Job Plot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Within
 In solutions where two species are present (i.e. species A and species B), one species (A) may bind to the other species (B). In some cases, more than one A will bind with a single B. One way to determine the amount of A binding to B is by using a Job plot.
In this method, the sum of the
In solutions where two species are present (i.e. species A and species B), one species (A) may bind to the other species (B). In some cases, more than one A will bind with a single B. One way to determine the amount of A binding to B is by using a Job plot.
In this method, the sum of the
chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
, a Job plot, otherwise known as the method of continuous variation or Job's method, is a method used in analytical chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute t ...
to determine the stoichiometry
Stoichiometry () is the relationships between the masses of reactants and Product (chemistry), products before, during, and following chemical reactions.
Stoichiometry is based on the law of conservation of mass; the total mass of reactants must ...
of a binding event. The method is named after Paul Job and is also used in instrumental analysis
Instrumental analysis is a field of analytical chemistry that investigates analytes using scientific instruments.
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy measures the interaction of the molecules with electromagnetic spectrum, electromagnetic radiation. Spec ...
and advanced chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, chemical equilibrium is the state in which both the Reagent, reactants and Product (chemistry), products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time, so that there is no observable chan ...
texts and research articles. Job first published his method in 1928, while studying the associations of ions in solution. By plotting the UV absorbance of a solution of against the mole fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the to ...
of , he produced a graph which provided information about the equilibrium complexes present in solution.
Theory
 In solutions where two species are present (i.e. species A and species B), one species (A) may bind to the other species (B). In some cases, more than one A will bind with a single B. One way to determine the amount of A binding to B is by using a Job plot.
In this method, the sum of the
In solutions where two species are present (i.e. species A and species B), one species (A) may bind to the other species (B). In some cases, more than one A will bind with a single B. One way to determine the amount of A binding to B is by using a Job plot.
In this method, the sum of the molar concentration
Molar concentration (also called molarity, amount concentration or substance concentration) is the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Specifically, It is a measure of the concentration of a chemical species, in particular, of a so ...
s of the two binding partners (e.g. a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
and ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
or a metal and a ligand) is held constant, but their mole fractions
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction, also called mole proportion or molar proportion, is a quantity defined as the ratio between the amount of a constituent substance, ''ni'' (expressed in unit of moles, symbol mol), and the total ...
are varied. An observable that is proportional to complex formation (such as absorption signal or enzymatic activity) is plotted against the mole fractions of these two components.
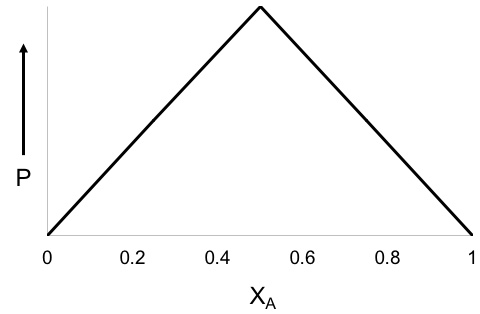
χA is the mole fraction of compound A and P is the physical property being measured to understand complex formation. This property is most oftentimes UV absorbance.
The maximum (or minimum) on the plot corresponds to the stoichiometry of the two species if sufficiently high concentrations are used. The plot also provides insight to understand the equilibrium constant (Keq) of complex formation. A greater curvature leads to a more evenly distributed equilibrium, while a more triangle-shaped plot signifies a large Keq. Further, after determining the equilibrium constant, we can determine what complexes (ratio of A and B) are present in solution. In addition, the peak of the Job Plot corresponds to the mole fraction of ligands bound to a molecule, which is important for studying ligand field theory
Ligand field theory (LFT) describes the bonding, orbital arrangement, and other characteristics of coordination complexes. It represents an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metal complexes. A transition metal ion has nine vale ...
. An early work of I. Ostromisslensky describes essentially this approach.
Requirements
There are several conditions that must be met in order for Job's method to be applicable. Firstly, the property being studied must vary in direct proportion to the concentration of the species. In the case of UV-visible spectroscopy, for example, this means that the system must conform to the Beer-Lambert law. In addition, the total concentration of the two binding partners, the pH andionic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such a ...
of the solution must all be maintained at fixed values throughout the experiment.
Finally, there must be only one complex in solution which predominates over all others under the conditions of the experiment. This requirement means that only systems with high association constants, or systems in which only one stoichiometry can form, are suitable for analysis by Job plot. As such, the use of the Job plot in supramolecular chemistry
Supramolecular chemistry refers to the branch of chemistry concerning Chemical species, chemical systems composed of a integer, discrete number of molecules. The strength of the forces responsible for spatial organization of the system range from w ...
has been advised against.
References
{{Analytical chemistry Scientific techniques