Kingdom Of Judea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an
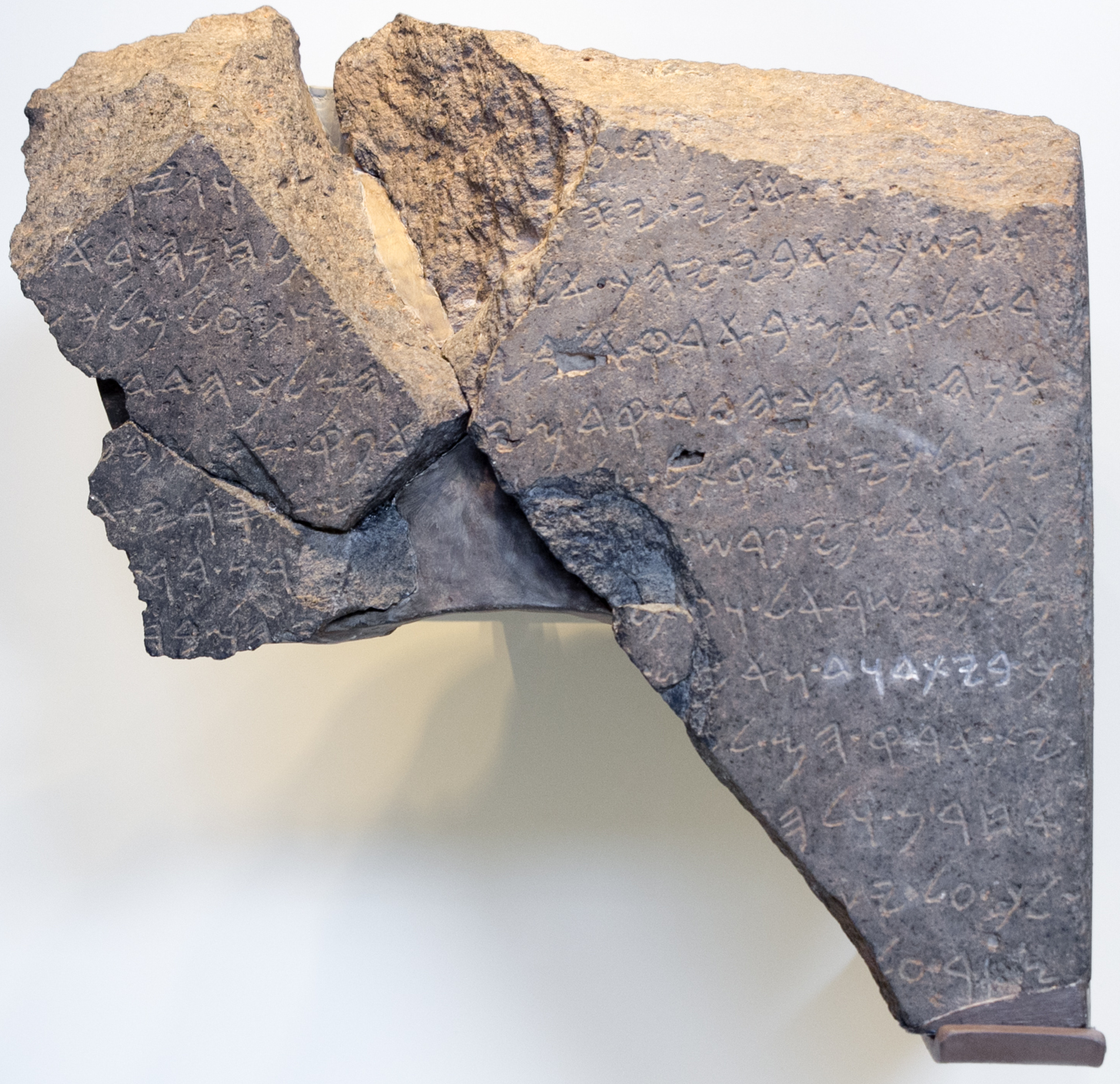 The Tel Dan Stele shows an historical " House of David" ruled a kingdom south of the lands of Samaria in the 9th century BC, and attestations of several Judean kings from the 8th century BC have been discovered, but they do little to indicate how developed the state actually was. The Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name "Judah" (written in
The Tel Dan Stele shows an historical " House of David" ruled a kingdom south of the lands of Samaria in the 9th century BC, and attestations of several Judean kings from the 8th century BC have been discovered, but they do little to indicate how developed the state actually was. The Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name "Judah" (written in
 The status of Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE is a major subject of debate. The oldest part of Jerusalem and its original urban core are the City of David, which does not show evidence of significant Israelite residential activity until the 9th century. However, unique administrative structures such as the
The status of Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE is a major subject of debate. The oldest part of Jerusalem and its original urban core are the City of David, which does not show evidence of significant Israelite residential activity until the 9th century. However, unique administrative structures such as the
 LMLK seals are ancient
LMLK seals are ancient
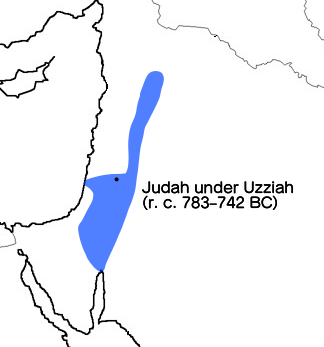 For the first 60 years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over Israel, and there was
For the first 60 years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over Israel, and there was
 After
After  During the long reign of
During the long reign of 
 When
When
 Despite the strong remonstrances of
Despite the strong remonstrances of
Israelite
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
kingdom of the Southern Levant
The Southern Levant is a geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southern Syria and/or the Sinai P ...
during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
. Centered in Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous L ...
, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. The other Israelite polity, the Kingdom of Israel, lay to the north. Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
are named after Judah and are primarily descended from it.
The Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
depicts the Kingdom of Judah as a successor to the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
United Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
, a term denoting the united monarchy under biblical kings Saul
Saul (; he, , ; , ; ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel. His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked the transition of Israel and Judah from a scattered t ...
, David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
and Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
and covering the territory of Judah and Israel. However, during the 1980s, some biblical scholars began to argue that the archaeological evidence for an extensive kingdom before the late-8th century BCE is too weak, and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. In the 10th and early 9th centuries BCE, the territory of Judah appears to have been sparsely populated, limited to small rural settlements, most of them unfortified. The Tel Dan Stele, discovered in 1993, shows that the kingdom, at least in some form, existed by the middle of the 9th century BCE, but it does not indicate the extent of its power. Recent excavations at Khirbet Qeiyafa, however, support the existence of a centrally organized and urbanized kingdom by the 10th century BCE, according to the excavators.
In the 7th century BCE, the kingdom's population increased greatly, prospering under Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
vassalage
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
, despite Hezekiah's revolt against the Assyrian king Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
. With the fall of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 605 BCE, competition emerged between Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ...
over control of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
, ultimately resulting in Judah's rapid decline. The early 6th century BCE saw a wave of Egyptian-backed Judahite rebellions against Babylonian rule being crushed. In 587 BCE, Nebuchadnezzar II besieged and destroyed Jerusalem, bringing an end to the kingdom. A large number of Judeans were exiled to Babylon, and the fallen kingdom was then annexed as a Babylonian province.
After Babylon's fall to the Persian Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was the largest empire the world had ...
, king Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
allowed the Jews who had been deported after the conquest of Judah to return. They were allowed to self-rule under Persian governance. It was not until 400 years later, following the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ende ...
, that the Jews fully regained independence.
Archaeological record
The formation of the Kingdom of Judah is a subject of heavy debate among scholars, with a dispute emerging between biblical minimalists and biblical maximalists on this particular topic. While it is generally agreed that the stories ofDavid
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
and Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
in the 10th century BCE tell little about the origins of Judah, currently, there is no consensus as to whether Judah developed as a split from the United Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
(as the Bible tells) or independently. Some scholars suggested that Jerusalem, the kingdom's capital, did not emerge as a significant administrative center until the end of the 8th century BCE. Before then, the archaeological evidence suggests its population was too small to sustain a viable kingdom. Much of the debate revolves around whether the archaeological discoveries conventionally dated to the 10th century should instead be dated to the 9th century, as proposed by Israel Finkelstein
Israel Finkelstein ( he, ישראל פינקלשטיין, born March 29, 1949) is an Israeli archaeologist, professor emeritus at Tel Aviv University and the head of the School of Archaeology and Maritime Cultures at the University of Haifa. Fin ...
. Recent archaeological discoveries by Eilat Mazar
Eilat Mazar ( he, אילת מזר; 10 September 195625 May 2021) was an Israeli archaeologist. She specialized in Jerusalem and Phoenician archaeology. She was also a key person in Biblical archaeology noted for her discovery of the Large Ston ...
in Jerusalem and Yosef Garfinkel
Yosef Garfinkel (hebrew: יוסף גרפינקל; born 1956) is an Israeli archaeologist and academic. He is Professor of Prehistoric Archaeology and of Archaeology of the Biblical Period at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem.
Biography
Yosef (Yo ...
in Khirbet Qeiyafa seem to support the existence of the United Monarchy, but the datings and identifications are not universally accepted.
 The Tel Dan Stele shows an historical " House of David" ruled a kingdom south of the lands of Samaria in the 9th century BC, and attestations of several Judean kings from the 8th century BC have been discovered, but they do little to indicate how developed the state actually was. The Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name "Judah" (written in
The Tel Dan Stele shows an historical " House of David" ruled a kingdom south of the lands of Samaria in the 9th century BC, and attestations of several Judean kings from the 8th century BC have been discovered, but they do little to indicate how developed the state actually was. The Nimrud Tablet K.3751, dated c. 733 BCE, is the earliest known record of the name "Judah" (written in Assyrian cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system, script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East, Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the ...
as Ya'uda or KUR.ia-ú-da-a-a).
Jerusalem
Stepped Stone Structure
The Stepped Stone Structure is the name given to the remains at a particular archaeological site (sometimes termed Area G) on the eastern side of the City of David, the oldest part of Jerusalem. The curved, , narrow stone structure is built over a ...
and the Large Stone Structure
The Large Stone Structure ( ''Mivne haEven haGadol'') is the name given to a set of remains interpreted by the excavator, Israeli archaeologist Eilat Mazar, as being part of a single large public building in the City of David, presumably the old ...
, which originally formed one structure, contain material culture dated to Iron I. On account of the apparent lack of settlement activity in the 10th century BCE, Israel Finkelstein argues that Jerusalem was then a small country village in the Judean hills, not a national capital, and Ussishkin argues that the city was entirely uninhabited. Amihai Mazar contends that if the Iron I/Iron IIa dating of administrative structures in the City of David are correct, which he believes to be the case, "Jerusalem was a rather small town with a mighty citadel, which could have been a center of a substantial regional polity." William G. Dever
William Gwinn Dever (born November 27, 1933, Louisville, Kentucky) is an American archaeologist, Old Testament scholar, and historian, specialized in the history of the Ancient Near East and the ancient kingdoms of Israel and Judah in biblical ...
argues that Jerusalem was a small and fortified city, probably inhabited only by the royal court, priests and clerks.
Literacy
A collection of military orders found in the ruins of a military fortress in theNegev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
dating to the period of the Kingdom of Judah indicates widespread literacy, based on the inscriptions, the ability to read and write extended throughout the chain of command from commanders to petty officers. According to Professor Eliezer Piasetsky, who participated in analyzing the texts, "Literacy existed at all levels of the administrative, military and priestly systems of Judah. Reading and writing were not limited to a tiny elite." That indicates the presence of a substantial educational infrastructure in Judah at the time.
LMLK Seals
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
stamped on the handles of large storage jars dating from reign of King Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
(circa 700 BCE) discovered mostly in and around Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. Several complete jars were found ''in situ
''In situ'' (; often not italicized in English) is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position." It can mean "locally", "on site", "on the premises", or "in place" to describe where an event takes place and is used in ...
'' buried under a destruction layer
A destruction layer is a stratum found in the excavation of an archaeological site showing evidence of the hiding and burial of valuables, the presence of widespread fire, mass murder, unburied corpses, loose weapons in public places, or other evid ...
caused by Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
at Lachish
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Th ...
. None of the original seals has been found, but some 2,000 impressions made by at least 21 seal types have been published.
LMLK stands for the Hebrew letters ''lamedh
Lamedh or Lamed is the twelfth letter of the Semitic abjads, including Hebrew Lāmed , Aramaic Lāmadh , Syriac Lāmaḏ ܠ, Arabic , and Phoenician Lāmed . Its sound value is .
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Lambda (Λ), Latin ...
mem lamedh kaph
Kaph (also spelled kaf) is the eleventh letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician kāp , Hebrew kāf , Aramaic kāp , Syriac kāp̄ , and Arabic kāf (in abjadi order).
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek kappa (Κ), Lati ...
'' (vocalized, ''lamelekh''; Phoenician ''lāmed mēm lāmed kāp'' – 𐤋𐤌𐤋𐤊), which can be translated as:
* " elongingto the king" f Judah* " elongingto King" (name of a person or deity)
* " elongingto the government" f Judah* "o be sent
O, or o, is the fifteenth letter and the fourth vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''o'' (pronounced ), plu ...
to the King"
Everyday life
According to a 2022 study, traces ofvanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the p ...
found in wine jars in Jerusalem might indicate that the local elite enjoyed wine flavored with vanilla during the 7-6th centuries BCE. Until very recently, vanilla was not at all known to be available to the Old World. Archeologists suggested that this discovery might be related to an international trade route that crossed the Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
during that period, probably under Assyrian and later, Egyptian rule.
Cities
Tel Be'er Sheva
Tel Sheva ( he, תל שבע, translit=) or Tel Be'er Sheva (), also known as Tell es-Seba (), is an archaeological site in the Southern District of Israel, believed to be the site of the ancient biblical town of Beer-sheba. The site lies east o ...
, believed to be the site of the ancient biblical town of Beer-sheba
Beersheba or Beer Sheva, officially Be'er-Sheva ( he, בְּאֵר שֶׁבַע, ''Bəʾēr Ševaʿ'', ; ar, بئر السبع, Biʾr as-Sabʿ, Well of the Oath or Well of the Seven), is the largest city in the Negev desert of southern Israel. ...
, was the main Judahite center in the Negev during the 9th and 8th centuries BCE.
Forts
TheJudaean Mountains
The Judaean Mountains, or Judaean Hills ( he, הרי יהודה, translit=Harei Yehuda) or the Hebron Mountains ( ar, تلال الخليل, translit=Tilal al-Khalīl, links=, lit=Hebron Mountains), is a mountain range in Palestine and Israel wh ...
and Shephelah
The Shephelah or Shfela, lit. "lowlands" ( hbo, הַשְּפֵלָה ''hašŠǝfēlā'', also Modern Hebrew: , ''Šǝfēlat Yəhūda'', the "Judaean foothills"), is a transitional region of soft-sloping rolling hills in south-central Israel str ...
have seen the discovery of several Judahite fortresses and towers. The fortifications had a large central courtyard surrounded by casemate walls with chambers on the outside wall, and they were square or rectangular in shape. Khirbet Abu et-Twein, which is situated on the Judaean Mountains between modern day Bat Ayin and Jab'a
Jab'a ( ar, الجبعة) is a Palestinian village in the central West Bank, located 17 kilometers north of Hebron and 15 kilometers southwest of Bethlehem. Located three kilometers east of the Green Line, it is located in the Seam Zone, surroun ...
, is one of the most noteworthy fortresses from the period. Great views of the Shepehla, including the Judahite towns of Azekah, Socho, Goded, Lachish, and Maresha, could be seen from this fort.
In the northern Negev, Tel Arad
Tel Arad ( he, תל ערד), in Arabic Tell 'Arad (تل عراد), is an archaeological tell, or mound, located west of the Dead Sea, about west of the modern Israeli city of Arad in an area surrounded by mountain ridges which is known as the ...
served as a key administrative and military stronghold. It protected the route from the Judaean Mountains to the Arabah
The Arabah, Araba or Aravah ( he, הָעֲרָבָה, ''hāʿĂrāḇā''; ar, وادي عربة, ''Wādī ʿAraba''; lit. "desolate and dry area") is a loosely defined geographic area south of the Dead Sea basin, which forms part of the borde ...
and on to Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀
''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territo ...
and Edom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
. It underwent numerous renovations and extensions. There are several other Judahite forts in the Negev, including Hurvat Uza, Tel Ira, Aroer, Tel Masos, and Tel Malhata. The main Judahite fortification in the Judaean Desert
The Judaean Desert or Judean Desert ( he, מִדְבַּר יְהוּדָה, Midbar Yehuda}, both ''Desert of Judah'' or ''Judaean Desert''; ar, صحراء يهودا, Sahraa' Yahuda) is a desert in Palestine and Israel that lies east of Jerusa ...
was found at Vered Yeriho; it protected the road from Jericho
Jericho ( ; ar, أريحا ; he, יְרִיחוֹ ) is a Palestinian city in the West Bank. It is located in the Jordan Valley, with the Jordan River to the east and Jerusalem to the west. It is the administrative seat of the Jericho Gove ...
to the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
. A few freestanding, elevated, isolated guard towers of the period were found around Jerusalem; towers of this type were discovered in the French Hill
French Hill ( he, הגבעה הצרפתית, ''HaGiv'a HaTzarfatit'', ar, التلة الفرنسية, ''at-tel al-faransiya''), also Giv'at Shapira ( he, גִּבְעַת שַׁפִּירָא) is an Israeli settlement in northern East Jerusa ...
and south to Giloh Giloh was a city in Judah. The biblical town has been identified with Beit Jala.
Ahitophel, one of King David's chief advisors, came from Giloh (Book of Joshua, ; cf. 2nd Samuel, ). Ahitophel was the grandfather of Bathsheba, "a daughter of Eli ...
.
It is clear from the position of Judaean strongholds that one of their primary purposes was to facilitate communications via fire signals
The smoke signal is one of the oldest forms of long-distance communication. It is a form of visual communication used over a long distance. In general smoke signals are used to transmit news, signal danger, or to gather people to a common area ...
across the Kingdom, a method well-documented in the Book of Jeremiah and the Lachish letters.
Biblical narrative
Jeroboam's revolt and the partition of the United Monarchy
According to the biblical account, theUnited Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
was founded by Saul
Saul (; he, , ; , ; ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first monarch of the United Kingdom of Israel. His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked the transition of Israel and Judah from a scattered t ...
during the late-11th century BCE, and reached its peak during the rule of David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
and Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), ...
. After the death of Solomon circa 930 BCE, the Israelites gathered in Shechem
Shechem ( ), also spelled Sichem ( ; he, שְׁכֶם, ''Šəḵem''; ; grc, Συχέμ, Sykhém; Samaritan Hebrew: , ), was a Canaanite and Israelite city mentioned in the Amarna Letters, later appearing in the Hebrew Bible as the first c ...
for the coronation of Solomon's son and successor, Rehoboam. Before the coronation took place, the northern tribes, led by Jeroboam
Jeroboam I (; Hebrew: ''Yārŏḇə‘ām''; el, Ἱεροβοάμ, Hieroboám) was the first king of the northern Kingdom of Israel. The Hebrew Bible describes the reign of Jeroboam to have commenced following a revolt of the ten northern I ...
, asked the new king to reduce the heavy taxes and labor requirements that his father Solomon had imposed. Rehoboam rejected their petition: “I will add to your yoke: my father hath chastised you with whips, I will chastise you with scorpions" (). As a result, ten of the tribes rebelled against Rehoboam and proclaimed Jeroboam their king, forming the northern Kingdom of Israel. At first, only the tribe of Judah
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tribe of Judah (, ''Shevet Yehudah'') was one of the twelve Tribes of Israel, named after Judah, the son of Jacob. Judah was the first tribe to take its place in the Land of Israel, occupying the southern ...
remained loyal to the House of David, but the tribe of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the Samaritan Pentate ...
soon joined Judah. Both kingdoms, Judah in the south and Israel in the north, co-existed uneasily after the split until the destruction of the Kingdom of Israel by Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
in 722/721.
Relations with the Kingdom of Israel
 For the first 60 years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over Israel, and there was
For the first 60 years, the kings of Judah tried to re-establish their authority over Israel, and there was perpetual war
Perpetual war, endless war, or a forever war, is a lasting state of war with no clear conditions that would lead to its conclusion. These wars are situations of ongoing tension that may escalate at any moment, similar to the Cold War. From the ...
between them. Israel and Judah were in a state of war throughout Rehoboam's 17-year reign. Rehoboam built elaborate defenses and strongholds, along with fortified cities. In the fifth year of Rehoboam's reign, Shishak
Shishak, Shishaq or Susac (, Tiberian: , ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Egyptian pharaoh who sacked Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE. He is usually identified with the pharaoh Shoshenq I.Troy Leiland Sagrillo. 2015.Shoshenq I and bib ...
, pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, brought a huge army and took many cities. In the sack of Jerusalem (10th century BCE), Rehoboam gave them all of the treasures out of the temple as a tribute and Judah became a vassal state of Egypt.
Rehoboam's son and successor, Abijah of Judah, continued his father's efforts to bring Israel under his control. He fought the Battle of Mount Zemaraim
The great Battle of Mount Zemaraim was reported in the Bible to have been fought in Mount Zemaraim, when the army of the Kingdom of Israel led by the king Jeroboam I encountered the army of the Kingdom of Judah led by the king Abijah I. About 500 ...
against Jeroboam
Jeroboam I (; Hebrew: ''Yārŏḇə‘ām''; el, Ἱεροβοάμ, Hieroboám) was the first king of the northern Kingdom of Israel. The Hebrew Bible describes the reign of Jeroboam to have commenced following a revolt of the ten northern I ...
of Israel and was victorious with a heavy loss of life on the Israel side. According to the Books of Chronicles
The Book of Chronicles ( he, דִּבְרֵי־הַיָּמִים ) is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Chronicles) in the Christian Old Testament. Chronicles is the final book of the Hebrew Bible, concluding the third sect ...
, Abijah and his people defeated them with a great slaughter, so that 500,000 chosen men of Israel fell slain, and Jeroboam posed little threat to Judah for the rest of his reign, and the border of the tribe of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the Samaritan Pentate ...
was restored to the original tribal border.
Abijah Abijah ( ') is a Biblical HebrewPetrovsky, p. 35 unisex nameSuperanskaya, p. 277 which means "my Father is Yah". The Hebrew form ' also occurs in the Bible.
Old Testament characters Women
* Abijah, who married King Ahaz of Judah. She is a ...
's son and successor, Asa of Judah
Asa (; el, Ασά; la, Asa) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the Kingdom of Judah and the fifth king of the House of David. The Hebrew Bible gives the period of his reign between 40–41 years. His reign is dated betwee ...
, maintained peace for the first 35 years of his reign, and he revamped and reinforced the fortresses originally built by his grandfather, Rehoboam. 2 Chronicles states that at the Battle of Zephath
The Battle of Zephath, according to the Hebrew Bible (), occurred during the period of 911-870 BCE, in the reign of King Asa of Judah. It was fought at the Valley of Zephath near Maresha, in modern-day Israel, between the armies of the Kingdom of J ...
, the Egyptian-backed chieftain Zerah
Zerah or Zérach ( / "sunrise" Standard Hebrew ''Zéraḥ'' / ''Záraḥ'', Tiberian Hebrew ''Zéraḥ'' / ''Zāraḥ'') refers to several different people in the Hebrew Bible.For the etymology see
An Edomite
Zerah was the name of an Edomite ch ...
the Ethiopian and his million men and 300 chariots were defeated by Asa's 580,000 men in the Valley of Zephath near Maresha
Tel Maresha ( he, תל מראשה) is the tell (archaeological mound) of the biblical Iron Age city of Maresha, and of the subsequent, post-586 BCE Idumean city known by its Hellenised name Marisa, Arabised as Marissa (ماريسا). The tell i ...
. The Bible does not state whether Zerah was a pharaoh or a general of the army. The Ethiopians were pursued all the way to Gerar, in the coastal plain, where they stopped out of sheer exhaustion. The resulting peace kept Judah free from Egyptian incursions until the time of Josiah
Josiah ( or ) or Yoshiyahu; la, Iosias was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE) who, according to the Hebrew Bible, instituted major religious reforms by removing official worship of gods other than Yahweh. Josiah is credited by most biblical s ...
, some centuries later.
In his 36th year, Asa was confronted by Baasha of Israel
Baasha ( he, , ''Baʿšāʾ'') was the third king of the northern Israelite Kingdom of Israel. He was the son of Ahijah of the Tribe of Issachar. Baasha's story is told in .
Reign
Baasha became king of Israel in the third year of Asa, king ...
, who built a fortress at Ramah on the border, less than ten miles from Jerusalem. The capital became under pressure, and the military situation was precarious. Asa took gold and silver from the Temple and sent them to Ben-Hadad I
Ben-Hadad I ( he, בן הדד, translit=bn hdd; arc, בר הדד, translit=br hdd), son of Tabrimmon and grandson of Hezion, was king of Aram-Damascus between 885 BC and 865 BC. Ben-Hadad I was reportedly a contemporary of kings Baasha of the ...
, the king of Aram-Damascus
The Kingdom of Aram-Damascus () was an Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later ye ...
, in exchange for the Damascene king cancelling his peace treaty with Baasha. Ben-Hadad attacked Ijon, Dan and many important cities of the tribe of Naphtali
The Tribe of Naphtali () was one of the northernmost of the twelve tribes of Israel. It is one of the ten lost tribes.
Biblical narratives
In the biblical account, following the completion of the conquest of Canaan by the Israelites, Joshua al ...
, and Baasha was forced to withdraw from Ramah. Asa tore down the unfinished fortress and used its raw materials to fortify Geba and Mizpah in Benjamin
Mizpah ( he, מִצְפָּה ''miṣpāh'', 'watch-tower, look-out') was a city of the tribe of Benjamin referred to in the Hebrew Bible.
Tell en-Nasbeh is one of three sites often identified with Mizpah of Benjamin, and is located about 12 kilo ...
on his side of the border.
Asa's successor, Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat (; alternatively spelled Jehosaphat, Josaphat, or Yehoshafat; ; el, Ἰωσαφάτ, Iosafát; la, Josaphat), according to 1 Kings 22:41, was the son of Asa, and the fourth king of the Kingdom of Judah, in succession to his fathe ...
, changed the policy towards Israel and instead pursued alliances and co-operation with the northern kingdom. The alliance with Ahab
Ahab (; akk, 𒀀𒄩𒀊𒁍 ''Aḫâbbu'' 'a-ḫa-ab-bu'' grc-koi, Ἀχαάβ ''Achaáb''; la, Achab) was the seventh king of Israel, the son and successor of King Omri and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, according to the Hebrew Bib ...
was based on marriage. The alliance led to disaster for the kingdom with the Battle of Ramoth-Gilead
Ramoth-Gilead ( he, רָמֹת גִּלְעָד, meaning "Heights of Gilead"), was a Levitical city and city of refuge east of the Jordan River in the Hebrew Bible, also called "Ramoth in Gilead" (; ; ) or "Ramoth Galaad" in the Douay–Rheims Bib ...
. He then entered into an alliance with Ahaziah of Israel
Ahaziah (, "Yah has grasped"; also gr, Ὀχοζίας, ''Ochozias'' in the Septuagint and the Douai-Rheims translation) was the eighth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel and the son of Ahab and Jezebel. Like his father, he reigned from Sa ...
for the purpose of carrying on maritime commerce with Ophir
Ophir (; ) is a port or region mentioned in the Bible, famous for its wealth. King Solomon received a shipment from Ophir every three years (1 Kings 10:22) which consisted of gold, silver, sandalwood, pearls, ivory, apes, and peacocks.
...
. However, the fleet that was then equipped at Ezion-Geber
Ezion-Geber ( Ancient: ''Ġeṣyōn Geḇer''; also Asiongaber) is a city only known from the Hebrew Bible, in Idumea, a seaport on the northern extremity of the Gulf of Aqaba, in modern terms somewhere in the area of modern Aqaba and Eilat.
Acco ...
was immediately wrecked. A new fleet was fitted out without the co-operation of the king of Israel. Although it was successful, the trade was not prosecuted. He joined Jehoram of Israel
Jehoram ( ''Yəhōrām''; also Joram) was the ninth king of the northern Kingdom of Israel ( 2 Kings 8:16, 2 Kings 8:25–28). He was the son of Ahab and Jezebel, and brother to Ahaziah and Athaliah.
According to 2 Kings, 2 Kings 8:16, in t ...
in a war against the Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀
''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territo ...
ites, who were under tribute to Israel. This war was successful, and the Moabites were subdued. However, on seeing Mesha
King Mesha ( Moabite: 𐤌𐤔𐤏 *''Māšaʿ''; Hebrew: מֵישַׁע ''Mēšaʿ'') was a king of Moab in the 9th century BC, known most famously for having the Mesha Stele inscribed and erected at Dibon. In this inscription he calls himself ...
's act of offering his own son in a human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherein ...
on the walls of Kir-haresheth filled Jehoshaphat with horror, and he withdrew and returned to his own land.
Jehoshaphat
Jehoshaphat (; alternatively spelled Jehosaphat, Josaphat, or Yehoshafat; ; el, Ἰωσαφάτ, Iosafát; la, Josaphat), according to 1 Kings 22:41, was the son of Asa, and the fourth king of the Kingdom of Judah, in succession to his fathe ...
's successor, Jehoram of Judah
Jehoram of Judah (, ) or Joram (; el, Ἰωράμ, Ioram; la, Joram or Ioram), was the fifth king of Judah, and the son of king Jehoshaphat. Jehoram rose to the throne at the age of 32 and reigned for 8 years (, ), although he was ill during hi ...
, formed an alliance with Israel by marrying Athaliah, the daughter of Ahab
Ahab (; akk, 𒀀𒄩𒀊𒁍 ''Aḫâbbu'' 'a-ḫa-ab-bu'' grc-koi, Ἀχαάβ ''Achaáb''; la, Achab) was the seventh king of Israel, the son and successor of King Omri and the husband of Jezebel of Sidon, according to the Hebrew Bib ...
. Despite the alliance with the stronger northern kingdom, Jehoram Jehoram (meaning " Jehovah is exalted" in Biblical Hebrew) was the name of several individuals in the Tanakh. The female version of this name is Athaliah.
*The son of Toi, King of Hamath who was sent by his father to congratulate David on the oc ...
's rule of Judah was shaky. Edom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
revolted, and he was forced to acknowledge its independence. A raid by Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
and Ethiopians
Ethiopians are the native inhabitants of Ethiopia, as well as the global diaspora of Ethiopia. Ethiopians constitute several component ethnic groups, many of which are closely related to ethnic groups in neighboring Eritrea and other parts o ...
looted the king's house and carried off all of his family except for his youngest son, Ahaziah of Judah Ahaziah ( he, אֲחַזְיָהוּ, "held by Yah(-weh)"; Douay–Rheims: Ochozias) was the name of two kings mentioned in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;
.
Clash of empires
 After
After Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
became the sole ruler in c. 715 BCE, he formed alliances with Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border wit ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and made a stand against Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the A ...
by refusing to pay tribute. In response, Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
of Assyria attacked the fortified cities of Judah. Hezekiah paid three hundred talents of silver and thirty talents of gold to Assyria, which required him to empty the temple and royal treasury of silver and strip the gold from the doorposts of Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th ...
. However, Sennacherib besieged Jerusalem in 701 BCE though the city was never taken.
 During the long reign of
During the long reign of Manasseh
Manasseh () is both a given name and a surname. Its variants include Manasses and Manasse.
Notable people with the name include:
Surname
* Ezekiel Saleh Manasseh (died 1944), Singaporean rice and opium merchant and hotelier
* Jacob Manasseh (die ...
(c. 687/686 – 643/642 BCE), Judah was a vassal of Assyrian rulers: Sennacherib and his successors, Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
and Ashurbanipal after 669 BCE. Manasseh is listed as being required to provide materials for Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
's building projects and as one of a number of vassals who assisted Ashurbanipal's campaign against Egypt.
 When
When Josiah
Josiah ( or ) or Yoshiyahu; la, Iosias was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE) who, according to the Hebrew Bible, instituted major religious reforms by removing official worship of gods other than Yahweh. Josiah is credited by most biblical s ...
became king of Judah in c. 641/640 BCE, the international situation was in flux. To the east, the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
was beginning to disintegrate, the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ...
had not yet risen to replace it and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
to the west was still recovering from Assyrian rule. In the power vacuum, Judah could govern itself for the time being without foreign intervention. However, in the spring of 609 BCE, Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
Necho II
Necho II (sometimes Nekau, Neku, Nechoh, or Nikuu; Greek: Νεκώς Β'; ) of Egypt was a king of the 26th Dynasty (610–595 BC), which ruled from Sais. Necho undertook a number of construction projects across his kingdom. In his reign, accordi ...
personally led a sizable army up to the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers'') ...
to aid the Assyrians.
* Taking the coastal route into Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
at the head of a large army, Necho passed the low tracts of Philistia
Philistia (; Koine Greek (LXX): Γῆ τῶν Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''gê tôn Phulistieìm''), also known as the Philistine Pentapolis, was a confederation of cities in the Southwest Levant, which included the cities of Ashdod, Ashk ...
and Sharon
Sharon ( he, שָׁרוֹן ''Šārôn'' "plain") is a given name as well as an Israeli surname.
In English-speaking areas, Sharon is now predominantly a feminine given name. However, historically it was also used as a masculine given name. In I ...
. However, the passage over the ridge of hills, which shuts in on the south the great Jezreel Valley
The Jezreel Valley (from the he, עמק יזרעאל, translit. ''ʿĒmeq Yīzrəʿēʿl''), or Marj Ibn Amir ( ar, مرج ابن عامر), also known as the Valley of Megiddo, is a large fertile plain and inland valley in the Northern Distr ...
, was blocked by the Judean army, led by Josiah, who may have considered that the Assyrians and the Egyptians were weakened by the death of Pharaoh Psamtik I
Wahibre Psamtik I ( Ancient Egyptian: ) was the first pharaoh of the Twenty-sixth Dynasty of Egypt, the Saite period, ruling from the city of Sais in the Nile delta between 664–610 BC. He was installed by Ashurbanipal of the Neo-Assyrian Empir ...
only a year earlier (610 BCE). Presumably in an attempt to help the Babylonians, Josiah attempted to block the advance at Megiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junction, ...
, where a fierce battle was fought and Josiah was killed. Necho then joined forces with the Assyrian Ashur-uballit II
Ashur-uballit II, also spelled Assur-uballit II and Ashuruballit II ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur has kept alive"), was the final ruler of Assyria, ruling from his predecessor Sinsharishkun's death at the Fall of Nineveh in 612 BC ...
, and they crossed the Euphrates and lay siege to Harran
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border cr ...
. The combined forces failed to hold the city after capturing it temporarily, and Necho retreated back to northern Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. The event also marked the disintegration of the Assyrian Empire.
On his return march to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
in 608 BCE, Necho found that Jehoahaz had been selected to succeed his father, Josiah. Necho deposed Jehoahaz, who had been king for only three months, and replaced him with his older brother, Jehoiakim
Jehoiakim, also sometimes spelled Jehoikim; la, Joakim was the eighteenth and antepenultimate king of Judah from 609 to 598 BC. He was the second son of king Josiah () and Zebidah, the daughter of Pedaiah of Rumah. His birth name was Eliakim.; ...
. Necho imposed on Judah a levy of a hundred talents of silver (about 3 tons or about 3.4 metric tons) and a talent of gold (about ). Necho then took Jehoahaz back to Egypt as his prisoner, never to return.
Jehoiakim
Jehoiakim, also sometimes spelled Jehoikim; la, Joakim was the eighteenth and antepenultimate king of Judah from 609 to 598 BC. He was the second son of king Josiah () and Zebidah, the daughter of Pedaiah of Rumah. His birth name was Eliakim.; ...
ruled originally as a vassal of the Egyptians by paying a heavy tribute. However, when the Egyptians were defeated by the Babylonians at Carchemish
Carchemish ( Turkish: ''Karkamış''; or ), also spelled Karkemish ( hit, ; Hieroglyphic Luwian: , /; Akkadian: ; Egyptian: ; Hebrew: ) was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during it ...
in 605 BCE, Jehoiakim changed allegiances to pay tribute to Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
. In 601 BCE, in the fourth year of his reign, Nebuchadnezzar attempted to invade Egypt but was repulsed with heavy losses. The failure led to numerous rebellions among the states of the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
that owed allegiance to Babylon. Jehoiakim also stopped paying tribute to Nebuchadnezzar and took a pro-Egyptian position. Nebuchadnezzar soon dealt with the rebellions. According to the Babylonian Chronicles
The Babylonian Chronicles are a series of tablets recording major events in Babylonian history. They are thus one of the first steps in the development of ancient historiography. The Babylonian Chronicles were written in Babylonian cuneiform, f ...
