|
Stadial
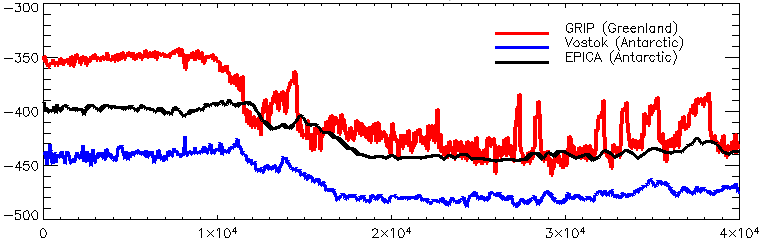
Stadials and interstadials are phases dividing the Quaternary period, or the last 2.6 million years. Stadials are periods of colder climate while interstadials are periods of warmer climate. Each Quaternary climate phase is associated with a Marine Isotope Stage (MIS) number, which describe alternation between warmer and cooler temperatures as measured by oxygen isotope data. Stadials have even MIS numbers and interstadials odd MIS numbers. The current Holocene interstadial is MIS 1 and the Last glacial maximum stadial is MIS 2. Marine Isotope Stages are sometimes further subdivided into stadials and interstadials by minor climate fluctuations within the overall stadial or interstadial regime, which are indicated by letters. The odd-numbered interstadial MIS 5, also known as the Sangamonian interglacial, contains two periods of relative cooling, and so is subdivided into three interstadials (5a, 5c, 5e) and two stadials (5b, 5d). A stadial isotope stage like MIS 6 would be su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch (c. 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP) and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and long lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial (c. 14,670 to 12,900 BP). The change was relatively sudden, taking place in decades, and it resulted in a decline of temperatures in Greenland by 4~10 °C (7.2~18 °F), and advances of glaciers and drier conditions over much of the temperate Northern Hemisphere. A number of theories have been put forward about the cause, and the most widely supported by scientists is that the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation, which transports warm water fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fluctuations around the Strait of Magellan suggest the peak in glacial surface area was constrained to betwee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
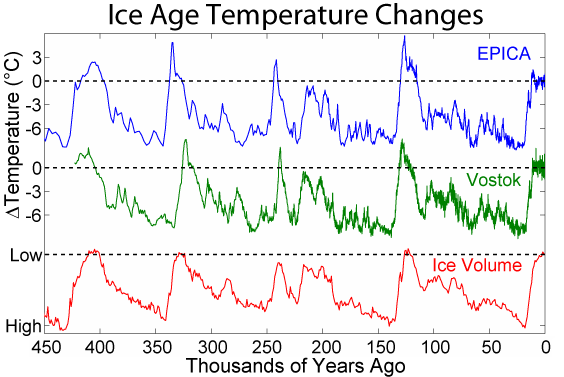
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth hypothesis proposes that, during one or more of Earth's Greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse Climate, climates, the Earth's surface, planet's surface became entirely or nearly entirely Freezing, frozen. It is believed that this occurred sometime before 650 M.Y.A. (million years ago) during the Cryogenian period. Proponents of the hypothesis argue that it best explains sedimentary Deposition (geology), deposits that are generally believed to be of glacial origin at tropical palaeolatitudes and other enigmatic features in the geological record. Opponents of the hypothesis contest the geological evidence for Glacial period, global glaciation and the geophysical feasibility of an ice- or slush-covered ocean, and they emphasize the difficulty of escaping an all-frozen condition. A number of unanswered questions remain, including whether Earth was a full snowball or a "slushball" with a thin Equator, equatorial band of open (or seasonally open) water. The snowball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse And Icehouse Earth
Throughout Earth's climate history (Paleoclimate) its climate has fluctuated between two primary states: greenhouse and icehouse Earth. Both climate states last for millions of years and should not be confused with glacial and interglacial periods, which occur as alternate phases within an icehouse period and tend to last less than 1 million years. There are five known Icehouse periods in Earth's climate history, which are known as the Huronian, Cryogenian, Andean-Saharan, Late Paleozoic, and Late Cenozoic glaciations. The main factors involved in changes of the paleoclimate are believed to be the concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide (), changes in Earth's orbit, long-term changes in the solar constant, and oceanic and orogenic changes from tectonic plate dynamics. Greenhouse and icehouse periods have played key roles in the evolution of life on Earth by directly and indirectly forcing biotic adaptation and turnover at various spatial scales across time. Greenhouse Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denekamp
Denekamp () is a town in the Dutch province of Overijssel. It is a part of the region of Twente and the municipality of Dinkelland, and lies about 9 km northeast of Oldenzaal. The town was first noted as early as the 10th century when it was referred to as Daginghem, and means "settlement of the people of Dago or Dano". The village started around the church which was built in 1275. It remained isolated and small until 1829 when the road from Deventer to Hamburg was built. The location became a municipality in 1818 incorporating the settlements of Noord Deurningen, Lattrop, Breklenkamp, Tilligte, Nutter and Agelo. The municipality merged with Ootmarsum and Weerselo in 2001; the new municipality was first called "Denekamp", but was renamed in 2002 to Dinkelland. The Town is known in the hardstyle scene, to be home of various Hardstyle DJ's. Notable people from Denekamp *Roméo Dallaire (1946-), Canadian senator and retired general. *Hennie Kuiper (1949-), world champion cycl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glinde, Schleswig-Holstein
Glinde () is a town in Germany in southern Schleswig-Holstein, approximately 7 km east of Hamburg. History The name Glinde was first mentioned in a document dated from March 25, 1229. In the document Graf Adolf IV. of Schauenburg and Holstein gave the village to a Cistercian convent. (The monastery was later moved to the location of the modern town Reinbek). The King of Denmark and Duke of Schleswig-Holstein, Frederick I of Denmark, took possession of the monastery during the Protestant Reformation. 1544 his son Christian III shared it with his brothers. The affiliation changed several times. 1948, the municipalities Glinde, Oststeinbek, Havighorst and Schönningstedt were amalgamated to the Amt Glinde. After Schönningstedt and subsequently (1949) Havighorst left the association, Glinde and Oststeinbek became independent municipalities in 1978. On June 24, 1979 (the 750th anniversary of the village), Glinde received its town charter A city charter or town charter (generi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oerel
Oerel is a municipality in the Rotenburg (district), district of Rotenburg, in Lower Saxony, Germany. Oerel belonged to the Archdiocese of Bremen, Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen, established in 1180. In 1648 the Prince-Archbishopric was transformed into the Duchy of Bremen, which was first ruled in personal union by the Swedish Crown - interrupted by a Danish occupation (1712–1715) - and from 1715 on by the House of Hanover, Hanoverian Crown. In 1807 the ephemeral Kingdom of Westphalia annexed the Duchy, before First French Empire, France annexed it in 1810. In 1813 the Duchy was restored to the Electorate of Hanover, which - after its upgrade to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814 - incorporated the Duchy in a real union and the Ducal territory, including Oerel, became part of the new Stade (region), Stade Region, established in 1823. References Municipalities in Lower Saxony {{Rotenburg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odderade
Odderade is a municipality in the district of Dithmarschen, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Dithmarschen {{Dithmarschen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brørup
Brørup is a railway town, with a population of 4,516 (1 January 2022),BY3: Population 1. January by rural and urban areas, area and population density The Mobile Statbank from in , in |



.jpg)
