King's Own (Royal Lancaster Regiment) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The King's Own Royal Regiment (Lancaster) was a
 Authorisation to recruit the regiment was given on 13 July 1680 to the
Authorisation to recruit the regiment was given on 13 July 1680 to the
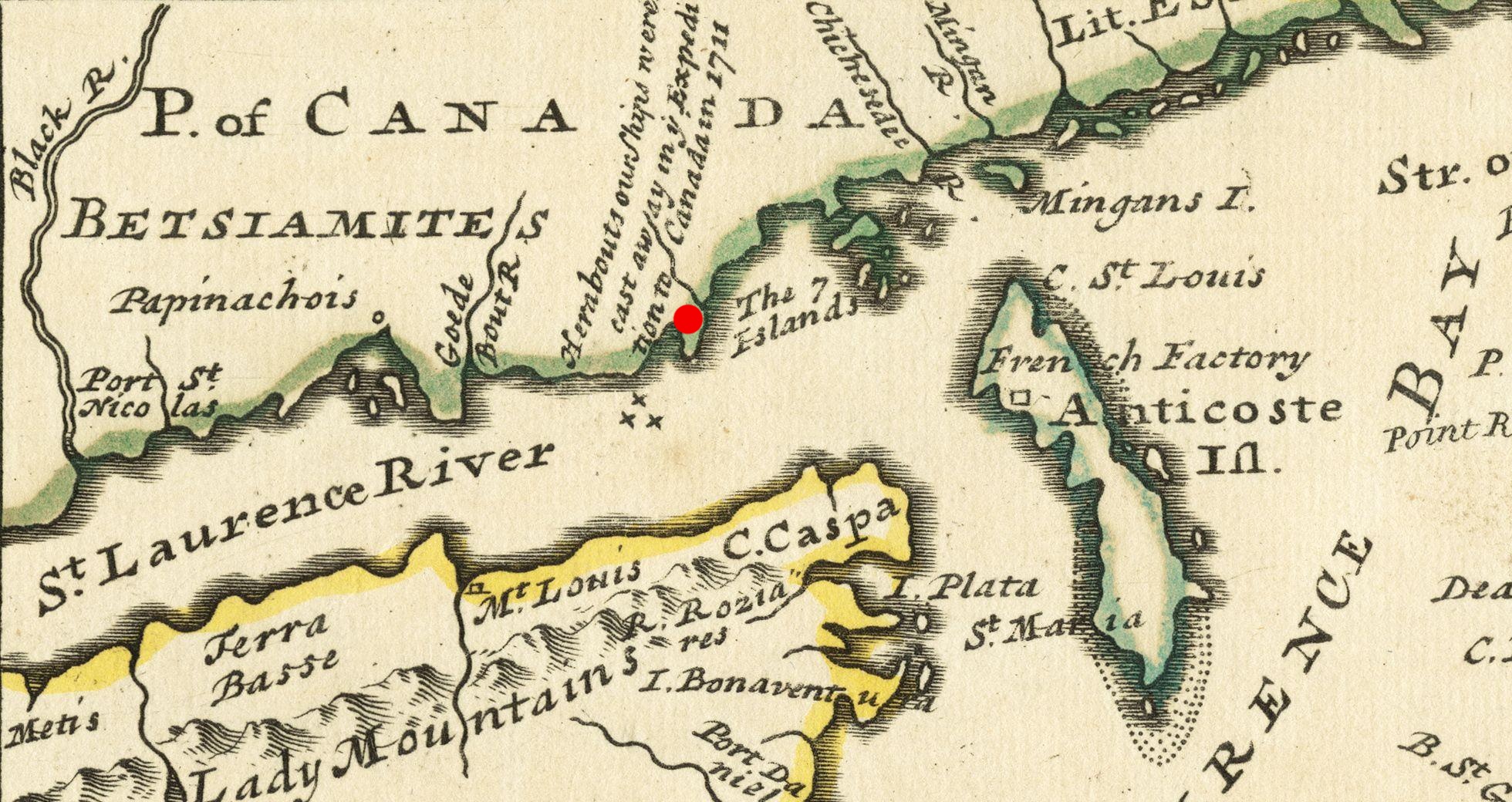 When the
When the  With the accession of George I in 1714, it was retitled The Kings Own and spent the next 30 years in Scotland and England. Sent to Flanders in 1744 during the
With the accession of George I in 1714, it was retitled The Kings Own and spent the next 30 years in Scotland and England. Sent to Flanders in 1744 during the
 The regiment raised 14 Territorial and New Army battalions during the
The regiment raised 14 Territorial and New Army battalions during the
 The 1st Battalion, King's Own was stationed in
The 1st Battalion, King's Own was stationed in
 The 4th Battalion, King's Own Royal Regiment was transferred to the
The 4th Battalion, King's Own Royal Regiment was transferred to the
/ref> Before the war, the 5th Battalion, King's Own transferred from 164th (North Lancashire) Infantry Brigade, 55th (West Lancashire) Infantry Division to 126th (East Lancashire) Infantry Brigade,
 The regiment's battle honours were as follows:
*Namur 1695, Gibraltar 1704-05, Guadeloupe 1759, St. Lucia 1778, Corunna, Badajoz, Salamanca, Vittoria, San Sebastian, Nive, Peninsula, Bladensburg, Waterloo, Alma, Inkerman, Sevastopol, Abyssinia, South Africa 1879, Relief of Ladysmith, South Africa 1899-1902
*''The Great War (16 battalions)'': Le Cateau, Retreat from Mons, Marne 1914, Aisne 1914, Armentières 1914, Ypres 1915 '17, Gravenstafel, St Julien, Frezenberg, Bellewaarde, Festubert 1915, Loos, Somme 1916 '18, Albert 1916 '18, Bazentin, Delville Wood, Pozières, Guillemont, Ginchy, Flers-Courcelette, Morval, Le Transloy, Ancre Heights, Ancre 1916, Arras 1917 '18, Scarpe 1917 '18, Arleux, Messines 1917, Pilckem, Menin Road, Polygon Wood, Broodseinde, Poelcappelle, Passchendaele, Cambrai 1917 '18, St. Quentin, Lys, Estaires, Hazebrouck, Béthune, Bapaume 1918, Drocourt-Quéant, Hindenburg Line, Canal du Nord, Selle, Valenciennes, Sambre, France and Flanders 1914-18, Struma, Doiran 1917 '18, Macedonia 1915-18, Suvla, Sari Bair, Gallipoli 1915, Egypt 1916, Tigris 1916, Kut al Amara 1917, Baghdad, Mesopotamia 1916-18
*''The Second World War'':
The regiment's battle honours were as follows:
*Namur 1695, Gibraltar 1704-05, Guadeloupe 1759, St. Lucia 1778, Corunna, Badajoz, Salamanca, Vittoria, San Sebastian, Nive, Peninsula, Bladensburg, Waterloo, Alma, Inkerman, Sevastopol, Abyssinia, South Africa 1879, Relief of Ladysmith, South Africa 1899-1902
*''The Great War (16 battalions)'': Le Cateau, Retreat from Mons, Marne 1914, Aisne 1914, Armentières 1914, Ypres 1915 '17, Gravenstafel, St Julien, Frezenberg, Bellewaarde, Festubert 1915, Loos, Somme 1916 '18, Albert 1916 '18, Bazentin, Delville Wood, Pozières, Guillemont, Ginchy, Flers-Courcelette, Morval, Le Transloy, Ancre Heights, Ancre 1916, Arras 1917 '18, Scarpe 1917 '18, Arleux, Messines 1917, Pilckem, Menin Road, Polygon Wood, Broodseinde, Poelcappelle, Passchendaele, Cambrai 1917 '18, St. Quentin, Lys, Estaires, Hazebrouck, Béthune, Bapaume 1918, Drocourt-Quéant, Hindenburg Line, Canal du Nord, Selle, Valenciennes, Sambre, France and Flanders 1914-18, Struma, Doiran 1917 '18, Macedonia 1915-18, Suvla, Sari Bair, Gallipoli 1915, Egypt 1916, Tigris 1916, Kut al Amara 1917, Baghdad, Mesopotamia 1916-18
*''The Second World War'':
 The King's Own Royal Regiment Museum is part of the Lancaster City Museum in
The King's Own Royal Regiment Museum is part of the Lancaster City Museum in
Col George Jackson Hay, ''An Epitomized History of the Militia (The Constitutional Force)'', London:United Service Gazette, 1905/Ray Westlake Military Books, 1987
ISBN 0-9508530-7-0. *
King's Own Royal Regiment Museum
The Long, Long Trail
The Regimental Warpath 1914–1918
The Royal Artillery 1939–45
{{Authority control King's Own King's Own Military units and formations established in 1680 Regiments of the British Army in World War I Regiments of the British Army in World War II Regiments of the British Army in the American Revolutionary War Regiments of the British Army in the Crimean War King's Own Military units and formations in Lancashire Military units and formations in Lancaster, Lancashire R Musical instrument museums
line infantry
Line infantry was the type of infantry that composed the basis of European land armies from the late 17th century to the mid-19th century. Maurice of Nassau and Gustavus Adolphus are generally regarded as its pioneers, while Turenne and Mo ...
regiment
A regiment is a military unit. Its role and size varies markedly, depending on the country, service and/or a specialisation.
In Medieval Europe, the term "regiment" denoted any large body of front-line soldiers, recruited or conscripted ...
of the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gur ...
. It served under various titles and fought in many wars and conflicts, including both the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
and the Second World Wars
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, from 1680 to 1959. In 1959, the regiment was amalgamated with the Border Regiment to form the King's Own Royal Border Regiment
The King's Own Royal Border Regiment was an infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1959 until 2006, and was part of the King's Division. It was formed at Barnard Castle on 1 October 1959 through the amalgamation of the King's O ...
.
Previous names include the 2nd Tangier Regiment, Her Royal Highness the Duchess of York and Albany's Regiment of Foot, The Queen's Regiment of Foot, and The King's Own Regiment.
History
Formation
 Authorisation to recruit the regiment was given on 13 July 1680 to the
Authorisation to recruit the regiment was given on 13 July 1680 to the Earl of Plymouth
Earl of Plymouth is a title that has been created three times: twice in the Peerage of England and once in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
History
The first creation was in 1675 for Charles FitzCharles, one of the dozens of illegitimat ...
, an illegitimate son of Charles II; its nominal strength was 1,000 men, half recruited in London by Lieutenant-Colonel Charles Trelawny and half from the West Country. Raised for service in the Tangier Garrison
The Tangier Garrison was the land force which oversaw the defence of English Tangier between 1661 and 1684 when it was evacuated. It was part of the English Army, the de facto standing army that Charles II established following the Restoratio ...
, it was known as the 2nd Tangier Regiment; Plymouth died shortly after arriving in Tangier and Edward Sackville assumed command, with Trelawney formally appointed as colonel in 1682. Tangier was abandoned in 1684 and on returning to England, the regiment was given the title Her Royal Highness the Duchess of York and Albany's Regiment of Foot; after James II became monarch in 1685, this changed to The Queen's Regiment of Foot.
During the Monmouth Rebellion
The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ire ...
, it fought at Sedgemoor
Sedgemoor is a low-lying area of land in Somerset, England. It lies close to sea level south of the Polden Hills, historically largely marsh (or "moor" in its older sense). The eastern part is known as King's Sedgemoor, and the western part Wes ...
in July 1685; at the November 1688 Glorious Revolution, Trelawny and half the regiment deserted to William III. He was briefly replaced by the loyalist Charles Orby, then reinstated when James went into exile. From 1690 to 1691, it served in the Williamite War in Ireland
The Williamite War in Ireland (1688–1691; ga, Cogadh an Dá Rí, "war of the two kings"), was a conflict between Jacobite supporters of deposed monarch James II and Williamite supporters of his successor, William III. It is also called the ...
, including the Battle of the Boyne
The Battle of the Boyne ( ga, Cath na Bóinne ) was a battle in 1690 between the forces of the deposed King James II of England and Ireland, VII of Scotland, and those of King William III who, with his wife Queen Mary II (his cousin and J ...
and sieges of Cork and Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
. When the war ended with the October 1691 Treaty of Limerick
}), signed on 3 October 1691, ended the 1689 to 1691 Williamite War in Ireland, a conflict related to the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War. It consisted of two separate agreements, one with military terms of surrender, signed by commanders of a Frenc ...
, it returned to England.Cannon, p. 19
Transferred to Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
in March 1692, it took part in the latter stages of the 1689 to 1697 Nine Years' War. The regiment fought at the battles of Steenkerque
Steenkerque (French; nl, Steenkerke; in older English references also ''Steenkerke'', ''Steenkirk'', ''Steinkerque'', ''Steinkerke'' or ''Steinkirk''; wa, Stinkerke) is a village of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of Braine-le-Comte ...
in August 1692, and Landen
Landen () is a city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Flemish Brabant. The municipality comprises the city of Landen proper and the villages of Attenhoven, Eliksem, Ezemaal, Laar, Neerlanden, Neerwinden, Overwinden, Rumsdorp, Wa ...
in July 1693 and the Siege of Namur in summer 1695. After the Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included England ...
in 1697, it was reduced in strength and used to garrison Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west.
Plymout ...
and Penryn.
18th century
 When the
When the War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was a European great power conflict that took place from 1701 to 1714. The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Phili ...
began in 1702, it was reformed as a regiment of marines and fought at the Battle of Vigo Bay
The Battle of Vigo Bay, also known as the Battle of Rande (; ), was a naval engagement fought on 23 October 1702 during the opening years of the War of the Spanish Succession. The engagement followed an Anglo-Dutch attempt to capture the Spanish ...
in October 1702 and the capture of Gibraltar
The Capture of Gibraltar by Anglo-Dutch forces of the Grand Alliance occurred between 1 and 4 August 1704 during the War of the Spanish Succession. Since the beginning of the war the Alliance had been looking for a harbour in the Iberian Penins ...
in August 1704. In 1711, it was redesignated line infantry and took part in the Quebec Expedition. In what remains one of the worst naval disasters in British history, the fleet ran aground in thick fog and over 890 men lost, including 200 members of the regiment.
 With the accession of George I in 1714, it was retitled The Kings Own and spent the next 30 years in Scotland and England. Sent to Flanders in 1744 during the
With the accession of George I in 1714, it was retitled The Kings Own and spent the next 30 years in Scotland and England. Sent to Flanders in 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession () was a European conflict that took place between 1740 and 1748. Fought primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italy, the Atlantic and Mediterranean, related conflicts included King George' ...
, it garrisoned Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest i ...
and when the 1745 Jacobite Rising
The Jacobite rising of 1745, also known as the Forty-five Rebellion or simply the '45 ( gd, Bliadhna Theàrlaich, , ), was an attempt by Charles Edward Stuart to regain the British throne for his father, James Francis Edward Stuart. It took pl ...
broke out in August, it was transferred to Scotland and fought at the Battle of Falkirk Muir
The Battle of Falkirk Muir (Scottish Gaelic: ''Blàr na h-Eaglaise Brice''), also known as the Battle of Falkirk, took place on 17 January 1746 during the Jacobite rising of 1745. Although it resulted in a Jacobite victory, their inability to t ...
in January 1746. At the Battle of Culloden
The Battle of Culloden (; gd, Blàr Chùil Lodair) was the final confrontation of the Jacobite rising of 1745. On 16 April 1746, the Jacobite Army (1745), Jacobite army of Charles Edward Stuart was decisively defeated by a Kingdom of Great Bri ...
in April, it was based in the front line and took the brunt of the Jacobite charge; it suffered the heaviest casualties on the government side, with 18 dead and 108 wounded. The regiment's commander, Sir Robert Rich, was among the wounded, losing his left hand. Lord Robert Kerr
Lord Robert Kerr (died 16 April 1746) was a Scottish nobleman of the Clan Kerr and the second son of William Kerr, 3rd Marquess of Lothian. His family's surname at the time he lived was often also spelt as 'Ker'.
He is thought to have gone on a g ...
, captain of the regiment's grenadier company, was among the dead. The two Regulation Colours
The Regulation Colours are the standard colours used in the armed forces of the countries falling under the Commonwealth of Nations.
British Armed Forces colours
British Armed Forces units usually carry two Regulation Colours: the Regulation K ...
(flags) carried by the regiment during the battle both survive and are now part of the collection of the National Museum of Scotland
The National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh, Scotland, was formed in 2006 with the merger of the new Museum of Scotland, with collections relating to Scottish antiquities, culture and history, and the adjacent Royal Scottish Museum (opened in ...
.
Following the army reforms of 1751, the regiment was retitled 4th (King's Own) Regiment of Foot. At the start of the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754– ...
in 1756, it was part of the Menorca
Menorca or Minorca (from la, Insula Minor, , smaller island, later ''Minorica'') is one of the Balearic Islands located in the Mediterranean Sea belonging to Spain. Its name derives from its size, contrasting it with nearby Majorca. Its capi ...
garrison; forced to surrender in June it was transported to Gibraltar. It spent the rest of the war in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Great ...
, taking part in the capture of Guadeloupe
Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands— Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ...
, Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago language, Kalinago: or ) is an island and an Overseas department and region, overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of ...
and Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindi ...
before returning home in July 1764.Cannon, pp. 60
When the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
began in 1774, it was sent to North America; over the next three years, it took part in numerous actions, including Lexington and Concord, Bunker Hill, Long Island and the Battle of White Marsh
The Battle of White Marsh or Battle of Edge Hill was a battle of the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War fought December 5–8, 1777, in the area surrounding Whitemarsh Township, Pennsylvania. The battle, which took the form ...
in December 1777. In early 1778, it returned to Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerindi ...
where it was part of the garrison during the December 1778 naval battle of St. Lucia, part of the Anglo-French War.
Napoleonic Wars
The regiment was sent toNova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native En ...
in May 1787 and took part in the capture of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon (french: link=no, Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Pierre et Miquelon ), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in t ...
in May 1793. After returning to England, it embarked for the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
in September 1799 and fought at the Battle of Alkmaar in October 1799 during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland
The Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland (or Anglo-Russian expedition to Holland, or Helder Expedition) was a military campaign from 27 August to 19 November 1799 during the War of the Second Coalition, in which an expeditionary force of British an ...
.
The regiment was sent to Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, In recognized minority languages of Portugal:
:* mwl, República Pertuesa is a country located on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Macaronesian ...
in August 1808 for service in the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
and fought under General Sir John Moore at the Battle of Corunna
The Battle of Corunna (or ''A Coruña'', ''La Corunna'', ''La Coruña'' or ''La Corogne''), in Spain known as Battle of Elviña, took place on 16 January 1809, when a French corps under Marshal of the Empire Jean de Dieu Soult attacked a Brit ...
in January 1809, before being evacuated to England later that month. It returned to the Peninsula in October 1810 where it fought at the Siege of Badajoz in March 1812, the Battle of Salamanca
The Battle of Salamanca (in French and Spanish known as the Battle of Arapiles) on 22July 1812 was a battle in which an Anglo-Portuguese army under the Earl of Wellington defeated Marshal Auguste Marmont's French forces at Arapiles, so ...
in July 1812 and the Battle of Vitoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leadin ...
in June 1813 as well as the Siege of San Sebastián
In the siege of San Sebastián (7 July – 8 September 1813), part of the Peninsular War, Allied forces under the command of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington failed to capture the city in a siege. However in a second siege the Alli ...
in September 1813. It then pursued the French Army into France and saw action at the Battle of the Nivelle
The Battle of Nivelle (10 November 1813) took place in front of the river Nivelle near the end of the Peninsular War (1808–1814). After the Allied siege of San Sebastian, Wellington's 80,000 British, Portuguese and Spanish troops (2 ...
in November 1813 and at the Battle of the Nive
The Battles of the Nive (9–13 December 1813) were fought towards the end of the Peninsular War. Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington's Anglo-Portuguese and Spanish army defeated Marshal Nicolas Soult's French army on French soil ...
in December 1813. It embarked for North America in June 1814 for service in the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It ...
and saw action at the Battle of Bladensburg
The Battle of Bladensburg was a battle of the Chesapeake campaign of the War of 1812, fought on 24 August 1814 at Bladensburg, Maryland, northeast of Washington, D.C.
Called "the greatest disgrace ever dealt to American arms," a United Kingdom ...
in August 1814, the Burning of Washington
The Burning of Washington was a British invasion of Washington City (now Washington, D.C.), the capital of the United States, during the Chesapeake Campaign of the War of 1812. It is the only time since the American Revolutionary War that a ...
later in August 1814 the Battle of Baltimore
The Battle of Baltimore (September 12–15, 1814) was a sea/land battle fought between British invaders and American defenders in the War of 1812. American forces repulsed sea and land invasions off the busy port city of Baltimore, Maryland ...
in September 1814, and the Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the Fren ...
in January 1815, as well as the capture of Fort Bowyer in February 1815. It briefly returned to England in May 1815, before embarking for Flanders
Flanders (, ; Dutch: ''Vlaanderen'' ) is the Flemish-speaking northern portion of Belgium and one of the communities, regions and language areas of Belgium. However, there are several overlapping definitions, including ones related to cultu ...
a few weeks later to fight at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armies of the Seventh C ...
in June.
The Victorian era
Detachments of the regiment were used as guards upon convict ships travelling to Australia, with the detachments arriving from 1832. Detachments were stationed in Sydney, Tasmania, Victoria, South Australia and Swan River.Cannon, p. 140 The regiment was relieved in 1837 and headed to India. During theCrimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included t ...
, the regiment fought at the Battle of Alma
The Battle of the Alma (short for Battle of the Alma River) was a battle in the Crimean War between an allied expeditionary force (made up of French, British, and Ottoman forces) and Russian forces defending the Crimean Peninsula on 20Septem ...
in September 1854 and Battle of Inkerman
The Battle of Inkerman was fought during the Crimean War on 5 November 1854 between the allied armies of Britain and France against the Imperial Russian Army. The battle broke the will of the Russian Army to defeat the allies in the field, and ...
in November 1854 and took part in the Siege of Sevastopol in winter 1854. It also saw action in Abyssinia in 1868, and in South Africa in 1879.
The regiment was not fundamentally affected by the Cardwell Reforms
The Cardwell Reforms were a series of reforms of the British Army undertaken by Secretary of State for War Edward Cardwell between 1868 and 1874 with the support of Liberal prime minister William Ewart Gladstone. Gladstone paid little attentio ...
of the 1870s, which gave it a depot at Bowerham Barracks in Lancaster Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
*Duke of Lancaster
*Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty
...
from 1873, or by the Childers reforms
The Childers Reforms of 1881 reorganised the infantry regiments of the British Army. The reforms were done by Secretary of State for War Hugh Childers during 1881, and were a continuation of the earlier Cardwell Reforms.
The reorganisation was ...
of 1881 – as it already possessed two battalions, there was no need for it to amalgamate with another regiment. Under the reforms the regiment became the King's Own (Royal Lancaster Regiment) on 1 July 1881. After the Childers reforms took effect, the regiment contained the following battalions:
* 1st Battalion (Regular)
* 2nd Battalion (Regular)
* 3rd (1st Royal Lancashire Militia) Battalion based in Lancaster Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
*Duke of Lancaster
*Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty
...
, from the 1st Bn of the former 1st Royal Lancashire Militia (The Duke of Lancaster's Own) based in Lancaster Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
*Duke of Lancaster
*Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty
...
* 4th (1st Royal Lancashire Militia) Battalion, from the 2nd Bn of the former Militia
* 1st Volunteer Battalion based in Ulverston
Ulverston is a market town and a civil parish in the South Lakeland district of Cumbria, England. In the 2001 census the parish had a population of 11,524, increasing at the 2011 census to 11,678. Historically in Lancashire, it lies a few mi ...
, former 10th Lancashire Rifle Volunteer Corps
The 2nd Battalion embarked for South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
in December 1899, to serve in the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South ...
, and saw action at the Battle of Spion Kop
The Battle of Spioen Kop ( nl, Slag bij Spionkop; af, Slag van Spioenkop) was a military engagement between British forces and two Boer Republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State, during the campaign by the British to ...
in January 1900. The 3rd and 4th Militia battalions were embodied and embarked for South Africa in February and January 1900 respectively.Hay, pp. 242–8.
In 1908, the Volunteers and Militia were reorganised nationally, with the former becoming the Territorial Force
The Territorial Force was a part-time volunteer component of the British Army, created in 1908 to augment British land forces without resorting to conscription. The new organisation consolidated the 19th-century Volunteer Force and yeomanry i ...
and the latter the Special Reserve
The Special Reserve was established on 1 April 1908 with the function of maintaining a reservoir of manpower for the British Army and training replacement drafts in times of war. Its formation was part of the military reforms implemented by Rich ...
; the regiment now had one Reserve and two Territorial battalions.
First World War
 The regiment raised 14 Territorial and New Army battalions during the
The regiment raised 14 Territorial and New Army battalions during the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
.
Regular Army battalions
The 1st Battalion landed atBoulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the C ...
in August 1914 as part of the 12th Brigade in the 4th Division of the British Expeditionary Force. It was nearly destroyed as a fighting unit at the Battle of Le Cateau
The Battle of Le Cateau was fought on the Western Front during the First World War on 26 August 1914. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army had retreated after their defeats at the Battle of Charleroi (21–23 Aug ...
on 26 August 1914, when it suffered some 400 casualties in a single two minute burst of machine gun fire. It served on the Western Front for the rest of the war. The 2nd Battalion returned from India in December 1914 and landed at Le Havre in January 1915 as part of the 83rd Brigade in the 28th Division. It took heavy casualties at the Battle of Frezenberg in May 1915Beckett, p. 61 before moving to Egypt in October 1915 and then to Salonika
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capi ...
.
Special Reserve (formerly Militia) battalion
The 3rd (Reserve) Battalion remained in the United Kingdom throughout the war and supplied drafts of trained infantrymen as replacements to the regular battalions that were serving overseas.Territorial battalions
The 1/4th Battalion was mobilised in the164th (North Lancashire) Brigade
The 164th (North Lancashire) Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Army that saw active service in the First World War as part of the 55th (West Lancashire) Division. As the 164th Infantry Brigade, it remained in the United Kingdom throug ...
of the 55th (West Lancashire) Division
The 55th (West Lancashire) Division was an infantry division of the British Army's Territorial Force (TF) that saw extensive combat during the First World War. It was raised initially in 1908 as the West Lancashire Division. Following the out ...
; it was temporarily attached to 154th (3rd Highland) Brigade in 51st (Highland) Division
The 51st (Highland) Division was an infantry division of the British Army that fought on the Western Front in France during the First World War from 1915 to 1918. The division was raised in 1908, upon the creation of the Territorial Force, as ...
and landed in France in May 1915; it returned to 164 Brigade in January 1916. The 1/5th Battalion was mobilised in the 164th (North Lancashire) Brigade of the 55th (West Lancashire) Division; it landed in France in February 1915 and was temporarily attached to 28th Division and 1st Division; it returned to 166th (South Lancashire) Brigade in the 55th Division in January 1916.
The 2/4th Battalion was formed September 1914 as a 2nd Line duplicate of 1/4th Battalion; it became the 4th (Reserve) Battalion and absorbed 5th (Reserve) Battalion 1916; it was stationed in Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 ...
from June 1918. The 2/5th Battalion was formed September 1914 as a 2nd Line duplicate of 1/5th Battalion; it was attached to the 164th (North Lancashire) Brigade of the 55th (West Lancashire) Division February 1915, then to 170th (2/1st North Lancashire) Brigade of 57th (2nd West Lancashire) Division; it landed in France February 1917. The 3/4th Battalion was formed June 1915 as a reserve battalion; it amalgamated with 2/4th Battalion in January 1916. The 3/5th Battalion was formed June 1915 as a reserve battalion; it remained in the United Kingdom and supplied drafts of trained infantrymen to the 1/5th and 2/5th battalions; it 5th (Reserve) Battalion. The 12th Battalion was formed on 1 January 1917 from 41st Provisional Battalion (TF) in 218th Brigade of 73rd Division, a Home Defence formation; it was disbanded March 1918.
Kitchener's Army battalions
The 6th (Service) Battalion was formed in August 1914; it was attached to 38th Brigade in 13th (Western) Division; it landed at Gallipoli July 1915 and later served inMesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
. The 7th (Service) Battalion was formed in September 1914; it was attached to 56th Brigade in 19th (Western) Division; it landed in France in July 1915 and was disbanded February 1918 due to an Army-wide reorganisation. The 8th (Service) Battalion was formed in October 1914; it was attached to 76th Brigade in 25th Division; it landed in France in September 1915 and served on the Western Front for the war: it helped to slow the German Advance at the Battle of St. Quentin on 21 March 1918.
The 9th (Service) Battalion was formed in October 1914; it was attached to 65th Brigade in 22nd Division and served in Salonika. The 10th (Reserve) Battalion was formed in October 1914; it remained in the United Kingdom and supplied drafts to the Service battalions overseas; it converted into 43rd Training Reserve Battalion in September 1916. The 11th (Service) Battalion was formed in August 1915 as a Bantam battalion; it was attached to 120th Brigade in 40th Division; it landed in France in June 1916 and was disbanded in February 1918. The 12th (Reserve) Battalion was formed in January 1916; it remained in the United Kingdom and supplied drafts to the Service battalions overseas; it converted into 76th Training Reserve Battalion in September 1916.
Inter-War
In 1921, the regiment was re-designated the King's Own Royal Regiment (Lancaster).Second World War
The following battalions served during theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
:
Regular Army battalions
 The 1st Battalion, King's Own was stationed in
The 1st Battalion, King's Own was stationed in Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
on the outbreak of war, moving to Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former ...
in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
at the end of 1939. It later served with the 17th Indian Infantry Brigade. It subsequently served in Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
and Syria with 25th Indian Infantry Brigade, with which it served until October 1943, of 10th Indian Infantry Division
The 10th Indian Infantry Division was a war formed infantry division of the Indian Army during World War II. In four years, the division travelled over from Tehran to Trieste, fought three small wars, and fought two great campaigns: th ...
. In August 1942, the battalion embarked from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
for Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is ...
, but the transport was torpedoed and the troops had to return and re-embark later. In May 1943, the battalion returned to Syria, and then it joined 234th Infantry Brigade in the Aegean Islands in October 1943. Here, the bulk of the battalion was captured by the Germans on 16 November, after the Battle of Leros
The Battle of Leros was the central event of the Dodecanese campaign of the Second World War, and is widely used as an alternate name for the whole campaign. After the Armistice of Cassibile the Italian garrison on the Greek island Leros was ...
, with only 57 officers and men managing to escape the island. The 1st Battalion was reformed in 25th Indian Infantry Brigade, on 30 January 1944, by amalgamating with the 8th Battalion, King's Own. The reformed battalion, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Richard Neville Anderson, later served in the Italian Campaign with 25th Indian Brigade for the rest of the war.
The 2nd Battalion formed part of the British garrison of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
when war broke out. It joined 14th Infantry Brigade in Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East J ...
in March 1940 and moved with it to Egypt in July. The battalion served with 16th Infantry Brigade
The 16th Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Army that saw active service during the Second Boer War and the First and Second World Wars.
History Second Boer War
During the Second Boer War, the 16th brigade was active in Sout ...
of 6th Infantry Division 6th Division may refer to:
Infantry divisions
*6th Division (Australia)
*6th Division (Austria)
* 6th (United Kingdom) Division
*Finnish 6th Division (Winter War)
* Finnish 6th Division (Continuation War)
*6th Division (Reichswehr)
* 6th Division ...
(later redesignated 70th Infantry Division) in the defence of Tobruk and later formed part of the garrison of Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
. In September 1943, the battalion was stationed with 70th Division at Bangalore
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most ...
in India when it was selected for attachment to the second Long Range Penetration or Chindits
The Chindits, officially as Long Range Penetration Groups, were special operations units of the British and Indian armies which saw action in 1943–1944 during the Burma Campaign of World War II.
The British Army Brigadier Orde Wingate fo ...
brigade ( 111th Indian Infantry Brigade) for the Burma Campaign. It formed 41 and 46 Columns in the Second Chindit Campaign, crossing into Burma in March 1944 and being flown out to India in July 1944.Joslen, p. 536. From November 1944 to February 1945, the battalion was assigned to 14th Airlanding Brigade in 44th Indian Airborne Division
The 44th Indian Airborne Division was an airborne forces division of the Indian Army during World War II, created in 1944. It provided a parachute battalion for one minor airborne operation, but the war ended before the complete formation could ...
.
Territorial Army battalions
 The 4th Battalion, King's Own Royal Regiment was transferred to the
The 4th Battalion, King's Own Royal Regiment was transferred to the Royal Artillery
The Royal Regiment of Artillery, commonly referred to as the Royal Artillery (RA) and colloquially known as "The Gunners", is one of two regiments that make up the artillery arm of the British Army. The Royal Regiment of Artillery comprises t ...
and converted to artillery in November 1938, forming the 56th (King's Own) Anti-Tank Regiment, Royal Artillery. On the outbreak of war, the 56th Anti-Tank Regiment mobilised in the 42nd (East Lancashire) Division, with which it served in the Battle of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of French Third Rep ...
in May 1940 and was evacuated at Dunkirk. In 1942, it was sent to join 70th Infantry Division in India, where it was converted into a Light Anti-Aircraft/Anti-Tank Regiment in 1943. In this guise, it served in the Burma Campaign, mainly with 5th Indian Infantry Division. It reconverted to the anti-tank role in late 1944 and in June 1945 it returned to India as a Royal Artillery training unit.
In June 1939, the 56th Anti-Tank Regiment spun off a duplicate unit, the 66th Anti-Tank Regiment, which served in Home Forces throughout the war, mainly with the 55th (West Lancashire) Infantry Division. In September 1941, the 56th and 66th Anti-Tank Regiments each provided a battery to help form a new regiment for overseas service, 83rd Anti-Tank Regiment. This regiment served in Iraq, Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East J ...
and Egypt.83 A/T at RA 39–45./ref> Before the war, the 5th Battalion, King's Own transferred from 164th (North Lancashire) Infantry Brigade, 55th (West Lancashire) Infantry Division to 126th (East Lancashire) Infantry Brigade,
42nd (East Lancashire) Infantry Division
The 42nd (East Lancashire) Infantry Division was an infantry division of the British Army. The division was raised in 1908 as part of the Territorial Force (TF), originally as the East Lancashire Division, and was redesignated as the 42nd (East ...
. The battalion, under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Hayman Hayman-Joyce, mobilised with the rest of the 42nd Division and served with the British Expeditionary Force in the battles of France and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
in 1940. When the division was converted to armour, becoming the 42nd Armoured Division, in October 1941, 5th Battalion was transferred to the Royal Armoured Corps
The Royal Armoured Corps is the component of the British Army, that together with the Household Cavalry provides its armour capability, with vehicles such as the Challenger 2 Tank and the Scimitar Reconnaissance Vehicle. It includes most of the ...
and became the 107th Regiment Royal Armoured Corps. The regiment continued to wear the King's Own cap badge on the black beret of the Royal Armoured Corps
The Royal Armoured Corps is the component of the British Army, that together with the Household Cavalry provides its armour capability, with vehicles such as the Challenger 2 Tank and the Scimitar Reconnaissance Vehicle. It includes most of the ...
, as did all infantry units converted in this way. However, the regiment was disbanded in December 1943 and a few of its officers and men were sent to 151st Regiment Royal Armoured Corps
The 151st Regiment Royal Armoured Corps (10th Bn King's Own) (151 RAC) was an armoured regiment of the British Army's Royal Armoured Corps that was raised during the Second World War.
History Origin
The 151st Regiment RAC was formed on 1 December ...
, which had been converted from the 10th Battalion, King's Own.
Hostilities-only battalions
The 6th, 7th, 8th and 9th Battalions were all formed in 1940 as pioneer battalions and raised specifically for hostilities-only. All four units served with the British Expeditionary Force as GHQ (General Headquarters) troops during the 1940 campaign in bothFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
.
After being evacuated at Dunkirk, the 6th Battalion later served in a succession of Home Forces formations: 218th Independent Infantry Brigade (Home), 48th Division, 54th Division, 76th Division. The battalion never again served overseas and was disbanded in July 1944.
The 7th Battalion served with the 71st Independent Infantry Brigade before being sent to form part of the Gibraltar garrison, with the 2nd Gibraltar Brigade
The 2nd Gibraltar Brigade was a British Army garrison brigade during the Second World War.
History
After serving as part of the Garrison of Gibraltar from 24 April 1941 to 1 December 1943, it was redesignated as the 28th Infantry Brigade and a ...
, in June 1942. In March 1943, the battalion was sent to India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
where it joined 150th Indian Training Brigade but it did not see action against the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. The battalion was disbanded after the war in 1947.
The 8th Battalion joined the Malta garrison in August 1941 and served through the Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterize ...
. It was assigned to the 232nd Infantry Brigade and briefly joined the 233rd Infantry Brigade. In November 1943, the battalion was moved to Palestine
__NOTOC__
Palestine may refer to:
* State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia
* Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia
* Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East J ...
and then Italy with the 25th Indian Infantry Brigade, part of the 10th Indian Infantry Division. In Italy, on 30 January 1944, the 8th Battalion was disbanded and its personnel merged with the few surviving remnants of the 1st Battalion, King's Own, which had been virtually lost during the fighting at Leros.
The 9th Battalion served in the 47th (Reserve) Infantry Division in the United Kingdom until December 1941. The battalion was transferred to the Royal Artillery and was converted into the 90th Anti-Tank Regiment, Royal Artillery, serving with the 45th Division from February 1942 until November 1943 when it was disbanded.
The 50th (Holding) Battalion was formed in the United Kingdom on 28 May 1940. On 9 October 1940, it was renumbered as the 10th Battalion. 10th Battalion was assigned to 225th Independent Infantry Brigade (Home), formed for service in the United Kingdom. When the brigade was converted into a tank brigade in December 1941, the battalion became the 151st Regiment Royal Armoured Corps
The 151st Regiment Royal Armoured Corps (10th Bn King's Own) (151 RAC) was an armoured regiment of the British Army's Royal Armoured Corps that was raised during the Second World War.
History Origin
The 151st Regiment RAC was formed on 1 December ...
. When 107th RAC was disbanded in December 1943, a cadre transferred to 151st RAC, which adopted the number of 107th to perpetuate the 5th Battalion, King's Own, a 1st Line Territorial Army battalion. The new 107th Regiment went on to serve in the North-west Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnographically.
Geographic definitions
Geographically, Northwe ...
from 1944-1945.
Post-war
After the war, all the units created during the war were disbanded; also, following Indian independence, there was no longer a need to maintain such a large overseas garrison and thus the 2nd Battalion was disbanded in 1948. The regiment received the freedom ofLancaster Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
*Duke of Lancaster
*Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty
...
in 1953, before being amalgamated with the Border Regiment into the King's Own Royal Border Regiment
The King's Own Royal Border Regiment was an infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1959 until 2006, and was part of the King's Division. It was formed at Barnard Castle on 1 October 1959 through the amalgamation of the King's O ...
on 31 October 1959. In 1953 and 1954, the 1st Battalion of the regiment was stationed in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
following the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
.
Battle honours
St Omer-La Bassée
ST, St, or St. may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Stanza, in poetry
* Suicidal Tendencies, an American heavy metal/hardcore punk band
* Star Trek, a science-fiction media franchise
* Summa Theologica, a compendium of Catholic philosophy ...
, Dunkirk 1940, North-West Europe 1940, Defence of Habbaniya, Falluja, Iraq 1941, Merjayun, Jebel Mazar, Syria 1941, Tobruk 1941, Tobruk Sortie, North Africa 1940-42, Montone, Citta di Castello, San Martino Sogliano, Lamone Bridgehead, Italy 1944-45, Malta 1941-42, Chindits 1944, Burma 1944
Victoria Crosses
The following members of the regiment were awarded theVictoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
:
* Private (later Sergeant) Thomas Grady
Thomas Grady VC DCM ( ga, Tomás Ó Grádaigh; 18 September 1835 – 18 May 1891) was born in Claddagh, County Galway and was an Irish recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of t ...
, Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included t ...
* Private Albert Halton, 1st Battalion, Great War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
* Private Harry Christian, 2nd Battalion, Great War
* Lance-Sergeant Tom Fletcher Mayson, 1/4th Battalion, Great War
* Second Lieutenant Joseph Henry Collin
Joseph Henry Collin VC ( ga, Seosamh Annraoi Ó Coileáin; 10 April 1893 – 9 April 1918) was an English recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to B ...
, 1/4th Battalion, Great War
* Lance-Corporal (later Corporal) James Hewitson, 1/4th Battalion, Great War
* Lance-Corporal Jack White
John Anthony White (; born July 9, 1975), commonly known as Jack White, is an American musician, best known as the lead singer and guitarist of the duo the White Stripes. White has enjoyed consistent critical and popular success and is widely c ...
, 6th (Service) Battalion, Great War
* Private James Miller, 7th (Service) Battalion, Great War
* Corporal Thomas Neely
Lance Sergeant Thomas Patrick Neely, (28 March 1897 – 1 October 1918) was an English recipient of the Victoria Cross (VC), the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. A soldi ...
, 8th (Service) Battalion, Great War
Regimental museum
Lancaster, Lancashire
Lancaster (, ) is a city and the county town of Lancashire, England, standing on the River Lune. Its population of 52,234 compares with one of 138,375 in the wider City of Lancaster local government district. The House of Lancaster was a branch ...
. The museum, which opened in 1929, exhibits regimental uniforms, medals, regalia, silver, paintings, medals, weapons and other memorabilia reflecting the regiment's history.
Colonels-in-Chief
The colonels-in-chief were as follows: *1903 F.M. HMKing Edward VII
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until Death and state funeral of Edward VII, his death in 1910.
The second chil ...
*1913 F.M. HM King George V
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
Born during the reign of his grandmother Q ...
Colonels
The colonels of the regiment were as follows: *1680 Col.Charles FitzCharles, 1st Earl of Plymouth
Charles FitzCharles, 1st Earl of Plymouth (1657 – 17 October 1680) was the illegitimate son of King Charles II of England, by Catherine Pegge. He had a sister called Catherine FitzCharles who is believed to have become a nun. His mother went ...
(bastard son of Charles II, d. 1680)
*1680 Lt-Gen. Hon Percy Kirke
Lieutenant General Percy Kirke (c. 1646 – 31 October 1691), English soldier, was the son of George Kirke, a court official to Charles I and Charles II.
Career
In 1666 Kirke obtained his first Army commission in Lord Admiral's regiment, an ...
(senior)
*1682 Col. Charles Trelawny
;The Queen Consort's Regiment of Foot - (1688)
*1688 Col. Sir Charles Orby, 2nd Bt.
*1688 Maj-Gen. Charles Trelawny eappointed*1692 Brig-Gen. Henry Trelawny
Brigadier-General Henry Trelawny (ca. 1658 – 8 January 1702) was a British Army officer of Cornish descent, a Member of Parliament and Vice-Admiral of Cornwall.
Origins
He was the seventh and youngest son of Sir Jonathan Trelawny, 2nd Bar ...
*1702 Lt-Gen. William Seymour
;The King's Own Regiment of Foot - (1715)
*1717 Brig-Gen. The Hon. Henry Berkeley
*1719 Gen. Charles Cadogan, 2nd Baron Cadogan
*1734 Lt-Gen. William Barrell
Lieutenant-General William Barrell (died 9 August 1749) was an officer of the British Army.
Career
Barrell joined the Army as a captain on 27 March 1698.''A List of the Colonels, Lieutenant Colonels, Majors, Captains, Lieutenants, and Ensigns ...
*1749 Lt-Gen. Sir Robert Rich, 5th Baronet
Lieutenant-General Sir Robert Rich, 5th Baronet (1717 – 19 May 1785) was a British Army general and Governor of Londonderry and Culmore.
He fought at the Battle of Culloden in 1746 as colonel of the 4th King's Own (Barrell's) Regiment, where h ...
;4th (The King's Own) Regiment of Foot - (1751)
*1756 Lt-Gen. Alexander Duroure
Lieutenant General Alexander Duroure ( – 1 February 1765) was a British Army officer who served as colonel of the 4th (King's Own) Regiment of Foot.
He was of Huguenot extraction, the son of Francis Du Roure, a French immigrant who had served ...
*1765 Col. The Hon. Robert Brudenell
;4th (The King's Own Royal) Regiment of Foot - (1767)
*1768 F.M. Studholme Hodgson
*1782 Lt-Gen. Sir John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne (24 February 1722 – 4 August 1792) was a British general, dramatist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1761 to 1792. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several bat ...
*1792 Gen. George Morrison
*1799 Gen. John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham
General John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, also 2nd Viscount Pitt and 2nd Baron Chatham, (9 October 1756 – 24 September 1835) was a British soldier and politician. He spent a lengthy period in the cabinet but is best known for commanding the dis ...
, KG
*1835 Gen. John Hodgson
*1846 Gen. Sir Thomas Bradford, GCB, GCH
*1853 Gen. Sir John Bell, GCB
*1876 Gen. Studholme John Hodson
;The King's Own (Royal Lancaster Regiment) - (1881)
*1890 Gen. William Sankey, CB
*1892 Lt-Gen. William Wilby, CB
*1894 Gen. Sir William Gordon Cameron, GCB, VD
*1913 Gen. Sir Archibald Hunter, GCB, GCVO, DSO, LLD, TD
;The King's Own Royal Regiment (Lancaster) - (1921)
*1926 Lt-Gen. Sir Oswald Cuthbert Borrett, KCB, CMG, CBE, DSO
*1945 Maj-Gen. Russell Mortimer Luckock
Major-General Russell Mortimer Luckock (27 November 1877 – 1950) was a British Army officer who served as colonel of the King's Own Royal Regiment (Lancaster).
Military career
Mortimer Luckock, the son of Rt. Rev. Herbert Mortimer Luckock, wa ...
, CB, CMG, DSO
*1947 Brig. John Herbert Hardy, CBE, MC
*1957 Maj-Gen. Richard Neville Anderson, CB, CBE, DSO (continued 1961 in King's Own Royal Border Regiment; also 10th Gurkha Rifles
The 10th Princess Mary's Own Gurkha Rifles, (abbreviated to 10 GR), was originally a rifle regiment of the British Indian Army. The regiment was formed in 1890, taking its lineage from a police unit and over the course of its existence it had a ...
)
Footnotes
References
Bibliography
* * * *J.B.M. Frederick, ''Lineage Book of British Land Forces 1660-1978'', Volume I, 1984: Microform Academic Publishers,Wakefield
Wakefield is a cathedral city in West Yorkshire, England located on the River Calder. The city had a population of 99,251 in the 2011 census.https://www.nomisweb.co.uk/census/2011/ks101ew Census 2011 table KS101EW Usual resident population ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. .
Col George Jackson Hay, ''An Epitomized History of the Militia (The Constitutional Force)'', London:United Service Gazette, 1905/Ray Westlake Military Books, 1987
ISBN 0-9508530-7-0. *
Further reading
*External links
King's Own Royal Regiment Museum
The Long, Long Trail
The Regimental Warpath 1914–1918
The Royal Artillery 1939–45
{{Authority control King's Own King's Own Military units and formations established in 1680 Regiments of the British Army in World War I Regiments of the British Army in World War II Regiments of the British Army in the American Revolutionary War Regiments of the British Army in the Crimean War King's Own Military units and formations in Lancashire Military units and formations in Lancaster, Lancashire R Musical instrument museums