Kerberos (mythology) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, Cerberus (; grc-gre, Κέρβερος ''Kérberos'' ), often referred to as the hound of Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
, is a multi-headed dog that guards the gates of the Underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld.
...
to prevent the dead from leaving. He was the offspring of the monsters Echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
and Typhon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
, and was usually described as having three heads, a serpent for a tail, and snakes protruding from multiple parts of his body. Cerberus is primarily known for his capture by Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive ...
, the last of Heracles' twelve labours
The Labours of Hercules or Labours of Heracles ( grc-gre, wikt:ὁ, οἱ wikt:Ἡρακλῆς, Ἡρακλέους wikt:ἆθλος, ἆθλοι, ) are a series of episodes concerning a penance carried out by Heracles, the greatest of the ...
.
Descriptions
Descriptions of Cerberus vary, including the number of his heads. Cerberus was usually three-headed, though not always. Cerberus had several multi-headed relatives. His father was the multi snake-headedTyphon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
, and Cerberus was the brother of three other multi-headed monsters, the multi-snake-headed Lernaean Hydra
The Lernaean Hydra or Hydra of Lerna ( grc-gre, Λερναῖα Ὕδρα, ''Lernaîa Hýdra''), more often known simply as the Hydra, is a serpentine water monster in Greek and Roman mythology. Its lair was the lake of Lerna in the Argolid, whi ...
; Orthrus
In Greek mythology, Orthrus ( grc-gre, Ὄρθρος, ''Orthros'') or Orthus ( grc-gre, Ὄρθος, ''Orthos'') was, according to the mythographer Apollodorus, a two-headed dog who guarded Geryon's cattle and was killed by Heracles. He was the ...
, the two-headed dog who guarded the Cattle of Geryon
In Greek mythology, Geryon ( or ;"Geryon"
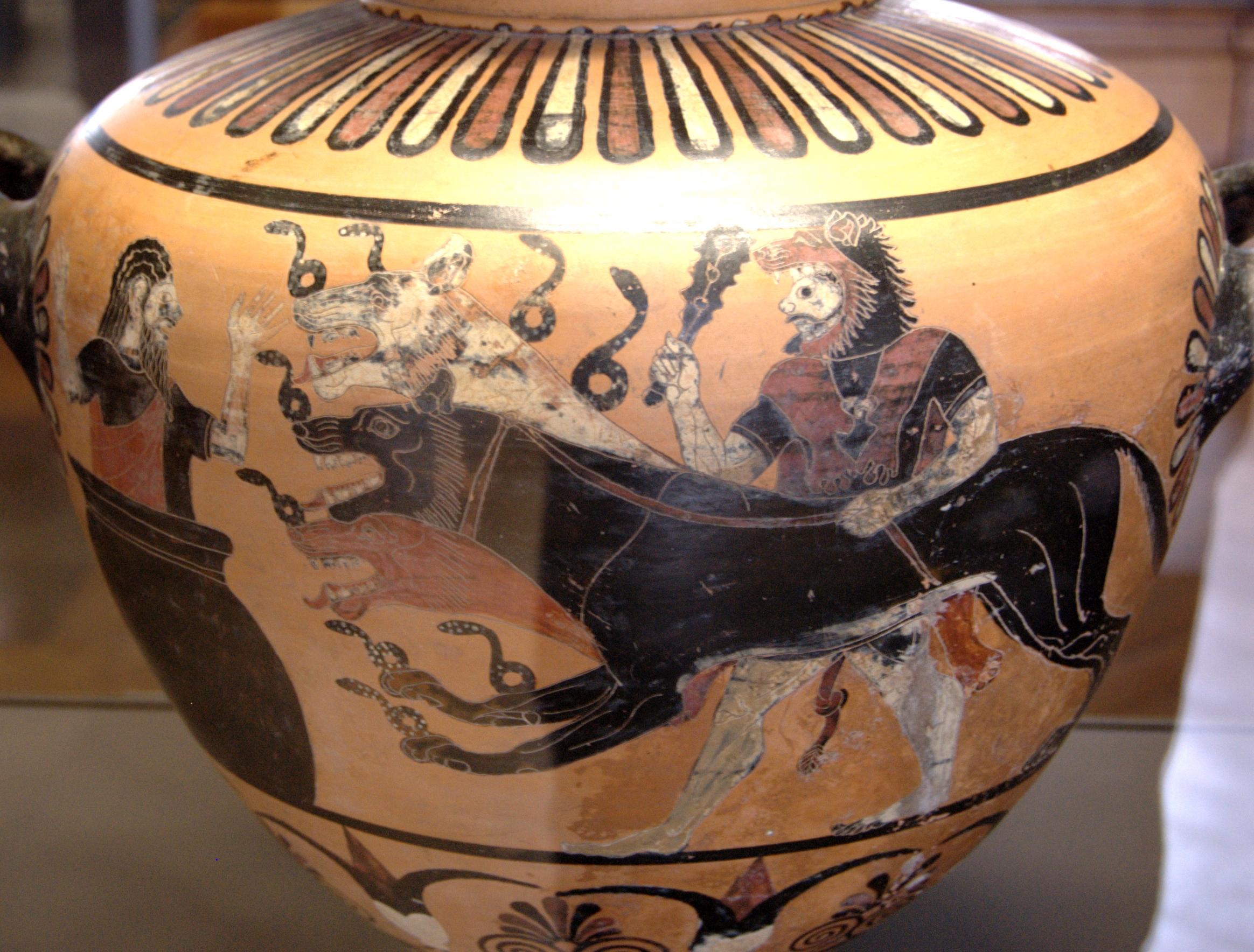
'' In art Cerberus is most commonly depicted with two dog heads (visible), never more than three, but occasionally with only one. On one of the two earliest depictions (c. 590–580 BC), a
In art Cerberus is most commonly depicted with two dog heads (visible), never more than three, but occasionally with only one. On one of the two earliest depictions (c. 590–580 BC), a
 Cerberus' only mythology concerns his capture by Heracles. As early as Homer we learn that Heracles was sent by Eurystheus, the king of Tiryns, to bring back Cerberus from
Cerberus' only mythology concerns his capture by Heracles. As early as Homer we learn that Heracles was sent by Eurystheus, the king of Tiryns, to bring back Cerberus from
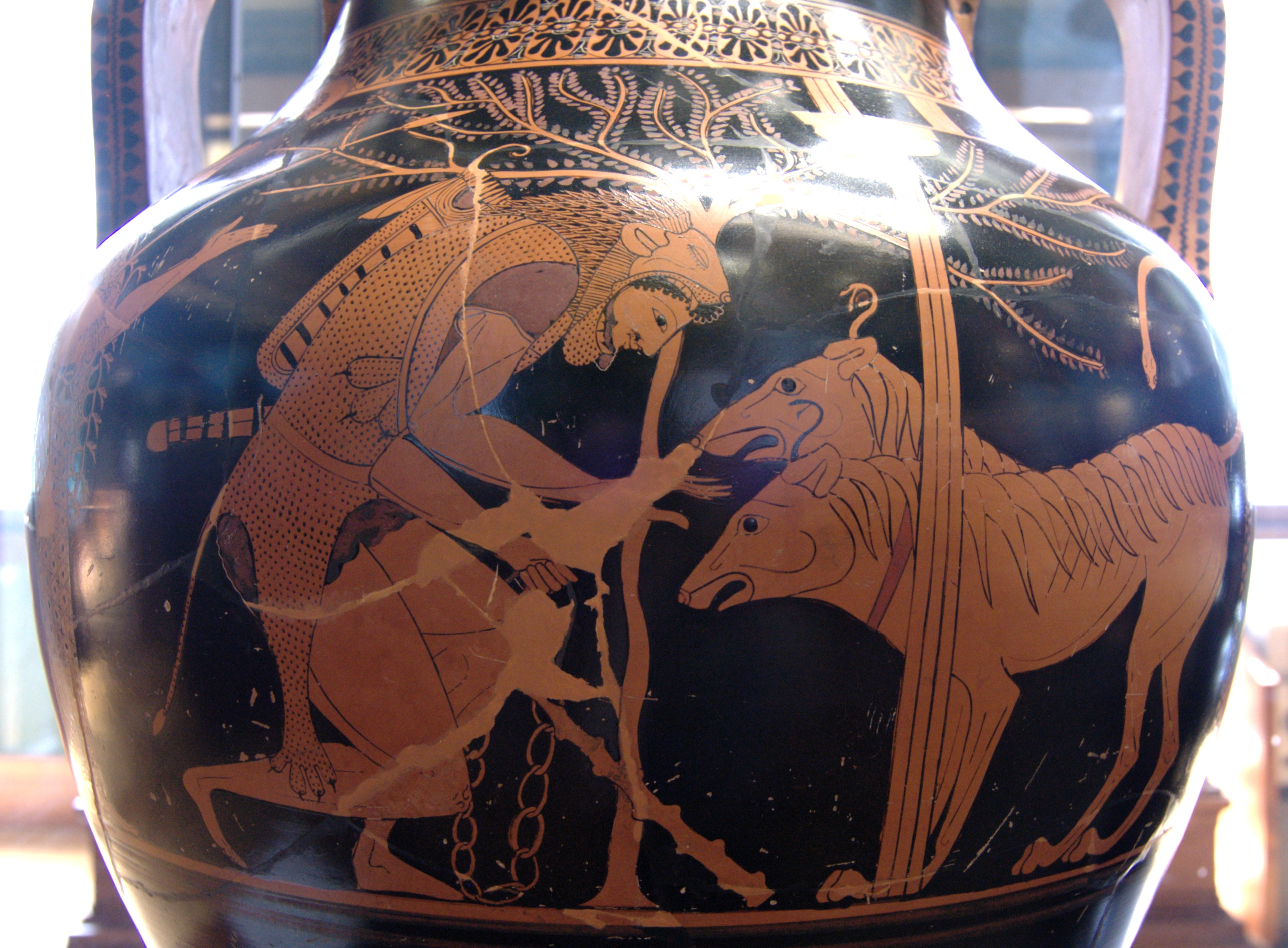
 There are various versions of how Heracles accomplished Cerberus' capture. According to Apollodorus, Heracles asked Hades for Cerberus, and Hades told Heracles he would allow him to take Cerberus only if he "mastered him without the use of the weapons which he carried", and so, using his lion-skin as a shield, Heracles squeezed Cerberus around the head until he submitted.
In some early sources Cerberus' capture seems to involve Heracles fighting Hades. Homer (''Iliad'' 5.395–397) has Hades injured by an arrow shot by Heracles. A scholium to the ''Iliad'' passage, explains that Hades had commanded that Heracles "master Cerberus without shield or Iron". Heracles did this, by (as in Apollodorus) using his lion-skin instead of his shield, and making stone points for his arrows, but when Hades still opposed him, Heracles shot Hades in anger. Consistent with the no iron requirement, on an early-sixth-century BC lost Corinthian cup, Heracles is shown attacking Hades with a stone, while the iconographic tradition, from c. 560 BC, often shows Heracles using his wooden club against Cerberus.
Euripides has Amphitryon ask Heracles: "Did you conquer him in fight, or receive him from the goddess .e. Persephone To which Heracles answers: "In fight", and the ''Pirithous'' fragment says that Heracles "overcame the beast by force". However, according to Diodorus, Persephone welcomed Heracles "like a brother" and gave Cerberus "in chains" to Heracles. Aristophanes has Heracles seize Cerberus in a stranglehold and run off, while Seneca has Heracles again use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to subdue Cerberus, after which a quailing Hades and Persephone allow Heracles to lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. Cerberus is often shown being chained, and Ovid tells that Heracles dragged the three headed Cerberus with chains of adamant.
There are various versions of how Heracles accomplished Cerberus' capture. According to Apollodorus, Heracles asked Hades for Cerberus, and Hades told Heracles he would allow him to take Cerberus only if he "mastered him without the use of the weapons which he carried", and so, using his lion-skin as a shield, Heracles squeezed Cerberus around the head until he submitted.
In some early sources Cerberus' capture seems to involve Heracles fighting Hades. Homer (''Iliad'' 5.395–397) has Hades injured by an arrow shot by Heracles. A scholium to the ''Iliad'' passage, explains that Hades had commanded that Heracles "master Cerberus without shield or Iron". Heracles did this, by (as in Apollodorus) using his lion-skin instead of his shield, and making stone points for his arrows, but when Hades still opposed him, Heracles shot Hades in anger. Consistent with the no iron requirement, on an early-sixth-century BC lost Corinthian cup, Heracles is shown attacking Hades with a stone, while the iconographic tradition, from c. 560 BC, often shows Heracles using his wooden club against Cerberus.
Euripides has Amphitryon ask Heracles: "Did you conquer him in fight, or receive him from the goddess .e. Persephone To which Heracles answers: "In fight", and the ''Pirithous'' fragment says that Heracles "overcame the beast by force". However, according to Diodorus, Persephone welcomed Heracles "like a brother" and gave Cerberus "in chains" to Heracles. Aristophanes has Heracles seize Cerberus in a stranglehold and run off, while Seneca has Heracles again use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to subdue Cerberus, after which a quailing Hades and Persephone allow Heracles to lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. Cerberus is often shown being chained, and Ovid tells that Heracles dragged the three headed Cerberus with chains of adamant.
 There were several locations which were said to be the place where Heracles brought up Cerberus from the underworld. The geographer Strabo (63/64 BC – c. AD 24) reports that "according to the myth writers" Cerberus was brought up at Tainaron, the same place where Euripides has Heracles enter the underworld. Seneca has Heracles enter and exit at Tainaron. Apollodorus, although he has Heracles enter at Tainaron, has him exit at Troezen. The geographer Pausanias tells us that there was a temple at Troezen with "altars to the gods said to rule under the earth", where it was said that, in addition to Cerberus being "dragged" up by Heracles, Semele was supposed to have been brought up out of the underworld by
There were several locations which were said to be the place where Heracles brought up Cerberus from the underworld. The geographer Strabo (63/64 BC – c. AD 24) reports that "according to the myth writers" Cerberus was brought up at Tainaron, the same place where Euripides has Heracles enter the underworld. Seneca has Heracles enter and exit at Tainaron. Apollodorus, although he has Heracles enter at Tainaron, has him exit at Troezen. The geographer Pausanias tells us that there was a temple at Troezen with "altars to the gods said to rule under the earth", where it was said that, in addition to Cerberus being "dragged" up by Heracles, Semele was supposed to have been brought up out of the underworld by
 The earliest mentions of Cerberus (c. 8th – 7th century BC) occur in Homer's '' Iliad'' and '' Odyssey'', and
The earliest mentions of Cerberus (c. 8th – 7th century BC) occur in Homer's '' Iliad'' and '' Odyssey'', and 
 Seneca, in his tragedy ''Hercules Furens'' gives a detailed description of Cerberus and his capture.
Seneca's Cerberus has three heads, a mane of snakes, and a snake tail, with his three heads being covered in gore, and licked by the many snakes which surround them, and with hearing so acute that he can hear "even ghosts". Seneca has Heracles use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to beat Cerberus into submission, after which Hades and Persephone, quailing on their thrones, let Heracles lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. But upon leaving the underworld, at his first sight of daylight, a frightened Cerberus struggles furiously, and Heracles, with the help of Theseus (who had been held captive by Hades, but released, at Heracles' request) drag Cerberus into the light. Seneca, like Diodorus, has Heracles parade the captured Cerberus through Greece.
Apollodorus' Cerberus has three dog-heads, a serpent for a tail, and the heads of many snakes on his back. According to Apollodorus, Heracles' twelfth and final labor was to bring back Cerberus from Hades. Heracles first went to Eumolpus to be initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries. Upon his entering the underworld, all the dead flee Heracles except for Meleager and the Gorgon Medusa. Heracles drew his sword against Medusa, but Hermes told Heracles that the dead are mere "empty phantoms". Heracles asked Hades (here called Pluto) for Cerberus, and Hades said that Heracles could take Cerberus provided he was able to subdue him without using weapons. Heracles found Cerberus at the gates of Acheron, and with his arms around Cerberus, though being bitten by Cerberus' serpent tail, Heracles squeezed until Cerberus submitted. Heracles carried Cerberus away, showed him to Eurystheus, then returned Cerberus to the underworld.
In an apparently unique version of the story, related by the sixth-century AD
Seneca, in his tragedy ''Hercules Furens'' gives a detailed description of Cerberus and his capture.
Seneca's Cerberus has three heads, a mane of snakes, and a snake tail, with his three heads being covered in gore, and licked by the many snakes which surround them, and with hearing so acute that he can hear "even ghosts". Seneca has Heracles use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to beat Cerberus into submission, after which Hades and Persephone, quailing on their thrones, let Heracles lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. But upon leaving the underworld, at his first sight of daylight, a frightened Cerberus struggles furiously, and Heracles, with the help of Theseus (who had been held captive by Hades, but released, at Heracles' request) drag Cerberus into the light. Seneca, like Diodorus, has Heracles parade the captured Cerberus through Greece.
Apollodorus' Cerberus has three dog-heads, a serpent for a tail, and the heads of many snakes on his back. According to Apollodorus, Heracles' twelfth and final labor was to bring back Cerberus from Hades. Heracles first went to Eumolpus to be initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries. Upon his entering the underworld, all the dead flee Heracles except for Meleager and the Gorgon Medusa. Heracles drew his sword against Medusa, but Hermes told Heracles that the dead are mere "empty phantoms". Heracles asked Hades (here called Pluto) for Cerberus, and Hades said that Heracles could take Cerberus provided he was able to subdue him without using weapons. Heracles found Cerberus at the gates of Acheron, and with his arms around Cerberus, though being bitten by Cerberus' serpent tail, Heracles squeezed until Cerberus submitted. Heracles carried Cerberus away, showed him to Eurystheus, then returned Cerberus to the underworld.
In an apparently unique version of the story, related by the sixth-century AD
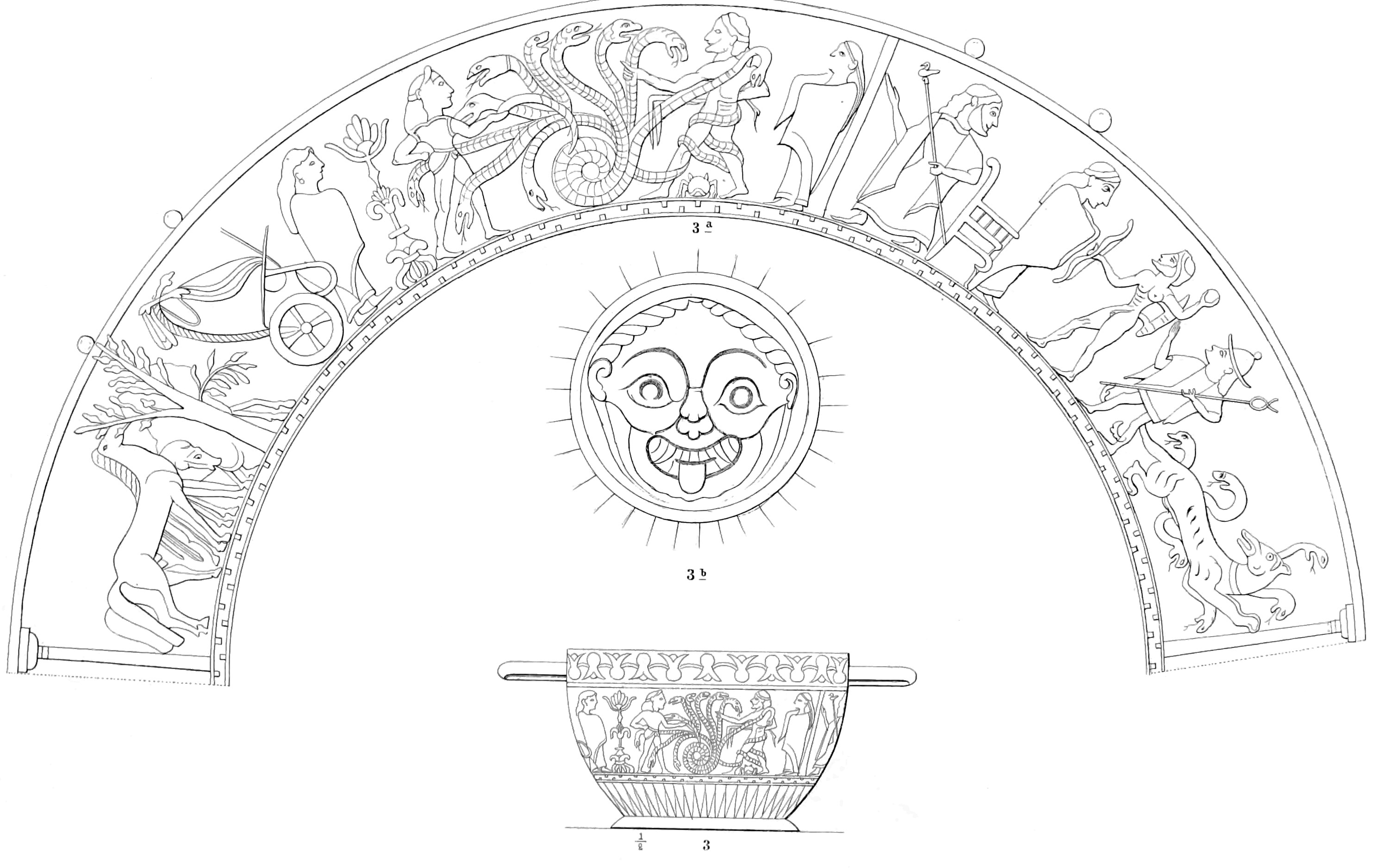 The capture of Cerberus was a popular theme in ancient Greek and Roman art. The earliest depictions date from the beginning of the sixth century BC. One of the two earliest depictions, a
The capture of Cerberus was a popular theme in ancient Greek and Roman art. The earliest depictions date from the beginning of the sixth century BC. One of the two earliest depictions, a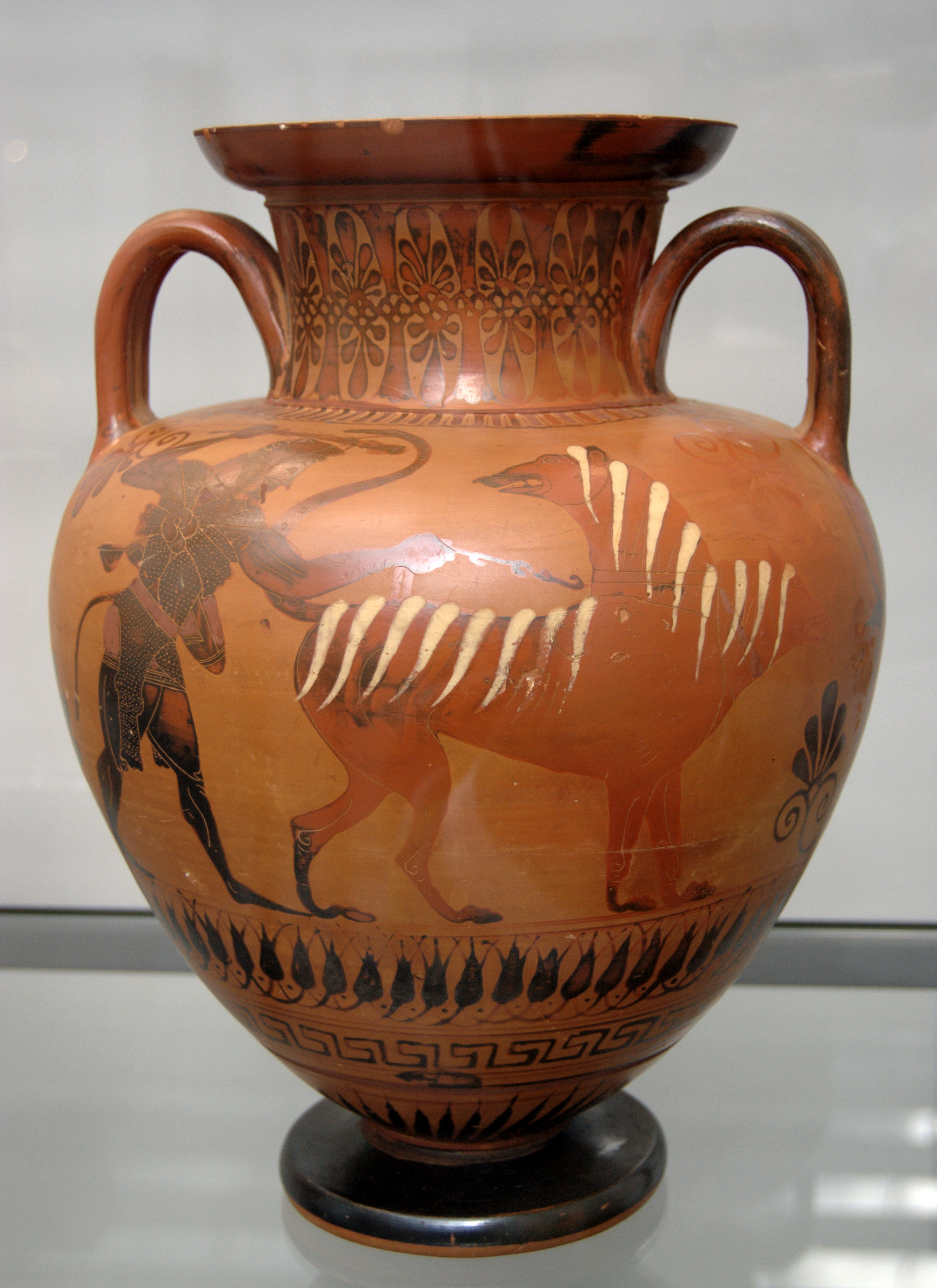  As in the Corinthian and Laconian cups (and possibly the relief ''pithos'' fragment), Cerberus is often depicted as part snake. In Attic vase painting, Cerberus is usually shown with a snake for a tail or a tail which ends in the head of a snake. Snakes are also often shown rising from various parts of his body including snout, head, neck, back, ankles, and paws.
Two Attic amphoras from Vulci, one (c. 530–515 BC) by the
As in the Corinthian and Laconian cups (and possibly the relief ''pithos'' fragment), Cerberus is often depicted as part snake. In Attic vase painting, Cerberus is usually shown with a snake for a tail or a tail which ends in the head of a snake. Snakes are also often shown rising from various parts of his body including snout, head, neck, back, ankles, and paws.
Two Attic amphoras from Vulci, one (c. 530–515 BC) by the
 The etymology of Cerberus' name is uncertain. Ogden refers to attempts to establish an Indo-European etymology as "not yet successful". It has been claimed to be related to the Sanskrit word सर्वरा ''sarvarā'', used as an epithet of one of the dogs of Yama, from a Proto-Indo-European word *''k̑érberos'', meaning "spotted". Lincoln (1991), among others, critiques this etymology. This etymology was also rejected by Manfred Mayrhofer, who proposed an Austro-Asiatic origin for the word, and Beekes. Lincoln notes a similarity between Cerberus and the Norse mythological dog Garmr, relating both names to a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ger-'' "to growl" (perhaps with the suffixes ''-*m/*b'' and ''-*r''). However, as Ogden observes, this analysis actually requires ''Kerberos'' and ''Garmr'' to be derived from two ''different'' Indo-European roots (*''ker-'' and *''gher-'' respectively), and so does not actually establish a relationship between the two names.
Though probably not Greek, Greek etymologies for Cerberus have been offered. An etymology given by
The etymology of Cerberus' name is uncertain. Ogden refers to attempts to establish an Indo-European etymology as "not yet successful". It has been claimed to be related to the Sanskrit word सर्वरा ''sarvarā'', used as an epithet of one of the dogs of Yama, from a Proto-Indo-European word *''k̑érberos'', meaning "spotted". Lincoln (1991), among others, critiques this etymology. This etymology was also rejected by Manfred Mayrhofer, who proposed an Austro-Asiatic origin for the word, and Beekes. Lincoln notes a similarity between Cerberus and the Norse mythological dog Garmr, relating both names to a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ger-'' "to growl" (perhaps with the suffixes ''-*m/*b'' and ''-*r''). However, as Ogden observes, this analysis actually requires ''Kerberos'' and ''Garmr'' to be derived from two ''different'' Indo-European roots (*''ker-'' and *''gher-'' respectively), and so does not actually establish a relationship between the two names.
Though probably not Greek, Greek etymologies for Cerberus have been offered. An etymology given by
''
Chimera
Chimera, Chimaera, or Chimaira (Greek for " she-goat") originally referred to:
* Chimera (mythology), a fire-breathing monster of Ancient Lycia said to combine parts from multiple animals
* Mount Chimaera, a fire-spewing region of Lycia or Cilicia ...
, who had three heads: that of a lion, a goat, and a snake. And, like these close relatives, Cerberus was, with only the rare iconographic exception, multi-headed.
In the earliest description of Cerberus, Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
's ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' (, , , i.e. "the genealogy or birth of the gods") is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 10 ...
'' (c. 8th – 7th century BC), Cerberus has fifty heads, while Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
(c. 522 – c. 443 BC) gave him one hundred heads. However, later writers almost universally give Cerberus three heads. An exception is the Latin poet Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ' ...
's Cerberus which has a single dog head, and one hundred snake heads. Perhaps trying to reconcile these competing traditions, Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
's Cerberus has three dog heads and the heads of "all sorts of snakes" along his back, while the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
poet John Tzetzes
John Tzetzes ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης Τζέτζης, Iōánnēs Tzétzēs; c. 1110, Constantinople – 1180, Constantinople) was a Byzantine poet and grammarian who is known to have lived at Constantinople in the 12th century.
He was able to p ...
(who probably based his account on Apollodorus) gives Cerberus fifty heads, three of which were dog heads, the rest being the "heads of other beasts of all sorts".
 In art Cerberus is most commonly depicted with two dog heads (visible), never more than three, but occasionally with only one. On one of the two earliest depictions (c. 590–580 BC), a
In art Cerberus is most commonly depicted with two dog heads (visible), never more than three, but occasionally with only one. On one of the two earliest depictions (c. 590–580 BC), a Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
ian cup from Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
* ...
(see below), now lost, Cerberus was shown as a normal single-headed dog. The first appearance of a three-headed Cerberus occurs on a mid-sixth-century BC Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
n cup (see below).
Horace's many snake-headed Cerberus followed a long tradition of Cerberus being part snake. This is perhaps already implied as early as in Hesiod's ''Theogony'', where Cerberus' mother is the half-snake Echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
, and his father the snake-headed Typhon. In art, Cerberus is often shown as being part snake, for example the lost Corinthian cup showed snakes protruding from Cerberus' body, while the mid sixth-century BC Laconian cup gives Cerberus a snake for a tail. In the literary record, the first certain indication of Cerberus' serpentine nature comes from the rationalized account of Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Per ...
(fl. 500–494 BC), who makes Cerberus a large poisonous snake. Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
refers to Cerberus' composite nature, and Euphorion of Chalcis
Euphorion of Chalcis ( el, Εὐφορίων ὁ Χαλκιδεύς) was a Greek poet and grammarian, born at Chalcis in Euboea about 275 BC.
Euphorion spent much of his life in Athens, where he amassed great wealth. After studying philosophy w ...
(3rd century BC) describes Cerberus as having multiple snake tails, and presumably in connection to his serpentine nature, associates Cerberus with the creation of the poisonous aconite
Aconite may refer to:
*'' Aconitum'', a plant genus containing the monkshoods
*Aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the na ...
plant. Virgil has snakes writhe around Cerberus' neck, Ovid's Cerberus has a venomous mouth, necks "vile with snakes", and "hair inwoven with the threatening snake", while Seneca gives Cerberus a mane consisting of snakes, and a single snake tail.
Cerberus was given various other traits. According to Euripides, Cerberus not only had three heads but three bodies, and according to Virgil he had multiple backs. Cerberus ate raw flesh (according to Hesiod), had eyes which flashed fire (according to Euphorion), a three-tongued mouth (according to Horace), and acute hearing (according to Seneca).
The Twelfth Labour of Heracles
 Cerberus' only mythology concerns his capture by Heracles. As early as Homer we learn that Heracles was sent by Eurystheus, the king of Tiryns, to bring back Cerberus from
Cerberus' only mythology concerns his capture by Heracles. As early as Homer we learn that Heracles was sent by Eurystheus, the king of Tiryns, to bring back Cerberus from Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
the king of the underworld. According to Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, this was the twelfth and final labour imposed on Heracles. In a fragment from a lost play ''Pirithous'', (attributed to either Euripides or Critias) Heracles says that, although Eurystheus commanded him to bring back Cerberus, it was not from any desire to see Cerberus, but only because Eurystheus thought that the task was impossible.
Heracles was aided in his mission by his being an initiate of the Eleusinian Mysteries. Euripides has his initiation being "lucky" for Heracles in capturing Cerberus. And both Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
and Apollodorus say that Heracles was initiated into the Mysteries, in preparation for his descent into the underworld. According to Diodorus, Heracles went to Athens, where Musaeus Musaeus, Musaios ( grc, Μουσαῖος) or Musäus may refer to:
Greek poets
* Musaeus of Athens, legendary polymath, considered by the Greeks to be one of their earliest poets (mentioned by Socrates in Plato's Apology)
* Musaeus of Ephesus, liv ...
, the son of Orpheus, was in charge of the initiation rites, while according to Apollodorus, he went to Eumolpus at Eleusis
Elefsina ( el, Ελευσίνα ''Elefsina''), or Eleusis (; Ancient Greek: ''Eleusis'') is a suburban city and Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in the West Attica regional unit of Greece. It is situated about northwest ...
.
Heracles also had the help of Hermes, the usual guide of the underworld, as well as Athena. In the ''Odyssey'', Homer has Hermes and Athena as his guides. And Hermes and Athena are often shown with Heracles on vase paintings depicting Cerberus' capture. By most accounts, Heracles made his descent into the underworld through an entrance at Tainaron
Cape Matapan ( el, Κάβο Ματαπάς, Maniot dialect: Ματαπά), also named as Cape Tainaron or Taenarum ( el, Ακρωτήριον Ταίναρον), or Cape Tenaro, is situated at the end of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. Cape Matapan ...
, the most famous of the various Greek entrances to the underworld. The place is first mentioned in connection with the Cerberus story in the rationalized account of Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Per ...
(fl. 500–494 BC), and Euripides, Seneca, and Apolodorus, all have Heracles descend into the underworld there. However Xenophon reports that Heracles was said to have descended at the Acherusian Chersonese near Heraclea Pontica, on the Black Sea, a place more usually associated with Heracles' exit from the underworld (see below). Heraclea, founded c. 560 BC, perhaps took its name from the association of its site with Heracles' Cerberian exploit.
Theseus and Pirithous
While in the underworld, Heracles met the heroes Theseus and Pirithous, where the two companions were being held prisoner by Hades for attempting to carry off Hades' wife Persephone. Along with bringing back Cerberus, Heracles also managed (usually) to rescue Theseus, and in some versions Pirithous as well. According to Apollodorus, Heracles found Theseus and Pirithous near the gates of Hades, bound to the "Chair of Forgetfulness, to which they grew and were held fast by coils of serpents", and when they saw Heracles, "they stretched out their hands as if they should be raised from the dead by his might", and Heracles was able to free Theseus, but when he tried to raise up Pirithous, "the earth quaked and he let go." The earliest evidence for the involvement of Theseus and Pirithous in the Cerberus story, is found on a shield-band relief (c. 560 BC) fromOlympia
The name Olympia may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Olympia'' (1938 film), by Leni Riefenstahl, documenting the Berlin-hosted Olympic Games
* ''Olympia'' (1998 film), about a Mexican soap opera star who pursues a career as an athlet ...
, where Theseus and Pirithous (named) are seated together on a chair, arms held out in supplication, while Heracles approaches, about to draw his sword. The earliest literary mention of the rescue occurs in Euripides, where Heracles saves Theseus (with no mention of Pirithous). In the lost play ''Pirithous'', both heroes are rescued, while in the rationalized account of Philochorus, Heracles was able to rescue Theseus, but not Pirithous. In one place Diodorus says Heracles brought back both Theseus and Pirithous, by the favor of Persephone, while in another he says that Pirithous remained in Hades, or according to "some writers of myth" that neither Theseus, nor Pirithous returned. Both are rescued in Hyginus.
Capture
 There are various versions of how Heracles accomplished Cerberus' capture. According to Apollodorus, Heracles asked Hades for Cerberus, and Hades told Heracles he would allow him to take Cerberus only if he "mastered him without the use of the weapons which he carried", and so, using his lion-skin as a shield, Heracles squeezed Cerberus around the head until he submitted.
In some early sources Cerberus' capture seems to involve Heracles fighting Hades. Homer (''Iliad'' 5.395–397) has Hades injured by an arrow shot by Heracles. A scholium to the ''Iliad'' passage, explains that Hades had commanded that Heracles "master Cerberus without shield or Iron". Heracles did this, by (as in Apollodorus) using his lion-skin instead of his shield, and making stone points for his arrows, but when Hades still opposed him, Heracles shot Hades in anger. Consistent with the no iron requirement, on an early-sixth-century BC lost Corinthian cup, Heracles is shown attacking Hades with a stone, while the iconographic tradition, from c. 560 BC, often shows Heracles using his wooden club against Cerberus.
Euripides has Amphitryon ask Heracles: "Did you conquer him in fight, or receive him from the goddess .e. Persephone To which Heracles answers: "In fight", and the ''Pirithous'' fragment says that Heracles "overcame the beast by force". However, according to Diodorus, Persephone welcomed Heracles "like a brother" and gave Cerberus "in chains" to Heracles. Aristophanes has Heracles seize Cerberus in a stranglehold and run off, while Seneca has Heracles again use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to subdue Cerberus, after which a quailing Hades and Persephone allow Heracles to lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. Cerberus is often shown being chained, and Ovid tells that Heracles dragged the three headed Cerberus with chains of adamant.
There are various versions of how Heracles accomplished Cerberus' capture. According to Apollodorus, Heracles asked Hades for Cerberus, and Hades told Heracles he would allow him to take Cerberus only if he "mastered him without the use of the weapons which he carried", and so, using his lion-skin as a shield, Heracles squeezed Cerberus around the head until he submitted.
In some early sources Cerberus' capture seems to involve Heracles fighting Hades. Homer (''Iliad'' 5.395–397) has Hades injured by an arrow shot by Heracles. A scholium to the ''Iliad'' passage, explains that Hades had commanded that Heracles "master Cerberus without shield or Iron". Heracles did this, by (as in Apollodorus) using his lion-skin instead of his shield, and making stone points for his arrows, but when Hades still opposed him, Heracles shot Hades in anger. Consistent with the no iron requirement, on an early-sixth-century BC lost Corinthian cup, Heracles is shown attacking Hades with a stone, while the iconographic tradition, from c. 560 BC, often shows Heracles using his wooden club against Cerberus.
Euripides has Amphitryon ask Heracles: "Did you conquer him in fight, or receive him from the goddess .e. Persephone To which Heracles answers: "In fight", and the ''Pirithous'' fragment says that Heracles "overcame the beast by force". However, according to Diodorus, Persephone welcomed Heracles "like a brother" and gave Cerberus "in chains" to Heracles. Aristophanes has Heracles seize Cerberus in a stranglehold and run off, while Seneca has Heracles again use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to subdue Cerberus, after which a quailing Hades and Persephone allow Heracles to lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. Cerberus is often shown being chained, and Ovid tells that Heracles dragged the three headed Cerberus with chains of adamant.
Exit from the underworld
 There were several locations which were said to be the place where Heracles brought up Cerberus from the underworld. The geographer Strabo (63/64 BC – c. AD 24) reports that "according to the myth writers" Cerberus was brought up at Tainaron, the same place where Euripides has Heracles enter the underworld. Seneca has Heracles enter and exit at Tainaron. Apollodorus, although he has Heracles enter at Tainaron, has him exit at Troezen. The geographer Pausanias tells us that there was a temple at Troezen with "altars to the gods said to rule under the earth", where it was said that, in addition to Cerberus being "dragged" up by Heracles, Semele was supposed to have been brought up out of the underworld by
There were several locations which were said to be the place where Heracles brought up Cerberus from the underworld. The geographer Strabo (63/64 BC – c. AD 24) reports that "according to the myth writers" Cerberus was brought up at Tainaron, the same place where Euripides has Heracles enter the underworld. Seneca has Heracles enter and exit at Tainaron. Apollodorus, although he has Heracles enter at Tainaron, has him exit at Troezen. The geographer Pausanias tells us that there was a temple at Troezen with "altars to the gods said to rule under the earth", where it was said that, in addition to Cerberus being "dragged" up by Heracles, Semele was supposed to have been brought up out of the underworld by Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
.
Another tradition had Cerberus brought up at Heraclea Pontica (the same place which Xenophon had earlier associated with Heracles' descent) and the cause of the poisonous plant aconite
Aconite may refer to:
*'' Aconitum'', a plant genus containing the monkshoods
*Aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the na ...
which grew there in abundance. Herodorus of Heraclea and Euphorion said that when Heracles brought Cerberus up from the underworld at Heraclea, Cerberus "vomited bile" from which the aconite
Aconite may refer to:
*'' Aconitum'', a plant genus containing the monkshoods
*Aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the na ...
plant grew up. Ovid, also makes Cerberus the cause of the poisonous aconite, saying that on the "shores of Scythia", upon leaving the underworld, as Cerberus was being dragged by Heracles from a cave, dazzled by the unaccustomed daylight, Cerberus spewed out a "poison-foam", which made the aconite plants growing there poisonous. Seneca's Cerberus too, like Ovid's, reacts violently to his first sight of daylight. Enraged, the previously submissive Cerberus struggles furiously, and Heracles and Theseus must together drag Cerberus into the light.
Pausanias reports that according to local legend Cerberus was brought up through a chasm in the earth dedicated to Clymenus (Hades) next to the sanctuary of Chthonia In Greek mythology, the name Chthonia (Ancient Greek: Χθωνία means 'of the earth') may refer to:
*Chthonia, an Athenian princess and the youngest daughter of King Erechtheus and Praxithea, daughter of Phrasimus and Diogeneia. She was sacrific ...
at Hermione, and in Euripides' ''Heracles'', though Euripides does not say that Cerberus was brought out there, he has Cerberus kept for a while in the "grove of Chthonia In Greek mythology, the name Chthonia (Ancient Greek: Χθωνία means 'of the earth') may refer to:
*Chthonia, an Athenian princess and the youngest daughter of King Erechtheus and Praxithea, daughter of Phrasimus and Diogeneia. She was sacrific ...
" at Hermione. Pausanias also mentions that at Mount Laphystion in Boeotia, that there was a statue of Heracles Charops ("with bright eyes"), where the Boeotians said Heracles brought up Cerberus. Other locations which perhaps were also associated with Cerberus being brought out of the underworld include, Hierapolis
Hierapolis (; grc, Ἱεράπολις, lit. "Holy City") was originally a Phrygian cult centre of the Anatolian mother goddess of Cybele and later a Greek city. Its location was centred upon the remarkable and copious hot springs in classica ...
, Thesprotia, and Emeia near Mycenae.
Presented to Eurystheus, returned to Hades
In some accounts, after bringing Cerberus up from the underworld, Heracles paraded the captured Cerberus through Greece. Euphorion has Heracles lead Cerberus through Midea in Argolis, as women and children watch in fear, andDiodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
says of Cerberus, that Heracles "carried him away to the amazement of all and exhibited him to men." Seneca has Juno complain of Heracles "highhandedly parading the black hound through Argive cities" and Heracles greeted by laurel-wreathed crowds, "singing" his praises.
Then, according to Apollodorus, Heracles showed Cerberus to Eurystheus, as commanded, after which he returned Cerberus to the underworld. However, according to Hesychius of Alexandria, Cerberus escaped, presumably returning to the underworld on his own.
Principal sources
 The earliest mentions of Cerberus (c. 8th – 7th century BC) occur in Homer's '' Iliad'' and '' Odyssey'', and
The earliest mentions of Cerberus (c. 8th – 7th century BC) occur in Homer's '' Iliad'' and '' Odyssey'', and Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
's ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' (, , , i.e. "the genealogy or birth of the gods") is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 10 ...
''. Homer does not name or describe Cerberus, but simply refers to Heracles being sent by Eurystheus to fetch the "hound of Hades", with Hermes and Athena as his guides, and, in a possible reference to Cerberus' capture, that Heracles shot Hades with an arrow. According to Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, Cerberus was the offspring of the monsters Echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
and Typhon
Typhon (; grc, Τυφῶν, Typhôn, ), also Typhoeus (; grc, Τυφωεύς, Typhōeús, label=none), Typhaon ( grc, Τυφάων, Typháōn, label=none) or Typhos ( grc, Τυφώς, Typhṓs, label=none), was a monstrous serpentine giant an ...
, was fifty-headed, ate raw flesh, and was the "brazen-voiced hound of Hades", who fawns on those that enter the house of Hades, but eats those who try to leave.
Stesichorus (c. 630 – 555 BC) apparently wrote a poem called ''Cerberus'', of which virtually nothing remains. However the early-sixth-century BC-lost Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
ian cup from Argos
Argos most often refers to:
* Argos, Peloponnese, a city in Argolis, Greece
** Ancient Argos, the ancient city
* Argos (retailer), a catalogue retailer operating in the United Kingdom and Ireland
Argos or ARGOS may also refer to:
Businesses
* ...
, which showed a single head, and snakes growing out from many places on his body, was possibly influenced by Stesichorus' poem. The mid-sixth-century BC cup from Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
gives Cerberus three heads and a snake tail, which eventually becomes the standard representation.
Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
(c. 522 – c. 443 BC) apparently gave Cerberus one hundred heads. Bacchylides (5th century BC) also mentions Heracles bringing Cerberus up from the underworld, with no further details. Sophocles (c. 495 – c. 405 BC), in his '' Women of Trachis'', makes Cerberus three-headed, and in his '' Oedipus at Colonus'', the Chorus asks that Oedipus
Oedipus (, ; grc-gre, Οἰδίπους "swollen foot") was a mythical Greek king of Thebes. A tragic hero in Greek mythology, Oedipus accidentally fulfilled a prophecy that he would end up killing his father and marrying his mother, thereby ...
be allowed to pass the gates of the underworld undisturbed by Cerberus, called here the "untamable Watcher of Hades". Euripides (c. 480 – 406 BC) describes Cerberus as three-headed, and three-bodied, says that Heracles entered the underworld at Tainaron, has Heracles say that Cerberus was not given to him by Persephone, but rather he fought and conquered Cerberus, "for I had been lucky enough to witness the rites of the initiated", an apparent reference to his initiation into the Eleusinian Mysteries, and says that the capture of Cerberus was the last of Heracles' labors. The lost play ''Pirthous'' (attributed to either Euripides or his late contemporary Critias) has Heracles say that he came to the underworld at the command of Eurystheus, who had ordered him to bring back Cerberus alive, not because he wanted to see Cerberus, but only because Eurystheus thought Heracles would not be able to accomplish the task, and that Heracles "overcame the beast" and "received favour from the gods".

Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
(c. 425 – 348 BC) refers to Cerberus' composite nature, citing Cerberus, along with Scylla
In Greek mythology, Scylla), is obsolete. ( ; grc-gre, Σκύλλα, Skúlla, ) is a legendary monster who lives on one side of a narrow channel of water, opposite her counterpart Charybdis. The two sides of the strait are within an arrow's r ...
and the Chimera, as an example from "ancient fables" of a creature composed of many animal forms "grown together in one". Euphorion of Chalcis
Euphorion of Chalcis ( el, Εὐφορίων ὁ Χαλκιδεύς) was a Greek poet and grammarian, born at Chalcis in Euboea about 275 BC.
Euphorion spent much of his life in Athens, where he amassed great wealth. After studying philosophy w ...
(3rd century BC) describes Cerberus as having multiple snake tails, and eyes that flashed, like sparks from a blacksmith's forge, or the volcaninc Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( it, Etna or ; scn, Muncibbeḍḍu or ; la, Aetna; grc, Αἴτνα and ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina a ...
. From Euphorion, also comes the first mention of a story which told that at Heraclea Pontica, where Cerberus was brought out of the underworld, by Heracles, Cerberus "vomited bile" from which the poisonous aconite
Aconite may refer to:
*'' Aconitum'', a plant genus containing the monkshoods
*Aconitine
Aconitine is an alkaloid toxin produced by various plant species belonging to the genus ''Aconitum'' (family Ranunculaceae), known also commonly by the na ...
plant grew up.
According to Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
(1st century BC), the capture of Cerberus was the eleventh of Heracles' labors, the twelfth and last being stealing the Apples of the Hesperides
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides (; , ) are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides () from their reputed father, the Titan Atlas ...
. Diodorus says that Heracles thought it best to first go to Athens to take part in the Eleusinian Mysteries, "Musaeus Musaeus, Musaios ( grc, Μουσαῖος) or Musäus may refer to:
Greek poets
* Musaeus of Athens, legendary polymath, considered by the Greeks to be one of their earliest poets (mentioned by Socrates in Plato's Apology)
* Musaeus of Ephesus, liv ...
, the son of Orpheus, being at that time in charge of the initiatory rites", after which, he entered into the underworld "welcomed like a brother by Persephone", and "receiving the dog Cerberus in chains he carried him away to the amazement of all and exhibited him to men."
In Virgil's '' Aeneid'' (1st century BC), Aeneas and the Sibyl encounter Cerberus in a cave, where he "lay at vast length", filling the cave "from end to end", blocking the entrance to the underworld. Cerberus is described as "triple-throated", with "three fierce mouths", multiple "large backs", and serpents writhing around his neck. The Sibyl throws Cerberus a loaf laced with honey and herbs to induce sleep, enabling Aeneas to enter the underworld, and so apparently for Virgil—contradicting Hesiod—Cerberus guarded the underworld against entrance. Later Virgil describes Cerberus, in his bloody cave, crouching over half-gnawed bones. In his '' Georgics'', Virgil refers to Cerberus, his "triple jaws agape" being tamed by Orpheus' playing his lyre.
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ' ...
(65 – 8 BC) also refers to Cerberus yielding to Orphesus' lyre, here Cerberus has a single dog head, which "like a Fury's is fortified by a hundred snakes", with a "triple-tongued mouth" oozing "fetid breath and gore".
Ovid (43 BC – AD 17/18) has Cerberus' mouth produce venom, and like Euphorion, makes Cerberus the cause of the poisonous plant aconite. According to Ovid, Heracles dragged Cerberus from the underworld, emerging from a cave "where 'tis fabled, the plant grew / on soil infected by Cerberian teeth", and dazzled by the daylight, Cerberus spewed out a "poison-foam", which made the aconite plants growing there poisonous.
 Seneca, in his tragedy ''Hercules Furens'' gives a detailed description of Cerberus and his capture.
Seneca's Cerberus has three heads, a mane of snakes, and a snake tail, with his three heads being covered in gore, and licked by the many snakes which surround them, and with hearing so acute that he can hear "even ghosts". Seneca has Heracles use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to beat Cerberus into submission, after which Hades and Persephone, quailing on their thrones, let Heracles lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. But upon leaving the underworld, at his first sight of daylight, a frightened Cerberus struggles furiously, and Heracles, with the help of Theseus (who had been held captive by Hades, but released, at Heracles' request) drag Cerberus into the light. Seneca, like Diodorus, has Heracles parade the captured Cerberus through Greece.
Apollodorus' Cerberus has three dog-heads, a serpent for a tail, and the heads of many snakes on his back. According to Apollodorus, Heracles' twelfth and final labor was to bring back Cerberus from Hades. Heracles first went to Eumolpus to be initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries. Upon his entering the underworld, all the dead flee Heracles except for Meleager and the Gorgon Medusa. Heracles drew his sword against Medusa, but Hermes told Heracles that the dead are mere "empty phantoms". Heracles asked Hades (here called Pluto) for Cerberus, and Hades said that Heracles could take Cerberus provided he was able to subdue him without using weapons. Heracles found Cerberus at the gates of Acheron, and with his arms around Cerberus, though being bitten by Cerberus' serpent tail, Heracles squeezed until Cerberus submitted. Heracles carried Cerberus away, showed him to Eurystheus, then returned Cerberus to the underworld.
In an apparently unique version of the story, related by the sixth-century AD
Seneca, in his tragedy ''Hercules Furens'' gives a detailed description of Cerberus and his capture.
Seneca's Cerberus has three heads, a mane of snakes, and a snake tail, with his three heads being covered in gore, and licked by the many snakes which surround them, and with hearing so acute that he can hear "even ghosts". Seneca has Heracles use his lion-skin as shield, and his wooden club, to beat Cerberus into submission, after which Hades and Persephone, quailing on their thrones, let Heracles lead a chained and submissive Cerberus away. But upon leaving the underworld, at his first sight of daylight, a frightened Cerberus struggles furiously, and Heracles, with the help of Theseus (who had been held captive by Hades, but released, at Heracles' request) drag Cerberus into the light. Seneca, like Diodorus, has Heracles parade the captured Cerberus through Greece.
Apollodorus' Cerberus has three dog-heads, a serpent for a tail, and the heads of many snakes on his back. According to Apollodorus, Heracles' twelfth and final labor was to bring back Cerberus from Hades. Heracles first went to Eumolpus to be initiated into the Eleusinian Mysteries. Upon his entering the underworld, all the dead flee Heracles except for Meleager and the Gorgon Medusa. Heracles drew his sword against Medusa, but Hermes told Heracles that the dead are mere "empty phantoms". Heracles asked Hades (here called Pluto) for Cerberus, and Hades said that Heracles could take Cerberus provided he was able to subdue him without using weapons. Heracles found Cerberus at the gates of Acheron, and with his arms around Cerberus, though being bitten by Cerberus' serpent tail, Heracles squeezed until Cerberus submitted. Heracles carried Cerberus away, showed him to Eurystheus, then returned Cerberus to the underworld.
In an apparently unique version of the story, related by the sixth-century AD Pseudo-Nonnus Pseudo-Nonnus, also called Nonnus Abbas (i.e. "Nonnus the Abbot"), was a 6th-century commentator on Gregory of Nazianzus. His ''Commentaries'' consist of scholia explaining the meaning of Gregory's many allusions to Greek mythology. It was written i ...
, Heracles descended into Hades to abduct Persephone, and killed Cerberus on his way back up.
Iconography
Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part o ...
ian cup (c. 590–580 BC) from Argos (now lost), shows a naked Heracles, with quiver on his back and bow in his right hand, striding left, accompanied by Hermes. Heracles threatens Hades with a stone, who flees left, while a goddess, perhaps Persephone or possibly Athena, standing in front of Hades' throne, prevents the attack. Cerberus, with a single canine head and snakes rising from his head and body, flees right. On the far right a column indicates the entrance to Hades' palace. Many of the elements of this scene—Hermes, Athena, Hades, Persephone, and a column or portico—are common occurrences in later works. The other earliest depiction, a relief ''pithos
Pithos (, grc-gre, πίθος, plural: ' ) is the Greek name of a large storage container. The term in English is applied to such containers used among the civilizations that bordered the Mediterranean Sea in the Neolithic, the Bronze Age and ...
'' fragment from Crete (c. 590–570 BC), is thought to show a single lion-headed Cerberus with a snake (open-mouthed) over his back being led to the right.
A mid-sixth-century BC Laconia
Laconia or Lakonia ( el, Λακωνία, , ) is a historical and administrative region of Greece located on the southeastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. Its administrative capital is Sparta. The word ''laconic''—to speak in a blunt, c ...
n cup by the Hunt Painter
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products ( fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, ...
adds several new features to the scene which also become common in later works: three heads, a snake tail, Cerberus' chain and Heracles' club. Here Cerberus has three canine heads, is covered by a shaggy coat of snakes, and has a tail which ends in a snake head. He is being held on a chain leash by Heracles who holds his club raised over head.
In Greek art, the vast majority of depictions of Heracles and Cerberus occur on Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a '' loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the ...
vases. Although the lost Corinthian cup shows Cerberus with a single dog head, and the relief ''pithos'' fragment (c. 590–570 BC) apparently shows a single lion-headed Cerberus, in Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a '' loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the ...
vase painting Cerberus usually has two dog heads. In other art, as in the Laconian cup, Cerberus is usually three-headed. Occasionally in Roman art Cerberus is shown with a large central lion head and two smaller dog heads on either side.
 As in the Corinthian and Laconian cups (and possibly the relief ''pithos'' fragment), Cerberus is often depicted as part snake. In Attic vase painting, Cerberus is usually shown with a snake for a tail or a tail which ends in the head of a snake. Snakes are also often shown rising from various parts of his body including snout, head, neck, back, ankles, and paws.
Two Attic amphoras from Vulci, one (c. 530–515 BC) by the
As in the Corinthian and Laconian cups (and possibly the relief ''pithos'' fragment), Cerberus is often depicted as part snake. In Attic vase painting, Cerberus is usually shown with a snake for a tail or a tail which ends in the head of a snake. Snakes are also often shown rising from various parts of his body including snout, head, neck, back, ankles, and paws.
Two Attic amphoras from Vulci, one (c. 530–515 BC) by the Bucci Painter Bucci is an Italian surname. Notable people with the surname include:
*Alberto Bucci (1948–2019), Italian professional basketball coach
*Andrés Bucci, Chilean electronic music producer and DJ
*Andrew Bucci (1922–2014), American artist
*Annalis ...
(Munich 1493), the other (c. 525–510 BC) by the Andokides painter
Andokides was an ancient Athenian vase painter, active from approximately 530 to 515 B.C. His work is unsigned and his true name unknown. He was identified as a unique artistic personality through stylistic traits found in common among several pai ...
(Louvre F204), in addition to the usual two heads and snake tail, show Cerberus with a mane down his necks and back, another typical Cerberian feature of Attic vase painting. Andokides' amphora also has a small snake curling up from each of Cerberus' two heads.
Besides this lion-like mane and the occasional lion-head mentioned above, Cerberus was sometimes shown with other leonine features. A pitcher (c. 530–500) shows Cerberus with mane and claws, while a first-century BC sardonyx cameo shows Cerberus with leonine body and paws. In addition, a limestone relief fragment from Taranto (c. 320–300 BC) shows Cerberus with three lion-like heads.
During the second quarter of the 5th century BC the capture of Cerberus disappears from Attic vase painting. After the early third century BC, the subject becomes rare everywhere until the Roman period. In Roman art the capture of Cerberus is usually shown together with other labors. Heracles and Cerberus are usually alone, with Heracles leading Cerberus.
Etymology
 The etymology of Cerberus' name is uncertain. Ogden refers to attempts to establish an Indo-European etymology as "not yet successful". It has been claimed to be related to the Sanskrit word सर्वरा ''sarvarā'', used as an epithet of one of the dogs of Yama, from a Proto-Indo-European word *''k̑érberos'', meaning "spotted". Lincoln (1991), among others, critiques this etymology. This etymology was also rejected by Manfred Mayrhofer, who proposed an Austro-Asiatic origin for the word, and Beekes. Lincoln notes a similarity between Cerberus and the Norse mythological dog Garmr, relating both names to a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ger-'' "to growl" (perhaps with the suffixes ''-*m/*b'' and ''-*r''). However, as Ogden observes, this analysis actually requires ''Kerberos'' and ''Garmr'' to be derived from two ''different'' Indo-European roots (*''ker-'' and *''gher-'' respectively), and so does not actually establish a relationship between the two names.
Though probably not Greek, Greek etymologies for Cerberus have been offered. An etymology given by
The etymology of Cerberus' name is uncertain. Ogden refers to attempts to establish an Indo-European etymology as "not yet successful". It has been claimed to be related to the Sanskrit word सर्वरा ''sarvarā'', used as an epithet of one of the dogs of Yama, from a Proto-Indo-European word *''k̑érberos'', meaning "spotted". Lincoln (1991), among others, critiques this etymology. This etymology was also rejected by Manfred Mayrhofer, who proposed an Austro-Asiatic origin for the word, and Beekes. Lincoln notes a similarity between Cerberus and the Norse mythological dog Garmr, relating both names to a Proto-Indo-European root ''*ger-'' "to growl" (perhaps with the suffixes ''-*m/*b'' and ''-*r''). However, as Ogden observes, this analysis actually requires ''Kerberos'' and ''Garmr'' to be derived from two ''different'' Indo-European roots (*''ker-'' and *''gher-'' respectively), and so does not actually establish a relationship between the two names.
Though probably not Greek, Greek etymologies for Cerberus have been offered. An etymology given by Servius Servius is the name of:
* Servius (praenomen), the personal name
* Maurus Servius Honoratus, a late fourth-century and early fifth-century grammarian
* Servius Tullius, the Roman king
* Servius Sulpicius Rufus, the 1st century BC Roman jurist
See ...
(the late-fourth-century commentator on Virgil)—but rejected by Ogden—derives Cerberus from the Greek word ''creoboros'' meaning "flesh-devouring". Another suggested etymology derives Cerberus from "Ker berethrou", meaning "evil of the pit".
Cerberus rationalized
At least as early as the 6th century BC, some ancient writers attempted to explain away various fantastical features of Greek mythology; included in these are various rationalized accounts of the Cerberus story. The earliest such account (late 6th century BC) is that ofHecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; el, Ἑκαταῖος ὁ Μιλήσιος; c. 550 BC – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Per ...
. In his account Cerberus was not a dog at all, but rather simply a large venomous snake, which lived on Tainaron
Cape Matapan ( el, Κάβο Ματαπάς, Maniot dialect: Ματαπά), also named as Cape Tainaron or Taenarum ( el, Ακρωτήριον Ταίναρον), or Cape Tenaro, is situated at the end of the Mani Peninsula, Greece. Cape Matapan ...
. The serpent was called the "hound of Hades" only because anyone bitten by it died immediately, and it was this snake that Heracles brought to Eurystheus. The geographer Pausanias (who preserves for us Hecataeus' version of the story) points out that, since Homer does not describe Cerberus, Hecataeus' account does not necessarily conflict with Homer, since Homer's "Hound of Hades" may not in fact refer to an actual dog.
Other rationalized accounts make Cerberus out to be a normal dog. According to Palaephatus (4th century BC) Cerberus was one of the two dogs who guarded the cattle of Geryon
In Greek mythology, Geryon ( or ;"Geryon"
''

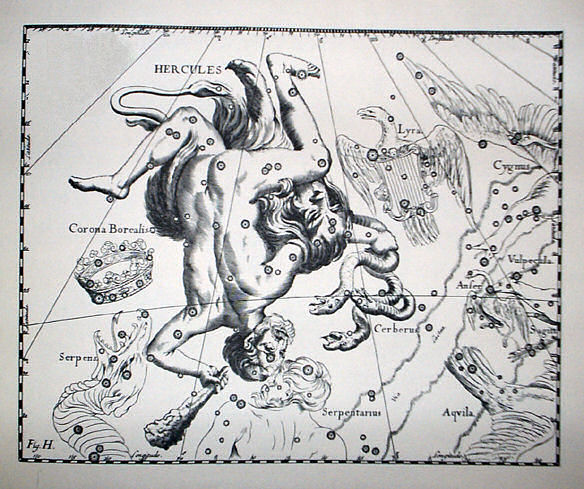 In the constellation Cerberus introduced by Johannes Hevelius in 1687, Cerberus is drawn as a three-headed snake, held in Hercules' hand (previously these stars had been depicted as a branch of the tree on which grew the
In the constellation Cerberus introduced by Johannes Hevelius in 1687, Cerberus is drawn as a three-headed snake, held in Hercules' hand (previously these stars had been depicted as a branch of the tree on which grew the
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Apuleius, '' Metamorphoses (The Golden Ass)'', Volume I: Books 1–6. Edited and translated by J. Arthur Hanson.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Aristophanes, ''Frogs'', Matthew Dillon, Ed., Perseus Digital Library, Tufts University, 1995
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Bacchylides, ''Odes'', translated by Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1991
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Bloomfield, Maurice, ''Cerberus, the Dog of Hades: The History of an Idea'', Open Court publishing Company, 1905
Online version at Internet Archive
* Bowra, C. M., ''Greek Lyric Poetry: From Alcman to Simonides'', Clarendon Press, 2001. . *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Fowler, R. L. (2000), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 1: Text and Introduction'', Oxford University Press, 2000. . * Fowler, R. L. (2013), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 2: Commentary'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Freeman, Kathleen, ''Ancilla to the Pre-Socratic Philosophers: A Complete Translation of the Fragments in Diels, Fragmente Der Vorsokratiker'', Harvard University Press, 1983. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
* Harding, Phillip, ''The Story of Athens: The Fragments of the Local Chronicles of Attika'', Routledge, 2007. . * Hawes, Greta, ''Rationalizing Myth in Antiquity'', OUP Oxford, 2014. . *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer, ''The Iliad with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PhD in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer; ''The Odyssey with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PH.D. in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1919
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hopman, Marianne Govers, ''Scylla: Myth, Metaphor, Paradox'', Cambridge University Press, 2013. . *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hyginus, Gaius Julius
''The Myths of Hyginus''
Edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960. * Kirk, G. S. 1990 ''The Iliad: A Commentary: Volume 2, Books 5–8'', . * Lansing, Richard (editor), ''The Dante Encyclopedia'', Routledge, 2010. . * Lightfoot, J. L. ''Hellenistic Collection: Philitas. Alexander of Aetolia. Hermesianax. Euphorion. Parthenius''. Edited and translated by J. L. Lightfoot.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Markantonatos, Andreas, ''Tragic Narrative: A Narratological Study of Sophocles' Oedipus at Colonus'', Walter de Gruyter, 2002. . * Nimmo Smith, Jennifer, ''A Christian's Guide to Greek Culture: The Pseudo-nonnus Commentaries on Sermons 4, 5, 39 and 43''. Liverpool University Press, 2001. . * Ogden, Daniel (2013a), ''Drakōn: Dragon Myth and Serpent Cult in the Greek and Roman Worlds'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Ogden, Daniel (2013b), ''Dragons, Serpents, and Slayers in the Classical and early Christian Worlds: A sourcebook'', Oxford University Press. . * Ovid. ''Heroides. Amores''. Translated by Grant Showerman. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, '' Metamorphoses'', Brookes More. Boston. Cornhill Publishing Co. 1922
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Papadopoulou, Thalia, ''Heracles and Euripidean Tragedy'', Cambridge University Press, 2005. . * Pausanias, ''Pausanias Description of Greece with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Pepin, Ronald E., ''The Vatican Mythographers'', Fordham University Press, 2008. *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Pipili, Maria, ''Laconian Iconography of the Sixth Century B.C.'', Oxford University, 1987. *
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Plutarch. ''Lives, Volume I: Theseus and Romulus. Lycurgus and Numa. Solon and Publicola''. Translated by Bernadotte Perrin.
''Theseus'' at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Internet Archive
* Room, Adrian, ''Who's Who in Classical Mythology'', Gramercy Books, 2003. . * Schefold, Karl (1966), ''Myth and Legend in Early Greek Art'', London, Thames and Hudson. * Schefold, Karl (1992), ''Gods and Heroes in Late Archaic Greek Art'', assisted by Luca Giuliani, Cambridge University Press, 1992. . * Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume I: Hercules. Trojan Women. Phoenician Women. Medea. Phaedra''. Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume II: Oedipus. Agamemnon. Thyestes. Hercules on Oeta. Octavia''. Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Smallwood, Valerie, "M. Herakles and Kerberos (Labour XI)" in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' V.1 Artemis Verlag, Zürich and Munich, 1990. . pp. 85–100. * Sophocles, '' Women of Trachis'', Translated by Robert Torrance. Houghton Mifflin. 1966
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Statius, ''Statius with an English Translation by J. H. Mozley'', Volume I, ''Silvae'', ''Thebaid'', Books I–IV,
Internet Archive
* Statius, ''Statius with an English Translation by J. H. Mozley'', Volume II, ''Thebaid'', Books V–XII, ''Achilleid'',
Internet Archive
* Stern, Jacob, ''Palaephatus Πεπὶ Ὰπίστων, On Unbelievable Tales'', Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, 1996. . * Trypanis, C. A., Gelzer, Thomas; Whitman, Cedric, ''CALLIMACHUS, MUSAEUS, Aetia, Iambi, Hecale and Other Fragments. Hero and Leander'', Harvard University Press, 1975. . * Tzetzes, ''
Internet Archive
. * Virgil, '' Aeneid'', Theodore C. Williams. trans. Boston. Houghton Mifflin Co. 1910
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Virgil, ''Bucolics, Aeneid, and Georgics of Vergil''. J. B. Greenough. Boston. Ginn & Co. 1900
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* West, David, ''Horace, Odes 3'', Oxford University Press, 2002. . * West, M. L. (2003), ''Greek Epic Fragments: From the Seventh to the Fifth Centuries BC''. Edited and translated by Martin L. West.
Online version at Harvard University Press
* Whitbread, Leslie George
''Fulgentius the Mythographer''
Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1971. * Woodford, Susan, Spier, Jeffrey, "Kerberos", in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' VI.1 Artemis Verlag, Zürich and Munich, 1992. . pp. 24–32. * Xenophon, '' Anabasis'' in ''Xenophon in Seven Volumes'', 3. Carleton L. Brownson. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; William Heinemann, Ltd., London. 1922
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
''
Orthrus
In Greek mythology, Orthrus ( grc-gre, Ὄρθρος, ''Orthros'') or Orthus ( grc-gre, Ὄρθος, ''Orthos'') was, according to the mythographer Apollodorus, a two-headed dog who guarded Geryon's cattle and was killed by Heracles. He was the ...
. Geryon lived in a city named Tricranium (in Greek ''Tricarenia'', "Three-Heads"), from which name both Cerberus and Geryon came to be called "three-headed". Heracles killed Orthus, and drove away Geryon's cattle, with Cerberus following along behind. Molossus, a Mycenaen, offered to buy Cerberus from Eurystheus (presumably having received the dog, along with the cattle, from Heracles). But when Eurystheus refused, Molossus stole the dog and penned him up in a cave in Tainaron. Eurystheus commanded Heracles to find Cerberus and bring him back. After searching the entire Peloponnesus, Heracles found where it was said Cerberus was being held, went down into the cave, and brought up Cerberus, after which it was said: "Heracles descended through the cave into Hades and brought up Cerberus."
In the rationalized account of Philochorus, in which Heracles rescues Theseus, Perithous is eaten by Cerberus. In this version of the story, Aidoneus (i.e., "Hades") is the mortal king of the Molossians, with a wife named Persephone, a daughter named Kore (another name for the goddess Persephone) and a large mortal dog named Cerberus, with whom all suitors of his daughter were required to fight. After having stolen Helen, to be Theseus' wife, Theseus and Perithous, attempt to abduct Kore, for Perithous, but Aidoneus catches the two heroes, imprisons Theseus, and feeds Perithous to Cerberus. Later, while a guest of Aidoneus, Heracles asks Aidoneus to release Theseus, as a favor, which Aidoneus grants.
A 2nd-century AD Greek known as Heraclitus the paradoxographer Heraclitus Paradoxographus ( el, Ἡράκλειτος) is the author of the lesser-known of two works known as ''Peri Apiston'' (''On Unbelievable Tales''). Palaephatus was the author of a better-known work of paradoxography with the same title, me ...
(not to be confused with the 5th-century BC Greek philosopher Heraclitus)—claimed that Cerberus had two pups that were never away from their father, which made Cerberus appear to be three-headed.
Cerberus allegorized

Servius Servius is the name of:
* Servius (praenomen), the personal name
* Maurus Servius Honoratus, a late fourth-century and early fifth-century grammarian
* Servius Tullius, the Roman king
* Servius Sulpicius Rufus, the 1st century BC Roman jurist
See ...
, a medieval commentator on Virgil's '' Aeneid'', derived Cerberus' name from the Greek word ''creoboros'' meaning "flesh-devouring" (see above), and held that Cerberus symbolized the corpse-consuming earth, with Heracles' triumph over Cerberus representing his victory over earthly desires. Later, the mythographer Fulgentius Fulgentius is a Latin male given name which means "bright, brilliant". It may refer to:
*Fabius Planciades Fulgentius (5th–6th century), Latin grammarian
*Saint Fulgentius of Ruspe (5th–6th century), bishop of Ruspe, North Africa, possib ...
, allegorizes Cerberus' three heads as representing the three origins of human strife: "nature, cause, and accident", and (drawing on the same flesh-devouring etymology as Servius) as symbolizing "the three ages—infancy, youth, old age, at which death enters the world." The Byzantine historian and bishop Eusebius wrote that Cerberus was represented with three heads, because the positions of the sun above the earth are three—rising, midday, and setting.
The later Vatican Mythographers repeat and expand upon the traditions of Servius and Fulgentius. All three Vatican Mythographers repeat Servius' derivation of Cerberus' name from ''creoboros''. The Second Vatican Mythographer repeats (nearly word for word) what Fulgentius had to say about Cerberus, while the Third Vatican Mythographer, in another very similar passage to Fugentius', says (more specifically than Fugentius), that for "the philosophers" Cerberus represented hatred, his three heads symbolizing the three kinds of human hatred: natural, causal, and casual (i.e. accidental).
The Second and Third Vatican Mythographers, note that the three brothers Zeus, Poseidon and Hades each have tripartite insignia, associating Hades' three-headed Cerberus, with Zeus' three-forked thunderbolt, and Poseidon's three-pronged trident, while the Third Vatican Mythographer adds that "some philosophers think of Cerberus as the tripartite earth: Asia, Africa, and Europe. This earth, swallowing up bodies, sends souls to Tartarus."
Virgil described Cerberus as "ravenous" (''fame rabida''), and a rapacious Cerberus became proverbial. Thus Cerberus came to symbolize avarice, and so, for example, in Dante's '' Inferno,'' Cerberus is placed in the Third Circle of Hell, guarding over the gluttons, where he "rends the spirits, flays and quarters them," and Dante (perhaps echoing Servius' association of Cerbeus with earth) has his guide Virgil take up handfuls of earth and throw them into Cerberus' "rapacious gullets."
Constellation
 In the constellation Cerberus introduced by Johannes Hevelius in 1687, Cerberus is drawn as a three-headed snake, held in Hercules' hand (previously these stars had been depicted as a branch of the tree on which grew the
In the constellation Cerberus introduced by Johannes Hevelius in 1687, Cerberus is drawn as a three-headed snake, held in Hercules' hand (previously these stars had been depicted as a branch of the tree on which grew the Apples of the Hesperides
In Greek mythology, the Hesperides (; , ) are the nymphs of evening and golden light of sunsets, who were the "Daughters of the Evening" or "Nymphs of the West". They were also called the Atlantides () from their reputed father, the Titan Atlas ...
).
Snake genus
In 1829 French naturalistGeorges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, Baron Cuvier (; 23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier, was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuvier ...
gave the name '' Cerberus'' to a genus of Asian snakes, which are commonly called "dog-faced water snakes" in English.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . ("Cerberus", p. 50).
See also
* List of Greek mythological creatures * Dormarch – part of the Cŵn Annwn * Hellhound * Ammit, a chthonic creature in Egyptian mythology *Cadejo
The cadejo () is a supernatural Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit that appears as a dog-shaped creature with blue eyes when it's calm and red eyes when it's attacking. It roams isolated roads at night, according to Central American folklore of ...
Notes
References
*Apollodorus
Apollodorus (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀπολλόδωρος ''Apollodoros'') was a popular name in ancient Greece. It is the masculine gender of a noun compounded from Apollo, the deity, and doron, "gift"; that is, "Gift of Apollo." It may refer to: ...
, ''Apollodorus, The Library, with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Apuleius, '' Metamorphoses (The Golden Ass)'', Volume I: Books 1–6. Edited and translated by J. Arthur Hanson.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 44. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1996Online version at Harvard University Press
* Aristophanes, ''Frogs'', Matthew Dillon, Ed., Perseus Digital Library, Tufts University, 1995
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Bacchylides, ''Odes'', translated by Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1991
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Bloomfield, Maurice, ''Cerberus, the Dog of Hades: The History of an Idea'', Open Court publishing Company, 1905
Online version at Internet Archive
* Bowra, C. M., ''Greek Lyric Poetry: From Alcman to Simonides'', Clarendon Press, 2001. . *
Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
, ''Diodorus Siculus: The Library of History''. Translated by C. H. Oldfather. Twelve volumes. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press; London: William Heinemann, Ltd. 1989.
* Euripides. ''Fragments: Oedipus-Chrysippus. Other Fragments''. Edited and translated by Christopher Collard, Martin Cropp. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 506. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2009.
* Euripides, '' Heracles'', translated by E. P. Coleridge in ''The Complete Greek Drama'', edited by Whitney J. Oates and Eugene O'Neill, Jr. Volume 1. New York. Random House. 1938Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Fowler, R. L. (2000), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 1: Text and Introduction'', Oxford University Press, 2000. . * Fowler, R. L. (2013), ''Early Greek Mythography: Volume 2: Commentary'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Freeman, Kathleen, ''Ancilla to the Pre-Socratic Philosophers: A Complete Translation of the Fragments in Diels, Fragmente Der Vorsokratiker'', Harvard University Press, 1983. . * Gantz, Timothy, ''Early Greek Myth: A Guide to Literary and Artistic Sources'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1996, Two volumes: (Vol. 1), (Vol. 2). * Hard, Robin, ''The Routledge Handbook of Greek Mythology: Based on H.J. Rose's "Handbook of Greek Mythology"'', Psychology Press, 2004,
Google Books
* Harding, Phillip, ''The Story of Athens: The Fragments of the Local Chronicles of Attika'', Routledge, 2007. . * Hawes, Greta, ''Rationalizing Myth in Antiquity'', OUP Oxford, 2014. . *
Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, ''Theogony
The ''Theogony'' (, , , i.e. "the genealogy or birth of the gods") is a poem by Hesiod (8th–7th century BC) describing the origins and genealogies of the Greek gods, composed . It is written in the Epic dialect of Ancient Greek and contains 10 ...
'', in ''The Homeric Hymns and Homerica with an English Translation by Hugh G. Evelyn-White'', Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1914Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer, ''The Iliad with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PhD in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1924
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Homer; ''The Odyssey with an English Translation by A.T. Murray, PH.D. in two volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann, Ltd. 1919
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hopman, Marianne Govers, ''Scylla: Myth, Metaphor, Paradox'', Cambridge University Press, 2013. . *
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus (; 8 December 65 – 27 November 8 BC), known in the English-speaking world as Horace (), was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus (also known as Octavian). The rhetorician Quintilian regarded his ' ...
, ''The Odes and Carmen Saeculare of Horace''. John Conington. trans. London. George Bell and Sons. 1882Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Hyginus, Gaius Julius
''The Myths of Hyginus''
Edited and translated by Mary A. Grant, Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1960. * Kirk, G. S. 1990 ''The Iliad: A Commentary: Volume 2, Books 5–8'', . * Lansing, Richard (editor), ''The Dante Encyclopedia'', Routledge, 2010. . * Lightfoot, J. L. ''Hellenistic Collection: Philitas. Alexander of Aetolia. Hermesianax. Euphorion. Parthenius''. Edited and translated by J. L. Lightfoot.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 508. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2010. Online version at Harvard University Press
* *
Lucan
Marcus Annaeus Lucanus (3 November 39 AD – 30 April 65 AD), better known in English as Lucan (), was a Roman poet, born in Corduba (modern-day Córdoba), in Hispania Baetica. He is regarded as one of the outstanding figures of the Imperial ...
, ''Pharsalia'', Sir Edward Ridley. London. Longmans, Green, and Co. 1905Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Markantonatos, Andreas, ''Tragic Narrative: A Narratological Study of Sophocles' Oedipus at Colonus'', Walter de Gruyter, 2002. . * Nimmo Smith, Jennifer, ''A Christian's Guide to Greek Culture: The Pseudo-nonnus Commentaries on Sermons 4, 5, 39 and 43''. Liverpool University Press, 2001. . * Ogden, Daniel (2013a), ''Drakōn: Dragon Myth and Serpent Cult in the Greek and Roman Worlds'', Oxford University Press, 2013. . * Ogden, Daniel (2013b), ''Dragons, Serpents, and Slayers in the Classical and early Christian Worlds: A sourcebook'', Oxford University Press. . * Ovid. ''Heroides. Amores''. Translated by Grant Showerman. Revised by G. P. Goold.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
41. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1977. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Ovid, '' Metamorphoses'', Brookes More. Boston. Cornhill Publishing Co. 1922
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Papadopoulou, Thalia, ''Heracles and Euripidean Tragedy'', Cambridge University Press, 2005. . * Pausanias, ''Pausanias Description of Greece with an English Translation by W.H.S. Jones, Litt.D., and H.A. Ormerod, M.A., in 4 Volumes''. Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1918
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Pepin, Ronald E., ''The Vatican Mythographers'', Fordham University Press, 2008. *
Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar is ...
, ''Odes'', Diane Arnson Svarlien. 1990Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Pipili, Maria, ''Laconian Iconography of the Sixth Century B.C.'', Oxford University, 1987. *
Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, ''Republic Books 6–10'', Translated by Paul Shorey, Cambridge, Massachusetts, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1969Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Plutarch. ''Lives, Volume I: Theseus and Romulus. Lycurgus and Numa. Solon and Publicola''. Translated by Bernadotte Perrin.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 46. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1914. ''Theseus'' at the Perseus Digital Library
*
Propertius
Sextus Propertius was a Latin elegiac poet of the Augustan age. He was born around 50–45 BC in Assisium and died shortly after 15 BC.
Propertius' surviving work comprises four books of ''Elegies'' ('). He was a friend of the poets Gallus a ...
''Elegies'' Edited and translated by G. P. Goold. Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
18. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 1990.Online version at Harvard University Press
*
Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; el, Κόϊντος Σμυρναῖος, ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose ''Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus Smy ...
, ''Quintus Smyrnaeus: The Fall of Troy'', Translator: A.S. Way; Harvard University Press, Cambridge MA, 1913Internet Archive
* Room, Adrian, ''Who's Who in Classical Mythology'', Gramercy Books, 2003. . * Schefold, Karl (1966), ''Myth and Legend in Early Greek Art'', London, Thames and Hudson. * Schefold, Karl (1992), ''Gods and Heroes in Late Archaic Greek Art'', assisted by Luca Giuliani, Cambridge University Press, 1992. . * Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume I: Hercules. Trojan Women. Phoenician Women. Medea. Phaedra''. Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 62. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2002. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Seneca, ''Tragedies, Volume II: Oedipus. Agamemnon. Thyestes. Hercules on Oeta. Octavia''. Edited and translated by John G. Fitch.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 78. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2004. Online version at Harvard University Press
* Smallwood, Valerie, "M. Herakles and Kerberos (Labour XI)" in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' V.1 Artemis Verlag, Zürich and Munich, 1990. . pp. 85–100. * Sophocles, '' Women of Trachis'', Translated by Robert Torrance. Houghton Mifflin. 1966
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Statius, ''Statius with an English Translation by J. H. Mozley'', Volume I, ''Silvae'', ''Thebaid'', Books I–IV,
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 206, London: William Heinemann, Ltd., New York: G. P. Putnamm's Sons, 1928. Internet Archive
* Statius, ''Statius with an English Translation by J. H. Mozley'', Volume II, ''Thebaid'', Books V–XII, ''Achilleid'',
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 207, London: William Heinemann, Ltd., New York: G. P. Putnamm's Sons, 1928. Internet Archive
* Stern, Jacob, ''Palaephatus Πεπὶ Ὰπίστων, On Unbelievable Tales'', Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, 1996. . * Trypanis, C. A., Gelzer, Thomas; Whitman, Cedric, ''CALLIMACHUS, MUSAEUS, Aetia, Iambi, Hecale and Other Fragments. Hero and Leander'', Harvard University Press, 1975. . * Tzetzes, ''
Chiliades
John Tzetzes ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης Τζέτζης, Iōánnēs Tzétzēs; c. 1110, Constantinople – 1180, Constantinople) was a Byzantine poet and grammarian who is known to have lived at Constantinople in the 12th century.
He was able to p ...
'', editor Gottlieb Kiessling, F.C.G. Vogel, 1826. (English translation, Books II–IV, by Gary BerkowitzInternet Archive
. * Virgil, '' Aeneid'', Theodore C. Williams. trans. Boston. Houghton Mifflin Co. 1910
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* Virgil, ''Bucolics, Aeneid, and Georgics of Vergil''. J. B. Greenough. Boston. Ginn & Co. 1900
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
* West, David, ''Horace, Odes 3'', Oxford University Press, 2002. . * West, M. L. (2003), ''Greek Epic Fragments: From the Seventh to the Fifth Centuries BC''. Edited and translated by Martin L. West.
Loeb Classical Library
The Loeb Classical Library (LCL; named after James Loeb; , ) is a series of books originally published by Heinemann in London, but is currently published by Harvard University Press. The library contains important works of ancient Greek and L ...
No. 497. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2003Online version at Harvard University Press
* Whitbread, Leslie George
''Fulgentius the Mythographer''
Columbus: Ohio State University Press, 1971. * Woodford, Susan, Spier, Jeffrey, "Kerberos", in '' Lexicon Iconographicum Mythologiae Classicae (LIMC)'' VI.1 Artemis Verlag, Zürich and Munich, 1992. . pp. 24–32. * Xenophon, '' Anabasis'' in ''Xenophon in Seven Volumes'', 3. Carleton L. Brownson. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts; William Heinemann, Ltd., London. 1922
Online version at the Perseus Digital Library
External links
* {{Authority control Characters in Book VI of the Aeneid Greek underworld Mythological dogs Mythological hybrids Symbols of Hades Labours of Hercules Mythological canines Deeds of Hermes Monsters in Greek mythology Mythical many-headed creatures Greek legendary creatures Dogs in religion