Kentville, Nova Scotia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kentville is an incorporated town in
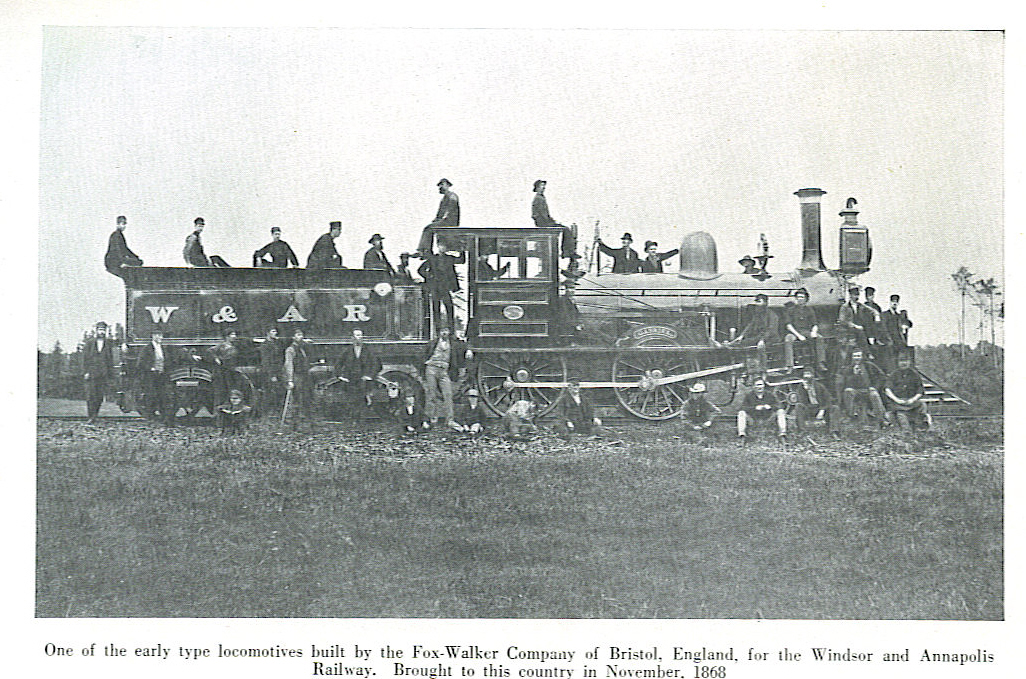 When the
When the
/ref> The town became a major travel centre highlighted by the large Cornwallis Inn built at the town's centre by the railway. The town boomed during
The town became a major travel centre highlighted by the large Cornwallis Inn built at the town's centre by the railway. The town boomed during
Kentville instead sold its utility to
Pumpkin People Festival
Other Annual Festivals and Events hosted in Kentville
Devil's Half Acre Motorcycle RallyValley Electronic Music and Art Expo
(new in 2018
Open Street Chalk Art FestivalKentville Multicultural Festival
(currently the largest Multicultural Festival in NS) Kentville Harvest Festival KBC's Great Big Country Fair
is located in nearby
Ghostarchive
and th
Wayback Machine
Town of Kentville Official Site
{{Authority control Communities in Kings County, Nova Scotia Towns in Nova Scotia General Service Areas in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
. It is the most populous town in the Annapolis Valley
The Annapolis Valley is a valley and region in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula, formed by a trough between two parallel mountain ranges along the shore of the Bay of Fundy. St ...
. As of 2021, the town's population was 6,630. Its census agglomeration
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of st ...
is 26,929.
History
Kentville owes its location to theCornwallis River
The Cornwallis River is in Kings County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It has a meander length of approximately through eastern Kings County, from its source on the North Mountain at Grafton to its mouth near Wolfville on the Minas Basin. The lower ...
which, downstream from Kentville, becomes a large tidal river at the Minas Basin. The riverbank at the current location of Kentville provided an easy fording point. The Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Miꞌkmaw'' or ''Miꞌgmaw''; ; ) are a First Nations people of the Northeastern Woodlands, indigenous to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as the northe ...
name for the location was "Penooek". The ford and later the bridge in Kentville made the area an important crossroads for other settlements in the Annapolis Valley. Kentville also marked the limit of navigation of sailing ships.
Acadian settlement
The area was first settled byAcadians
The Acadians (french: Acadiens , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Most Acadians live in the region of Acadia, as it is the region where the des ...
, who built many dykes along the river to keep the high Bay of Fundy
The Bay of Fundy (french: Baie de Fundy) is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its extremely high tidal range is the hi ...
tides out of their farmland. These dykes created the ideal fertile soil that the Annapolis Valley
The Annapolis Valley is a valley and region in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula, formed by a trough between two parallel mountain ranges along the shore of the Bay of Fundy. St ...
is known for. The Acadians were expelled from the area in the Bay of Fundy Campaign (1755)
The Bay of Fundy campaign occurred during the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War) when the British ordered the Expulsion of the Acadians from Acadia after the Battle of Fort Beauséjour (1755). The campaign ...
by the British authorities because they would not swear allegiance to the British king. The area was then settled by New England Planters
The New England Planters were settlers from the New England colonies who responded to invitations by the lieutenant governor (and subsequently governor) of Nova Scotia, Charles Lawrence, to settle lands left vacant by the Bay of Fundy Campaign ( ...
. Settlement was expedited by the United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America duri ...
during the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
.
English settlement
The town was originally known as Horton's Corner, but was named Kentville in 1826 afterPrince Edward Augustus, Duke of Kent
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn, (Edward Augustus; 2 November 1767 – 23 January 1820) was the fourth son and fifth child of King George III. His only legitimate child became Queen Victoria.
Prince Edward was created Duke of Kent an ...
(son of King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
and father of Queen Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
), who resided in Nova Scotia from 1794 to 1800. The village was at first relatively small and dwarfed by larger valley towns with better harbours such as Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although u ...
and Wolfville
Wolfville is a Canadian town in the Annapolis Valley, Kings County, Nova Scotia, located about northwest of the provincial capital, Halifax. The town is home to Acadia University and Landmark East School.
The town is a tourist destination du ...
. The crossroads location did attract early shopkeepers and several stagecoach inns. Small schooners were able to land cargos in the "Klondyke" neighhourhood by the Cornwallis River which marked the height of navigation. Kentville developed a reputation for rowdy drinking and horse races in the early 19th century, earning the nickname "The Devil's Half Acre." Celebrated local musician, Chase Ross, later released an album entitled "Devil's Half Acre" to critical acclaim in the early years of the new millennium.
Growth
 When the
When the Windsor and Annapolis Railway
The Windsor and Annapolis Railway (W&AR) was a historic Canadian railway that operated in Nova Scotia's Annapolis Valley.
The railway ran from Windsor to Annapolis Royal and leased connections to Nova Scotia's capital of Halifax. The W&AR played ...
(later named Dominion Atlantic Railway
The Dominion Atlantic Railway was a historic railway which operated in the western part of Nova Scotia in Canada, primarily through an agricultural district known as the Annapolis Valley.
The Dominion Atlantic Railway was unusually diverse for a ...
) established its headquarters in Kentville in 1868 and began shipping Annapolis Valley
The Annapolis Valley is a valley and region in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula, formed by a trough between two parallel mountain ranges along the shore of the Bay of Fundy. St ...
apples to British markets, the community began to thrive. The railway not only employed a large number of people (up to a third of the town's population), but also attracted other industries such as mills, dairies, a large foundry, and a carriage works which even entered automobile production. A branch line of the Dominion Atlantic, the Cornwallis Valley Railway
The Cornwallis Valley Railway (CVR) was a historic Canadian railway in Nova Scotia's Annapolis Valley. It was built in 1889 and ran from Kentville to Kingsport serving the Cornwallis Township area of Kings County. For most of its history, it ...
, was built north to Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although u ...
and Kingsport in 1889, further developing the apple industry and creating a suburban line for workers, shoppers and schoolchildren to commute to and from Kentville. The railway also attracted large institutional developments such as a regional TB hospital, the Kentville Sanitorium, a federal agricultural research station, and an army training base at Camp Aldershot."Kentville", ''Dominion Atlantic Railway Digital Preservation Initiative''/ref>
 The town became a major travel centre highlighted by the large Cornwallis Inn built at the town's centre by the railway. The town boomed during
The town became a major travel centre highlighted by the large Cornwallis Inn built at the town's centre by the railway. The town boomed during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
with heavy wartime railway traffic on the Dominion Atlantic and the training of thousands of troops at Camp Aldershot. Many residents fought overseas in the local West Nova Scotia Regiment
The West Nova Scotia Regiment is a line infantry regiment of the Canadian Army, part of the Primary Reserve, and is part of the 5th Canadian Division's 36 Canadian Brigade Group. The regiment recruits volunteers from the South-Western part of th ...
as well as other branches of service. A Royal Canadian Navy minesweeper was named after the town, and her crew often took leave in Kentville.
Post war challenges
Kentville faced serious challenges after World War II. The dominant apple industry suffered severe declines due to the loss of its British export market. The nearby military training base at Camp Aldershot was significantly downsized and the town's major employer, theDominion Atlantic Railway
The Dominion Atlantic Railway was a historic railway which operated in the western part of Nova Scotia in Canada, primarily through an agricultural district known as the Annapolis Valley.
The Dominion Atlantic Railway was unusually diverse for a ...
suffered serious declines with the collapse of the apple industry and the growth of highway travel. Further decline followed in the 1970s as the town lost its retail core to the growth of shopping malls and later "big box" stores in nearby New Minas. The town was also eclipsed in restaurant, upscale retail and cultural institutions by the nearby university town of Wolfville
Wolfville is a Canadian town in the Annapolis Valley, Kings County, Nova Scotia, located about northwest of the provincial capital, Halifax. The town is home to Acadia University and Landmark East School.
The town is a tourist destination du ...
. Railway passenger service ended in 1990. Freight service ended in October 1993 and the Kentville rail shops were closed and moved to Windsor, Nova Scotia
Windsor is a community located in Hants County, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is a service centre for the western part of the county and is situated on Highway 101.
The community has a history dating back to its use by the Mi'kmaq Nation for sev ...
. Kentville lost many heritage buildings in the postwar period and is one of the only towns in Nova Scotia without a single designated heritage building. Major losses included the large railway station, one of the most historic in Canada which was demolished in 1990. In July 2007 the town demolished the last railway structure in town, the DAR Roundhouse, despite a province-wide protest, a move which earned the Town of Kentville a place on the "2008 Worst" List of the Heritage Canada Foundation
The National Trust for Canada (french: La Fiducie nationale du Canada; formerly known as the Heritage Canada Foundation) is a national registered charity in Canada with the mandate to inspire and lead action to save historic places, and promot ...
.
Demographics
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted byStatistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultur ...
, Kentville had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
Industries
During the early part of the 20th century Kentville emerged as the business centre of Kings County and despite the post-war loss of commerce to other valley communities, it remains the professional centre of theAnnapolis Valley
The Annapolis Valley is a valley and region in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia. It is located in the western part of the Nova Scotia peninsula, formed by a trough between two parallel mountain ranges along the shore of the Bay of Fundy. St ...
. Kentville is home to numerous professional services such as lawyers offices, doctors, and investment firms. On the outskirts of the town is the Valley Regional Hospital, built in 1991. The town is also home to the Annapolis Valley Regional Industrial Park which employs numerous people in the area through a variety of different businesses.
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
, especially fruit crops such as apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
s, remain a prominent industry
Industry may refer to:
Economics
* Industry (economics), a generally categorized branch of economic activity
* Industry (manufacturing), a specific branch of economic activity, typically in factories with machinery
* The wider industrial sector ...
in the Kentville area, and throughout the eastern part of the valley. Kentville is home to one of the largest agricultural research facilities in Nova Scotia founded in 1911, known to the locals as The Research Station. The site now employs over 200 people and sits on of the land at the east end of the town.
Kentville shares its northern boundary along the Cornwallis River with Camp Aldershot, a military training base founded in 1904. At its peak during World War II, the camp housed approximately 7000 soldiers. Kentville native Donald Ripley wrote a book chronicling Camp Aldershot and its effect on the town entitled ''On The Home Front''. Today the camp functions as an army reserve training centre and is the headquarters of The West Nova Scotia Regiment
The West Nova Scotia Regiment is a line infantry regiment of the Canadian Army, part of the Primary Reserve, and is part of the 5th Canadian Division's 36 Canadian Brigade Group. The regiment recruits volunteers from the South-Western part of th ...
.
Electric utility (sold 1997)
Kentville until 1997-8 was one of seven Nova Scotia towns (along with Riverport, Berwick,Canso
The Civil Air Navigation Services Organisation (CANSO) is a representative body of companies that provide air traffic control. It represents the interests of Air Navigation Service Providers (ANSPs). CANSO members are responsible for supporting ov ...
, Antigonish
, settlement_type = Town
, image_skyline = File:St Ninian's Cathedral Antigonish Spring.jpg
, image_caption = St. Ninian's Cathedral
, image_flag = Flag of Antigonish.pn ...
, Lunenburg and Mahone Bay
Mahone Bay is a bay on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada along the eastern end of Lunenburg County. The bay has many islands, and is a popular sailing area. Since 2003 the Mahone Islands Conservation Association has been working to prot ...
) to own its own electricity distribution utility within town limits – the Kentville Electric Commission. When the other six joined into the Municipal Electric Utilities of Nova Scotia
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality ...
in January 199Kentville instead sold its utility to
Nova Scotia Power
Nova Scotia Power Inc. is a vertical integration, vertically integrated electric utility in Nova Scotia, Canada. It is privately owned by Emera and regulated by the provincial government via the Nova Scotia Utility and Review Board (NSUARB). Nov ...
, a privately owned generator and distributor whose service area covered the rest of the province.
Community events
The Apple Blossom Festival, founded in 1933 is held each May to celebrate the blossoming of local apple industry, one of the region's richest forms of agriculture. Kentville is also well known for itPumpkin People Festival
Other Annual Festivals and Events hosted in Kentville
Devil's Half Acre Motorcycle Rally
(new in 2018
Open Street Chalk Art Festival
(currently the largest Multicultural Festival in NS) Kentville Harvest Festival KBC's Great Big Country Fair
Climate
Kentville experiences ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(''Dfb DFB may refer to:
* Deerfield Beach, Florida, a city
* Decafluorobutane, a fluorocarbon gas
* Dem Franchize Boyz, former hip hop group, Atlanta, Georgia
* Dfb, Köppen climate classification for Humid continental climate
* Distributed-feedback ...
''). The highest temperature ever recorded in Kentville was on 12 August 1944. The coldest temperature ever recorded was on 1 February 1920. Kentville's USDA Hardiness zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most wide ...
is 6a.
Famous residents
(From in or near Kentville, including the former Township of Cornwallis) * Composer Robert Aitken * Former NHLerJerry Byers
Jerry William Byers (March 29, 1952 – December 25, 2006) was a Canadian professional ice hockey forward (ice hockey), forward.
Career
Byers was drafted in the first round, twelfth overall, by the Minnesota North Stars in the 1972 NHL Amateur Dr ...
* Actor Peter Donat
Peter Donat (born Pierre Collingwood Donat; January 20, 1928 – September 10, 2018) was a Canadian-American actor.
Early life
Pierre Collingwood Donat was born in Kentville, Nova Scotia, Canada, the son of Marie (née Bardet) and Philip Ernst ...
* Inventor of kerosene Abraham Gesner
Abraham Pineo Gesner, ONB (; May 2, 1797 – April 29, 1864) was a Canadian physician and geologist who invented kerosene. Gesner was born in Cornwallis, Nova Scotia (now called Chipmans Corner) and lived much of his life in Saint John, New Bru ...
* Comedian Jay Malone
Jay Malone is a Canadians, Canadian comedian from Kentville, Nova Scotia.
Early career
Malone began doing standup comedy in 1999 while studying at the University of New Brunswick in Fredericton, New Brunswick, Fredericton. He entered a comedy co ...
* Linguist Silas Tertius Rand
Silas Tertius Rand (May 18, 1810 – October 4, 1889) was a Canadian Baptist clergyman, missionary, ethnologist, linguist and translator. His work centred on the Mi'kmaq people of Maritime Canada and he was the first to record the legend of Gloos ...
* Zoologist Austin L. Rand
Austin Loomer Rand (16 December 1905 – 6 November 1982) was a Canadian zoologist.
He was born in Kentville, Nova Scotia in 1905 and grew up in nearby Wolfville, where he was mentored by the noted local ornithologist Robie W. Tufts. He received a ...
* Boxer Bryan Gibson
Bryan Gibson (born November 10, 1947 in Kentville, Nova Scotia) is a retired boxer from Canada, who represented his native country at the 1976 Summer Olympics, and is the first boxer of African descent from Nova Scotia to compete in the Olympics. ...
* CFL All Canadian Bruce Beaton
Bruce Beaton (born June 13, 1968 in Port Hood, Nova Scotia) is a former professional Canadian football offensive lineman who played 13 seasons in the Canadian Football League for five different teams. He was named CFL All-Star three times and was ...
* Blue Man Group
Blue Man Group is an American performance art company formed in 1987. It was purchased in July 2017 by the Canadian company Cirque du Soleil. Blue Man Group is known for its stage productions, which incorporate many kinds of music and art, bot ...
member Scott Bishop
* Blues Guitarist Dutch Mason
Dutch Mason, (19 February 1938 – 23 December 2006) was a Canadian musician from Halifax, Nova Scotia. He was inducted into the Canadian Jazz and Blues Hall of Fame, and was inducted into the Order of Canada in 2005.
Career
Dutch started p ...
* Filmmaker Dylan Mohan Gray
Dylan Mohan Gray is an Indian and Canadian filmmaker. His documentary feature film '' Fire in the Blood'',http://fireintheblood.com premiered in competition at the 2013 Sundance Film Festival and went on to enjoy the longest theatrical run of ...
* Author Maria Mutch
* Federal Cabinet Minister Anita Anand (professor)
Anita Anand (born May 20, 1967) is a Canadian lawyer and politician who serves as the minister of national defence since 2021. She has represented the riding of Oakville in the House of Commons since the 2019 federal election, sitting as ...
* MLS Forward Jacob Shaffelburg
Jacob Everett Shaffelburg (born November 26, 1999) is a Canadian professional soccer player who plays as a winger for Major League Soccer club Nashville SC and the Canadian national team.
Early life
Shaffelburg played youth soccer for Valle ...
* Author and musician Thibault Jacquot-Paratte
Education
Education in the area is serviced by Kings County Academy in Kentville, serving grades primary through eight, the local high school is Northeast Kings Education Centre, located 15–20 minutes away in Canning. There are also several post secondary institutions, the Kingstec campus of theNova Scotia Community College
Nova Scotia Community College, commonly referred to as NSCC, is a community college serving the province of Nova Scotia through a network of 14 campuses and three community learning centres.
The college delivers over 130 programs in five academ ...
is located on the northern fringe of the town and Acadia Universityis located in nearby
Wolfville
Wolfville is a Canadian town in the Annapolis Valley, Kings County, Nova Scotia, located about northwest of the provincial capital, Halifax. The town is home to Acadia University and Landmark East School.
The town is a tourist destination du ...
. The town operates a library and C@P site. Kentville is also home to the Kings County Museum
The Kings County Museum is a museum in Kentville, Nova Scotia, Canada, exploring the history of Kings County, Nova Scotia. It is housed in the restored 1903 Kings County Courthouse. The museum hosts a variety of permanent and changing displays a ...
, located in Kentville's old courthouse.
Other nearby elementary schools include the Aldershot Elementary School, and the Glooscap Elementary School.
Recreation
Kentville also boasts a number of high quality recreational facilities. The Kentville Arena (now the Kentville Centennial Arena) is thought to have hosted the first ever summer ice hockey school. The town also houses a large indoor soccer arena and numerous other outdoor baseball and soccer fields, and playgrounds for local children. Kentville Memorial Park (considered to be one of the best baseball parks in Canada east of Montreal) is home to the Kentville Wildcats, a senior baseball team, who have won several NSSBL championships and one Canadian championship. Kentville swimming pool is home to the Kentville Marlins Swim Team.Sister city
* Camrose,Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada
* Castel di Sangro
Castel di Sangro (locally ''Caštiéllë'') is a city and ''comune'' of 6,461 people (as of 2013) in the Province of L'Aquila, in Abruzzo, Central Italy. It is the main city of the Alto Sangro e Altopiano delle Cinque Miglia area.
Geography
Cast ...
, Abruzzo
Abruzzo (, , ; nap, label=Neapolitan language, Abruzzese Neapolitan, Abbrùzze , ''Abbrìzze'' or ''Abbrèzze'' ; nap, label=Sabino dialect, Aquilano, Abbrùzzu; #History, historically Abruzzi) is a Regions of Italy, region of Southern Italy wi ...
, Italy Archived aGhostarchive
and th
Wayback Machine
See also
*List of municipalities in Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is the seventh-most populous province in Canada with 969,383 residents as of the 2021 Census of Population, and the second-smallest province in land area at . Nova Scotia's 49 municipalities cover of the territory's land mass, a ...
Notes
References
*''The Devil's Half Acre: A Look at Kentville's Past'' Mable Nichols, Kentville Centennial Committee, 1968. *''Historic Kentville'' Louis V. Comeau, Nimbus, 2003.External links
Town of Kentville Official Site
{{Authority control Communities in Kings County, Nova Scotia Towns in Nova Scotia General Service Areas in Nova Scotia