Konstanz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Konstanz ( , , , locally , ), also known as Constance in English, is a university city with approximately 83,000 inhabitants located at the western end of
 The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the
The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the

Konstanz RoemerTurm.jpg, The late Roman fortress ''Constantia'' at the ''Münsterplatz''
Konstanz Konzil.jpg, The ''Konzilgebäude'' in Konstanz
MPano 07 3.jpg, Konstanz Cathedral
Konstanz Marktstätte.jpg, Konstanz ''Marktstätte'', the main square in the old town
Official website
*
Konstanz: history and images
University of Konstanz
Pictures Konstanz
Online journal about Constance
University of Applied Sciences
Photos of the Carnival (~Shrovetide, ~Mardi Grass) in Constance
Südkurier
( Südkurier) Local newspaper for Konstanz {{Authority control Towns in Baden-Württemberg Populated places on Lake Constance Populated places on the Rhine Konstanz (district) Free imperial cities Germany–Switzerland border crossings Former states and territories of Baden-Württemberg Baden
Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
in the south of Germany. The city houses the University of Konstanz and was the residence of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Konstanz
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance, (german: Hochstift Konstanz, Fürstbistum Konstanz, Bistum Konstanz) was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dua ...
for more than 1,200 years.
Location
 The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the
The city is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg and situated at the banks of Lake Constance (''Bodensee'' in German). The river Rhine, which starts in the Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss ...
, passes through Lake Constance and leaves it, considerably larger, by flowing under a bridge connecting the two parts of the city. North of the river lies the larger part of the city with residential areas, industrial estates, and the University of Konstanz; while south of the river is the old town, which houses the administrative centre and shopping facilities in addition to the ''Hochschule'' or the ''University of Applied Sciences''. Car ferries provide access across Lake Constance to Meersburg
Meersburg () is a town in Baden-Württemberg in the southwest of Germany. It is on Lake Constance.
It is known for its medieval city. The lower town ("Unterstadt") and upper town ("Oberstadt") are reserved for pedestrians only, and connected by t ...
, and the ''Katamaran'' provides a shuttle service for pedestrians to Friedrichshafen. The Germany–Switzerland border runs along the southwestern and southern edge of the city, demarcating it from the Swiss town of Kreuzlingen
Kreuzlingen is a municipality in the district of Kreuzlingen in the canton of Thurgau in north-eastern Switzerland. It is the seat of the district and is the second-largest city of the canton, after Frauenfeld, with a population of about 22,000. ...
.
Subdivisions
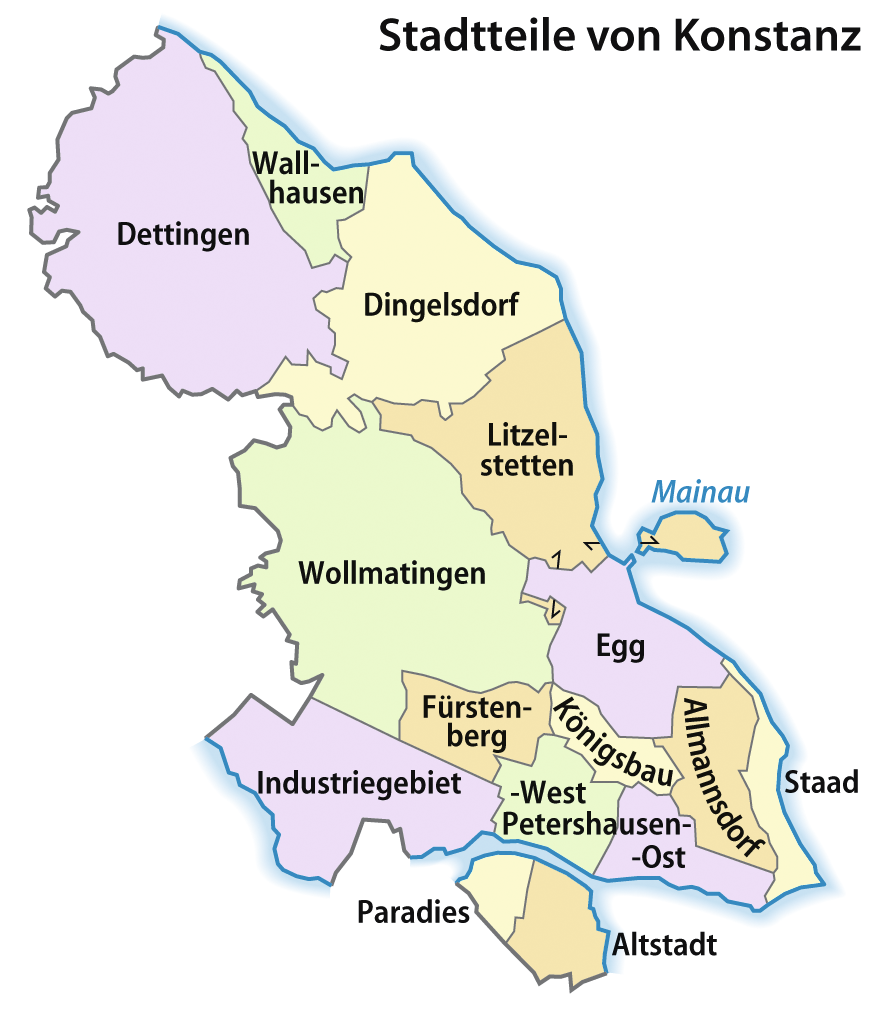
Konstanz is subdivided into 15 wards or districts (''Stadtteile''). The island of Mainau belonged to the ward of Litzelstetten, a separate municipality, until its incorporation into Konstanz on 1 December 1971.
History
The first traces of civilization in Konstanz date back to the lateStone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
.
During the reign of Augustus, the Celts living south of the Danube were conquered by the Romans. Around 40 AD, the first Romans settled on the site. This small town on the left bank of the Rhine was probably first called ''Drusomagus'' and belonged to the Roman province of '' Raetia''. Its later name, originally ''Constantia'', comes either from the Roman emperor Constantius Chlorus, who fought the Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
in the region and built a strong fortress around 300 AD, or from his grandson Constantius II, who visited the region in 354. The remains of the late Roman
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
fortress ''Constantia'' were discovered in 2003.
Around 585 the first bishop took up residence in Konstanz and this marked the beginning of the city's importance as a spiritual center. By the late Middle Ages, about one quarter of Konstanz's 6,000 inhabitants were exempt from taxation on account of clerical rights.
Trade thrived during the Middle Ages. Konstanz owned the only bridge in the region, which crossed the Rhine, making it a strategic location in the Duchy of Swabia
The Duchy of Swabia (German: ''Herzogtum Schwaben'') was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German Kingdom. It arose in the 10th century in the southwestern area that had been settled by Alemanni tribes in Late Antiquity.
While the ...
. Its linen
Linen () is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant.
Linen is very strong, absorbent, and dries faster than cotton. Because of these properties, linen is comfortable to wear in hot weather and is valued for use in garments. It also ...
production had made an international name for the city and it was prosperous. In 1192, Konstanz gained the status of Imperial City so it was henceforth subject only to the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
.
In 1414 to 1418, the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the res ...
took place, during which, on 6 July 1415, Jan Hus (Czech religious thinker, philosopher and reformer), who was seen as a threat to Christianity by the Roman Catholic Church, was burned at the stake. It was here that the Papal Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Vatican Standoff, the Great Occidental Schism, or the Schism of 1378 (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 1378 to 1417 in which bishops residing in Rome and Avignon b ...
was ended and Pope Martin V
Pope Martin V ( la, Martinus V; it, Martino V; January/February 1369 – 20 February 1431), born Otto (or Oddone) Colonna, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 11 November 1417 to his death in February 1431. Hi ...
was elected during the only conclave ever held north of the Alps. Ulrich von Richental
Ulrich of Richenthal (died c. 1438) was a chronicler of the Council of Constance.
Ulrich was a citizen of Konstanz (Constance). He was a landowner and a layman, perhaps a son of the town clerk of Constance, Johannes Richenthal, who lived in the s ...
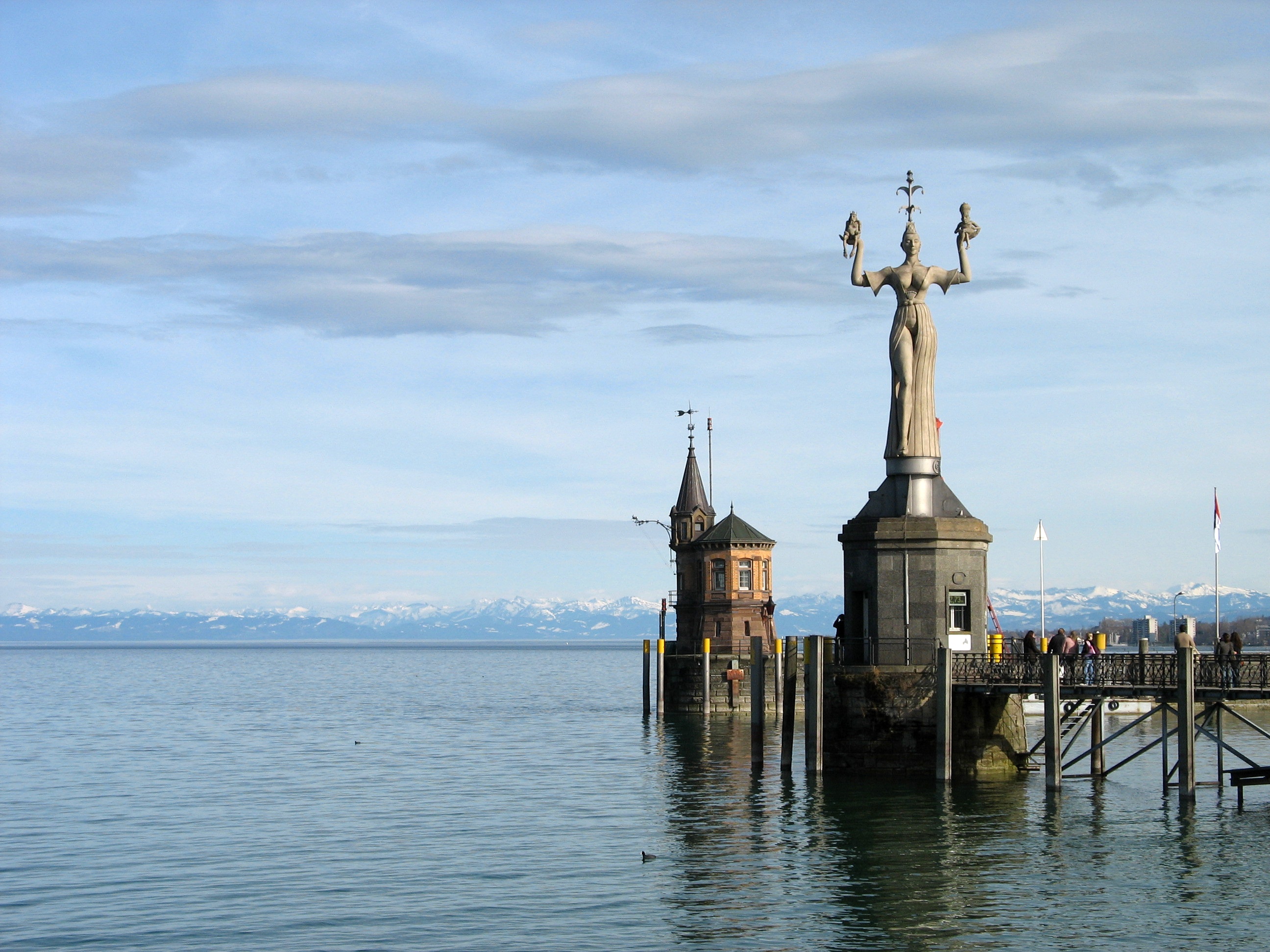
's illustrated chronicle of the Council of Constance testifies to all the major happenings during the council as well as showing the everyday life of medieval Konstanz. The ''Konzilgebäude'' where the conclave was held can still be seen standing by the harbour. Close by stands the '' Imperia'', a statue that was erected in 1993 to satirically commemorate the council.
In 1460, the Swiss Confederacy conquered Thurgau, Konstanz's natural hinterland. Konstanz then made an attempt to get admitted to the Swiss Confederacy, but the forest cantons voted against its entry, fearing overbearing city states; Konstanz then joined the Swabian League instead. In the Swabian War of 1499, Konstanz lost its last privileges over Thurgau to the Confederation.
The Protestant Reformation took hold in Konstanz in the 1520s, headed by Ambrosius Blarer. Soon the city declared itself officially Protestant, pictures were removed from the churches, and the bishop temporarily moved to Meersburg
Meersburg () is a town in Baden-Württemberg in the southwest of Germany. It is on Lake Constance.
It is known for its medieval city. The lower town ("Unterstadt") and upper town ("Oberstadt") are reserved for pedestrians only, and connected by t ...
, a small town across the lake. The city first followed the Tetrapolitan Confession, and then the Augsburg Confession
The Augsburg Confession, also known as the Augustan Confession or the Augustana from its Latin name, ''Confessio Augustana'', is the primary confession of faith of the Lutheran Church and one of the most important documents of the Protestant Re ...
. However, in 1548 Emperor Charles V imposed the Imperial Ban on Konstanz and it had to surrender to Habsburg Austria The term Habsburg Austria may refer to the lands ruled by the Austrian branch of the Habsburgs, or the historical Austria. Depending on the context, it may be defined as:
* The Duchy of Austria, after 1453 the Archduchy of Austria
* The ''Erbland ...
which had suddenly attacked. Thus Konstanz lost its status as an imperial city.
The new Habsburg rulers were eager to re-Catholicise the town and in 1604 a Jesuit College
The Jesuits (Society of Jesus) in the Catholic Church have founded and managed a number of educational institutions, including the notable secondary schools, colleges and universities listed here.
Some of these universities are in the United Stat ...
was opened. Its accompanying theatre, built in 1610, is the oldest theatre in Germany still performing regularly.
The city became part of the Grand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden (german: Großherzogtum Baden) was a state in the southwest German Empire on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.
It came into existence in the 12th century as the Margraviate of Baden and subs ...
in 1806. In 1821, the Bishopric of Constance was dissolved and became part of the Archdiocese of Freiburg. Konstanz became part of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871 during the unification of Germany. After World War I it was included within the Republic of Baden.
On 22 October 1940, 110 of the last Jewish residents were deported to Gurs internment camp in France. Most of those who were still alive in August 1942 were murdered in either Sobibór or Auschwitz
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It con ...
.
Because it almost lies within Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, directly adjacent to the Swiss border, Konstanz was not bombed by the Allied Forces during World War II. The city left all its lights on at night, and thus fooled the bombers into thinking it was actually part of Switzerland. After the war, Konstanz was included first in South Baden and then in the new state of Baden-Württemberg.
The ''Altstadt'' (Old Town), which is large considering the small size of modern Konstanz, has many old buildings and twisting alleys. The city skyline is dominated by Konstanz Cathedral, several other churches and three towers left over from the city wall, one of which marks the place of the former medieval bridge over the Rhine.
The University of Konstanz was established close to the town in 1966. It houses an excellent library with approximately two million books, all freely accessible 24 hours a day, as well as a botanical garden (the Botanischer Garten der Universität Konstanz The Botanischer Garten der Universität Konstanz (1.5 hectares) is a botanical garden maintained by the University of Konstanz. It is located about 250 meters northwest of the campus north parking lot in Konstanz, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, and op ...
). Especially since 2007, the university, being one of the nine German universities most successful in the German Universities Excellence Initiative, has gained considerable reputation as a so-called "elite university".
Konstanz was the birthplace of Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin, constructor of the famous Zeppelin airships.
In the late 2010s, Konstanz has become a popular destination for ''Einkaufstourismus'', or cross-border shopping by Swiss due to lower prices on basic items in Germany, a favorable exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
between the Swiss franc
The Swiss franc is the currency and legal tender of Switzerland and Liechtenstein. It is also legal tender in the Italian exclave of Campione d'Italia which is surrounded by Swiss territory. The Swiss National Bank (SNB) issues banknotes and the f ...
and the euro, and a generous German VAT refund for non- European Union residents. Retail chains such as H&M and dm have built large new stores near the town's central square to cater to this trade, and some Konstanz residents feel the city is losing its historic character in the process; many of them avoid the area on Saturdays. This has led to friction with officials from Kreuzlingen as their city has seen no economic benefit from this trade, and they have been requesting that their national government A national government is the government of a nation.
National government or
National Government may also refer to:
* Central government in a unitary state, or a country that does not give significant power to regional divisions
* Federal governme ...
bring up the issue of the VAT refund with Germany. Subsequently, Germany has introduced a minimum spend amount of €50.01 per receipt for the German VAT to be refunded. Customs clearance centres are conveniently located near shopping centres.
Climate
Its location in south-west Germany gives Konstanz a degraded oceanic climate ( Köppen: ''Cfb'') with warm and humid summers (moderated by the lake) as well as cold and snowy winters.Main sights
* Archaeological Museum * '' Imperia'', a 9 m-tall sculpture * Jan Hus Museum * Konstanz Cathedral * ''Konzil'' edifice, dating to the 15th century * Niederburg (Lower Castle) * Petershausen Abbey * Remains of a Roman fortress, near the Cathedral * ''Schnetztor'', fortified gate of the former city walls Konstanz was also home to a largesynagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worshi ...
, destroyed by the Nazi government in 1938.
Twin towns – sister cities
Konstanz istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Fontainebleau
Fontainebleau (; ) is a commune in the metropolitan area of Paris, France. It is located south-southeast of the centre of Paris. Fontainebleau is a sub-prefecture of the Seine-et-Marne department, and it is the seat of the ''arrondissement ...
, France (1960)
* Richmond upon Thames, England, United Kingdom (1983)
* Tábor, Czech Republic (1984)
* Lodi, Italy (1986)
* Suzhou
Suzhou (; ; Suzhounese: ''sou¹ tseu¹'' , Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Soochow, is a major city in southern Jiangsu province, East China. Suzhou is the largest city in Jiangsu, and a major economic center and focal point of trade ...
, China (2007)
Transport
Konstanz station is served by the High Rhine Railway running west toSingen
Singen (Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Singe'') is an industrial city in the very south of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany and just north of the German-Swiss border.
Location
Singen is an industrial city situated in the very south ...
with connections to all parts of Germany, and the Etzwilen–Konstanz line running south into Switzerland, connecting to major routes at Weinfelden. Services are provided by the Deutsche Bahn AG
The (; abbreviated as DB or DB AG) is the national railway company of Germany. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG). The Federal Republic of Germany is its single shareholder.
describes itself as the se ...
and also the Swiss Thurbo company and its German subsidiary. The nearest airport is at Friedrichshafen, which can be reached by a fast ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
service on the lake, which also connects Konstanz to other lakeside towns. The airport mainly hosts domestic flights, but flights to Austria and Turkey are available. The nearest international airports are in Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; Swabian: ; ) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is located on the Neckar river in a fertile valley known as the ''Stuttgarter Kessel'' (Stuttgart Cauldron) and lies an hour from the ...
, in Basel, and Zurich, which has a direct train from Konstanz. Bus services within the city are provided by Stadtwerke Konstanz GmbH.
Additionally Konstanz and Friedrichshafen have been connected by the two (since 2008, three) catamaran
A Formula 16 beachable catamaran
Powered catamaran passenger ferry at Salem, Massachusetts, United States
A catamaran () (informally, a "cat") is a multi-hulled watercraft featuring two parallel hulls of equal size. It is a geometry-stab ...
s ''Constance'' and ''Fridolin'' since 2005.
World Heritage Site
It is home to one or more prehistoric pile-dwelling (or stilt house) settlements that are part of the Prehistoric Pile dwellings around the Alps UNESCO World Heritage Site.Notable people
Public service and commerce
* Ulrich Zasius (1461–1536), jurist * Ernst Vögelin (1529–1589), pioneer book printer * Wacker von Wackenfels (1550–1619), diplomat, scholar and author * Johann Friedrich Cotta (1764–1832) a publisher, industrial pioneer and politician; in 1825 he started steamboats on Lake Constance. * Johann Leonhard Hug (1765–1846) a Catholic theologian, orientalist and biblical scholar. *Guillaume Henri Dufour
Guillaume Henri Dufour (15 September 178714 July 1875) was a Swiss military officer, structural engineer and topographer. He served under Napoleon I and held the Swiss office of General four times in his career, firstly in 1847 when he led the ...
(1787–1875) a Swiss military officer, structural engineer and topographer.
*Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin (1838–1917), a German general and inventor of the Zeppelin rigid airships.
*Josef Albert Amann
Josef Albert Amann (1 July 1866, in Munich – 17 October 1919, in Konstanz) was a German gynecologist. His father, Josef Albert Amann (1832–1906), was also a gynecologist.
He studied medicine at the University of Munich, where his teacher ...
(junior) (1866–1919), gynecologist
*Conrad Grober
Conrad may refer to:
People
* Conrad (name)
Places
United States
* Conrad, Illinois, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Conrad, Iowa, a city
* Conrad, Montana, a city
* Conrad Glacier, Washington ...
(1872–1948), priest and archbishop, teacher and pastor in Konstanz
* Friedrich Flick (1883–1972), entrepreneur and convicted Nazi war criminal
* (1885–1957), countess and Benedictine nun, religious superior at the Municipal Women's Clinic Konstanz
* Siegfried Adolf Handloser (1885–1954), doctor of the German Armed Forces Medical Services
* (1887–1944), victim of Nazism
* Werner Berger (1901–1964), SS-Oberscharführer and member of commando 99 in Buchenwald concentration camp
* (1911–1984), jurist
*Egon Mayer
Egon Mayer (19 August 1917 – 2 March 1944) was a Luftwaffe wing commander and fighter ace of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was credited with 102 enemy aircraft shot down in over 353 combat missions. His victories were all claime ...
(1917–1944), fighter ace in the Luftwaffe during World War II
* Werner Maihofer (1918–2009), politician (FDP), member of Bundestag, minister of the interior (1974–1978)
*Theo Sommer
Theo Sommer (10 June 1930 – 22 August 2022) was a German newspaper editor and intellectual. He began working for ''Die Zeit'' in 1958, rising to an editor-in-chief and publisher. His editorials for ''Die Zeit'' shaped the paper's social-liber ...
(1930–2022), newspaper editor at ''Die Zeit
''Die Zeit'' (, "The Time") is a German national weekly newspaper published in Hamburg in Germany. The newspaper is generally considered to be among the German newspapers of record and is known for its long and extensive articles.
History
The ...
'' since 1958, rising to editor-in-chief and publisher
* Rolf Böhme (1934–2019), Staatssekretär (1978–1982), mayor of Freiburg (1982–2002)
* (b. 1949), jurist, Lord Mayor of Konstanz 1996–2012
* Ian Murdock (1973–2015), American software engineer, founder of the Debian
Debian (), also known as Debian GNU/Linux, is a Linux distribution composed of free and open-source software, developed by the community-supported Debian Project, which was established by Ian Murdock on August 16, 1993. The first version of D ...
project
*Larissa Vassilian
Larissa Vassilian (born 17 June 1976) is a German journalist of German-Armenian descent. She became famous for her podcast ''"Schlaflos in München" (Sleepless in Munich)'', using the stage name Annik Rubens. The podcast had over 10,000 listeners ...
(born 1976), German-Armenian journalist

The arts
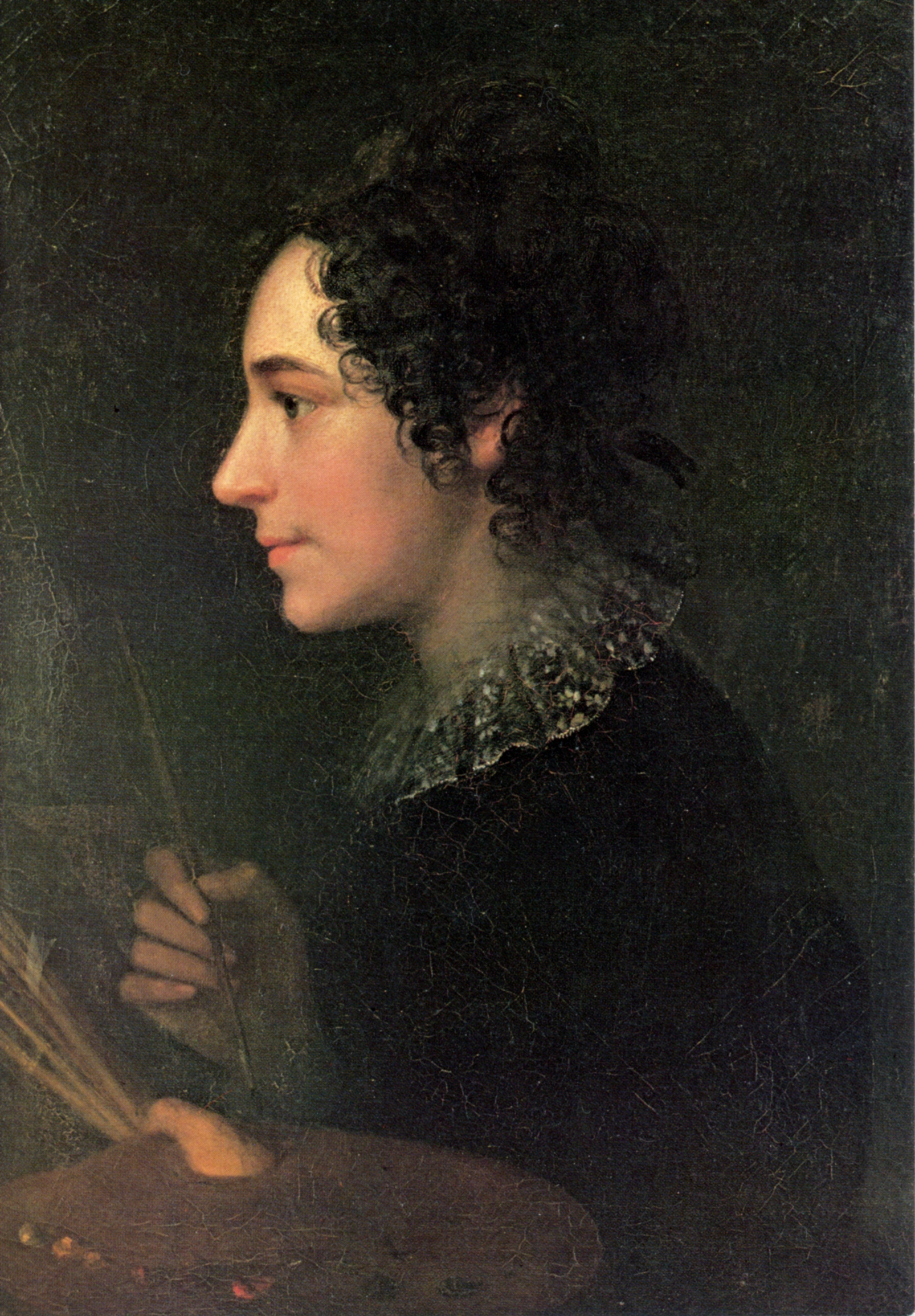
* Tobias Pock (1609–1683), Austrian Baroque painter of Swabian descent, a pioneer of sacral art *Marie Ellenrieder
Marie Ellenrieder (20 March 1791 – 5 June 1863) was a German painter known for her portraits and religious paintings.
Life and career
Ellenrieder was born in Konstanz, Germany in 1791, the daughter of Konrad and Anna Maria Herrmann, and ...
(1791–1863), painter
* (1883–1967), writer
* Anne Winterer (1894–1938), photographer
* François Stahly (1911–2006), French sculptor
* (1920–1984), art historian and founder of Bauhaus-Archive
* (born 1925), dialect author
*Berthold Keller
Berthold Keller (8 February 1927 – 28 June 2012) was a German trade union leader.
Born in Konstanz, Keller completed an apprenticeship as a tailor, and found work in a local clothing factory. In 1944, he was called up to the army, but was t ...
(1927–2012), trade unionist
* Martin Gotthard Schneider (1930–2017), church musician, songwriter and theologian
* Uli Trepte (1941–2009), musician
* Carola Zwick (born 1966), product designer
Gallery
See also
* Alexander-von-Humboldt-Gymnasium * Cathedral of Konstanz *Hochschule Konstanz
Konstanz University of Applied Sciences (german: Hochschule Konstanz Technik, Wirtschaft und Gestaltung) or HTWG, is a German university of applied sciences located in Konstanz, Baden-Württemberg. It is a member of Lake Constance Arts & Science ...
(University of Applied Sciences)
* University of Konstanz
* Tägermoos
Notes
References
External links
*Official website
*
Konstanz: history and images
University of Konstanz
Pictures Konstanz
Online journal about Constance
University of Applied Sciences
Photos of the Carnival (~Shrovetide, ~Mardi Grass) in Constance
Südkurier
( Südkurier) Local newspaper for Konstanz {{Authority control Towns in Baden-Württemberg Populated places on Lake Constance Populated places on the Rhine Konstanz (district) Free imperial cities Germany–Switzerland border crossings Former states and territories of Baden-Württemberg Baden