Late Glacial Maximum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that
 The average global temperature around 19,000 BC (about 21,000 years ago) was about 6 °C (11 °F) colder than today.
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), permanent summer ice covered about 8% of Earth's surface and 25% of the land area during the last glacial maximum.Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey
The average global temperature around 19,000 BC (about 21,000 years ago) was about 6 °C (11 °F) colder than today.
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), permanent summer ice covered about 8% of Earth's surface and 25% of the land area during the last glacial maximum.Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey
"Sea Level and Climate"
United States Geological Survey. The USGS also states that sea level was about lower than in present times (2012). When comparing to the present, the average global temperature was for the 2013–2017 period. "Land and Ocean Summary"
Berkeley Earth. Currently (as of 2012), about 3.1% of Earth's surface and 10.7% of the land area is covered in year-round ice. The formation of an ice sheet or Most of the world's deserts expanded. Exceptions were in what is now the
Most of the world's deserts expanded. Exceptions were in what is now the
PMIP Web Site
an
'Publications : Last Glacial Maximum.
*Paleoclimate Modelling Intercomparison Project Phase II (PMIP2
''PMIP2 Home page''
an
PMIP 2 Publications.
* {{Ice Ages Ice ages Glaciology
 The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's climate by causing drought, desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
, and a large drop in sea levels.
Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to between 25,200 and 23,100 years ago.
The LGM is referred to in Britain as the Dimlington Stadial
Stadials and interstadials are phases dividing the Quaternary period, or the last 2.6 million years. Stadials are periods of colder climate while interstadials are periods of warmer climate.
Each Quaternary climate phase is associated with a Ma ...
, dated to between 31,000 and 16,000 years.
In the archaeology of Paleolithic Europe
Paleolithic Europe, or Old Stone Age Europe, encompasses the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age in Europe from the arrival of the first archaic humans, about 1.4 million years ago until the beginning of the Mesolithic (also Epipaleolithic) around 10,000 ...
, the LGM spans the Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic
associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where t ...
, Gravettian
The Gravettian was an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by ...
, Solutrean
The Solutrean industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites have been found in modern-day France, Spain and Portugal.
Details
...
, Magdalenian
The Magdalenian cultures (also Madelenian; French: ''Magdalénien'') are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12,000 years ago. It is named after the type site of La Madele ...
and Périgordian
Périgordian is a term for several distinct but related Upper Palaeolithic cultures which are thought by some archaeologists to represent a contiguous tradition. Thought to have existed between c.35,000 BP and c.20,000 BP the Perigordian was th ...
cultures.
The LGM was followed by the Late Glacial Interstadial
The Late Glacial Interstadial (LGI) c. 14,670 to c. 12,890 BP, also called the Bølling–Allerød interstadial, represents the first ''pronounced'' warming since the end of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). Human populations, which had previousl ...
.
Glacial climate
 The average global temperature around 19,000 BC (about 21,000 years ago) was about 6 °C (11 °F) colder than today.
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), permanent summer ice covered about 8% of Earth's surface and 25% of the land area during the last glacial maximum.Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey
The average global temperature around 19,000 BC (about 21,000 years ago) was about 6 °C (11 °F) colder than today.
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), permanent summer ice covered about 8% of Earth's surface and 25% of the land area during the last glacial maximum.Richard Z. Poore, Richard S. Williams, Jr., and Christopher Tracey"Sea Level and Climate"
United States Geological Survey. The USGS also states that sea level was about lower than in present times (2012). When comparing to the present, the average global temperature was for the 2013–2017 period. "Land and Ocean Summary"
Berkeley Earth. Currently (as of 2012), about 3.1% of Earth's surface and 10.7% of the land area is covered in year-round ice. The formation of an ice sheet or
ice cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
requires both prolonged cold and precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
(snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
). Hence, despite having temperatures similar to those of glaciated areas in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
, East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea and ...
remained unglaciated except at higher elevations. This difference was because the ice sheets in Europe produced extensive anticyclone
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from abov ...
s above them. These anticyclones generated air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and humidity. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adapt to the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to la ...
es that were so dry on reaching Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
and Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer Manc ...
that precipitation sufficient for the formation of glaciers could never occur (except in Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (russian: полуостров Камчатка, Poluostrov Kamchatka, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and wes ...
where these westerly winds lifted moisture from the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it h ...
). The relative warmth of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
due to the shutting down of the Oyashio Current
, also known as Oya Siwo, Okhotsk or the Kurile current, is a cold subarctic ocean current that flows south and circulates counterclockwise in the western North Pacific Ocean. The waters of the Oyashio Current originate in the Arctic Ocean an ...
and the presence of large east-west mountain ranges were secondary factors preventing continental glaciation in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
.
All over the world, climates at the Last Glacial Maximum were cooler and almost everywhere drier. In extreme cases, such as South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
and the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, rainfall could have been diminished by up to 90% compared to the present, with flora diminished to almost the same degree as in glaciated areas of Europe and North America. Even in less affected regions, rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
cover was greatly diminished, especially in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
where a few refugia were surrounded by tropical grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
s.
The Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, Amazon jungle or ; es, Selva amazónica, , or usually ; french: Forêt amazonienne; nl, Amazoneregenwoud. In English, the names are sometimes capitalized further, as Amazon Rainforest, Amazon Forest, or Amazon Jungle. ...
was split into two large blocks by extensive savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
, and the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
probably were similarly affected, with deciduous forests expanding in their place except on the east and west extremities of the Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
shelf. Only in Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
and the Chocó region of Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
did tropical rainforests remain substantially intact – probably due to the extraordinarily heavy rainfall of these regions.
western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
, where changes in the jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering thermal wind, air currents in the Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are west ...
brought heavy rain to areas that are now desert and large pluvial lake
A pluvial lake is a body of water that accumulated in a basin because of a greater moisture availability resulting from changes in temperature and/or precipitation. These intervals of greater moisture availability are not always contemporaneous ...
s formed, the best known being Lake Bonneville
Lake Bonneville was the largest Late Pleistocene paleolake in the Great Basin of western North America. It was a pluvial lake that formed in response to an increase in precipitation and a decrease in evaporation as a result of cooler temperature ...
in Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
. This also occurred in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, where a major lake formed in the Dasht-e Kavir
Dasht-e Kavir ( fa, دشت كوير, lit=Low Plains in classical Persian, from ''khwar'' (low), and ''dasht'' (plain, flatland)), also known as Kavir-e Namak () and the Great Salt Desert, is a large desert lying in the middle of the Iranian Plat ...
.
In Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, shifting sand dunes covered half the continent, while the Chaco and Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazi ...
in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
became similarly dry. Present-day subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
regions also lost most of their forest cover, notably in eastern Australia, the Atlantic Forest
The Atlantic Forest ( pt, Mata Atlântica) is a South American forest that extends along the Atlantic coast of Brazil from Rio Grande do Norte state in the northeast to Rio Grande do Sul state in the south and inland as far as Paraguay and th ...
of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
, and southern China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, where open woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
became dominant due to drier conditions. In northern China – unglaciated despite its cold climate – a mixture of grassland and tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless moun ...
prevailed, and even here, the northern limit of tree growth was at least 20° farther south than today.
In the period before the Last Glacial Maximum, many areas that became completely barren desert were wetter than they are today, notably in southern Australia, where Aboriginal occupation is believed to coincide with a wet period between 40,000 and 60,000 years Before Present
Before Present (BP) years, or "years before present", is a time scale used mainly in archaeology, geology and other scientific disciplines to specify when events occurred relative to the origin of practical radiocarbon dating in the 1950s. Becaus ...
(BP, a formal measurement of uncalibrated radiocarbon years, counted from 1950 CE).
In New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
and neighbouring regions of the Pacific, temperatures may have been further depressed during part of the Last Glacial Maximum by the world's most recent supervolcanic eruption, the Oruanui eruption
The Oruanui eruption of New Zealand's Taupō Volcano (also known as the Kawakawa eruption or Kawakawa/Oruanui event) was the world's most recent Supervolcano#Known supereruptions, supereruption.}
Eruption
With a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 8, ...
, approximately 28,500 years BP.
However, it is estimated that during the Last Glacial Maximum, low-to-mid latitude land surfaces at low elevation cooled on average by 5.8 °C relative to their present day temperatures, based on an analysis of noble gases dissolved in groundwater rather than examinations of species abundances that have been used in the past.
World impact
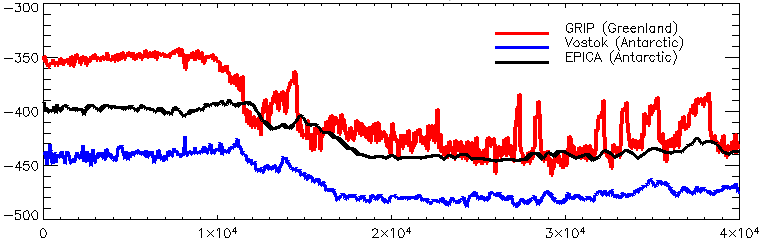
During the Last Glacial Maximum, much of the world was cold, dry, and inhospitable, with frequent storms and a dust-laden atmosphere. The dustiness of the atmosphere is a prominent feature in ice cores; dust levels were as much as 20 to 25 times greater than now.Cowen, Robert C. "Dust Plays a Huge Role in Climate Change" ''Christian Science Monitor'' 3 April 2008 (), and Claquin et al., "Radiative Forcing of Climate by Ice-Age Atmospheric Dust", Climate Dynamics (2003) 20: 193–202. (www.rem.sfu.ca/COPElab/Claquinetal2003_CD_glacialdustRF.pdf) This was probably due to a number of factors: reduced vegetation, stronger global winds, and less precipitation to clear dust from the atmosphere. The massive sheets of ice locked away water, lowering the sea level, exposing continental shelves, joining land masses together, and creating extensivecoastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
s. During the last glacial maximum, 21,000 years ago, the sea level was about 125 meters (about 410 feet) lower than it is today.
Africa and the Middle East
In Africa and the Middle East, many smaller mountain glaciers formed, and theSahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
and other sandy deserts were greatly expanded in extent.
The Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Persis, Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a Mediterranean sea (oceanography), me ...
averages about 35 metres in depth and the seabed between Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi (, ; ar, أَبُو ظَبْيٍ ' ) is the capital and second-most populous city (after Dubai) of the United Arab Emirates. It is also the capital of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi and the centre of the Abu Dhabi Metropolitan Area.
...
and Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
is even shallower, being mostly less than 15 metres deep. For thousands of years the Ur-Shatt (a confluence of the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
-Euphrates River
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
s) provided fresh water to the Gulf, as it flowed through the Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( fa, تنگه هرمز ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' ar, مَضيق هُرمُز ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the ...
into the Gulf of Oman
The Gulf of Oman or Sea of Oman ( ar, خليج عمان ''khalīj ʿumān''; fa, دریای عمان ''daryâ-ye omân''), also known as Gulf of Makran or Sea of Makran ( ar, خلیج مکران ''khalīj makrān''; fa, دریای مکرا� ...
.
Bathymetric
Bathymetry (; ) is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors (''seabed topography''), lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water d ...
data suggests there were two palaeo-basins in the Persian Gulf. The central basin may have approached an area of 20,000 km2, comparable at its fullest extent to lakes such as Lake Malawi
Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, is an African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania.
It is the fifth largest fre ...
in Africa. Between 12,000 and 9,000 years ago much of the Gulf's floor was not covered by water, only being flooded by the sea after 8,000 years ago.
It is estimated that annual average temperatures in Southern Africa were 6 °C lower than at present during the Last Glacial Maximum. This alone would however not have been enough to create a widespread glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
or permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
in the Drakensberg Mountains
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
or the Lesotho Highlands
The Lesotho Highlands are formed by the Drakensberg and Maloti mountain ranges in the east and central parts of the country of Lesotho. Foothills form a divide between the lowlands and the highlands. Snow is common in the highlands in the winter ...
. Seasonal freezing of the ground in the Lesotho Highlands might have reached depths of 2 meter or more below the surface. A few small glaciers did however develop during the Last Glacial Maximum, in particular in south-facing slopes. In the Hex River Mountains
The Hex River Mountains ( af, Hexrivierberge) make up the second highest mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa and are located 120 kilometres (75 miles) north-east of Cape Town. They form part of a large anticline in the Ca ...
, in the Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 2020 ...
, block stream
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
s and terraces found near the summit of Matroosberg evidences past periglacial activity which likely occurred during the Last Glacial Maximum.
Asia
There were ice sheets in modernTibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
(although scientists continue to debate the extent to which the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
was covered with ice) as well as in Baltistan
Baltistan ( ur, ; bft, སྦལ་ཏི་སྟཱན, script=Tibt), also known as Baltiyul or Little Tibet ( bft, སྦལ་ཏི་ཡུལ་།, script=Tibt), is a mountainous region in the Pakistani-administered territory of Gilg ...
and Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory which constitutes a part of the larger Kashmir region and has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. (subscription required) Quote: "Jammu and ...
