Leukemia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of
 The most common symptoms in children are easy
The most common symptoms in children are easy
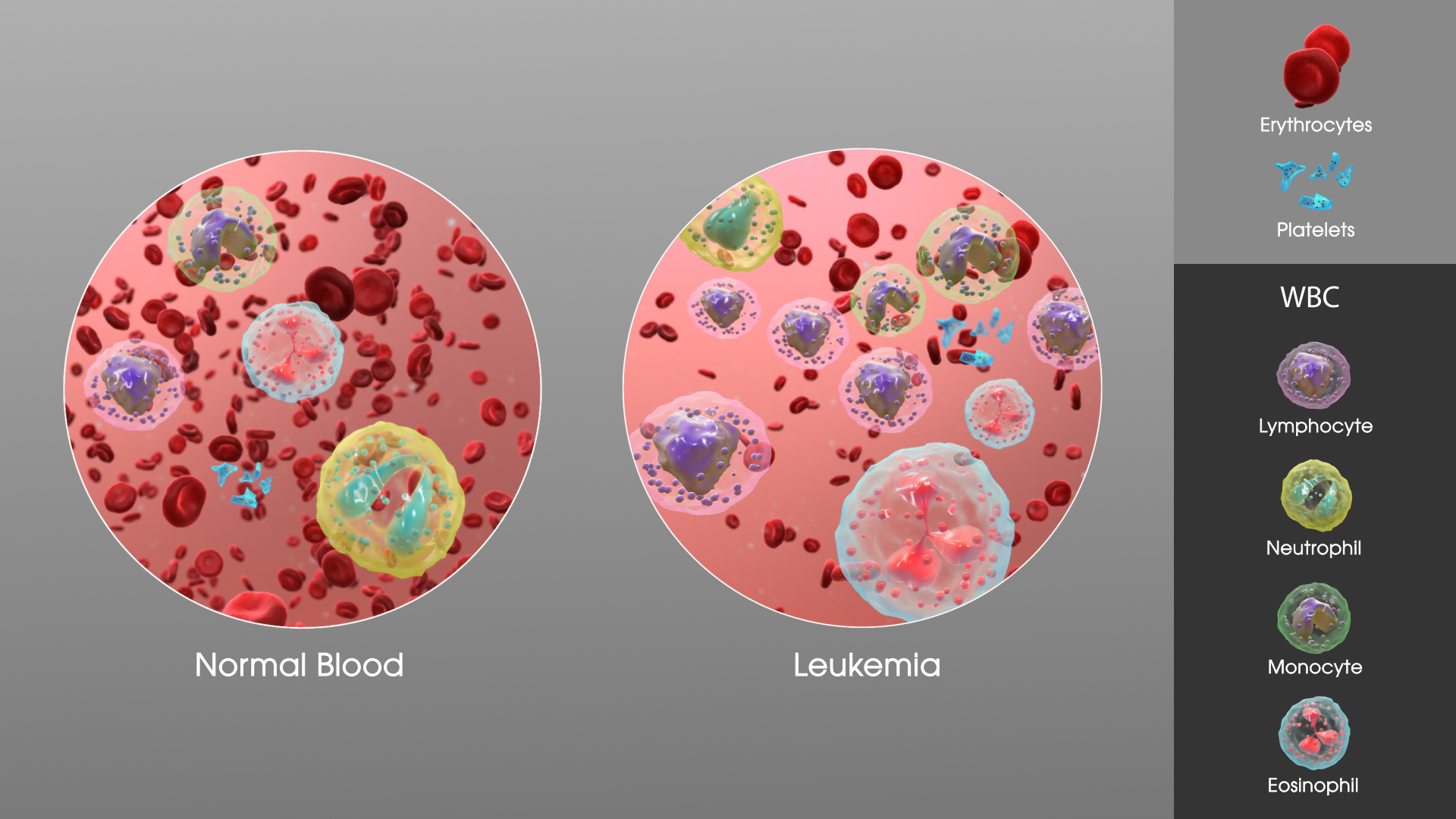 Diagnosis is usually based on repeated
Diagnosis is usually based on repeated
People with hairy cell leukemia who are symptom-free typically do not receive immediate treatment. Treatment is generally considered necessary when the person shows signs and symptoms such as low blood cell counts (e.g., infection-fighting neutrophil count below 1.0 K/μL), frequent infections, unexplained bruises, anemia, or fatigue that is significant enough to disrupt the person's everyday life. Typical treatment approach
People who need treatment usually receive either one week of cladribine, given daily by intravenous infusion or a simple injection under the skin, or six months of pentostatin, given every four weeks by intravenous infusion. In most cases, one round of treatment will produce a prolonged remission. Other treatments include
 In 2010, globally, approximately 281,500 people died of leukemia. In 2000, approximately 256,000 children and adults around the world developed a form of leukemia, and 209,000 died from it. This represents about 3% of the almost seven million deaths due to cancer that year, and about 0.35% of all deaths from any cause. Of the sixteen separate sites the body compared, leukemia was the 12th most common class of neoplastic disease and the 11th most common cause of cancer-related death. Leukemia occurs more commonly in the
In 2010, globally, approximately 281,500 people died of leukemia. In 2000, approximately 256,000 children and adults around the world developed a form of leukemia, and 209,000 died from it. This represents about 3% of the almost seven million deaths due to cancer that year, and about 0.35% of all deaths from any cause. Of the sixteen separate sites the body compared, leukemia was the 12th most common class of neoplastic disease and the 11th most common cause of cancer-related death. Leukemia occurs more commonly in the
 Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist
Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist
Leukaemia information
from
blood cancer
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are al ...
s that usually begin in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
s. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells
In cell biology, precursor cells—also called blast cells—are partially differentiated, or intermediate, and are sometimes referred to as progenitor cells. A precursor cell is a stem cell with the capacity to differentiate into only one cell t ...
''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
, bone pain
Bone pain (also known medically by several other names) is pain coming from a bone, and is caused by damaging stimuli. It occurs as a result of a wide range of diseases or physical conditions or both, and may severely impair the quality of life. ...
, fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cell
A blood cell (also called a hematopoietic cell, hemocyte, or hematocyte) is a cell produced through hematopoiesis and found mainly in the blood. Major types of blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), ...
s. Diagnosis is typically made by blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s or bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of condit ...
.
The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
, petrochemicals (such as benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, ...
(ALL), acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympt ...
(AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. In CLL, the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to colle ...
(CLL) and chronic myeloid leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumula ...
(CML)—and a number of less common types. Leukemias and lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph node ...
s both belong to a broader group of tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s that affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid system, known as tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all ...
.
Treatment may involve some combination of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
, targeted therapy
Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy (oncology), hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medici ...
, and bone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
, with supportive and palliative care
Palliative care (from Latin root "to cloak") is an interdisciplinary medical care-giving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating or reducing suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Man ...
provided as needed. Certain types of leukemia may be managed with watchful waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed.
Related terms include ''expe ...
. The success of treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of the person. Outcomes have improved in the developed world. Five-year survival rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surv ...
was 67% in the United States in the period from 2014 to 2020. Updated as required. In children under 15 in first-world countries, the five-year survival rate is greater than 60% or even 90%, depending on the type of leukemia. For infants (those diagnosed under the age of 1), the survival rate is around 40%. In children who are cancer-free five years after diagnosis of acute leukemia, the cancer is unlikely to return.
In 2015, leukemia was present in 2.3 million people worldwide and caused 353,500 deaths. In 2012, it had newly developed in 352,000 people. It is the most common type of cancer in children, with three-quarters of leukemia cases in children being the acute lymphoblastic type. However, over 90% of all leukemias are diagnosed in adults, CLL and AML being most common. It occurs more commonly in the developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
.
Classification
General classification
Clinically and pathologically, leukemia is subdivided into a variety of large groups. The first division is between its '' acute'' and '' chronic'' forms: *Acute leukemia
Acute leukemia or acute leukaemia is a family of serious medical conditions relating to an original diagnosis of leukemia. In most cases, these can be classified according to the lineage, myeloid or lymphoid, of the malignant cells that grow uncont ...
is characterized by a rapid increase in the number of immature blood cells. The crowding that results from such cells makes the bone marrow unable to produce healthy blood cells resulting in low hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
and low platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s. Immediate treatment is required in acute leukemia because of the rapid progression and accumulation of the malignant cell
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse; the term is most familiar as a characterization of cancer.
A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not ...
s, which then spill over into the bloodstream and spread to other organs of the body. Acute forms of leukemia are the most common forms of leukemia in children.
* Chronic leukemia Chronic leukemia is an increase of abnormal white blood cells. It differs from acute leukemia, and is categorized as myelogenous, lymphocytic or myeloproliferative.
Chronic leukemia may refer to:
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia
* Chronic lymphocytic ...
is characterized by the excessive buildup of relatively mature, but still abnormal, white blood cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s (or, more rarely, red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s). Typically taking months or years to progress, the cells are produced at a much higher rate than normal, resulting in many abnormal white blood cells. Whereas acute leukemia must be treated immediately, chronic forms are sometimes monitored for some time before treatment to ensure maximum effectiveness of therapy. Chronic leukemia mostly occurs in older people but can occur in any age group.
Additionally, the diseases are subdivided according to which kind of blood cell is affected. This divides leukemias into lymphoblastic or '' lymphocytic leukemias'' and myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + '' -oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue ...
or '' myelogenous leukemias'':
* In lymphoblastic or lymphocytic leukemias, the cancerous change takes place in a type of marrow cell that normally goes on to form lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s, which are infection-fighting immune system cells. Most lymphocytic leukemias involve a specific subtype of lymphocyte, the B cell.
* In myeloid or myelogenous leukemias, the cancerous change takes place in a type of marrow cell that normally goes on to form red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), referred to as erythrocytes (, with -''cyte'' translated as 'cell' in modern usage) in academia and medical publishing, also known as red cells, erythroid cells, and rarely haematids, are the most common type of blood cel ...
s, some other types of white cells, and platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s.
Combining these two classifications provides a total of four main categories. Within each of these main categories, there are typically several subcategories. Finally, some rarer types are usually considered to be outside of this classification scheme.
Specific types
*Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, ...
(ALL) is the most common type of leukemia in young children. It also affects adults, especially those 65 and older. Standard treatments involve chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
and radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle ...
. Subtypes include precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia, precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Burkitt's leukemia, and acute biphenotypic leukemia. While most cases of ALL occur in children, 80% of deaths from ALL occur in adults.
* Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. In CLL, the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell. In patients with CLL, B cell lymphocytes can begin to colle ...
(CLL) most often affects adults over the age of 55. It sometimes occurs in younger adults, but it almost never affects children. Two-thirds of affected people are men. The five-year survival rate is 85%. It is incurable, but there are many effective treatments. One subtype is B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, referred to as B-PLL, is a rare blood cancer. It is a more aggressive, but still treatable, form of leukemia.
Specifically, B-PLL is a prolymphocytic leukemia (PLL) that affects prolymphocytes – immature forms ...
, a more aggressive disease.
