Join-patterns provides a way to write
concurrent,
parallel and
distributed computer programs by
message passing
In computer science, message passing is a technique for invoking behavior (i.e., running a program) on a computer. The invoking program sends a message to a process (which may be an actor or object) and relies on that process and its supporting ...
. Compared to the use of
threads and locks, this is a high level programming model using communication constructs model to abstract the complexity of concurrent environment and to allow
scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
. Its focus is on the execution of a
chord between messages atomically consumed from a group of channels.
This template is based on
join-calculus and uses
pattern matching
In computer science, pattern matching is the act of checking a given sequence of tokens for the presence of the constituents of some pattern. In contrast to pattern recognition, the match usually must be exact: "either it will or will not be a ...
. Concretely, this is done by allowing the join definition of several functions and/or channels by matching concurrent call and messages patterns. It is a type of
concurrency pattern because it makes easier and more flexible for these entities to communicate and deal with the multi-threaded programming paradigm.
Description
The join-pattern (or a chord in
Cω) is like a super pipeline with synchronisation and matching. In fact, this concept is summarise by match and join a set of message available from different
message queue
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter- thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the ...
s, then handles them all simultaneously with one handler.
It could be represented by the keywords to specify the first communication that we expected, with the to join/pair other channels and the to run some tasks with the different collected messages. A constructed join pattern typically takes this form:
j.When(a1).And(a2). ... .And(an).Do(d)
More precisely, when a message matches with a chain of linked patterns causes its ''handler'' to run (in a new thread if it's in asynchronous context) otherwise the message is queued until one of its patterns is enabled; if there are several matches, an unspecified pattern is selected.
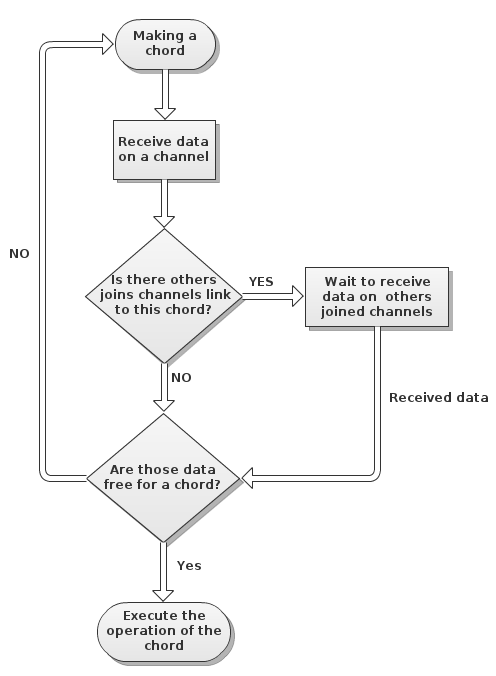
Join-pattern is defined by a set of pi-calculus channels that supports two different operations, sending and receiving, we need two join calculus names to implement it: a channel name for sending (a message), and a function name for receiving a value (a request). The meaning of the join definition is that a call to returns a value that was sent on a channel . Each time functions are concurrently, triggers the return process and synchronizes with other joins.
J ::= //join patterns
, x //message send pattern
, x(y) //function call pattern
, J , JBIS //synchronization

In most of cases, the order of synchronous calls is not guaranteed for performance reasons. Finally, during the match the messages available in the queue could be stolen by some intervening thread; indeed, the awakened thread may have to wait again.
History
π-calculus – 1992
The
π-calculus
In theoretical computer science, the -calculus (or pi-calculus) is a process calculus. The -calculus allows channel names to be communicated along the channels themselves, and in this matter, it is able to describe concurrent computations whose ...
belongs to the family of
process calculi, allows mathematical formalisms for describing and analyzing properties of concurrent computation by using channel names to be communicated along the channels themselves, and in this way it is able to describe concurrent computations whose network configuration may change during the computation.
Join-Calculus – 1993
Join patterns first appeared in Fournet and Gonthier’s foundational join-calculus, an asynchronous process algebra designed for efficient implementation in a distributed setting. The
join-calculus is a
process calculus
In computer science, the process calculi (or process algebras) are a diverse family of related approaches for formally modelling concurrent systems. Process calculi provide a tool for the high-level description of interactions, communications, and ...
as expressive as the full
π-calculus
In theoretical computer science, the -calculus (or pi-calculus) is a process calculus. The -calculus allows channel names to be communicated along the channels themselves, and in this matter, it is able to describe concurrent computations whose ...
. It was developed to provide a formal basis for the design of distributed programming languages, and therefore intentionally avoids communications constructs found in other process calculi, such as
rendezvous communications.
Distributed Join-Calculus – 1996
The Join-Calculus is both a name passing calculus and a core language for concurrent and distributed programming.
That's why the Distributed Join-Calculus
based on the Join-Calculus with the
distributed programming
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
The components of a distributed system commu ...
was created on 1996. This work use the mobile agents where agents are not only programs but core images of running processes with their communication capabilities.
JoCaml, Funnel and Join Java – 2000
JoCamland Funnel are functional languages supporting declarative join patterns. They present the ideas to direct implement a process calculi in a functional setting.
Another extensions to (non-generic) Java, JoinJava, were independently proposed by von Itzstein and Kearney.
Polyphonic C# – 2002
Cardelli, Benton and Fournet proposed an object-oriented version of join patterns for C# called
Polyphonic C#.
Cω – 2003
Cω is adaptation of join-calculus to an object-oriented setting. This variant of Polyphonic C# was included in the public release of Cω (a.k.a. Comega) in 2004.
Scala Joins – 2007
Scala Joins is a library to use Join-Pattern with Scala in the context of extensible pattern matching in order to integrate joins into an existing actor-based concurrency framework.
JErlang – 2009
Erlang is a language which natively supports the concurrent, real time and distributed paradigm. Concurrency between processes was complex, that's why the project build a new language
JErlang(''J'' stands for ''Join'') using based on the Join-calculus.
Join-pattern in classic programming literature
"Join-patterns can be used to easily encode related concurrency idioms like actors and active objects."
*
Barriers
*
Dining philosophers problem
var j = Join.Create();
Synchronous.Channel[] hungry;
Asynchronous.Channel[] chopstick;
j.Init(out hungry, n);
j.Init(out chopstick, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
* Mutual exclusion
*
Producers/Consumers
class Buffer
*
Reader-writer locking
*
Semaphores
Fundamental features and concepts
*
Join-calculus : The first apparition of the Join-Pattern comes out with this process calculus.
*
Message passing
In computer science, message passing is a technique for invoking behavior (i.e., running a program) on a computer. The invoking program sends a message to a process (which may be an actor or object) and relies on that process and its supporting ...
: Join-pattern works with a message passing system for parallel reason.
*
Channel : Channels are used to synchronize and pass messages between concurrently executing threads. In general, a channel may be involved in more than one join pattern, each pattern defines a different continuation that may run when the channel is invoked .
*
Synchronous : The join-pattern could use a synchronous channel which return a result. The continuation of a synchronous pattern runs in the thread of the synchronous sender.
*
Asynchronous
Asynchrony is any dynamic far from synchronization. If and as parts of an asynchronous system become more synchronized, those parts or even the whole system can be said to be in sync.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and com ...
: It could also use an asynchronous channel which return no result but take arguments. The continuation of an asynchronous pattern runs in a newly spawned thread. A join pattern may be purely asynchronous, provided its continuation is a subroutine and its When clause only lists asynchronous channels.
* Combine synchronous and asynchronous : Merging the declarations of synchronous and asynchronous buffer would yield a module that supports the two communication type of consumers.
*
Scheduler : There is a scheduling between join patterns (e.g.
a round-robin scheduler, first-match scheduler).
*
Design patterns : The join-pattern is first of all a behavioral and a concurrency pattern.
*
Concurrent programming
Concurrent means happening at the same time. Concurrency, concurrent, or concurrence may refer to:
Law
* Concurrence, in jurisprudence, the need to prove both ''actus reus'' and ''mens rea''
* Concurring opinion (also called a "concurrence"), a ...
: It's execute in a concurrent way.
*
Pattern matching
In computer science, pattern matching is the act of checking a given sequence of tokens for the presence of the constituents of some pattern. In contrast to pattern recognition, the match usually must be exact: "either it will or will not be a ...
: The join-pattern works with matching tasks.
*
Parallel programming
Parallel computing is a type of computing, computation in which many calculations or Process (computing), processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. ...
: It performs tasks in parallel.
*
Distributed programming
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
The components of a distributed system commu ...
: Jobs could be scatter on different agent and environments with this pattern.
*
Software transactional memory : Software transactional memory (STM) is one of the possible implementation for the communications between joint.
*
Overlapping : The pattern could allow patterns declared on overlapping sets of channels.
Application domain
Mobile agent
A
mobile agent is an autonomous software agent with a certain social ability and most importantly, mobility. It is composed of computer software and data which can move between different computers automatically while continuing their executions.
The mobile agents can be used to match concurrency and distribution if one uses the Join-calculus. That's why a new concept named "distributed Join-calculus" was created; it's an extension of Join-calculus with locations and primitives to describe the mobility.
This innovation use agents as running processes with their communication capabilities to allow an idea of location, which is a physical site expressing the actual position of the agent. Thanks to the Join-calculus, one location can be moved atomically to another site.
The processes of an agent is specified as a set which define its functionality including asynchronous emission of a message, migration to other location. Consequently, locations are organized in a tree to represent the movement of the agent easier. With this representation, a benefit of this solution is the possibility to create a simple model of failure. Usually a crash of a physical site causes the permanent failure of all its locations. But with the join-calculus a problem with a location can be detected at any other running location, allowing error recovery.
In 2007, an extension of the basic join calculus with methods which make agents proactive has come out. The agents can observe an environment shared between them. With this environment, it is possible to define shared variables with all agents (e.g. a naming service to discover agents between themselves).
Compilation
Join-languages are built on top of the join-calculus taken as a core language. So all the calculus are analysed with asynchronous processes and the join pattern provides a model to synchronize the result.
To do this, it exists two Compilers:
* Join Compiler: A compiler of a language named "join langage". This language has been created only for the join calculus
Jocaml Compiler: A compiler of an extension of Objectif Caml created to use the join calculus.
This two compiler works with the same system, an automaton.
let A(n) , B() = P(n)
and A(n) , C() = Q(n)
;;
It represents the consumption of message arrive at a completed join model. Each state is a possibly step for the code execution and each transitions is the reception of a message to change between two steps. And so when all messages are grab, the compiler execute the body join code corresponding to the completed model joint.
So in the join-calculus, the basic values are the names like on the example is A,B or C. So the two compiler representing this values with two ways.
Join compiler use a vector with Two slots, the first to the name it-self and the second to a queue of pending messages.
Jocaml use name like a pointer on definitions. This definitions store the others pointer of the others names with a status field and a matching date structure by message.
The fundamental difference is when the guard process is executed, for the first, it was verify if all names are the pending messages ready whereas the second use only one variable and access at the others to know if the model is completed.
Recent research describe the compilation scheme as the combination of two basic steps: dispatching and forwarding. The design and correctness of the dispatcher essentially stems from pattern matching theory, while inserting an internal forwarding step in communications is a natural idea, which intuitively does not change process behavior. They made the observation that ''the worth observing is a direct implementation of extended join-pattern matching at the runtime level would significantly complicate the management of message queues, which would then need to be scanned in search of matching messages before consuming them.''
Implementations and libraries
There are many uses of the Join-patterns with different languages. Some languages use join-patterns as a base of theirs implementations, for example the
Polyphonic C# o
MC# but others languages integrate join-pattern by a library like Scala Joins
for Scala or the Joins library for VB.
Moreover, the join-pattern is used through some languages like
Scheme to upgrade the join-pattern.
Join Java
Join Java
is a language based on the
Java programming language
Java is a high-level, general-purpose, memory-safe, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' ( WORA), meaning that compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Jav ...
allowing the use of the join calculus. It introduces three new language constructs:
* Join methods is defined by two or more Join fragments. A Join method will execute once all the fragments of the Join pattern have been called. If the return type is a standard Java type then the leading fragment will block the caller until the Join pattern is complete and the method has executed. If the return type is of type signal then the leading fragment will return immediately. All trailing fragments are asynchronous so will not block the caller.
Example:
class JoinExample
* Asynchronous methods are defined by using the signal return type. This has the same characteristics as the void type except that the method will return immediately. When an asynchronous method is called a new thread is created to execute the body of the method.
Example:
class ThreadExample
* Ordering modifiers
Join fragments can be repeated in multiple Join patterns so there can be a case when multiple Join patterns are completed when a fragment is called. Such a case could occur in the example below if B(), C() and D() then A() are called. The final A() fragment completes three of the patterns so there are three possible methods that may be called. The ordered class modifier is used here to determine which Join method will be called. The default and when using the unordered class modifier is to pick one of the methods at random. With the ordered modifier the methods are prioritised according to the order they are declared.
Example:
class ordered SimpleJoinPattern
The closest related language is the
Polyphonic C#.
JErlang
In
Erlang coding synchronisation between multiple processes is not straightforward. That's why the
JErlang,
an extension of
Erlang was created, The J is for Join. Indeed, To overcome this limitation JErlang was implemented, a
Join-Calculus inspired extension to
Erlang.
The features of this language are:
* Joins allows first Match semantics and the possibility of having multiple patterns with a preservation of the messages's order.
operation() ->
receive
and and ->
;
and and ->
;
and and ->
;
end
end
* Guards provides additional filtering not expressing in terms of patterns. Limited number of expression without side-effects
receive
and
when (Lower <= M and M <= Upper ) ->
commit_transaction(M, Transaction)
end
* With Non-linear patterns, messages can match multiple joins
receive
and ->
end
...
receive
and and ->
perform_transaction(Pin, Id)
end
* propagation allows for copying correct messages instead of removing them.
receive
prop() and ->
perform_action(Action, Id);
and ->
logout_user(Id)
end
...
receive
and and ->
perform_transaction(Pin, Id)
end
* Synchronous calls
receive
and
and ->
Pid1 ! ,
Pid2 !
end
C++
Yigong Liu has written som
classes for the join patternincluding all useful tools like
asynchronous
Asynchrony is any dynamic far from synchronization. If and as parts of an asynchronous system become more synchronized, those parts or even the whole system can be said to be in sync.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and com ...
and synchronous channels,
chords, etc. It's integrated in the projec
Boost c++
template
class buffer: public joint ;
This example shows us a thread safe buffer and message queue with the basic operations put and get.
C#
Polyphonic C#
Polyphonic C# is an extension of the C# programming language. It introduces a new concurrency model with synchronous and asynchronous (which return control to the caller) methods and chords (also known as ‘synchronization patterns’ or ‘join patterns’).
public class Buffer
This is a simple buffer example.
MC# MC#
language is an adaptation of the Polyphonic C# language for the case of concurrent distributed computations.
public handler Get2 long () & channel c1 (long x)
& channel c2 (long y)
This example demonstrates the using of chords as a synchronization tool.
Parallel C# Parallel C#
is based Polyphonic C# and they add some new concepts like movables methods, high-order functions.
using System;
class Test13
This example demonstrates how to use joins.
Cω
Cω adds new language features to support
concurrent programming
Concurrent means happening at the same time. Concurrency, concurrent, or concurrence may refer to:
Law
* Concurrence, in jurisprudence, the need to prove both ''actus reus'' and ''mens rea''
* Concurring opinion (also called a "concurrence"), a ...
(based on the earlier
Polyphonic C#). The Joins Concurrency Library for C# and other .NET languages is derived of this project.
Scalable Join Patterns
It's an easy to use declarative and scalable join-pattern library. In opposite to the Russo library,
it has no global lock. In fact, it's working with a
compare-and-swap In computer science, compare-and-swap (CAS) is an atomic instruction used in multithreading to achieve synchronization. It compares the contents of a memory location with a given (the previous) value and, only if they are the same, modifies the ...
CAS and Atomic message system. The library use three improvements for the join-pattern :
* Stealing message for unused resources (allowing barging);
* Lazy queue saves both on allocation and potentially on interprocessor communication by avoiding allocate or enqueue with an optimistic fast-path;
* A status "WOKEN" : ensures that a blocked synchronous caller is woken only once.
JoCaml
JoCaml is the first language where the join-pattern was implemented. Indeed, at the beginning all the different implementation was compiled with the JoCaml Compiler
JoCaml languageis an extension of the
OCaml
OCaml ( , formerly Objective Caml) is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, High-level programming language, high-level, Comparison of multi-paradigm programming languages, multi-paradigm programming language which extends the ...
language. It extends OCaml with support for concurrency and synchronization, the distributed execution of programs, and the dynamic relocation of active program fragments during execution.
gives
Coffee
Tea
Refund 5
Hume
Hume is a
strict,
strongly typed functional language for limited resources platforms, with concurrency based on asynchronous message passing,
dataflow programming, and a
Haskell
Haskell () is a general-purpose, statically typed, purely functional programming language with type inference and lazy evaluation. Designed for teaching, research, and industrial applications, Haskell pioneered several programming language ...
like syntax.
Hume does not provide synchronous messaging.
It wraps a join-pattern set with a channel in common as a ''box'', listing all channels in an ''in'' tuple and specifying all possible outputs in an ''out'' tuple.
Every join-pattern in the set must conform to the ''box'' input tuple type specifying a '*' for non required channels, giving an expression whose type conform to the output tuple, marking '*' the non fed outputs.
A ''wire'' clause specifies
# a tuple of corresponding input origins or sources and optionally start values
# a tuple of output destinations, being channels or sinks (stdout, ..).
A ''box'' can specify exception handlers with expressions conforming to the output tuple.
data Coins = Nickel , Dime;
data Drinks = Coffee , Tea;
data Buttons = BCoffee , BTea , BCancel;
type Int = int 32 ;
type String = string ;
show u = u as string ;
box coffee
in ( coin :: Coins, button :: Buttons, value :: Int ) -- input channels
out ( drink_outp :: String, value’ :: Int, refund_outp :: String) -- named outputs
match
-- * wildcards for unfilled outputs, and unconsumed inputs
( Nickel, *, v) -> ( *, v + 5, *)
, ( Dime, *, v) -> ( *, v + 10, *)
, ( *, BCoffee, v) -> vend Coffee 10 v
, ( *, BTea, v) -> vend Tea 5 v
, ( *, BCancel, v) -> let refund u = "Refund " ++ show u ++ "\n"
in ( *, 0, refund v)
;
vend drink cost credit = if credit >= cost
then ( serve drink, credit - cost, *)
else ( *, credit, *);
serve drink = case drink of
Coffee -> "Cofee\n"
Tea -> "Tea\n"
;
box control
in (c :: char)
out (coin :: Coins, button:: Buttons)
match
'n' -> (Nickel, *)
, 'd' -> (Dime, *)
, 'c' -> (*, BCoffee)
, 't' -> (*, BTea)
, 'x' -> (*, BCancel)
, _ -> (*, *)
;
stream console_outp to "std_out" ;
stream console_inp from "std_in" ;
-- dataflow wiring
wire cofee
-- inputs (channel origins)
(control.coin, control.button, coffee.value’ initially 0)
-- outputs destinations
(console_outp, coffee.value, console_outp)
;
wire control
(console_inp)
(coffee.coin, coffee.button)
;
Visual Basic
Concurrent Basic – CB
An extension of Visual Basic 9.0 with asynchronous concurrency constructs, called Concurrent Basic (for short CB), offer the join patterns. CB (builds on earlier work on Polyphonic C#, Cω and the Joins Library) adopts a simple event-like syntax familiar to VB programmers, allows one to declare generic concurrency abstractions and provides more natural support for inheritance, enabling a subclass to augment the set of patterns. CB class can declare method to execute ''when'' communication has occurred on a particular set of local channels asynchronous and synchronous, forming a join pattern.
This example shows all new keywords used by Concurrent Basic: Asynchronous, Synchronous and When.
Joins library (C# and VB)
This library is a high-level abstractions of the Join Pattern using objects and generics. Channels are special delegate values from some common Join object (instead of methods).
class Buffer
This example shows how to use methods of the Join object.
Scala
The Scala Joins library uses the Join-Pattern. The
pattern matching
In computer science, pattern matching is the act of checking a given sequence of tokens for the presence of the constituents of some pattern. In contrast to pattern recognition, the match usually must be exact: "either it will or will not be a ...
facilities of this language have been generalized to allow representation independence for objects used in pattern matching. So now it's possible to use a new type of abstraction in libraries. The advantage of join patterns is that they allow a declarative specification of the synchronization between different threads. Often, the join patterns corresponds closely to a finite state machine that specifies the valid states of the object.
In Scala, it's possible to solve many problem with the pattern matching and Scala Joins, for example the Reader-Writer.
With a class we declare events in regular fields. So, it's possible to use the Join construct to enable a pattern matching via a list of case declarations. That list is representing by => with on each side a part of the declaration. The left-side is a model of join pattern to show the combination of events asynchronous and synchronous and the right-side is the body of join which is executed with the join model is completed.
In Scala, it's also possible to use the Scala's actor library
with the join pattern. For example, an unbounded buffer:
an
Chymystare newer implementations of the Join Pattern, improving upon Dr. Philipp Haller'
Scala Joins
Haskell Join Language
is an implementation of the Join Pattern in Haskell.
Scheme
The Join Patterns allows a new programming type especially for the multi-core architectures available in many programming situations with a high-levels of abstraction. This is based on the Guards and Propagation. So an example of this innovation has been implemented in Scheme .
Guards is essential to guarantee that only data with a matching key is updated/retrieved. Propagation can cancel an item, reads its contents and puts backs an item into a store. Of course, the item is also in the store during the reading. The guards is expressed with shared variables. And so the novelty is that the join pattern can contains now propagated and simplified parts. So in Scheme, the part before / is propagated and the part after / is removed.
The use of the Goal-Based is to divise the work in many tasks and joins all results at the end with the join pattern. A system named "MiniJoin" has implemented to use the intermediate result to solve the others tasks if it's possible. If is not possible it waits the solution of others tasks to solve itself.
So the concurrent join pattern application executed in parallel on a multi-core architecture doesn't guarantee that parallel execution lead to conflicts. To Guarantee this and a high degree of parallelism, a Software Transactional Memory (STM) within a highlytuned concurrent data structure based on atomic compare-and-swap (CAS) is use. This allows to run many concurrents operations in parallel on multi-core architecture. Moreover, an atomic execution is used to prevent the "false conflict" between CAS and STM.
Other similar design patterns
Join Pattern is not the only pattern to perform multitasks but it's the only one that allow communication between resources, synchronization and join different processes.
* Sequence pattern : consists of waiting that a task have completed to switch to another (the classic implementation).
* Split pattern (''parallel split'') : perform several tasks in parallel at the same time (e.g.
Map reduce
MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets with a Parallel computing, parallel and distributed computing, distributed algorithm on a Cluster (computing), cluster.
A MapReduce progr ...
).
See also
*
Joins (concurrency library) – Joins is an asynchronous concurrent computing API from Microsoft Research for the .NET Framework.
*
Join-calculus – The join-calculus was developed to provide a formal basis for the design of distributed programming languages.
*
Actor model
The actor model in computer science is a mathematical model of concurrent computation that treats an ''actor'' as the basic building block of concurrent computation. In response to a message it receives, an actor can: make local decisions, create ...
- another alternative to threads that uses message passing
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Notes
External links
Concurrent BasicScalable Joins The Joins Concurrency Library* INRIA
Join Calculus homepage
{{Types of programming languages
Distributed computing
Software design patterns
 Join-pattern is defined by a set of pi-calculus channels that supports two different operations, sending and receiving, we need two join calculus names to implement it: a channel name for sending (a message), and a function name for receiving a value (a request). The meaning of the join definition is that a call to returns a value that was sent on a channel . Each time functions are concurrently, triggers the return process and synchronizes with other joins.
Join-pattern is defined by a set of pi-calculus channels that supports two different operations, sending and receiving, we need two join calculus names to implement it: a channel name for sending (a message), and a function name for receiving a value (a request). The meaning of the join definition is that a call to returns a value that was sent on a channel . Each time functions are concurrently, triggers the return process and synchronizes with other joins.
 In most of cases, the order of synchronous calls is not guaranteed for performance reasons. Finally, during the match the messages available in the queue could be stolen by some intervening thread; indeed, the awakened thread may have to wait again.
In most of cases, the order of synchronous calls is not guaranteed for performance reasons. Finally, during the match the messages available in the queue could be stolen by some intervening thread; indeed, the awakened thread may have to wait again.