets are transmitted every second #* Keep-alive mechanism for link member: (default: slow = 30s, fast=1s) # Selectable load-balancing mode is available in some implementations # LACP mode : #*Active: Enables LACP unconditionally. #*Passive: Enables LACP only when an LACP device is detected. (This is the default state)Advantages over static configuration
* Failover occurs automatically: When a link has an intermediate failure, for example in a media converter between the devices, a peer system may not perceive any connectivity problems. With static link aggregation, the peer would continue sending traffic down the link causing the connection to fail. * Dynamic configuration: The device can confirm that the configuration at the other end can handle link aggregation. With static link aggregation, a cabling or configuration mistake could go undetected and cause undesirable network behavior.Practical notes
LACP works by sending frames (LACPDUs) down all links that have the protocol enabled. If it finds a device on the other end of a link that also has LACP enabled, that device will independently send frames along the same links in the opposite direction enabling the two units to detect multiple links between themselves and then combine them into a single logical link. LACP can be configured in one of two modes: active or passive. In active mode, LACPDUs are sent 1 per second along the configured links. In passive mode, LACPDUs are not sent until one is received from the other side, a speak-when-spoken-to protocol.Proprietary link aggregation
In addition to the IEEE link aggregation substandards, there are a number of proprietary aggregation schemes including Cisco's EtherChannel and Port Aggregation Protocol, Juniper's Aggregated Ethernet, AVAYA's Multi-Link Trunking, Split Multi-Link Trunking, Routed Split Multi-Link Trunking and Distributed Split Multi-Link Trunking, ZTE's Smartgroup, Huawei's Eth-Trunk, and Connectify's Speedify. Most high-end network devices support some form of link aggregation. Software-based implementations – such as the *BSD ''lagg'' package, Linux ''bonding'' driver,Solaris
Solaris may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Literature, television and film
* ''Solaris'' (novel), a 1961 science fiction novel by Stanisław Lem
** ''Solaris'' (1968 film), directed by Boris Nirenburg
** ''Solaris'' (1972 film), directed by ...
''dladm aggr'', etc. – exist for many operating systems.
Linux drivers
The Linux ''bonding'' driverThe Linux Foundation: Bondingprovides a method for aggregating multiple network interface controllers (NICs) into a single logical bonded interface of two or more so-called ''(NIC) slaves''. The majority of modern
Linux distribution
A Linux distribution (often abbreviated as distro) is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one ...
s come with a Linux kernel
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU ope ...
which has the Linux bonding driver integrated as a loadable kernel module
In computing, a loadable kernel module (LKM) is an object file that contains code to extend the running kernel, or so-called ''base kernel'', of an operating system. LKMs are typically used to add support for new hardware (as device drivers) and/ ...
and the ''ifenslave'' (if = etworkinterface) user-level
A modern computer operating system usually segregates virtual memory into user space and kernel space. Primarily, this separation serves to provide memory protection and hardware protection from malicious or errant software behaviour.
Kernel ...
control program pre-installed. Donald Becker
thumbnail,
Donald Becker is an American computer programmer who wrote Ethernet drivers for the Linux operating system.
Becker, in collaboration with Thomas Sterling, created the Beowulf clustering software while at NASA, to connect many in ...
programmed the original Linux bonding driver. It came into use with the Beowulf cluster patches for the Linux kernel 2.0.
Modes for the Linux bonding driver (network interface aggregation modes) are supplied as parameters to the kernel bonding module at load time. They may be given as command-line
arguments to the ''insmod'' or ''modprobe'' commands, but are usually specified in a Linux distribution-specific configuration file. The behavior of the single logical bonded interface depends upon its specified bonding driver mode. The default parameter is balance-rr.
;Round-robin (balance-rr): Transmit alternate network packets in sequential order from the first available NIC slave through the last. This mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance. This mode can cause congestion control issues due to the packet reordering it can introduce.
;Active-backup (active-backup): Only one NIC slave in the bond is active. A different slave becomes active if, and only if, the active slave fails. The single logical bonded interface's MAC address is externally visible on only one NIC
NIC may refer to:
Banking and insurance companies
* National Insurance Corporation, Uganda
* NIC Bank, a commercial bank in Kenya
Politics, government and economics
* National Ice Center, an agency that provides worldwide navigational ice a ...
(port) to simplify forwarding in the network switch. This mode provides fault tolerance.
;XOR (balance-xor): Transmit network packets based on a hash of the packet's source and destination. The default algorithm only considers MAC addresses (''layer2''). Newer versions allow selection of additional policies based on IP addresses (''layer2+3'') and TCP/UDP port numbers (''layer3+4''). This selects the same NIC slave for each destination MAC address, IP address, or IP address and port combination, respectively. Single connections will have guaranteed ''in order'' packet delivery and will transmit at the speed of a single NIC. This mode provides load balancing and fault tolerance.
;Broadcast (broadcast): Transmit network packets on all slave network interfaces. This mode provides fault tolerance.
;IEEE 802.3ad Dynamic link aggregation (802.3ad, LACP): Creates aggregation groups that share the same speed and duplex settings. Utilizes all slave network interfaces in the active aggregator group according to the 802.3ad specification. This mode is similar to the XOR mode above and supports the same balancing policies. The link is set up dynamically between two LACP-supporting peers.
;Adaptive transmit load balancing (balance-tlb): Linux bonding driver mode that does not require any special network-switch support. The outgoing network packet traffic is distributed according to the current load (computed relative to the speed) on each network interface slave. Incoming traffic is received by one currently designated slave network interface. If this receiving slave fails, another slave takes over the MAC address of the failed receiving slave.
;Adaptive load balancing (balance-alb): includes ''balance-tlb'' plus ''receive load balancing'' (rlb) for IPv4 traffic and does not require any special network switch support. The receive load balancing is achieved by ARP negotiation. The bonding driver intercepts the ARP Replies sent by the local system on their way out and overwrites the source hardware address with the unique hardware address of one of the NIC slaves in the single logical bonded interface such that different network-peers use different MAC addresses for their network packet traffic.
The Linux Team driver provides an alternative to bonding driver. The main difference is that Team driver kernel part contains only essential code and the rest of the code (link validation, LACP implementation, decision making, etc.) is run in userspace as a part of ''teamd'' daemon.
Usage
Network backbone
Link aggregation offers an inexpensive way to set up a high-speed backbone network that transfers much more data than any single port or device can deliver. Link aggregation also allows the network's backbone speed to grow incrementally as demand on the network increases, without having to replace everything and deploy new hardware. Most backbone installations install more cabling or fiber optic pairs than is initially necessary. This is done because labor costs are higher than the cost of the cable, and running extra cable reduces future labor costs if networking needs change. Link aggregation can allow the use of these extra cables to increase backbone speeds for little or no extra cost if ports are available.Order of frames
When balancing traffic, network administrators often wish to avoid reordering Ethernet frames. For example, TCP suffers additional overhead when dealing with out-of-order packets. This goal is approximated by sending all frames associated with a particular session across the same link. Common implementations use L2 or L3 hashes (i.e. based on the MAC or the IP addresses), ensuring that the same flow is always sent via the same physical link. However, this may not provide even distribution across the links in the trunk when only a single or very few pairs of hosts communicate with each other, i.e. when the hashes provide too little variation. It effectively limits the client bandwidth in aggregate. In the extreme, one link is fully loaded while the others are completely idle and aggregate bandwidth is limited to this single member's maximum bandwidth. For this reason, an even load balancing and full utilization of all trunked links is almost never reached in real-life implementations.Use on network interface cards
NICs trunked together can also provide network links beyond the throughput of any one single NIC. For example, this allows a central file server to establish an aggregate 2-gigabit connection using two 1-gigabit NICs teamed together. Note the data signaling rate will still be 1 Gbit/s, which can be misleading depending on methodologies used to test throughput after link aggregation is employed.Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
Server 2012 supports link aggregation natively. Previous Windows Server versions relied on manufacturer support of the feature within their device driver
In computing, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabling operating systems and ot ...
software. Intel, for example, released Advanced Networking Services (ANS) to bond Intel Fast Ethernet and Gigabit cards.
Nvidia supports teaming with their Nvidia Network Access Manager/Firewall Tool. HP has a teaming tool for HP-branded NICs which supports several modes of link aggregation including 802.3ad with LACP. In addition, there is a basic layer-3 aggregation that allows servers with multiple IP interfaces on the same network to perform load balancing, and for home users with more than one internet connection, to increase connection speed by sharing the load on all interfaces.
Broadcom offers advanced functions via Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS), via which the teaming functionality of BASP (Broadcom Advanced Server Program) is available, offering 802.3ad static LAGs, LACP, and "smart teaming" which doesn't require any configuration on the switches to work. It is possible to configure teaming with BACS with a mix of NICs from different vendors as long as at least one of them is from Broadcom and the other NICs have the required capabilities to support teaming.BroadcoWindows Management Applications
, visited 8 July 2012
Linux and UNIX
Linux,FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular ...
, NetBSD
NetBSD is a free and open-source Unix operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). It was the first open-source BSD descendant officially released after 386BSD was forked. It continues to be actively developed and is a ...
, OpenBSD
OpenBSD is a security-focused, free and open-source, Unix-like operating system based on the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD). Theo de Raadt created OpenBSD in 1995 by forking NetBSD 1.0. According to the website, the OpenBSD project em ...
, macOS, OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris () is a discontinued open-source computer operating system based on Solaris and created by Sun Microsystems. It was also, perhaps confusingly, the name of a project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around th ...
and commercial Unix distributions such as AIX implement Ethernet bonding at a higher level and, as long as the NIC is supported by the kernel, can deal with NICs from different manufacturers or using different drivers.
Virtualization platforms
Citrix XenServer
Citrix Systems, Inc. is an American multinational cloud computing and virtualization technology company that provides server, application and desktop virtualization, networking, software as a service (SaaS), and cloud computing technologies. ...
and VMware ESX have native support for link-aggregation. XenServer offers both static LAGs as well as LACP. vSphere 5.1 (ESXi) supports both static LAGs and LACP natively with their virtual distributed switch.
Microsoft's Hyper-V does not offer bonding or teaming from the hyper-visor or OS-level, but the above-mentioned methods for teaming under Windows applies to Hyper-V as well.
Limitations
Single switch
With the modes ''balance-rr'', ''balance-xor'', ''broadcast'' and ''802.3ad'', all physical ports in the link aggregation group must reside on the same logical switch, which, in most common scenarios, will leave a single point of failure when the physical switch to which all links are connected goes offline. The modes ''active-backup'', ''balance-tlb'', and ''balance-alb'' can also be set up with two or more switches. But after failover (like all other modes), in some cases, active sessions may fail (due to ARP problems) and have to be restarted. However, almost all vendors have proprietary extensions that resolve some of this issue: they aggregate multiple physical switches into one logical switch. The Split multi-link trunking (SMLT) protocol allows multiple Ethernet links to be split across multiple switches in a stack, preventing any single point of failure and additionally allowing all switches to be load balanced across multiple aggregation switches from the single access stack. These devices synchronize state across an Inter-Switch Trunk (IST) such that they appear to the connecting (access) device to be a single device (switch block) and prevent any packet duplication. SMLT provides enhanced resiliency with sub-second failover and sub-second recovery for all speed trunks (10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s, 1,000 Mbit/s, and 10 Gbit/s) while operating transparently to end-devices.Same link speed
In most implementations, all the ports used in an aggregation consist of the same physical type, such as all copper ports (10/100/1000BASE‑T), all multi-mode fiber ports, or all single-mode fiber ports. However, all the IEEE standard requires is that each link be full duplex and all of them have an identical speed (10, 100, 1,000 or 10,000 Mbit/s). Many switches are PHY independent, meaning that a switch could have a mixture of copper, SX, LX, LX10 or otherGBIC
A gigabit interface converter (GBIC) is a standard for transceivers, first defined in 1995 and commonly used with Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel for some time. By offering a standard, hot swappable electrical interface, a single gigabit por ...
/ SFP modular transceivers. While maintaining the same PHY is the usual approach, it is possible to aggregate a 1000BASE-SX fiber for one link and a 1000BASE-LX (longer, diverse path) for the second link, but the important thing is that the speed will be 1 Gbit/s full duplex for both links. One path may have a slightly longer propagation time but since most implementations keep a single traffic flow on the same physical link (using a hash of either MAC addresses, IP addresses, or IP/ transport-layer port combinations as index) that isn't an issue usually.
Ethernet aggregation mismatch
Aggregation mismatch refers to not matching the aggregation type on both ends of the link. Some switches do not implement the 802.1AX standard but support static configuration of link aggregation. Therefore, link aggregation between similarly statically configured switches will work but will fail between a statically configured switch and a device that is configured for LACP.Examples
Ethernet
On Ethernet interfaces, channel bonding requires assistance from both the Ethernet switch and the host computer's operating system, which must "stripe" the delivery of frames across the network interfaces in the same manner that I/O is striped across disks in a RAID 0 array. For this reason, some discussions of channel bonding also refer to Redundant Array of Inexpensive Nodes (RAIN) or to "redundant array of independent network interfaces".Modems
In analog modems, multipledial-up
Dial-up Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an Internet service provider (ISP) by dialing a telephone number on a conventional telepho ...
links over POTS
Pot may refer to:
Containers
* Flowerpot, a container in which plants are cultivated
* Pottery, ceramic ware made by potters
* A type of cookware
Places
* Ken Jones Aerodrome, IATA airport code POT
* Palestinian Occupied Territories, the We ...
may be bonded. Throughput over such bonded connections can come closer to the aggregate bandwidth of the bonded links than can throughput under routing schemes which simply load-balance outgoing network connections over the links.
