|
Jesse Ramsden
Jesse Ramsden FRS FRSE (6 October 1735 – 5 November 1800) was a British mathematician, astronomical and scientific instrument maker. His reputation was built on the engraving and design of dividing engines which allowed high accuracy measurements of angles and lengths in instruments. He produced instruments for astronomy that were especially well known for maritime use where they were needed for the measurement of latitudes and for his surveying instruments which were widely used for cartography and land survey both across the British Empire and outside. An achromatic eyepiece that he invented for telescopes and microscopes continues to be known as the Ramsden eyepiece. Life Ramsden was born at Salterhebble, Halifax, West Riding of Yorkshire, England the son of Thomas Ramsden, an innkeeper and his wife Abigail née Flather. Having attended the free school at Halifax from 1744 to 1747, he was sent at the age of twelve to his maternal uncle, Mr Craven, in the North Riding, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mezzotint
Mezzotint is a monochrome printmaking process of the '' intaglio'' family. It was the first printing process that yielded half-tones without using line- or dot-based techniques like hatching, cross-hatching or stipple. Mezzotint achieves tonality by roughening a metal plate with thousands of little dots made by a metal tool with small teeth, called a "rocker". In printing, the tiny pits in the plate retain the ink when the face of the plate is wiped clean. This technique can achieve a high level of quality and richness in the print. ''Mezzotint'' is often combined with other ''intaglio'' techniques, usually etching and engraving. The process was especially widely used in England from the eighteenth century, to reproduce portraits and other paintings. It was somewhat in competition with the other main tonal technique of the day, aquatint. Since the mid-nineteenth century it has been relatively little used, as lithography and other techniques produced comparable results more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Riding Of Yorkshire
The West Riding of Yorkshire is one of three historic subdivisions of Yorkshire, England. From 1889 to 1974 the administrative county County of York, West Riding (the area under the control of West Riding County Council), abbreviated County of York (WR), was based closely on the historic boundaries. The lieutenancy at that time included the City of York and as such was named West Riding of the County of York and the County of the City of York. Its boundaries roughly correspond to the present ceremonial counties of West Yorkshire, South Yorkshire and the Craven, Harrogate and Selby districts of North Yorkshire, along with smaller parts in Lancashire (for example, the parishes of Barnoldswick, Bracewell, Brogden and Salterforth became part of the Pendle district of Lancashire and the parishes of Great Mitton, Newsholme and Bowland Forest Low became part of the Ribble Valley district also in Lancashire), Cumbria, Greater Manchester and, since 1996, the unitary East Riding of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
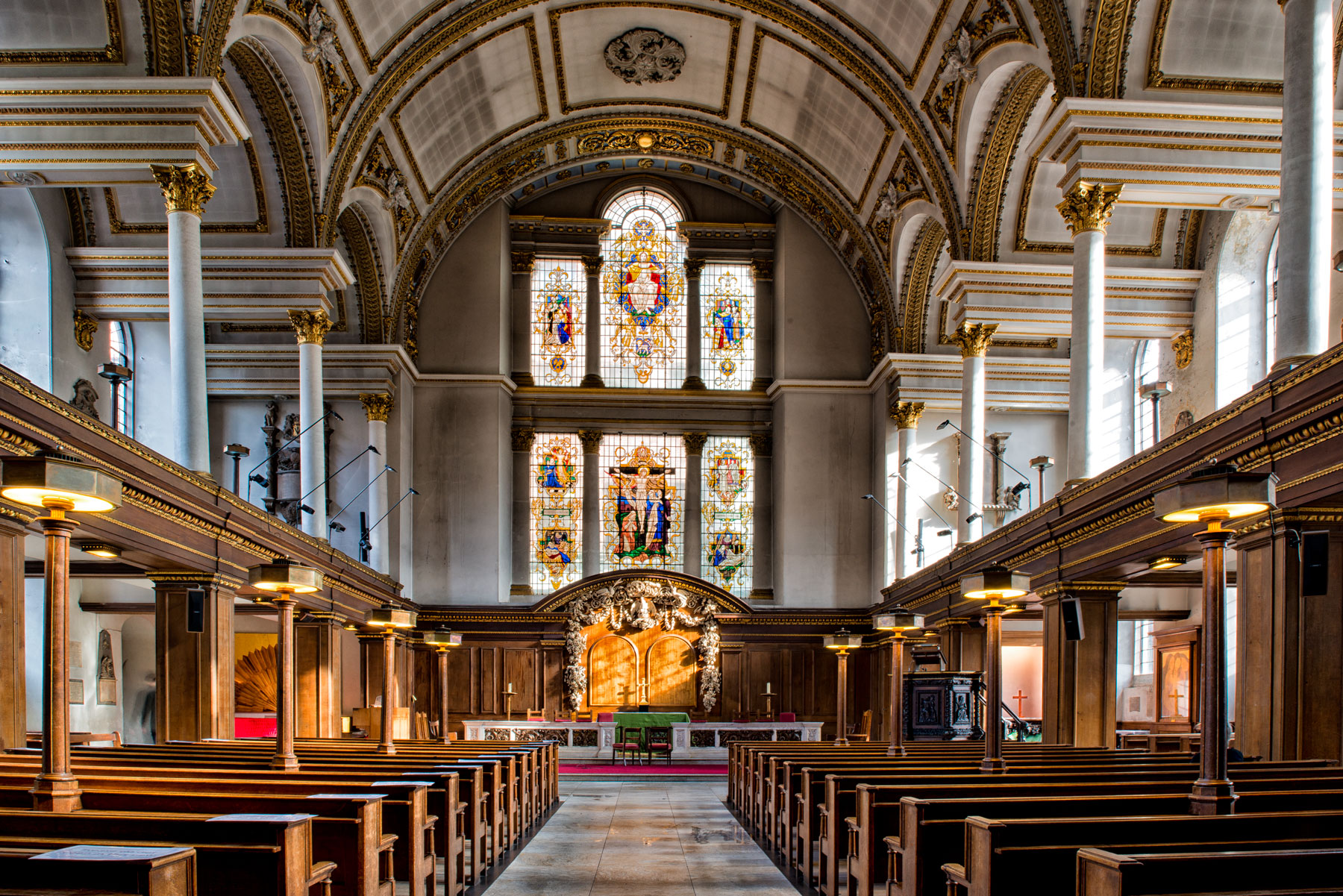
St James's Church, Piccadilly
St James's Church, Piccadilly, also known as St James's Church, Westminster, and St James-in-the-Fields, is an Anglican church on Piccadilly in the centre of London, United Kingdom. The church was designed and built by Sir Christopher Wren. The church is built of red brick with Portland stone dressings. Its interior has galleries on three sides supported by square pillars and the nave has a barrel vault supported by Corinthian columns. The carved marble font and limewood reredos are both notable examples of the work of Grinling Gibbons. In 1902, an outside pulpit was erected on the north wall of the church. It was designed by Temple Moore and carved by Laurence Arthur Turner. It was damaged in 1940, but restored at the same time as the rest of the fabric. History In 1662, Henry Jermyn, 1st Earl of St Albans, was granted land for residential development on what was then the outskirts of London. He set aside land for the building of a parish church and churchyard on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philosophical Transactions
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the first journal in the world exclusively devoted to science, and therefore also the world's longest-running scientific journal. It became an official society publication in 1752. The use of the word ''philosophical'' in the title refers to natural philosophy, which was the equivalent of what would now be generally called ''science''. Current publication In 1887 the journal expanded and divided into two separate publications, one serving the physical sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences'') and the other focusing on the life sciences ('' Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences''). Both journals now publish themed issues and issues resulting from pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by King Charles II as The Royal Society and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the Society's President, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the President are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
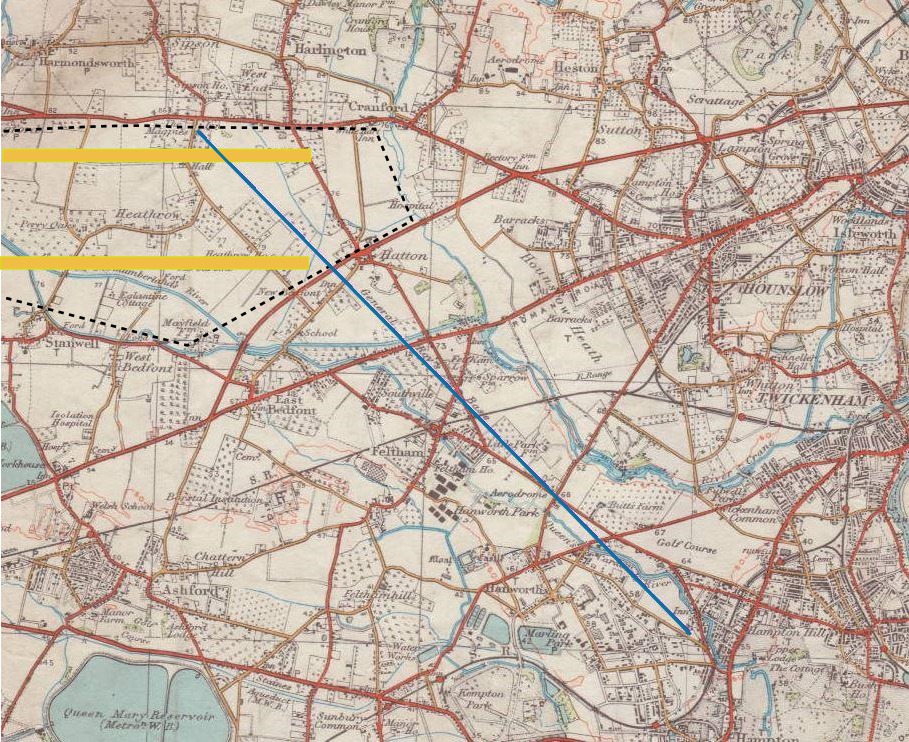
Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790)
The Anglo-French Survey (1784–1790) was the geodetic survey to measure the relative position of Royal Greenwich Observatory, Greenwich Observatory and the Paris Observatory via triangulation (surveying), triangulation. The English operations, executed by William Roy, consisted of the measurements of bases at Hounslow Heath (1784) and Romney Marsh (1787), the measurements of the angles of the triangles (1787–1788) and finally the calculation of all the triangles (1788–1790). The survey is very significant as the first precise survey within Britain, and the forerunner of the work of the Ordnance Survey which was founded in 1791, one year after Roy's death. Cassini's memoir Late in life, when he was 57, Roy was granted the opportunity to establish his lasting reputation in the world of geodesy. The opening came from a completely unexpected direction. In 1783 César-François Cassini de Thury, Cassini de Thury addressed a memoir Concerning the Latitude and Longitude of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Roy
Major-General William Roy (4 May 17261 July 1790) was a Scottish military engineer, surveyor, and antiquarian. He was an innovator who applied new scientific discoveries and newly emerging technologies to the accurate geodetic mapping of Great Britain. His masterpiece is usually referred to as Roy's Map of Scotland. It was Roy's advocacy and leadership that led to the creation of the Ordnance Survey in 1791, the year after his death. His technical work in the establishment of a surveying baseline won him the Copley Medal in 1785. His maps and drawings of Roman archaeological sites in Scotland were the first accurate and systematic study of the subject, and have not been improved upon even today. Roy was a fellow of the Royal Society and a member of the Society of Antiquaries of London. Life and works Early life and family Roy was born at Milton Head in Carluke parish in South Lanarkshire on 4 May 1726. His father was a factor in the service of the Gordons/Hamiltons of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Longitude
The Commissioners for the Discovery of the Longitude at Sea, or more popularly Board of Longitude, was a British government body formed in 1714 to administer a scheme of prizes intended to encourage innovators to solve the problem of finding longitude at sea. Origins Navigators and scientists had been working on the problem of not knowing a ship's longitude. The establishment of the Board of Longitude was motivated by this problem and by the 1707 grounding of four ships of Vice-Admiral Sir Cloudesley Shovell's fleet off the Isles of Scilly, resulting in heavy loss of life. Established by Queen Anne the Longitude Act 1714 named 24 Commissioners of Longitude, key figures from politics, the Navy, astronomy and mathematics. However, the Board did not meet until at least 1737 when interest grew in John Harrison's marine timekeeper. The Board administered prizes for those who could demonstrate a working device or method. The main longitude prizes were: *£10,000 for a method that co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
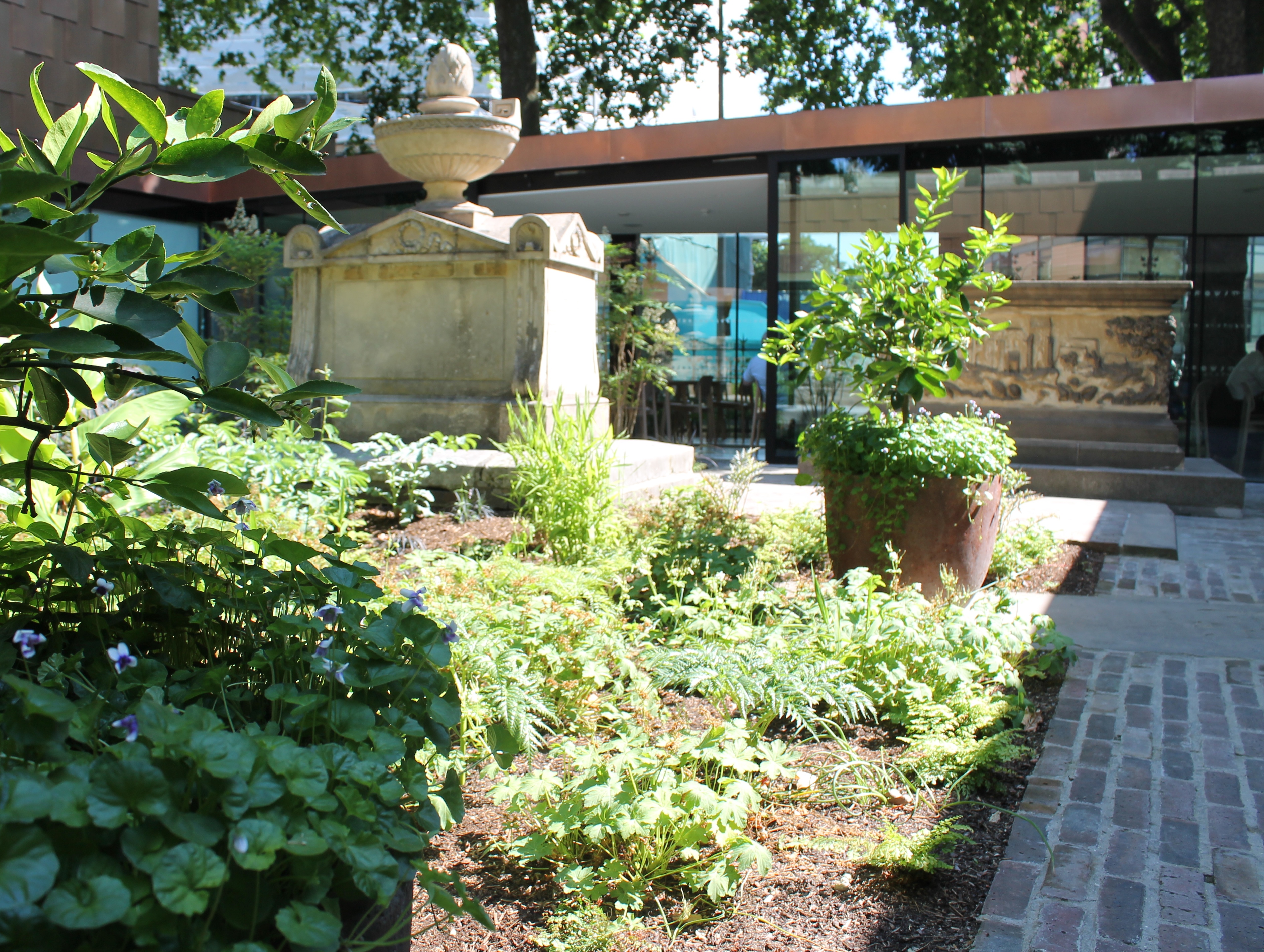
Garden Museum
The Garden Museum (formerly known as the Museum of Garden History) in London is Britain's only museum of the art, history and design of gardens. The museum re-opened in 2017 after an 18-month redevelopment project. The building is largely the Victorian reconstruction of the Church of St Mary-at-Lambeth which was deconsecrated in 1972 and was scheduled to be demolished. It is adjacent to Lambeth Palace on the south bank of the River Thames in London, on Lambeth Road. In 1976, John and Rosemary Nicholson traced the tomb of the two 17th-century royal gardeners and plant hunters John Tradescant the Elder and the Younger to the churchyard, and were inspired to create the Museum of Garden History.Tradescant Trust (1979) The Tradescant Story (London). It was the first museum in the world dedicated to the history of gardening. The Museum's main gallery is on the first floor, in the body of the church. The collection includes tools, art, and ephemera of gardening, including a gallery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |