jcuken on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
JCUKEN (''ЙЦУКЕН'', also known as ''YCUKEN'', ''YTsUKEN'' and ''JTSUKEN'') is the main Cyrillic













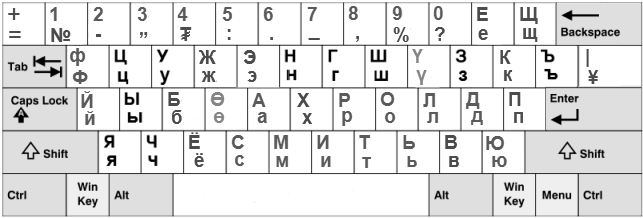


 ''Phonetic Cyrillic keyboard layout for Bulgarian in 2006 (Also known as "ЧШЕРТЪ" ChShert).''
''Phonetic Cyrillic keyboard layout for Bulgarian in 2006 (Also known as "ЧШЕРТЪ" ChShert).''


keyboard layout
A keyboard layout is any specific physical, visual or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key-meaning associations (respectively) of a computer keyboard, mobile phone, or other computer-controlled typographic keyboard.
is the actua ...
for the Russian language in computers and typewriter
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an inked ribbon selectivel ...
s. Earlier in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
''JIUKEN'' (''ЙІУКЕН'') layout was the main layout, but it was replaced by JCUKEN when the Russian alphabet reform of 1917 removed the letters Ѣ, І, Ѵ, and Ѳ. The letter Ъ had decreased in usage significantly after the reform.
Alternative layouts include the Russian phonetic keyboard layout
A phonetic keyboard layout is a setup in which the letters of a language correspond to the keys in the keyboard layout for another language and assumes a one-to-one correspondence between letters in the languages that is based on their sound.
Ph ...
s, in which Cyrillic letters correspond to similar-sounding Latin letter
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Ital ...
s in QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden t ...
and other layouts.
JCUKEN
PC
Typewriters
Used ontypewriters
A typewriter is a mechanical or electromechanical machine for typing characters. Typically, a typewriter has an array of keys, and each one causes a different single character to be produced on paper by striking an inked ribbon selectively ...
before personal computers. It is available in Microsoft Windows as a legacy layout.
JIUKEN
The JIUKEN layout was used before the Russian spelling reform of 1918. It includes the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I as well asyat
Yat or jat (Ѣ ѣ; italics: ) is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet and the Rusyn alphabet.
There is also another version of yat, the iotified yat (majuscule: , minuscule: ), which is a Cyrillic character combining a ...
, which were eliminated after the reform, but it does not include the letters fita
Fita (Ѳ ѳ; italics: ) is a letter of the Early Cyrillic alphabet. The shape and the name of the letter are derived from the Greek letter theta (Θ θ). In the ISO 9 system, Ѳ is romanized using F grave accent (F̀ f̀).
In the ...
and izhitsa
Izhitsa or Izhica (Ѵ, ѵ; italics: ; OCS: Ѷжица, Russian: Ижица, Ukrainian: Іжиця) is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet and several later alphabets, usually the last in the row. It originates from the Greek letter upsilo ...
, which were rare even before the reform. The numbers 1, 3 and 0 do not appear on the layout and were replaced with the decimal I
The dotted i (І і; italics: '), also called decimal i (и десятеричное, after its former numeric value), is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation o ...
, Ze, and O respectively. The letters Ц and Э are located side-by-side, and between the Che and the Es is the yat
Yat or jat (Ѣ ѣ; italics: ) is the thirty-second letter of the old Cyrillic alphabet and the Rusyn alphabet.
There is also another version of yat, the iotified yat (majuscule: , minuscule: ), which is a Cyrillic character combining a ...
. The letter yo is not included in this layout.
Other languages
JCUKEN is the basis for many other Cyrillic layouts. For the current moment Microsoft Windows supports the following layouts: Azerbaijani (Cyrillic), Bashkir, Belarusian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Mongolian, Tajik,Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
, Uzbek (Cyrillic), Yakut (Sakha). The Belarusian, Ukrainian and Mongolian layouts have been available since Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented operating system developed by Microsoft as part of its Windows 9x family of operating systems. The first operating system in the 9x family, it is the successor to Windows 3.1x, and was released to manufacturi ...
; Azeri, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tatar, Uzbek since Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and ...
; Bashkir and Tajik since Windows Vista
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years before, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of ...
; Yakut since Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009. It is the successor to Windows Vista, released nearly ...
.
Other operating systems such as Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, w ...
may have their own additional custom layouts for the same or other languages.
Belarusian
Theshort U
Short U (Ў ў; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. The only Slavic language using this letter in its orthography is Belarusian, though it is used as a phonetic symbol in some Russian and Ukrainian dictionaries. Among the non-Sl ...
(Ў ў) is located in place of the shcha
Shcha (Щ щ; italics: ), Shta or Sha with descender is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of in ''sheep'' (but longer). In Ukrainian and Rusy ...
(Щ щ). It is the only JCUKEN keyboard that lacks a key for И, as it is the only language in the Cyrillic script that does not contain the letter И itself; the decimal I
The dotted i (І і; italics: '), also called decimal i (и десятеричное, after its former numeric value), is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation o ...
(І і) replaces it. It also lacks a hard sign
The letter Ъ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam (ер голям – "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (russian: твёрдый знак, tvjórdyj znak, , rue, твердый знак, tverdyj znak) in ...
(Ъ ъ), usually seen just to the right of letter ha (Х х) as that position is taken by the Apostrophe.
Ukrainian
Thedecimal I
The dotted i (І і; italics: '), also called decimal i (и десятеричное, after its former numeric value), is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close front unrounded vowel , like the pronunciation o ...
replaces the yeru
Yeru or Eru (Ы ы; italics: ), usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel (more rear or upper than i) ...
(Ы ы) and the yest (Є є) replaces the E (Э э). The letter Yi (Ї ї) substitutes for the hard sign
The letter Ъ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam (ер голям – "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (russian: твёрдый знак, tvjórdyj znak, , rue, твердый знак, tverdyj znak) in ...
(Ъ ъ), and Ghe with upturn
Ghe with upturn (Ґ ґ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It is part of the Ukrainian alphabet, the Pannonian Rusyn alphabet and both the Carpathian Rusyn alphabets, and also some variants of the Urum and Belarusian (i.e. Bel ...
(Ґ ґ) is also used.
Tatar
The Russian letters which are rarely used in Tatar are typed with (right ). This layout is also suitable for Kalmyk and Turkmen (Cyrillic) as their alphabets are practically identical to Tatar. It is called as YÖUKEN.Bashkir
Kazakh
Kyrgyz
An "upgraded" version based on the basic Russian one, the additional Kyrgyz letters are typed with (right ). Thus, + У is Ү, + О is Ө, and + Н is Ң.Yakut (Sakha)
Tajik
This is a modified version of JCUKEN called YQUKEN, in which theKa with descender
Ka with descender (Қ қ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script used in a number of non-Slavic languages spoken in the territory of the former Soviet Union, including:
* the Turkic languages Kazakh, Uighur, Uzbek and several smalle ...
(Қ қ) substitutes the C (Ц ц). The yeru
Yeru or Eru (Ы ы; italics: ), usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel (more rear or upper than i) ...
(Ы ы) is replaced by the letter Che with descender
Che with descender (Ҷ ҷ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Che (Ч ч ). In the ISO 9 system of romanization, Che with descender is transliterated using the Latin letter ...
(Ҷ ч). Also, the soft sign
The soft sign (Ь, ь, italics ) also known as the front yer, front jer, or er malak (lit. "small er") is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short (or "reduced") front vowel. As with its companion, the b ...
(Ь ь) is replaced by the I with macron (Ӣ ӣ). Further, the Kha with descender
Kha with descender (Ҳ ҳ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Unicode, this letter is called "Ha with descender". Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Kha (Х х ).
Kha with descender is used in the alphabe ...
(Ҳ ҳ), the U with macron (Ӯ ӯ), and the ghayn
The Arabic letter ( ar, غَيْنْ ' or ') is the nineteenth letter of the Arabic alphabet, one of the six letters not in the twenty-two akin to the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ), it represents the sound or . In name and ...
(Ғ ғ) are used. (In Unicode, Kha with descender is known as "Ha with descender".)
Uzbek
Theshort U
Short U (Ў ў; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. The only Slavic language using this letter in its orthography is Belarusian, though it is used as a phonetic symbol in some Russian and Ukrainian dictionaries. Among the non-Sl ...
substitutes the shcha
Shcha (Щ щ; italics: ), Shta or Sha with descender is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of in ''sheep'' (but longer). In Ukrainian and Rusy ...
, like the Belarusian keyboard (see above), and the ka with descender
Ka with descender (Қ қ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script used in a number of non-Slavic languages spoken in the territory of the former Soviet Union, including:
* the Turkic languages Kazakh, Uighur, Uzbek and several smalle ...
substitutes the yery
Yeru or Eru (Ы ы; italics: ), usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel (more rear or upper than i) ...
. Moreover, the letter ghayn
The Arabic letter ( ar, غَيْنْ ' or ') is the nineteenth letter of the Arabic alphabet, one of the six letters not in the twenty-two akin to the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ), it represents the sound or . In name and ...
substitutes the minus sign
The plus and minus signs, and , are mathematical symbols used to represent the notions of positive and negative, respectively. In addition, represents the operation of addition, which results in a sum, while represents subtraction, resul ...
