Jutland on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of
Jutland ( da, Jylland ; german: Jütland ; ang, Ēota land ), known anciently as the Cimbric or Cimbrian Peninsula ( la, Cimbricus Chersonesus; da, den Kimbriske Halvø, links=no or ; german: Kimbrische Halbinsel, links=no), is a peninsula of Northern Europe that forms the continental portion of
 Jutland is a
Jutland is a
 The largest cities in the Danish section of Jutland are as follows:
# Aarhus
#
The largest cities in the Danish section of Jutland are as follows:
# Aarhus
#
 The southern third of the peninsula is made up of the German Bundesland of
The southern third of the peninsula is made up of the German Bundesland of

 Jutland has historically been one of the three lands of Denmark, the other two being
Jutland has historically been one of the three lands of Denmark, the other two being
Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
and part of northern Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. The names are derived from the Jutes and the Cimbri
The Cimbri (Greek Κίμβροι, ''Kímbroi''; Latin ''Cimbri'') were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic people (or Gaulish), Germanic people, or even Cimmerian. Several ancient sources indicate ...
, respectively.
As with the rest of Denmark, Jutland's terrain is flat, with a slightly elevated ridge down the central parts and relatively hilly terrains in the east. West Jutland is characterised by open lands, heaths, plains, and peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muskeg; a ...
s, while East Jutland is more fertile with lakes and lush forests. Southwest Jutland is characterised by the Wadden Sea, a large unique international coastal region stretching through Denmark, Germany, and the Netherlands.
Geography
 Jutland is a
Jutland is a peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on al ...
bounded by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
to the west, the Skagerrak
The Skagerrak (, , ) is a strait running between the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, the southeast coast of Norway and the west coast of Sweden, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area through the Danish Straits to the Baltic Sea.
T ...
to the north, the Kattegat
The Kattegat (; sv, Kattegatt ) is a sea area bounded by the Jutlandic peninsula in the west, the Danish Straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Skåne in S ...
and Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
to the east, and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
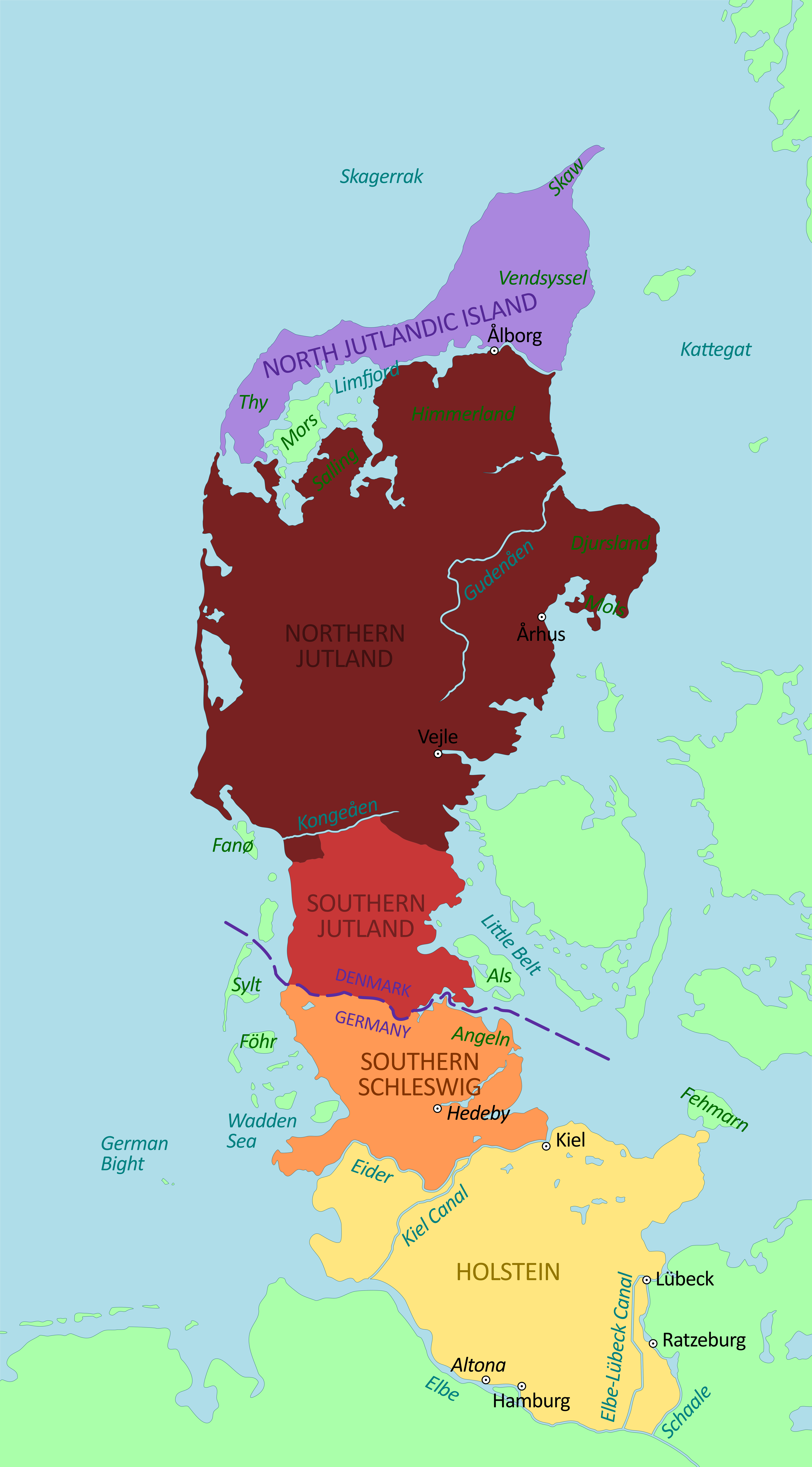
to the south. Geographically and historically, Jutland comprises the regions of South Jutland (historically also Slesvig), West Jutland, East Jutland (including Djursland) and North Jutland (including Himmerland, Vendsyssel, Hanherred Han Herred or Hanherrederne is a traditional district in northern Jutland, Denmark. It lies between Thy in the west and Vendsyssel in the east. To the north it faces the North Sea (Skagerrak) and to the south the Limfjord. There are only two towns ...
, and Thy). Since the mid-20th century, it has also become common to designate an area called Central Jutland (''Midtjylland''), but its definition varies. There are several historical subdivisions and regional names, and some are encountered today. They include ''Nørrejyllland'' (an historical name for the whole area north of South Jutland, and not identical with ''Nordjylland''), ''Sydvestjylland'', ''Sydjylland'' (the southernmost stretch of Nørrejylland, as opposed to the more southern ''Sønderjylland''), ''Nordvestjylland'', ''Kronjylland'', and others. Politically, Jutland currently comprises the three contemporary Danish Administrative Regions of North Jutland Region, Central Denmark Region and the Region of Southern Denmark, along with portions of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
.
The northernmost part of Jutland is separated from the mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or dem ...
by the Limfjord, a narrow stretch of water bisecting the peninsula from coast to coast. The Limfjord was formerly a long brackish water inlet, but the February flood of 1825 created a coast to coast connection. This area is called the North Jutlandic Island, Vendsyssel- Thy (after its districts) or simply ''Jutland north of the Limfjord''; it is only partly coterminous with the North Jutland Region.
The islands of Læsø, Anholt, and Samsø in Kattegat
The Kattegat (; sv, Kattegatt ) is a sea area bounded by the Jutlandic peninsula in the west, the Danish Straits islands of Denmark and the Baltic Sea to the south and the provinces of Bohuslän, Västergötland, Halland and Skåne in S ...
, and Als at the rim of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and fr ...
, are administratively and historically tied to Jutland, although the latter two are also regarded as traditional districts of their own. Inhabitants of Als, known as ''Alsinger'', would agree to be South Jutlanders, but not necessarily Jutlanders.
The Danish Wadden Sea Islands and the German North Frisian Islands stretch along the southwest coast of Jutland in the German Bight
The German Bight (german: Deutsche Bucht; da, tyske bugt; nl, Duitse bocht; fry, Dútske bocht; ; sometimes also the German Bay) is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and ...
.
Danish portion
 The largest cities in the Danish section of Jutland are as follows:
# Aarhus
#
The largest cities in the Danish section of Jutland are as follows:
# Aarhus
#Aalborg
Aalborg (, , ) is Denmark's fourth largest town (behind Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense) with a population of 119,862 (1 July 2022) in the town proper and an urban population of 143,598 (1 July 2022). As of 1 July 2022, the Municipality of ...
# Esbjerg
# Randers
# Kolding
# Horsens
# Vejle
# Herning
# Silkeborg
#Fredericia
Fredericia () is a town located in Fredericia Municipality in the southeastern part of the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The city is part of the Triangle Region, which includes the neighbouring cities of Kolding and Vejle. It was founded in ...
Aarhus, Silkeborg, Billund, Randers, Kolding, Horsens, Vejle, Fredericia
Fredericia () is a town located in Fredericia Municipality in the southeastern part of the Jutland peninsula in Denmark. The city is part of the Triangle Region, which includes the neighbouring cities of Kolding and Vejle. It was founded in ...
and Haderslev, along with a number of smaller towns, make up the suggested East Jutland metropolitan area, which is more densely populated than the rest of Jutland, although far from forming one consistent city.
Administratively, Danish Jutland comprises three of the five regions of Denmark
The five Regions of Denmark ( da, regioner) were created as administrative entities at a level above the municipalities and below the central government in the public sector as part of the 2007 Danish Municipal Reform, when the 13 counties ('' ...
, namely Nordjylland, Midtjylland, and the western half of Southern Denmark (which includes Funen). The five administrative regions came into effect on 1 January 2007, following a structural reform.
German portion
 The southern third of the peninsula is made up of the German Bundesland of
The southern third of the peninsula is made up of the German Bundesland of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
. The German parts are usually not seen as Jutland proper, but often described more abstract as part of the Jutlandic Peninsula, Cimbrian Peninsula or Jutland-Schleswig-Holstein.
Schleswig-Holstein has two historical parts: the former duchies of Schleswig (a Danish fief) and Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label= Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germ ...
(a German fief), both of which have passed back and forth between Danish and German rulers. The last adjustment of the Danish–German border followed the Schleswig Plebiscites in 1920 and resulted in Denmark regaining Northern Schleswig ( da, Nordslesvig or more commonly today: ''Sønderjylland'').
The historic southern border of Jutland was the river Eider, which forms the border between the former duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, as well as the border between the Danish and German realms from 850 to 1864. Although most of Schleswig-Holstein is geographically part of the peninsula, most German residents there would not identify themselves with Jutland or even as Jutlanders, but rather with Schleswig-Holstein.
The medieval law Code of Jutland applied to Schleswig until 1900, when it was replaced by the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
n Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch
The ''Bürgerliches Gesetzbuch'' (, ), abbreviated BGB, is the civil code of Germany. In development since 1881, it became effective on 1 January 1900, and was considered a massive and groundbreaking project.
The BGB served as a template in se ...
(''Civil Code''). Some rarely used clauses of the Jutlandic Code still apply north of the Eider.
Cities
The largest cities in the German area of the Jutland Peninsula are: #Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
# Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland pe ...
# Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the stat ...
# Flensburg.
Geology
Geologically, the Mid Jutland Region and the North Jutland Region as well as the Capital Region of Denmark are located in the north of Denmark which is rising because of post-glacial rebound. Some circular depressions in Jutland may be remnants of collapsed pingos that developed during the Last Ice Age .History

 Jutland has historically been one of the three lands of Denmark, the other two being
Jutland has historically been one of the three lands of Denmark, the other two being Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skå ...
and Zealand
Zealand ( da, Sjælland ) at 7,031 km2 is the largest and most populous island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 January 2020.
It is th ...
. Before that, according to Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
, Jutland or the ''Cimbric Chersonese'' was the home of Teutons, Cimbri
The Cimbri (Greek Κίμβροι, ''Kímbroi''; Latin ''Cimbri'') were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic people (or Gaulish), Germanic people, or even Cimmerian. Several ancient sources indicate ...
, and Charudes.
Many Angles, Saxons and Jutes migrated from Continental Europe to Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
starting around 450 AD. The Angles gave their name to the new emerging kingdoms called England (i.e., "Angle-land"). The Kingdom of Kent in south east England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
is associated with Jutish origins and migration, also attributed by Bede
Bede ( ; ang, Bǣda , ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, The Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable ( la, Beda Venerabilis), was an English monk at the monastery of St Peter and its companion monastery of St Paul in the Kingdom ...
in the ''Ecclesiastical History''. This is also supported by the archaeological record, with extensive Jutish finds in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
from the fifth and sixth centuries.
Saxons and Frisii migrated to the region in the early part of the Christian era. To protect themselves from invasion by the Christian Frankish emperors, beginning in the 5th century, the pagan Danes initiated the Danevirke, a defensive wall stretching from present-day Schleswig and inland halfway across the Jutland peninsula.
The pagan Saxons inhabited the southernmost part of the peninsula, adjoining the Baltic Sea, until the Saxon Wars in 772–804 in the Nordic Iron Age, when Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Em ...
violently subdued them and forced them to be Christianised. Old Saxony was politically absorbed into the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
and Abodrites (or Obotrites), a group of Wendish Slavs who pledged allegiance to Charlemagne and who had for the most part converted to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person to Christianity. Different Christian denominations may perform various different kinds of rituals or ceremonies initiation into their community of believe ...
, were moved into the area to populate it. Old Saxony was later referred to as Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label= Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of Germ ...
.
In medieval times, Jutland was regulated by the Law Code of Jutland (''Jyske Lov''). This civic code covered the Danish part of the Jutland Peninsula, i.e., north of the Eider (river), Funen as well as Fehmarn. Part of this area are now in Germany.
During the industrialisation of the 1800s, Jutland experienced a large and accelerating urbanisation and many people from the countryside chose to emigrate. Among the reasons was a high and accelerating population growth; in the course of the century, the Danish population grew two and a half times to about 2.5 million in 1901, with a million people added in the last part of the 1800s. This growth was not caused by an increase in the fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
, but by better nutrition, sanitation, hygiene, and health care services. More children survived, and people lived longer and healthier lives. Combined with falling grain prices on the international markets because of the Long Depression, and better opportunities in the cities due to an increasing industrialisation, many people in the countryside relocated to larger towns or emigrated. In the later half of the century, around 300,000 Danes, mainly unskilled labourers from rural areas, emigrated to the US or Canada. This amounted to more than 10% of the then total population, but some areas had an even higher emigration rate. In 1850, the largest Jutland towns of Aalborg, Aarhus and Randers had no more than about 8,000 inhabitants each; by 1901, Aarhus had grown to 51,800 citizens.
To speed transit between the Baltic and the North Sea, canals were built across the Jutland peninsula, including the Eider Canal in the late 18th century, and the Kiel Canal
The Kiel Canal (german: Nord-Ostsee-Kanal, literally "North- oEast alticSea canal", formerly known as the ) is a long freshwater canal in the Germany, German states of Germany, state of Schleswig-Holstein. The canal was finished in 1895, ...
, completed in 1895 and still in use.
In 1825, a severe North Sea storm on the west coast of Jutland breached the isthmus of Agger Tange in the Limfjord area, separating the northern part of Jutland from the mainland and effectively creating the North Jutlandic Island. The storm breach of Agger Tange created the Agger Channel, and another storm in 1862 created the Thyborøn
Thyborøn is a fishing village in Jutland, Denmark with a population of 1,890 (1 January 2022), Skagerrak Sea. The Agger Channel closed up again over the years, due to natural siltation, but the Thyborøn Channel widened and was fortified and secured in 1875.
World War I and Battle of Jutland
Denmark was neutral throughout theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
. However, Danes living in North Slesvig, since it was part of the German Empire from 1864 to 1920, were conscripted for the imperial German army. 5000 Danish South Jutlanders are estimated to have fallen in German military service during the War.
The 1916 Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland (german: Skagerrakschlacht, the Battle of the Skagerrak) was a naval battle fought between Britain's Royal Navy Grand Fleet, under Admiral Sir John Jellicoe, and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet, under Vic ...
was fought in the North Sea west of Jutland as one of the largest naval battles in history. In this pitched battle, the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
engaged the Imperial German Navy, leading to heavy casualties and losses of ships on both sides. The British fleet sustained greater losses, but remained in control of the North Sea, so in strategic terms, most historians regard Jutland either as a British victory or as indecisive. The battle is commemorated and explained at the Sea War Museum Jutland in Thyborøn
Thyborøn is a fishing village in Jutland, Denmark with a population of 1,890 (1 January 2022),
 Denmark had declared itself neutral, but was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany within a few hours on 9 April 1940. Scattered fighting took place in South Jutland and in Copenhagen. Sixteen Danish soldiers were killed.
Some months before the invasion, Germany had considered only occupying the northern tip of Jutland with Aalborg airfield, but Jutland as a whole was soon regarded as of high strategic importance. Work commenced on extending the
Denmark had declared itself neutral, but was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany within a few hours on 9 April 1940. Scattered fighting took place in South Jutland and in Copenhagen. Sixteen Danish soldiers were killed.
Some months before the invasion, Germany had considered only occupying the northern tip of Jutland with Aalborg airfield, but Jutland as a whole was soon regarded as of high strategic importance. Work commenced on extending the
 The local culture of Jutland commoners before industrial times was not described in much detail by contemporary texts. It was generally viewed with contempt by the Danish cultural elite in Copenhagen who perceived it as uncultivated, misguided or useless.
While the peasantry of eastern Denmark was dominated by the upper feudal class, manifested in large estates owned by families of noble birth and an increasingly subdued class of peasant tenants, the farmers of Western Jutland were mostly free owners of their own land or leasing it from the Crown, although under frugal conditions. Most of the less fertile and sparsely populated land of Western Jutland was never feudalised. East Jutland was more similar to Eastern Denmark in this respect. The north–south ridge forming the border between the fertile eastern hills and sandy western plains has been a significant cultural border until this day, also reflected in differences between the West and East Jutlandic dialect.
The local culture of Jutland commoners before industrial times was not described in much detail by contemporary texts. It was generally viewed with contempt by the Danish cultural elite in Copenhagen who perceived it as uncultivated, misguided or useless.
While the peasantry of eastern Denmark was dominated by the upper feudal class, manifested in large estates owned by families of noble birth and an increasingly subdued class of peasant tenants, the farmers of Western Jutland were mostly free owners of their own land or leasing it from the Crown, although under frugal conditions. Most of the less fertile and sparsely populated land of Western Jutland was never feudalised. East Jutland was more similar to Eastern Denmark in this respect. The north–south ridge forming the border between the fertile eastern hills and sandy western plains has been a significant cultural border until this day, also reflected in differences between the West and East Jutlandic dialect.
 When the industrialisation began in the 19th century, the social order was upheaved and with it the focus of the intelligentsia and the educated changed as well. Søren Kierkegaard (1818–1855) grew up in Copenhagen as the son of a stern and religious West Jutlandic wool merchant who had worked his way up from a frugal childhood. The very urban Kierkegaard visited his sombre ancestral lands in 1840, then a very traditional society. Writers like Steen Steensen Blicher (1782-1848) and H.C. Andersen (1805–1875) were among the first writers to find genuine inspiration in local Jutlandic culture and present it with affection and non-prejudice. Blicher was himself of Jutish origin and, soon after his pioneering work, many other writers followed with stories and tales set in Jutland and written in the homestead dialect. Many of these writers are often referred to as the Jutland Movement, artistically connected through their engagement with public
When the industrialisation began in the 19th century, the social order was upheaved and with it the focus of the intelligentsia and the educated changed as well. Søren Kierkegaard (1818–1855) grew up in Copenhagen as the son of a stern and religious West Jutlandic wool merchant who had worked his way up from a frugal childhood. The very urban Kierkegaard visited his sombre ancestral lands in 1840, then a very traditional society. Writers like Steen Steensen Blicher (1782-1848) and H.C. Andersen (1805–1875) were among the first writers to find genuine inspiration in local Jutlandic culture and present it with affection and non-prejudice. Blicher was himself of Jutish origin and, soon after his pioneering work, many other writers followed with stories and tales set in Jutland and written in the homestead dialect. Many of these writers are often referred to as the Jutland Movement, artistically connected through their engagement with public  With the railway system, and later the automobile and
With the railway system, and later the automobile and
– Bowdoin College
 Denmark had declared itself neutral, but was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany within a few hours on 9 April 1940. Scattered fighting took place in South Jutland and in Copenhagen. Sixteen Danish soldiers were killed.
Some months before the invasion, Germany had considered only occupying the northern tip of Jutland with Aalborg airfield, but Jutland as a whole was soon regarded as of high strategic importance. Work commenced on extending the
Denmark had declared itself neutral, but was invaded and occupied by Nazi Germany within a few hours on 9 April 1940. Scattered fighting took place in South Jutland and in Copenhagen. Sixteen Danish soldiers were killed.
Some months before the invasion, Germany had considered only occupying the northern tip of Jutland with Aalborg airfield, but Jutland as a whole was soon regarded as of high strategic importance. Work commenced on extending the Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticip ...
along the entire west coast of the peninsula. Its task was to resist a potential allied attack on Germany by landing on the west coast of Jutland. The Hanstholm fortress at the northwestern promontory of Jutland became the largest fortification of Northern Europe. The local villagers were evacuated to Hirtshals. Coastal areas of Jutland were declared a military zone where Danish citizens were required to carry identity cards, and access was regulated.
The small Danish airfield of Aalborg was seized as one of the first objects in the invasion by German paratroopers. The airfield was significantly expanded by the Germans in order to secure their traffic to Norway, and more airfields were built. Danish contractors and 50,000–100,000 workers were hired to fulfill the German projects. The alternative for workers was to be unemployed or sent to work in Germany. The fortifications have been estimated to be the largest construction project ever performed in Denmark at a cost of then 10 billion kroner, or 300-400 billion DKK today (45-60 billion USD or 40-54 billion euro in 2019). The Danish National Bank was forced to cover most of the cost. After the war, the remaining German prisoners of war were recruited to perform extensive mine clearance
Demining or mine clearance is the process of removing land mines from an area. In military operations, the object is to rapidly clear a path through a minefield, and this is often done with devices such as mine plows and blast waves. By cont ...
of 1.4 million mines along the coast.
Many of the seaside bunkers from World War II are still present at the west coast. Several of the fortifications in Denmark have been turned into museums, including Tirpitz Museum in Blåvand, Bunkermuseum Hanstholm, and Hirtshals Bunkermuseum.
In Southern Jutland, parts of the German minority
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
openly sided with Germany and volunteered for German military service. While some Danes initially feared a border revision, the German occupational force did not pursue the issue. In a judicial aftermath after the end of the war, many members of the German minority were convicted, and German schools were confiscated by Danish authorities. There were some instances of Danish mob attacks against German-minded citizens. In December 1945, the remaining part of the German minority issued a declaration of loyalty to Denmark and democracy, renouncing any demands for a border revision.
Culture
Up until theindustrialisation
Industrialisation ( alternatively spelled industrialization) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive re-organisation of an econ ...
of the 19th century, most people in Jutland lived a rural life as farmers and fishers. Farming and herding have formed a significant part of the culture since the late Neolithic Stone Age, and fishing ever since humans first populated the peninsula after the last Ice Age, some 12,000 years ago.
 The local culture of Jutland commoners before industrial times was not described in much detail by contemporary texts. It was generally viewed with contempt by the Danish cultural elite in Copenhagen who perceived it as uncultivated, misguided or useless.
While the peasantry of eastern Denmark was dominated by the upper feudal class, manifested in large estates owned by families of noble birth and an increasingly subdued class of peasant tenants, the farmers of Western Jutland were mostly free owners of their own land or leasing it from the Crown, although under frugal conditions. Most of the less fertile and sparsely populated land of Western Jutland was never feudalised. East Jutland was more similar to Eastern Denmark in this respect. The north–south ridge forming the border between the fertile eastern hills and sandy western plains has been a significant cultural border until this day, also reflected in differences between the West and East Jutlandic dialect.
The local culture of Jutland commoners before industrial times was not described in much detail by contemporary texts. It was generally viewed with contempt by the Danish cultural elite in Copenhagen who perceived it as uncultivated, misguided or useless.
While the peasantry of eastern Denmark was dominated by the upper feudal class, manifested in large estates owned by families of noble birth and an increasingly subdued class of peasant tenants, the farmers of Western Jutland were mostly free owners of their own land or leasing it from the Crown, although under frugal conditions. Most of the less fertile and sparsely populated land of Western Jutland was never feudalised. East Jutland was more similar to Eastern Denmark in this respect. The north–south ridge forming the border between the fertile eastern hills and sandy western plains has been a significant cultural border until this day, also reflected in differences between the West and East Jutlandic dialect.
 When the industrialisation began in the 19th century, the social order was upheaved and with it the focus of the intelligentsia and the educated changed as well. Søren Kierkegaard (1818–1855) grew up in Copenhagen as the son of a stern and religious West Jutlandic wool merchant who had worked his way up from a frugal childhood. The very urban Kierkegaard visited his sombre ancestral lands in 1840, then a very traditional society. Writers like Steen Steensen Blicher (1782-1848) and H.C. Andersen (1805–1875) were among the first writers to find genuine inspiration in local Jutlandic culture and present it with affection and non-prejudice. Blicher was himself of Jutish origin and, soon after his pioneering work, many other writers followed with stories and tales set in Jutland and written in the homestead dialect. Many of these writers are often referred to as the Jutland Movement, artistically connected through their engagement with public
When the industrialisation began in the 19th century, the social order was upheaved and with it the focus of the intelligentsia and the educated changed as well. Søren Kierkegaard (1818–1855) grew up in Copenhagen as the son of a stern and religious West Jutlandic wool merchant who had worked his way up from a frugal childhood. The very urban Kierkegaard visited his sombre ancestral lands in 1840, then a very traditional society. Writers like Steen Steensen Blicher (1782-1848) and H.C. Andersen (1805–1875) were among the first writers to find genuine inspiration in local Jutlandic culture and present it with affection and non-prejudice. Blicher was himself of Jutish origin and, soon after his pioneering work, many other writers followed with stories and tales set in Jutland and written in the homestead dialect. Many of these writers are often referred to as the Jutland Movement, artistically connected through their engagement with public social realism
Social realism is the term used for work produced by painters, printmakers, photographers, writers and filmmakers that aims to draw attention to the real socio-political conditions of the working class as a means to critique the power structure ...
of the Jutland region. The Golden Age painters also found inspiration and motives in the natural beauty of Jutland, including P. C. Skovgaard, Dankvart Dreyer, and art collective of the Skagen Painters
The Skagen Painters ( da, Skagensmalerne) were a group of Scandinavian artists who gathered in the village of Skagen, the northernmost part of Denmark, from the late 1870s until the turn of the century. Skagen was a summer destination whose sc ...
. Writer Evald Tang Kristensen (1843-1929) collected and published extensive accounts on the local rural Jutlandic folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, r ...
through many interviews and travels across the peninsula, including songs, legends, sayings and everyday life.
Peter Skautrup Centret at Aarhus University is dedicated to collect and archive information on Jutland culture and dialects from before the industrialisation. The centre was established in 1932 by Professor in Nordic languages Peter Skautrup (1896-1982).
mass communication
Mass communication is the process of imparting and exchanging information through mass media to large segments of the population. It is usually understood for relating to various forms of media, as its technologies are used for the dissemination o ...
, the culture of Jutland has merged with and formed the overall Danish national culture, although some unique local traits are still present in some cases. West Jutland is often claimed to have a mentality of self-sustainment, a superior work ethic and entrepreneurial spirit as well as slightly more religious and socially conservative values, and there are other voting patterns than in the rest of Denmark.
Dialect
The distinctive Jutish (or Jutlandic)dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that ...
s differ substantially from the standard Danish language
Danish (; , ) is a North Germanic language spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are also found in Greenland, the Faroe Islands, and the northern German region of Southern S ...
, especially those in the West Jutland and South Jutland parts. The Peter Skautrup Centre maintains and publishes an official dictionary of the Jutlandic dialects. Dialect usage, although in decline, is better preserved in Jutland than in eastern Denmark, and Jutlander speech remains a stereotype among many Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( or .; da, København ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a proper population of around 815.000 in the last quarter of 2022; and some 1.370,000 in the urban area; and the wider Copenhagen metropolitan ar ...
ers and eastern Danes.
Musicians and entertainers Ib Grønbech and Niels Hausgaard, both from Vendsyssel in Northern Jutland, use a distinct Jutish dialect.
In the southernmost and northernmost parts of Jutland, there are associations striving to conserve their respective dialects, including the North Frisian language-speaking areas in Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
.
Literature
In the Danish part of Jutland, literature tied to Jutland, and Jutland culture, grew significantly in the 1800s and early 1900s. That was a time when large numbers of people migrated to the towns during the industrialisation, and there was a surge of nationalism as well as a quest for social reform during the public foundation of the modern democratic national state. Steen Steensen Blicher wrote about the Jutland rural culture of his times in the early 1800s. Through his writings, he promoted and preserved the various Jutland dialects, as in ''E Bindstouw'', published in 1842. Danish social realist and radical writerJeppe Aakjær
Jeppe Aakjær (10 September 1866 – 22 (23) April 1930) was a Danish poet and novelist, a member of the ' Jutland Movement' in Danish literature". A regionalist, much of his writings were about his native Jutland. He was known for writin ...
used Jutlanders and Jutland culture in most of his works, for example in ''Af gammel Jehannes hans Bivelskistaarri. En bette Bog om stur Folk'' (1911), which was widely read in its time. He also translated poems of Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 175921 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the best known of the poets who ha ...
to his particular Central Western Jutish dialect.
Karsten Thomsen (1837–1889), an inn-keeper in Frøslev with artistic aspirations, wrote warmly about his homestead of South Jutland, using the dialect of his region explicitly.
Two songs are often regarded as regional anthems of Jutland: ''Jylland mellem tvende have'' ("Jutland between two seas", 1859) by Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales.
Andersen's fairy tales, consist ...
and ''Jyden han æ stærk aa sej'' ("The Jute, he is strong and tough", 1846) by Steen Steensen Blicher, the latter in dialect.
Jutland native Maren Madsen (1872-1965) emigrated to the American town of Yarmouth, Maine, in the late 19th century. She wrote a memoir documenting the transition, ''From Jutland's Brown Heather to the Land Across the Sea''.
Publisher Frederick William Anthoensen was born in Torland, South Jutland. He moved to the United States with his parents in 1884.Guide to the Fred Anthoensen Collection, 1901-1969– Bowdoin College
References
Sources
*External links
{{Coord, 55, N, 9, E, display=title Geography of Germany Geography of Denmark Peninsulas of Denmark Peninsulas of Europe Divided regions Peninsulas of the Baltic Sea Peninsulas of Schleswig-Holstein