* Acute myelogenous leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may includ ...
(AML) occurs far more commonly in adults than in children, and more commonly in men than women. It is treated with chemotherapy. The five-year survival rate is 20%. Subtypes of AML include acute promyelocytic leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML, APL) is a subtype of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a cancer of the white blood cells. In APL, there is an abnormal accumulation of immature granulocytes called promyelocytes. The disease is characterized by ...
, acute myeloblastic leukemia, and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia.
* Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumula ...
(CML) occurs mainly in adults; a very small number of children also develop this disease. It is treated with imatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
(Gleevec in United States, Glivec in Europe) or other drugs. The five-year survival rate is 90%. One subtype is chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a type of leukemia, which are cancers of the blood-forming cells of the bone marrow. In adults, blood cells are formed in the bone marrow, by a process that is known as haematopoiesis. In CMML, there are in ...
.
* Hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. The incidence of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is 0.28-0.30 cases per 100,000 people in Europe and the United States and the pre ...
(HCL) is sometimes considered a subset of chronic lymphocytic leukemia, but does not fit neatly into this category. About 80% of affected people are adult men. No cases in children have been reported. HCL is incurable but easily treatable. Survival is 96% to 100% at ten years.
* T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia
T-cell-prolymphocytic leukemia (T-PLL) is a mature T-cell leukemia with aggressive behavior and predilection for blood, bone marrow, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and skin involvement. T-PLL is a very rare leukemia, primarily affecting adults over t ...
(T-PLL) is a very rare and aggressive leukemia affecting adults; somewhat more men than women are diagnosed with this disease. Despite its overall rarity, it is the most common type of mature T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
leukemia; nearly all other leukemias involve B cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasm ...
. It is difficult to treat, and the median survival is measured in months.
* Large granular lymphocytic leukemia may involve either T-cells or NK cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells ...
s; like hairy cell leukemia, which involves solely B cells, it is a rare and indolent (not aggressive) leukemia.
* Adult T-cell leukemia is caused by human T-lymphotropic virus
The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infect primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World monk ...
(HTLV), a virus similar to HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
. Like HIV, HTLV infects CD4+ T-cells and replicates within them; however, unlike HIV, it does not destroy them. Instead, HTLV "immortalizes" the infected T-cells, giving them the ability to proliferate abnormally. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus types I and II (HTLV-I/II) are endemic in certain areas of the world.
* Clonal eosinophilia
Clonal hypereosinophilia, also termed primary hypereosinophilia or clonal eosinophilia, is a grouping of hematological disorders all of which are characterized by the development and growth of a pre-malignant or malignant population of eosinophil ...
s (also called ''clonal hypereosinophilias'') are a group of blood disorders characterized by the growth of eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
s in the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
, blood, and/or other tissues. They may be pre-cancerous or cancerous
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
. Clonal eosinophilias involve a "clone" of eosinophils, i.e., a group of genetically identical eosinophils that all grew from the same mutated
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral rep ...
ancestor cell. These disorders may evolve into chronic eosinophilic leukemia or may be associated with various forms of myeloid
Myeloid tissue, in the bone marrow sense of the word '' myeloid'' ('' myelo-'' + '' -oid''), is tissue of bone marrow, of bone marrow cell lineage, or resembling bone marrow, and myelogenous tissue (''myelo-'' + '' -genous'') is any tissue ...
neoplasms, lymphoid
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lympha ...
neoplasms, myelofibrosis
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is activation and growth of mutated cells in ...
, or the myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may includ ...
.
Pre-leukemia
* Transient myeloproliferative disease, also termed transient leukemia, involves the abnormal proliferation of a clone of non-cancerousmegakaryoblast
A megakaryoblast () is a precursor cell to a promegakaryocyte. During thrombopoiesis, the promegakaryocyte matures into the form of a megakaryocyte. From the megakaryocyte, platelets are formed. The megakaryoblast is the beginning of the thromb ...
s. The disease is restricted to individuals with Down syndrome or genetic changes similar to those in Down syndrome, develops in a baby during pregnancy or shortly after birth, and resolves within 3 months or, in ~10% of cases, progresses to acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Transient myeloid leukemia is a pre-leukemic condition.
* Clonal hematopoiesis
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential, or CHIP, is a common aging-related phenomenon in which hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) or other early blood cell progenitors contribute to the formation of a genetically distinct subpopulation of b ...
is a common age-related phenomenon with a low risk of progression to myelodysplastic syndrome
A myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is one of a group of cancers in which blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature, and as a result, do not develop into healthy blood cells. Early on, no symptoms typically are seen. Later, symptoms may includ ...
(MDS) and leukemia. Once MDS has developed, the risk of progression to acute leukemia can be assessed using the International Prognostic Scoring System ( IPSS).
* Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis has a low risk of progression to B-cell leukemia.
Signs and symptoms
 The most common symptoms in children are easy
The most common symptoms in children are easy bruising
A bruise, also known as a contusion, is a type of hematoma of tissue, the most common cause being capillaries damaged by trauma, causing localized bleeding that extravasates into the surrounding interstitial tissues. Most bruises occur clo ...
, pale skin, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, and an enlarged spleen
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulatin ...
or liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
.
Damage to the bone marrow, by way of displacing the normal bone marrow cells with higher numbers of immature white blood cells, results in a lack of blood platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
s, which are important in the blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a thrombus, blood clot. It results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The process of co ...
process. This means people with leukemia may easily become bruised, bleed excessively, or develop pinprick bleeds (petechia
A petechia (; : petechiae) is a small red or purple spot ( 1 cm in diameter) and purpura (3 to 10 mm in diameter). The term is typically used in the plural (petechiae), since a single petechia is seldom noticed or significant.
Causes Physical t ...
e).
White blood cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
s, which are involved in fighting pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s, may be suppressed or dysfunctional. This could cause the person's immune system to be unable to fight off a simple infection or to start attacking other body cells. Because leukemia prevents the immune system from working normally, some people experience frequent infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
, ranging from infected tonsil
The tonsils ( ) are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil (or pharyngeal tonsil), two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual t ...
s, sores in the mouth, or diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
to life-threatening pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
or opportunistic infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts more severe on those with a weakened immune system. These types of infections are considered serious and can be caused b ...
s.
Finally, the red blood cell deficiency leads to anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
, which may cause dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
and pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eye ...
.
Some people experience other symptoms, such as fevers, chills, night sweats, weakness in the limbs, feeling fatigued and other common flu-like symptoms
Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss ...
. Some people experience nausea or a feeling of fullness due to an enlarged liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
; this can result in unintentional weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
. Blasts affected by the disease may come together and become swollen in the liver or in the lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped Organ (anatomy), organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphoc ...
causing pain and leading to nausea.
If the leukemic cells invade the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, then neurological symptoms (notably headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
s) can occur. Uncommon neurological symptoms like migraines
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may includ ...
, seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, or coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
can occur as a result of brain stem pressure. All symptoms associated with leukemia can be attributed to other diseases. Consequently, leukemia is always diagnosed through medical test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic ...
s.
The word ''leukemia'', which means 'white blood', is derived from the characteristic high white blood cell count that presents in most affected people before treatment. The high number of white blood cells is apparent when a blood sample is viewed under a microscope, with the extra white blood cells frequently being immature or dysfunctional. The excessive number of cells can also interfere with the level of other cells, causing further harmful imbalance in the blood count.
Some people diagnosed with leukemia do not have high white blood cell counts visible during a regular blood count. This less-common condition is called ''aleukemia''. The bone marrow still contains cancerous white blood cells that disrupt the normal production of blood cells, but they remain in the marrow instead of entering the bloodstream, where they would be visible in a blood test. For a person with aleukemia, the white blood cell counts in the bloodstream can be normal or low. Aleukemia can occur in any of the four major types of leukemia, and is particularly common in hairy cell leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia is an uncommon hematological malignancy characterized by an accumulation of abnormal B lymphocytes. The incidence of hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is 0.28-0.30 cases per 100,000 people in Europe and the United States and the pre ...
.
Causes
Studies in 2009 and 2010 have shown a positive correlation between exposure toformaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
and the development of leukemia, particularly myeloid leukemia. The different leukemias likely have different causes.
Leukemia, like other cancers, results from mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosi ...
in the DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. Certain mutations can trigger leukemia by activating oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
s or deactivating tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results ...
s, and thereby disrupting the regulation of cell death, differentiation or division. These mutations may occur spontaneously or as a result of exposure to radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
or carcinogen
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and biologic agents such as viruse ...
ic substances.
Among adults, the known causes are natural and artificial ionizing radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching ...
and petrochemicals, notably benzene
Benzene is an Organic compound, organic chemical compound with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar hexagonal Ring (chemistry), ring with one hyd ...
and alkylating chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
agents for previous malignancies. Use of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
is associated with a small increase in the risk of developing acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympt ...
in adults. Cohort and case-control studies have linked exposure to some petrochemicals
Petrochemicals (sometimes abbreviated as petchems) are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable so ...
and hair dye
Hair coloring, or hair dyeing, is the practice of changing the color of the hair on humans' heads. The main reasons for this are cosmetic: to cover gray or white hair, to alter hair to create a specific look, to change a color to suit preferen ...
s to the development of some forms of leukemia. Diet has very limited or no effect, although eating more vegetables may confer a small protective benefit.
Viruses have also been linked to some forms of leukemia. For example, human T-lymphotropic virus
The primate T-lymphotropic viruses (PTLVs) are a group of retroviruses that infect primates, using their lymphocytes to reproduce. The ones that infect humans are known as human T-lymphotropic virus (HTLV), and the ones that infect Old World monk ...
(HTLV-1) causes adult T-cell leukemia.
A few cases of maternal-fetal transmission (a baby acquires leukemia because its mother had leukemia during the pregnancy) have been reported. Children born to mothers who use fertility drugs to induce ovulation are more than twice as likely to develop leukemia during their childhoods than other children.
In a recent systematic review and meta-analysis of any type of leukemia in neonates using phototherapy
Light therapy, also called phototherapy or bright light therapy is the exposure to direct sunlight or artificial light at controlled wavelengths in order to treat a variety of medical disorders, including seasonal affective disorder (SAD), circ ...
, typically to treat neonatal jaundice
Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral ...
, a statistically significant association was detected between using phototherapy and myeloid leukemia. However, it is still questionable whether phototherapy is genuinely the cause of cancer or simply a result of the same underlying factors that gave rise to cancer.
Radiation
Large doses of Sr-90 (called a bone seeking radioisotope) fromnuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device used to initiate and control a Nuclear fission, fission nuclear chain reaction. They are used for Nuclear power, commercial electricity, nuclear marine propulsion, marine propulsion, Weapons-grade plutonium, weapons ...
accidents, increases the risk of bone cancer
A bone tumor is an neoplastic, abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as benign, noncancerous (benign) or malignant, cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body su ...
and leukemia in animals and is presumed to do so in people.
Genetic conditions
Some people have a genetic predisposition towards developing leukemia. This predisposition is demonstrated by family histories andtwin studies
Twin studies are studies conducted on Identical twin, identical or Fraternal twin, fraternal twins. They aim to reveal the importance of environmental and genetics, genetic influences for traits, phenotypes, and disorders. Twin research is consid ...
. The affected people may have a single gene or multiple genes in common. In some cases, families tend to develop the same kinds of leukemia as other members; in other families, affected people may develop different forms of leukemia or related blood cancers.
In addition to these genetic issues, people with chromosomal abnormalities or certain other genetic conditions have a greater risk of leukemia. For example, people with Down syndrome have a significantly increased risk of developing forms of acute leukemia (especially acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with haematopoiesis, normal blood cell production. Sympt ...
), and Fanconi anemia
Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic disease characterized by aplastic anemia, congenital defects, endocrinological abnormalities, and an increased incidence of developing cancer. The study of Fanconi anemia has improve ...
is a risk factor for developing acute myeloid leukemia. Mutation in SPRED1 gene has been associated with a predisposition to childhood leukemia.
Inherited bone marrow failure syndromes represent a kind of premature aging of the bone marrow. In people with these syndromes and in older adults, mutations associated with clonal hematopoiesis
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential, or CHIP, is a common aging-related phenomenon in which hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) or other early blood cell progenitors contribute to the formation of a genetically distinct subpopulation of b ...
may arise as an adaptive response to a progressively deteriorating hematopoietic niche, i.e., a depleting pool of Hematopoietic stem cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within the ...
. The mutated stem cells then acquire a self-renewal advantage.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myeloid leukemia, is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumula ...
is associated with a genetic abnormality called the Philadelphia translocation; 95% of people with CML carry the Philadelphia mutation, although this is not exclusive to CML and can be observed in people with other types of leukemia.
Non-ionizing radiation
Whether or not non-ionizing radiation causes leukemia has been studied for several decades. TheInternational Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC; ) is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organization of the United Nations.
Its role is to conduct and coordinate research into the causes of cancer. It also cance ...
expert working group undertook a detailed review of all data on static and extremely low frequency
Extremely low frequency (ELF) is the ITU designation for electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz, and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively. In atmospheric sc ...
electromagnetic energy, which occurs naturally and in association with the generation, transmission, and use of electrical power. They concluded that there is limited evidence that high levels of ELF
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic peoples, Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in Norse mythology, North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'' ...
magnetic (but not electric) fields might cause some cases of childhood leukemia. No evidence for a relationship to leukemia or another form of malignancy in adults has been demonstrated. Since exposure to such levels of ELFs is relatively uncommon, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
concludes that ELF exposure, if later proven to be causative, would account for just 100 to 2400 cases worldwide each year, representing 0.2 to 4.9% of the total incidence of childhood leukemia for that year (about 0.03 to 0.9% of all leukemias).
Diagnosis
 Diagnosis is usually based on repeated
Diagnosis is usually based on repeated complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC) or full haemogram (FHG), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide cytometry, information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blo ...
s and a bone marrow examination
Bone marrow examination refers to the pathologic analysis of samples of bone marrow obtained by bone marrow biopsy (often called trephine biopsy) and bone marrow aspiration. Bone marrow examination is used in the diagnosis of a number of conditi ...
following observations of the symptoms. Sometimes, blood tests may not show that a person has leukemia, especially in the early stages of the disease or during remission. A lymph node biopsy can be performed to diagnose certain types of leukemia in certain situations.
Following diagnosis, blood chemistry tests can be used to determine the degree of liver and kidney damage or the effects of chemotherapy on the person. When concerns arise about other damages due to leukemia, doctors may use an X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
, MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
, or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
. These can potentially show leukemia's effects on such body parts as bones (X-ray), the brain (MRI), or the kidneys, spleen, and liver (ultrasound). CT scans
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
can be used to check lymph nodes in the chest, though this is uncommon.
Despite the use of these methods to diagnose whether or not a person has leukemia, many people have not been diagnosed because many of the symptoms are vague, non-specific, and can refer to other diseases. For this reason, the American Cancer Society estimates that at least one-fifth of the people with leukemia have not yet been diagnosed.
Treatment
Most forms of leukemia are treated with pharmaceuticalmedication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceutical drug, medicinal product, medicinal drug or simply drug) is a drug used to medical diagnosis, diagnose, cure, treat, or preventive medicine, prevent disease. Drug therapy (pharmaco ...
, typically combined into a multi-drug chemotherapy regimen
A chemotherapy regimen is a regimen for chemotherapy, defining the drugs to be used, their dosage, the frequency and duration of treatments, and other considerations. In modern oncology, many regimens combine several chemotherapy drugs in combi ...
. Some are also treated with radiation therapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a therapy, treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of treatment of cancer, cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignancy, malignant cell (biology), ...
. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
is effective.
Acute lymphoblastic
Management of ALL is directed towards control of bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease. Additionally, treatment must prevent leukemic cells from spreading to other sites, particularly thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
(CNS); periodic lumbar punctures are used for diagnostic purposes and to administer intrathecal prophylactic methotrexate. In general, ALL treatment is divided into several phases:
* ''Induction chemotherapy'' to bring about bone marrow remission. For adults, standard induction plans include prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
, vincristine
Vincristine, also known as leurocristine and sold under the brand name Oncovin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes acute lymphocytic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia, Hodgkin lym ...