DSL
Similarly, multiple DSL lines can be bonded to give higher bandwidth; in the United Kingdom, ADSL is sometimebonded
to give for example 512kbit/s upload bandwidth and 4 megabit/s download bandwidth, in areas that only have access to 2 megabit/s bandwidth.
DOCSIS
Under the DOCSIS 3.0 and 3.1 specifications for data over cable TV (CATV) systems, multiple channels may be bonded. Under DOCSIS 3.0, up to 32 downstream and 8 upstream channels may be bonded. These are typically 6 or 8 MHz wide. DOCSIS 3.1 defines more complicated arrangements involving aggregation at the level subcarriers and larger notional channels.Wireless Broadband
Broadband bonding is a type of channel bonding that refers to aggregation of multiple channels at OSI layers at level four or above. Channels bonded can be wired links such as a T-1 or DSL line. Additionally, it is possible to bond multiple cellular links for an aggregated wireless bonded link. Previous bonding methodologies resided at lower OSI layers, requiring coordination with telecommunications companies for implementation. Broadband bonding, because it is implemented at higher layers, can be done without this coordination. Commercial implementations of Broadband Channel Bonding include: * Wistron AiEdge Corporation's U-Bonding Technology * Mushroom Networks' Broadband Bonding Service Mushroom Networks' Broadband Bonding Service/ref> * Connectify's Speedify fast bonding VPN - software app for multiple platforms: PC, Mac, iOS and Android Connectify's Speedify Service
/ref> * Peplink's SpeedFusion Bonding Technology Peplink's SpeedFusion Bonding Technology
/ref> * Viprinet's Multichannel VPN Bonding Technology Viprinet's Multichannel VPN Bonding Technology
/ref> * Elsight's Multichannel Secure Data Link Elsight Multichannel Secure Data Link
/ref> * Synopi's Natiply Internet Bonding Technology Synopi's Natiply Internet Bonding Technology
/ref> * ComBOX Networks multi-wan bonding as a service comBOX multi-wan services Broadband bonding
/ref>
Wi-Fi
* On 802.11 (Wi-Fi), channel bonding is used inSuper G
Super giant slalom, or super-G, is a racing discipline of alpine skiing. Along with the faster downhill, it is regarded as a "speed" event, in contrast to the technical events giant slalom and slalom. It debuted as an official World Cup event ...
technology, referred to as 108Mbit/s. It bonds two channels of standard 802.11g
IEEE 802.11g-2003 or 802.11g is an amendment to the IEEE 802.11 specification that operates in the 2.4 GHz microwave band. The standard has extended throughput to up to 54 Mbit/s using the same 20 MHz bandwidth as 802.11b uses to achieve 11 Mbit/ ...
, which has 54Mbit/s data signaling rate
In telecommunication, data signaling rate (DSR), also known as gross bit rate, is the aggregate rate at which data passes a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system.
# The DSR is usually expressed in bits per second.
# Th ...
.
* On IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11n-2009 or 802.11n is a wireless-networking standard that uses multiple antennas to increase data rates. The Wi-Fi Alliance has also retroactively labelled the technology for the standard as Wi-Fi 4. It standardized support for multiple ...
, a mode with a channel width of 40 MHz is specified. This is not channel bonding, but a single channel with double the older 20 MHz channel width, thus using two adjacent 20 MHz bands. This allows direct doubling of the PHY data rate from a single 20 MHz channel, but the MAC and user-level throughput also depends on other factors so may not double.
See also
*FlexE
FlexE, short for Flexible Ethernet, is a communications protocol published by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF).
Overview
The OIF published the FlexE Interoperability Agreement (IA) in 2016. FlexE enables equipment to support new Ethernet c ...
* Inverse multiplexer
* Multi-chassis link aggregation group
* Spanning Tree Protocol
References
;General *Tech Tips - Bonding Modes
External links
Mikrotik link Aggregation / Bonding Guide
* ttp://www.ibm.com/developerworks/aix/library/au-managevlans/index.html?ca=drs Managing VLANs on mission-critical shared Ethernet adapters - IBMbr>Network overview by Rami Rosen (section about bonding)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Link Aggregation Ethernet Link protocols Bonding protocols Network performance Network architecture