, after invading "the land of Hatti (Syria/Palestine)" in 599 BCE, he laid siege to Jerusalem. Jehoiakim died in 598 BCE during the siege and was succeeded by his son Jeconiah
Jeconiah ( he, יְכָנְיָה ''Yəḵonəyā'' , meaning "Yah has established"; el, Ιεχονιας; la, Iechonias, Jechonias), also known as Coniah and as Jehoiachin ( he, יְהוֹיָכִין ''Yəhōyāḵīn'' ; la, Ioachin, Joach ...
at an age of either eight or eighteen. The city fell about three months later, on 2 Adar (March 16) 597 BCE. Nebuchadnezzar pillaged both Jerusalem and the Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
and carted all of his spoils to Babylon. Jeconiah
Jeconiah ( he, יְכָנְיָה ''Yəḵonəyā'' , meaning "Yah has established"; el, Ιεχονιας; la, Iechonias, Jechonias), also known as Coniah and as Jehoiachin ( he, יְהוֹיָכִין ''Yəhōyāḵīn'' ; la, Ioachin, Joach ...
and his court and other prominent citizens and craftsmen, along with a sizable portion of the Jewish population of Judah, numbering about 10,000 were deported from the land and dispersed throughout the Babylonian Empire
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state ...
. Among them was Ezekiel. Nebuchadnezzar appointed Zedekiah
Zedekiah (), was the 20th and last king of Judah before the destruction of the kingdom by King Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon. His birth name was Mattaniah/Mattanyahu ( he, מַתַּנְיָהוּ, ''Mattanyāhū'', "Gift of God"; el, Μαθ� ...
, Jehoiakim's brother, the king of the reduced kingdom, who was made a tributary of Babylon.
Destruction and dispersion
 Despite the strong remonstrances of
Despite the strong remonstrances of Jeremiah
Jeremiah, Modern: , Tiberian: ; el, Ἰερεμίας, Ieremíās; meaning " Yah shall raise" (c. 650 – c. 570 BC), also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish ...
and others, Zedekiah revolted against Nebuchadnezzar by ceasing to pay tribute to him and entered an alliance with Pharaoh Hophra. In 589 BCE, Nebuchadnezzar II returned to Judah and again besieged Jerusalem. Many Jews fled to surrounding Moab
Moab ''Mōáb''; Assyrian: 𒈬𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀 ''Mu'abâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒁀𒀀𒀀
''Ma'bâ'', 𒈠𒀪𒀊 ''Ma'ab''; Egyptian: 𓈗𓇋𓃀𓅱𓈉 ''Mū'ībū'', name=, group= () is the name of an ancient Levantine kingdom whose territo ...
, Ammon
Ammon (Ammonite: 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''ʻAmān''; he, עַמּוֹן ''ʻAmmōn''; ar, عمّون, ʻAmmūn) was an ancient Semitic-speaking nation occupying the east of the Jordan River, between the torrent valleys of Arnon and Jabbok, in p ...
, Edom
Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ...
and other countries to seek refuge. The city fell after a siege, which lasted either eighteen or thirty months, and Nebuchadnezzar again pillaged both Jerusalem and the Temple and then destroyed both. After killing all of Zedekiah's sons, Nebuchadnezzar took Zedekiah to Babylon and so put an end to the independent Kingdom of Judah. According to the Book of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah ( he, ספר יִרְמְיָהוּ) is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the boo ...
, in addition to those killed during the siege, some 4,600 people were deported after the fall of Judah. By 586 BCE, much of Judah had been devastated, and the former kingdom had suffered a steep decline of both its economy and its population.
Aftermath
Babylonian Yehud
Jerusalem apparently remained uninhabited for much of the 6th century, and the centre of gravity shifted to Benjamin, the relatively unscathed northern section of the kingdom, where the town of Mizpah became the capital of the new Babylonian province ofYehud
Yehud ( he, יְהוּד) is a city in the Central District of Israel that is part of the joint municipality of Yehud-Monosson. In 2007, the city's population stood at approximately 30,000 people (including Neve Monosson – see below).
History ...
for the remnant of the Jewish population in a part of the former kingdom. That was standard Babylonian practice. When the Philistine city of Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border wit ...
was conquered in 604 BCE, the political, religious and economic elite (but not the bulk of the population) was banished and the administrative centre shifted to a new location.
Gedaliah
Gedaliah, Gedalia, Gedallah Hirsch, E. G. and Greenstone, J. H. (1906)Gedallah Jewish Encyclopedia or Gedalya(h) ( or ; he, גְּדַלְיָּה ''Gəḏalyyā'' or ''Gəḏalyyāhū'', meaning "Jah has become Great") was, according to the na ...
was appointed governor of the Yehud province, supported by a Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
n guard. The administrative centre of the province was Mizpah in Benjamin
Mizpah ( he, מִצְפָּה ''miṣpāh'', 'watch-tower, look-out') was a city of the tribe of Benjamin referred to in the Hebrew Bible.
Tell en-Nasbeh is one of three sites often identified with Mizpah of Benjamin, and is located about 12 kilo ...
, not Jerusalem. On hearing of the appointment, many of the Judeans who had taken refuge in surrounding countries were persuaded to return to Judah. However, Gedaliah was soon assassinated by a member of the royal house, and the Chaldean soldiers killed. The population that was left in the land and those who had returned fled to Egypt for fear a Babylonian reprisal, under the leadership of Yohanan ben Kareah Kareah or Careah (meaning in Hebrew "bald"), according to the Book of Jeremiah, was the father of Johanan and Jonathan, who for a time were loyal to Gedaliah, the Babylonian governor of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ...
. They ignored the urging of the prophet Jeremiah
Jeremiah, Modern: , Tiberian: ; el, Ἰερεμίας, Ieremíās; meaning " Yah shall raise" (c. 650 – c. 570 BC), also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewish ...
against the move. In Egypt, the refugees settled in Migdol
Migdol, or migdal, is a Hebrew word (מגדּלה מגדּל, מגדּל מגדּול) which means either a tower (from its size or height), an elevated stage (a rostrum or pulpit), or a raised bed (within a river). Physically, it can mean fo ...
, Tahpanhes, Noph Noph or Moph was the Hebrew name for the ancient Egyptian city of Memphis, capital of Lower Egypt,
References
Hebrew Bible cities
Ancient Egypt
{{Egypt-geo-stub ...
and Pathros
Pathros ( he, פַּתְרוֹס; ; grc-gre, Φαθωρῆς, ; Koine grc-gre, Παθούρης, ) refers to Upper Egypt, primarily the Thebaid where it extended from Elephantine fort to modern Asyut north of Thebes. Gardiner argues it exten ...
, and Jeremiah went with them as a moral guardian.
Exile of elites to Babylon
The numbers that were deported to Babylon and that made their way to Egypt and the remnant that remained in the land and in surrounding countries are subject to academic debate. TheBook of Jeremiah
The Book of Jeremiah ( he, ספר יִרְמְיָהוּ) is the second of the Latter Prophets in the Hebrew Bible, and the second of the Prophets in the Christian Old Testament. The superscription at chapter Jeremiah 1:1–3 identifies the boo ...
reports that 4,600 were exiled to Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
. The Books of Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of Israel also including the books ...
suggest that it was 10,000 and later 8,000.
Yehud under Persian rule
In 539 BCE, theAchaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
conquered Babylonia and allowed the exiles to return to Yehud Medinata
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a self-governing region under its local Jewish population. The province was a part ...
and to rebuild the Temple, which was completed in the sixth year of Darius (515 BCE) under Zerubbabel
According to the biblical narrative, Zerubbabel, ; la, Zorobabel; Akkadian: 𒆰𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠 ''Zērubābili'' was a governor of the Achaemenid Empire's province Yehud Medinata and the grandson of Jeconiah, penultimate king of Judah. Zerubbab ...
, the grandson of the second to last king of Judah, Jeconiah
Jeconiah ( he, יְכָנְיָה ''Yəḵonəyā'' , meaning "Yah has established"; el, Ιεχονιας; la, Iechonias, Jechonias), also known as Coniah and as Jehoiachin ( he, יְהוֹיָכִין ''Yəhōyāḵīn'' ; la, Ioachin, Joach ...
. Yehud Medinata was a peaceful part of the Achaemenid Empire until its fall in c. 333 BCE to Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
.
Religion
The major theme of the Hebrew Bible's narrative is the loyalty of Judah, especially its kings, toYahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he posse ...
, which it states is the God of Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. Accordingly, all of the kings of Israel and many of the kings of Judah were "bad" in terms of the biblical narrative by failing to enforce monotheism
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
. Of the "good" kings, Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
(727–698 BCE) is noted for his efforts at stamping out idolatry (in his case, the worship of Baal
Baal (), or Baal,; phn, , baʿl; hbo, , baʿal, ). ( ''baʿal'') was a title and honorific meaning "owner", "lord" in the Northwest Semitic languages spoken in the Levant during antiquity. From its use among people, it came to be applied t ...
and Asherah
Asherah (; he, אֲשֵׁרָה, translit=Ăšērā; uga, 𐎀𐎘𐎗𐎚, translit=ʾAṯiratu; akk, 𒀀𒅆𒋥, translit=Aširat; Qatabanian language, Qatabanian: ') in ancient Semitic religion, is a fertility goddess who appears in a ...
, among other traditional Near Eastern divinities),, Emory University, 1997 but his successors, Manasseh of Judah
Manasseh (; Hebrew: ''Mənaššé'', "Forgetter"; akk, 𒈨𒈾𒋛𒄿 ''Menasî'' 'me-na-si-i'' grc-gre, Μανασσῆς ''Manasses''; la, Manasses) was the fourteenth king of the Kingdom of Judah. He was the oldest of the sons of Hezekia ...
(698–642 BCE) and Amon (642–640 BCE), revived idolatry, which drew down on the kingdom the anger of Yahweh. King Josiah
Josiah ( or ) or Yoshiyahu; la, Iosias was the 16th king of Judah (–609 BCE) who, according to the Hebrew Bible, instituted major religious reforms by removing official worship of gods other than Yahweh. Josiah is credited by most biblical s ...
(640–609 BCE) returned to the worship of Yahweh alone, but his efforts were too late, and Israel's unfaithfulness caused God to permit the kingdom's destruction by the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ...
in the Siege of Jerusalem (587/586 BCE).
It is now widely agreed among academic scholars that the Books of Kings are not an accurate portrayal of religious attitudes in Judah or Israel of the time.
Evidence of cannabis residues has been found on two altars in Tel Arad
Tel Arad ( he, תל ערד), in Arabic Tell 'Arad (تل عراد), is an archaeological tell, or mound, located west of the Dead Sea, about west of the modern Israeli city of Arad in an area surrounded by mountain ridges which is known as the ...
dating to the 8th century BC. Researchers believe that cannabis may have been used for ritualistic psychoactive purposes in Judah.
See also
*Kings of Judah
The Kings of Judah were the monarchs who ruled over the ancient Kingdom of Judah. According to the biblical account, this kingdom was founded after the death of Saul, when the tribe of Judah elevated David to rule over it. After seven years, Davi ...
* List of artifacts in biblical archaeology
The following is a list of inscribed artifacts, items made or given shape by humans, that are significant to biblical archaeology.
Selected artifacts significant to biblical chronology
These table lists inscriptions which are of particular sign ...
* List of Jewish states and dynasties
This is a list of dynasties and states that have historically had ties to either ethnic Jews or their religion of Judaism.
In the Land of Israel
* Twelve Tribes of Israel
* Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy),
* Kingdom of Israel (Samaria),
...
* United Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
, the kingdom before the split
* Kingdom of Israel, the Northern Kingdom
* Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
, the modern country
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Judah, Kingdom of 586 BC 6th-century BC disestablishments 10th-century BC establishments Ancient Levant Books of Kings Former monarchies of Western Asia History of Palestine (region) Historic Jewish communities Political entities in the Land of Israel States and territories disestablished in the 6th century BC States and territories established in the 10th century BC Jewish polities Former kingdoms