, and an anthracycline
Anthracyclines are a class of drugs used in cancer chemotherapy that are extracted from '' Streptomyces peucetius'' bacterium. These compounds are used to treat many cancers, including leukemias, lymphomas, breast, stomach, uterine, ovarian, b ...
drug; other drug plans may include L-asparaginase
Asparaginase is an enzyme that is used as a medication and in food manufacturing. As a medication, L-asparaginase is used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL). It is given by injection into a vein, or ...
or cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
. For children with low-risk ALL, standard therapy usually consists of three drugs (prednisone, L-asparaginase, and vincristine) for the first month of treatment.
* ''Consolidation therapy'' or ''intensification therapy'' to eliminate any remaining leukemia cells. There are many different approaches to consolidation, but it is typically a high-dose, multi-drug treatment that is undertaken for a few months. People with low- to average-risk ALL receive therapy with antimetabolite
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolat ...
drugs such as methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
and 6-mercaptopurine
Mercaptopurine (6-MP), sold under the brand name Purinethol among others, is a medication used for cancer and autoimmune diseases. Specifically it is used to treat acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), Crohn's d ...
(6-MP). People who are high-risk receive higher drug doses of these drugs, plus additional drugs.
* '' CNS prophylaxis'' (preventive therapy) to stop cancer from spreading to the brain and nervous system in high-risk people. Standard prophylaxis
Preventive healthcare, or prophylaxis, is the application of healthcare measures to prevent diseases.Hugh R. Leavell and E. Gurney Clark as "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life, and promoting physical and mental health a ...
may include radiation of the head and/or drugs delivered directly into the spine.
* ''Maintenance treatments'' with chemotherapeutic drugs to prevent disease recurrence once remission has been achieved. Maintenance therapy usually involves lower drug doses and may continue for up to three years.
* Alternatively, '' allogeneic bone marrow transplantation'' may be appropriate for high-risk or relapsed people.
Chronic lymphocytic
Decision to treat
Hematologist
Hematology ( spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production ...
s base CLL treatment on both the stage and symptoms of the individual person. A large group of people with CLL have low-grade disease, which does not benefit from treatment. Individuals with CLL-related complications or more advanced disease often benefit from treatment. In general, the indications for treatment are:
* Falling hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin ...
or platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no ...
count
* Progression to a later stage of disease
* Painful, disease-related overgrowth of lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
s or spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
* An increase in the rate of lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
production
Treatment approach
Most CLL cases are incurable by present treatments, so treatment is directed towards suppressing the disease for many years, rather than curing it. The primary chemotherapeutic plan iscombination
In mathematics, a combination is a selection of items from a set that has distinct members, such that the order of selection does not matter (unlike permutations). For example, given three fruits, say an apple, an orange and a pear, there are ...
chemotherapy with chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
, plus a corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
such as prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
or prednisolone
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid, a steroid hormone used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammation, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, Electrolyte imbalance, electrolyte imbalances and skin conditions. Some of ...
. The use of a corticosteroid has the additional benefit of suppressing some related autoimmune diseases, such as immunohemolytic anemia or immune-mediated thrombocytopenia. In resistant cases, single-agent treatments with nucleoside drugs such as fludarabine, pentostatin, or cladribine may be successful. Younger and healthier people may choose allogeneic
Allotransplant (''allo-'' meaning "other" in Greek) is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, ...
or autologous
Autotransplantation is the transplantation of organs, tissues, or even particular proteins from one part of the body to another in the same person ('' auto-'' meaning "self" in Greek).
The autologous tissue (also called autogenous, autogenei ...
bone marrow transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
in the hope of a permanent cure.
Acute myelogenous
Many different anti-cancer drugs are effective for the treatment of AML. Treatments vary somewhat according to the age of the person and according to the specific subtype of AML. Overall, the strategy is to control bone marrow and systemic (whole-body) disease, while offering specific treatment for the central nervous system (CNS), if involved. In general, most oncologists rely on combinations of drugs for the initial, ''induction phase'' of chemotherapy. Such combination chemotherapy usually offers the benefits of early remission and a lower risk of disease resistance. ''Consolidation'' and ''maintenance'' treatments are intended to prevent disease recurrence. Consolidation treatment often entails a repetition of induction chemotherapy or the intensification of chemotherapy with additional drugs. By contrast, maintenance treatment involves drug doses that are lower than those administered during the induction phase.Chronic myelogenous
There are many possible treatments for CML, but the standard of care for newly diagnosed people isimatinib
Imatinib, sold under the brand names Gleevec and Glivec (both marketed worldwide by Novartis) among others, is an oral targeted therapy medication used to treat cancer. Imatinib is a small molecule inhibitor targeting multiple tyrosine kinases ...
(Gleevec) therapy. Compared to most anti-cancer drugs, it has relatively few side effects and can be taken orally at home. With this drug, more than 90% of people will be able to keep the disease in check for at least five years, so that CML becomes a chronic, manageable condition.
In a more advanced, uncontrolled state, when the person cannot tolerate imatinib, or if the person wishes to attempt a permanent cure, then an allogeneic bone marrow transplantation may be performed. This procedure involves high-dose chemotherapy and radiation followed by infusion of bone marrow from a compatible donor. Approximately 30% of people die from this procedure.
Hairy cell
Decision to treatPeople with hairy cell leukemia who are symptom-free typically do not receive immediate treatment. Treatment is generally considered necessary when the person shows signs and symptoms such as low blood cell counts (e.g., infection-fighting neutrophil count below 1.0 K/μL), frequent infections, unexplained bruises, anemia, or fatigue that is significant enough to disrupt the person's everyday life. Typical treatment approach
People who need treatment usually receive either one week of cladribine, given daily by intravenous infusion or a simple injection under the skin, or six months of pentostatin, given every four weeks by intravenous infusion. In most cases, one round of treatment will produce a prolonged remission. Other treatments include
rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and ad ...
infusion or self-injection with Interferon-alpha. In limited cases, the person may benefit from ''splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of ...
'' (removal of the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
). These treatments are not typically given as the first treatment because their success rates are lower than cladribine or pentostatin.
T-cell prolymphocytic
Most people with T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, a rare and aggressive leukemia with a median survival of less than one year, require immediate treatment. T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is difficult to treat, and it does not respond to most available chemotherapeutic drugs. Many different treatments have been attempted, with limited success in certain people: purine analogues (pentostatin, fludarabine, cladribine), chlorambucil, and various forms of combination chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, prednisone CHOP, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, prednisone OP vincristine, doxorubicin, prednisone, etoposide, cyclophosphamide, bleomycin VAPEC-B). Alemtuzumab (Campath), amonoclonal antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodie ...
that attacks white blood cells, has been used in treatment with greater success than previous options.
Some people who successfully respond to treatment also undergo stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
to consolidate the response.
Juvenile myelomonocytic
Treatment forjuvenile myelomonocytic leukemia
Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML) is a rare form of chronic leukemia (cancer of the blood) that affects children, commonly those aged four and younger. The name JMML now encompasses all diagnoses formerly referred to as juvenile chronic mye ...
can include splenectomy
A splenectomy is the surgical procedure that partially or completely removes the spleen. The spleen is an important organ in regard to immunological function due to its ability to efficiently destroy encapsulated bacteria. Therefore, removal of ...
, chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated chemo, sometimes CTX and CTx) is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (list of chemotherapeutic agents, chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) in a standard chemotherapy re ...
, and bone marrow transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood, in order to replicate inside a patient and produce a ...
.
Prognosis
The success of treatment depends on the type of leukemia and the age of the person. Outcomes have improved in the developed world. The averagefive-year survival rate
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surv ...
is 65% in the United States. In children under 15, the five-year survival rate is greater (60 to 85%), depending on the type of leukemia. In children with acute leukemia who are cancer-free after five years, the cancer is unlikely to return.
Outcomes depend on whether it is acute or chronic, the specific abnormal white blood cell type, the presence and severity of anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
or thrombocytopenia
In hematology, thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets (also known as thrombocytes) in the blood. Low levels of platelets in turn may lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding. It is the most common coag ...
, the degree of tissue abnormality, the presence of metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, ...
and lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that includ ...
and bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It i ...
infiltration, the availability of therapies and the skills of the health care team. Treatment outcomes may be better when people are treated at larger centers with greater experience.
Epidemiology
developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
.
United States
About 245,000 people in the United States are affected with some form of leukemia, including those that have achieved remission or cure. Rates from 1975 to 2011 have increased by 0.7% per year among children. Approximately 44,270 new cases of leukemia were diagnosed in the year 2008 in the US. This represents 2.9% of all cancers (excluding simple basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers) in the United States, and 30.4% of allblood cancer
Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (American English) or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues (British English) are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are al ...
s.
Among children with some form of cancer, about a third have a type of leukemia, most commonly acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a cancer of the Lymphocyte, lymphoid line of blood cells characterized by the development of large numbers of lymphoblast, immature lymphocytes. Symptoms may include feeling tired, pale skin color, fever, ...
. A type of leukemia is the second most common form of cancer in infants (under the age of 12 months) and the most common form of cancer in older children. Boys are somewhat more likely to develop leukemia than girls, and white American children are almost twice as likely to develop leukemia than black American children. Only about 3% cancer diagnoses among adults are for leukemias, but because cancer is much more common among adults, more than 90% of all leukemias are diagnosed in adults.
Race is a risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
in the United States. Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
s, especially those under the age of 20, are at the highest risk for leukemia, while whites
White is a racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly European ancestry. It is also a skin color specifier, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, ethnicity and point of view.
De ...
, Native Americans, Asian Americans
Asian Americans are Americans with Asian diaspora, ancestry from the continent of Asia (including naturalized Americans who are Immigration to the United States, immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of those immigrants).
A ...
, and Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tli ...
are at higher risk than African Americans
African Americans, also known as Black Americans and formerly also called Afro-Americans, are an American racial and ethnic group that consists of Americans who have total or partial ancestry from any of the Black racial groups of Africa ...
.
More men than women are diagnosed with leukemia and die from the disease. Around 30 percent more men than women have leukemia.
Australia
In Australia, leukemia is the eleventh most common cancer. In 2014–2018, Australians diagnosed with leukemia had a 64% chance (65% for males and 64% for females) of surviving for five years compared to the rest of the Australian population–there was a 21% increase in survival rates between 1989–1993.UK
Overall, leukemia is the eleventh most common cancer in the UK (around 8,600 people were diagnosed with the disease in 2011), and it is the ninth most common cause of cancer death (around 4,800 people died in 2012).History
 Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist
Leukemia was first described by anatomist and surgeon Alfred-Armand-Louis-Marie Velpeau in 1827. A more complete description was given by pathologist Rudolf Virchow
Rudolf Ludwig Carl Virchow ( ; ; 13 October 18215 September 1902) was a German physician, anthropologist, pathologist, prehistorian, biologist, writer, editor, and politician. He is known as "the father of modern pathology" and as the founder o ...
in 1845. Around ten years after Virchow's findings, pathologist Franz Ernst Christian Neumann
Franz Ernst Christian Neumann (30 January 1834 – 6 March 1918) was a German pathologist who was a native of Königsberg. His common name was Ernst Neumann.
Life
He was the son of physicist Franz Ernst Neumann (1798–1895), and grandson of chem ...
found that the bone marrow of a deceased person with leukemia was colored "dirty green-yellow" as opposed to the normal red. This finding allowed Neumann to conclude that a bone marrow problem was responsible for the abnormal blood of people with leukemia.
By 1900, leukemia was viewed as a family of diseases as opposed to a single disease. By 1947, Boston pathologist Sidney Farber
Sidney Farber (September 30, 1903 – March 30, 1973) was an American pediatric pathologist at Boston Children's Hospital. He is regarded as the father of modern chemotherapy for his work using folic acid antagonists to combat leukemia, which l ...
believed from past experiments that aminopterin
Aminopterin (or 4-aminopteroic acid), the 4–amino derivative of folic acid, is an antineoplastic drug with immunosuppressive properties often used in chemotherapy. Aminopterin is a synthetic derivative of pterin. Aminopterin works as an enzyme ...
, a folic acid mimic, could potentially cure leukemia in children. The majority of the children with ALL who were tested showed signs of improvement in their bone marrow, but none of them were actually cured. Nevertheless, this result did lead to further experiments.
In 1962, researchers Emil J. Freireich, Jr. and Emil Frei III used combination chemotherapy to attempt to cure leukemia. The tests were successful with some people surviving long after the tests.
Etymology
Observing an abnormally large number of white blood cells in a blood sample from a person, Virchow called the condition ''Leukämie'' inGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
, which he formed from the two Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
words ''leukos'' ( λευκός), meaning 'white', and ''haima'' ( αἷμα), meaning 'blood'. It was formerly also called ''leucemia''.
Society and culture
According toSusan Sontag
Susan Lee Sontag (; January 16, 1933 – December 28, 2004) was an American writer, critic, and public intellectual. She mostly wrote essays, but also published novels; she published her first major work, the essay "Notes on "Camp", Notes on 'Ca ...
, leukemia was often romanticized in 20th-century fiction, portrayed as a joy-ending, clean disease whose fair, innocent and gentle victims die young or at the wrong time. As such, it was the cultural successor to tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, which held this cultural position until it was discovered to be an infectious disease. The 1970 romance novel '' Love Story'' is an example of this romanticization of leukemia.
In the United States, around $5.4 billion is spent on treatment a year.
Research directions
Significant research into the causes, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of leukemia is being performed. Hundreds ofclinical trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
are being planned or conducted at any given time. Studies may focus on effective means of treatment, better ways of treating the disease, improving the quality of life for people, or appropriate care in remission or after cures.
In general, there are two types of leukemia research: clinical or translational research
Translational research (also called translation research, translational science, or, when the context is clear, simply translation) is research aimed at translating (converting) results in basic research into results that directly benefit humans ...
and basic research
Basic research, also called pure research, fundamental research, basic science, or pure science, is a type of scientific research with the aim of improving scientific theories for better understanding and prediction of natural or other phenome ...
. Clinical/translational research focuses on studying the disease in a defined and generally immediately applicable way, such as testing a new drug in people. By contrast, basic science research studies the disease process at a distance, such as seeing whether a suspected carcinogen can cause leukemic changes in isolated cells in the laboratory or how the DNA changes inside leukemia cells as the disease progresses. The results from basic research studies are generally less immediately useful to people with the disease.
Treatment through gene therapy
Gene therapy is Health technology, medical technology that aims to produce a therapeutic effect through the manipulation of gene expression or through altering the biological properties of living cells.
The first attempt at modifying human DNA ...
is currently being pursued. One such approach used genetically modified T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
s, known as chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T cells), to attack cancer cells. In 2011, a year after treatment, two of the three people with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia were reported to be cancer-free and in 2013, three of five subjects who had acute lymphocytic leukemia were reported to be in remission for five months to two years. Subsequent studies with a variety of CAR-T types continue to be promising. As of 2018, two CAR-T therapies have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
. CAR-T treatment has significant side effects, and loss of the antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
...
targeted by the CAR-T cells is a common mechanism for relapse. The stem cells that cause different types of leukemia are also being researched.
Pregnancy
Leukemia is rarely associated with pregnancy, affecting only about 1 in 10,000 pregnant women. How it is handled depends primarily on the type of leukemia. Nearly all leukemias appearing in pregnant women are acute leukemias. Acute leukemias normally require prompt, aggressive treatment, despite significant risks ofpregnancy loss Pregnancy loss is the loss of an embryo or fetus. The terms early pregnancy loss and late pregnancy loss are often used but there is no consensus over their definitions.
Unintentional pregnancy loss
* Miscarriage
** Toxic abortion, caused by poll ...
and birth defects
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth de ...
, especially if chemotherapy is given during the developmentally sensitive first trimester
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception usually occurs following vaginal intercourse, but can also ...
. Chronic myelogenous leukemia can be treated with relative safety at any time during pregnancy with Interferon-alpha hormones. Treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemias, which are rare in pregnant women, can often be postponed until after the end of the pregnancy.
See also
* Acute erythroid leukemia * Antileukemic drugs, medications used to kill leukemia cells * Cancer-related fatigue *Hematologic disease
Hematologic diseases are disorders which primarily affect the blood and blood-forming organs. Hematologic diseases include rare genetic disorders, anemia, HIV, sickle cell disease and complications from chemotherapy or transfusions.
Myeloid
* ...
s, the large class of blood-related disorders, including leukemia
* Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone ...
References
External links
Leukaemia information
from
Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK (CRUK) is the world's largest independent cancer research organisation. It is registered as a charity in the United Kingdom and Isle of Man, and was formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and t ...
{{Authority control
Articles containing video clips
Lymphatic vessel diseases
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate