Kandyan Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Kandy was a monarchy on the island of Sri Lanka, located in the central and eastern portion of the island. It was founded in the late 15th century and endured until the early 19th century.
Initially a client kingdom of the
Kandyan Kingdom Full view book These include: * Kanda Uda Pasrata * The Senkadagala Kingdom * The Kanda Udarata * The Mahanuwara Kingdom * Sri Wardhanapura * Sinhalé * Thun Sinhalaya or Tri Sinhala * Kande Nuwara * The Kingdom of Kandy
 Much of the Kandy Kingdom's territory was located in Sri Lanka's mountainous and thickly forested interior, with mountain passes to the capital providing plenty of opportunities for defenders to stage ambushes. Routes to the city were kept secret, and spreading information concerning them could often result in
Much of the Kandy Kingdom's territory was located in Sri Lanka's mountainous and thickly forested interior, with mountain passes to the capital providing plenty of opportunities for defenders to stage ambushes. Routes to the city were kept secret, and spreading information concerning them could often result in

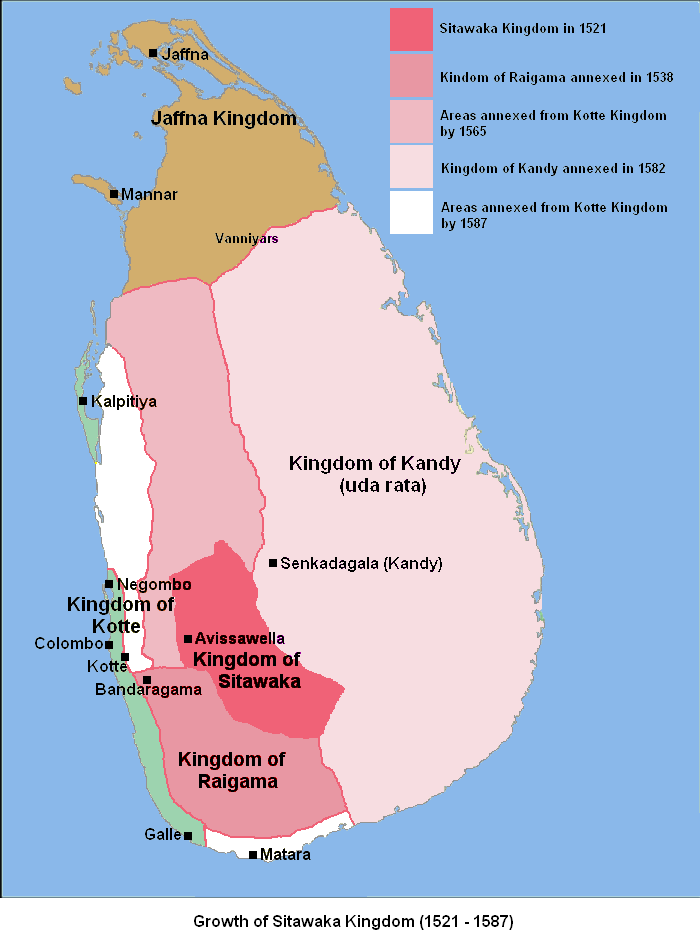 Following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, the kingdom of Kotte split into three competing states – Sithawaka, Raigama, and Bhuvanekabahu VII's kingdom of Kotte. Of these Sithawaka, under the dynamic leadership of Mayadunne, posed the greatest threat to the autonomy of the other states. In 1522, the Kandyans secured Portuguese protection against Sithawaka, but any potential for alliance ended in 1546 when Portuguese and Kotte forces invaded the kingdom. Kandy subsequently lent aid to the Jaffna Kingdom against the Portuguese in 1560.
Kandy territory was invaded twice in the 1570s and 1580s, first in 1574, and then in 1581 by the newly crowned king of Sithawaka Rajasinghe I. Rajasinghe – who had already scored a significant victory over the Portuguese at the
Following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, the kingdom of Kotte split into three competing states – Sithawaka, Raigama, and Bhuvanekabahu VII's kingdom of Kotte. Of these Sithawaka, under the dynamic leadership of Mayadunne, posed the greatest threat to the autonomy of the other states. In 1522, the Kandyans secured Portuguese protection against Sithawaka, but any potential for alliance ended in 1546 when Portuguese and Kotte forces invaded the kingdom. Kandy subsequently lent aid to the Jaffna Kingdom against the Portuguese in 1560.
Kandy territory was invaded twice in the 1570s and 1580s, first in 1574, and then in 1581 by the newly crowned king of Sithawaka Rajasinghe I. Rajasinghe – who had already scored a significant victory over the Portuguese at the
 Relations between the Dutch Republic and the Kandyans were initiated on 2 June 1602 when Dutch explorer
Relations between the Dutch Republic and the Kandyans were initiated on 2 June 1602 when Dutch explorer 
 Relations between the Dutch and the Kandyans had been difficult from the onset and the alliance fell apart in the 1640s. The two sides joined forces again in the 1650s to expel the Portuguese, but a final break occurred in 1656 in the aftermath of the fall of Colombo after a six-month siege and the final expulsion of the Portuguese from Sri Lanka. Rajasinha demanded that the fort be handed over to the Kandyans for demolition; in November, the Dutch refused and drove the king and his army from the vicinity. Rajasinha's hold over his own population was tenuous, and rebellions against him in 1664 and 1671 gave the Dutch the opportunity to seize large parts of Sabaragamuwa in 1665, as well as Kalpitiya, Kottiyar, Batticaloa and Trincomalee. The seizure of the ports was a serious blow to the Kandyan kingdom – not only were Dutch holdings now more or less coterminous with the territory the Portuguese had held, but all Kandyan trade was now in Dutch hands. Rajasinha attempted to negotiate an alliance with
Relations between the Dutch and the Kandyans had been difficult from the onset and the alliance fell apart in the 1640s. The two sides joined forces again in the 1650s to expel the Portuguese, but a final break occurred in 1656 in the aftermath of the fall of Colombo after a six-month siege and the final expulsion of the Portuguese from Sri Lanka. Rajasinha demanded that the fort be handed over to the Kandyans for demolition; in November, the Dutch refused and drove the king and his army from the vicinity. Rajasinha's hold over his own population was tenuous, and rebellions against him in 1664 and 1671 gave the Dutch the opportunity to seize large parts of Sabaragamuwa in 1665, as well as Kalpitiya, Kottiyar, Batticaloa and Trincomalee. The seizure of the ports was a serious blow to the Kandyan kingdom – not only were Dutch holdings now more or less coterminous with the territory the Portuguese had held, but all Kandyan trade was now in Dutch hands. Rajasinha attempted to negotiate an alliance with
 Kirti Sri Rajasinha died in the midst of these events in January 1796, and was succeeded by his brother Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha. The new king rejected the terms of Migastenne's treaty, depriving the kingdom of the opportunity to regain the lands it had lost a generation earlier. It proved to be a fateful decision; the British immediately set about organising their new acquisitions, establishing systems of government, education, and justice. With the appointment of Frederick North (1798–1805) as the first
Kirti Sri Rajasinha died in the midst of these events in January 1796, and was succeeded by his brother Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha. The new king rejected the terms of Migastenne's treaty, depriving the kingdom of the opportunity to regain the lands it had lost a generation earlier. It proved to be a fateful decision; the British immediately set about organising their new acquisitions, establishing systems of government, education, and justice. With the appointment of Frederick North (1798–1805) as the first
 The British fought their way to Kandy, encountering Kandyan resistance led in part by a
The British fought their way to Kandy, encountering Kandyan resistance led in part by a  In November 1814, ten British subjects were captured and mutilated in Kandyan territory. Governor
In November 1814, ten British subjects were captured and mutilated in Kandyan territory. Governor
, Asian Tribune, Sat, 2011-03-12. Retrieved 21 October 2013.Sumanawathie's success brings lustre back to Uva Wellassa
Ceylon Daily News, 21 October 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013. Brownrigg also issued a Sri Lanka Gazette Notification that condemned anyone who participated in the Great Uprising with property confiscation, extradition to Mauritius, and even execution. (This Gazette Notification labelling the rebels as "traitors" was only revoked two centuries later, in 2017, with 81 leaders of the freedom struggle being formally declared as National Heroes.) Molligoda, however, ensured the road to Kandy remained open and on 30 October Keppetipola was captured. His associate Madugalle Adikaram was captured on 1 November, and thereafter the rebellion collapsed. Both leaders were beheaded on 26 November 1817. Viewing the convention as null and void, the British set about breaking the power of the nobility. Though smaller uprisings occurred in 1820, 1823, and 1824, none of them seriously threatened the British government of the highlands. The area of the central highlands in which the Kandyan kingdom was situated had the natural protection of rivers, waterways, hills and rocky mountainous terrain. The prominent location of the Kandyan kingdom with its cool climate had greatly contributed to protecting the independence of the nation for nearly three centuries.


 The Kingdom of Kandy was governed by customs and traditions that have descended over the centuries which forms the basis of both the civil and criminal legal system that existed in the kingdom. Parts of this traditional law have been codified into the current legal framework of Sri Lanka as the
The Kingdom of Kandy was governed by customs and traditions that have descended over the centuries which forms the basis of both the civil and criminal legal system that existed in the kingdom. Parts of this traditional law have been codified into the current legal framework of Sri Lanka as the
 The Kingdom of Kandy did not maintain a large standing army. The King maintained a full-time
The Kingdom of Kandy did not maintain a large standing army. The King maintained a full-time
 The state religion was Buddhism. Due to the activities of the Portuguese, ordained Buddhist monks were absent by the Dutch era. After the arrival of the Nayak dynasty, Buddhism was again firmly established in the island. The dynasty of Vimaladharmasurya I largely tolerated the presence of
The state religion was Buddhism. Due to the activities of the Portuguese, ordained Buddhist monks were absent by the Dutch era. After the arrival of the Nayak dynasty, Buddhism was again firmly established in the island. The dynasty of Vimaladharmasurya I largely tolerated the presence of

British Ceylon and Kingdom of Kandy 1805 (map)
Kandyan KingdomDiscover Charming Kandy
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom Of Kandy Kingdoms of Sri Lanka Former countries in South Asia Former monarchies of South Asia 1815 disestablishments in Ceylon History of Kandy 1469 establishments in Asia 15th-century establishments in Sri Lanka States and territories established in the 1460s
Kingdom of Kotte
The Kingdom of Kotte ( si, කෝට්ටේ රාජධානිය, Kottay Rajadhaniya), named after its capital, Kotte, was a Sinhalese kingdom that flourished in Sri Lanka during the 15th century.
Kotte, under the rule of Ming-backed ...
, Kandy gradually established itself as an independent force during the tumultuous 16th and 17th centuries, allying at various times with the Jaffna Kingdom, the Madurai Nayak dynasty of South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
, Sitawaka Kingdom, and the Dutch colonizers to ensure its survival.
From the 1590s, it was the sole independent native polity on the island of Sri Lanka and through a combination of hit-and-run tactics
Hit-and-run tactics are a tactical doctrine of using short surprise attacks, withdrawing before the enemy can respond in force, and constantly maneuvering to avoid full engagement with the enemy. The purpose is not to decisively defeat the en ...
and diplomacy kept European colonial forces at bay, before finally falling under British colonial rule
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts est ...
in 1818.
The kingdom was absorbed into the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
as a protectorate
A protectorate, in the context of international relations, is a state that is under protection by another state for defence against aggression and other violations of law. It is a dependent territory that enjoys autonomy over most of its int ...
following the Kandyan Convention of 1815, and definitively lost its autonomy following the Uva Rebellion
UVA most often refers to:
* Ultraviolet A, a type of ultraviolet radiation
* University of Virginia, a public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States
Uva or UVA may also refer to:
Places
* Uva, Missouri, an unincorpora ...
of 1817.
Name
Over the years, the Kingdom of Kandy has been known by many names.Chapter 1Kandyan Kingdom Full view book These include: * Kanda Uda Pasrata * The Senkadagala Kingdom * The Kanda Udarata * The Mahanuwara Kingdom * Sri Wardhanapura * Sinhalé * Thun Sinhalaya or Tri Sinhala * Kande Nuwara * The Kingdom of Kandy
Geography and climate
 Much of the Kandy Kingdom's territory was located in Sri Lanka's mountainous and thickly forested interior, with mountain passes to the capital providing plenty of opportunities for defenders to stage ambushes. Routes to the city were kept secret, and spreading information concerning them could often result in
Much of the Kandy Kingdom's territory was located in Sri Lanka's mountainous and thickly forested interior, with mountain passes to the capital providing plenty of opportunities for defenders to stage ambushes. Routes to the city were kept secret, and spreading information concerning them could often result in death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain ...
. Many routes into the hill country became impassable during the annual monsoon, and malaria was rife. Throughout its existence Kandyan forces used the land to their advantage, engaging in guerrilla warfare against invading forces, and evacuating major urban centres when enemy forces drew near – a tactic used with particular effect during the Kandyan Wars
The Kandyan Wars (or the Kandian Wars) refers generally to the period of warfare between the British colonial forces and the Kingdom of Kandy, on the island of what is now Sri Lanka, between 1796 and 1818. More specifically it is used to descri ...
. Though the kingdom had intermittent access to the port of Batticaloa it had no naval forces and could not prevent the Portuguese and Dutch from maintaining a strong presence in lowland areas.
History
Foundation
The city of Senkadagalapura may have been founded as early as the mid-14th century during the reign ofVikramabahu III of Gampola
Vikramabahu III was King of Gampola who ruled from 1357 to 1374. He succeeded his Uncle Parakramabahu V as King of Gampola and was succeeded by his nephew Bhuvanaikabahu V.
See also
* List of Sri Lankan monarchs
* History of Sri Lanka
T ...
(1357–1374). Central Sri Lanka was ruled by the kings of Kotte from the early 15th to late 16th centuries; with Kotte's weakening in the face of Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
influence the area developed into an autonomous domain with Senkadagalapura at its capital. Following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, and the subsequent partition of the kingdom of Kotte, Kandy asserted its independence and emerged as a serious rival to the eastern and southern kingdoms.
Rise: 1521–1594

 Following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, the kingdom of Kotte split into three competing states – Sithawaka, Raigama, and Bhuvanekabahu VII's kingdom of Kotte. Of these Sithawaka, under the dynamic leadership of Mayadunne, posed the greatest threat to the autonomy of the other states. In 1522, the Kandyans secured Portuguese protection against Sithawaka, but any potential for alliance ended in 1546 when Portuguese and Kotte forces invaded the kingdom. Kandy subsequently lent aid to the Jaffna Kingdom against the Portuguese in 1560.
Kandy territory was invaded twice in the 1570s and 1580s, first in 1574, and then in 1581 by the newly crowned king of Sithawaka Rajasinghe I. Rajasinghe – who had already scored a significant victory over the Portuguese at the
Following the Spoiling of Vijayabahu in 1521, the kingdom of Kotte split into three competing states – Sithawaka, Raigama, and Bhuvanekabahu VII's kingdom of Kotte. Of these Sithawaka, under the dynamic leadership of Mayadunne, posed the greatest threat to the autonomy of the other states. In 1522, the Kandyans secured Portuguese protection against Sithawaka, but any potential for alliance ended in 1546 when Portuguese and Kotte forces invaded the kingdom. Kandy subsequently lent aid to the Jaffna Kingdom against the Portuguese in 1560.
Kandy territory was invaded twice in the 1570s and 1580s, first in 1574, and then in 1581 by the newly crowned king of Sithawaka Rajasinghe I. Rajasinghe – who had already scored a significant victory over the Portuguese at the Battle of Mulleriyawa
The Battle of Mulleriyawa ( si, මුල්ලේරියාව සටන) in 1559 was part of the Sinhalese–Portuguese War. It was one of the most decisive battles in Sri Lankan history and considered as the worst defeat of Portuguese dur ...
– succeeded in annexing the kingdom outright; the Kandyan king Karalliyadde Kumara Bandara (also known as Jayavira III) fled north to the Jaffna Kingdom with his daughter, Kusumasana Devi (also known as Dona Catherina of Kandy
Kusumāsana Devi (died 10 July 1613), also known as , was ruling Queen of Kandy in 1581. She was deposed, but queen consort of Kandy by marriage to Vimaladharmasuriya I of Kandy from 1594 to 1604.
Life
In her infancy she and her father Karaliy ...
) and her husband Yamasinghe Bandara. Both eventually adopted Portuguese worship, converted to Christianity and adopted the names Dona Catherina and Don Philipe respectively. In the meanwhile the Portuguese also laid claim to the Kandyan realm, citing Dharmapala
A ''dharmapāla'' (, , ja, 達磨波羅, 護法善神, 護法神, 諸天善神, 諸天鬼神, 諸天善神諸大眷屬) is a type of wrathful god in Buddhism. The name means "'' dharma'' protector" in Sanskrit, and the ''dharmapālas'' are a ...
's donation
A donation is a gift for charity, humanitarian aid, or to benefit a cause. A donation may take various forms, including money, alms, services, or goods such as clothing, toys, food, or vehicles. A donation may satisfy medical needs such as ...
of 1580 as a precedentPatrick Peebles, ''The History of Sri Lanka'', 2006, p 37
Sithawakan rule over Kandy proved difficult to enforce. Wirasundara Mudiyanse, Rajasinghe's viceroy in the area, rebelled soon after the initial conquest; though his uprising was crushed another occurred in 1588. Resistance eventually coalesced around Konnappu Bandara, son of Wirasundara, who had fled to Portuguese lands following his father's murder by agents of Rajasinghe. Between 1591 and 1594, he returned to the area, seized the Kandyan throne under the name Wimaladharmasuriya I and married Dona Catherina. Victories over the Sithawakans and the Portuguese (who occupied Kandy briefly in 1592) secured his position.
The strategic situation in Sri Lanka changed dramatically during Wimaladharmasurya's rise to power. To the north, the Portuguese deposed the king Puviraja Pandaram
Puviraja Pandaram ( ta, புவிராஜ பண்டாரம்) (died 1591) ruled the Jaffna kingdom during a period of chaos during and after the death of his father Cankili I in 1565. He became king in 1561 following a local uprising a ...
of the Jaffna Kingdom in 1591 and installed his son Ethirimana Cinkam
Ethirimanna Cinkam ( ta, எதிர்மன்னசிங்கம்) (died 1617) was the penultimate ruler of the Aryacakravarti line of Kings of the Jaffna Kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. He came to power due to the second Portuguese expedi ...
as client king. In 1594, Rajasinghe I died and the kingdom of Sithawaka disintegrated. Kandy remained the sole native polity outside of European dominance. In 1595, Wimaladharmasuriya brought the sacred Tooth Relic
The relic of the tooth of Buddha (Pali ''danta dhātuya'') is venerated in Sri Lanka as a sacred cetiya relic of Lord Buddha, who is the founder of Buddhism, the fourth largest religion worldwide.
History The relic in India
According to Sri Lanka ...
– the traditional symbol of royal and religious authority amongst the Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
– to Kandy, and Kandy entered a long period of attritionary warfare with the Portuguese, starting with the Campaign of Danture
The Danture campaign comprised a series of encounters between the Portuguese and the Kingdom of Kandy in 1594, part of the Sinhalese–Portuguese War. It is considered a turning point in the indigenous resistance to Portuguese expansion. For t ...
.
Consolidation and interactions with the Dutch: 1594–1739
Hostilities between the Portuguese and the Kandyans continued throughout the rest of Wimaladharmasuriya's reign. The Kandyans lent aid to a rebellion led by Domingos Corrêa and later Simão Corrêa, Sinhalese subjects of Dharmapala, between 1594 and 1596. A Portuguese incursion in 1604 saw them capture Balane, but dissent amongst their Lascarin troops forced a withdrawal back to the coast. Relations between the Dutch Republic and the Kandyans were initiated on 2 June 1602 when Dutch explorer
Relations between the Dutch Republic and the Kandyans were initiated on 2 June 1602 when Dutch explorer Joris van Spilbergen
Joris van Spilbergen (1568 in Antwerp – January 31, 1620 in Bergen op Zoom) was a Dutch naval officer.
Joris van Spilbergen was born in Antwerp in 1568.
His first major expedition was in 1596, when he sailed to Africa.
He then left for As ...
arrived at Santhamuruthu on the eastern coast of Sri Lanka. Later that year the Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock ...
despatched Sebald de Weert
Sebald or Sebalt de Weert (May 2, 1567 – May 30 or June 1603) was a Flemish captain and vice-admiral of the Dutch East India Company (known in Dutch as ''Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie'', VOC). He is most widely remembered for accurately p ...
to Kandy in an attempt to negotiate a treaty. The visit ended in disaster when the visitors offended their Kandyan hosts with their behaviour and in the ensuing fracas, de Weert and several of his entourage were killed.
Wimaladharmasuriya died in 1604. The throne passed to his cousin, Senarat, who at the time of the king's death was an ordained priest, but left the sangha
Sangha is a Sanskrit word used in many Indian languages, including Pali meaning "association", "assembly", "company" or "community"; Sangha is often used as a surname across these languages. It was historically used in a political context t ...
and married Dona Catherina. ''Kuruvita Rala
Kuruvita Rala (also spelled ''Kuruwita Rala,'' also known as ''Antonio Barreto'' and ''Kuruvita Bandara'') was a Sri Lankan rebel leader and prince of Uva, who served as regent in the kingdom of Kandy. He was also a relation of Dona Catherina, Q ...
'', the Prince of Uva of the Karava lineage, raided the Kandy Kingdom and drove Senerat out of his capital. In 1611 Portuguese forces captured Kandy in the name of the pretender Mayadunne of Uva and torched the city yet again. In 1619, Cankili II
Cankili II ( ta, சங்கிலி குமாரன், translit=Caṅkili Kumāraṉ; died 1619) was the last king of the Jaffna kingdom and was a usurper who came to throne with a palace massacre of the royal prince and the regent Ara ...
was deposed and the Jaffna Kingdom absorbed into the Portuguese Empire. Despite these setbacks, Senarat survived as the king and in 1612 had even concluded a treaty with the VOC
VOC, VoC or voc may refer to:
Science and technology
* Open-circuit voltage (VOC), the voltage between two terminals when there is no external load connected
* Variant of concern, a category used during the assessment of a new variant of a virus
...
. When help came it was in the form of a Danish East India Company
The Danish East India Company ( da, Ostindisk Kompagni) refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-fo ...
fleet which arrived in 1620, but failed to secure Trincomalee and was expelled by the Portuguese.
The Portuguese strengthened their position throughout the 1620s, building forts at Kalutara
Kalutara ( si, කළුතර, ta, களுத்துறை) or Kalutota is a major city in Kalutara District, Western Province, Sri Lanka. It is also the administrative capital of Kalutara District. It is located approximately south o ...
, Trincomalee
Trincomalee (; ta, திருகோணமலை, translit=Tirukōṇamalai; si, ත්රිකුණාමළය, translit= Trikuṇāmaḷaya), also known as Gokanna and Gokarna, is the administrative headquarters of the Trincomalee Dis ...
, Batticaloa, and in Sabaragamuwa
The Sabaragamuwa Province ( si, සබරගමුව පළාත ''Sabaragamuwa Paḷāta'', ta, சபரகமுவ மாகாணம் ''Sabaragamuwa Mākāṇam'') is one of the nine provinces of Sri Lanka, the first level administrati ...
, and upgrading fortifications in Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo m ...
, Galle
Galle ( si, ගාල්ල, translit=Gālla; ta, காலி, translit=Kāli) (formerly Point de Galle) is a major city in Sri Lanka, situated on the southwestern tip, from Colombo. Galle is the provincial capital and largest city of Southern ...
, and Manikkadawara. A disastrous defeat at the Battle of Randeniwela
The Battle of Randeniwela was a battle fought on 25 August 1630 in the Sinhalese–Portuguese War. It was fought between Portuguese Empire and King Senarth's youngest son Prince Maha Astana, who would later become Rajasinghe II against Por ...
on 2 August 1630 in which Portuguese captain-general Constantino de Sá de Noronha was killed resulted in large parts of Portuguese Ceilao being overrun by the Kandyans. Internal instability yet again prevented the Kandyans from securing their acquisitions, and by the time of Senarat's death in 1635 lowland Sri Lanka was once again under Portuguese control.
The throne now passed to Senarat's son Rajasinha II
King Rajasinghe II, also known as Rajasingha II (pre coronation, Prince Deva Astana), was a Sinhalese King, reigned 1629 – 6 December 1687; third king of the Kingdom of Kandy in Sri Lanka. Rajasingha requested Netherlands, Dutch aid to help exp ...
, who led the Kandyans to a major victory over the Portuguese at Gannoruwa on 28 March 1638. The battle was to be the last major military victory for the kingdom of Kandy and succeeded in severely weakening the Portuguese presence in Sri Lanka. In May of that year he concluded a wide-ranging alliance with the Dutch, who were by now in control of Batavia
Batavia may refer to:
Historical places
* Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies, present-day Jakarta, the former capital of the Dutch East In ...
. Batticaloa and Trincomalee fell in 1639, Galle in 1640, and Kandyan forces seized Portuguese territories further inland.

 Relations between the Dutch and the Kandyans had been difficult from the onset and the alliance fell apart in the 1640s. The two sides joined forces again in the 1650s to expel the Portuguese, but a final break occurred in 1656 in the aftermath of the fall of Colombo after a six-month siege and the final expulsion of the Portuguese from Sri Lanka. Rajasinha demanded that the fort be handed over to the Kandyans for demolition; in November, the Dutch refused and drove the king and his army from the vicinity. Rajasinha's hold over his own population was tenuous, and rebellions against him in 1664 and 1671 gave the Dutch the opportunity to seize large parts of Sabaragamuwa in 1665, as well as Kalpitiya, Kottiyar, Batticaloa and Trincomalee. The seizure of the ports was a serious blow to the Kandyan kingdom – not only were Dutch holdings now more or less coterminous with the territory the Portuguese had held, but all Kandyan trade was now in Dutch hands. Rajasinha attempted to negotiate an alliance with
Relations between the Dutch and the Kandyans had been difficult from the onset and the alliance fell apart in the 1640s. The two sides joined forces again in the 1650s to expel the Portuguese, but a final break occurred in 1656 in the aftermath of the fall of Colombo after a six-month siege and the final expulsion of the Portuguese from Sri Lanka. Rajasinha demanded that the fort be handed over to the Kandyans for demolition; in November, the Dutch refused and drove the king and his army from the vicinity. Rajasinha's hold over his own population was tenuous, and rebellions against him in 1664 and 1671 gave the Dutch the opportunity to seize large parts of Sabaragamuwa in 1665, as well as Kalpitiya, Kottiyar, Batticaloa and Trincomalee. The seizure of the ports was a serious blow to the Kandyan kingdom – not only were Dutch holdings now more or less coterminous with the territory the Portuguese had held, but all Kandyan trade was now in Dutch hands. Rajasinha attempted to negotiate an alliance with France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, who seized Trincomalee but were expelled by the Dutch in 1672. Kandyan campaigns in 1675 and 1684 recaptured some territory, but by the time of Rajasinha's death in 1687 neither city had returned to Kandyan control.H. W. Codrington, ''A Short History of Sri Lanka'', chap. 9.
Rajasinha's son ascended to the throne as Vimaladharmasuriya II, and his twenty-year reign (1687–1707) proved relatively peaceable. A trade war broke out in 1701 when the Kandyans closed their borders with Dutch territories in order to stimulate trade through the ports of Puttalam
Puttalam ( si, පුත්තලම, translit=Puttalama; ta, புத்தளம், translit=Puttaḷam) is the largest town in Puttalam District, North Western Province, Sri Lanka. Puttalam is the administrative capital of the Puttalam Di ...
and Kottiyar. As a result, the Dutch lost control of the areca nut
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ''Areca'' is derived from a name ...
trade and retaliated; by 1707 Kandyan borders had reopened and both ports were closed. Upon his death Vimaladharmasurya was succeeded by his son, who ruled as Vira Narendra Sinha. Several anti-Dutch uprisings occurred in the lowlands during the course of the 1720s and 1730s; the Kandyans in turn declared war on the Dutch in 1736 and seized some territory. Hostilities subsided with the appointment of Gustaaf Willem van Imhoff
Gustaaf Willem, Baron van Imhoff (8 August 1705 – 1 November 1750) was a Dutch colonial administrator for the Dutch East India Company (VOC). He served as Governor of Ceylon from 1736 to 1740 and as Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies fr ...
as Governor, and by 1737 the Dutch and Kandyans were once again at peace.
The Nayakkars and the coming of the British: 1739–1803
A succession crisis emerged upon Narendrasinha's death in 1739. The king had one son – Unambuve Bandara – by a Sinhalese consort. However, succession to the Kandyan throne was reserved exclusively for those ofkshatriya
Kshatriya ( hi, क्षत्रिय) (from Sanskrit ''kṣatra'', "rule, authority") is one of the four varna (social orders) of Hindu society, associated with warrior aristocracy. The Sanskrit term ''kṣatriyaḥ'' is used in the con ...
ancestry on both their mother and father's side, and Unambuve's mother had been of a lower caste. With the support of the bhikku
A ''bhikkhu'' (Pali: भिक्खु, Sanskrit: भिक्षु, ''bhikṣu'') is an ordained male in Buddhist monasticism. Male and female monastics ("nun", ''bhikkhunī'', Sanskrit ''bhikṣuṇī'') are members of the Sangha (Buddhist c ...
Weliwita Sarankara, the crown passed to the brother of one of Narendrasinha's senior wives, a member of the Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
-speaking and Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
-speaking Nayak house from southern India. He was crowned Sri Vijaya Rajasinha later that year. The Nayak Kings were of Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
origin who practiced Shaivite
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions rangin ...
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
and were patrons of Theravada Buddhism
''Theravāda'' () ( si, ථේරවාදය, my, ထေရဝါဒ, th, เถรวาท, km, ថេរវាទ, lo, ເຖຣະວາດ, pi, , ) is the most commonly accepted name of Buddhism's oldest existing school. The school' ...
. The Nayak rulers played a huge role in reviving Buddhism in the island. They spoke Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
, which was also used as the court language in Kandy alongside Sinhala.
Relations between the Sinhalese
Sinhala may refer to:
* Something of or related to the Sinhalese people of Sri Lanka
* Sinhalese people
* Sinhala language, one of the three official languages used in Sri Lanka
* Sinhala script, a writing system for the Sinhala language
** Sinha ...
populace, including the Kandyan aristocracy, and the Nayakkars remained fraught throughout the 18th and early 19th centuries. As early as Narendrasinha's reign, attempts at appointing Nayakkars to prominent positions in court had caused rebellion, including one in 1732 that the king had only been able to crush with Dutch assistance. The Nayakkar nobility – which tended to be exclusivist and monopolise access to the king – was seen as forming an elite group privileged above the native aristocracy, the powerful adigars. Though Sri Vijaya Rajasinha's reign (1739–1747) proved relatively peaceful, his successor Kirti Sri Rajasinha had to deal with two major rebellions. The first, in 1749, was directed at his father Narenappa; the second, in 1760, was a far more dangerous insurrection which attempted to replace him with a Siam
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bo ...
ese prince. Despite these tensions, however, the Nayakkar dynasty endured, establishing support by their patronage of Buddhism and Kandyan culture.
Throughout the reigns of Sri Vijaya Rajasinha and Kirti Sri Rajasinha the Kandyans launched numerous raids and incursions into Dutch territory, including the annexation of villages in 1741, 1743, and 1745. The Dutch governors, subservient to Batavia
Batavia may refer to:
Historical places
* Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies, present-day Jakarta, the former capital of the Dutch East In ...
, were under strict orders to avoid conflict with the kingdom, without ceding any of their privileges, including the monopoly of the cinnamon trade. In 1761, however, Kirti Sri Rajasinha launched a major invasion of the low country, annexing Matara and Hanwella
Hanwella is a town in Sri Lanka, situated about from Colombo, the commercial capital of the country. Hanwella lies on the Colombo-Ratnapura main road, on the banks of the Kelani River.
Geography
This historic city belongs to the Colombo dist ...
as well as numerous frontier districts. It was to prove to be a disaster; the Dutch re-captured Matara and Hanwella in 1762, seized Puttalam
Puttalam ( si, පුත්තලම, translit=Puttalama; ta, புத்தளம், translit=Puttaḷam) is the largest town in Puttalam District, North Western Province, Sri Lanka. Puttalam is the administrative capital of the Puttalam Di ...
and Chilaw
Chilaw ( si, හලාවත, translit=Halāvata, ta, சிலாபம், translit=Cilāpam) is a large town in Puttalam District, North Western Province, Sri Lanka. It is governed by an urban council. The town is located 80 kilometres away f ...
in 1763, and then drove inland in a two-pronged invasion. The Kandyans evacuated Senkadagala, which the Dutch torched; outlying agricultural lands were also ravaged, leaving the kingdom on the brink of starvation by 1764. Kirti Sri Rajasinha requested assistance from the British in 1762 but failed to secure an alliance. By 1765 the Dutch were in a position to force a treaty upon the Kandyans returning not only the border districts but all of Kandy's coastal provinces to the Dutch; henceforth, the kingdom would be effectively cut off from the outside world. Relations between the Dutch and the Kandyans remained peaceable after this until the final expulsion of the former from the island in 1796.
Though several British sailors and priests had landed in Sri Lanka as early as the 1590s, the most famous was Robert Knox
Robert Knox (4 September 1791 – 20 December 1862) was a Scottish anatomist and ethnologist best known for his involvement in the Burke and Hare murders. Born in Edinburgh, Scotland, Knox eventually partnered with anatomist and former teach ...
who published ''An Historical Relation of the Island Ceylon
''An Historical Relation of the Island Ceylon together With somewhat Concerning Severall Remarkable passages of my life that hath hapned since my Deliverance out of Captivity'' is a book written by the English trader and sailor Robert Knox in 16 ...
'' based on his experiences during the reign of Rajasinghe II
King Rajasinghe II, also known as Rajasingha II (pre coronation, Prince Deva Astana), was a Sinhalese King, reigned 1629 – 6 December 1687; third king of the Kingdom of Kandy in Sri Lanka. Rajasingha requested Dutch aid to help expel the Portu ...
in 1681. One hundred years later, British involvement in Sri Lankan affairs commenced in earnest with the seizure of Trincomalee by Admiral Edward Hughes as part of general British-Dutch hostilities during the American War of Independence.
The tumult of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
had spread to the Netherlands by 1795, and Dutch Zeylan sided with the Batavian Republic during the ensuing conflict. The British rapidly annexed Dutch possessions in Sri Lanka, taking Trincomalee
Trincomalee (; ta, திருகோணமலை, translit=Tirukōṇamalai; si, ත්රිකුණාමළය, translit= Trikuṇāmaḷaya), also known as Gokanna and Gokarna, is the administrative headquarters of the Trincomalee Dis ...
(which had been returned to the Dutch in 1794) between 28 and 31 August, Batticaloa on 18 September, and the entirety of Jaffna
Jaffna (, ) is the capital city of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. It is the administrative headquarters of the Jaffna District located on a peninsula of the same name. With a population of 88,138 in 2012, Jaffna is Sri Lanka's 12th mo ...
on 28 September. Migastenne Disawa, the Kandyan ambassador, negotiated a treaty in Madras securing the return of much of the eastern coast to the Kandyans in February 1796; by the 15 of that month, Colombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo m ...
had fallen and Dutch rule on the island had come to an end.
 Kirti Sri Rajasinha died in the midst of these events in January 1796, and was succeeded by his brother Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha. The new king rejected the terms of Migastenne's treaty, depriving the kingdom of the opportunity to regain the lands it had lost a generation earlier. It proved to be a fateful decision; the British immediately set about organising their new acquisitions, establishing systems of government, education, and justice. With the appointment of Frederick North (1798–1805) as the first
Kirti Sri Rajasinha died in the midst of these events in January 1796, and was succeeded by his brother Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha. The new king rejected the terms of Migastenne's treaty, depriving the kingdom of the opportunity to regain the lands it had lost a generation earlier. It proved to be a fateful decision; the British immediately set about organising their new acquisitions, establishing systems of government, education, and justice. With the appointment of Frederick North (1798–1805) as the first British governor of Ceylon
The governor of Ceylon was the representative in Ceylon of the British Crown from 1795 to 1948. In this capacity, the governor was president of the Executive Council and Commander-in-Chief of the British Forces in Ceylon. The governor was the ...
, any hope of the Kandyans regaining their eastern territories essentially disappeared.
Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha died of illness on 26 July 1798 with no heir. The English East India Company and the Crown both had control over the island from 1798 until it became the British crown colony of Ceylon in 1802. Much of the king's reign had been dominated by the powerful First Minister, Pilima Talawe, who now moved to enthroned a young relative of the king, 18-year-old Konnasami as Sri Vikrama Rajasinha. Muttusami, brother-in-law of Sri Rajadhi Rajasinha also claimed the throne of Kandy, but Pilima Talauve arrested him and his sisters. The First Minister, was close to the British however could not control Sri Vickrama Rajasinha, he coveted the throne for himself, and at meetings with the British at Avissawella
Avissawella, ( si, අවිස්සාවේල්ල, ta, அவிசாவளை) is a township in Sri Lanka, governed by an Urban Council, situated on the A4 route from Colombo to Ratnapura, Colombo District, Western Province, Sri Lanka ...
between 1799 and 1801 requested British assistance in deposing Sri Vickrama Rajasinha. Complex negotiations ensued, with various ideas – including the king being moved to British lands with Pilima Talawe acting as his viceroy in Kandy - were discussed and rejected by both sides.
The territories still possessed by the Dutch on the island were formally ceded to the British in the 1802 treaty of Amiens
The Treaty of Amiens (french: la paix d'Amiens, ) temporarily ended hostilities between France and the United Kingdom at the end of the War of the Second Coalition. It marked the end of the French Revolutionary Wars; after a short peace it s ...
, but the English Company still retained a monopoly on the colony's trade. Agents of the British were put in charge of lucrative pearl fisheries, cotton plantations, salt, and tobacco monopolies. In the first three years, the government received £396,000 from pearl fisheries. This compensated for the lower price of cinnamon because of Dutch stocks in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
.
Amidst rising tension, matters came to a head when a group of Moorish British subjects were detained and beaten by agents of Pilima Talawe's. British demands for reparations were ignored by the Kandyans and so North ordered a British force to invade Kandyan lands starting the First Kandyan War. On 31 January 1803, a British force led by General Hay Macdowall marched to Kandy and found it evacuated. The British force installed Muttusami, but he was not respected by the Kandyans. The British were surrounded by hostile people, lacked food, and suffered disease. Macdowall became ill and put Major Davie in charge. The British abandoned Kandy with the sick left behind were put to death. Kandyan forces defeated the retreating British at the Mahavali River, executing Muttusami and all the British prisoners except Davie and three others. This Kandyan war lasted for two years, becoming the longest and most intensive period of the Kandyan Wars
The Kandyan Wars (or the Kandian Wars) refers generally to the period of warfare between the British colonial forces and the Kingdom of Kandy, on the island of what is now Sri Lanka, between 1796 and 1818. More specifically it is used to descri ...
, because Governor North continued to send forces to the frontiers.
Annexation and rebellion: 1803–1817
 The British fought their way to Kandy, encountering Kandyan resistance led in part by a
The British fought their way to Kandy, encountering Kandyan resistance led in part by a Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
commander known as Sangunglo. Upon their arrival they found the city deserted. Rather than torching it, they installed a puppet king, Muttusami, and left a small garrison in the town before withdrawing. The Kandyans recaptured the city, leaving only one survivor, and harried British forces down to the Mahaveli river, but were routed at Hanwella. The following year another British incursion resulted in a stalemate, and an uneasy truce was in place by 1805.
In the following decade, Sri Wickrama Rajasinha's increasingly erratic and capricious rule led to serious unrest amongst the population. A major rebellion in the Seven Korales nearly dethroned him in 1808. The powerful Pilima Talawe rebelled in 1810, was captured, and executed. In 1814, the king ordered Ehelepola Adigar, Dissava
The Mahâ Dissâvas was a Great Officer in the Amātya Mandalaya, or Sinhalese Council of State, in the Sinhalese Kingdoms of monarchical Sri Lanka. Like many of the existing high offices at the time it had combined legislative and judicial ...
of Sabaragamuwa, to Kandy. Ehelepola, suspecting a trap, refused; in revenge, the king had his wife and three children executed. Such was the cruelty of the execution that the Kandyan populace, not unused to sights of public execution, now turned en masse against the king.Codrington, ''A Short History'', chap. 11 The king was also hugely unpopular amongst the clergy for his sudden and brutal seizures of temple lands.
 In November 1814, ten British subjects were captured and mutilated in Kandyan territory. Governor
In November 1814, ten British subjects were captured and mutilated in Kandyan territory. Governor Robert Brownrigg
General Sir Robert Brownrigg, 1st Baronet, GCB (8 February 1758 – 27 April 1833) was an Irish-born British statesman and soldier. He brought the last part of Sri Lanka under British rule.
Early career
Brownrigg was commissioned as an e ...
ordered several British forces moved inland from their coastal strongholds in January 1815, accompanied by native forces under Ehelepola. Molligoda, Ehelepola's successor in Sabaragamuwa and Dissava of the Four Korales, defected to the British in February; Kandy was seized on 14 February, and Sri Wickrama Rajasinghe himself captured on 18 February. The king was subsequently exiled to India, where he died in 1832. His son died childless in 1843, bringing the Nayakkar line to an end.
On 2 March 1815, British agents – including Robert Brownrigg
General Sir Robert Brownrigg, 1st Baronet, GCB (8 February 1758 – 27 April 1833) was an Irish-born British statesman and soldier. He brought the last part of Sri Lanka under British rule.
Early career
Brownrigg was commissioned as an e ...
and John D'Oyly – met with the nobility of the kingdom and concluded in a conference known as the Kandyan Convention. The resulting agreement allowed for the protection of Buddhism and the preservation of local systems of government under the authority of the British Governor in Colombo and supervised by British agents in Sabaragamuwa, the Three Korales, and Uva. In practice, however, local chiefs such as Ehelepola and Molligoda were acutely aware that they were ultimately answerable to the British, and were in practice junior to British colonial officials who now had free access to their domains.
Rebellion broke out in 1817 in the Wellassa region, spreading rapidly to Uva and Walapane. Keppitipola, Dissave of Uva, was sent to quash the uprising, but defected and joined the rebels instead. By July, every major Kandyan chief except Molligoda had joined the rebellion; several, including Ehelepola, had already been captured. Brownrigg responded to the rebellion by ordering that all males between 15 and 60 years of age in Uva Province to be driven out, exiled or killed. In addition, the irrigation systems in Uva and Wellassa were destroyed, "one hundred thousand" paddy fields in Wellassa were burnt, all property was appropriated, and cattle and other animals were slaughtered en masse.Sri Lanka is to revoke British Governor's infamous Gazette Notification, Asian Tribune, Sat, 2011-03-12. Retrieved 21 October 2013.Sumanawathie's success brings lustre back to Uva Wellassa
Ceylon Daily News, 21 October 2013. Retrieved 21 October 2013. Brownrigg also issued a Sri Lanka Gazette Notification that condemned anyone who participated in the Great Uprising with property confiscation, extradition to Mauritius, and even execution. (This Gazette Notification labelling the rebels as "traitors" was only revoked two centuries later, in 2017, with 81 leaders of the freedom struggle being formally declared as National Heroes.) Molligoda, however, ensured the road to Kandy remained open and on 30 October Keppetipola was captured. His associate Madugalle Adikaram was captured on 1 November, and thereafter the rebellion collapsed. Both leaders were beheaded on 26 November 1817. Viewing the convention as null and void, the British set about breaking the power of the nobility. Though smaller uprisings occurred in 1820, 1823, and 1824, none of them seriously threatened the British government of the highlands. The area of the central highlands in which the Kandyan kingdom was situated had the natural protection of rivers, waterways, hills and rocky mountainous terrain. The prominent location of the Kandyan kingdom with its cool climate had greatly contributed to protecting the independence of the nation for nearly three centuries.
Administration

King
According to the Kandyan administrative system, the king was head of all spheres. He was also known as "Lankeshwara Thrisinhaladheeshwara". It was accepted that the king owned all lands and therefore was known as "Bhupathi". Even though the king was called "Adeeshwara", it was customary to consult the principal chiefs andBuddhist priest
A ''bhikkhu'' (Pali: भिक्खु, Sanskrit: भिक्षु, ''bhikṣu'') is an ordained male in Buddhist monasticism. Male and female monastics (" nun", ''bhikkhunī'', Sanskrit ''bhikṣuṇī'') are members of the Sangha (Buddhist ...
s. The king had to follow the customs and traditions which were in popular practice at that time, otherwise, the people would rebel against him if he did not. Not obeying these would be detrimental to the power of the king, an example being Vikrama Rajasinha
Sri Vikrama Rajasinha ( Sinhala:ශ්රී වික්රම රාජසිංහ, Tamil:ஸ்ரீ விக்கிரம ராஜசிங்க; 1780 – January 30, 1832, born Kannasamy Nayaka) was the last of four Kings to rule ...
, who had to surrender to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, merely because he ignored the advice of the Buddhist priests and chieftains and did not follow the age old traditions. The King would have judicial authority in civil and criminal cases.
The kings of Kandy became the rulers of the whole island with Vimaladharmasuriya I
Vimaladharmasūriya I was a king of Kandy from 1590 to 1604. His reputation was built when he successfully repulsed two major Portuguese offensives on Kandy, the Battle of Danture in 1594 and the Battle of Balana in 1602, in both of which the P ...
.
Offices of state
The King would appoint persons deemed trustworthy and capable to high offices of state. ;Adikar The highest offices of state were that of the two Adikars (known as ''Adikarams'') called ''Pallegampahe'' and ''Udagampahe'', holding equal powers and privileges within their jurisdiction. The Pallegampahe Adikar held precedence over the Udagampahe Adikar. The Adikars are distinguished from the other chiefs with the honour of the title of ''Maha Nilame'' (Great Officer). There was no time limit for the office holder as he held the post at the pleasure of the King, which meant throughout his life, if not incurred the displeasure of the King. The police and the jails were under their control. Adikars were consulted on the appointment of all other chiefs, the chief priest as well as for grants of lands, or rewards for services. It was not hereditary, although members of the same family have been appointed. ;Disawe Dissava were provincial governors. The Kandyan kingdom consisted of twenty-one provinces of which twelve principles are called ''Desavonies'' with each placed under a chief called a ''Dissava'' who served as its governor. These are: *Hathara Koralaya (The Four Korales) *Hath Koralaya (The Seven Korales) *Uva *Matale *Sabaragamuwa *Thun Koralaya (The Three Korales) *Walapane *Udapalala *Nuwarakalawiya *Wellassa *Bintenne *Tamankaduwa Appointed by the King, a Dissava had administrative and judicial authority both civil and criminal over the Desavonies as king's personal representative. They had jurisdiction over all persons and lands within their province, except for those attached to the King's court or household. There was no time limit for the office holder as he held the post at the pleasure of the King, which meant throughout his life, if not incurred the displeasure of the King. It was not hereditary, although members of the same family have been appointed. ;Lekam Lekams (Secretary in Sinhala) were chiefs of departments of the Kandyan kingdom. ;Rate Mahatmaya Rate Mahaththayas were governors of smaller districts namely Udanuwere, Hewahete, Yatinuwere, Kotmale, Tunpanahe, Dumbara. ;Diyawadana Nilame Diyawadana Nilame was an officer of the Royal household, charged with safeguarding and carrying out ancient rituals for the Sacred Relic of the tooth of the Buddha. The Diyawadana Nilame has the responsibility of overseeing all aspects of the Sri Dalada Maligawa. One of his principal duty of organizing the annual pageant, the KandyEsala Perahera
The Kandy Esala Perahera (the Sri Dalada Perahara procession of Kandy) also known as The Festival of the Tooth is a festival held in July and August in Kandy, Sri Lanka. This historical procession is held annually to pay homage to the Sacred To ...
.
Law and criminal justice

 The Kingdom of Kandy was governed by customs and traditions that have descended over the centuries which forms the basis of both the civil and criminal legal system that existed in the kingdom. Parts of this traditional law have been codified into the current legal framework of Sri Lanka as the
The Kingdom of Kandy was governed by customs and traditions that have descended over the centuries which forms the basis of both the civil and criminal legal system that existed in the kingdom. Parts of this traditional law have been codified into the current legal framework of Sri Lanka as the Kandyan law
Kandyan law is the customary law that originates from the Kingdom of Kandy, which is applicable to Sri Lankans who are Buddhist and from the former provinces of the Kandyan Kingdom. It is one of three customary laws which are still in use in Sri ...
. The King had ultimate judicial authority in civil and criminal cases in both original and appellate cases. Principle chiefs exercised civil and criminal jurisdiction over persons within their jurisdiction.
;Maha Naduwe
The ''Maha Naduwe'' (the Great Court) consists of the King, Adikars, Disawes, Lekams, and the Mohandirams forms the highest court of the land held in different times and locations hearing both civil and criminal cases. The court language of Kandy was under the Nayaks was the Tamil language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of P ...
.
Military
 The Kingdom of Kandy did not maintain a large standing army. The King maintained a full-time
The Kingdom of Kandy did not maintain a large standing army. The King maintained a full-time Royal Guard
A royal guard is a group of military bodyguards, soldiers or armed retainers responsible for the protection of a royal person, such as the emperor or empress, king or queen, or prince or princess. They often are an elite unit of the regular arm ...
at the Palace. In the provinces, local garrisons were maintained to guard strategic mountain passes or to suppress rebellions. During times of war or military campaign, these would be supplemented with local militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
.
Kandyan forces, throughout their history, relied heavily on the mountainous terrain of the kingdom and primarily engaged in guerrilla-style hit-and-run attacks, ambushes
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mount ...
