Kuwait Emir Cup Seasons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to the north and Saudi Arabia to the south. Kuwait also shares maritime borders with Iran. Kuwait has a coastal length of approximately . Most of the country's population reside in the urban agglomeration of the capital city
 During the Ubaid period (6500 BC), Kuwait was the central site of interaction between the peoples of Mesopotamia and Neolithic Eastern Arabia, including
During the Ubaid period (6500 BC), Kuwait was the central site of interaction between the peoples of Mesopotamia and Neolithic Eastern Arabia, including 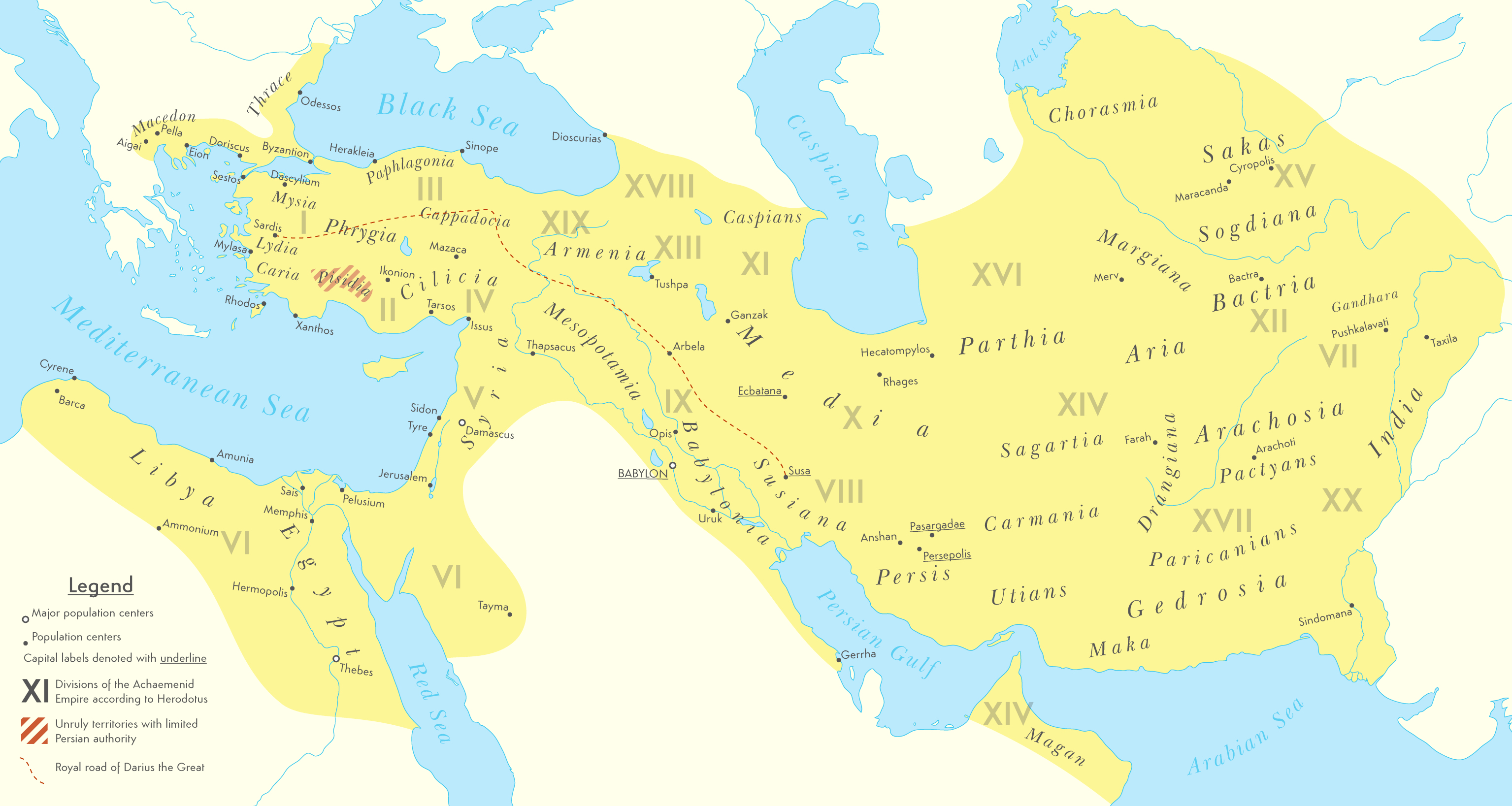 Following the
Following the  At the time of Alexander the Great, the mouth of the
At the time of Alexander the Great, the mouth of the
/ref>James K. Hoffmeier, ''The Archaeology of the Bible'',
 In 1521, Kuwait was under Portuguese control. In the late 16th century, the Portuguese built a defensive settlement in Kuwait. In 1613,
In 1521, Kuwait was under Portuguese control. In the late 16th century, the Portuguese built a defensive settlement in Kuwait. In 1613,  According to Kuwaiti authors, the instability in Basra helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait. In the late 18th century, Kuwait was a haven for Basra merchants fleeing Ottoman persecution. Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf, its ships renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Kuwaitis also developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf. In the 19th century, Kuwait became significant in the
According to Kuwaiti authors, the instability in Basra helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait. In the late 18th century, Kuwait was a haven for Basra merchants fleeing Ottoman persecution. Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf, its ships renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Kuwaitis also developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf. In the 19th century, Kuwait became significant in the
 The
The  The
The
 Although Kuwait formally gained independence in 1961, Iraq initially refused to recognize the country's independence by maintaining that Kuwait is part of Iraq, albeit Iraq later briefly backed down following a show of force by Britain and Arab League support of Kuwait's independence. The short-lived Operation Vantage crisis evolved in July 1961, as the Iraqi government threatened to invade Kuwait and the invasion was finally averted following plans by the Arab League to form an international Arab force against the potential Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. As a result of Operation Vantage, the Arab League took over the border security of Kuwait and the British had withdrawn their forces by 19 October. Iraqi prime minister Abd al-Karim Qasim was killed in a coup in 1963 but, although Iraq recognised Kuwaiti independence and the military threat was perceived to be reduced, Britain continued to monitor the situation and kept forces available to protect Kuwait until 1971. There had been no Iraqi military action against Kuwait at the time: this was attributed to the political and military situation within Iraq which continued to be unstable. A treaty of friendship between Iraq and Kuwait was signed in 1963 by which Iraq recognised the 1932 border of Kuwait. After the 1967 Six Day War Kuwait along with other Arab speaking countries voted the three no's of the Khartoum Resolution: no peace with Israel, no Recognition of Israel, no negotiations with Israel. The Kuwait-Iraq 1973 Sanita border skirmish evolved on 20 March 1973, when Iraqi army units occupied El-Samitah near the Kuwaiti border, which evoked an international crisis.
On 6 February 1974, 1974 attack on the Japanese Embassy in Kuwait, Palestinian militants occupied the Japanese embassy in Kuwait, taking the ambassador and ten others hostage. The militants' motive was to support the Japanese Red Army members and Palestinian militants who were holding hostages on a Singaporean ferry in what is known as the Laju incident, ''Laju'' incident. Ultimately, the hostages were released, and the guerrillas allowed to fly to Aden. This was the first time Palestinian guerrillas struck in Kuwait as the Al Sabah ruling family, headed by Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, funded the Palestinian resistance movement. Kuwait had been a regular endpoint for Palestinian aircraft hijacking, plane hijacking in the past and had considered itself safe.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was considered the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's #Television and theatre, theatre industry was well known throughout the Arab world.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the Freedom of the press, freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, ''Al-Arabi (magazine), Al-Arabi'' magazine was first published. The magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait because they enjoyed greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
Kuwaiti society embraced liberal and non-traditional attitudes throughout the 1960s and 1970s. For example, most Kuwaiti women did not wear the hijab in the 1960s and 70s.
Although Kuwait formally gained independence in 1961, Iraq initially refused to recognize the country's independence by maintaining that Kuwait is part of Iraq, albeit Iraq later briefly backed down following a show of force by Britain and Arab League support of Kuwait's independence. The short-lived Operation Vantage crisis evolved in July 1961, as the Iraqi government threatened to invade Kuwait and the invasion was finally averted following plans by the Arab League to form an international Arab force against the potential Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. As a result of Operation Vantage, the Arab League took over the border security of Kuwait and the British had withdrawn their forces by 19 October. Iraqi prime minister Abd al-Karim Qasim was killed in a coup in 1963 but, although Iraq recognised Kuwaiti independence and the military threat was perceived to be reduced, Britain continued to monitor the situation and kept forces available to protect Kuwait until 1971. There had been no Iraqi military action against Kuwait at the time: this was attributed to the political and military situation within Iraq which continued to be unstable. A treaty of friendship between Iraq and Kuwait was signed in 1963 by which Iraq recognised the 1932 border of Kuwait. After the 1967 Six Day War Kuwait along with other Arab speaking countries voted the three no's of the Khartoum Resolution: no peace with Israel, no Recognition of Israel, no negotiations with Israel. The Kuwait-Iraq 1973 Sanita border skirmish evolved on 20 March 1973, when Iraqi army units occupied El-Samitah near the Kuwaiti border, which evoked an international crisis.
On 6 February 1974, 1974 attack on the Japanese Embassy in Kuwait, Palestinian militants occupied the Japanese embassy in Kuwait, taking the ambassador and ten others hostage. The militants' motive was to support the Japanese Red Army members and Palestinian militants who were holding hostages on a Singaporean ferry in what is known as the Laju incident, ''Laju'' incident. Ultimately, the hostages were released, and the guerrillas allowed to fly to Aden. This was the first time Palestinian guerrillas struck in Kuwait as the Al Sabah ruling family, headed by Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, funded the Palestinian resistance movement. Kuwait had been a regular endpoint for Palestinian aircraft hijacking, plane hijacking in the past and had considered itself safe.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was considered the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's #Television and theatre, theatre industry was well known throughout the Arab world.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the Freedom of the press, freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, ''Al-Arabi (magazine), Al-Arabi'' magazine was first published. The magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait because they enjoyed greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
Kuwaiti society embraced liberal and non-traditional attitudes throughout the 1960s and 1970s. For example, most Kuwaiti women did not wear the hijab in the 1960s and 70s.
 After the Iran–Iraq War ended, Kuwait declined an Iraqi request to forgive its US$65 billion debt. An economic rivalry between the two countries ensued after Kuwait increased its oil production by 40 percent. Tensions between the two countries increased further in July 1990, after Iraq complained to
After the Iran–Iraq War ended, Kuwait declined an Iraqi request to forgive its US$65 billion debt. An economic rivalry between the two countries ensued after Kuwait increased its oil production by 40 percent. Tensions between the two countries increased further in July 1990, after Iraq complained to 
"U.S. Calls Qatar, Kuwait Lax Over Terror Financing"
''The Wall Street Journal'', 23 October 2014 From 2014 to 2015, Kuwait was frequently described as the world's Kuwait and state-sponsored terrorism, biggest source of terrorism funding, particularly for ISIS and Al-Qaeda. On 26 June 2015, a 2015 Kuwait mosque bombing, suicide bombing took place at a Shia Muslim mosque in Kuwait. The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claimed responsibility for the attack. Twenty-seven people were killed and 227 people were wounded. It was the largest terror attack in Kuwait's history. In the aftermath, a lawsuit was filed accusing the Kuwaiti government of negligence and direct responsibility for the terror attack. Due to declining oil prices since the late 2010s, Kuwait has been facing one of the worst economic crunches in the entire region. Historically, Kuwait's infrastructure projects market has underperformed its potential due to political deadlock between the government and parliament. Sabah Al Ahmad Sea City was inaugurated in mid-2016. In 2020, the Kuwaiti government experienced its first fiscal deficit since 1995. In recent years, Kuwait has invested significantly in its economic relations with China. China has been Kuwait's largest trade partner since 2016. Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have various cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa which is currently under construction in northern Kuwait. The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah Causeway is part of the first phase of the Madinat al-Hareer, Silk City project. The causeway was inaugurated in May 2019 as part of Kuwait Vision 2035, it connects Kuwait City to northern Kuwait. The Kuwait National Cultural District comprises the Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace.Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre
New Kuwait. In 2020, Kuwait's domestic travel and tourism spending was $6.1 billion. The COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait, COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated Kuwait's economic crisis. Kuwait's economy faced a budget deficit of $46 billion in 2020. In September 2020, Kuwait's Crown Prince Sheikh Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah became the 16th Emir of Kuwait and the successor to Emir Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, who died at the age of 91. In October 2020, Sheikh Mishal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah was appointed as the Crown Prince. Kuwait currently has the largest US military presence in the Middle East region. There are over 14,000 US military personnel stationed in the country. Camp Arifjan is the largest US military base in Kuwait.

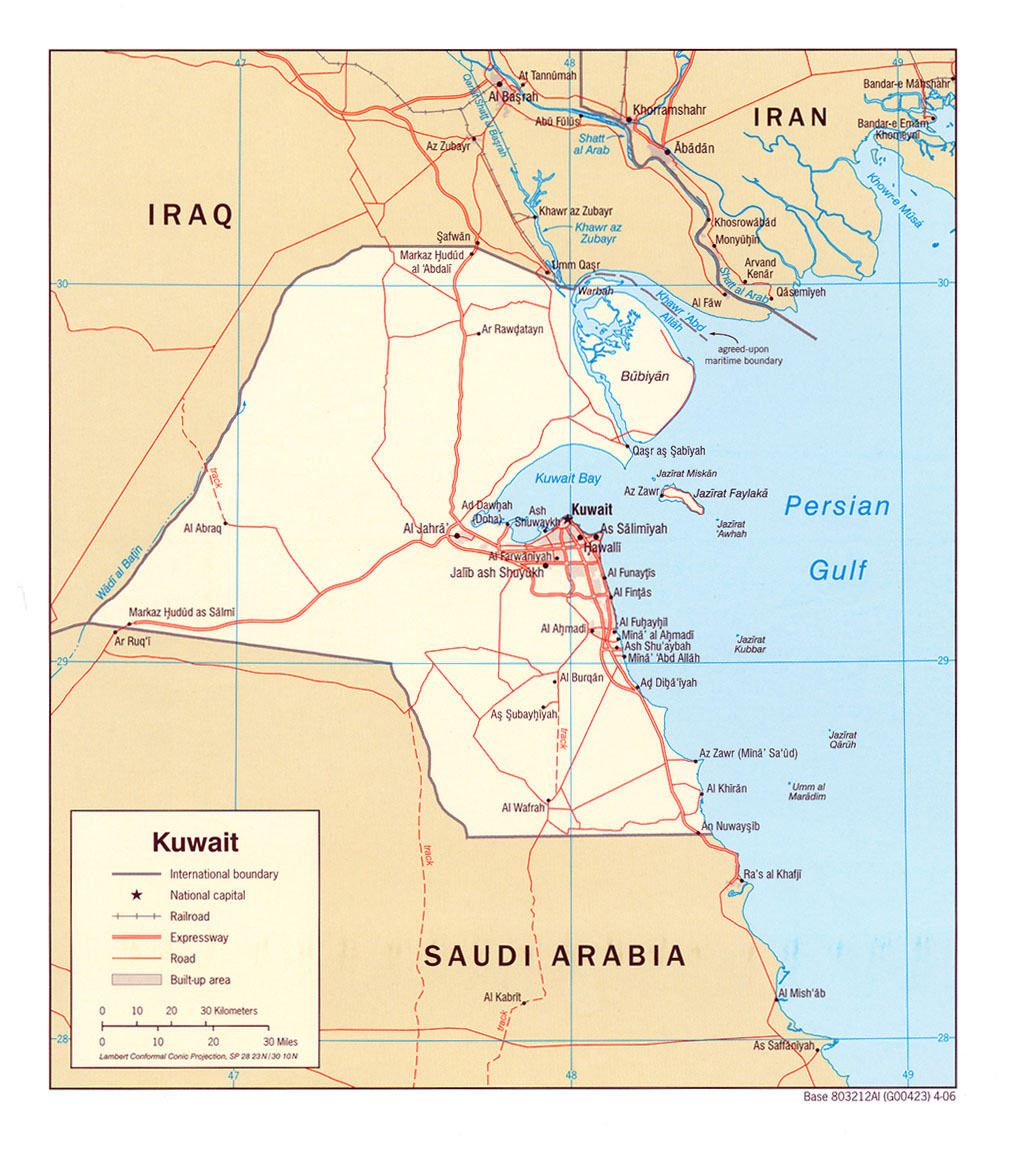 Located in the north-east corner of the
Located in the north-east corner of the
according to the World Bank.
 Executive power is executed by the government. The Emir appoints the prime minister, who in turn chooses the Cabinet of Kuwait, cabinet of ministers comprising the government. In recent decades, numerous policies of the Kuwaiti government have been characterized as "demographic engineering", especially in relation to Kuwait's Bedoon#Kuwait, stateless Bedoon crisis and the Kuwaiti nationality law#History of naturalization in Kuwait, history of naturalization in Kuwait.
The Emir appoints all the judges and many judges are foreign nationals from Egypt. The Constitutional Court is charged with ruling on the conformity of laws and decrees with the constitution. Kuwait has an active public sphere and civil society with political and social organizations that are parties in all but name. Professional groups like the Kuwait Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Chamber of Commerce maintain their autonomy from the government.
The legislative branch consists of the National Assembly (Kuwait), National Assembly, which has nominal oversight authority. As per article 107 of the Constitution of Kuwait, Kuwait constitution, the Emir can dissolve the parliament so long as an election for a new assembly are held within two months of the dissolution. Due to frequent cabinet resignations, Kuwait has a new government every eight months. The political instability has significantly hampered the country's economic development and infrastructure.
The Emir has suspended the constitution twice: in 1976 under Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah and 1986 under Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah. Kuwait is regularly characterized as being a "rentier state" in which the ruling family uses oil revenues to buy the political acquiescence of the citizenry; more than 70% of government spending consists of public sector salaries and subsidies. Kuwait has the highest public sector wage bill in the GCC region as public sector wages account for 12.4% of GDP.
