|
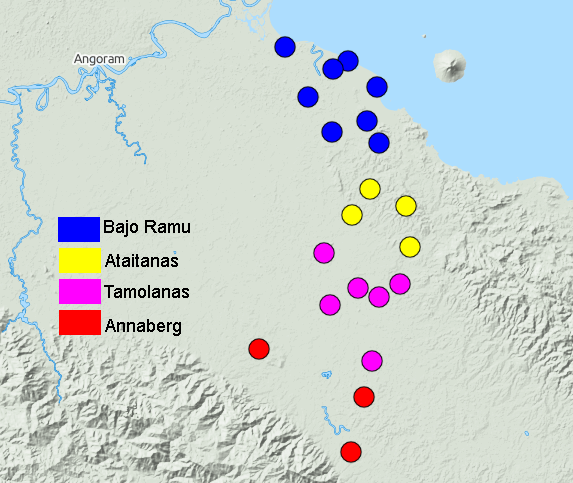
Langam Language
Pondi, also known as Langam, is a Keram language spoken in Langam village () of Keram Rural LLG, East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. The majority of Pondi speakers are ethnic-Pondis. Due to the small community in which Pondi is spoken, the language has no known dialect. The most notable language variation in Pondi is based on age as the older generations are more fluent. It is related both Ulwa and Mwaki. Pondi is endangered because of the growing use and popularity of the Tok Pisin Tok Pisin ( ,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh ; ), often referred to by English speakers as New Guinea Pidgin or simply Pidgin, is an English-based creole languages, English creole language spoken throughou ... language, which is used more by the younger generations of speakers. The language is predicted to not be spoken in the next one hundred years. The lexicon of the Pondi language has many words that they acquired from other languages, however, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
East Sepik Province
East Sepik is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Wewak. East Sepik has an estimated population of 450,530 people (2011 census) and is 43,426 km square in size. Its density is 10.4 people per square kilometer. History Cherubim Dambui was appointed as East Sepik's first premier by Prime Minister of Papua New Guinea, Prime Minister Michael Somare upon the creation of the provincial government in 1976. Dambui remained interim premier until 1979, when he became East Sepik's permanent premier with a full term. He remained in office until 1983. Geography Wewak, the provincial capital, is located on the coast of East Sepik. There are a scattering of islands off shore, and coastal ranges dominate the landscape just inland of the coast. The remainder of the province's geography is dominated by the Sepik River, which is one of the largest rivers in the world in terms of water flow and is known for flooding—the river's level can alter by as much as five metres in the cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ramu Languages
The Ramu languages are a family of some thirty languages of Northern Papua New Guinea. They were identified as a family by John Z'graggen in 1971 and linked with the Sepik languages by Donald Laycock two years later. Malcolm Ross (2005) classifies them as one branch of a Ramu – Lower Sepik language family. Z'graggen had included the Yuat languages, but that now seems doubtful. With no comprehensive grammar yet available for any of the Ramu languages, the Ramu group remains one of the most poorly documented language groups in the Sepik-Ramu basin. Classification The small families listed below in boldface are clearly valid units. The first five, sometimes classified together as ''Lower Ramu,'' are relatable through lexical data, so their relationship is widely accepted. Languages of the Ottilien family share plural morphology with Nor–Pondo. Late 20th century Laycock (1973) included the Arafundi family, apparently impressionistically, but Arafundi is poorly known. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Keram Languages
The Keram languages of New Guinea are part of the Ramu family. They are the Mongol–Langam languages and a pair of languages sometimes thought to belong to the Grass family. (See Grass languages for the history of classification.) Foley (2018) classifies most of them in the Grass branch of the Ramu family, while Usher classifies them as coordinate with the Ramu family, leaving a reduced number of languages in the Grass branch. They are named for the Keram River. Languages *East Keram River ** Ambakich (Aion) ** Ap Ma (Kambot) *West Keram River ( Mongol–Langam) ** Mwakai (Mongol) ** Pondi (Langam) ** Ulwa (Yaul) Pronouns Usher (2020) reconstructs the pronouns of East Keram and West Keram as follows:East Keram River [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mongol–Langam Languages
The Mongol–Langam, Koam, or Ulmapo languages are a language group of Keram Rural LLG, East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea belonging to the Ramu languages, Ramu language family. Foley (2018) includes them within the Grass languages, but they were not included in Foley (2005). The Koam languages are spoken next to the Yuat languages, but two groups are unrelated. Names The name ''Koam'' is used by Foley (2018), while the name ''Ulmapo'' (coined from the first two letters of each of the three daughter languages) is used by Barlow (2018) and ''Glottolog'' 4.0. Languages According to Summer Institute of Linguistics data from 2003, the member languages had the following number of speakers: *Mongol language (Papua New Guinea), Mongol (Mwakai), 340 speakers *Langam language, Langam (Pondi), 420 speakers *Yaul language, Yaul (Ulwa), 1,210 speakers Classification Donald Laycock (1973) noted that the Mongol–Langam languages mark nouns for pluralisation, like the Lower Sepik language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Keram Language
The Keram languages of New Guinea are part of the Ramu family. They are the Mongol–Langam languages and a pair of languages sometimes thought to belong to the Grass family. (See Grass languages for the history of classification.) Foley (2018) classifies most of them in the Grass branch of the Ramu family, while Usher classifies them as coordinate with the Ramu family, leaving a reduced number of languages in the Grass branch. They are named for the Keram River. Languages *East Keram River ** Ambakich (Aion) ** Ap Ma (Kambot) *West Keram River ( Mongol–Langam) ** Mwakai (Mongol) ** Pondi (Langam) ** Ulwa (Yaul) Pronouns Usher (2020) reconstructs the pronouns of East Keram and West Keram as follows:East Keram River [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Keram Rural LLG
Keram Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of East Sepik Province, Papua New Guinea. Wards *01. Chimundo *02. Kambot *03. Kambot *04. Kambot *05. Bobten *06. Korokopa *07. Pusyten *08. Kekten *09. Buten *10. Yemen *11. Manu *12. Kambugu *13. Pamban *14. Bopaten *15. Langam ( Langam language speakers) *16. Mongol ( Mongol language (New Guinea) speakers) *17. Wom ( Wom language (Papua New Guinea) speakers) *18. Raten *19. Ketro/Samban *20. Baniamta *21. Kamen *22. Marua *23. Yanboe *24. Nainten *25. Yar *26. Bagaram *27. Kivim *28. Longwuk *29. Mungum *30. Mingnias *31. Togo *32. Monjito *33. Likan *34. Klorowom *35. Sori *36. Paniten *37. Pataka *38. Mui See also *Keram languages The Keram languages of New Guinea are part of the Ramu family. They are the Mongol–Langam languages and a pair of languages sometimes thought to belong to the Grass family. (See Grass languages for the history of classification.) Foley (2018) ... * Keram River References * * {{EastSepik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951 and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Parachurch organization, Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistics, linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' is not ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and Exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SIL International
SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics International) is an evangelical Christian nonprofit organization whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development. Based on its language documentation work, SIL publishes a database, '' Ethnologue'', of its research into the world's languages, and develops and publishes software programs for language documentation, such as FieldWorks Language Explorer (FLEx) and Lexique Pro. Its main offices in the United States are located at the International Linguistics Center in Dallas, Texas. History Early History William Cameron Townsend, a Presbyterian minister, founded the organization in 1934, after undertaking a Christian mission with the Disciples of Christ among the Kaqchikel Maya people in Guatemala in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yaul Language
Yaul, also known as Ulwa, is a severely endangered Keram language of Papua New Guinea. It is spoken fluently by fewer than 700 people and semi-fluently by around 1,250 people in four villages of the Angoram District of the East Sepik Province: Manu, Maruat, Dimiri, and Yaul. Currently, no children are being taught Ulwa, which has led to the rapid decline of intergenerational transmission for this language. According to Barlow (2018), speakers in Maruat, Dimiri, and Yaul villages speak similar versions of Ulwa, while those in Manu speak a considerably different version. Thus, he postulates that there are two different dialects of Ulwa. Word Order The word order in Ulwa is generally fixed. There are two categories for word order, and this is based on if the clause is transitive or intransitive. In a transitive clause, the object follows the subject and precedes the verb, leading to a SOV word order. With intransitive clauses, the subject precedes the verb: SV. Below is an exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tok Pisin
Tok Pisin ( ,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh ; ), often referred to by English speakers as New Guinea Pidgin or simply Pidgin, is an English-based creole languages, English creole language spoken throughout Papua New Guinea. It is an official Languages of Papua New Guinea, language of Papua New Guinea and the most widely used language in the country. In parts of the southern provinces of Western Province (Papua New Guinea), Western, Gulf Province, Gulf, Central Province (Papua New Guinea), Central, Oro Province, Oro, and Milne Bay Province, Milne Bay, the use of Tok Pisin has a shorter history and is less universal, especially among older people. Between five and six million people use Tok Pisin to some degree, though not all speak it fluently. Many now learn it as a first language, in particular the children of parents or grandparents who originally spoke different languages (for example, a mother from Madang and a father from Rabaul). Ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Languages Of East Sepik Province
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity, with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement, which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences, and the ability to refer to objects, events, and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |