Isoform on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar
isoform.io
The specificity of translated isoforms is derived by the protein's structure/function, as well as the cell type and developmental stage during which they are produced. Determining specificity becomes more complicated when a protein has multiple subunits and each subunit has multiple isoforms. For example, the 5' AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme, which performs different roles in human cells, has 3 subunits: * α, catalytic domain, has two isoforms: α1 and α2 which are encoded from
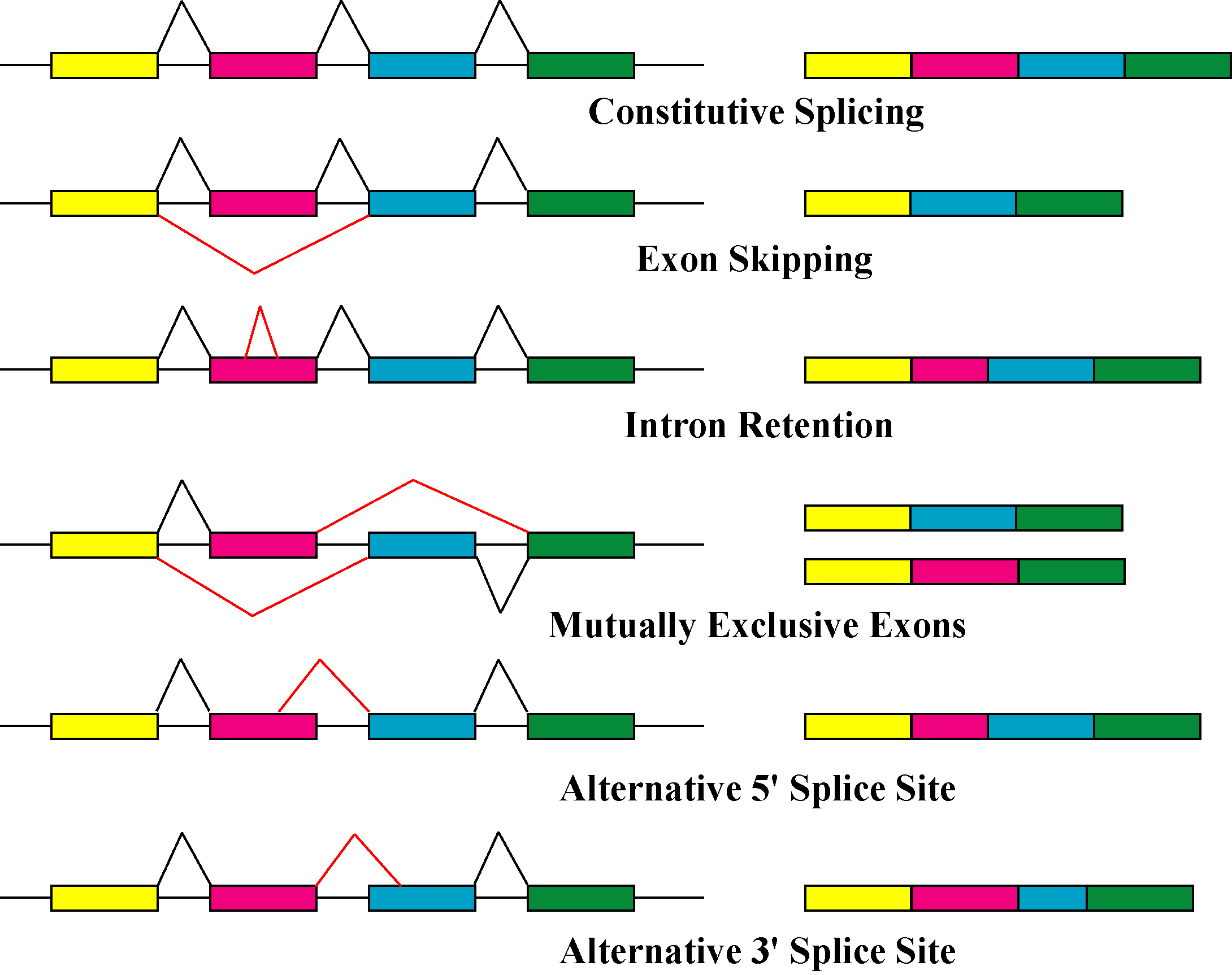 The primary mechanisms that produce protein isoforms are alternative splicing and variable promoter usage, though modifications due to genetic changes, such as
The primary mechanisms that produce protein isoforms are alternative splicing and variable promoter usage, though modifications due to genetic changes, such as
MeSH entry protein isoforms
Definitions Isoform
{{DEFAULTSORT:Protein Isoform Protein structure
 A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
that originate from a single gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isoforms have unique functions. A set of protein isoforms may be formed from alternative splicings, variable promoter usage, or other post-transcriptional modifications of a single gene; post-translational modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosome ...
s are generally not considered. (For that, see Proteoform
Proteoforms are the different forms of a protein produced from the genome with a variety of sequence variations, splice isoforms, and post-translational modifications
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymati ...
s.) Through RNA splicing
RNA splicing is a process in molecular biology where a newly-made precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript is transformed into a mature messenger RNA (mRNA). It works by removing all the introns (non-coding regions of RNA) and ''splicing'' b ...
mechanisms, mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
has the ability to select different protein-coding segments ( exons) of a gene, or even different parts of exons from RNA to form different mRNA sequences. Each unique sequence produces a specific form of a protein.
The discovery of isoforms could explain the discrepancy between the small number of protein coding regions genes revealed by the human genome project
The Human Genome Project (HGP) was an international scientific research project with the goal of determining the base pairs that make up human DNA, and of identifying, mapping and sequencing all of the genes of the human genome from both a ...
and the large diversity of proteins seen in an organism: different proteins encoded by the same gene could increase the diversity of the proteome
The proteome is the entire set of proteins that is, or can be, expressed by a genome, cell, tissue, or organism at a certain time. It is the set of expressed proteins in a given type of cell or organism, at a given time, under defined conditions. ...
. Isoforms at the RNA level are readily characterized by cDNA transcript studies. Many human genes possess confirmed alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be ...
isoforms. It has been estimated that ~100,000 expressed sequence tags ( ESTs) can be identified in humans. Isoforms at the protein level can manifest in the deletion of whole domains or shorter loops, usually located on the surface of the protein.
Definition
One single gene has the ability to produce multiple proteins that differ both in structure and composition; this process is regulated by thealternative splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be ...
of mRNA, though it is not clear to what extent such a process affects the diversity of the human proteome, as the abundance of mRNA transcript isoforms does not necessarily correlate with the abundance of protein isoforms. Three-dimensional protein structure comparisons can be used to help determine which, if any, isoforms represent functional protein products, and the structure of most isoforms in the human proteome has been predicted by AlphaFold
AlphaFold is an artificial intelligence (AI) program developed by DeepMind, a subsidiary of Alphabet, which performs predictions of protein structure. The program is designed as a deep learning system.
AlphaFold AI software has had two major ve ...
and publicly released aisoform.io
The specificity of translated isoforms is derived by the protein's structure/function, as well as the cell type and developmental stage during which they are produced. Determining specificity becomes more complicated when a protein has multiple subunits and each subunit has multiple isoforms. For example, the 5' AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an enzyme, which performs different roles in human cells, has 3 subunits: * α, catalytic domain, has two isoforms: α1 and α2 which are encoded from
PRKAA1
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAA1'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the serine/threonine protein kinase family. It is the catalytic subunit of the 5' ...
and PRKAA2
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAA2'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a catalytic subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a h ...
* β, regulatory domain, has two isoforms: β1 and β2 which are encoded from PRKAB1
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAB1'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting o ...
and PRKAB2
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit beta-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAB2'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer consisting o ...
* γ, regulatory domain, has three isoforms: γ1, γ2, and γ3 which are encoded from PRKAG1
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAG1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer ...
, PRKAG2
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAG2'' gene.
Function
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a heterotrimeric protein composed of a catalytic alpha subunit, a noncatalytic beta s ...
, and PRKAG3
5'-AMP-activated protein kinase subunit gamma-3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKAG3'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a regulatory subunit of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). AMPK is a heterotrimer ...
In human skeletal muscle, the preferred form is α2β2γ1. But in the human liver, the most abundant form is α1β2γ1.
Mechanism
 The primary mechanisms that produce protein isoforms are alternative splicing and variable promoter usage, though modifications due to genetic changes, such as
The primary mechanisms that produce protein isoforms are alternative splicing and variable promoter usage, though modifications due to genetic changes, such as mutations
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
and polymorphisms are sometimes also considered distinct isoforms.
Alternative splicing is the main post-transcriptional modification
Transcriptional modification or co-transcriptional modification is a set of biological processes common to most eukaryotic cells by which an RNA primary transcript is chemically altered following transcription from a gene to produce a mature, fu ...
process that produces mRNA transcript isoforms, and is a major molecular mechanism that may contribute to protein diversity. The spliceosome
A spliceosome is a large ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex found primarily within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. The spliceosome is assembled from small nuclear RNAs ( snRNA) and numerous proteins. Small nuclear RNA (snRNA) molecules bind to specif ...
, a large ribonucleoprotein
Nucleoproteins are proteins conjugated with nucleic acids (either DNA or RNA). Typical nucleoproteins include ribosomes, nucleosomes and viral nucleocapsid proteins.
Structures
Nucleoproteins tend to be positively charged, facilitating int ...
, is the molecular machine inside the nucleus responsible for RNA cleavage and ligation
Ligation may refer to:
* Ligation (molecular biology), the covalent linking of two ends of DNA or RNA molecules
* In medicine, the making of a ligature (tie)
* Chemical ligation, the production of peptides from amino acids
* Tubal ligation, a meth ...
, removing non-protein coding segments (introns
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene ...
).
Because splicing is a process that occurs between transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, the fir ...
and translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
, its primary effects have mainly been studied through genomics
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, three-dim ...
techniques—for example, microarray analyses and RNA sequencing
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a sequencing technique which uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, analyzing the continuously changing ...
have been used to identify alternatively spliced transcripts and measure their abundances. Transcript abundance is often used as a proxy for the abundance of protein isoforms, though proteomics experiments using gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry have demonstrated that the correlation between transcript and protein counts is often low, and that one protein isoform is usually dominant. One 2015 study states that the cause of this discrepancy likely occurs after translation, though the mechanism is essentially unknown. Consequently, although alternative splicing has been implicated as an important link between variation and disease, there is no conclusive evidence that it acts primarily by producing novel protein isoforms.
Alternative splicing generally describes a tightly regulated process in which alternative transcripts are intentionally generated by the splicing machinery. However, such transcripts are also produced by splicing errors in a process called "noisy splicing," and are also potentially translated into protein isoforms. Although ~95% of multi-exonic genes are thought to be alternatively spliced, one study on noisy splicing observed that most of the different low-abundance transcripts are noise, and predicts that most alternative transcript and protein isoforms present in a cell are not functionally relevant.
Other transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory steps can also produce different protein isoforms. Variable promoter usage occurs when the transcriptional machinery of a cell (RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
, transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The func ...
, and other enzymes
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
) begin transcription at different promoters—the region of DNA near a gene that serves as an initial binding site—resulting in slightly modified transcripts and protein isoforms.
Characteristics
Generally, one protein isoform is labeled as the canonical sequence based on criteria such as its prevalence and similarity toorthologous
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a s ...
—or functionally analogous—sequences in other species. Isoforms are assumed to have similar functional properties, as most have similar sequences, and share some to most exons with the canonical sequence. However, some isoforms show much greater divergence (for example, through trans-splicing
''Trans''-splicing is a special form of RNA processing where exons from two different primary RNA transcripts are joined end to end and ligated. It is usually found in eukaryotes and mediated by the spliceosome, although some bacteria and archa ...
), and can share few to no exons with the canonical sequence. In addition, they can have different biological effects—for example, in an extreme case, the function of one isoform can promote cell survival, while another promotes cell death—or can have similar basic functions but differ in their sub-cellular localization. A 2016 study, however, functionally characterized all the isoforms of 1,492 genes and determined that most isoforms behave as "functional alloforms." The authors came to the conclusion that isoforms behave like distinct proteins after observing that the functional of most isoforms did not overlap. Because the study was conducted on cells ''in vitro'', it is not known if the isoforms in the expressed human proteome share these characteristics. Additionally, because the function of each isoform must generally be determined separately, most identified and predicted isoforms still have unknown functions.
Related Concept
Glycoform
A glycoform is an isoform of a protein that differs only with respect to the number or type of attached glycan.Glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
often consist of a number of different glycoforms, with alterations in the attached saccharide
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
or oligosaccharide
An oligosaccharide (/ˌɑlɪgoʊˈsækəˌɹaɪd/; from the Greek ὀλίγος ''olígos'', "a few", and σάκχαρ ''sácchar'', "sugar") is a saccharide polymer containing a small number (typically two to ten) of monosaccharides (simple sugar ...
. These modifications may result from differences in biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules. ...
during the process of glycosylation, or due to the action of glycosidases
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the rea ...
or glycosyltransferases
Glycosyltransferases (GTFs, Gtfs) are enzymes ( EC 2.4) that establish natural glycosidic linkages. They catalyze the transfer of saccharide moieties from an activated nucleotide sugar (also known as the " glycosyl donor") to a nucleophilic gly ...
. Glycoforms may be detected through detailed chemical analysis of separated glycoforms, but more conveniently detected through differential reaction with lectins
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in rec ...
, as in lectin affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating a biomolecule from a mixture, based on a highly specific macromolecular binding interaction between the biomolecule and another substance. The specific type of binding interaction depends on the ...
and lectin
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that are highly specific for sugar groups that are part of other molecules, so cause agglutination of particular cells or precipitation of glycoconjugates and polysaccharides. Lectins have a role in rec ...
affinity electrophoresis
Affinity electrophoresis is a general name for many analytical methods used in biochemistry and biotechnology. Both qualitative and quantitative information may be obtained through affinity electrophoresis. The methods include the so-called elect ...
. Typical examples of glycoproteins consisting of glycoforms are the blood proteins
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood pr ...
as orosomucoid
Orosomucoid (ORM) or alpha-1-acid glycoprotein (''α1AGp'', ''AGP'' or ''AAG'') is an acute phase protein found in plasma. It is an alpha-globulin glycoprotein and is modulated by two polymorphic genes. It is synthesized primarily in hepatoc ...
, antitrypsin
Alpha-1 antitrypsin or α1-antitrypsin (A1AT, α1AT, A1A, or AAT) is a protein belonging to the serpin superfamily. It is encoded in humans by the ''SERPINA1'' gene. A protease inhibitor (biology), protease inhibitor, it is also known as alpha1� ...
, and haptoglobin
Haptoglobin (abbreviated as Hp) is the protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HP'' gene. In blood plasma, haptoglobin binds with high affinity to ''free'' hemoglobin released from erythrocytes, and thereby inhibits its deleterious oxidative ...
. An unusual glycoform variation is seen in neuronal cell adhesion molecule, NCAM involving polysialic acids, PSA.
Examples
*G-actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over ...
: despite its conserved nature, it has a varying number of isoforms (at least six in mammals).
* Creatine kinase
Creatine kinase (CK), also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phosphocreatine kinase, is an enzyme () expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and uses adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create pho ...
, the presence of which in the blood can be used as an aid in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
, exists in 3 isoforms.
* Hyaluronan synthase
Hyaluronan synthases (HAS) are membrane-bound enzymes that use UDP-α-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and UDP-α-D-glucuronate as substrates to produce the glycosaminoglycan hyaluronan at the cell surface and extrude it through the membrane into the extr ...
, the enzyme responsible for the production of hyaluronan, has three isoforms in mammalian cells.
* UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase ( UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, UGT) is a microsomal glycosyltransferase () that catalyzes the transfer of the glucuronic acid component of UDP-glucuronic acid to a small hydrophobic molecule. This is ...
, an enzyme superfamily responsible for the detoxification pathway of many drugs, environmental pollutants, and toxic endogenous compounds has 16 known isoforms encoded in the human genome.
*G6PDA: normal ratio of active isoforms in cells of any tissue is 1:1 shared with G6PDG. This is precisely the normal isoform ratio in hyperplasia. Only one of these isoforms is found during neoplasia.Pathoma, Fundamentals of Pathology
Monoamine oxidase, a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, exists in two isoforms, MAO-A and MAO-B.
See also
*Gene isoform Gene isoforms are mRNAs that are produced from the same locus but are different in their transcription start sites (TSSs), protein coding DNA sequences (CDSs) and/or untranslated regions (UTRs), potentially altering gene function.
Cis-regulatory e ...
References
External links
MeSH entry protein isoforms
Definitions Isoform
{{DEFAULTSORT:Protein Isoform Protein structure