|
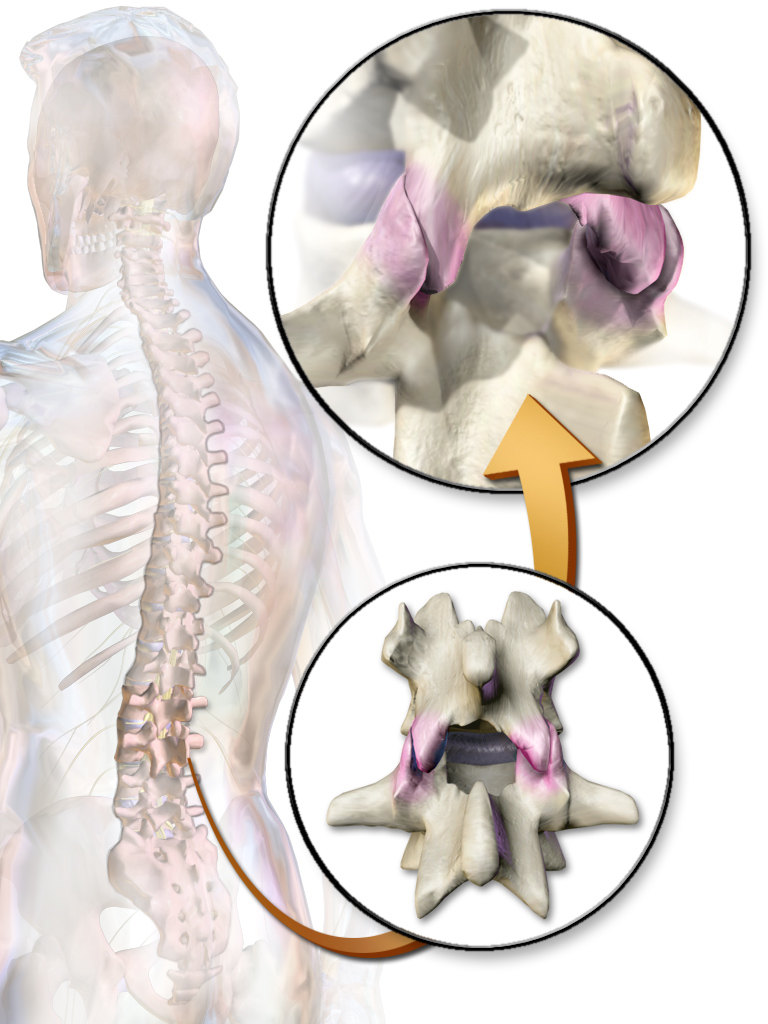
Facet Joint
The facet joints (or zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital ner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae, with the lower ones being much larger than the upper. They are distinguished by the presence of facets on the sides of the bodies for articulation with the heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth vertebrae contain cert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging-associated Diseases
An aging-associated disease (commonly termed age-related disease, ARD) is a disease that is most often seen with increasing frequency with increasing senescence. They are essentially complications of senescence, distinguished from the aging process itself because all adult animals age ( with rare exceptions) but not all adult animals experience all age-associated diseases. The term does not refer to age-specific diseases, such as the childhood diseases chicken pox and measles, only diseases of the elderly. They are also not accelerated aging diseases, all of which are genetic disorders. Examples of aging-associated diseases are atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, cancer, arthritis, cataracts, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, hypertension and Alzheimer's disease. The incidence of all of these diseases increases exponentially with age. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two thirds—100,000 per day—die of age-related causes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Spine
Spinal posture is the position of the spine in the human body. It is debated what the optimal spinal posture is, and whether poor spinal posture causes lower back pain. Neutral spine Looking directly at the front or back of the body, the 33 vertebrae in the spinal column should appear completely vertical. From a side view, the cervical (neck) region of the spine (C1–C7) is bent inward, the thoracic (upper back) region (T1–T12) bends outward, and the lumbar (lower back) region (L1–L5) bends inward. The sacrum (tailbone area) (S1–S5 fused) and coccyx (on average 4 fused) rest between the pelvic bones. A neutral pelvis is in fact slightly anteriorly rotated which means the anterior superior iliac spines should be just in front of the pubic symphysis not in the same vertical line. Posture abnormalities In medicine and occupations concerned with physical fitness, the concept of good posture is referred to as "neutral spine". In this context, proper posture or "neutral spine" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteopathic Medicine
Osteopathy () is a type of alternative medicine that emphasizes physical manipulation of the body's muscle tissue and bones. Practitioners of osteopathy are referred to as osteopaths. Osteopathic manipulation is the core set of techniques in osteopathy. Parts of osteopathy, such as craniosacral therapy, have no therapeutic value and have been labeled as pseudoscience and quackery. The techniques are based on an ideology created by Andrew Taylor Still (1828–1917) which posits the existence of a "myofascial continuity"—a tissue layer that "links every part of the body with every other part". Osteopaths attempt to diagnose and treat what was originally called "the osteopathic lesion", but which is now named "somatic dysfunction", by manipulating a person's bones and muscles. Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment (OMT) techniques are most commonly used to treat back pain and other musculoskeletal issues. Osteopathic manipulation is still included in the curricula of osteopathic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blausen 0391 FacetJointInjection
Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. is the creator and owner of a library of two- and three-dimensional medical and scientific images and animations, a developer of information technology allowing access to that content, and a business focused on licensing and distributing the content. It was founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas, in 1991, and is privately held. Background Blausen Medical Communications, Inc. (BMC) is a privately held company founded by Bruce Blausen in Houston, Texas in 1991. BMC created and owns a library of medical and scientific images and animations, and has developed information technology tools allowing access to the library; as well, it licenses and otherwise works to distribute the content. As of this date, BMC's animation library comprised approximately 1,500 animations and over 27,000 two- and three-dimensional images designed for point-of-care patient education, which could be accessed by consumers or professional caregivers (primarily via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Computed Tomography
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. There is no universally accepted, strict definition of the bounds of the X-ray band. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 nanometers to 10 picometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range of 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and photon energies in the range of 100 eV to 100 keV, respectively. X-rays can penetrate many solid substances such as construction materials and living tissue, so X-ray radiography is widely used in medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, physician assistant, a certified nurse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erector Spinae Muscles
The erector spinae ( ) or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes (gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) to maintain stable posture standing or sitting. Structure The erector spinae is not just one muscle, but a group of muscles and tendons which run more or less the length of the spine on the left and the right, from the sacrum, or sacral region, and hips to the base of the skull. They are also known as the sacrospinalis group of muscles. These muscles lie on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae and extend throughout the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical regions. The erector spinae is covered in the lumbar and thoracic regions by the thoracolumbar fascia, and in the cervical region by the nuchal ligament. This large muscular and tendinous mass varies in size and structure at different parts of the vertebral column. In the sacral region, it is narrow and poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referred Pain
Referred pain, also called reflective pain, is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus. An example is the case of angina pectoris brought on by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), where pain is often felt in the left side of neck, left shoulder, and back rather than in the thorax (chest), the site of the injury. The International Association for the Study of Pain has not officially defined the term; hence several authors have defined it differently. Referred pain is when the pain is located away from or adjacent to the organ involved; for instance, when a person has pain only in their jaw or left arm, but not in the chest. Referred pain has been described since the late 1880s. Despite an increasing amount of literature on the subject, the biological mechanism of referred pain is unknown, although there are several hypotheses. Characteristics * The size of referred pain is related to the intensity and duration of ongoing/evoked pain. * Tempo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knee Arthritis
Arthritis of the knee is typically a particularly debilitating form of arthritis. The knee may become affected by almost any form of arthritis. The word ''arthritis'' refers to inflammation of the joints. Types of arthritis include those related to wear and tear of cartilage, such as osteoarthritis, to those associated with inflammation resulting from an overactive immune system (such as rheumatoid arthritis).Arthritis Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment Information on MedicineNet.com Retrieved on 2010-01-22. Causes It is not always certain why arthritis of the knee develops. The knee may become affected by almost any form of arthritis, including those related t ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Foramen
The intervertebral foramen (also called neural foramen, and often abbreviated as IV foramen or IVF) is a foramen between two spinal vertebrae. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina. The foramina, or openings, are present between every pair of vertebrae in these areas. A number of structures pass through the foramen. These are the root of each spinal nerve, the spinal artery of the segmental artery, communicating veins between the internal and external plexuses, recurrent meningeal (sinu-vertebral) nerves, and transforaminal ligaments. When the spinal vertebrae are articulated with each other, the bodies form a strong pillar that supports the head and trunk, and the vertebral foramen constitutes a canal for the protection of the medulla spinalis (spinal cord). The size of the foramina is variable due to placement, pathology, spinal loading, and posture. Foramina can be occluded by arthritic degenerative changes and space-occupying les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |