Kurdistan Democratic Party Politicians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture,
 In the tenth and eleventh centuries, several Kurdish principalities emerged in the region: in the north the Shaddadids (951–1174) (in east Transcaucasia between the
In the tenth and eleventh centuries, several Kurdish principalities emerged in the region: in the north the Shaddadids (951–1174) (in east Transcaucasia between the
 At the
At the
 The incorporation into Turkey of the Kurdish-inhabited regions of eastern Anatolia was opposed by many Kurds, and has resulted in a long-running separatist conflict in which tens of thousands of lives have been lost. The region saw several major Kurdish rebellions, including the Koçgiri rebellion of 1920 under the Ottomans, then successive insurrections under the Turkish state, including the 1924 Sheikh Said rebellion, the Republic of Ararat in 1927, and the 1937 Dersim rebellion. All were forcefully put down by the authorities. The region was declared a closed military area from which foreigners were banned between 1925 and 1965.
In an attempt to deny their existence, the Turkish government categorized Kurds as "
The incorporation into Turkey of the Kurdish-inhabited regions of eastern Anatolia was opposed by many Kurds, and has resulted in a long-running separatist conflict in which tens of thousands of lives have been lost. The region saw several major Kurdish rebellions, including the Koçgiri rebellion of 1920 under the Ottomans, then successive insurrections under the Turkish state, including the 1924 Sheikh Said rebellion, the Republic of Ararat in 1927, and the 1937 Dersim rebellion. All were forcefully put down by the authorities. The region was declared a closed military area from which foreigners were banned between 1925 and 1965.
In an attempt to deny their existence, the Turkish government categorized Kurds as "
Minority Rules
'' New York Times'', 17 February 2008 Many people who spoke, published, or sang in Kurdish were arrested and imprisoned. Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, political parties that represented Kurdish interests were banned. In 1983, the Kurdish provinces were included in the a state of emergency region, which was placed under martial law in response to the activities of the militant separatist organization the
NY Times, 28 September 2007 A guerrilla war took place through the 1980s and 1990s in which much of the countryside was evacuated, thousands of Kurdish villages were destroyed by the government, and numerous
, BBC News, 8 May 2007 Turkey has historically feared that a Kurdish state in Northern Iraq would encourage and support Kurdish separatists in the adjacent Turkish provinces, and have therefore historically strongly opposed Kurdish independence in Iraq. However, following the chaos in Iraq after the US invasion, Turkey has increasingly worked with the autonomous Kurdistan Regional Government. The word 'Kurdistan', whether written or spoken, can still lead to detention and prosecution in Turkey. Kurdistan has been characterized as an "international colony" by the scholar
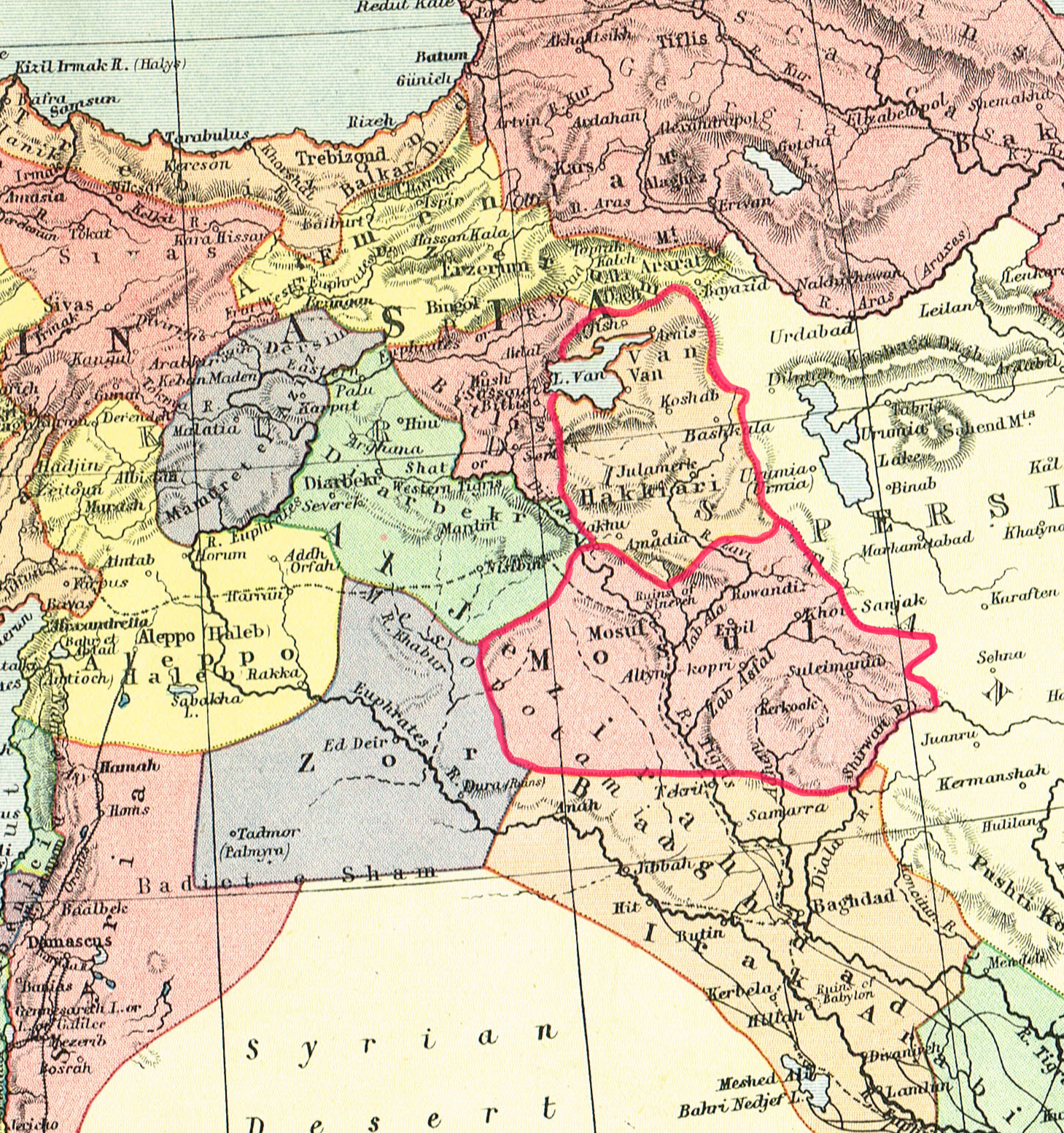
 According to the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Kurdistan covers about 190,000 km² (or 73,000 square miles), and its chief towns are Diyarbakır (Amed), Bitlis (Bedlîs) and
According to the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Kurdistan covers about 190,000 km² (or 73,000 square miles), and its chief towns are Diyarbakır (Amed), Bitlis (Bedlîs) and
 The northern, northwestern and northeastern parts of Kurdistan are referred to as upper Kurdistan, and includes the areas from west of Amed to Lake Urmia.
The lowlands of southern Kurdistan are called lower Kurdistan. The main cities in this area are Kirkuk and Arbil.
The northern, northwestern and northeastern parts of Kurdistan are referred to as upper Kurdistan, and includes the areas from west of Amed to Lake Urmia.
The lowlands of southern Kurdistan are called lower Kurdistan. The main cities in this area are Kirkuk and Arbil.
File:Newen village in Hawraman 2015.jpg, A typical Kurdish village in Hawraman, Kurdistan
File:Canyon, north eastern Kurdistan.jpg, Canyon in
languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
, and national identity have historically been based. Geographically, Kurdistan roughly encompasses the northwestern Zagros and the eastern Taurus mountain ranges.
Kurdistan generally comprises the following four regions: southeastern Turkey ( Northern Kurdistan), northern Iraq ( Southern Kurdistan), northwestern Iran ( Eastern Kurdistan), and northern Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
( Western Kurdistan). Some definitions also include parts of southern Transcaucasia. Certain Kurdish nationalist
Kurdish nationalism (, ) is a nationalist political movement which asserts that Kurds are a nation and espouses the creation of an independent Kurdistan from Iran, Iraq, Syria and Turkey.
Early Kurdish nationalism had its roots in the Ottoman ...
organizations seek to create an independent nation state consisting of some or all of these areas with a Kurdish majority, while others campaign for greater autonomy within the existing national boundaries.
Historically, the word "Kurdistan" is first attested in 11th century Seljuk chronicles. Many disparate Kurdish dynasties, emirates, principalities, and chiefdoms were established from the 8th to 19th centuries. Administratively, the 20th century saw the establishment of the short-lived areas of the Kurdish state (1918–1919), Kingdom of Kurdistan (1921–1924), Kurdistansky Uyezd i.e. "Red Kurdistan" (1923–1929), Republic of Ararat (1927–1930), and Republic of Mahabad (1946).
Iraqi Kurdistan first gained autonomous status in a 1970 agreement with the Iraqi government, and its status was re-confirmed as the autonomous Kurdistan Region within the federal Iraqi republic in 2005. There is also a Kurdistan Province in Iran, but it is not self-ruled. Kurds fighting in the Syrian Civil War were able to take control of large sections of northern Syria and establish self-governing regions in an Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria
The Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES), also known as Rojava, is a de facto autonomous region in northeastern Syria. It consists of self-governing sub-regions in the areas of Afrin, Jazira, Euphrates, Raqqa, Tabqa, M ...
, where they call for autonomy in a federal Syria after the war.
Etymology and delineation
Kurdistan means "Land of the Kurds" and was first attested in 11th-century Seljuk chronicles.The exact origins of the name ''Kurd'' are unclear. The suffix ''-stan
The suffix -stan ( fa, ـستان, translit=''stân'' after a vowel; ''estân'' or ''istân'' after a consonant), has the meaning of "a place abounding in" or "a place where anything abounds" in the Persian language. It appears in the names of ...
'' ( Persian: ـستان, translit.
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus '' trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → , Cyrillic → , Greek → the digraph , Armenian → or ...
''stân'') is Persian for land.
"Kurdistan" was also formerly spelled ''Curdistan''. One of the ancient names of Kurdistan is ''Corduene
Corduene hy, Կորճայք, translit=Korchayk; ; romanized: ''Kartigini'') was an ancient historical region, located south of Lake Van, present-day eastern Turkey.
Many believe that the Kardouchoi—mentioned in Xenophon’s Anabasis as havin ...
''.A.D. Lee, ''The Role of Hostages in Roman Diplomacy with Sasanian Persia'', Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte, Vol. 40, No. 3 (1991), pp. 366–74 (see p. 371) The 19th-century Kurdistan Eyalet ckb:ئەیالەتی کوردستان
Kurdistan Eyalet (Ottoman Turkish: ''Eyâlet-i Kurdistan'') was an eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. It was the first time that the Ottoman Empire used the term "Kurdistan" to refer to an administrative unit rath ...
was the first time that the Ottoman Empire used the term 'Kurdistan' to refer to an administrative unit rather than a geographical region.
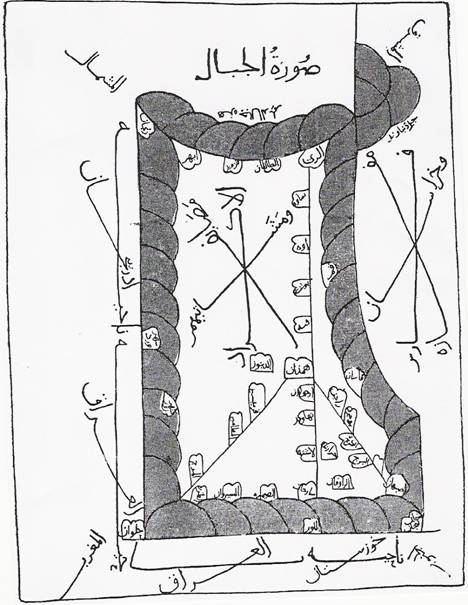
Albeit admitting a thorough delineation is difficult, the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published in ...
'' delineated Kurdistan as following:
History
Ancient history
Various groups, among them the Guti,Hurrians
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern Mes ...
, Mannai ( Mannaeans), and Armenians, lived in this region in antiquity. The original Mannaean homeland was situated east and south of the Lake Urmia, roughly centered around modern-day Mahabad. The region came under Persian rule during the reign of Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
and Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
.
The Kingdom of Corduene
Corduene hy, Կորճայք, translit=Korchayk; ; romanized: ''Kartigini'') was an ancient historical region, located south of Lake Van, present-day eastern Turkey.
Many believe that the Kardouchoi—mentioned in Xenophon’s Anabasis as havin ...
, which emerged from the declining Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, was located to the south and south-east of Lake Van
Lake Van ( tr, Van Gölü; hy, Վանա լիճ, translit=Vana lič̣; ku, Gola Wanê) is the largest lake in Turkey. It lies in the far east of Turkey, in the provinces of Van and Bitlis in the Armenian highlands. It is a saline soda lake ...
between Persia and Mesopotamia and ruled northern Mesopotamia and southeastern Anatolia from 189 BC to AD 384 as vassals of the vying Parthian and Roman empires. Corduene became a vassal state of the Roman Republic in 66 BC and remained allied with the Romans until AD 384. After 66 BC, it passed another 5 times between Rome and Persia. Corduene was situated to the east of Tigranocerta, that is, to the east and south of present-day Diyarbakır in south-eastern Turkey.
Some historians have correlated a connection between Corduene with the modern names of Kurds and Kurdistan; ''T. A. Sinclair'' dismissed this identification as false, while a common association is asserted in the '' Columbia Encyclopedia''.
Some of the ancient districts of Kurdistan and their corresponding modern names:
# Corduene or Gordyene ( Siirt, Bitlis and Şırnak)
# Sophene (Diyarbakır)
# Zabdicene or Bezabde (''Gozarto d'Qardu'' or ''Jazirat Ibn'' or Cizre
Cizre (; ar, جَزِيْرَة ٱبْن عُمَر, Jazīrat Ibn ʿUmar, or ''Madinat al-Jazira'', he, גזירא, Gzira, ku, Cizîr, ''Cizîra Botan'', or ''Cizîre'', syr, ܓܙܪܬܐ ܕܒܪ ܥܘܡܪ, Gāzartā,) is a city in the Cizre Dis ...
)
# Basenia ( Bayazid)
# Moxoene ( Muş)
# Nephercerta (''Miyafarkin'')
# Artemita (Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
)
One of the earliest records of the phrase ''land of the Kurds'' is found in an Assyrian Christian document of late antiquity, describing the stories of Assyrian saints of the Middle East, such as Abdisho. When the Sasanian Marzban asked Mar Abdisho about his place of origin, he replied that according to his parents, they were originally from ''Hazza,'' a village in Assyria. However, they were later driven out of Hazza by pagans, and settled in ''Tamanon,'' which according to Abdisho was in the ''land of the Kurds.'' Tamanon lies just north of the modern Iraq-Turkey border, while Hazza is 12 km southwest of modern Erbil
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000.
Hu ...
. In another passage in the same document, the region of the Khabur River is also identified as ''land of the Kurds''. According to Al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
and Yaqut al-Hamawi, Tamanon was located on the south-western or southern slopes of Mount Judi and south of Cizre
Cizre (; ar, جَزِيْرَة ٱبْن عُمَر, Jazīrat Ibn ʿUmar, or ''Madinat al-Jazira'', he, גזירא, Gzira, ku, Cizîr, ''Cizîra Botan'', or ''Cizîre'', syr, ܓܙܪܬܐ ܕܒܪ ܥܘܡܪ, Gāzartā,) is a city in the Cizre Dis ...
. Other geographical references to the Kurds in Syriac sources appear in Zuqnin chronicle, writings of Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian ( ar, ميخائيل السرياني, Mīkhaʾēl el Sūryani:),( syc, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܣܽܘܪܝܳܝܳܐ, Mīkhoʾēl Sūryoyo), died 1199 AD, also known as Michael the Great ( syr, ܡܺܝܟ݂ܳܐܝܶܠ ܪܰܒ݁ܳܐ, ...
and Bar Hebraeus. They mention the mountains of Qardu, city of Qardu and country of Qardawaye.
Post-classical history
 In the tenth and eleventh centuries, several Kurdish principalities emerged in the region: in the north the Shaddadids (951–1174) (in east Transcaucasia between the
In the tenth and eleventh centuries, several Kurdish principalities emerged in the region: in the north the Shaddadids (951–1174) (in east Transcaucasia between the Kur
The ancient Mesopotamian underworld, most often known in Sumerian as Kur, Irkalla, Kukku, Arali, or Kigal and in Akkadian as Erṣetu, although it had many names in both languages, was a dark, dreary cavern located deep below the ground, where ...
and Araxes
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
rivers) and the Rawadids
Rawwadid or Ravvadid (also Revend or Revendi) or Banū Rawwād () (955–1071) was a Sunni Muslim Kurdish dynasty, centered in the northwestern region of Adharbayjan (Azerbaijan) between the late 8th and early 13th centuries.
Originally of Azd ...
(955–1221) (centered on Tabriz and which controlled all of Azerbaijan), in the east the Hasanwayhids (959–1015) (in Zagros between Shahrizor and Khuzistan) and the Annazids
The Annazids or Banu Annaz (990/991–1117) was a Kurdish Sunni Muslim dynasty which ruled an oscillating territory on the present-day frontier between Iran and Iraq for about 130 years. The Annazids were related by marriage to the Hasanwayhids w ...
(990–1116) (centered in Hulwan) and in the west the Marwanids (990–1096) to the south of Diyarbakır and north of Jazira.
Kurdistan in the Middle Ages was a collection of semi-independent and independent states called emirates. It was nominally under indirect political or religious influence of Khalifs or Shahs. A comprehensive history of these states and their relationship with their neighbors is given in the text of ''Sharafnama'', written by Prince Sharaf al-Din Bitlisi in 1597. The emirates included Baban, Soran, Badinan and Garmiyan in the south; Bakran, Bohtan (or Botan) and Badlis
The Principality of Bitlis, also known as the Bitlis Khanate and the Bitlis Emirate (1182–early 19th century) was a Kurdish principality originated from the ''Rojaki'' (or ''Rozagi'') tribal confederation. The Rojaki defeated the Georgian King ...
in the north, and Mukriyan and Ardalan in the east.
The earliest medieval attestation of the toponym ''Kurdistan'' is found in a 12th-century Armenian historical text by Matteos Urhayeci. He described a battle near Amid and Siverek
Siverek (from hy, Սեւավերակ, lit=black ruins, translit=Sevaverag, ku, Sêwreg) is a city and district in the south-east of Turkey, in Şanlıurfa Province. Population 107,634 (city); 247,000 (district) (2000 census). Siverek is in Şanl� ...
in 1062 as to have taken place in ''Kurdistan''. The second record occurs in the prayer from the colophon of an Armenian manuscript of the Gospels
Gospel originally meant the Christian message ("the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words an ...
, written in 1200.
A later use of the term ''Kurdistan'' is found in Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through to t ...
documents in 1336 and in '' Nuzhat al-Qulub'', written by Hamdallah Mustawfi in 1340.
According to Sharaf al-Din Bitlisi in his Sharafnama, the boundaries of the Kurdish land begin at the Strait of Hormuz
The Strait of Hormuz ( fa, تنگه هرمز ''Tangeh-ye Hormoz'' ar, مَضيق هُرمُز ''Maḍīq Hurmuz'') is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the ...
in the Persian Gulf and stretch on an even line to the end of Malatya and Marash. Evliya Çelebi, who traveled in the region between 1640 and 1655, mentioned that Kurdistan includes Erzurum, Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
, Hakkari, Cizre
Cizre (; ar, جَزِيْرَة ٱبْن عُمَر, Jazīrat Ibn ʿUmar, or ''Madinat al-Jazira'', he, גזירא, Gzira, ku, Cizîr, ''Cizîra Botan'', or ''Cizîre'', syr, ܓܙܪܬܐ ܕܒܪ ܥܘܡܪ, Gāzartā,) is a city in the Cizre Dis ...
, Imaddiya, Mosul, Shahrizor, Harir
Harir ( ar, حرير, ku, ھەریر, Harîr) is a town and sub-district in Erbil Governorate in Kurdistan Region, Iraq. The town is located in the Shaqlawa District.
In the town, there was a church of Mar Yohanna.
History
Harir is mentioned ...
, Ardalan, Baghdad, Derne, Derteng, until Basra.
In the 16th century, after prolonged wars, Kurdish-inhabited areas were split between the Safavid
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
and Ottoman empires. A major division of Kurdistan occurred in the aftermath of the Battle of Chaldiran in 1514, and was formalized in the 1639 Treaty of Zuhab. In a geography textbook of late Ottoman military school by Ahmet Cevad Kurdistan span over the cities Erzurum, Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
, Urfa, Sulaymanyah, Kirkuk
Kirkuk ( ar, كركوك, ku, کەرکووک, translit=Kerkûk, , tr, Kerkük) is a city in Iraq, serving as the capital of the Kirkuk Governorate, located north of Baghdad. The city is home to a diverse population of Turkmens, Arabs, Kurds, ...
, Mosul and Diyarbakir among others and was one out of six regions of Ottoman Asia.
Modern history
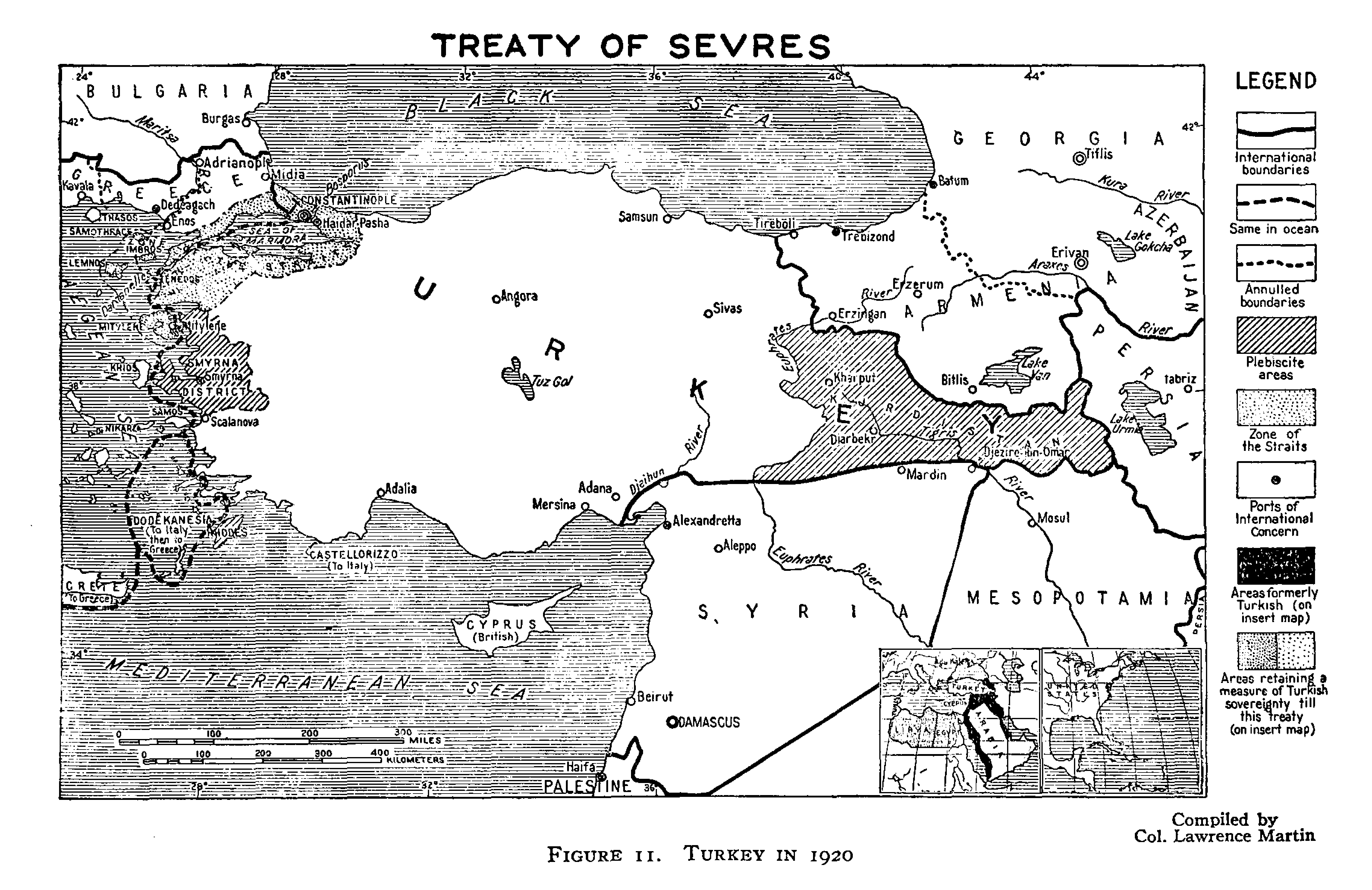
After the collapse of the Ottoman Empire, the Allies contrived to split Kurdistan (as detailed in the ultimately unratified Treaty of Sèvres) among several countries, including Kurdistan, Armenia and others. However, the reconquest of these areas by the forces of Kemal Atatürk (and other pressing issues) caused the Allies to accept the renegotiated Treaty of Lausanne (1923) and the borders of the modern Republic of Turkey, leaving the Kurds without a self-ruled region. Other Kurdish areas were assigned to the new British and French mandated states of Iraq andSyria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
.
 At the
At the San Francisco Peace Conference
The United Nations Conference on International Organization (UNCIO), commonly known as the San Francisco Conference, was a convention of delegates from 50 Allied nations that took place from 25 April 1945 to 26 June 1945 in San Francisco, Calif ...
of 1945, the Kurdish delegation proposed consideration of territory claimed by the Kurds, which encompassed an area extending from the Mediterranean shores near Adana to the shores of the Persian Gulf near Bushehr, and included the Lur inhabited areas of southern Zagros.
The historian Jordi Tejel
Jordi Tejel Gorgas is a historian specializing in modern history, state/society relations, and state-building in the Middle East. He is often cited in the media in relation to Kurdish state-building and Syrian Kurds.
Background
Tejel is curren ...
has identified "Greater Kurdistan" as being one of the "Kurdish myths" that the Kurdistan Democratic Party of Syria (KDPS) were involved in promoting to Kurds in Syria.
An academic source published by the University of Cambridge has described maps of greater Kurdistan created in the 1940s and forward as: "These maps have become some of the most influential propaganda tools for the Kurdish nationalist discourse. They depict a territorially exaggerated version of the territory of Kurdistan, extending into areas with no majority Kurdish populations. Despite their production with political aims related to specific claims on the demographic and ethnographic structure of the region, and their questionable methodologies, they have become 'Kurdistan in the minds of Kurds' and the boundaries they indicate have been readily accepted."
At the end of the 1991 Gulf War, the Coalition
A coalition is a group formed when two or more people or groups temporarily work together to achieve a common goal. The term is most frequently used to denote a formation of power in political or economical spaces.
Formation
According to ''A Gui ...
established a no-fly zone over northern Iraq to provide humanitarian relief to and safeguard the Kurds who would be subjected to Iraqi air attacks. Amid the withdrawal of Iraqi forces from three northern provinces, Kurdistan Region emerged in 1992 as an autonomous entity inside Iraq with its own local government and parliament.
A 2010 US report, written before the instability in Syria and Iraq that exists as of 2014, attested that "Kurdistan may exist by 2030". The weakening of the Iraqi state following the 2014 Northern Iraq offensive by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant has also presented an opportunity for independence for Iraqi Kurdistan, augmented by Turkey's move towards acceptance of such a state although it opposes moves toward Kurdish autonomy in Turkey and Syria.
Northern Kurdistan
 The incorporation into Turkey of the Kurdish-inhabited regions of eastern Anatolia was opposed by many Kurds, and has resulted in a long-running separatist conflict in which tens of thousands of lives have been lost. The region saw several major Kurdish rebellions, including the Koçgiri rebellion of 1920 under the Ottomans, then successive insurrections under the Turkish state, including the 1924 Sheikh Said rebellion, the Republic of Ararat in 1927, and the 1937 Dersim rebellion. All were forcefully put down by the authorities. The region was declared a closed military area from which foreigners were banned between 1925 and 1965.
In an attempt to deny their existence, the Turkish government categorized Kurds as "
The incorporation into Turkey of the Kurdish-inhabited regions of eastern Anatolia was opposed by many Kurds, and has resulted in a long-running separatist conflict in which tens of thousands of lives have been lost. The region saw several major Kurdish rebellions, including the Koçgiri rebellion of 1920 under the Ottomans, then successive insurrections under the Turkish state, including the 1924 Sheikh Said rebellion, the Republic of Ararat in 1927, and the 1937 Dersim rebellion. All were forcefully put down by the authorities. The region was declared a closed military area from which foreigners were banned between 1925 and 1965.
In an attempt to deny their existence, the Turkish government categorized Kurds as "Mountain Turks
The denial of Kurds was the official state policy of Turkey for several decades, which denied that Kurds constitute an own ethnic group and alleged that they instead are a subgroup of Turks and the words Kurd and Kurdistan were omitted by state in ...
" until 1991. The words "Kurds", "Kurdistan", or "Kurdish" were officially banned by the Turkish government. Following the military coup of 1980
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
, the Kurdish language was officially prohibited in public and private life.Toumani, MelineMinority Rules
'' New York Times'', 17 February 2008 Many people who spoke, published, or sang in Kurdish were arrested and imprisoned. Throughout the 1990s and early 2000s, political parties that represented Kurdish interests were banned. In 1983, the Kurdish provinces were included in the a state of emergency region, which was placed under martial law in response to the activities of the militant separatist organization the
Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of south ...
(PKK).Kurd, ''The Hutchinson Unabridged Encyclopedia including Atlas'', 2005NY Times, 28 September 2007 A guerrilla war took place through the 1980s and 1990s in which much of the countryside was evacuated, thousands of Kurdish villages were destroyed by the government, and numerous
summary execution
A summary execution is an execution in which a person is accused of a crime and immediately killed without the benefit of a full and fair trial. Executions as the result of summary justice (such as a drumhead court-martial) are sometimes include ...
s were carried out by both sides.Martin van Bruinessen, "Kurdistan." ''The Oxford Companion to the Politics of the World'', 2nd edition. Joel Krieger, ed. Oxford University Press, 2001. Food embargoes were placed on Kurdish villages and towns. Tens of thousands were killed in the violence and hundreds of thousands were forced to leave their homes.Kurdish rebels kill Turkey troops, BBC News, 8 May 2007 Turkey has historically feared that a Kurdish state in Northern Iraq would encourage and support Kurdish separatists in the adjacent Turkish provinces, and have therefore historically strongly opposed Kurdish independence in Iraq. However, following the chaos in Iraq after the US invasion, Turkey has increasingly worked with the autonomous Kurdistan Regional Government. The word 'Kurdistan', whether written or spoken, can still lead to detention and prosecution in Turkey. Kurdistan has been characterized as an "international colony" by the scholar
Ismail Besikci
Ishmael ''Ismaḗl''; Classical/Qur'anic Arabic: إِسْمَٰعِيْل; Modern Standard Arabic: إِسْمَاعِيْل ''ʾIsmāʿīl''; la, Ismael was the first son of Abraham, the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions; and is cons ...
.
Iraqi Kurdistan
The successful 2014 Northern Iraq offensive by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant, with the resultant weakening of the ability of the Iraqi state to project power, also presented a "golden opportunity" for the Kurds to increase their independence and possibly declare an independent Kurdish state. The Islamic State in Iraq and the Levant, who took more than 80 Turkish persons captive in Mosul during their offensive, is an enemy of Turkey, making Kurdistan useful for Turkey as a buffer state. On 28 June 2014 Hüseyin Çelik, a spokesman for the rulingJustice and Development Party Justice and Development Party may refer to several political parties, the best-known ones being:
* Justice and Development Party (Morocco)
* Justice and Development Party (Turkey)
Justice and Development Party may also refer to:
* Justice and Dev ...
(AKP), made comments to the '' Financial Times'' indicating Turkey's readiness to accept an independent Kurdistan in northern Iraq.
Syrian Civil War
Various sources have reported thatAl-Nusra
Al-Nusra Front or Jabhat al-Nusra ( ar, جبهة النصرة لأهل الشام, Jabhat an-Nuṣrah li-Ahl ish-Sham lit. ''Front of the Supporters of the People of Syria/the Levant''), known as Jabhat Fatah al-Sham ( ar, جبهة فتح ال ...
has issued a fatwā calling for Kurdish women and children in Syria to be killed, and the fighting in Syria has led tens of thousands of refugees to flee to Iraq's Kurdistan region. As of 2015, Turkey was actively supporting Al-Nusra, but as of January 2017, Turkey's foreign ministry has said that Al-Nusra is a terrorist group and has acted accordingly.
People
The Kurds are a people of Indo-Iranian origin. They speak an Iranian language known as Kurdish, and comprise the majority of the population of the region – however, included therein are Arab, Armenian, Assyrian,Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani may refer to:
* Something of, or related to Azerbaijan
* Azerbaijanis
* Azerbaijani language
See also
* Azerbaijan (disambiguation)
* Azeri (disambiguation)
* Azerbaijani cuisine
* Culture of Azerbaijan
The culture of Azerbaijan ...
, Jewish, Ossetian, Persian, and Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
communities. Most inhabitants are Muslim, but adherents to other religions are present as well – including Yarsanism, Yazidism, Alevis, Christians, and in the past, Jews, most of whom emigrated to Israel.
Geography
 According to the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Kurdistan covers about 190,000 km² (or 73,000 square miles), and its chief towns are Diyarbakır (Amed), Bitlis (Bedlîs) and
According to the '' Encyclopædia Britannica'', Kurdistan covers about 190,000 km² (or 73,000 square miles), and its chief towns are Diyarbakır (Amed), Bitlis (Bedlîs) and Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
(Wan) in Turkey, Erbil
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000.
Hu ...
(Hewlêr) and Sulaymaniyah in Iraq, and Kermanshah (Kirmanşan), Sanandaj
Sanandaj (Persian: سنندج, ; ku, سنە, Sine, often romanized as Senneh, is the capital of Kurdistan Province in Iran. With a population of 414,069, Sanandaj is the twenty third largest city in Iran and the second largest Kurdish city. San ...
(Sine), Ilam and Mahabad (Mehabad) in Iran. According to the Encyclopaedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published in ...
, Kurdistan covers around 190,000 km² (73,000 sq. mi.) in Turkey, 125,000 km² (48,000 sq. mi.) in Iran, 65,000 km² (25,000 sq. mi.) in Iraq, and 12,000 km² (5,000 sq. mi.) in Syria, with a total area of approximately 392,000 km² (151,000 sq. mi.).
Iraqi Kurdistan is divided into six governorate
A governorate is an administrative division of a state. It is headed by a governor. As English-speaking nations tend to call regions administered by governors either State (administrative division), states or province, provinces, the term ''govern ...
s, three of which (and parts of others) are under the control of the Kurdistan Regional Government. Iranian Kurdistan encompasses Kurdistan Province and the greater parts of West Azerbaijan, Kermanshah, and Īlām provinces. Syrian Kurdistan
Syrian Kurdistan is a Kurdish-inhabited area in northern Syria surrounding three noncontiguous enclaves along the Turkish and Iraqi borders: Afrin in the northwest, Kobani in the north, and Jazira in the northeast.
Syrian Kurdistan is often ...
is located primarily in northern Syria, and covers the province of Al Hasakah and northern Raqqa Governorate, northern Aleppo Governorate and also Jabal al-Akrad (Mountain of the Kurds) region. The major cities in this region are Qamishli (Kurdish: Qamişlo) and Al Hasakah (Kurdish: Hasakah).
Turkish Kurdistan encompasses a large area of Eastern Anatolia Region and southeastern Anatolia of Turkey and it is home to an estimated 6 to 8 million Kurds. There are another 9 to 12 million Turkish citizens of Kurdish descent in predominantly Turkish regions of Turkey as the majority of Turkish Kurds no longer live in Southeastern Anatolia.
Subdivisions (Upper and Lower Kurdistan)
In ''A Dictionary of Scripture Geography'' (published 1846), John Miles describes Upper and Lower Kurdistan as following: The northern, northwestern and northeastern parts of Kurdistan are referred to as upper Kurdistan, and includes the areas from west of Amed to Lake Urmia.
The lowlands of southern Kurdistan are called lower Kurdistan. The main cities in this area are Kirkuk and Arbil.
The northern, northwestern and northeastern parts of Kurdistan are referred to as upper Kurdistan, and includes the areas from west of Amed to Lake Urmia.
The lowlands of southern Kurdistan are called lower Kurdistan. The main cities in this area are Kirkuk and Arbil.
Climate
Much of the region is typified by acontinental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
– hot in the summer, cold in the winter. Despite this, much of the region is fertile and has historically exported grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
and livestock. Precipitation varies between 200 and 400 mm a year in the plains, and between 700 and 3,000 mm a year on the high plateau between mountain chains. The mountainous zone along the borders with Iran and Turkey experiences dry summers, rainy and sometimes snowy winters, and damp springs, while to the south the climate progressively transitions toward semi-arid and desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
zones.
Flora and fauna
Kurdistan is one of the most mountainous regions in the world with a cold climate receiving annual precipitation adequate to sustain temperate forests and shrubs. Mountain chains harbor pastures and forested valleys, totaling approximately 16 million hectares (160,000 km²), includingfir
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family (biology), family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North America, North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The ...
s and countryside is mostly oaks, conifers
Conifers are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All extan ...
, platanus, willow, poplar and, to the west of Kurdistan, olive trees.
The region north of the mountainous region on the border with Iran and Turkey features meadow grasses and such wild trees as, Abies cilicica, Fagus sylvatica, Quercus calliprinos, Quercus brantii, Quercus infectoria, Quercus ithaburensis, Quercus macranthera
''Quercus macranthera'', commonly called the Caucasian oak, or the Persian oak, is a species of deciduous tree native to Western Asia (northern Iran, Turkey;
and in the Caucasus in Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan) that is occasionally grown as a ...
, Cupressus sempervirens
''Cupressus sempervirens'', the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress, Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, sou ...
, Platanus orientalis, Pinus brutia, Juniperus foetidissima, Juniperus excelsa, Juniperus oxycedrus, Prunus cerasus, Salix alba, Fraxinus excelsior, Paliurus spina-christi, Olea europaea
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
, Ficus carica
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of small tree in the flowering plant family Moraceae. Native to the Mediterranean and western Asia, it has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the w ...
, Populus euphratica, Populus nigra, Crataegus monogyna, Crataegus azarolus, Prunus cerasifera, rose hips, Cercis siliquastrum, pistachio trees, pear and Sorbus graeca
''Sorbus graeca'', also known as the Greek whitebeam and fan-leaved service-tree is a species of whitebeam, member of the genus ''Sorbus'' in the rose family (Rosaceae).
Description
Distribution and habitat
The tree is native to most of ...
. The desert in the south is mostly steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
and would feature xeric plants such as palm trees, tamarix, date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
, fraxinus
''Fraxinus'' (), common name, commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of Subtropics, subtropic ...
, poa
''Poa'' is a genus of about 570 species of grasses, native to the temperate regions of both hemispheres. Common names include meadow-grass (mainly in Europe and Asia), bluegrass (mainly in North America), tussock (some New Zealand species), a ...
, white wormwood and chenopodiaceae. The steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
and desert in the south, by contrast, have such species as palm trees and date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as date or date palm, is a flowering plant species in the palm family, Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across northern Africa, the Middle Eas ...
.
Animals found in the region include the Syrian brown bear, wild boar, gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly ...
, the golden jackal, Indian crested porcupine, the red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the Order (biology), order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe ...
, goitered gazelle, Eurasian otter, striped hyena, Persian fallow deer, long-eared hedgehog, onager, mangar and the Euphrates softshell turtle
The Euphrates softshell turtle (''Rafetus euphraticus''), also known as the Mesopotamian softshell turtle, is a species of softshell turtle in the family Trionychidae. It is found throughout much of the Euphrates–Tigris river basin in Iraq ...
. Birds include, the hooded crow, common starling
The common starling or European starling (''Sturnus vulgaris''), also known simply as the starling in Great Britain and Ireland, is a medium-sized passerine bird in the starling family, Sturnidae. It is about long and has glossy black plumage ...
, Eurasian magpie
The Eurasian magpie or common magpie (''Pica pica'') is a resident breeding bird throughout the northern part of the Eurasian continent. It is one of several birds in the crow family (corvids) designated magpies, and belongs to the Holarctic ra ...
, European robin, water pipit, spotted flycatcher, namaqua dove
The Namaqua dove (''Oena capensis'') is a small pigeon. It is the only species in the genus ''Oena.'' It is found over much of Sub-Saharan Africa as well as Arabia and Madagascar.
Taxonomy
The Namaqua dove is the only species in the monotypic ...
, saker falcon, griffon vulture, little crake and collared pratincole, among others.
Mountains
Mountains are important geographical and symbolic features of Kurdish life, as evidenced by the saying "Kurds have no friends but the mountains." Mountains are regarded as sacred by the Kurds. Included in the region are Mount Judi andArarat
Ararat or in Western Armenian Ararad may refer to:
Personal names
* Ararat ( hy, Արարատ), a common first name for Armenian males (pronounced Ararad in Western Armenian)
* Ararat or Araratian, a common family name for Armenians (pronounced A ...
(both prominent in Kurdish folklore), Zagros, Qandil, Shingal
Sinjar ( ar, سنجار, Sinjār; ku, شنگال, translit=Şingal, syr, ܫܝܓܪ, Shingar) is a town in the Sinjar District of the Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. It is located about five kilometers south of the Sinjar Mountains. Its ...
, Mount Abdulaziz
Mount Abdulaziz or ''Abd al-Aziz'' ( ar, جبل عبدالعزيز, Jabal ʿAbdulʿazīz) is a mountain ridge located in the southwestern part of the Hasakah Governorate, some 35 km west-south-west from the center of the city of Hasakah, in ...
, Kurd Mountains, Jabal al-Akrad, Shaho, Gabar, Hamrin
Hamrin is a town in northern Iraq which sits on the western shore of a man-made lake of the same name, both of which are at the southern extreme of the Hamrin Mountains. Hamrin is home to approximately 25,000 people. Most revenue comes from fishi ...
, and Nisir.
Water resources
Iraqi Kurdistan is a region relatively rich in water, especially for countries in the Middle East region. It is the source for much of the water supply for neighboring countries. It means that political stability and peace in the region are important to the water supply of the region and preventing wars. Many think that for conserving the water "returning to traditional water-conserving cultivation techniques" will be needed, as well as "communal economy" Rivers The plateaus and mountains of Kurdistan, which are characterized by heavy rain and snow fall, act as a water reservoir for the Near and Middle East, forming the source of the Tigris andEuphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
rivers, as well as other numerous smaller rivers, such as the Little Khabur
The Khabur or Little Khabur ( ku, Xabûr, ''Ava Xabûr'' or ''Xabîr'', tr, Habur, ''Khabir'' or ''Habur Suyu'' (''Habur Water'')) is a river that rises in Turkey and flows through Iraq to join the Tigris at the tripoint of Turkey, Iraq and Syr ...
, Khabur, Tharthar, Ceyhan, Araxes
, az, Araz, fa, ارس, tr, Aras
The Aras (also known as the Araks, Arax, Araxes, or Araz) is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan excl ...
, Kura, Sefidrud, Karkha, and Hezil. Among rivers of historical importance to Kurds are the Murat (Arasān) and Buhtān rivers in Turkey; the Peshkhābur, the Little Zab
The Little Zab or Lower Zab (, ''al-Zāb al-Asfal''; or '; , ''Zâb-e Kuchak''; , ''Zāba Taḥtāya'') is a river that originates in Iran and joins the Tigris just south of Al Zab in the Kurdistan region of Iraq. It is approximately long and dr ...
, the Great Zab
The Great Zab or Upper Zab ( (''al-Zāb al-Kabīr''), or , , ''(zāba ʻalya)'') is an approximately long river flowing through Turkey and Iraq. It rises in Turkey near Lake Van and joins the Tigris in Iraq south of Mosul. The drainage basin o ...
, and the Diyala in Iraq; and the Jaghatu (Zarrinarud), the Tātā'u (Siminarud), the Zohāb (Zahāb), and the Gāmāsiyāb in Iran.
These rivers, which flow from heights of three to four thousand meters above sea level, are significant both as water sources and for the production of energy. Iraq and Syria dammed many of these rivers and their tributaries. Turkey has an extensive dam system under construction as part of the GAP (Southeast Anatolia Project); though incomplete, the GAP already supplies a significant proportion of Turkey's electrical energy needs. Due to the extraordinary archaeological richness of the region, almost any dam impacts historic sites. With the outbreak of the Syrian civil war, Turkey is was accused of withholding water from the reservoir Lake Assad in Syria, while filling the Atatürk dam in Turkey.
Lakes
Kurdistan extends to Lake Urmia in Iran on the east. The region includes Lake Van, the largest body of water in Turkey; the only lake in the Middle East with a larger surface is Lake Urmia – though not nearly as deep as Lake Van, which has a much larger volume. Urmia, Van
A van is a type of road vehicle used for transporting goods or people. Depending on the type of van, it can be bigger or smaller than a pickup truck and SUV, and bigger than a common car. There is some varying in the scope of the word across th ...
, as well as Zarivar Lake
Lake Zrewar , also known as Zrewar or Zrewar (Kurdish: ''Zrêbar'' or ''Zrêwar'', ''زرێبار''), ( fa, زریوار ''Zarivār''), is a lake in the Zagros Mountains, within Kurdistan Province of western Iran.
Etymology
its name is composed o ...
west of Marivan, and Lake Dukan
Lake Dukan (or Lake Dokan) ''(Arabic:بحيرة دوكان)'' is a lake in Kurdistan Region Iraq. It is located close to the city of Ranya, and is a reservoir on the Little Zab created by the construction of the Dukan Dam. The Dukan Dam was built ...
near the city of Sulaymaniyah, are frequented by tourists.
Petroleum and mineral resources
Kurdistan Region is estimated to contain around of oil, making it the sixth largest reserve in the world. Extraction of these reserves began in 2007.Al-Hasakah
Al-Hasakah ( ar, ٱلْحَسَكَة, al-Ḥasaka; ku, Heseke/حەسەکە; syr, ܚܣܝܟܐ Hasake), is the capital city of the Al-Hasakah Governorate, in the northeastern corner of Syria. With a 2004 census population of 188,160, it is the e ...
province, also known as Jazira region, has geopolitical importance of oil and is suitable for agricultural lands.
In November 2011, Exxon
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, ...
challenged the Iraqi central government's authority with the signing of oil and gas contracts for exploration rights to six parcels of land in Kurdistan, including one contract in the disputed territories, just east of the Kirkuk mega-field. This act caused Baghdad to threaten to revoke Exxon's contract in its southern fields, most notably the West-Qurna Phase 1 project. Exxon responded by announcing its intention to leave the West-Qurna project.
As of July 2007, the Kurdish government solicited foreign companies to invest in 40 new oil sites, with the hope of increasing regional oil production over the following five years by a factor of five, to about . Gas and associated gas reserves are in excess of . Notable companies active in Kurdistan include ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil Corporation (commonly shortened to Exxon) is an American multinational oil and gas corporation headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is the largest direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil, and was formed on November 30, ...
, Total
Total may refer to:
Mathematics
* Total, the summation of a set of numbers
* Total order, a partial order without incomparable pairs
* Total relation, which may also mean
** connected relation (a binary relation in which any two elements are comp ...
, Chevron, Talisman Energy, Genel Energy, Hunt Oil
Hunt Oil Co. is an independent oil and gas company headquartered in Dallas, Texas. It conducts its main oil production activities in the United States, Canada and, as of 1984, in Yemen. In the past, the company was owned by american oil tycoon ...
, Gulf Keystone Petroleum, and Marathon Oil
Marathon Oil Corporation is an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration incorporated in Ohio and headquartered in the Marathon Oil Tower in Houston, Texas. A direct descendant of Standard Oil, it also runs international gas operations ...
.
Other mineral resources that exist in significant quantities in the region include coal, copper, gold, iron, limestone (which is used to produce cement), marble, and zinc. The world's largest deposit of rock sulfur is located just southwest of Erbil
Erbil, also called Hawler (, ar, أربيل, Arbīl; syr, ܐܲܪܒܹܝܠ, Arbel), is the capital and most populated city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq. It lies in the Erbil Governorate. It has an estimated population of around 1,600,000.
Hu ...
.
In July 2012, Turkey and the Kurdistan Region signed an agreement by which Turkey would regularly supply the KRG with refined petroleum products in exchange for crude oil.
Gallery
Rawanduz
Rawandiz ( ar, رواندز; ku, ڕەواندز, Rewandiz) is a city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq, located in the Erbil Governorate, close to the borders with Iran and Turkey, it is located 10 km to the east from Bekhal Waterfall. T ...
in northern Iraqi Kurdistan
File:Zebar valley.jpg, Zê river in Zebari region, Iraqi Kurdistan.
File:piranshahr2014.jpg, The city of Piranshahr, center of Mokrian district, northwestern Iran
File:Batman(city).jpg, The city of Batman, Northern Kurdistan (eastern Turkey)
File:20190510 174828.Sargallu.Sulaymaniyah.Kurdistan.jpg, Countryside in Sulaymaniyah
See also
* Assyrian homeland * Irredentism * Lists of active separatist movementsReferences
Sources
*Further reading
* Beşikçi, İsmail. ''Selected Writingsbout
Bout can mean:
People
*Viktor Bout, suspected arms dealer
*Jan Everts Bout, early settler to New Netherland
*Marcel Bout
Musical instruments
* The outward-facing round parts of the body shape of violins, guitars, and other stringed instrumen ...
Kurdistan and Turkish Colonialism''. London: Published jointly by Kurdistan Solidarity Committee and Kurdistan Information Centre, 1991. 44 p. Without ISBN
*
* King, Diane E. ''Kurdistan on the Global Stage: Kinship, Land, and Community in Iraq'' (Rutgers University Press; 2014) 267 pages; Scholarly study of traditional social networks, such as patron-client relations, as well as technologically mediated communication, in a study of gender, kinship, and social life in Iraqi Kurdistan.
* Öcalan, Abdullah, ''Interviews and Speeches bout the Kurdish cause'. London: Published jointly by Kurdistan Solidarity Committee and Kurdistan Information Centre, 1991. 46 p. Without ISBN
* Reed, Fred A. ''Anatolia Junction: a Journey into Hidden Turkey''. Burnaby, B.C.: Talonbooks ic 1999. 320 p., ill. with b&w photos. ''N.B''.: Includes a significant coverage of the Turkish sector of historic Kurdistan, the Kurds, and their resistance movement.
External links
* {{Portalbar, Asia, Geography, Kurdistan Iranian countries and territories Divided regions Cultural regions Historical regions Kurdistan independence movement Kurdish irredentism