, and quick raids. One of the hallmarks of the clashes between the kingdom and its European foes was the inability of either side to take and hold land or to permanently cut off supply routes, with the exception being the Dutch, who managed to do so for an extended period of time in 1762.
In the 16th and 17th century, the Kandyan Kings relied on mercenaries, often Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of India
*Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Telugu language
** Telugu (Unicode block), a block of Telugu characters in Unicode
S ...
military adventurers. With the arrival of the Nayakkars, large numbers of South Indian Tamil soldiers made up the king's personal guard. In addition to this, various Europeans were in the King's service during this period (including a master gunner), and large contingents of Malays, who were very highly regarded as fighters.
As for the armies, each of the local chieftains could call upon a militia that often accompanied them on their journeys around the kingdom. The bulk of the Kandyan army consisted of local peasant conscripts – irregulars pressed into service in times of war – who tended to bring with them around twenty days' worth of supplies and functioned in discrete units often out of contact with each other. One of the reasons for the Kandyan's inability to hold the land they captured was poor logistical support, as many soldiers had to return to base to replenish their supplies once they ran out.
By the 1760s bows and arrows had been phased out in favour of firearms. Kandyan gunsmiths specialised in manufacturing light flintlocks known as Bondikula with smaller bores than European guns, with their barrels extended for accuracy. Larger bondikula guns known as Maha thuwakku were used as Wall Guns, they weighed around 28 kg and were mounted on a tripod where the gunner would rest the butt stock from the chest to the shoulder before firing. In addition to field artillery similar to that of Europeans Kandyans also developed a unique form of light cannon better suited for mountain warfare called the ''kodithuwakkuwa'' which consisted of a gun barrel placed on a wooden stock supported by a wooden block or iron forelegs.
Economy
During the reign ofVimaladharmasuriya I
Vimaladharmasūriya I was a king of Kandy from 1590 to 1604. His reputation was built when he successfully repulsed two major Portuguese offensives on Kandy, the Battle of Danture in 1594 and the Battle of Balana in 1602, in both of which the P ...
many steps were taken to develop and improve the economy of the Kingdom of Kandy. He took steps to improve the iron industry
Ferrous metallurgy is the metallurgy of iron and its alloys. The earliest surviving prehistoric iron artifacts, from the 4th millennium BC in Egypt, were made from meteoritic iron-nickel. It is not known when or where the smelting of iron from ...
the Uva Province
Uva Province ( si, ඌව පළාත, Uva Paḷāta, ta, ஊவா மாகாணம், Uvā Mākāṇam) is Sri Lanka's second least populated province, with 1,259,880 people, created in 1896. It consists of two districts: Badulla and M ...
and agriculture in places such as Kothmale, Walapane, Harispaththuwa, Uva, Hewaheta
Hewaheta is a village in Sri Lanka. It is located within Central Province.
Notable people
Charles Spearman Armstrong (1847–1924) was a pioneer in growing tea and cinchona in Sri Lanka at the Rookwood plantation, near Hewaheta, from 1864. His gr ...
, Udunuwara, Yatinuwara and Ududumbara.
Imports of the Kandyan Kingdom included silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of ''Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
, and sugar while exports included cinnamon, pepper
Pepper or peppers may refer to:
Food and spice
* Piperaceae or the pepper family, a large family of flowering plant
** Black pepper
* ''Capsicum'' or pepper, a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family Solanaceae
** Bell pepper
** Chili ...
and areca nut
''Areca'' is a genus of 51 species of palms in the family Arecaceae, found in humid tropical forests from the islands of the Philippines, Malaysia and India, across Southeast Asia to Melanesia. The generic name ''Areca'' is derived from a name ...
.
The Kingdom of Kandy used multiple currencies some of which originated from its predecessor the Kingdom of Kotte. The Silver coins 'Ridi (Massa)' and 'Panama' were introduced by the end of the 16th century while the gold coins ‘Ran Panam’ and ‘Ran massa’ had been introduced earlier. Later the 'Thangam Massa', 'Podi (small) Thangama', 'Ridiya' were introduced. By the 18th century the ‘Waragama’ originating from India and the copper coin ‘Salli’ became widespread with an exchange rate of one 'Ridiya' for sixty-four 'Salli' coins. The influence of the Dutch resulted in the Stuiver entering circulation gaining the name 'Thuttu' among Sinhalese. Hook-shaped coins the Larin were already in use during the Kingdom of Kotte and is believed to have been introduced by Persian traders. These were locally replicated as Angutu Massa with a silver finish.
Administrative divisions
Divisions
In the early years of the kingdom, it consisted of areas or divisions.Rata Wasama
Rata Wasama was the provincial administration of the subdivisions of the Mahanuwara area in kingdom of kandy. There were nine Rata wasamas. Uda Nuwara Yatinuwara Thumpane Harispattuva Dumbara Heva heta Kothmale Uda Bulathgama Patha BulathgamaDemographics
Language
Religions
 The state religion was Buddhism. Due to the activities of the Portuguese, ordained Buddhist monks were absent by the Dutch era. After the arrival of the Nayak dynasty, Buddhism was again firmly established in the island. The dynasty of Vimaladharmasurya I largely tolerated the presence of
The state religion was Buddhism. Due to the activities of the Portuguese, ordained Buddhist monks were absent by the Dutch era. After the arrival of the Nayak dynasty, Buddhism was again firmly established in the island. The dynasty of Vimaladharmasurya I largely tolerated the presence of Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
, in particular Catholics fleeing Portuguese land following their occupation by the Dutch. On occasion, the Kandyan kings even protected Catholic agents, most famously Vimaladharmasurya II's protection of Joseph Vaz
Joseph Vaz ( Konkani: ''San Zuze Vaza''; pt, São José Vaz; kn, ಪವಿತ್ರಾ ಯೋಸೆಫ್ ವಾಸ್ ಸಂತರು ''Pavitra Yoseph Vaz Santaru''; ta, புனித யோசேப் வாஸ் முனிவர் ...
. The religious environment, however, changed dramatically with the arrival of the Nayak dynasty. In 1743 Sri Vijaya Rajasinha ordered churches burned and commenced a general repression of the faith, which continued until Kirti Sri Rajasinha commanded its cessation.H. W. Codrington, ''A Short History of Ceylon'', chap. 9
Art and architecture

See also
*History of Sri Lanka
The history of Sri Lanka is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions, comprising the areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia and Indian Ocean.
The early human remains found on the island of Sri ...
* Kandyan era frescoes
Kandyan era frescoes are mural paintings created during the Kingdom of Kandy (1469–1815) in Sri Lanka, a time when kings gave a special place to arts and literature.
As there was a political instability in Sri Lanka after the Anuradhapura Er ...
* Kastane
Kasthane is a short traditional ceremonial/decorative single-edged Sri Lankan sword. The sword is featured in the Flag of Sri Lanka
Design
Kastanes often have elaborate hilts, especially shaped and described as a rich mythical style inherited fr ...
* Stranger King
* ''''
References
External links
British Ceylon and Kingdom of Kandy 1805 (map)
Kandyan Kingdom
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom Of Kandy Kingdoms of Sri Lanka Former countries in South Asia Former monarchies of South Asia 1815 disestablishments in Ceylon History of Kandy 1469 establishments in Asia 15th-century establishments in Sri Lanka States and territories established in the 1460s