Kawasaki Ki-45 Toryu on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
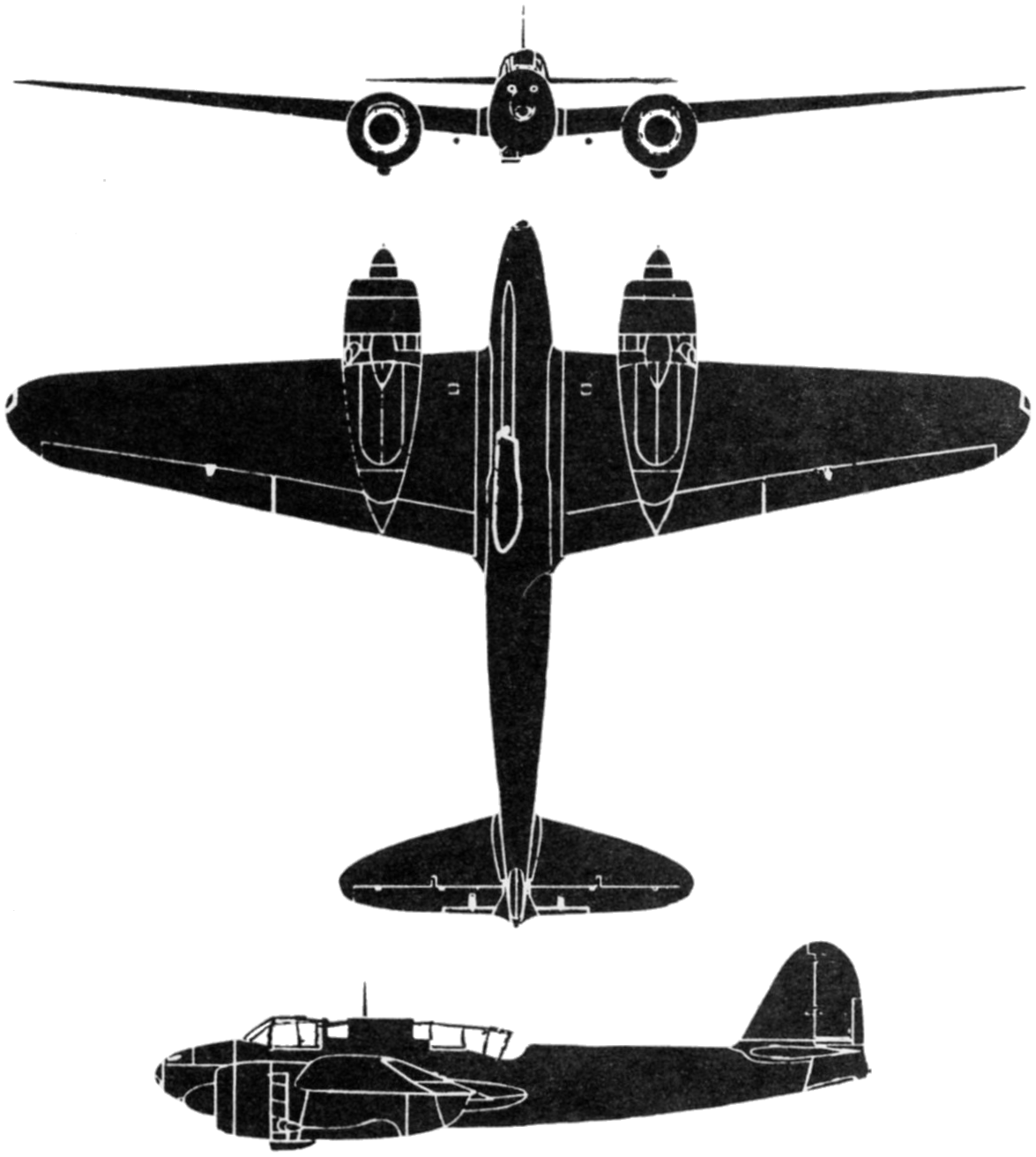
The Kawasaki Ki-45 ''Toryu'' (屠龍, "Dragonslayer") was a two-seat, twin-engine heavy fighter used by the
 The Ki-45 was initially used as a long-range
The Ki-45 was initially used as a long-range

 ; Ki-45: Prototype aircraft
; KI-45 Type 1: Modified operative models
; Ki-45 KAI: Prototype aircraft
; Ki-45 KAI: Pre-series aircraft
; Ki-45 KAIa (ko/甲):''Toryu'': Two-seat fighter Type 2 of the army (Mark A) initial model of series, one 20 mm Ho-3 in ventral position, two Ho-103 12.7 mm in the nose and a flexible 7.92 mm in the back position
; Ki-45 KAIb (otsu/乙): retrofit version based on the KAIa, 20 mm belly cannon replaced by a 37 mm type 94 anti-tank gun
; Ki-45 KAIc (hei/丙): Mark C version against naval objectives, one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 automatic cannon in the nose, one 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine gun in the back position.
; Ki-45 KAId (tei/丁): Mark D, a modified Model B, night fighter version, equipped with one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 cannon in nose and two fixed 20 mm
; Ki-45: Prototype aircraft
; KI-45 Type 1: Modified operative models
; Ki-45 KAI: Prototype aircraft
; Ki-45 KAI: Pre-series aircraft
; Ki-45 KAIa (ko/甲):''Toryu'': Two-seat fighter Type 2 of the army (Mark A) initial model of series, one 20 mm Ho-3 in ventral position, two Ho-103 12.7 mm in the nose and a flexible 7.92 mm in the back position
; Ki-45 KAIb (otsu/乙): retrofit version based on the KAIa, 20 mm belly cannon replaced by a 37 mm type 94 anti-tank gun
; Ki-45 KAIc (hei/丙): Mark C version against naval objectives, one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 automatic cannon in the nose, one 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine gun in the back position.
; Ki-45 KAId (tei/丁): Mark D, a modified Model B, night fighter version, equipped with one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 cannon in nose and two fixed 20 mm
 ;
* Imperial Japanese Army Air Force
**No. 25 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 71 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 84 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 4 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 5 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 13 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 16 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 21 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 27 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 45 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 53 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 65 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 70 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**Akeno Army Fighter Training School
;
* Manchukuo Air Force
;
* People's Liberation Army Air Force
;
* Imperial Japanese Army Air Force
**No. 25 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 71 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 84 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 4 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 5 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 13 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 16 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 21 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 27 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 45 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 53 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 65 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 70 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**Akeno Army Fighter Training School
;
* Manchukuo Air Force
;
* People's Liberation Army Air Force
Fred Hargesheimer and ERA/Univac Story
{{Authority control Ki-45, Kawasaki Ki-045 Low-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1941 Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft
Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emperor o ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The army gave it the designation "Type 2 Two-Seat Fighter"; the Allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
reporting name was "Nick". Originally serving as a long-range escort-fighter, the design — as with most heavy fighters of the period — fell prey to smaller, lighter, more agile single-engine fighters. As such, the Ki-45 instead served as a day and nighttime interceptor
Interceptor may refer to:
Vehicles
* Interceptor aircraft (or simply "interceptor"), a type of point defense fighter aircraft designed specifically to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft
* Ford Crown Victoria Police Interceptor, a police car
* ...
and strike-fighter.
Design and development
In response to the rapid emergence in Europe of twin-engine heavy fighters such as the Messerschmitt Bf 110, the army ordered development of a twin-engine, two-seat fighter in 1937, and assigned the proposal by Kawasaki Shipbuilding the designation of ''Ki-38''. This only went as far as a mock up, but by December of that year the army ordered a workingprototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototyp ...
as the ''Ki-45'', which first flew in January 1939. Results from the test flights, however, did not meet the army's expectations. The Ha-20 ''Otsu'' engine was underpowered and failure-prone, while the airframe suffered from nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a "streamlined body, sized according to what it contains", such as an engine, fuel, or equipment on an aircraft. When attached by a pylon entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attached ...
stall.
The Ki-45 did not enter service, but the army, insistent on having a working twin-engine fighter, ordered Kawasaki to continue development. Kawasaki responded by replacing the engines with the proven Nakajima Ha-25. Flight tests were promising.
In October 1940, the army ordered continued improvements such as switching to 805 kW (1,080 hp) Mitsubishi Ha-102 engines. This craft, designated ''Ki-45 Kai'', was completed in September 1941 and was officially adopted for use by the army in February 1942 as the "Type 2 two-seat fighter".
The prototype of a single-seat fighter variant, the ''Ki-45 II'', was also built; development continued under the designation Ki-96.
Operational history
 The Ki-45 was initially used as a long-range
The Ki-45 was initially used as a long-range bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped ...
escort. The 84th Independent Flight Wing (Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai) used them in June 1942 in attacks on Guilin, where they encountered, but were no match for, Curtiss P-40s flown by the Flying Tigers
The First American Volunteer Group (AVG) of the Republic of China Air Force, nicknamed the Flying Tigers, was formed to help oppose the Japanese invasion of China. Operating in 1941–1942, it was composed of pilots from the United States Ar ...
. In September of the same year, they met P-40s over Hanoi
Hanoi or Ha Noi ( or ; vi, Hà Nội ) is the capital and second-largest city of Vietnam. It covers an area of . It consists of 12 urban districts, one district-leveled town and 17 rural districts. Located within the Red River Delta, Hanoi is ...
with similar results. It became clear that the Ki-45 could not hold its own against single-engine fighters in aerial combat.
It was subsequently deployed in several theaters in the roles of interception, attack
Attack may refer to:
Warfare and combat
* Offensive (military)
* Charge (warfare)
* Attack (fencing)
* Strike (attack)
* Attack (computing)
* Attack aircraft
Books and publishing
* ''The Attack'' (novel), a book
* '' Attack No. 1'', comic an ...
(anti-ground as well as anti-shipping) and fleet defense. Its greatest strength turned out to be as an anti-bomber interceptor
Interceptor may refer to:
Vehicles
* Interceptor aircraft (or simply "interceptor"), a type of point defense fighter aircraft designed specifically to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft
* Ford Crown Victoria Police Interceptor, a police car
* ...
, as was the case with the Bf 110 in Europe. In New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of ...
, the IJAAF used the aircraft in an anti-ship role, where the Ki-45 was heavily armed with one 37 mm (1.46 in) and two 20 mm cannons and could carry two 250 kg (550 lb) bombs on hard points under the wings. 1,675 Ki-45s of all versions were produced during the war.
The first production type (''Ko'') was armed with two 12.7 mm (.50 in) Ho-103 machine gun
A machine gun is a fully automatic, rifled autoloading firearm designed for sustained direct fire with rifle cartridges. Other automatic firearms such as automatic shotguns and automatic rifles (including assault rifles and battle rifles) a ...
in the nose, a single Type 97 20 mm cannon in the belly offset to the right, and a trainable 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine gun in the rear cabin; this was followed by the ''Otsu'' with the lower 20 mm cannon replaced by a 37 mm (1.46 in) type 94 tank gun, to counter B-17 Flying Fortress
The Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress is a four-engined heavy bomber developed in the 1930s for the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC). Relatively fast and high-flying for a bomber of its era, the B-17 was used primarily in the European Theater ...
bombers. While the firepower was devastating, manual reloading meant that typically only two rounds could be fired on each gunnery pass. The next type (''Hei'') restored the 20 mm cannon, and this time placed an automatic 37 mm (1.46 in) gun in the nose. A later addition in the ''Tei'' type were twin obliquely-firing 20 mm Ho-5 cannons behind the cockpit, and often propulsive exhaust stacks.
Soon after entering service, the Ki-45 was assigned to home defense, and several were dispatched against the Doolittle raid, though they did not see action. The craft's heavy armament proved to be effective against the B-29 Superfortress raids which started in June 1944
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 2 – WWII:
** Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in Nor ...
. However, its performance was insufficient to counter B-29s flying at 10,000 m (32,800 ft). Modifications such as reduction of fuel and ordnance were attempted to raise performance, to little avail, and in the end aircraft were used effectively in aerial ramming
Aerial ramming or air ramming is the ramming of one aircraft with another. It is a last-ditch tactic in air combat, sometimes used when all else has failed. Long before the invention of aircraft, ramming tactics in naval warfare and ground warfare ...
attacks.
They were also used in '' kamikaze'' attacks, such as the attack on on 2 April 1945 off Okinawa. The commanding officer and 54 crew were killed when a Toryu clipped the stacks from astern, and rammed the bridge. A second Toryu hit the foredeck, opening a 7 m (23 ft) hole in the deck. The ensuing fires demolished the ship, and after the surviving crew was rescued by fellow fast transports, destroyer escort and destroyer-transport , the ship was towed out to sea and scuttled.
In 1945, the forward and upward-firing guns showed some results with the commencement of night time bombing raids, but the lack of radar was a considerable handicap. By the spring of 1945, the advent of American carrier-based fighters and Iwo Jima
Iwo Jima (, also ), known in Japan as , is one of the Japanese Volcano Islands and lies south of the Bonin Islands. Together with other islands, they form the Ogasawara Archipelago. The highest point of Iwo Jima is Mount Suribachi at high.
...
-based P-51s and P-47s escorting B-29s over the skies of Japan brought the Ki-45's career to an end.
The next version, the ''Kawasaki Ki-45 KAId'', was developed specifically as a night fighter, which was supposed to be equipped with centimetric radar in the nose; due to production difficulties, this did not occur. The aircraft took part in night defense of the Home Islands and equipped four ''sentais'' from the autumn of 1944 to the war's end. They obtained notable successes, and one Ki-45 ''sentai'' claimed 150 victories, including eight USAAF B-29 Superfortresses in their first combat.
The Ki-45 was to be replaced in the ground-attack role by the Ki-102, but was not wholly supplanted by the war's end.
Three Ki-45s fell into communist Chinese hands after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Unlike most captured Japanese aircraft, which were employed in the training role, the three Ki-45s were assigned to the 1st Squadron of the Combat Flying Group in March 1949 and were used in combat missions. These aircraft were retired in the early 1950s.
Variants
There is sometimes a confusion in the different subtypes. The information below is based on Japanese work, not on usual 'western' data. Even the NASM claims that the Ki-45 on display is a ''hei'' (c) type whereas Japanese press would read it is a ''tei'' (d) type nightfighter version with dorsal armament.
 ; Ki-45: Prototype aircraft
; KI-45 Type 1: Modified operative models
; Ki-45 KAI: Prototype aircraft
; Ki-45 KAI: Pre-series aircraft
; Ki-45 KAIa (ko/甲):''Toryu'': Two-seat fighter Type 2 of the army (Mark A) initial model of series, one 20 mm Ho-3 in ventral position, two Ho-103 12.7 mm in the nose and a flexible 7.92 mm in the back position
; Ki-45 KAIb (otsu/乙): retrofit version based on the KAIa, 20 mm belly cannon replaced by a 37 mm type 94 anti-tank gun
; Ki-45 KAIc (hei/丙): Mark C version against naval objectives, one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 automatic cannon in the nose, one 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine gun in the back position.
; Ki-45 KAId (tei/丁): Mark D, a modified Model B, night fighter version, equipped with one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 cannon in nose and two fixed 20 mm
; Ki-45: Prototype aircraft
; KI-45 Type 1: Modified operative models
; Ki-45 KAI: Prototype aircraft
; Ki-45 KAI: Pre-series aircraft
; Ki-45 KAIa (ko/甲):''Toryu'': Two-seat fighter Type 2 of the army (Mark A) initial model of series, one 20 mm Ho-3 in ventral position, two Ho-103 12.7 mm in the nose and a flexible 7.92 mm in the back position
; Ki-45 KAIb (otsu/乙): retrofit version based on the KAIa, 20 mm belly cannon replaced by a 37 mm type 94 anti-tank gun
; Ki-45 KAIc (hei/丙): Mark C version against naval objectives, one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 automatic cannon in the nose, one 7.92 mm (.312 in) machine gun in the back position.
; Ki-45 KAId (tei/丁): Mark D, a modified Model B, night fighter version, equipped with one 37 mm (1.46 in) Ho-203 cannon in nose and two fixed 20 mm Ho-5 cannon
The Ho-5 (Army Type 2) was a Japanese aircraft autocannon used during World War II. Developed from the Ho-103 machine gun, it was a version of the American Model 1921 Browning aircraft machine gun. It replaced the Ho-1 and Ho-3 (Army Type 97 ...
s in a Schräge Musik-style dorsal frontal position, and one 7.92 mm (.312 in) Type 98 machine gun in the back position
; Ki-45 II : Single-seat fighter prototype; later re-designated '' Ki-96''
Total production: 1,691 or 1,701 units.
Operators
 ;
* Imperial Japanese Army Air Force
**No. 25 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 71 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 84 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 4 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 5 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 13 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 16 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 21 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 27 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 45 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 53 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 65 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 70 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**Akeno Army Fighter Training School
;
* Manchukuo Air Force
;
* People's Liberation Army Air Force
;
* Imperial Japanese Army Air Force
**No. 25 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 71 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 84 Dokuritsu Hikō Chutai IJAAF
**No. 4 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 5 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 13 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 16 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 21 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 27 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 45 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 53 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 65 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**No. 70 Hikō Sentai IJAAF
**Akeno Army Fighter Training School
;
* Manchukuo Air Force
;
* People's Liberation Army Air Force
Surviving aircraft
Only one Ki-45 KAIc remains today. It was one of about 145 Japanese aircraft brought to the United States aboard the USS ''Barnes'' for evaluation after World War II. It underwent an overhaul at Middletown Air Depot, Pennsylvania, and was test-flown at Wright Field, Ohio, and Naval Air Station Anacostia in Washington, D.C.. The United States Army Air Forces donated the Toryu to the Smithsonian Institution in June 1946. The fuselage only is currently on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center, alongside a Nakajima J1N and Aichi M6A, but the rest of the aircraft is in storage at the Paul E. Garber Preservation, Restoration, and Storage Facility.Specifications (Ki-45 KAIc)

See also
References
:Notes ;Bibliography * "Army Type 2 two-seat fighter Toryu". ''Famous Airplanes of the World #21.'' Tokyo: Bunrindo, 1990. . * (new edition 1987 by Putnam Aeronautical Books, .) * * *External links
Fred Hargesheimer and ERA/Univac Story
{{Authority control Ki-45, Kawasaki Ki-045 Low-wing aircraft Aircraft first flown in 1941 Twin piston-engined tractor aircraft