keratometry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
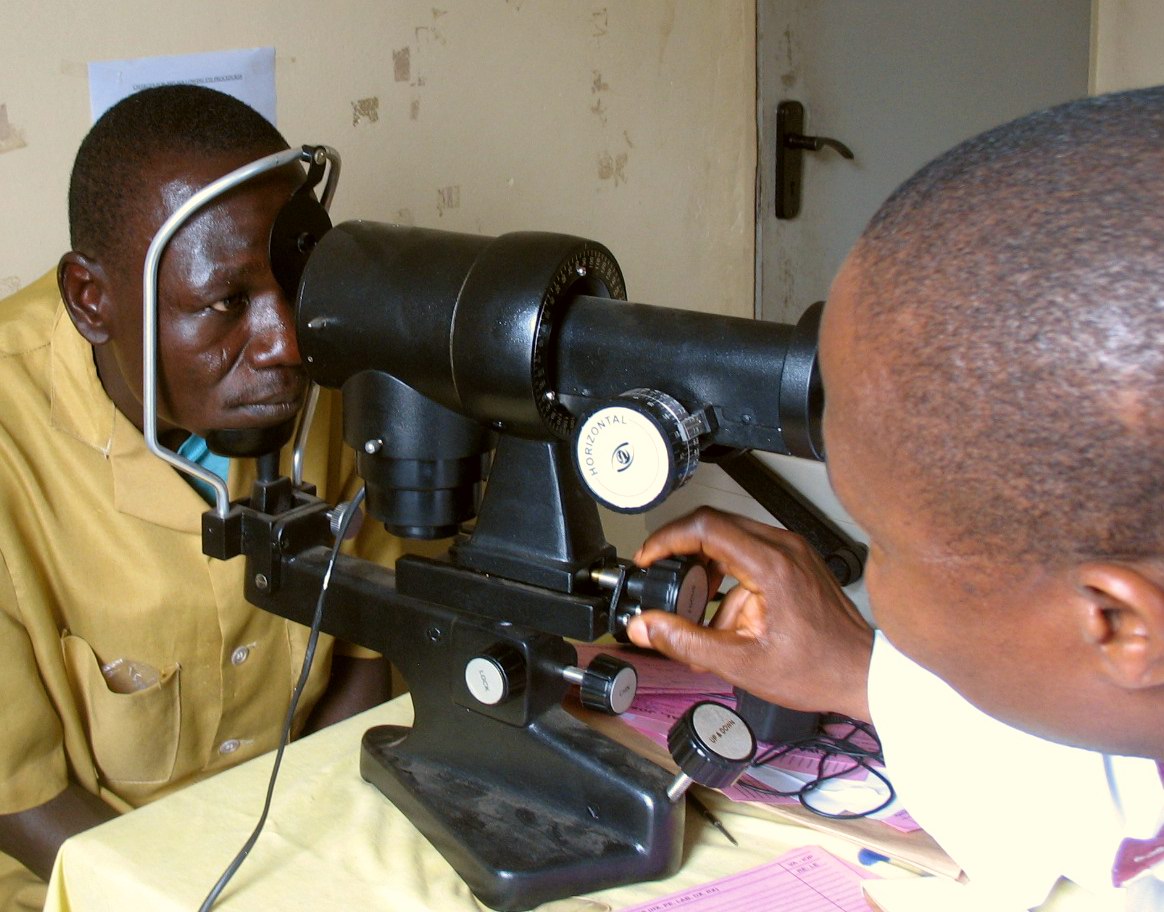
 A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the
A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the

 A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the
A keratometer, also known as an ophthalmometer, is a diagnostic instrument for measuring the curvature of the anterior surface of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
, particularly for assessing the extent and axis of astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at n ...
. It was invented by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
physiologist Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Associatio ...
in 1851, although an earlier model was developed in 1796 by Jesse Ramsden
Jesse Ramsden FRS FRSE (6 October 1735 – 5 November 1800) was a British mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker. His reputation was built on the engraving and design of dividing engines which allowed high accuracy measure ...
and Everard Home
Sir Everard Home, 1st Baronet, FRS (6 May 1756, in Kingston upon Hull – 31 August 1832, in London) was a British surgeon.
Home was born in Kingston-upon-Hull and educated at Westminster School. He gained a scholarship to Trinity College, Ca ...
.
A keratometer uses the relationship between object size (O), image size (I), the distance between the reflective surface and the object (d), and the radius of the reflective surface (R). If three of these variables are known (or fixed), the fourth can be calculated using the formula
:
There are two distinct variants of determining R; Javal-Schiotz type keratometers have a fixed image size and are typically 'two position', whereas Bausch and Lomb type keratometers have a fixed object size and are usually 'one position'.
Javal-Schiotz Principles
The Javal-Schiotz keratometer is a two position instrument which uses a fixed image and doubling size and adjustable object size to determine the radius of curvature of the reflective surface. It uses two self illuminated mires (the object), one a red square, the other a green staircase design, which are held on a circumferential track in order to maintain a fixed distance from the eye. In order to get repeatable, accurate measurements, it is important that the instrument stays focused. It uses the Scheiner principle, common in autofocus devices, in which the converging reflected rays coming towards the eyepiece are viewed through (at least) two separate symmetrical apertures.Bausch and Lomb principles
The Bausch and Lomb Keratometer is a one position keratometer that gives readings in dioptric form. It differs from the Javal-Schiotz in that object size is fixed, image size is the manipulable variable. The reflected rays are passed through a Scheiner disc with 4 apertures – As there are two prisms, each aligned perpendicular to the other, the major and minor axis powers can be measured independently without adjusting the orientation of the instrument. In converting the measurements obtained from the corneal surface into a dioptric value, the B&L keratometer uses the general lens formula (n’-n)/R and assumes an n’ of 1.3375 (compared to the actual corneal refractive index of n’=1.376). This is a fictional value, which includes an allowance for the small, yet significant, negative power of the posterior corneal surface. This allows for a readout in both refractive power ( dioptres) and radius of curvature (millimeters).References
* Gutmark R and Guyton DL. Origins of the Keratometer and its Evolving Role in Ophthalmology. Survey of Ophthalmology 2010; 55(5): 481-497 * Javal L, Schiötz H. ''Un opthalmomètre pratique''. Annales d’oculistique, Paris, 1881, 86: 5-21. Ophthalmic equipment Ophthalmology Optometry German inventions Hermann von Helmholtz