Although Kuwaiti women outnumber men in the workforce, the political participation of Women in Kuwait, Kuwaiti women has been limited. Kuwaiti women are considered among the most emancipated women in the Middle East. In 2014 and 2015, Kuwait was ranked first among Arab countries in the Global Gender Gap Report. In 2013, 53% of Kuwaiti women participated in the labor force. Kuwait has higher female citizen participation in the workforce than other GCC countries. According to the Social Progress Index, Kuwait ranks first in Social Progress Index, social progress in the Arab world and Muslim world and second highest in the Middle East after Israel. Kuwait ranks among the world's top countries by List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy, Women in the workforce, women's workforce participation, Global Food Security Index, global food security, and school security, school order and safety.
Executive power is executed by the government. The Emir appoints the prime minister, who in turn chooses the Cabinet of Kuwait, cabinet of ministers comprising the government. In recent decades, numerous policies of the Kuwaiti government have been characterized as "demographic engineering", especially in relation to Kuwait's Bedoon#Kuwait, stateless Bedoon crisis and the Kuwaiti nationality law#History of naturalization in Kuwait, history of naturalization in Kuwait.
The Emir appoints all the judges and many judges are foreign nationals from Egypt. The Constitutional Court is charged with ruling on the conformity of laws and decrees with the constitution. Kuwait has an active public sphere and civil society with political and social organizations that are parties in all but name. Professional groups like the Kuwait Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Chamber of Commerce maintain their autonomy from the government.
The legislative branch consists of the National Assembly (Kuwait), National Assembly, which has nominal oversight authority. As per article 107 of the Constitution of Kuwait, Kuwait constitution, the Emir can dissolve the parliament so long as an election for a new assembly are held within two months of the dissolution. Due to frequent cabinet resignations, Kuwait has a new government every eight months. The political instability has significantly hampered the country's economic development and infrastructure.
The Emir has suspended the constitution twice: in 1976 under Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah and 1986 under Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah. Kuwait is regularly characterized as being a "rentier state" in which the ruling family uses oil revenues to buy the political acquiescence of the citizenry; more than 70% of government spending consists of public sector salaries and subsidies. Kuwait has the highest public sector wage bill in the GCC region as public sector wages account for 12.4% of GDP.
Although Kuwaiti women outnumber men in the workforce, the political participation of Women in Kuwait, Kuwaiti women has been limited. Kuwaiti women are considered among the most emancipated women in the Middle East. In 2014 and 2015, Kuwait was ranked first among Arab countries in the Global Gender Gap Report. In 2013, 53% of Kuwaiti women participated in the labor force. Kuwait has higher female citizen participation in the workforce than other GCC countries. According to the Social Progress Index, Kuwait ranks first in Social Progress Index, social progress in the Arab world and Muslim world and second highest in the Middle East after Israel. Kuwait ranks among the world's top countries by List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy, Women in the workforce, women's workforce participation, Global Food Security Index, global food security, and school security, school order and safety.
 The foreign affairs of Kuwait are handled at the level of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Kuwait), Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The first foreign affairs department bureau was established in 1961. Kuwait became the 111th member state of the United Nations in May 1963. It is a long-standing member of the Arab League and Gulf Cooperation Council.
Before the Gulf War, Kuwait was the only "pro-Soviet" state in the Persian Gulf region. Kuwait acted as a conduit for the Soviets to the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, and Kuwait was used to demonstrate the benefits of a pro-Soviet stance. In July 1987, Kuwait refused to allow U.S. military bases in its territory. As a result of the Gulf War, Kuwait's relations with the U.S. have improved (major non-NATO ally). Kuwait is also a major ally of Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN and enjoys a close economic relationship with China while working to establish a model of cooperation in numerous fields.
Kuwait is a major non-NATO ally to the United States and currently has the largest US military presence in the entire Middle East region. The United States government utilizes Kuwait-based military bases as staging hubs, training ranges, and logistical support for regional and international military operations. The bases include Camp Arifjan, Camp Buehring, Ali Al Salem Air Field, and the naval base Camp Patriot.
Kuwait also has strong economic ties to China and Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN.
Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have many important cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa and Mubarak Al Kabeer Port.
The foreign affairs of Kuwait are handled at the level of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Kuwait), Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The first foreign affairs department bureau was established in 1961. Kuwait became the 111th member state of the United Nations in May 1963. It is a long-standing member of the Arab League and Gulf Cooperation Council.
Before the Gulf War, Kuwait was the only "pro-Soviet" state in the Persian Gulf region. Kuwait acted as a conduit for the Soviets to the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, and Kuwait was used to demonstrate the benefits of a pro-Soviet stance. In July 1987, Kuwait refused to allow U.S. military bases in its territory. As a result of the Gulf War, Kuwait's relations with the U.S. have improved (major non-NATO ally). Kuwait is also a major ally of Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN and enjoys a close economic relationship with China while working to establish a model of cooperation in numerous fields.
Kuwait is a major non-NATO ally to the United States and currently has the largest US military presence in the entire Middle East region. The United States government utilizes Kuwait-based military bases as staging hubs, training ranges, and logistical support for regional and international military operations. The bases include Camp Arifjan, Camp Buehring, Ali Al Salem Air Field, and the naval base Camp Patriot.
Kuwait also has strong economic ties to China and Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN.
Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have many important cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa and Mubarak Al Kabeer Port.
, World Bank. Database updated on 14 April 2015. The Kuwaiti dinar is the highest-valued unit of currency in the world. According to the World Bank, Kuwait is the fifth richest country in the world by gross national income, gross national income per capita, and one of five nations with a GNI per capita above $70,000. As a result of various diversification policies, petroleum now accounts for 43% of total GDP and 70% of export earnings. The biggest non-oil industry is steel manufacturing. It is noteworthy in the study that Kuwait ranked first in the Arab world and 11th globally in the number of small and medium enterprises per 1,000 people, with a score of 67.3 points. sorces ( https://www.arabtimesonline.com/news/kuwait-billionaires-richest-worldwide/) In the past five years, there has been a significant rise in entrepreneurship and small business start-ups in Kuwait. The informal sector is also on the rise, mainly due to the popularity of Instagram businesses. In 2020, Kuwait ranked fourth in the MENA region in startup funding after the UAE, Egypt and Saudi Arabia. In 2019, Iraq was Kuwait's leading export market and food/agricultural products accounted for 94.2% of total export commodities. Globally, Kuwait's main export products were mineral fuels including oil (89.1% of total exports), aircraft and spacecraft (4.3%), organic chemicals (3.2%), plastics (1.2%), iron and steel (0.2%), gems and precious metals (0.1%), machinery including computers (0.1%), aluminum (0.1%), copper (0.1%), and salt, sulphur, stone and cement (0.1%). Kuwait was the world's biggest exporter of sulfonated, nitrated and nitrosated hydrocarbons in 2019. Kuwait was ranked 63rd out of 157 countries in the 2019 Economic Complexity Index (ECI). In recent years, Kuwait has enacted certain measures to regulate foreign labor due to security concerns. For instance, workers from Georgia (country), Georgia are subject to heightened scrutiny when applying for entry visas, and an outright ban was imposed on the entry of domestic workers from Guinea-Bissau and Vietnam. Workers from Bangladesh are also banned. In April 2019, Kuwait added Ethiopia, Burkina Faso, Bhutan, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau to the list of banned countries bringing the total to 20. According to Migrant Rights, the bans are put in place mainly due to the fact that these countries lack embassies and labour corporations in Kuwait. Kuwait is currently considered the region's most oil-dependent country with the lowest share of economic diversification.
 ;Kuwait Space Rocket
The Kuwait Space Rocket (KSR) is a Kuwaiti project to build and launch the first suborbital spaceflight, suborbital Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid bi-propellant rocket in Arabia. The project is divided into two phases with two separate vehicles: an initial testing phase with KSR-1 as a test article (aerospace), test vehicle capable of reaching an altitude of and a more expansive suborbital test phase with the KSR-2 planned to fly to an altitude of .
;TSCK experiment in space
Kuwait's Orbital Space in collaboration with the Kuwait Scientific Center (TSCK) introduced for the first time in Kuwait the opportunity for students to send a science experiment to space. The objectives of this initiative was to allow students to learn about (a) how science space missions are done; (b) Micro-g environment, microgravity (weightlessness) environment; (c) how to do science like a real scientist. This opportunity was made possible through Orbital Space agreement with DreamUp PBC and NanoRacks, Nanoracks LLC, which are collaborating with NASA under a Space Act Agreement. The students' experiment was named "Kuwait's Experiment: E.coli Consuming Carbon Dioxide to Combat Climate Change". The experiment was launched on SpaceX CRS-21 (SpX-21) spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) on 6 December 2020. Astronaut Shannon Walker (member of the ISS Expedition 64) conducted the experiment on behalf of the students.
;National satellite project
In July 2021, Kuwait University announced that it is launching a national satellite project as part of state-led efforts to pioneer the country's sustainable space sector.
;Kuwait Space Rocket
The Kuwait Space Rocket (KSR) is a Kuwaiti project to build and launch the first suborbital spaceflight, suborbital Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid bi-propellant rocket in Arabia. The project is divided into two phases with two separate vehicles: an initial testing phase with KSR-1 as a test article (aerospace), test vehicle capable of reaching an altitude of and a more expansive suborbital test phase with the KSR-2 planned to fly to an altitude of .
;TSCK experiment in space
Kuwait's Orbital Space in collaboration with the Kuwait Scientific Center (TSCK) introduced for the first time in Kuwait the opportunity for students to send a science experiment to space. The objectives of this initiative was to allow students to learn about (a) how science space missions are done; (b) Micro-g environment, microgravity (weightlessness) environment; (c) how to do science like a real scientist. This opportunity was made possible through Orbital Space agreement with DreamUp PBC and NanoRacks, Nanoracks LLC, which are collaborating with NASA under a Space Act Agreement. The students' experiment was named "Kuwait's Experiment: E.coli Consuming Carbon Dioxide to Combat Climate Change". The experiment was launched on SpaceX CRS-21 (SpX-21) spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) on 6 December 2020. Astronaut Shannon Walker (member of the ISS Expedition 64) conducted the experiment on behalf of the students.
;National satellite project
In July 2021, Kuwait University announced that it is launching a national satellite project as part of state-led efforts to pioneer the country's sustainable space sector.
 The country's public transportation network consists almost entirely of bus routes. The state owned Kuwait Public Transportation Company was established in 1962. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait as well as longer distance services to other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states. The main private bus company is CityBus, which operates about 20 routes across the country. Another private bus company, Kuwait Gulf Link Public Transport Services, was started in 2006. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait and longer distance services to neighbouring Arab countries.
There are two airports in Kuwait. Kuwait International Airport serves as the principal hub for international air travel. State-owned Kuwait Airways is the largest airline in the country. A portion of the airport complex is designated as Al Mubarak Air Base, which contains the headquarters of the Kuwait Air Force, as well as the Kuwait Air Force Museum. In 2004, the first private airline of Kuwait, Jazeera Airways, was launched. In 2005, the second private airline, Wataniya Airways was founded.
Kuwait has one of the largest shipping industries in the region. The Kuwait Ports Public Authority manages and operates ports across Kuwait. The country's principal commercial seaports are Shuwaikh and Shuaiba, which handled combined cargo of 753,334 TEU in 2006. Mina Al-Ahmadi, the largest port in the country, handles most of Kuwait's oil exports. Mubarak Al Kabeer Port in Bubiyan Island is currently under construction. The port is expected to handle 2 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU when operations start.
The country's public transportation network consists almost entirely of bus routes. The state owned Kuwait Public Transportation Company was established in 1962. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait as well as longer distance services to other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states. The main private bus company is CityBus, which operates about 20 routes across the country. Another private bus company, Kuwait Gulf Link Public Transport Services, was started in 2006. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait and longer distance services to neighbouring Arab countries.
There are two airports in Kuwait. Kuwait International Airport serves as the principal hub for international air travel. State-owned Kuwait Airways is the largest airline in the country. A portion of the airport complex is designated as Al Mubarak Air Base, which contains the headquarters of the Kuwait Air Force, as well as the Kuwait Air Force Museum. In 2004, the first private airline of Kuwait, Jazeera Airways, was launched. In 2005, the second private airline, Wataniya Airways was founded.
Kuwait has one of the largest shipping industries in the region. The Kuwait Ports Public Authority manages and operates ports across Kuwait. The country's principal commercial seaports are Shuwaikh and Shuaiba, which handled combined cargo of 753,334 TEU in 2006. Mina Al-Ahmadi, the largest port in the country, handles most of Kuwait's oil exports. Mubarak Al Kabeer Port in Bubiyan Island is currently under construction. The port is expected to handle 2 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU when operations start.
 Kuwait's 2018 population was 4.6 million people, of which 1.8 million were Kuwaitis, 800,000 are other Arabs, 1.6 million Asian expatriates, and 47,227 Africans.
Kuwait's 2018 population was 4.6 million people, of which 1.8 million were Kuwaitis, 800,000 are other Arabs, 1.6 million Asian expatriates, and 47,227 Africans.
 Kuwait's official state religion is Maliki Sunni Islam. The
Kuwait's official state religion is Maliki Sunni Islam. The
 Kuwait has the oldest performing arts industry in the Arabian Peninsula. Kuwait's television drama industry is the largest and most active Gulf Arab drama industry and annually produces a minimum of fifteen serials. Kuwait is the main production centre of the Gulf television drama and comedy scene. Most Gulf television drama and comedy productions are filmed in Kuwait. Kuwaiti soap operas are the most-watched soap operas from the Gulf region. Soap operas are most popular during the time of Ramadan, when families gather to break their fast. Although usually performed in the Kuwaiti Arabic, Kuwaiti dialect, they have been shown with success as far away as Tunisia. Kuwait is frequently dubbed the "Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood of the Gulf" due to the popularity of its television soap operas and theatre.
Kuwait is known for its home-grown tradition of theatre. Kuwait is the only country in the Gulf Arab region with a theatrical tradition. The theatrical movement in Kuwait constitutes a major part of the country's cultural life. Theatrical activities in Kuwait date back to the 1920s when the first spoken dramas were released. Theatre activities are still popular today.
Theatre in Kuwait is subsidized by the government, previously by the Ministry of Social Affairs and now by the National Council for Culture, Arts, and Letters (NCCAL). Every urban district has a public theatre. The public theatre in Salmiya is named after actor Abdulhussain Abdulredha. The annual Kuwait Theater Festival is the largest theatrical arts festival in Kuwait.
Kuwait is the main centre of scenography, scenographic and performing arts education in the GCC region. Many famous Arab actors and singers attribute their success to training in Kuwait. The Higher Institute of Theatrical Arts (HIDA) provides higher education in theatrical arts. The institute has several divisions and attracts theatrical students from all over the GCC region. Many actors have graduated from the institute, such as Souad Abdullah, Mohammed Khalifa, Mansour Al-Mansour, along with a number of prominent critics such as Ismail Fahd Ismail.
Kuwait is the birthplace of various popular musical genres, such as Sawt (music), sawt and fijiri. Traditional Kuwaiti music is a reflection of the country's seafaring heritage, which was influenced by many diverse cultures. Kuwait is widely considered the centre of folk music, traditional music in the GCC region. Kuwaiti music has considerably influenced the music culture in other GCC countries. Kuwait pioneered Khaliji (music), contemporary Khaliji music. Kuwaitis were the first commercial recording artists in the Gulf region. The first known Kuwaiti recordings were made between 1912 and 1915. Saleh and Daoud Al-Kuwaity pioneered the Kuwaiti sawt music genre and wrote over 650 songs, many of which are considered traditional and still played daily on radio stations both in Kuwait and the rest of the Arab world.
Kuwait is home to various music festivals, including the International Music Festival hosted by the National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL). The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre contains the largest opera house in the Middle East. Kuwait has several academic institutions specializing in university-level music education. The Higher Institute of Musical Arts was established by the government to provide bachelor's degrees in music. In addition, the College of Basic Education offers bachelor's degrees in music education. The Institute of Musical Studies offers music education qualifications equivalent to secondary school.
Kuwait has a reputation for being the central music influence of the GCC countries. Over the last decade of satellite television stations, many Kuwaiti musicians have become household names in other Arab countries. For example, Bashar Al Shatty became famous due to ''Star Academy (Arabia), Star Academy''. Contemporary Kuwaiti music is popular throughout the Arab world. Nawal El Kuwaiti, Nabeel Shoail and Abdallah Al Rowaished are the most popular contemporary performers.Badley, Bill. "Sounds of the Arabian Peninsula". 2000. In Broughton, Simon and Ellingham, Mark with McConnachie, James and Duane, Orla (Ed.), ''World Music, Vol. 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East'', pp 351-354. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books.
Kuwait has the oldest performing arts industry in the Arabian Peninsula. Kuwait's television drama industry is the largest and most active Gulf Arab drama industry and annually produces a minimum of fifteen serials. Kuwait is the main production centre of the Gulf television drama and comedy scene. Most Gulf television drama and comedy productions are filmed in Kuwait. Kuwaiti soap operas are the most-watched soap operas from the Gulf region. Soap operas are most popular during the time of Ramadan, when families gather to break their fast. Although usually performed in the Kuwaiti Arabic, Kuwaiti dialect, they have been shown with success as far away as Tunisia. Kuwait is frequently dubbed the "Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood of the Gulf" due to the popularity of its television soap operas and theatre.
Kuwait is known for its home-grown tradition of theatre. Kuwait is the only country in the Gulf Arab region with a theatrical tradition. The theatrical movement in Kuwait constitutes a major part of the country's cultural life. Theatrical activities in Kuwait date back to the 1920s when the first spoken dramas were released. Theatre activities are still popular today.
Theatre in Kuwait is subsidized by the government, previously by the Ministry of Social Affairs and now by the National Council for Culture, Arts, and Letters (NCCAL). Every urban district has a public theatre. The public theatre in Salmiya is named after actor Abdulhussain Abdulredha. The annual Kuwait Theater Festival is the largest theatrical arts festival in Kuwait.
Kuwait is the main centre of scenography, scenographic and performing arts education in the GCC region. Many famous Arab actors and singers attribute their success to training in Kuwait. The Higher Institute of Theatrical Arts (HIDA) provides higher education in theatrical arts. The institute has several divisions and attracts theatrical students from all over the GCC region. Many actors have graduated from the institute, such as Souad Abdullah, Mohammed Khalifa, Mansour Al-Mansour, along with a number of prominent critics such as Ismail Fahd Ismail.
Kuwait is the birthplace of various popular musical genres, such as Sawt (music), sawt and fijiri. Traditional Kuwaiti music is a reflection of the country's seafaring heritage, which was influenced by many diverse cultures. Kuwait is widely considered the centre of folk music, traditional music in the GCC region. Kuwaiti music has considerably influenced the music culture in other GCC countries. Kuwait pioneered Khaliji (music), contemporary Khaliji music. Kuwaitis were the first commercial recording artists in the Gulf region. The first known Kuwaiti recordings were made between 1912 and 1915. Saleh and Daoud Al-Kuwaity pioneered the Kuwaiti sawt music genre and wrote over 650 songs, many of which are considered traditional and still played daily on radio stations both in Kuwait and the rest of the Arab world.
Kuwait is home to various music festivals, including the International Music Festival hosted by the National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL). The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre contains the largest opera house in the Middle East. Kuwait has several academic institutions specializing in university-level music education. The Higher Institute of Musical Arts was established by the government to provide bachelor's degrees in music. In addition, the College of Basic Education offers bachelor's degrees in music education. The Institute of Musical Studies offers music education qualifications equivalent to secondary school.
Kuwait has a reputation for being the central music influence of the GCC countries. Over the last decade of satellite television stations, many Kuwaiti musicians have become household names in other Arab countries. For example, Bashar Al Shatty became famous due to ''Star Academy (Arabia), Star Academy''. Contemporary Kuwaiti music is popular throughout the Arab world. Nawal El Kuwaiti, Nabeel Shoail and Abdallah Al Rowaished are the most popular contemporary performers.Badley, Bill. "Sounds of the Arabian Peninsula". 2000. In Broughton, Simon and Ellingham, Mark with McConnachie, James and Duane, Orla (Ed.), ''World Music, Vol. 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East'', pp 351-354. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books.
 The new Kuwait National Cultural District (KNCD) consists of various cultural venues including Sheikh Abdullah Al Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace. With a capital cost of more than US$1 billion, it is one of the largest cultural districts in the world. The Abdullah Salem Cultural Centre is the largest museum complex in the Middle East. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network.
Sadu House is among Kuwait's most important cultural institutions. Bait Al-Othman Museum, Bait Al-Othman is the largest museum specializing in Kuwait's history. Kuwait Scientific Center, The Scientific Center is one of the largest science museums in the Middle East. The Museum of Modern Art (Kuwait), Museum of Modern Art showcases the history of modern art in Kuwait and the region. The Kuwait Maritime Museum presents the country's maritime heritage in the pre-oil era. Several traditional Kuwaiti dhow ships are open to the public, such as Fateh Al-Khayr and Al-Hashemi-II which entered the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest wooden dhow ever built. The Historical, Vintage, and Classical Cars Museum displays vintage cars from Kuwait's motoring heritage. The Kuwait National Museum, National Museum, established in 1983, has been described as "underused and overlooked".
Several Kuwaiti museums are devoted to Islamic art, most notably the Tareq Rajab Museums and Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres. The Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres include education wings, conservation labs, and research libraries. There are several libraries, art libraries in Kuwait. Khalifa Al-Qattan's Mirror House is the most popular art museum in Kuwait. Many museums in Kuwait are private enterprises. In contrast to the top-down approach in other Gulf states, museum development in Kuwait reflects a greater sense of civic identity and demonstrates the strength of civil society in Kuwait, which has produced many independent cultural enterprises.
The new Kuwait National Cultural District (KNCD) consists of various cultural venues including Sheikh Abdullah Al Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace. With a capital cost of more than US$1 billion, it is one of the largest cultural districts in the world. The Abdullah Salem Cultural Centre is the largest museum complex in the Middle East. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network.
Sadu House is among Kuwait's most important cultural institutions. Bait Al-Othman Museum, Bait Al-Othman is the largest museum specializing in Kuwait's history. Kuwait Scientific Center, The Scientific Center is one of the largest science museums in the Middle East. The Museum of Modern Art (Kuwait), Museum of Modern Art showcases the history of modern art in Kuwait and the region. The Kuwait Maritime Museum presents the country's maritime heritage in the pre-oil era. Several traditional Kuwaiti dhow ships are open to the public, such as Fateh Al-Khayr and Al-Hashemi-II which entered the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest wooden dhow ever built. The Historical, Vintage, and Classical Cars Museum displays vintage cars from Kuwait's motoring heritage. The Kuwait National Museum, National Museum, established in 1983, has been described as "underused and overlooked".
Several Kuwaiti museums are devoted to Islamic art, most notably the Tareq Rajab Museums and Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres. The Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres include education wings, conservation labs, and research libraries. There are several libraries, art libraries in Kuwait. Khalifa Al-Qattan's Mirror House is the most popular art museum in Kuwait. Many museums in Kuwait are private enterprises. In contrast to the top-down approach in other Gulf states, museum development in Kuwait reflects a greater sense of civic identity and demonstrates the strength of civil society in Kuwait, which has produced many independent cultural enterprises.
 Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Kuwait. The Kuwait Football Association (KFA) is the governing body of football in Kuwait. The KFA organises the Kuwait national football team, men's, Kuwait women's national football team, women's, and futsal national teams. The Kuwaiti Premier League is the top league of Kuwaiti football, featuring eighteen teams. The Kuwait national football team have been the champions of the 1980 AFC Asian Cup, runners-up of the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, and have taken third place of the 1984 AFC Asian Cup. Kuwait has also been to one FIFA World Cup, in 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982; they drew 1–1 with Czechoslovakia national football team, Czechoslovakia before losing to France national football team, France and England national football team, England, failing to advance from the first round. Kuwait is home to many football clubs including Al-Arabi SC (Kuwait), Al-Arabi, Fahaheel (football club), Al-Fahaheel, Al Jahra (football club), Al-Jahra, Al Kuwait Kaifan, Al-Kuwait, Al Naser Sporting Club, Al-Naser, Al Salmiya Club, Al-Salmiya, Al-Shabab (Kuwait), Al-Shabab, Al Qadsia Kuwait, Al Qadsia, Al Yarmouk (football club), Al-Yarmouk, Al Kazma Kuwait, Kazma, Khaitan,
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Kuwait. The Kuwait Football Association (KFA) is the governing body of football in Kuwait. The KFA organises the Kuwait national football team, men's, Kuwait women's national football team, women's, and futsal national teams. The Kuwaiti Premier League is the top league of Kuwaiti football, featuring eighteen teams. The Kuwait national football team have been the champions of the 1980 AFC Asian Cup, runners-up of the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, and have taken third place of the 1984 AFC Asian Cup. Kuwait has also been to one FIFA World Cup, in 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982; they drew 1–1 with Czechoslovakia national football team, Czechoslovakia before losing to France national football team, France and England national football team, England, failing to advance from the first round. Kuwait is home to many football clubs including Al-Arabi SC (Kuwait), Al-Arabi, Fahaheel (football club), Al-Fahaheel, Al Jahra (football club), Al-Jahra, Al Kuwait Kaifan, Al-Kuwait, Al Naser Sporting Club, Al-Naser, Al Salmiya Club, Al-Salmiya, Al-Shabab (Kuwait), Al-Shabab, Al Qadsia Kuwait, Al Qadsia, Al Yarmouk (football club), Al-Yarmouk, Al Kazma Kuwait, Kazma, Khaitan,
Kuwait City
Kuwait City ( ar, مدينة الكويت) is the capital and largest city of Kuwait. Located at the heart of the country on the south shore of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf, it is the political, cultural and economical centre of the emirate, ...
. , Kuwait has a population of 4.45 million people of which 1.45 million are Kuwaiti citizens while the remaining 3.00 million are foreign nationals from over 100 countries.
Historically, most of present-day Kuwait was part of ancient Mesopotamia. Pre-oil Kuwait was a strategic trade port between Mesopotamia, Persia and India. Oil reserves were discovered in commercial quantities in 1938. In 1946, crude oil was exported for the first time. From 1946 to 1982, the country underwent large-scale modernization, largely based on income from oil production. In the 1980s, Kuwait experienced a period of geopolitical instability and an economic crisis following the stock market crash. In 1990, after oil production disputes with neighbouring Iraq, Kuwait was invaded
An invasion is a military offensive in which large numbers of combatants of one geopolitical entity aggressively enter territory owned by another such entity, generally with the objective of either: conquering; liberating or re-establishing con ...
, and later annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
into one of Iraq's governorates by Iraq under Saddam Hussein."OPEC pressures Kuwait to moderate quota demand", ''New Straits Times'', 7 June 1989 The Iraqi occupation of Kuwait came to an end on February 26, 1991, after military intervention
Interventionism refers to a political practice of intervention, particularly to the practice of governments to interfere in political affairs of other countries, staging military or trade interventions. Economic interventionism refers to a diffe ...
by a military coalition
A coalition is a group formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political or economical spaces.
Formation
According to ''A Gui ...
led by the United States and various other countries.
Kuwait is an emirate. The emir is the head of state and the Al Sabah
The House of Sabah ( ar, آل صباح ''Āl Ṣubāḥ'') is the ruling family of Kuwait.
History Origin
The Al Sabah family originate from the Bani Utbah confederation. Prior to settling in Kuwait, the Al Sabah family were expelled from Umm ...
is the ruling family which dominates the country's political system. Kuwait's official state religion is Islam. Kuwait is a developing country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
with a high-income economy, backed by the world's sixth largest oil reserves. The Kuwaiti dinar is the highest valued currency in the world. In 2009, Kuwait had the highest Human Development Index in the Arab world. Kuwait has the largest number of stateless people in the entire region. Kuwait is a founding member of the GCC and is also a member of the UN, AL, OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC, ) is a cartel of countries. Founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela), it has, since 1965, been headquart ...
and the OIC.
Kuwait named the emir's son as the country's new prime minister on July 24, 2022 to replace caretaker premier Sheikh Sabah al-Khalid, who faced a combative parliament as head of cabinet in a feud hindering fiscal reform.
Etymology
The country's name is from the Arabic diminutive form of ( or ), meaning "fortress built near water". Since 1961, the official name of the state is the "State of Kuwait".History
Antiquity
Following the post-glacial flooding of the Persian Gulf basin, debris from the Tigris–Euphrates river formed a substantial delta, creating most of the land in present-day Kuwait and establishing the present coastlines. One of the earliest evidence of human habitation in Kuwait dates back to 8000 BC whereMesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
tools were found in Burgan. Historically, most of present-day Kuwait was part of ancient Mesopotamia.
 During the Ubaid period (6500 BC), Kuwait was the central site of interaction between the peoples of Mesopotamia and Neolithic Eastern Arabia, including
During the Ubaid period (6500 BC), Kuwait was the central site of interaction between the peoples of Mesopotamia and Neolithic Eastern Arabia, including Bahra 1
Bahra 1 is an archaeological site in the Subiya region on the coast of Kuwait Bay (Kuwait) associated with the Ubaid culture. It is one of the earliest Ubaid culture settlements in the Persian Gulf region, about 5500–4900 BC.
History of rese ...
and site H3 in Subiya. The Neolithic inhabitants of Kuwait were among the world's earliest maritime traders. One of the world's earliest reed-boats was discovered at site H3 dating back to the Ubaid period. Other Neolithic sites in Kuwait are located in Khiran and Sulaibikhat
Sulaibikhat ( ar, الصليبخات, aṣ-Ṣulaybikhāt) is a district of Kuwait City in Kuwait. It comprises five blocks.
Sulaibkhat Camp
The British camp was built in Sulaibikhat during the British mandate, and consisted of approximately 20 ...
.
Mesopotamian
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
s first settled in the Kuwaiti island of Failaka
Failaka Island ( ar, فيلكا '' / ''; Kuwaiti Arabic: فيلچا ) is a Kuwaiti Island in the Persian Gulf. The island is 20 km off the coast of Kuwait City in the Persian Gulf. The name "Failaka" is thought to be derived from the ancient ...
in 2000 B.C. Traders from the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian city of Ur inhabited Failaka and ran a mercantile business. The island had many Mesopotamian-style buildings typical of those found in Iraq dating from around 2000 B.C. In 4000 BC until 2000 BC, Kuwait was home to the Dilmun civilization. Dilmun included Al-Shadadiya, Akkaz, Umm an Namil, and Failaka
Failaka Island ( ar, فيلكا '' / ''; Kuwaiti Arabic: فيلچا ) is a Kuwaiti Island in the Persian Gulf. The island is 20 km off the coast of Kuwait City in the Persian Gulf. The name "Failaka" is thought to be derived from the ancient ...
. At its peak in 2000 BC, Dilmun controlled the Persian Gulf trading routes.
During the Dilmun era (from ca. 3000 BC), Failaka was known as "Agarum
Agarum (also transliterated as Agaru or Akarum, cuneiform: ''a-kà-rum'' or ''a-ga-rum'') is a bronze-age Ancient Near East, Near Eastern proper name, probably a toponym for a region or island in the Eastern Arabia and Persian Gulf. Agarum has be ...
", the land of Enzak
Inzak (also Enzag, Enzak, Anzak; in older publications Enshag) was the main god of the pantheon of Dilmun. The precise origin of his name remains a matter of scholarly debate. He might have been associated with date palms. His cult center was Aga ...
, a great god in the Dilmun civilization according to Sumerian cuneiform texts found on the island. As part of Dilmun, Failaka became a hub for the civilization from the end of the 3rd to the middle of the 1st millennium BC. After the Dilmun civilization, Failaka was inhabited by the Kassites
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylon ...
of Mesopotamia, and was formally under the control of the Kassite dynasty of Babylon. Studies indicate traces of human settlement can be found on Failaka dating back to as early as the end of the 3rd millennium BC, and extending until the 20th century AD. Many of the artifacts found in Falaika are linked to Mesopotamian civilizations and seem to show that Failaka was gradually drawn toward the civilization based in Antioch.
Under Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
, the bay of Kuwait was under Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n control. Cuneiform documents found in Failaka indicate the presence of Babylonians in the island's population. Babylonian Kings were present in Failaka during the Neo-Babylonian Empire period, Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 ...
had a governor in Failaka and Nebuchadnezzar II had a palace and temple in Falaika. Failaka also contained temples dedicated to the worship of Shamash
Utu (dUD "Sun"), also known under the Akkadian name Shamash, ''šmš'', syc, ܫܡܫܐ ''šemša'', he, שֶׁמֶשׁ ''šemeš'', ar, شمس ''šams'', Ashurian Aramaic: 𐣴𐣬𐣴 ''š'meš(ā)'' was the ancient Mesopotamian sun god. ...
, the Mesopotamian sun god in the Babylonian pantheon.
 Following the
Following the Fall of Babylon
The Fall of Babylon denotes the end of the Neo-Babylonian Empire after it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire in 539 BCE.
Nabonidus (Nabû-na'id, 556–539 BCE), son of the Assyrian priestess Adda-Guppi, came to the throne in 556 BCE, afte ...
, the bay of Kuwait came under the control of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
(c. 550‒330 BC) as the bay was repopulated after seven centuries of abandonment. Failaka was under the control of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
as evidenced by the archaeological discovery of Achaemenid strata. There are Aramaic inscriptions that testify Achaemenid presence.
In 4th century BC, the ancient Greeks colonized the bay of Kuwait under Alexander the Great. The ancient Greeks named mainland Kuwait ''Larissa'' and Failaka was named ''Ikaros
IKAROS (Interplanetary Kite-craft Accelerated by Radiation Of the Sun) is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) experimental spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched on 20 May 2010, aboard an H-IIA rocket, together with the ''Akatsuki'' (V ...
''. The bay of Kuwait was named ''Hieros Kolpos''. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
and Arrian
Arrian of Nicomedia (; Greek: ''Arrianos''; la, Lucius Flavius Arrianus; )
was a Greek historian, public servant, military commander and philosopher of the Roman period.
''The Anabasis of Alexander'' by Arrian is considered the best ...
, Alexander the Great named Failaka ''Ikaros'' because it resembled the Aegean island of that name in size and shape. Some elements of Greek mythology were mixed with the local cults. "Ikaros" was also the name of a prominent city situated in Failaka. Large Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
forts and Greek temples were uncovered. Archaeological remains of Greek colonization were also discovered in Akkaz, Umm an Namil, and Subiya.
 At the time of Alexander the Great, the mouth of the
At the time of Alexander the Great, the mouth of the Euphrates River
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
was located in northern Kuwait. The Euphrates river flowed directly into the Persian Gulf via Khor Subiya which was a river channel at the time. Failaka was located 15 kilometers from the mouth of the Euphrates river. By the first century BC, the Khor Subiya river channel dried out completely.
In 127 BC, Kuwait was part of the Parthian Empire and the kingdom of Characene was established around Teredon
Teredon was an ancient port city in southern Mesopotamia. The place could not be localized so far archaeologically, but is believed to be in Kuwait near Basra. The place is mentioned several times by ancient writers. It is said to have been founded ...
in present-day Kuwait. Characene was centered in the region encompassing southern Mesopotamia, Characene coins were discovered in Akkaz, Umm an Namil, and Failaka. A busy Parthian commercial station was situated in Kuwait.
The earliest recorded mention of Kuwait was in 150 AD in the geographical treatise '' Geography'' by Greek scholar Ptolemy. Ptolemy mentioned the Bay of Kuwait as ''Hieros Kolpos'' (''Sacer Sinus'' in the Latin versions).
In 224 AD, Kuwait became part of the Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
. At the time of the Sassanid Empire, Kuwait was known as ''Meshan'', which was an alternative name of the kingdom of Characene. Akkaz was a Partho- Sassanian site; the Sassanid religion's tower of silence was discovered in northern Akkaz. Late Sassanian settlements were discovered in Failaka. In Bubiyan, there is archaeological evidence of Sassanian to early Islamic periods of human presence as evidenced by the recent discovery of torpedo-jar pottery shards on several prominent beach ridges.
Most of present-day Kuwait is still archaeologically unexplored. According to several famous archaeologists and geologists, Kuwait was likely the original location of the Pishon River which watered the mythical Garden of Eden
In Abrahamic religions, the Garden of Eden ( he, גַּן־עֵדֶן, ) or Garden of God (, and גַן־אֱלֹהִים ''gan-Elohim''), also called the Terrestrial Paradise, is the Bible, biblical paradise described in Book of Genesis, Genes ...
.The Pishon River - Found/ref>James K. Hoffmeier, ''The Archaeology of the Bible'',
Lion Hudson
Lion Hudson is UK's largest publisher of children's Christian books. It is based in Oxford, UK.
It had its origins as Lion Publishing (founded in 1971) and Hudson International (founded in 1977) which merged to become Lion Hudson PLC in 2003. ...
: Oxford, England, 34-35 Juris Zarins
Juris Zarins (Zariņš) (born 1945, in Germany) is an American-Latvian archaeologist and professor at Missouri State University, who specializes in the Middle East.
Biography
Zarins is ethnically Latvian, but was born in Germany at the end of ...
argued that the Garden of Eden was situated at the head of the Persian Gulf (present-day Kuwait), where the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers run into the sea, from his research on this area using information from many different sources, including LANDSAT images from space. His suggestion about the Pishon River was supported by James A. Sauer of the American Center of Oriental Research
The American Center of Research (ACOR) is a private, not-for-profit scholarly and educational organization. Based in Alexandria, Virginia, with a facility in Amman, Jordan, ACOR promotes knowledge of Jordan and the interconnected region, past and ...
. Sauer made an argument from geology and history that Pishon River was the now-defunct Kuwait River. With the aid of satellite photos, Farouk El-Baz traced the dry channel from Kuwait up the Wadi Al-Batin.
In 636 AD, the Battle of Chains
The Battle of Sallasil ( ar, معركة ذات السلاسل ''Dhat al-Salasil'') or the Battle of Chains was the first battle fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Persian Empire in April 629. The battle was fought in Kazima ...
between the Sassanid Empire and Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
was fought in Kuwait. At the time, Kuwait was under the control of the Sassanid Empire. The Battle of Chains was the first battle of the Rashidun Caliphate in which the Muslim army sought to extend its frontiers.
As a result of Rashidun victory in 636 AD, the bay of Kuwait was home to the city of Kazma
Kazma () is an ancient city in Kuwait. It is located in Al Jahra Governorate, north of Kuwait City, the capital of Kuwait. It is an ancient city with a long history, known to Persians and Arabs since the Sassanid, Jahiliyyah and the early Isla ...
(also known as "Kadhima" or "Kāzimah") in the early Islamic era. Medieval Arabic sources contain multiple references to the bay of Kuwait in the early Islamic period. According to medieval sources, the city functioned as a trade port and resting place for pilgrims on their way from Iraq to Hejaz. The city was controlled by the kingdom of Al-Hirah
Al-Hirah ( ar, الحيرة, translit=al-Ḥīra Middle Persian: ''Hērt'' ) was an ancient city in Mesopotamia located south of what is now Kufa in south-central Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of I ...
in Iraq. In the early Islamic period, the bay of Kuwait was known for being a fertile area. The Kuwaiti city of Kazma was also a stop for caravans coming from Persia and Mesopotamia en route to the Arabian Peninsula. The poet Al-Farazdaq
Hammam ibn Ghalib ( ar, همام بن غالب; born c. 641; died 728–730), most commonly known as Al-Farazdaq () or Abu Firas, was an Arab poet.
He was born in, Kazma. He was a member of Darim, one of the most respected divisions of the Bani T ...
, recognized as one of the greatest classical poets of the Arabs, was born in the Kuwaiti city of Kazma.
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
Nestorian settlements flourished across the bay of Kuwait from the 5th century until the 9th century. Excavations have revealed several farms, villages and two large churches dating from the 5th and 6th century. Archaeologists are currently excavating nearby sites to understand the extent of the settlements that flourished in the eighth and ninth centuries A.D. An old island tradition is that a community grew up around a Christian mystic and hermit. The small farms and villages were eventually abandoned. Remains of Byzantine era Nestorian churches were found in Akkaz and Al-Qusur. Pottery at the site can be dated from as early as the first half of the 7th century through the 9th century.
1521–1918: Founding
 In 1521, Kuwait was under Portuguese control. In the late 16th century, the Portuguese built a defensive settlement in Kuwait. In 1613,
In 1521, Kuwait was under Portuguese control. In the late 16th century, the Portuguese built a defensive settlement in Kuwait. In 1613, Kuwait City
Kuwait City ( ar, مدينة الكويت) is the capital and largest city of Kuwait. Located at the heart of the country on the south shore of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf, it is the political, cultural and economical centre of the emirate, ...
was founded as a fishing village. Administratively, it was a sheikhdom, ruled by local sheikh
Sheikh (pronounced or ; ar, شيخ ' , mostly pronounced , plural ' )—also transliterated sheekh, sheyikh, shaykh, shayk, shekh, shaik and Shaikh, shak—is an honorific title in the Arabic language. It commonly designates a chief of a ...
s from Bani Khalid
Bani Khalid ( ar, بني خالد) is an Arab tribal confederation mainly inhabiting Eastern Arabia and Najd. The tribe ruled southern Iraq, Kuwait, and Eastern Arabia (al-Hasa and al-Qatif) from the 15th century to the 18th century, and agai ...
clan. In 1682 or 1716, the Bani Utbah
The Bani Utbah ( ar, بني عتبة, banī ʿUtbah, plural Utub; ar, العتوب ', singular Utbi; ar, العتبي ') is an Arab tribal confederation that originated in Najd. The confederation is thought to have been formed when a group of ...
settled in Kuwait City, which at this time was still inhabited by fishermen and primarily functioned as a fishing village under Bani Khalid control. Sometime after the death of the Bani Khalid's leader Barrak Bin Urair and the fall of the Bani Khalid Emirate, the Utub were able to wrest control of Kuwait as a result of successive matrimonial alliances.
In the early eighteenth century, Kuwait prospered as a maritime port city and rapidly became the principal commercial center for the transit of goods between Baghdad, India, Muscat, and Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
. By the mid-1700s, Kuwait had established itself as the major trading route from the Persian Gulf to Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
. During the Persian siege of Basra in 1775–79, Iraqi merchants took refuge in Kuwait and were partly instrumental in the expansion of Kuwait's boat-building and trading activities. As a result, Kuwait's maritime commerce boomed, as the Indian trade routes with Baghdad, Aleppo, Smyrna and Constantinople were diverted to Kuwait during this time. The East India Company was diverted to Kuwait in 1792. The East India Company secured the sea routes between Kuwait, India and the east coasts of Africa. After the Persians withdrew from Basra in 1779, Kuwait continued to attract trade away from Basra. The flight of many of Basra's leading merchants to Kuwait continued to play a significant role in Basra's commercial stagnation well into the 1850s.
 According to Kuwaiti authors, the instability in Basra helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait. In the late 18th century, Kuwait was a haven for Basra merchants fleeing Ottoman persecution. Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf, its ships renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Kuwaitis also developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf. In the 19th century, Kuwait became significant in the
According to Kuwaiti authors, the instability in Basra helped foster economic prosperity in Kuwait. In the late 18th century, Kuwait was a haven for Basra merchants fleeing Ottoman persecution. Kuwait was the center of boat building in the Persian Gulf, its ships renowned throughout the Indian Ocean. Kuwaitis also developed a reputation as the best sailors in the Persian Gulf. In the 19th century, Kuwait became significant in the horse trade Horse trade may refer to:
*Horse Trade Theater Group
*Horse trading
Horse trading, in its literal sense, is the buying and selling of horses, also called "horse dealing". Due to the difficulties in evaluating the merits of a horse offered for s ...
, with regular shipments in sailing vessels. In the mid 19th century, it was estimated that Kuwait exported an average of 800 horses to India annually.
In the 1890s, threatened by the Ottoman Empire, ruler Sheikh Mubarak Al Sabah
Sheikh Mubarak Al-Sabah (1837 – 28 November 1915) ( ar, الشيخ مبارك بن صباح الصباح) "the Great" ( ar, مبارك الكبير) was the seventh ruler of the Sheikhdom of Kuwait from 18 May 1896 until his death on 18 Novem ...
signed an agreement with the British government in India (subsequently known as the Anglo-Kuwaiti Agreement of 1899) making Kuwait a British protectorate. This gave Britain exclusive access and trade with Kuwait, while denying Ottoman provinces to the north a port on the Persian Gulf. The Sheikhdom of Kuwait remained a British protectorate until 1961.
During the reign of Mubarak, Kuwait was dubbed the "Marseilles
Marseille ( , , ; also spelled in English as Marseilles; oc, Marselha ) is the prefecture of the French department of Bouches-du-Rhône and capital of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region. Situated in the camargue region of southern Franc ...
of the Persian Gulf" because its economic vitality attracted a large variety of people. The population was cosmopolitan, ethnically and religiously diverse, including Arabs, Persians, Africans, Jews and Armenians. Kuwait was known for its religious tolerance.
After the Anglo-Ottoman Convention of 1913, Kuwait was established as an autonomous '' kaza,'' or district, of the Ottoman Empire and a '' de facto'' protectorate of Great Britain.
In the first decades of the twentieth century, Kuwait had a well-established elite: wealthy trading families linked by marriage and shared economic interests, long-settled and urban, most claiming descent from the original 30 Bani Utubi families. The wealthiest were merchants who acquired their wealth from long-distance commerce, shipbuilding and pearling. They were a cosmopolitan elite who traveled extensively to India, Africa and Europe, and educated their sons abroad more than other Gulf Arab elite. Western visitors noted the Kuwaiti elite used European office systems, typewriters, and followed European culture with curiosity. The richest were involved in general trade. The Kuwaiti merchant families of Al-Ghanim and Al-Hamad were estimated to be worth millions before the 1940s.
In the early 20th century, Kuwait immensely declined in regional economic importance, mainly due to many trade blockades and the world economic depression. Before Mary Bruins Allison
Mary Bruins Allison (March 19, 1903 – September 15, 1994) was one of the first American women to be trained in medicine in the United States to worked as a missionary physician in Arabia. While attending medical college in Philadelphia, she le ...
visited Kuwait in 1934, Kuwait lost its prominence in long-distance trade. During World War I, the British Empire imposed a trade blockade against Kuwait because Kuwait's ruler at the time, Salim Al-Mubarak Al-Sabah, supported the Ottoman Empire. The British economic blockade heavily damaged Kuwait's economy.
1919–1945: After World War I
In 1919, Sheikh Salim Al-Mubarak Al-Sabah intended to build a commercial city in the south of Kuwait. This caused a diplomatic crisis with Najd, but Britain intervened, discouraging Sheikh Salim. In 1920, an attempt by theIkhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
to build a stronghold in southern Kuwait led to the Battle of Hamdh. The Battle of Hamdh involved 2,000 Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
fighters against 100 Kuwaiti cavalrymen
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating a ...
and 200 Kuwaiti infantrymen. The battle lasted for six days and resulted in heavy but unknown casualties on both sides resulting in the victory of the Ikhwan forces and leading to the battle of Jahra around the Kuwait Red Fort. The Battle of Jahra happened as the result of the Battle of Hamdh. A force of three to four thousand Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
, led by Faisal Al-Dawish
Faisal bin Sultan al-Duwaish (Arabic: فيصل بن سلطان .الدويش المطيري c. 1882 – 1931) was Prince of the Mutair tribe and one of Arabia's Ikhwan leaders, who assisted Abdulaziz in the unification of Saudi Arabia. The moth ...
, attacked the Red Fort at Al-Jahra, defended by fifteen hundred men. The fort was besieged and the Kuwaiti position precarious; had the fort fallen, Kuwait would likely have been incorporated into Ibn Saud's empire. The Ikhwan attack repulsed for the while, negotiations began between Salim and Al-Dawish; the latter threatened another attack if the Kuwaiti forces did not surrender. The local merchant class convinced Salim to call in help from British troops, who showed up with airplanes and three warships, ending the attacks. After the Battle of Jahra, Ibn Saud's warriors, the Ikhwan
The Ikhwan ( ar, الإخوان, al-ʾIkhwān, The Brethren), commonly known as Ikhwan min ta'a Allah ( ar, إخوان من أطاع الله), was a traditionalist religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a signif ...
, demanded that Kuwait follows five rules: evict all the Shias, adopt the Ikhwan doctrine, label the Turks " heretics", abolish smoking, munkar and prostitution, and destroy the American missionary hospital.
 The
The Kuwait–Najd War
The Kuwait–Najd War erupted in the aftermath of World War I. The war occurred because Ibn Saud of Najd wanted to annex Kuwait. The sharpened conflict between Sheikhdom of Kuwait, Kuwait and Emirate of Nejd and Hasa, Najd led to the death of hun ...
of 1919–20 erupted in the aftermath of World War I
The aftermath of World War I saw drastic political, cultural, economic, and social change across Eurasia, Africa, and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Four empires collapsed due to the war, old countries were abolished, ne ...
. The war occurred because Ibn Saud
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud ( ar, عبد العزيز بن عبد الرحمن آل سعود, ʿAbd al ʿAzīz bin ʿAbd ar Raḥman Āl Suʿūd; 15 January 1875Ibn Saud's birth year has been a source of debate. It is generally accepted ...
of Najd wanted to annex Kuwait. The sharpened conflict between Kuwait and Najd led to the death of hundreds of Kuwaitis. The war resulted in sporadic border clashes throughout 1919–1920.
When Percy Cox was informed of the border clashes in Kuwait, he sent a letter to the Ruler of Arabistan Sheikh Khazʽal Ibn Jabir
Khazal bin Jabir bin Merdaw al-Kabi ( ar, خزعل بن جابر بن مرداو الكعبي، fa, شیخ خزعل) (18 August 1863 – 24 May 1936), ''Muaz us-Sultana'', and ''Sardar-e- Aqdas'' (''Most Sacred Officer of the Imperial Order ...
offering the Kuwaiti throne to either him or one of his heirs, knowing that Khaz'al would be a wiser ruler than the Al Sabah family. Khaz'al, who considered the Al Sabah as his own family, replied "Do you expect me to allow the stepping down of Al Mubarak from the throne of Kuwait? Do you think I can accept this?" He then asked:
Following the Kuwait–Najd War in 1919–20, Ibn Saud imposed a trade blockade against Kuwait from the years 1923 until 1937. The goal of the Saudi economic and military attacks on Kuwait was to annex as much of Kuwait's territory as possible. At the Uqair conference in 1922, the boundaries of Kuwait and Najd were set; as a result of British interference, Kuwait had no representative at the Uqair conference. After the Uqair conference, Kuwait was still subjected to a Saudi economic blockade and intermittent Saudi raiding
Raiding may refer to:
* The present participle of the verb Raid (disambiguation), which itself has several meanings
* Raid (military)
* Raid (video games), a group of video game players who join forces
* Raiding, Austria, a town in Austria
* Par ...
.
 The
The Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
harmed Kuwait's economy, starting in the late 1920s. International trading was one of Kuwait's main sources of income before oil. Kuwaiti merchants were mostly intermediary merchants. As a result of the decline of European demand for goods from India and Africa, Kuwait's economy suffered. The decline in international trade resulted in an increase in gold smuggling by Kuwaiti ships to India. Some Kuwaiti merchant families became rich from this smuggling. Kuwait's pearl industry also collapsed as a result of the worldwide economic depression. At its height, Kuwait's pearl industry had led the world's luxury market, regularly sending out between 750 and 800 ships to meet the European elite's desire for pearls. During the economic depression, luxuries like pearls were in little demand. The Japanese invention of cultured pearl
Cultured pearls are formed within a cultured pearl sac with human intervention in the interior of productive living molluscs in a variety of conditions depending upon the mollusc and the goals. Just as the same as natural pearls, cultured pearls ...
s also contributed to the collapse of Kuwait's pearl industry.
In 1937, Freya Stark wrote about the extent of poverty in Kuwait at the time:
Attempts by Faisal king of Iraq to build a railway to Kuwait and port facilities on the Gulf were rejected by Britain. These and other similar British colonial policies made Kuwait a focus of the Arab national movement in Iraq, and a symbol of Iraqi humiliation at the hands of the British.
Throughout the 1930s, Kuwaiti people opposed the British imposed separation of Kuwait from Iraq. In 1938, the "Free Kuwaiti Movement" was established by Kuwaiti youth who opposed British rule and submitted a petition requesting the Iraqi government reunifies Kuwait and Iraq. Due to fears of armed uprising in Kuwait, the Al Sabah agreed to the establishment of a legislative council to represent the "Free Kuwaiti Movement" demanding the reunification of Iraq and Kuwait. The council's first meeting in 1938 resulted in unanimous resolutions demanding the reunification of Kuwait and Iraq.
On 22 February 1938, oil was first discovered in the Burgan field
The Burgan field is an oil field situated in the desert of southeastern Kuwait. Burgan field can also refer to the Greater Burgan—a group of three closely spaced fields, which includes Burgan field itself as well as the much smaller Magwa and ...
.
In March 1939, a popular armed uprising erupted within Kuwait to reunify with Iraq. The Al Sabah family, along with British military support, violently put down the uprising, and killed and imprisoned its participants. King Ghazi of Iraq publicly demanded the release of the Kuwaiti prisoners and warned the Al Sabah family to end the repression of the "Free Kuwaiti Movement".Batatu, Hanna 1978. "The Old Social Classes and the Revolutionary Movements of Iraq: A Study of Iraq's Old Landed and Commercial Classes and of its Communists, Ba'athists and Free Officers" Princeton p. 189
1946–1982: State-building
Between 1946 and 1982, Kuwait experienced a period of prosperity driven by oil and its liberal atmosphere. In popular discourse, the years between 1946 and 1982 are referred to as the "Golden Era of Kuwait". In 1950, a major public-work programme began to enable Kuwaitis to enjoy a modern standard of living. By 1952, the country became the largest oil exporter in the Persian Gulf region. This massive growth attracted many foreign workers, especially from Palestine, India, and Egypt – with the latter being particularly political within the context of the Arab Cold War. In June 1961, Kuwait became independent with the end of the Sheikhdom of Kuwait#History as a Protected State of Britain, British protectorate and the Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salim Al-Sabah became Emir of Kuwait. Kuwait's Public holidays in Kuwait, national day, however, is celebrated on 25 February, the anniversary of the coronation of Sheikh Abdullah (it was originally celebrated on 19 June, the date of independence, but concerns over the summer heat caused the government to move it). Under the terms of the newly drafted Constitution of Kuwait, Constitution, Kuwait held its first Kuwaiti parliamentary election, 1963, parliamentary elections in 1963. Kuwait was the first of the Arab states of the Persian Gulf to establish a constitution and parliament. Although Kuwait formally gained independence in 1961, Iraq initially refused to recognize the country's independence by maintaining that Kuwait is part of Iraq, albeit Iraq later briefly backed down following a show of force by Britain and Arab League support of Kuwait's independence. The short-lived Operation Vantage crisis evolved in July 1961, as the Iraqi government threatened to invade Kuwait and the invasion was finally averted following plans by the Arab League to form an international Arab force against the potential Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. As a result of Operation Vantage, the Arab League took over the border security of Kuwait and the British had withdrawn their forces by 19 October. Iraqi prime minister Abd al-Karim Qasim was killed in a coup in 1963 but, although Iraq recognised Kuwaiti independence and the military threat was perceived to be reduced, Britain continued to monitor the situation and kept forces available to protect Kuwait until 1971. There had been no Iraqi military action against Kuwait at the time: this was attributed to the political and military situation within Iraq which continued to be unstable. A treaty of friendship between Iraq and Kuwait was signed in 1963 by which Iraq recognised the 1932 border of Kuwait. After the 1967 Six Day War Kuwait along with other Arab speaking countries voted the three no's of the Khartoum Resolution: no peace with Israel, no Recognition of Israel, no negotiations with Israel. The Kuwait-Iraq 1973 Sanita border skirmish evolved on 20 March 1973, when Iraqi army units occupied El-Samitah near the Kuwaiti border, which evoked an international crisis.
On 6 February 1974, 1974 attack on the Japanese Embassy in Kuwait, Palestinian militants occupied the Japanese embassy in Kuwait, taking the ambassador and ten others hostage. The militants' motive was to support the Japanese Red Army members and Palestinian militants who were holding hostages on a Singaporean ferry in what is known as the Laju incident, ''Laju'' incident. Ultimately, the hostages were released, and the guerrillas allowed to fly to Aden. This was the first time Palestinian guerrillas struck in Kuwait as the Al Sabah ruling family, headed by Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, funded the Palestinian resistance movement. Kuwait had been a regular endpoint for Palestinian aircraft hijacking, plane hijacking in the past and had considered itself safe.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was considered the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's #Television and theatre, theatre industry was well known throughout the Arab world.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the Freedom of the press, freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, ''Al-Arabi (magazine), Al-Arabi'' magazine was first published. The magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait because they enjoyed greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
Kuwaiti society embraced liberal and non-traditional attitudes throughout the 1960s and 1970s. For example, most Kuwaiti women did not wear the hijab in the 1960s and 70s.
Although Kuwait formally gained independence in 1961, Iraq initially refused to recognize the country's independence by maintaining that Kuwait is part of Iraq, albeit Iraq later briefly backed down following a show of force by Britain and Arab League support of Kuwait's independence. The short-lived Operation Vantage crisis evolved in July 1961, as the Iraqi government threatened to invade Kuwait and the invasion was finally averted following plans by the Arab League to form an international Arab force against the potential Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. As a result of Operation Vantage, the Arab League took over the border security of Kuwait and the British had withdrawn their forces by 19 October. Iraqi prime minister Abd al-Karim Qasim was killed in a coup in 1963 but, although Iraq recognised Kuwaiti independence and the military threat was perceived to be reduced, Britain continued to monitor the situation and kept forces available to protect Kuwait until 1971. There had been no Iraqi military action against Kuwait at the time: this was attributed to the political and military situation within Iraq which continued to be unstable. A treaty of friendship between Iraq and Kuwait was signed in 1963 by which Iraq recognised the 1932 border of Kuwait. After the 1967 Six Day War Kuwait along with other Arab speaking countries voted the three no's of the Khartoum Resolution: no peace with Israel, no Recognition of Israel, no negotiations with Israel. The Kuwait-Iraq 1973 Sanita border skirmish evolved on 20 March 1973, when Iraqi army units occupied El-Samitah near the Kuwaiti border, which evoked an international crisis.
On 6 February 1974, 1974 attack on the Japanese Embassy in Kuwait, Palestinian militants occupied the Japanese embassy in Kuwait, taking the ambassador and ten others hostage. The militants' motive was to support the Japanese Red Army members and Palestinian militants who were holding hostages on a Singaporean ferry in what is known as the Laju incident, ''Laju'' incident. Ultimately, the hostages were released, and the guerrillas allowed to fly to Aden. This was the first time Palestinian guerrillas struck in Kuwait as the Al Sabah ruling family, headed by Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, funded the Palestinian resistance movement. Kuwait had been a regular endpoint for Palestinian aircraft hijacking, plane hijacking in the past and had considered itself safe.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait was considered the most developed country in the region. Kuwait was the pioneer in the Middle East in diversifying its earnings away from oil exports. The Kuwait Investment Authority is the world's first sovereign wealth fund. From the 1970s onward, Kuwait scored highest of all Arab countries on the Human Development Index. Kuwait University was established in 1966. Kuwait's #Television and theatre, theatre industry was well known throughout the Arab world.
In the 1960s and 1970s, Kuwait's press was described as one of the Freedom of the press, freest in the world. Kuwait was the pioneer in the literary renaissance in the Arab region. In 1958, ''Al-Arabi (magazine), Al-Arabi'' magazine was first published. The magazine went on to become the most popular magazine in the Arab world. Many Arab writers moved to Kuwait because they enjoyed greater freedom of expression than elsewhere in the Arab world. The Iraqi poet Ahmed Matar left Iraq in the 1970s to take refuge in the more liberal environment of Kuwait.
Kuwaiti society embraced liberal and non-traditional attitudes throughout the 1960s and 1970s. For example, most Kuwaiti women did not wear the hijab in the 1960s and 70s.
1982–1990: Gulf War
In the early 1980s, Kuwait experienced a major economic crisis after the Souk Al-Manakh stock market crash and 1980s oil glut, decrease in oil price. During the Iran–Iraq War, Kuwait supported Iraq. Throughout the 1980s, there were several Terrorism in Kuwait, terror attacks in Kuwait, including the 1983 Kuwait bombings, hijacking of 1983 Kuwait bombings#Aircraft hijackings (1984–1988), several Kuwait Airways planes and the attempted assassination of Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Emir Jaber in 1985. Kuwait was a regional hub of science and technology in the 1960s and 1970s up until the early 1980s; the scientific research sector significantly suffered due to the terror attacks. After the Iran–Iraq War ended, Kuwait declined an Iraqi request to forgive its US$65 billion debt. An economic rivalry between the two countries ensued after Kuwait increased its oil production by 40 percent. Tensions between the two countries increased further in July 1990, after Iraq complained to
After the Iran–Iraq War ended, Kuwait declined an Iraqi request to forgive its US$65 billion debt. An economic rivalry between the two countries ensued after Kuwait increased its oil production by 40 percent. Tensions between the two countries increased further in July 1990, after Iraq complained to OPEC
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC, ) is a cartel of countries. Founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members (Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela), it has, since 1965, been headquart ...
claiming that Kuwait was stealing its oil from a field near the border by slant drilling of the Rumaila field.
In August 1990, Iraqi forces Invasion of Kuwait, invaded and annexed Kuwait without any warning. After a series of failed diplomatic negotiations, the United States led a coalition to remove the Iraqi forces from Kuwait, in what became known as the Gulf War. On 26 February 1991, in phase of code-named Operation Desert Storm, the coalition succeeded in driving out the Iraqi forces. As they retreated, Iraqi forces carried out a Kuwaiti oil fires, scorched earth policy by setting oil wells on fire. During the Iraqi occupation, more than 1,000 Kuwaiti civilians were killed. In addition, more than 600 Kuwaitis went missing during Iraq's occupation; remains of approximately 375 were found in mass graves in Iraq. Kuwait celebrates February 26 as Liberation Day (Kuwait), Liberation Day. The event marked the country as the centre of the last major war in the 20th century.

1991–Present: Present era
In the early 1990s, Kuwait Palestinian exodus from Kuwait (Gulf War), expelled approximately 400,000 Palestinian expats. Kuwait's policy was a response to alignment of Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat and the PLO with Saddam Hussein. Kuwait also deported thousands of Iraqis and Yemenis after the Gulf War. In addition, hundreds of thousands of Bedoon, stateless Bedoon were expelled from Kuwait in the early-to-mid 1990s. At the House of Commons of the United Kingdom in 1995, it was announced that the Al Sabah ruling family deported 150,000 stateless Bedoon to refugee camps in the Kuwaiti desert near the Iraqi border with minimal water, insufficient food, and no basic shelter. The Kuwaiti authorities also threatened to murder the stateless Bedoon. As a result, many of the stateless Bedoon fled to Iraq where they still remain stateless people even today. In March 2003, Kuwait became the springboard for the US-led invasion of Iraq. In 2005, women won the right to vote and run in elections. Upon the death of the Emir Jaber in January 2006, Sheikh Saad Al-Sabah succeeded him but was removed nine days later due to his failing health. As a result, Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah was sworn in as Emir. From 2006 onwards, Kuwait suffered from chronic political deadlock between the government and parliament which resulted in multiple cabinet reshuffles and dissolutions. This significantly hampered investment and economic reforms in Kuwait, making the country's economy much more dependent on oil. From 2006 to 2009, Kuwait had the highest Human Development Index ranking in the Arab world. China awarded Kuwait Investment Authority an additional $700 million quota on top of $300 million awarded in March 2012. The quota is the highest to be granted by China to foreign investment entities. In 2014 and 2015, Kuwait was ranked first among Arab countries in the Global Gender Gap Report. In March 2014, David S. Cohen (attorney), David S. Cohen, who was then Under Secretary of the Treasury for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence, Secretary of the Treasury for Terrorism and Financial Intelligence, accused Kuwait of funding terrorism. Since the end of the Gulf War in 1991, accusations of Kuwait and state-sponsored terrorism, Kuwait funding terrorism have been very common and come from a wide variety of sources including intelligence reports, Western government officials, scholarly research, and renowned journalists.William Mauldin"U.S. Calls Qatar, Kuwait Lax Over Terror Financing"
''The Wall Street Journal'', 23 October 2014 From 2014 to 2015, Kuwait was frequently described as the world's Kuwait and state-sponsored terrorism, biggest source of terrorism funding, particularly for ISIS and Al-Qaeda. On 26 June 2015, a 2015 Kuwait mosque bombing, suicide bombing took place at a Shia Muslim mosque in Kuwait. The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claimed responsibility for the attack. Twenty-seven people were killed and 227 people were wounded. It was the largest terror attack in Kuwait's history. In the aftermath, a lawsuit was filed accusing the Kuwaiti government of negligence and direct responsibility for the terror attack. Due to declining oil prices since the late 2010s, Kuwait has been facing one of the worst economic crunches in the entire region. Historically, Kuwait's infrastructure projects market has underperformed its potential due to political deadlock between the government and parliament. Sabah Al Ahmad Sea City was inaugurated in mid-2016. In 2020, the Kuwaiti government experienced its first fiscal deficit since 1995. In recent years, Kuwait has invested significantly in its economic relations with China. China has been Kuwait's largest trade partner since 2016. Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have various cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa which is currently under construction in northern Kuwait. The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah Causeway is part of the first phase of the Madinat al-Hareer, Silk City project. The causeway was inaugurated in May 2019 as part of Kuwait Vision 2035, it connects Kuwait City to northern Kuwait. The Kuwait National Cultural District comprises the Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace.Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre
New Kuwait. In 2020, Kuwait's domestic travel and tourism spending was $6.1 billion. The COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait, COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated Kuwait's economic crisis. Kuwait's economy faced a budget deficit of $46 billion in 2020. In September 2020, Kuwait's Crown Prince Sheikh Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah became the 16th Emir of Kuwait and the successor to Emir Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, who died at the age of 91. In October 2020, Sheikh Mishal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah was appointed as the Crown Prince. Kuwait currently has the largest US military presence in the Middle East region. There are over 14,000 US military personnel stationed in the country. Camp Arifjan is the largest US military base in Kuwait.
Geography

 Located in the north-east corner of the
Located in the north-east corner of the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, Kuwait is one of the smallest countries in the world in terms of land area. Kuwait lies between latitudes 28th parallel north, 28° and 31st parallel north, 31° N, and longitudes 46th meridian east, 46° and 49th meridian east, 49° E. Kuwait is generally low-lying, with the highest point being above sea level. Mutla Ridge is the highest point in Kuwait.
Kuwait has List of islands of Kuwait, ten islands. With an area of , the Bubiyan is the largest island in Kuwait and is connected to the rest of the country by a bridge. 0.6% of Kuwaiti land area is considered arable with sparse vegetation found along its coastline. Kuwait City
Kuwait City ( ar, مدينة الكويت) is the capital and largest city of Kuwait. Located at the heart of the country on the south shore of Kuwait Bay on the Persian Gulf, it is the political, cultural and economical centre of the emirate, ...
is located on Kuwait Bay, a natural deep-water harbor.
Kuwait's Burgan field
The Burgan field is an oil field situated in the desert of southeastern Kuwait. Burgan field can also refer to the Greater Burgan—a group of three closely spaced fields, which includes Burgan field itself as well as the much smaller Magwa and ...
has a total capacity of approximately of proven oil reserves. During the 1991 Kuwaiti oil fires, more than 500 oil lakes were created covering a combined surface area of about . The resulting soil contamination due to oil and soot accumulation had made eastern and south-eastern parts of Kuwait uninhabitable. Sand and oil residue had reduced large parts of the Kuwaiti desert to semi-asphalt surfaces. The oil spills during the Gulf War also drastically affected Kuwait's marine resources.
Climate
Due to Kuwait's proximity to Iraq and Iran, the winter season in Kuwait is colder than other coastal countries in the region (especially UAE, Qatar, and Bahrain). Kuwait is also less humid than other coastal countries in the region. The spring season in March is warm with occasional thunderstorms. The frequent winds from the northwest are cold in winter and hot in summer. Southeasterly damp winds spring up between July and October. Hot and dry south winds prevail in spring and early summer. The shamal, a northwesterly wind common during June and July, causes dramatic sandstorms. Summers in Kuwait are some of the hottest on earth. The highest recorded temperature was at Mitribah on 21 July 2016, which is the highest temperature recorded in Asia. Kuwait List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita, emits a lot of carbon dioxide per person compared to most other countries. In recent years, Kuwait has been regularly ranked among the world's highest countries in term of List of countries by carbon dioxide emissions per capita, CO2 per capita emissions.CO2 emissions (metric tons per capita)according to the World Bank.
Nature reserves
At present, there are five protected areas in Kuwait recognized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature, IUCN. In response to Kuwait becoming the List of parties to the Ramsar Convention, 169th signatory of the Ramsar Convention, Bubiyan Island's Mubarak al-Kabeer reserve was designated as the country's first Wetland of International Importance. The 50,948 ha reserve consists of small lagoons and shallow Saltmarsh, salt marshes and is important as a stop-over for migrating birds on two migration routes. The reserve is home to the world's largest breeding colony of crab-plover.Biodiversity
Currently, List of birds of Kuwait, 444 species of birds have been recorded in Kuwait, 18 species of which breed in the country. Due to its location at the head of the Persian Gulf near the mouth of the Tigris–Euphrates river, Kuwait is situated at the crossroads of many major bird migration routes and between two and three million birds pass each year. Kuwait's marine and littoral ecosystems contain the bulk of the country's biodiversity heritage. The marshes in northern Kuwait and Jahra have become increasingly important as a refuge for passage migrants. Twenty eight species of mammal are found in Kuwait; animals such as gerboa, desert rabbits and hedgehogs are common in the desert. Large carnivores, such as the wolf, caracal and jackal, are longer present. Among the endangered mammalian species are the red fox and wild cat. Forty reptile species have been recorded although none are endemic to Kuwait. Kuwait, Oman and Yemen are the only locations where the endangered smoothtooth blacktip shark is confirmed as occurring. Kuwaiti islands are important breeding areas for four species of tern and the socotra cormorant. Kubbar Island has been recognised an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports a bird colony, breeding colony of white-cheeked terns.Water and sanitation
Kuwait is part of the Tigris–Euphrates river system basin. Several Tigris–Euphrates confluences form parts of the Kuwait–Iraq border. Bubiyan Island is part of the Shatt al-Arab delta. Kuwait is partially part of the Mesopotamian Marshes. Kuwait does not currently have any permanent rivers within its territory. However, Kuwait does have several List of wadis of Kuwait, wadis, the most notable of which is Wadi Al-Batin which forms the border between Kuwait and Iraq. Kuwait also has several river-like marine channels around Bubiyan Island, most notably Khawr Abd Allah which is now an estuary, but once was the point where the Shatt al-Arab emptied into the Persian Gulf. Khawr Abd Allah is located in southern Iraq and northern Kuwait, the Iraq-Kuwait border divides the lower portion of the estuary, but adjacent to the port of Umm Qasr the estuary becomes wholly Iraqi. It forms the northeast coastline of Bubiyan Island and the north coastline of Warbah Island. Kuwait relies on water desalination as a primary source of fresh water for drinking and domestic purposes. There are currently more than six desalination plants. Kuwait was the first country in the world to use desalination to supply water for large-scale domestic use. The history of desalination in Kuwait dates back to 1951 when the first distillation plant was commissioned. In 1965, the Kuwaiti government commissioned the Swedish engineering company of VBB (Sweco) to develop and implement a plan for a modern water-supply system for Kuwait City. The company built Kuwait Water Towers, five groups of water towers, thirty-one towers total, designed by its chief architect Sune Lindström, called "the mushroom towers". For a sixth site, the Emir of Kuwait, Sheikh Jaber al-Ahmad al-Jaber al-Sabah, Jaber Al-Ahmed, wanted a more spectacular design. This last group, known as Kuwait Towers, consists of three towers, two of which also serve as water towers. Water from the desalination facility is pumped up to the tower. The thirty-three towers have a standard capacity of 102,000 cubic meters of water. "The Water Towers" (Kuwait Tower and the Kuwait Water Towers) were awarded the Aga Khan Award for Architecture (1980 Cycle). Kuwait's fresh water resources are limited to groundwater, desalinated seawater, and treated wastewater effluents. There are three major municipal wastewater treatment plants. Most water demand is currently satisfied through seawater desalination plants. Sewage disposal is handled by a national sewage network that covers 98% of facilities in the country.Government and politics
Political system
Kuwait is a semi-constitutional emirate, which is sometimes described as "Anocracy, anocratic". The Polity data series and The Economist, Economist Democracy Index both categorize Kuwait as an autocracy (dictatorship). Freedom House rates the country as "partly free" in the Freedom in the World survey. The Emir of Kuwait, Emir is the head of state. The political system consists of an Cabinet of Kuwait, appointed government (dominated by the House of Sabah, Al Sabah ruling family), Legal system of Kuwait, appointed judiciary, and National Assembly (Kuwait), elected legislature. The Constitution of Kuwait was promulgated in 1962. Executive power is executed by the government. The Emir appoints the prime minister, who in turn chooses the Cabinet of Kuwait, cabinet of ministers comprising the government. In recent decades, numerous policies of the Kuwaiti government have been characterized as "demographic engineering", especially in relation to Kuwait's Bedoon#Kuwait, stateless Bedoon crisis and the Kuwaiti nationality law#History of naturalization in Kuwait, history of naturalization in Kuwait.
The Emir appoints all the judges and many judges are foreign nationals from Egypt. The Constitutional Court is charged with ruling on the conformity of laws and decrees with the constitution. Kuwait has an active public sphere and civil society with political and social organizations that are parties in all but name. Professional groups like the Kuwait Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Chamber of Commerce maintain their autonomy from the government.
The legislative branch consists of the National Assembly (Kuwait), National Assembly, which has nominal oversight authority. As per article 107 of the Constitution of Kuwait, Kuwait constitution, the Emir can dissolve the parliament so long as an election for a new assembly are held within two months of the dissolution. Due to frequent cabinet resignations, Kuwait has a new government every eight months. The political instability has significantly hampered the country's economic development and infrastructure.
The Emir has suspended the constitution twice: in 1976 under Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah and 1986 under Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah. Kuwait is regularly characterized as being a "rentier state" in which the ruling family uses oil revenues to buy the political acquiescence of the citizenry; more than 70% of government spending consists of public sector salaries and subsidies. Kuwait has the highest public sector wage bill in the GCC region as public sector wages account for 12.4% of GDP.
Although Kuwaiti women outnumber men in the workforce, the political participation of Women in Kuwait, Kuwaiti women has been limited. Kuwaiti women are considered among the most emancipated women in the Middle East. In 2014 and 2015, Kuwait was ranked first among Arab countries in the Global Gender Gap Report. In 2013, 53% of Kuwaiti women participated in the labor force. Kuwait has higher female citizen participation in the workforce than other GCC countries. According to the Social Progress Index, Kuwait ranks first in Social Progress Index, social progress in the Arab world and Muslim world and second highest in the Middle East after Israel. Kuwait ranks among the world's top countries by List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy, Women in the workforce, women's workforce participation, Global Food Security Index, global food security, and school security, school order and safety.
Executive power is executed by the government. The Emir appoints the prime minister, who in turn chooses the Cabinet of Kuwait, cabinet of ministers comprising the government. In recent decades, numerous policies of the Kuwaiti government have been characterized as "demographic engineering", especially in relation to Kuwait's Bedoon#Kuwait, stateless Bedoon crisis and the Kuwaiti nationality law#History of naturalization in Kuwait, history of naturalization in Kuwait.
The Emir appoints all the judges and many judges are foreign nationals from Egypt. The Constitutional Court is charged with ruling on the conformity of laws and decrees with the constitution. Kuwait has an active public sphere and civil society with political and social organizations that are parties in all but name. Professional groups like the Kuwait Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Chamber of Commerce maintain their autonomy from the government.
The legislative branch consists of the National Assembly (Kuwait), National Assembly, which has nominal oversight authority. As per article 107 of the Constitution of Kuwait, Kuwait constitution, the Emir can dissolve the parliament so long as an election for a new assembly are held within two months of the dissolution. Due to frequent cabinet resignations, Kuwait has a new government every eight months. The political instability has significantly hampered the country's economic development and infrastructure.
The Emir has suspended the constitution twice: in 1976 under Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah and 1986 under Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmed Al-Sabah. Kuwait is regularly characterized as being a "rentier state" in which the ruling family uses oil revenues to buy the political acquiescence of the citizenry; more than 70% of government spending consists of public sector salaries and subsidies. Kuwait has the highest public sector wage bill in the GCC region as public sector wages account for 12.4% of GDP.
Although Kuwaiti women outnumber men in the workforce, the political participation of Women in Kuwait, Kuwaiti women has been limited. Kuwaiti women are considered among the most emancipated women in the Middle East. In 2014 and 2015, Kuwait was ranked first among Arab countries in the Global Gender Gap Report. In 2013, 53% of Kuwaiti women participated in the labor force. Kuwait has higher female citizen participation in the workforce than other GCC countries. According to the Social Progress Index, Kuwait ranks first in Social Progress Index, social progress in the Arab world and Muslim world and second highest in the Middle East after Israel. Kuwait ranks among the world's top countries by List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy, Women in the workforce, women's workforce participation, Global Food Security Index, global food security, and school security, school order and safety.
Al Sabah dynasty
Article 4 of the Constitution of Kuwait, Kuwait constitution stipulates that Kuwait is a hereditary emirate whose emir must be an heir of Mubarak Al-Sabah. Mubarak had four sons, but an informal pattern of alternation between the descendants of his sons Jaber II Al-Sabah, Jabir and Salim Al-Mubarak Al-Sabah, Salem emerged since his death in 1915. This pattern of succession had one exception before 2006, when Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Sabah Al-Salim, a son of Salem, was named crown prince to succeed his half-brother Sheikh Abdullah Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Abdullah Al-Salem as a consequence of infighting and lack of consensus within the ruling family council. The alternating system was resumed when Sheikh Sabah Al-Salim named Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah, Jaber Al-Ahmed of the Jabir branch as his crown prince, eventually ruling as Emir for 29 years from 1977 to 2006. On January 15, 2006, Emir Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmed died and his crown prince, Sheikh Saad Al-Salim Al-Sabah, Saad Al-Abdullah of the Salem branch was named Emir. On January 23, 2006, the National Assembly unanimously voted in favor of Sheikh Saad Al-Abdullah abdicating in favor of Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, Sabah Al-Ahmed, citing his illness with a form of dementia. Instead of naming a successor from the Salem branch as per convention, Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmed named his half-brother Sheikh Nawaf Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, Nawaf Al-Ahmed as crown prince and his nephew Sheikh Nasser Al-Mohammed Al-Sabah, Nasser Al-Mohammed as prime minister. Article 4 of the Kuwait constitution stipulates that the incoming Emir's choice of crown prince needs to be approved by an absolute majority of the National Assembly (Kuwait), National Assembly. If this approval is not achieved, the emir is constitutionally required to submit three alternative candidates for crown prince to the National Assembly. This process has caused contenders for power to engage in alliance-building in the political scene, which has taken historically private feuding within the ruling family to the "public arena and the political realm".Foreign relations
 The foreign affairs of Kuwait are handled at the level of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Kuwait), Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The first foreign affairs department bureau was established in 1961. Kuwait became the 111th member state of the United Nations in May 1963. It is a long-standing member of the Arab League and Gulf Cooperation Council.
Before the Gulf War, Kuwait was the only "pro-Soviet" state in the Persian Gulf region. Kuwait acted as a conduit for the Soviets to the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, and Kuwait was used to demonstrate the benefits of a pro-Soviet stance. In July 1987, Kuwait refused to allow U.S. military bases in its territory. As a result of the Gulf War, Kuwait's relations with the U.S. have improved (major non-NATO ally). Kuwait is also a major ally of Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN and enjoys a close economic relationship with China while working to establish a model of cooperation in numerous fields.
Kuwait is a major non-NATO ally to the United States and currently has the largest US military presence in the entire Middle East region. The United States government utilizes Kuwait-based military bases as staging hubs, training ranges, and logistical support for regional and international military operations. The bases include Camp Arifjan, Camp Buehring, Ali Al Salem Air Field, and the naval base Camp Patriot.
Kuwait also has strong economic ties to China and Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN.
Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have many important cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa and Mubarak Al Kabeer Port.
The foreign affairs of Kuwait are handled at the level of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Kuwait), Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The first foreign affairs department bureau was established in 1961. Kuwait became the 111th member state of the United Nations in May 1963. It is a long-standing member of the Arab League and Gulf Cooperation Council.
Before the Gulf War, Kuwait was the only "pro-Soviet" state in the Persian Gulf region. Kuwait acted as a conduit for the Soviets to the other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, and Kuwait was used to demonstrate the benefits of a pro-Soviet stance. In July 1987, Kuwait refused to allow U.S. military bases in its territory. As a result of the Gulf War, Kuwait's relations with the U.S. have improved (major non-NATO ally). Kuwait is also a major ally of Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN and enjoys a close economic relationship with China while working to establish a model of cooperation in numerous fields.
Kuwait is a major non-NATO ally to the United States and currently has the largest US military presence in the entire Middle East region. The United States government utilizes Kuwait-based military bases as staging hubs, training ranges, and logistical support for regional and international military operations. The bases include Camp Arifjan, Camp Buehring, Ali Al Salem Air Field, and the naval base Camp Patriot.
Kuwait also has strong economic ties to China and Association of Southeast Asian Nations, ASEAN.
Under the Belt and Road Initiative, Kuwait and China have many important cooperation projects including South al-Mutlaa and Mubarak Al Kabeer Port.
Military
The Military of Kuwait traces its original roots to the Kuwaiti cavalrymen and infantrymen that used to protect Kuwait and its wall since the early 1900s. These cavalrymen and infantrymen formed the defense and security forces in metropolitan areas and were charged with protecting outposts outside the wall of Kuwait. The Military of Kuwait consists of several joint defense forces. The governing bodies are the Ministry of Defense (Kuwait), Kuwait Ministry of Defense, the Ministry of Interior (Kuwait), Kuwait Ministry of Interior, the Kuwait National Guard, and the Kuwait Fire Service Directorate. The Emir of Kuwait is the commander-in-chief of all defense forces by default.Legal system
Kuwait follows the "Civil law (legal system), civil law system" modeled after the French legal system, Kuwait's legal system is largely secular. Sharia law governs only family law for Muslim residents, while non-Muslims in Kuwait have a secular family law. For the application of family law, there are three separate court sections: Sunni Islam, Sunni (Maliki), Shia Islam, Shia, and Dhimmi, non-Muslim. According to the United Nations, Kuwait's legal system is a mix of English law#Common law, English common law, Law of France, French civil law, Egyptian Civil Code, Egyptian civil law and Islamic law. The Judiciary, court system in Kuwait is secular. Unlike other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Kuwait does not have Sharia courts. Sections of the civil court system administer family law. Kuwait has the most secular commercial law in the Arab States of the Persian Gulf, Persian Gulf region. The parliament criminalized alcohol consumption in 1983. Kuwait's Code of Personal Status (Kuwait), Code of Personal Status was promulgated in 1984.Administrative divisions
Kuwait is divided into Governorates of Kuwait, six governorates: Al Asimah Governorate (Kuwait), Al Asimah Governorate (or Capital Governorate); Hawalli Governorate; Farwaniya Governorate; Mubarak Al-Kabeer Governorate; Ahmadi Governorate; and Jahra Governorate. The governorates are further Areas of Kuwait, subdivided into areas.Human rights and corruption
Human rights in Kuwait has been the subject of significant criticism, particularly regarding the Bedoon (stateless people). The Kuwaiti government's handling of the stateless Bedoon crisis has come under criticism from many human rights organisations and even the United Nations. According to Human Rights Watch in 1995, Kuwait has produced 300,000 stateless Bedoon. Kuwait has the largest number of stateless people in the entire region. Since 1986, the Kuwaiti government has refused to grant any form of documentation to the Bedoon including birth certificates, death certificates, identity cards, marriage certificates, and driving licences. The Kuwaiti Bedoon crisis resembles the Rohingya crisis in Myanmar (Burma). According to several human rights organizations, Kuwait is committing ethnic cleansing and genocide against the stateless Bedoon. On the other hand, human rights organizations have criticized Kuwait for the human rights abuses toward foreign nationals. Foreign nationals account for 70% of Kuwait's total population. The kafala system leaves foreign nationals prone to exploitation. Administrative deportation is very common in Kuwait for minor offenses, including minor traffic violations. Kuwait is one of the world's worst offenders in Trafficking in human beings, human trafficking. Hundreds of thousands of foreign nationals are subjected to numerous human rights abuses including involuntary servitude. They are subjected to physical and sexual abuse, non-payment of wages, poor work conditions, threats, confinement to the home, and withholding of passports to restrict their freedom of movement. Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in Kuwait, COVID-19 pandemic vaccination rollout, Kuwait has been regularly accused of implementing a xenophobic vaccine policy toward foreign nationals. Kuwait's mistreatment of foreign workers has resulted in various high-profile diplomatic crises. In 2018, there was a 2018 Kuwait–Philippines diplomatic crisis, diplomatic crisis between Kuwait and the Philippines due to the mistreatment of Filipino workers in Kuwait. Approximately 60% of Filipinos in Kuwait are employed as domestic workers. In July 2018, Kuwaiti fashionista Sondos Alqattan released a controversial video criticizing domestic workers from the Philippines. In 2020, there was a diplomatic crisis between Kuwait and Egypt due to the mistreatment of Egyptian workers in Kuwait. Various Kuwaitis have been jailed after they criticized the Al Sabah ruling family. In 2010, the U.S. State Department said it had concerns about the case of Kuwaiti blogger and journalist Mohammad Abdul-Kader al-Jassem who was on trial for allegedly criticizing the ruling al-Sabah family, and faced up to 18 years in prison if convicted. He was detained after a complaint against him was issued by the office of Kuwait's Emir Sheikh Sabah al-Ahmad al-Sabah. Extensive corruption among Kuwait's high-level government officials is a serious problem resulting in tensions between the government and the public. In the Corruption Perceptions Index 2007, Kuwait was ranked 60th out of 179 countries for corruption (least corrupt countries are at the top of the list). On a scale of 0 to 10 with 0 the most corrupt and 10 the most transparent, Transparency International rated Kuwait 4.3. In 2009, 20% of the youth in juvenile centres had dyslexia, as compared to the 6% of the general population. Data from a 1993 study found that there is a higher rate of psychiatric morbidity in Kuwaiti prisons than in the general population.Economy
Kuwait has a wealthy petroleum-based economy. Kuwait is one of the richest countries in the world."GDP per capita, PPP (current international $)", World Development Indicators database, World Bank. Database updated on 14 April 2015. The Kuwaiti dinar is the highest-valued unit of currency in the world. According to the World Bank, Kuwait is the fifth richest country in the world by gross national income, gross national income per capita, and one of five nations with a GNI per capita above $70,000. As a result of various diversification policies, petroleum now accounts for 43% of total GDP and 70% of export earnings. The biggest non-oil industry is steel manufacturing. It is noteworthy in the study that Kuwait ranked first in the Arab world and 11th globally in the number of small and medium enterprises per 1,000 people, with a score of 67.3 points. sorces ( https://www.arabtimesonline.com/news/kuwait-billionaires-richest-worldwide/) In the past five years, there has been a significant rise in entrepreneurship and small business start-ups in Kuwait. The informal sector is also on the rise, mainly due to the popularity of Instagram businesses. In 2020, Kuwait ranked fourth in the MENA region in startup funding after the UAE, Egypt and Saudi Arabia. In 2019, Iraq was Kuwait's leading export market and food/agricultural products accounted for 94.2% of total export commodities. Globally, Kuwait's main export products were mineral fuels including oil (89.1% of total exports), aircraft and spacecraft (4.3%), organic chemicals (3.2%), plastics (1.2%), iron and steel (0.2%), gems and precious metals (0.1%), machinery including computers (0.1%), aluminum (0.1%), copper (0.1%), and salt, sulphur, stone and cement (0.1%). Kuwait was the world's biggest exporter of sulfonated, nitrated and nitrosated hydrocarbons in 2019. Kuwait was ranked 63rd out of 157 countries in the 2019 Economic Complexity Index (ECI). In recent years, Kuwait has enacted certain measures to regulate foreign labor due to security concerns. For instance, workers from Georgia (country), Georgia are subject to heightened scrutiny when applying for entry visas, and an outright ban was imposed on the entry of domestic workers from Guinea-Bissau and Vietnam. Workers from Bangladesh are also banned. In April 2019, Kuwait added Ethiopia, Burkina Faso, Bhutan, Guinea and Guinea-Bissau to the list of banned countries bringing the total to 20. According to Migrant Rights, the bans are put in place mainly due to the fact that these countries lack embassies and labour corporations in Kuwait. Kuwait is currently considered the region's most oil-dependent country with the lowest share of economic diversification.
Petroleum and natural gas
Despite its relatively small territory, Kuwait has proven crude List of countries by proven oil reserves#Countries, oil reserves of 104 billion barrels, estimated to be 10% of the world's reserves. Kuwait also has substantial List of countries by natural gas proven reserves, natural gas reserves. All natural resources in the country are state property. As part of Kuwait Vision 2035, Kuwait aims to position itself as a global hub for the petrochemical industry. Al Zour Refinery is the largest refinery in the Middle East. It is Kuwait's largest environmentally friendly oil refinery, where this refers to the effect on the local environment as opposed to the global environmental impact of burning the resulting oil. This Al Zour Refinery is a Kuwait-China cooperation project under the Belt and Road Initiative. Al Zour LNG Terminal is the Middle East's largest import terminal for liquefied natural gas. It is the world's largest capacity LNG storage and regasification green field project. The project has attracted investments worth US$3 billion. Other megaprojects include biofuel and clean fuels.Steel manufacturing
Steel manufacturing is Kuwait's second biggest industry. United Steel Industrial Company (KWT Steel) is Kuwait's main steel manufacturing company, the company caters to all of Kuwait's domestic market demands (particularly construction). Kuwait is self-sufficient in steel.Agriculture
In 2016, Kuwait's food self-sufficiency ratio was 49.5% in vegetables, 38.7% in meat, 12.4% in dairy, 24.9% in fruits, and 0.4% in cereals. 8.5% of Kuwait's entire territory consists of agricultural land, although arable land constitutes 0.6% of Kuwait's entire territory. Historically, Jahra was a predominantly agricultural area. There are currently various farms in Jahra.Finance
The Kuwait Investment Authority (KIA) is Kuwait's largest sovereign wealth fund specializing in foreign investment. The KIA is the world's oldest sovereign wealth fund. Since 1953, the Kuwaiti government has directed investments into Europe, United States and Asia Pacific. In 2021, the holdings were valued at around $700 billion in assets. It is the Sovereign wealth fund#Largest sovereign wealth funds, 3rd largest sovereign wealth fund in the world. Kuwait has a leading position in the financial industry in the GCC. The Emir has promoted the idea that Kuwait should focus its energies, in terms of economic development, on the financial industry. The historical preeminence of Kuwait (among the GCC monarchies) in finance dates back to the founding of the National Bank of Kuwait in 1952. The bank was the first local publicly traded corporation in the GCC region. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, an alternative stock market, trading in shares of GCC companies, emerged in Kuwait, the Souk Al-Manakh stock market crash, Souk Al-Manakh. At its peak, its market capitalization was the third highest in the world, behind only the United States and Japan, and ahead of the United Kingdom and France. Kuwait has a large wealth-management industry that stands out in the region. Kuwaiti investment companies administer more assets than those of any other GCC country, save the much larger Saudi Arabia. The Kuwait Financial Centre, in a rough calculation, estimated that Kuwaiti firms accounted for over one-third of the total assets under management in the GCC. The relative strength of Kuwait in the financial industry extends to its stock market. For many years, the total valuation of List of companies of Kuwait, all companies listed on the Kuwait Stock Exchange far exceeded the value of those on any other GCC bourse, except Saudi Arabia. In 2011, financial and banking companies made up more than half of the market capitalization of the Kuwaiti bourse; among all the GCC states, the market capitalization of Kuwaiti financial-sector firms was, in total, behind only that of Saudi Arabia. In recent years, Kuwaiti investment companies have invested large percentages of their assets abroad, and their foreign assets have become substantially larger than their domestic assets. Kuwait is a major source of foreign economic assistance to other states through the Kuwait Fund for Arab Economic Development, an autonomous state institution created in 1961 on the pattern of international development agencies. In 1974, the fund's lending mandate was expanded to include all developing countries in the world.Health
Kuwait has a state-funded healthcare system, which provides treatment without charge to Kuwaiti nationals. There are outpatient clinics in every residential area in Kuwait. A public insurance scheme exists to provide reduced cost healthcare to expatriates. Private healthcare providers also run medical facilities in the country, available to members of their insurance schemes. As part of Kuwait Vision 2035, many new hospitals recently opened. In the years leading up to the COVID-19 pandemic, Kuwait invested in its health care system at a rate that was proportionally higher than most other GCC countries. Under the Kuwait Vision 2035 healthcare strategy, the public hospital sector significantly increased its capacity. Many new hospitals recently opened, Kuwait currently has 20 public hospitals. The new Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Hospital is the largest hospital in the Middle East. Kuwait also has 16 private hospitals. Private sector hospitals in Kuwait offer multiple specialities. This trend is likely to grow further, especially in tapping opportunities to reduce treatments performed overseas and develop inbound medical tourism market by developing high end speciality hospitals.Science and technology
Kuwait has a growing scientific research sector. According to the United States Patent and Trademark Office, Kuwait has registered 448 patents as of 31 December 2015, Kuwait is the second largest patent producer in the Arab world. In the early 2010s, Kuwait produced the largest number of scientific publications and patents per capita in the Arab world and OIC. The Kuwaiti government has implemented various programs to foster innovation resulting in patent rights. Between 2010 and 2014, Kuwait registered the highest growth in patents in the Arab world. The WIPO Global Innovation Index found that Kuwait ranks relatively high for its innovation efficiency ratio (which shows how much innovation output a country is getting for its inputs). Kuwait was ranked 72nd in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 60th in 2019. Kuwait was the first country in the region to implement 5G technology. Kuwait is among the world's leading markets in 5G penetration.Space and satellite programmes
Kuwait has an emerging space industry which is largely driven by private sector initiatives. ;Um Alaish 4 Seven years after the launch of the world's first communications satellite, Telstar 1, Kuwait in October 1969 inaugurated the first satellite ground station in the Middle East, "Um Alaish". The Um Alaish satellite station complex housed several satellite ground stations including Um Alaish 1 (1969), Um Alaish 2 (1977), and Um Alaish 3 (1981). It provided satellite communication services in Kuwait until 1990 when it was destroyed by the Iraqi armed forces during the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. In 2019, Kuwait's Orbital Space established an amateur satellite ground station to provide free access to signals from satellites in orbit passing over Kuwait. The station was named Um Alaish 4 to continue the legacy of "Um Alaish" satellite station. Um Alaish 4 is a member of FUNcube distributed ground station network and the Satellite Networked Open Ground Station project (SatNOGS). ;Kuwait's first satellite Kuwait's Orbital Space in collaboration with the Space Challenges Program and EnduroSat introduced an international initiative called "Code in Space". The initiative allows students from around the world to send and execute their own code in space. The code is transmitted from a satellite ground station to a CubeSat, cubesat (Small satellite, nanosatellite) orbiting earth above sea level. The code is then executed by the satellite's onboard computer and tested under real space environment conditions. The nanosatellite is called "QMR-KWT" (Arabic: قمر الكويت) which means "Moon of Kuwait", translated from Arabic. QMR-KWT launched to space on 30 June 2021 on SpaceX Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket and was part of the payload of a satellite carrier called ION SCV Dauntless David by D-Orbit. It was deployed into its final orbit (Sun-synchronous orbit) on 16 July 2021. QMR-KWT is Kuwait's first satellite. ;Kuwait Space Rocket
The Kuwait Space Rocket (KSR) is a Kuwaiti project to build and launch the first suborbital spaceflight, suborbital Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid bi-propellant rocket in Arabia. The project is divided into two phases with two separate vehicles: an initial testing phase with KSR-1 as a test article (aerospace), test vehicle capable of reaching an altitude of and a more expansive suborbital test phase with the KSR-2 planned to fly to an altitude of .
;TSCK experiment in space
Kuwait's Orbital Space in collaboration with the Kuwait Scientific Center (TSCK) introduced for the first time in Kuwait the opportunity for students to send a science experiment to space. The objectives of this initiative was to allow students to learn about (a) how science space missions are done; (b) Micro-g environment, microgravity (weightlessness) environment; (c) how to do science like a real scientist. This opportunity was made possible through Orbital Space agreement with DreamUp PBC and NanoRacks, Nanoracks LLC, which are collaborating with NASA under a Space Act Agreement. The students' experiment was named "Kuwait's Experiment: E.coli Consuming Carbon Dioxide to Combat Climate Change". The experiment was launched on SpaceX CRS-21 (SpX-21) spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) on 6 December 2020. Astronaut Shannon Walker (member of the ISS Expedition 64) conducted the experiment on behalf of the students.
;National satellite project
In July 2021, Kuwait University announced that it is launching a national satellite project as part of state-led efforts to pioneer the country's sustainable space sector.
;Kuwait Space Rocket
The Kuwait Space Rocket (KSR) is a Kuwaiti project to build and launch the first suborbital spaceflight, suborbital Liquid-propellant rocket, liquid bi-propellant rocket in Arabia. The project is divided into two phases with two separate vehicles: an initial testing phase with KSR-1 as a test article (aerospace), test vehicle capable of reaching an altitude of and a more expansive suborbital test phase with the KSR-2 planned to fly to an altitude of .
;TSCK experiment in space
Kuwait's Orbital Space in collaboration with the Kuwait Scientific Center (TSCK) introduced for the first time in Kuwait the opportunity for students to send a science experiment to space. The objectives of this initiative was to allow students to learn about (a) how science space missions are done; (b) Micro-g environment, microgravity (weightlessness) environment; (c) how to do science like a real scientist. This opportunity was made possible through Orbital Space agreement with DreamUp PBC and NanoRacks, Nanoracks LLC, which are collaborating with NASA under a Space Act Agreement. The students' experiment was named "Kuwait's Experiment: E.coli Consuming Carbon Dioxide to Combat Climate Change". The experiment was launched on SpaceX CRS-21 (SpX-21) spaceflight to the International Space Station (ISS) on 6 December 2020. Astronaut Shannon Walker (member of the ISS Expedition 64) conducted the experiment on behalf of the students.
;National satellite project
In July 2021, Kuwait University announced that it is launching a national satellite project as part of state-led efforts to pioneer the country's sustainable space sector.
Education
Kuwait had the highest literacy rate in the Arab world in 2010. The general education system consists of four levels: kindergarten (lasting for 2 years), primary education, primary (lasting for 5 years), Middle school, intermediate (lasting for 4 years) and secondary education, secondary (lasting for 3 years). Schooling at primary and intermediate level is compulsory for all students aged 6 – 14. All the levels of state education, including higher education, are free. The public education system is undergoing a revamp due to a project in conjunction with the World Bank.Tourism
In 2020, Kuwait's domestic travel and tourism spending reached $6.1 billion (up from $1.6 billion in 2019) with family tourism a rapidly growing segment. The World Travel and Tourism Council, WTTC named Kuwait as one of the world's fastest-growing countries in travel and tourism GDP in 2019, with 11.6% year-on-year growth. In 2016, the tourism industry generated nearly $500 million in revenue. In 2015, tourism accounted for 1.5 percent of the GDP. Sabah Al Ahmad Sea City is one of Kuwait's biggest attractions. The Amiri Diwan of Kuwait, Amiri Diwan recently inaugurated the new Kuwait National Cultural District (KNCD), which comprises Sheikh Abdullah Al Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace. With a capital cost of more than US$1 billion, the project is one of the largest cultural investments in the world. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network. Al Shaheed Park is the largest green roof project ever undertaken in the Arab world. The annual "Hala Febrayer" festival attracts many tourists from neighboring GCC countries, and includes a variety of events including music concerts, parades, and carnivals. The festival is a month-long commemoration of the liberation of Kuwait, and runs from 1 to 28 February. Liberation Day itself is celebrated on 26 February.Transport
Kuwait has an extensive and modern network of highways. Roads in Kuwait, Roadways extended , of which is paved. There are more than two million passenger cars, and 500,000 commercial taxis, buses, and trucks in use. On major highways the maximum speed is . Since there is no railway system in the country, most people travel by automobiles. The country's public transportation network consists almost entirely of bus routes. The state owned Kuwait Public Transportation Company was established in 1962. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait as well as longer distance services to other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states. The main private bus company is CityBus, which operates about 20 routes across the country. Another private bus company, Kuwait Gulf Link Public Transport Services, was started in 2006. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait and longer distance services to neighbouring Arab countries.
There are two airports in Kuwait. Kuwait International Airport serves as the principal hub for international air travel. State-owned Kuwait Airways is the largest airline in the country. A portion of the airport complex is designated as Al Mubarak Air Base, which contains the headquarters of the Kuwait Air Force, as well as the Kuwait Air Force Museum. In 2004, the first private airline of Kuwait, Jazeera Airways, was launched. In 2005, the second private airline, Wataniya Airways was founded.
Kuwait has one of the largest shipping industries in the region. The Kuwait Ports Public Authority manages and operates ports across Kuwait. The country's principal commercial seaports are Shuwaikh and Shuaiba, which handled combined cargo of 753,334 TEU in 2006. Mina Al-Ahmadi, the largest port in the country, handles most of Kuwait's oil exports. Mubarak Al Kabeer Port in Bubiyan Island is currently under construction. The port is expected to handle 2 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU when operations start.
The country's public transportation network consists almost entirely of bus routes. The state owned Kuwait Public Transportation Company was established in 1962. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait as well as longer distance services to other Arab states of the Persian Gulf, Gulf states. The main private bus company is CityBus, which operates about 20 routes across the country. Another private bus company, Kuwait Gulf Link Public Transport Services, was started in 2006. It runs local bus routes across Kuwait and longer distance services to neighbouring Arab countries.
There are two airports in Kuwait. Kuwait International Airport serves as the principal hub for international air travel. State-owned Kuwait Airways is the largest airline in the country. A portion of the airport complex is designated as Al Mubarak Air Base, which contains the headquarters of the Kuwait Air Force, as well as the Kuwait Air Force Museum. In 2004, the first private airline of Kuwait, Jazeera Airways, was launched. In 2005, the second private airline, Wataniya Airways was founded.
Kuwait has one of the largest shipping industries in the region. The Kuwait Ports Public Authority manages and operates ports across Kuwait. The country's principal commercial seaports are Shuwaikh and Shuaiba, which handled combined cargo of 753,334 TEU in 2006. Mina Al-Ahmadi, the largest port in the country, handles most of Kuwait's oil exports. Mubarak Al Kabeer Port in Bubiyan Island is currently under construction. The port is expected to handle 2 million Twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU when operations start.
Demographics
 Kuwait's 2018 population was 4.6 million people, of which 1.8 million were Kuwaitis, 800,000 are other Arabs, 1.6 million Asian expatriates, and 47,227 Africans.
Kuwait's 2018 population was 4.6 million people, of which 1.8 million were Kuwaitis, 800,000 are other Arabs, 1.6 million Asian expatriates, and 47,227 Africans.
Ethnic groups
Expatriates in Kuwait account for around 60% of Kuwait's total population. At the end of December 2018, 57.65% of Kuwait's total population were Arabs (including Arab expats). Indian people, Indians and Egyptians are the largest expat communities respectively.Religion
 Kuwait's official state religion is Maliki Sunni Islam. The
Kuwait's official state religion is Maliki Sunni Islam. The Al Sabah
The House of Sabah ( ar, آل صباح ''Āl Ṣubāḥ'') is the ruling family of Kuwait.
History Origin
The Al Sabah family originate from the Bani Utbah confederation. Prior to settling in Kuwait, the Al Sabah family were expelled from Umm ...
ruling family including the Emir, adhere to the Maliki, Maliki madhhab of Sunni Islam. Most Kuwaiti citizens are Muslim; there is no official national census but it is estimated that 60%–70% are Sunni and 30%–40% are Shia. The country includes a Christianity in Kuwait#Kuwaiti Christians, native Christian community, estimated to be composed of between 259 and 400 Christian Kuwaiti citizens. Kuwait is the only Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf, GCC country besides Bahrain to have a local Christian population who hold citizenship. There is also a small number of Kuwaiti citizens who follow the Baháʼí Faith. Kuwait also has a large community of expatriate Christians, Hinduism, Hindus, Buddhism, Buddhists, and Sikhism, Sikhs.
Languages
Kuwait's official language is Modern Standard Arabic, but its everyday usage is limited to journalism and education. Kuwaiti Arabic is the variant of Arabic used in everyday life. English is widely understood and often used as a business language. Besides English, French is taught as a third language for the students of the humanities at schools, but for two years only. Kuwaiti Arabic is a variant of Gulf Arabic, sharing similarities with the dialects of neighboring coastal areas in Eastern Arabia. Due to immigration during its pre-oil history as well as trade, Kuwaiti Arabic borrowed a lot of words from Persian language, Persian, Languages of India, Indian languages, Balochi language, Turkish, English and Italian. Due to historical immigration, Kuwaiti Persian is used among 'Ajam of Kuwait, Ajam Kuwaitis. The Iranian languages, Iranian sub-dialects of Larestani, Khonji, Bastaki and Gerashi also influenced the vocabulary of Kuwaiti Arabic. Most Shia Kuwaiti citizens are of Iranian ancestry.Culture
Kuwaiti popular culture, in the form of theatre, radio, music, and television soap opera, flourishes and is even exported to neighboring states. Within the Arab states of the Persian Gulf, the culture of Kuwait is the closest to the culture of Bahrain; this is evident in the close association between the two states in theatrical productions and soap operas.Performing arts
 Kuwait has the oldest performing arts industry in the Arabian Peninsula. Kuwait's television drama industry is the largest and most active Gulf Arab drama industry and annually produces a minimum of fifteen serials. Kuwait is the main production centre of the Gulf television drama and comedy scene. Most Gulf television drama and comedy productions are filmed in Kuwait. Kuwaiti soap operas are the most-watched soap operas from the Gulf region. Soap operas are most popular during the time of Ramadan, when families gather to break their fast. Although usually performed in the Kuwaiti Arabic, Kuwaiti dialect, they have been shown with success as far away as Tunisia. Kuwait is frequently dubbed the "Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood of the Gulf" due to the popularity of its television soap operas and theatre.
Kuwait is known for its home-grown tradition of theatre. Kuwait is the only country in the Gulf Arab region with a theatrical tradition. The theatrical movement in Kuwait constitutes a major part of the country's cultural life. Theatrical activities in Kuwait date back to the 1920s when the first spoken dramas were released. Theatre activities are still popular today.
Theatre in Kuwait is subsidized by the government, previously by the Ministry of Social Affairs and now by the National Council for Culture, Arts, and Letters (NCCAL). Every urban district has a public theatre. The public theatre in Salmiya is named after actor Abdulhussain Abdulredha. The annual Kuwait Theater Festival is the largest theatrical arts festival in Kuwait.
Kuwait is the main centre of scenography, scenographic and performing arts education in the GCC region. Many famous Arab actors and singers attribute their success to training in Kuwait. The Higher Institute of Theatrical Arts (HIDA) provides higher education in theatrical arts. The institute has several divisions and attracts theatrical students from all over the GCC region. Many actors have graduated from the institute, such as Souad Abdullah, Mohammed Khalifa, Mansour Al-Mansour, along with a number of prominent critics such as Ismail Fahd Ismail.
Kuwait is the birthplace of various popular musical genres, such as Sawt (music), sawt and fijiri. Traditional Kuwaiti music is a reflection of the country's seafaring heritage, which was influenced by many diverse cultures. Kuwait is widely considered the centre of folk music, traditional music in the GCC region. Kuwaiti music has considerably influenced the music culture in other GCC countries. Kuwait pioneered Khaliji (music), contemporary Khaliji music. Kuwaitis were the first commercial recording artists in the Gulf region. The first known Kuwaiti recordings were made between 1912 and 1915. Saleh and Daoud Al-Kuwaity pioneered the Kuwaiti sawt music genre and wrote over 650 songs, many of which are considered traditional and still played daily on radio stations both in Kuwait and the rest of the Arab world.
Kuwait is home to various music festivals, including the International Music Festival hosted by the National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL). The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre contains the largest opera house in the Middle East. Kuwait has several academic institutions specializing in university-level music education. The Higher Institute of Musical Arts was established by the government to provide bachelor's degrees in music. In addition, the College of Basic Education offers bachelor's degrees in music education. The Institute of Musical Studies offers music education qualifications equivalent to secondary school.
Kuwait has a reputation for being the central music influence of the GCC countries. Over the last decade of satellite television stations, many Kuwaiti musicians have become household names in other Arab countries. For example, Bashar Al Shatty became famous due to ''Star Academy (Arabia), Star Academy''. Contemporary Kuwaiti music is popular throughout the Arab world. Nawal El Kuwaiti, Nabeel Shoail and Abdallah Al Rowaished are the most popular contemporary performers.Badley, Bill. "Sounds of the Arabian Peninsula". 2000. In Broughton, Simon and Ellingham, Mark with McConnachie, James and Duane, Orla (Ed.), ''World Music, Vol. 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East'', pp 351-354. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books.
Kuwait has the oldest performing arts industry in the Arabian Peninsula. Kuwait's television drama industry is the largest and most active Gulf Arab drama industry and annually produces a minimum of fifteen serials. Kuwait is the main production centre of the Gulf television drama and comedy scene. Most Gulf television drama and comedy productions are filmed in Kuwait. Kuwaiti soap operas are the most-watched soap operas from the Gulf region. Soap operas are most popular during the time of Ramadan, when families gather to break their fast. Although usually performed in the Kuwaiti Arabic, Kuwaiti dialect, they have been shown with success as far away as Tunisia. Kuwait is frequently dubbed the "Hollywood, Los Angeles, Hollywood of the Gulf" due to the popularity of its television soap operas and theatre.
Kuwait is known for its home-grown tradition of theatre. Kuwait is the only country in the Gulf Arab region with a theatrical tradition. The theatrical movement in Kuwait constitutes a major part of the country's cultural life. Theatrical activities in Kuwait date back to the 1920s when the first spoken dramas were released. Theatre activities are still popular today.
Theatre in Kuwait is subsidized by the government, previously by the Ministry of Social Affairs and now by the National Council for Culture, Arts, and Letters (NCCAL). Every urban district has a public theatre. The public theatre in Salmiya is named after actor Abdulhussain Abdulredha. The annual Kuwait Theater Festival is the largest theatrical arts festival in Kuwait.
Kuwait is the main centre of scenography, scenographic and performing arts education in the GCC region. Many famous Arab actors and singers attribute their success to training in Kuwait. The Higher Institute of Theatrical Arts (HIDA) provides higher education in theatrical arts. The institute has several divisions and attracts theatrical students from all over the GCC region. Many actors have graduated from the institute, such as Souad Abdullah, Mohammed Khalifa, Mansour Al-Mansour, along with a number of prominent critics such as Ismail Fahd Ismail.
Kuwait is the birthplace of various popular musical genres, such as Sawt (music), sawt and fijiri. Traditional Kuwaiti music is a reflection of the country's seafaring heritage, which was influenced by many diverse cultures. Kuwait is widely considered the centre of folk music, traditional music in the GCC region. Kuwaiti music has considerably influenced the music culture in other GCC countries. Kuwait pioneered Khaliji (music), contemporary Khaliji music. Kuwaitis were the first commercial recording artists in the Gulf region. The first known Kuwaiti recordings were made between 1912 and 1915. Saleh and Daoud Al-Kuwaity pioneered the Kuwaiti sawt music genre and wrote over 650 songs, many of which are considered traditional and still played daily on radio stations both in Kuwait and the rest of the Arab world.
Kuwait is home to various music festivals, including the International Music Festival hosted by the National Council for Culture, Arts and Letters (NCCAL). The Sheikh Jaber Al-Ahmad Cultural Centre contains the largest opera house in the Middle East. Kuwait has several academic institutions specializing in university-level music education. The Higher Institute of Musical Arts was established by the government to provide bachelor's degrees in music. In addition, the College of Basic Education offers bachelor's degrees in music education. The Institute of Musical Studies offers music education qualifications equivalent to secondary school.
Kuwait has a reputation for being the central music influence of the GCC countries. Over the last decade of satellite television stations, many Kuwaiti musicians have become household names in other Arab countries. For example, Bashar Al Shatty became famous due to ''Star Academy (Arabia), Star Academy''. Contemporary Kuwaiti music is popular throughout the Arab world. Nawal El Kuwaiti, Nabeel Shoail and Abdallah Al Rowaished are the most popular contemporary performers.Badley, Bill. "Sounds of the Arabian Peninsula". 2000. In Broughton, Simon and Ellingham, Mark with McConnachie, James and Duane, Orla (Ed.), ''World Music, Vol. 1: Africa, Europe and the Middle East'', pp 351-354. Rough Guides Ltd, Penguin Books.
Visual arts
Kuwait has the oldest modern arts movement in the Arabian Peninsula. Beginning in 1936, Kuwait was the first Gulf Arab country to grant scholarships in the arts. The Kuwaiti artist Mojeb al-Dousari was the earliest recognized visual artist in the Gulf Arab region. He is regarded as the founder of portrait art in the region. The Sultan Gallery was the first professional Arab art gallery in the Gulf. Kuwait is home to more than Art of Kuwait#Art galleries, 30 art galleries. In recent years, Kuwait's contemporary art scene has boomed. Khalifa Al-Qattan was the first artist to hold a solo exhibition in Kuwait. He founded a new art theory in the early 1960s known as "circulism". Other notable Kuwaiti artists include Sami Mohammad, Thuraya Al-Baqsami and Suzan Bushnaq. The government organizes various arts festivals, including the Al Qurain Cultural Festival and Formative Arts Festival. The Kuwait International Biennial was inaugurated in 1967, more than 20 Arab and foreign countries have participated in the biennial. Prominent participants include Layla Al-Attar. In 2004, the Al Kharafi Biennial for Contemporary Arab Art was inaugurated.Cuisine
Kuwaiti cuisine is a fusion of Arabian cuisine, Arabian, Iranian cuisine, Iranian, and Mesopotamian cuisine, Mesopotamian cuisines. Kuwaiti cuisine is part of the Eastern Arabian cuisine. A prominent dish in Kuwaiti cuisine is ''machboos'', a rice-based dish usually prepared with basmati rice seasoned with spices, and chicken or mutton. Seafood is a significant part of the Kuwaiti diet, especially fish. Mutabbaq samak is a national dish in Kuwait. Other local favourites are ''hamour'' (grouper), which is typically served grilled, fried, or with biryani rice because of its texture and taste; ''safi'' (rabbitfish); ''maid'' (mulletfish); and ''sobaity'' (sea bream). Kuwait's traditional flatbread is called Iranian ''khubz''. It is a large flatbread baked in a special oven and it is often topped with sesame seeds. Numerous local bakeries dot the country; the bakers are mainly Iranians (hence the name of the bread, "Iranian ''khubuz''"). Bread is often served with mahyawa fish sauce.Museums
 The new Kuwait National Cultural District (KNCD) consists of various cultural venues including Sheikh Abdullah Al Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace. With a capital cost of more than US$1 billion, it is one of the largest cultural districts in the world. The Abdullah Salem Cultural Centre is the largest museum complex in the Middle East. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network.
Sadu House is among Kuwait's most important cultural institutions. Bait Al-Othman Museum, Bait Al-Othman is the largest museum specializing in Kuwait's history. Kuwait Scientific Center, The Scientific Center is one of the largest science museums in the Middle East. The Museum of Modern Art (Kuwait), Museum of Modern Art showcases the history of modern art in Kuwait and the region. The Kuwait Maritime Museum presents the country's maritime heritage in the pre-oil era. Several traditional Kuwaiti dhow ships are open to the public, such as Fateh Al-Khayr and Al-Hashemi-II which entered the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest wooden dhow ever built. The Historical, Vintage, and Classical Cars Museum displays vintage cars from Kuwait's motoring heritage. The Kuwait National Museum, National Museum, established in 1983, has been described as "underused and overlooked".
Several Kuwaiti museums are devoted to Islamic art, most notably the Tareq Rajab Museums and Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres. The Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres include education wings, conservation labs, and research libraries. There are several libraries, art libraries in Kuwait. Khalifa Al-Qattan's Mirror House is the most popular art museum in Kuwait. Many museums in Kuwait are private enterprises. In contrast to the top-down approach in other Gulf states, museum development in Kuwait reflects a greater sense of civic identity and demonstrates the strength of civil society in Kuwait, which has produced many independent cultural enterprises.
The new Kuwait National Cultural District (KNCD) consists of various cultural venues including Sheikh Abdullah Al Salem Cultural Centre, Sheikh Jaber Al Ahmad Cultural Centre, Al Shaheed Park, and Al Salam Palace (Kuwait), Al Salam Palace. With a capital cost of more than US$1 billion, it is one of the largest cultural districts in the world. The Abdullah Salem Cultural Centre is the largest museum complex in the Middle East. The Kuwait National Cultural District is a member of the Global Cultural Districts Network.
Sadu House is among Kuwait's most important cultural institutions. Bait Al-Othman Museum, Bait Al-Othman is the largest museum specializing in Kuwait's history. Kuwait Scientific Center, The Scientific Center is one of the largest science museums in the Middle East. The Museum of Modern Art (Kuwait), Museum of Modern Art showcases the history of modern art in Kuwait and the region. The Kuwait Maritime Museum presents the country's maritime heritage in the pre-oil era. Several traditional Kuwaiti dhow ships are open to the public, such as Fateh Al-Khayr and Al-Hashemi-II which entered the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest wooden dhow ever built. The Historical, Vintage, and Classical Cars Museum displays vintage cars from Kuwait's motoring heritage. The Kuwait National Museum, National Museum, established in 1983, has been described as "underused and overlooked".
Several Kuwaiti museums are devoted to Islamic art, most notably the Tareq Rajab Museums and Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres. The Dar al Athar al Islamiyyah cultural centres include education wings, conservation labs, and research libraries. There are several libraries, art libraries in Kuwait. Khalifa Al-Qattan's Mirror House is the most popular art museum in Kuwait. Many museums in Kuwait are private enterprises. In contrast to the top-down approach in other Gulf states, museum development in Kuwait reflects a greater sense of civic identity and demonstrates the strength of civil society in Kuwait, which has produced many independent cultural enterprises.
Society
Kuwaiti society is markedly more open society, open than other Gulf Arab societies. Kuwaiti citizens are ethnically diverse, consisting of both Arabs and 'Ajam of Kuwait, Persians ('Ajam). Kuwait stands out in the region as the most liberal in empowering women in the public sphere. Women in Kuwait, Kuwaiti women outnumber men in the workforce. Kuwaiti political scientist Ghanim Alnajjar sees these qualities as a manifestation of Kuwaiti society as a whole, whereby in the Gulf Arab region it is "the least strict about traditions".Media
Kuwait produces more List of newspapers in Kuwait, newspapers and magazines per capita than its neighbors. The state-owned Kuwait News Agency (KUNA) is the largest media house in the country. The Ministry of Information regulates the media industry in Kuwait. Kuwait's media is annually classified as partly free in the Freedom of Press survey by Freedom House. Since 2005, Kuwait has frequently earned the highest ranking of all Arab countries in the annual Press Freedom Index by Reporters Without Borders. In 2009, 2011, 2013 and 2014, Kuwait surpassed Israel as the country with the greatest press freedom in the Middle East. Kuwait is also frequently ranked as the Arab country with the greatest press freedom in Freedom House's annual Freedom of Press survey. Kuwait has 15 satellite television channels, of which four are controlled by the Ministry of Information. State-owned Kuwait Television (KTV) offered first colored broadcast in 1974 and operates five television channels. Government-funded Radio Kuwait also offers daily informative programming in several languages including Arabic, Persian language, Persian, Urdu, and English on the AM broadcasting, AM and Shortwave, SW.Literature
Kuwait has in recent years produced several prominent contemporary writers such as Ismail Fahd Ismail, author of over twenty novels and numerous short story collections. There is also evidence that Kuwaiti literature has long been interactive with English literature, English and French literature.Sport
 Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Kuwait. The Kuwait Football Association (KFA) is the governing body of football in Kuwait. The KFA organises the Kuwait national football team, men's, Kuwait women's national football team, women's, and futsal national teams. The Kuwaiti Premier League is the top league of Kuwaiti football, featuring eighteen teams. The Kuwait national football team have been the champions of the 1980 AFC Asian Cup, runners-up of the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, and have taken third place of the 1984 AFC Asian Cup. Kuwait has also been to one FIFA World Cup, in 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982; they drew 1–1 with Czechoslovakia national football team, Czechoslovakia before losing to France national football team, France and England national football team, England, failing to advance from the first round. Kuwait is home to many football clubs including Al-Arabi SC (Kuwait), Al-Arabi, Fahaheel (football club), Al-Fahaheel, Al Jahra (football club), Al-Jahra, Al Kuwait Kaifan, Al-Kuwait, Al Naser Sporting Club, Al-Naser, Al Salmiya Club, Al-Salmiya, Al-Shabab (Kuwait), Al-Shabab, Al Qadsia Kuwait, Al Qadsia, Al Yarmouk (football club), Al-Yarmouk, Al Kazma Kuwait, Kazma, Khaitan,
Association football, Football is the most popular sport in Kuwait. The Kuwait Football Association (KFA) is the governing body of football in Kuwait. The KFA organises the Kuwait national football team, men's, Kuwait women's national football team, women's, and futsal national teams. The Kuwaiti Premier League is the top league of Kuwaiti football, featuring eighteen teams. The Kuwait national football team have been the champions of the 1980 AFC Asian Cup, runners-up of the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, and have taken third place of the 1984 AFC Asian Cup. Kuwait has also been to one FIFA World Cup, in 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982; they drew 1–1 with Czechoslovakia national football team, Czechoslovakia before losing to France national football team, France and England national football team, England, failing to advance from the first round. Kuwait is home to many football clubs including Al-Arabi SC (Kuwait), Al-Arabi, Fahaheel (football club), Al-Fahaheel, Al Jahra (football club), Al-Jahra, Al Kuwait Kaifan, Al-Kuwait, Al Naser Sporting Club, Al-Naser, Al Salmiya Club, Al-Salmiya, Al-Shabab (Kuwait), Al-Shabab, Al Qadsia Kuwait, Al Qadsia, Al Yarmouk (football club), Al-Yarmouk, Al Kazma Kuwait, Kazma, Khaitan, Sulaibikhat
Sulaibikhat ( ar, الصليبخات, aṣ-Ṣulaybikhāt) is a district of Kuwait City in Kuwait. It comprises five blocks.
Sulaibkhat Camp
The British camp was built in Sulaibikhat during the British mandate, and consisted of approximately 20 ...
, Sahel (Kuwaiti football club), Sahel, and Tadamon, Kuwait, Tadamon. The biggest football rivalry in Kuwait is between Al-Arabi SC (Kuwait), Al-Arabi and Al Qadsia Kuwait, Al Qadsia.
Basketball is one of the country's most popular sports. The Kuwait national basketball team is governed by the Kuwait Basketball Association (KBA). Kuwait made its international debut in 1959. The national team has been to the FIBA Asian Championship in basketball eleven times. The Kuwaiti Division I Basketball League is the highest professional basketball league in Kuwait. Kuwait national cricket team, Cricket in Kuwait is governed by the Kuwait Cricket Association. Other growing sports include Rugby union in Kuwait, rugby union. Kuwait men's national handball team, Handball is widely considered to be the national icon of Kuwait, although football is more popular among the overall population.
Kuwait national ice hockey team, Ice hockey in Kuwait is governed by the Kuwait Ice Hockey Association. Kuwait first joined the International Ice Hockey Federation in 1985, but was expelled in 1992 due to a lack of ice hockey activity. Kuwait was re-admitted into the IIHF in May 2009. In 2015, Kuwait won the IIHF Challenge Cup of Asia.
In February 2020, Kuwait held for the first time a leg of the Aquabike World Championship (powerboating), UIM Aquabike World Championship in front of Marina Beach City.
In May 2022, Kuwait hosted the Third Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Games at the 360 Marina. The event featured 16 different sports, including volleyball, basketball, swimming, athletics, karate and judo and attracted over 1,700 male and female players.
See also
* Outline of Kuwait * Index of Kuwait-related articlesReferences
Further reading
* * * Bianco, C. (2020a). The GCC monarchies: Perceptions of the Iranian threat amid shifting geopolitics. The International Spectator, 55(2), 92–107. * Bianco, C. (2020b). A Gulf apart: How Europe can gain influence with the Gulf Cooperation Council. European Council on Foreign Relations, February 2020. Available at https://ecfr.eu/archive/page/-/a_gulf_apart_how_europe_can_gain_influence_with_gulf_cooperation_council.pdf. * Bianco, C. (2021). Can Europe Choreograph a Saudi-Iranian Détente? European University Institute, Robert Schuman Center for Advanced Studies, Middle East Directions. Available at: https://cadmus.eui.eu/bitstream/handle/1814/70351/PB_2021_10-MED.pdf?sequence=1. * Bianco, C., & Stansfield, G. (2018). The intra-GCC crises: Mapping GCC fragmentation after 2011. International Affairs, 94(3), 613–635. * Miniaoui, Héla, ed. Economic Development in the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries: From Rentier States to Diversified Economies. Vol. 1. Springer Nature, 2020. * Guzansky, Y., & Even, S. (2020). The economic crisis in the Gulf States: A challenge to the "contract" between rulers and ruled. INSS Insight No. 1327, June 1, 2020. Available at https://www.INSS.org.il/publication/gulf-states-economy/?offset=7&posts=201&outher=Yoel%20Guzansky. * Guzansky, Y., & Marshall, Z. A. (2020). The Abraham accords: Immediate significance and long-term implications. Israel Journal of Foreign Affairs, 1–11. * Guzansky, Y., & Segal, E. (2020). All in the family: Leadership changes in the Gulf. INSS Insight No. 1378, August 30, 2020. Available at: https://www.INSS.org.il/publication/gulf-royal-families/?offset=1&posts=201&outher=Yoel%20Guzansky * Guzansky, Y., & Winter, O. (2020). Apolitical Normalization: A New Approach to Jews in Arab States. INSS Insight No. 1332, June 8, 2020. Available at: https://www.INSS.org.il/publication/judaism-in-the-arab-world/?offset=5&posts=201&outher=Yoel%20Guzansky. * Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290349218_The_political_algebra_of_global_value_change_General_models_and_implications_for_the_Muslim_world * * Woertz, Eckart. "Wither the self-sufficiency illusion? Food security in Arab Gulf States and the impact of COVID-19." Food Security 12.4 (2020): 757-760. * Zweiri, Mahjoob, Md Mizanur Rahman, and Arwa Kamal, eds. The 2017 Gulf Crisis: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Vol. 3. Springer Nature, 2020.External links
* {{authority control Kuwait, Arabic-speaking countries and territories Emirates Persian Gulf Member states of OPEC Member states of the Arab League Member states of the Gulf Cooperation Council Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation Member states of the United Nations Middle Eastern countries Near Eastern countries States and territories established in 1961 Western Asian countries Countries in Asia