Leucyl Aminopeptidase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Leucyl aminopeptidases (, ''leucine aminopeptidase'', ''LAPs'', ''leucyl peptidase'', ''peptidase S'', ''cytosol aminopeptidase'', ''cathepsin III'', ''L-leucine aminopeptidase'', ''leucinaminopeptidase'', ''leucinamide aminopeptidase'', ''FTBL proteins'', ''proteinates FTBL'', ''aminopeptidase II'', ''aminopeptidase III'', ''aminopeptidase I'') are
 The
The
 bovine lens LAP and PepA have been elucidated (Ref 1 and 2), however, the exact mechanism of tomato LAP-A is unknown at this time. A search of current literature does not indicate that new research is underway to determine the exact mechanism of LAP-A. Based on the biochemical similarities of the LAPs between kingdoms, the mechanism of LAP-A may be similar to bovine lens LAP and PepA.
bovine lens LAP and PepA have been elucidated (Ref 1 and 2), however, the exact mechanism of tomato LAP-A is unknown at this time. A search of current literature does not indicate that new research is underway to determine the exact mechanism of LAP-A. Based on the biochemical similarities of the LAPs between kingdoms, the mechanism of LAP-A may be similar to bovine lens LAP and PepA.
 The plant response in this octadecanoid pathway is similar to
The plant response in this octadecanoid pathway is similar to
M17.001
Bacteri
M17.003
Plant
M17.002
* {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Chemical pathology Tumor markers EC 3.4.11
enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
that preferentially catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
of leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- ca ...
residues at the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
of peptides
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
and proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
. Other N-terminal residues can also be cleaved, however. LAPs have been found across superkingdoms. Identified LAPs include human LAP, bovine
Bovines (subfamily Bovinae) comprise a diverse group of 10 genera of medium to large-sized ungulates, including cattle, bison, African buffalo, water buffalos, and the four-horned and spiral-horned antelopes. The evolutionary relationship betwee ...
lens LAP, porcine
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), often called swine, hog, or domestic pig when distinguishing from other members of the genus '' Sus'', is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is variously considered a subspecies of ''Sus s ...
LAP, ''Escherichia coli'' (''E. coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'') LAP (also known as PepA or XerB), and the solanaceous
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and orna ...
-specific acidic LAP (LAP-A) in tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
(''Solanum lycopersicum'').
Enzyme description, structure, and active site
 The
The active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) a ...
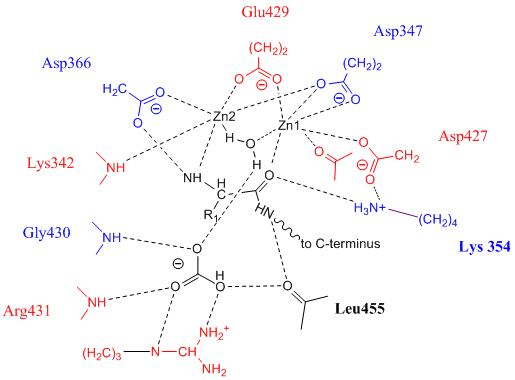
s in PepA and in bovine lens LAP have been found to be similar. Shown in the picture below is the proposed model for the active site of LAP-A in tomato based on the work of Strater ''et al''. It is also known that the biochemistry
Biochemistry or biological chemistry is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology and ...
of the LAPs from these three kingdoms
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
is very similar. PepA, bovine lens LAP, and LAP-A preferentially cleave N-terminal leucine, arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
, and methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
residues. These enzymes are all metallopeptidases requiring divalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
cations
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convent ...
for their enzymatic activity Enzymes are active in the presence of Mn+2, Mg+2 and Zn+2. These enzymes are also known to have high pH (pH 8) and temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
optima. At pH 8, the highest enzymatic activity is seen at 60 °C. PepA, bovine lens LAP and LAP-A are also known to form hexamer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative ...
s ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
''. The Gu et al. from 1999 demonstrated that six 55kDA enzymatically inactive LAP-A protomer
In structural biology, a protomer is the structural unit of an oligomeric protein. It is the smallest unit composed of at least two different protein chains that form a larger hetero-oligomer by association of two or more copies of this unit.
The ...
s come together to form the 353kDa bioactive LAP-A hexamer. Structures of the bovine lens LAP protomer and the biologically active hexamer have been constructed can be found through Protein Data Bank (2J9A).
Mechanism(s)
Historically, the mechanisms ofcarboxypeptidase
A carboxypeptidase ( EC number 3.4.16 - 3.4.18) is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes (cleaves) a peptide bond at the carboxy-terminal (C-terminal) end of a protein or peptide. This is in contrast to an aminopeptidases, which cleave peptide bonds at ...
s and endoprotease
Endopeptidase or endoproteinase are proteolytic peptidases that break peptide bonds of nonterminal amino acids (i.e. within the molecule), in contrast to exopeptidases, which break peptide bonds from end-pieces of terminal amino acids. For this re ...
have been much more well-studied and understood by researchers (Ref #6 Lipscomb 1990). Work within the past two decades has provided vital knowledge regarding the mechanisms of aminopeptidases. The mechanism of  bovine lens LAP and PepA have been elucidated (Ref 1 and 2), however, the exact mechanism of tomato LAP-A is unknown at this time. A search of current literature does not indicate that new research is underway to determine the exact mechanism of LAP-A. Based on the biochemical similarities of the LAPs between kingdoms, the mechanism of LAP-A may be similar to bovine lens LAP and PepA.
bovine lens LAP and PepA have been elucidated (Ref 1 and 2), however, the exact mechanism of tomato LAP-A is unknown at this time. A search of current literature does not indicate that new research is underway to determine the exact mechanism of LAP-A. Based on the biochemical similarities of the LAPs between kingdoms, the mechanism of LAP-A may be similar to bovine lens LAP and PepA.
Biological function
Once thought of as ahousekeeping gene
In molecular biology, housekeeping genes are typically constitutive genes that are required for the maintenance of basic cellular function, and are expressed in all cells of an organism under normal and patho-physiological conditions. Although ...
necessary only for protein turnover
In cell biology, protein turnover refers to the replacement of older proteins as they are broken down within the cell. Different types of proteins have very different turnover rates.
A balance between protein synthesis and protein degradation is ...
, studies have demonstrated that LAP-A has a regulatory role in the immune
In biology, immunity is the capability of multicellular organisms to resist harmful microorganisms. Immunity involves both specific and nonspecific components. The nonspecific components act as barriers or eliminators of a wide range of pathogens ...
response in tomato.
Background on plant immune response
In order to survive, plants must be able to respond to many biotic andabiotic
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them under ...
stresses, including pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
attack, piercing/sucking insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s, herbivory
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, and mechanical wounding. These stresses activate specialized signal transduction pathways
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
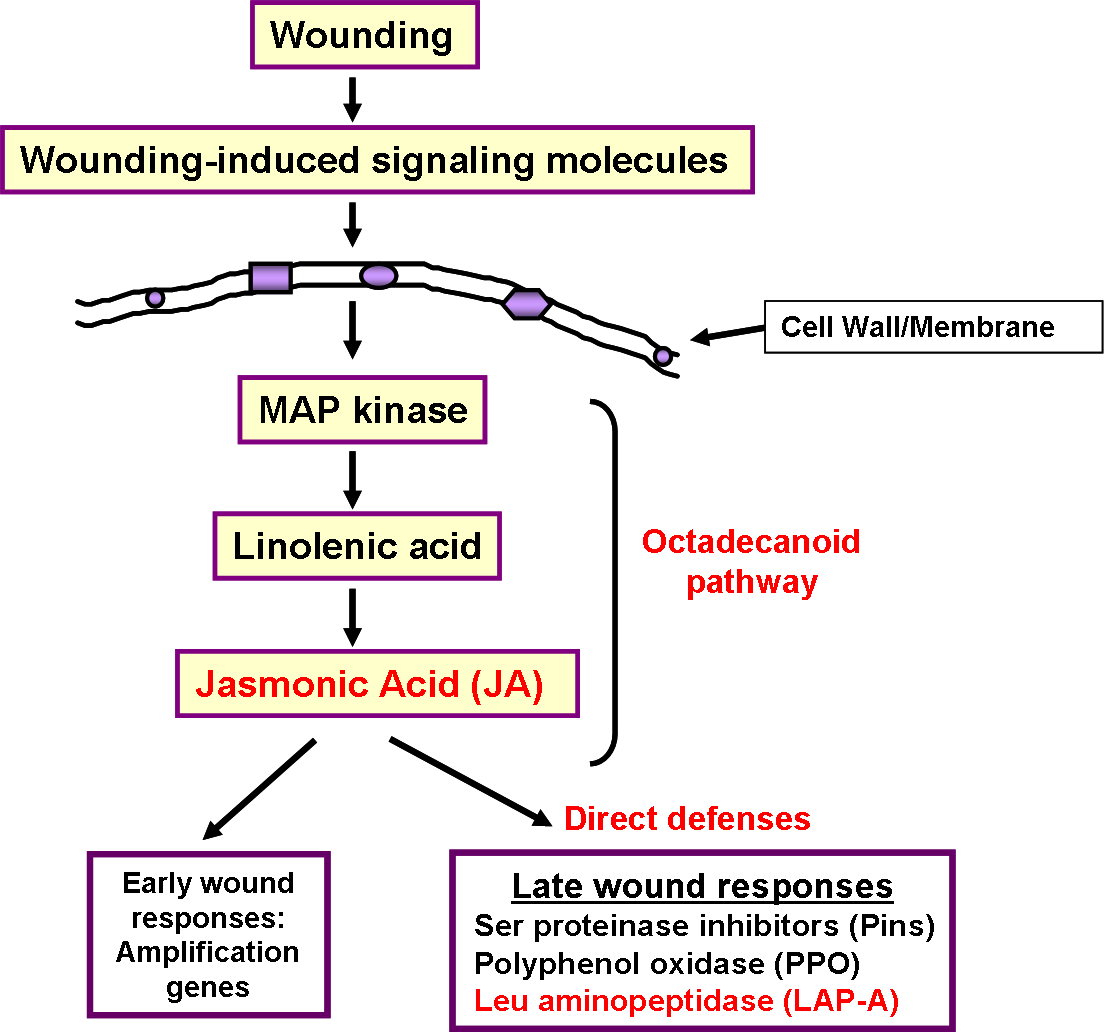
, which are specific to the stressor and the amount of tissue damage inflicted. Similar to mechanical wounding, chewing insects, such as the tobacco hornworm (Manduca sexta, one of the major pests of tomato), cause extensive tissue damage activating the jasmonic acid
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine. The molecule is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. It was first isolat ...
(JA)-mediated response (Walling 2000). This JA-mediated response revolves around the octadecanoid pathway
The octadecanoid pathway is a biosynthetic pathway for the production of the phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA), an important hormone for induction of defense genes. JA is synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid, which can be released from the plasma ...
, which is responsible for the synthesis of JA and several other potent signaling molecules, and ends in the regulation of two sets of genes
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
whose expression changes over time. The early genes amplify the wounding signal and can be detected 30 minutes to 2 hours after damage (Ryan 2000). Late gene expression can be seen 4–24 hours after wounding. Products of late-response genes act as deterrents to chewing-insect feeding, often by decreasing the nutritional value of the food ingested or interfering with insect gut function (Walling 2000). For example, serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
proteinase inhibitors (Pins) interfere with digestive proteases in the insect gut and polyphenol oxidase
Polyphenol oxidase (PPO; also polyphenol oxidase i, chloroplastic), an enzyme involved in fruit browning, is a tetramer that contains four atoms of copper per molecule.
PPO may accept monophenols and/or ''o''-diphenols as substrates. The ...
s (PPO) act to decrease the nutritive value of plant leaves after ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms ingest ...
by herbivores (Johnson et al. 1989; Ryan 2000; Orozco-Cardenas 2001). Please see the Picture 3 for a summary of the wound response in tomato. The plant response in this octadecanoid pathway is similar to
The plant response in this octadecanoid pathway is similar to mammalian
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a ...
prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derive ...
and
leukotriene
Leukotrienes are a family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced in leukocytes by the oxidation of arachidonic acid (AA) and the essential fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) by the enzyme arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase.
Leukotrienes ...
pathways (Ref Walling 2000). This particular pathway is inhibited by salicylic acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substance ...
.
Octadecanoid pathway
(LAP-A), a product of the octadecanoid pathway in some solanaceous plants, has been shown by Fowler ''et al.'' to have a regulatory role in the late wound response of tomato. Experiments were conducted using threegenotypes
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
of tomato plants: wildtype
The wild type (WT) is the phenotype of the typical form of a species as it occurs in nature. Originally, the wild type was conceptualized as a product of the standard "normal" allele at a locus, in contrast to that produced by a non-standard, "m ...
(WT), (LapA-SI) plants that were silenced for LAP-A, and LapA-OX that constitutively expressed LAP-A. Late-gene expression was inhibited in wounded LapA-SI plants, and the LapA-SI plants were also more susceptible to tobacco hornworm feeding, relative to wildtype (WT) plants. In comparison, the wounded LapA-OX leaves exhibited heightened levels of late gene RNA accumulation, an increased resistance to herbivory, and extended expression of late wound-response genes. These data suggest that LAP-A functions in regulating both the intensity and the persistence of the late wound response. However, unwounded LapA-OX did not accumulate late gene RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
transcripts, suggesting that presence of LAP-A alone is not sufficient to induce late gene expression. LAP-A is the first plant aminopeptidase shown to have a regulatory role in signal transduction pathway.
Osmoregulation
LAP proteins are expressed in a variety of marine organisms as a method of coping with the osmotic threat high salinity poses to the cell. During bouts of high salinity, LAP begins the catalysis of proteins in order to release amino acids into the cell in an attempt to balance the high ion concentrations in the external environment.References
;Sources * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* TheMEROPS
MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The classification scheme for peptidases was published by Rawlings & Barrett in 1993, and that for protein inhibitor ...
online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: AnimaM17.001
Bacteri
M17.003
Plant
M17.002
* {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Chemical pathology Tumor markers EC 3.4.11