Kellgren-Lawrence Grading Scale on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Radiographic systems to classify osteoarthritis vary by which joint is being investigated. In osteoarthritis, the choice of treatment is based on pain and decreased function, but radiography can be useful before surgery in order to prepare for the procedure.
 The most commonly used radiographic classification system for osteoarthritis of the hip joint is the Kellgren–Lawrence system (or KL system). It uses plain radiographs.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also be graded by Tönnis classification. There is no consensus whether it is more or less reliable than the Kellgren-Lawrence system.
The most commonly used radiographic classification system for osteoarthritis of the hip joint is the Kellgren–Lawrence system (or KL system). It uses plain radiographs.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also be graded by Tönnis classification. There is no consensus whether it is more or less reliable than the Kellgren-Lawrence system.

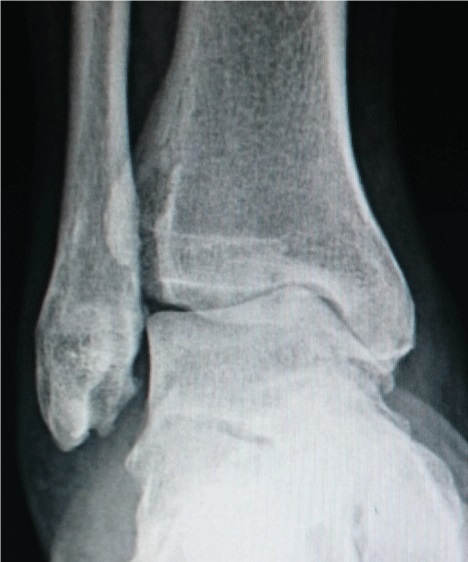 *For the ankle, the Kellgren–Lawrence scale, as described for the hip, has been recommended. The distances between the bones in the ankle are normally as follows:
:*Talus - medial malleolus: 1.70 ± 0.13 mm
:*Talus - tibial plafond: 2.04 ± 0.29 mm
:*Talus - lateral malleolus: 2.13 ± 0.20 mm
*For the ankle, the Kellgren–Lawrence scale, as described for the hip, has been recommended. The distances between the bones in the ankle are normally as follows:
:*Talus - medial malleolus: 1.70 ± 0.13 mm
:*Talus - tibial plafond: 2.04 ± 0.29 mm
:*Talus - lateral malleolus: 2.13 ± 0.20 mm
Vertebral column
There are many grading systems for degeneration ofintervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ...
s and facet joint
The facet joints (or zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and e ...
s in the cervical and lumbar vertebrae, of which the following radiographic systems can be recommended in terms of interobserver reliability:
*Kellgren grading of cervical disc degeneration
*Kellgren grading of cervical facet joint degeneration
*Lane grading of lumbar disc degeneration
*Thompson grading of lumbar disc degeneration (by magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
)
*Pathria grading of lumbar facet joint degeneration (by computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
)
*Weishaupt grading of lumbar facet joint degeneration (by MRI and computed tomography)
The Thomson grading system is regarded to have more academic than clinical value.
Shoulder
The Samilson–Prieto classification is preferable for osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral joint.Hip
 The most commonly used radiographic classification system for osteoarthritis of the hip joint is the Kellgren–Lawrence system (or KL system). It uses plain radiographs.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also be graded by Tönnis classification. There is no consensus whether it is more or less reliable than the Kellgren-Lawrence system.
The most commonly used radiographic classification system for osteoarthritis of the hip joint is the Kellgren–Lawrence system (or KL system). It uses plain radiographs.
Osteoarthritis of the hip joint may also be graded by Tönnis classification. There is no consensus whether it is more or less reliable than the Kellgren-Lawrence system.

Knee
For the grading of osteoarthritis in the knee, the International Knee Documentation Committee (IKDC) system is regarded to have the most favorable combination of interobserver precision and correlation to knee arthroscopy findings. It was formed by a group of knee surgeons from Europe and America who met in 1987 to develop a standard form to measure results of knee ligament reconstructions. The Ahlbäck system has been found to have comparable interobserver precision and arthroscopy correlation to the IKDC system, but most of the span of the Ahlbäck system focused at various degrees of bone defect or loss, and it is therefore less useful in early osteoarthritis. Systems that have been found to have lower interobserver precision and/or arthroscopy correlation are those developed by Kellgren and Lawrence, Fairbank, Brandt, and Jäger and Wirth. For the patellofemoral joint, a classification by Merchant 1974 uses a 45° "skyline" view of the patella:Other joints
*In the temporomandibular joint, ''subchondral sclerosis of the mandibular condyle'' has been described as an early change, ''condylar flattening'' as a feature of progressive osteoarthritis, and narrowing of the temporomandibular joint space as a late stage change. A joint space of between 1.5 and 4 mm is regarded as normal. *For the ankle, the Kellgren–Lawrence scale, as described for the hip, has been recommended. The distances between the bones in the ankle are normally as follows:
:*Talus - medial malleolus: 1.70 ± 0.13 mm
:*Talus - tibial plafond: 2.04 ± 0.29 mm
:*Talus - lateral malleolus: 2.13 ± 0.20 mm
*For the ankle, the Kellgren–Lawrence scale, as described for the hip, has been recommended. The distances between the bones in the ankle are normally as follows:
:*Talus - medial malleolus: 1.70 ± 0.13 mm
:*Talus - tibial plafond: 2.04 ± 0.29 mm
:*Talus - lateral malleolus: 2.13 ± 0.20 mm
See also
* WOMAC, a non-radiographic classification system of osteoarthritis, taking into accountpain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, ...
, stiffness and functional limitation.
References
{{Reflist Musculoskeletal radiographic signs Arthritis Medical scoring system