and the underscore
An underscore, ; also called an underline, low line, or low dash; is a line drawn under a segment of text. In proofreading, underscoring is a convention that says "set this text in italic type", traditionally used on manuscript or typescript a ...
, while the kha with descender
Kha with descender (Ҳ ҳ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Unicode, this letter is called "Ha with descender". Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Kha (Х х ).
Kha with descender is used in the alphabe ...
substitutes the plus sign and equal sign
The equals sign (British English, Unicode) or equal sign (American English), also known as the equality sign, is the mathematical symbol , which is used to indicate equality in some well-defined sense. In an equation, it is placed between two ...
.
Azerbaijani
This layout is a modified version called the JÜUKEN, and includes theChe with vertical stroke
Che with vertical stroke (Ҹ ҹ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Che (Cyrillic), Cyrillic letter Che (Ч ч ''Ч ч'').
Che with vertical stroke is used in the alphabet of the Azeri l ...
, shha, Ka with vertical stroke
Ka with vertical stroke (Ҝ ҝ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter Ka (К к) by the addition of a stroke through the short horizontal bar in the centre of the letter.
Ka with ve ...
, and the Je. It is the only JCUKEN without the usual Й, as the language lacks the glyph, which was replaced by Je in 1958.
Substitutions to this keyboard are: having the schwa replacing the ya, the oe replacing the yu, the ghayn
The Arabic letter ( ar, غَيْنْ ' or ') is the nineteenth letter of the Arabic alphabet, one of the six letters not in the twenty-two akin to the Phoenician alphabet (the others being , , , , ), it represents the sound or . In name and ...
replacing the soft sign
The soft sign (Ь, ь, italics ) also known as the front yer, front jer, or er malak (lit. "small er") is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Old Church Slavonic, it represented a short (or "reduced") front vowel. As with its companion, the b ...
, the Che with vertical stroke
Che with vertical stroke (Ҹ ҹ; italics: ) is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Che (Cyrillic), Cyrillic letter Che (Ч ч ''Ч ч'').
Che with vertical stroke is used in the alphabet of the Azeri l ...
replacing the hard sign
The letter Ъ (italics ) of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam (ер голям – "big er") in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign (russian: твёрдый знак, tvjórdyj znak, , rue, твердый знак, tverdyj znak) in ...
, the ue replacing the tsa and the shha replacing the shcha
Shcha (Щ щ; italics: ), Shta or Sha with descender is a letter of the Cyrillic script. In Russian, it represents the voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative , similar to the pronunciation of in ''sheep'' (but longer). In Ukrainian and Rusy ...
.
Mongolian
The Mongolian keyboard uses a modified version of JCUKEN, called FCUZHEN (ФЦУЖЭН), where letters specific to Russian are replaced by letters that see more use in Mongolian.
Other Cyrillic layouts
Serbian
The Serbian keyboard called LJNJERTZ (ЉЊЕРТЗ), where letters of Serbian language was used instead of Russian letters. It lacks theyer
A yer is either of two letters in Cyrillic alphabets, ъ (ѥръ, ''jerŭ'') and ь (ѥрь, ''jerĭ''). The Glagolitic alphabet used, as respective counterparts, the letters (Ⱏ) and (Ⱐ). They originally represented phonemically the "ult ...
s and yeru
Yeru or Eru (Ы ы; italics: ), usually called Y in modern Russian or Yery or Ery historically and in modern Church Slavonic, is a letter in the Cyrillic script. It represents the close central unrounded vowel (more rear or upper than i) ...
(Ъ ъ, Ь ь and Ы ы), Э, and Ё. It is based on the QWERTZ
The QWERTZ or QWERTZU keyboard is a typewriter and keyboard layout widely used in Central Europe. The name comes from the first six letters at the top left of the keyboard: ( ).
Overview
The main difference between QWERTZ and QWERTY is ...
keyboard.

Macedonian
Also utilizing a modification of the Serb-style LJNJERTZ (LJNJERTDZ), a single "dead key" is used for input for Macedonian letters Gje «Ѓ ѓ» and Kje «Ќ ќ», as well as the typewritten apostrophe (in combination with the «spacebar»): «м. к. á», «К к» → «Ќ ќ», «м. к. á», «space» → «'». Macedonian keyboard layouts under Microsoft Windows (KBDMAC.DLL and KBDMACST.DLL) do not use "dead keys". Instead, letters Gje and Kje are present as dedicated keys, and AltGr is used to access additional letters and punctuation.Bulgarian
''Standard Bulgarian keyboard from 2006 (YUEIShSht)'' ''Phonetic Cyrillic keyboard layout for Bulgarian in 2006 (Also known as "ЧШЕРТЪ" ChShert).''
''Phonetic Cyrillic keyboard layout for Bulgarian in 2006 (Also known as "ЧШЕРТЪ" ChShert).''

Latin JCUKEN
This was the predominant layout on the Soviet-made microcomputers during the 1980s - the Cyrillic characters on most keys being supplemented with their Latin equivalents, and punctuation filling gaps where no direct Latin equivalent exists.See also
*QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden t ...
References