. In Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, many smaller mountain glaciers formed, and permafrost covered Asia as far south as Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
. Because of lowered sea levels, many of today's islands were joined to the continents: the Indonesian islands as far east as Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
and Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
were connected to the Asian continent in a landmass called Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
. Palawan
Palawan (), officially the Province of Palawan ( cyo, Probinsya i'ang Palawan; tl, Lalawigan ng Palawan), is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in ...
was also part of Sundaland, while the rest of the Philippine Islands
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
formed one large island separated from the continent only by the Sibutu Passage
Sibutu Passage is a deep channel some 18 miles (29 km) wide that separates Borneo from the Sulu Archipelago. It has a deep sill allowing entry of deep water into the Sulu basin while connecting the Sulu Sea with the Sulawesi Sea that feeds ...
and the Mindoro Strait
The Mindoro Strait ( tgl, Kipot ng Mindoro) is one of the straits connecting the South China Sea with the Sulu Sea in the Philippines. It separates Mindoro Island from Busuanga Island (one of the Calamian Islands of Palawan Province). Located ...
.
Australasia
The Australian mainland, New Guinea, Tasmania and many smaller islands comprised a single land mass. This continent is now referred to sometimes asSahul
__NOTOC__
Sahul (), also called Sahul-land, Meganesia, Papualand and Greater Australia, was a paleocontinent that encompassed the modern-day landmasses of mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and the Aru Islands.
Sahul was in the south- ...
.
Between Sahul and Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
– a peninsula of South East Asia that comprised present-day Malaysia and western and northern Indonesia – there remained an archipelago of islands known as Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as ...
. The water gaps between these islands, Sahul and Sundaland were considerably narrower and fewer in number.
The two main islands of New Zealand, along with associated smaller islands, were joined as one landmass. Virtually all of the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) is a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern ...
were under permanent ice, with glaciers extending into much of the surrounding high country.
Europe
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
was largely covered by ice, with the southern boundary of the ice sheets passing through Germany and Poland. This ice extended northward to cover Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
and Franz Josef Land
, native_name =
, image_name = Map of Franz Josef Land-en.svg
, image_caption = Map of Franz Josef Land
, image_size =
, map_image = Franz Josef Land location-en.svg
, map_caption = Location of Franz Josef ...
and northeastward to occupy the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
, the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. ...
, and Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
, ending at the Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula (russian: Таймырский полуостров, Taymyrsky poluostrov) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administrat ...
in what is now northwestern Siberia.
In northwestern Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, the Fennoscandian Ice Sheet reached its LGM extent approximately 17,000 years ago, about five thousand years later than in Denmark, Germany and Western Poland. Outside the Baltic Shield, and in Russia in particular, the LGM ice margin of the Fennoscandian Ice Sheet was highly lobate. The main LGM lobes of Russia followed the Dvina, Vologda
Vologda ( rus, Вологда, p=ˈvoləɡdə) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Vologda Oblast, Russia, located on the river Vologda (river), Vologda within the watershed of the Northern Dvina. ...
and Rybinsk
Rybinsk ( rus, Рыбинск, p=ˈrɨbʲɪnsk), the second largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Yaroslavl Oblast in Russia, lies at the confluence of the Volga River, Volga and Sheksna Rivers, 267 kilometers north-north-eas ...
basins respectively. Lobes originated as result of ice following shallow topographic depressions filled with a soft sediment substrate.
Permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
covered Europe south of the ice sheet down to as far south as present-day Szeged
Szeged ( , ; see also #Etymology, other alternative names) is List of cities and towns of Hungary#Largest cities in Hungary, the third largest city of Hungary, the largest city and regional centre of the Southern Great Plain and the county seat ...
in Southern Hungary. Ice covered the whole of Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
. In addition, ice covered Ireland and almost all of Wales, with the southern boundary of the ice sheet running approximately from the current location of Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital and largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a Sir Caerdydd, links=no), and the city is the eleventh-largest in the United Kingd ...
north-north-east to Middlesbrough
Middlesbrough ( ) is a town on the southern bank of the River Tees in North Yorkshire, England. It is near the North York Moors national park. It is the namesake and main town of its local borough council area.
Until the early 1800s, the a ...
, and then across the now submerged land of Doggerland
Doggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the North Sea, that connected Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BCE. The flooded land is known as the Dogger Littoral. Geological sur ...
to Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
.
In the Cantabrian Mountains
, etymology=Named after the Cantabri
, photo=Cordillera Cantábrica vista desde el Castro Valnera.jpg
, photo_caption=Cantabrian Mountains parallel to the Cantabrian Sea seen from Castro Valnera in an east-west direction. In the background, ...
of the northwestern corner of the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
, which in the present day have no permanent glaciers, the LGM led to a local glacial recession as a result of increased aridity caused by the growth of other ice sheets farther to the east and north, which drastically limited annual snowfall over the mountains of northwestern Spain. The Cantabrian alpine glaciers had previously expanded between approximately 60,000 and 40,000 years ago during a local glacial maximum in the region.
North America
In North America, theLaurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years a ...
grew rapidly at the onset of the LGM until it covered essentially all of Canada east of the Rocky Mountains and extended roughly to the Missouri
Missouri is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee ...
and Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
s, and eastward to Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, reaching a total maximum volume of around 26.5 to 37 million cubic kilometres. In addition to the large Cordilleran Ice Sheet in Canada and Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, alpine glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s advanced and (in some locations) ice caps covered much of the Rocky and Sierra Nevada Mountains further south. Latitudinal gradients were so sharp that permafrost did not reach far south of the ice sheets except at high elevations. Glaciers forced the early human populations who had originally migrated from northeast Siberia into refugia, reshaping their genetic variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, ...
by mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
and drift
Drift or Drifts may refer to:
Geography
* Drift or ford (crossing) of a river
* Drift, Kentucky, unincorporated community in the United States
* In Cornwall, England:
** Drift, Cornwall, village
** Drift Reservoir, associated with the village
...
. This phenomenon established the older haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
s found among Native Americans, and later migrations are responsible for northern North American haplogroups.
On the Island of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii ) is the largest island in the United States, located in the state of Hawaii. It is the southeasternmost of the Hawaiian Islands, a chain of volcanic islands in the North Pacific Ocean. With an area of , it has 63% of th ...
, geologists have long recognized deposits formed by glaciers on Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea ( or ; ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a Wākea''); is a dormant volcano on the island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the highest point in the state of Hawaii and second-highest peak of an island on Earth. The peak is ...
during recent ice ages. The latest work indicates that deposits of three glacial episodes since 150,000 to 200,000 years ago are preserved on the volcano. Glacial moraines on the volcano formed about 70,000 years ago and from about 40,000 to 13,000 years ago. If glacial deposits were formed on Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
, they have long since been buried by younger lava flows.
South America
During the Last Glacial Maximumvalley glacier
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers ...
s in the southern Andes (38–43° S) merged and descended from the Andes occupying lacustrine and marine basins where they spread out forming large piedmont glacier lobes. Glaciers extended about 7 km west of the modern Llanquihue Lake
Lake Llanquihue is the second-largest lake in Chile with an area of about , after Lake General Carrera which shared with Argentina. It is situated in the southern Los Lagos Region in the Llanquihue and Osorno provinces. The lake's fan-like form ...
, but not more than 2 to 3 km south of it. Nahuel Huapi Lake
Nahuel Huapi Lake ( es, Lago Nahuel Huapí) is a lake in the lake region of northern Patagonia between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén, in Argentina. The tourist center of Bariloche is on the southern shore of the lake.
The June 2 ...
in Argentina was also glaciated by the same time. Over most of the Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
, glacier advance peaked in 26,000 years BP, forming a long north–south moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
system along the eastern coast of Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island ( es, Isla de Chiloé, , ) also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern ...
(41.5–43° S). By that time the glaciation at the latitude of Chiloé was of ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Las ...
type contrasting to the valley glaciation found further north in Chile.
Despite glacier advances much of the area west of Llanquihue Lake was still ice-free during the Last Glacial Maximum. During the coldest period of the Last Glacial Maximum vegetation at this location was dominated by Alpine herbs in wide open surfaces. The global warming that followed caused a slow change in vegetation towards a sparsely distributed vegetation dominated by ''Nothofagus
''Nothofagus'', also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America (Chile, Argentina) and Australasia (east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Gui ...
'' species. Within this parkland vegetation Magellanic moorland 250px, Magellanic moorland at Herschel Island, Cabo de Hornos National Park.
The Magellanic moorland or Magellanic tundra ( es, Tundra magallánica) is an ecoregion on the Patagonian archipelagos south of latitude 48° S. It is characterized by h ...
alternated with ''Nothofagus'' forest, and as warming progressed even warm-climate trees began to grow in the area. It is estimated that the tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snowp ...
was depressed about 1,000 m relative to present day elevations during the coldest period, but it rose gradually until 19,300 years BP. At that time a cold reversal caused a replacement of much of the arboreal vegetation with Magellanic moorland and Alpine species.
Little is known about the extent of glaciers during Last Glacial Maximum north of the Chilean Lake District
The Chilean Lake District is a zone in Southern Chile defined by its many lakes in the Andean foothills. The term is primarily used in tourism literature and advertising, in Chile Zona Sur is preferred as a geographical concept. The Chilean Lake ...
. To the north, in the dry Andes
file:Andes_clima.png, 200px, Map of the climatic regions of the Andes. The Dry Andes are shown in yellow. The Tropical Andes are shown in green and the Wet Andes in dark blue.
The Dry Andes ( es, Andes áridos) is a climatic and glaciology, glaciol ...
of Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and the Last Glacial Maximum is associated with increased humidity and the verified advance of at least some mountain glaciers.
In the Southern Hemisphere, the Patagonian Ice Sheet
upright=1.4, Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the Strait of Magellan area during the last glacial period. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots. Sea level was much lower than shown here.
The Patagonian Ice S ...
covered the whole southern third of Chile and adjacent areas of Argentina. On the western side of the Andes the ice sheet reached sea level as far north as in the 41 degrees south at Chacao Channel
The Chacao Channel ( es, Canal de Chacao) is located in Los Lagos Region, Chile and separates Chiloé Island from mainland Chile. The channel was created during the Quaternary glaciations by successive glaciers that flowed down from the Andes to ...
. The western coast of Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ...
was largely glaciated, but some authors have pointed out the possible existence of ice-free refugia for some plant species. On the eastern side of the Andes, glacier lobes occupied the depressions of Seno Skyring
Seno Skyring is a large inland sound lying north of Riesco Island and south of mainland South America in southern Chile. Alternatively called Skyring Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the ret ...
, Seno Otway
Seno Otway is a large inland sound lying between Brunswick Peninsula and Riesco Island in southern Chile. Alternatively called Otway Sound, this natural waterway occupies a valley blocked by a large terminal moraine left by the retreat of a glaci ...
, Inútil Bay
300px, Satellite image of Inútil Bay and the Strait of Magellan. Selected settlements are marked with yellow dots.
Inútil Bay (Spanish: ''Bahía Inútil'') or Useless Bay is a bay in the western and Chilean part of Tierra del Fuego Island. Loc ...
, and Beagle Channel
Beagle Channel (; Yahgan: ''Onašaga'') is a strait in the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago, on the extreme southern tip of South America between Chile and Argentina. The channel separates the larger main island of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego f ...
. On the Straits of Magellan, ice reached as far as Segunda Angostura
Segunda Angostura is a sound of the Strait of Magellan between the Patagonian mainland and Tierra del Fuego. It is located southwest of Primera Angostura, the narrowest part of the Strait between the island and the continent. The sound was named ...
.
Antarctica
Evidence from sediment cores in theScotia Sea
The Scotia Sea is a sea located at the northern edge of the Southern Ocean at its boundary with the South Atlantic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the Drake Passage and on the north, east, and south by the Scotia Arc, an undersea ridge and i ...
suggests the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise (as seen from the South Pole) from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feat ...
was weaker during the last glaciation than during the Holocene.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * **Bølling oscillation
The Bølling oscillation, also Bølling interstadial, was a cool temperate climatic interstadial between the glacial Oldest Dryas and Older Dryas stadials, between 14,700 and 14,100 BP, near to the end of the last glacial period. It is named aft ...
**Allerød oscillation
The Allerød oscillation ( da, Allerødtiden) was a warm and moist global interstadial that occurred c.13,900 to 12,900 BP, nearly at the end of the Last Glacial Period. It raised temperatures in the northern Atlantic region to almost present-da ...
*
*
*
* 5.9 kiloyear event
* 4.2-kiloyear event
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
Further reading
*Developments in Quaternary Science Series ** ** ** ** *External links
* * * (32 digital maps at 1:7 000 000 scale with accompanying digital chronological database and one poster (two sheets) with full map series.) * *Paleoclimate Modelling Intercomparison Project (PMIPPMIP Web Site
an
'Publications : Last Glacial Maximum.
*Paleoclimate Modelling Intercomparison Project Phase II (PMIP2
''PMIP2 Home page''
an
PMIP 2 Publications.
* {{Ice Ages Ice ages Glaciology