Inguinal Hernia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An inguinal hernia is a
 Hernias usually present as bulges in the groin area that can become more prominent when coughing, straining, or standing up. The bulge commonly disappears on lying down. Mild discomfort can develop over time. The inability to "reduce", or place the bulge back into the abdomen usually means the hernia is 'incarcerated' which requires emergency surgery.
Hernias usually present as bulges in the groin area that can become more prominent when coughing, straining, or standing up. The bulge commonly disappears on lying down. Mild discomfort can develop over time. The inability to "reduce", or place the bulge back into the abdomen usually means the hernia is 'incarcerated' which requires emergency surgery.
 As the hernia progresses, contents of the abdominal cavity, such as the intestines, can descend into the hernia and run the risk of being pinched within the hernia, causing an
As the hernia progresses, contents of the abdominal cavity, such as the intestines, can descend into the hernia and run the risk of being pinched within the hernia, causing an
File:Blausen 0560 InguinalHernia.png, Illustration of an inguinal hernia.
Image:Gray1084.png, Different types of inguinal hernias.
Image:Inguinal fossae.PNG, Inguinal fossae


 There are two types of inguinal
There are two types of inguinal  In Littre's hernia, the content of the hernial sac contains a
In Littre's hernia, the content of the hernial sac contains a
 An indirect inguinal hernia results from the failure of embryonic closure of the
An indirect inguinal hernia results from the failure of embryonic closure of the
 Surgical correction of inguinal hernias is called a
Surgical correction of inguinal hernias is called a 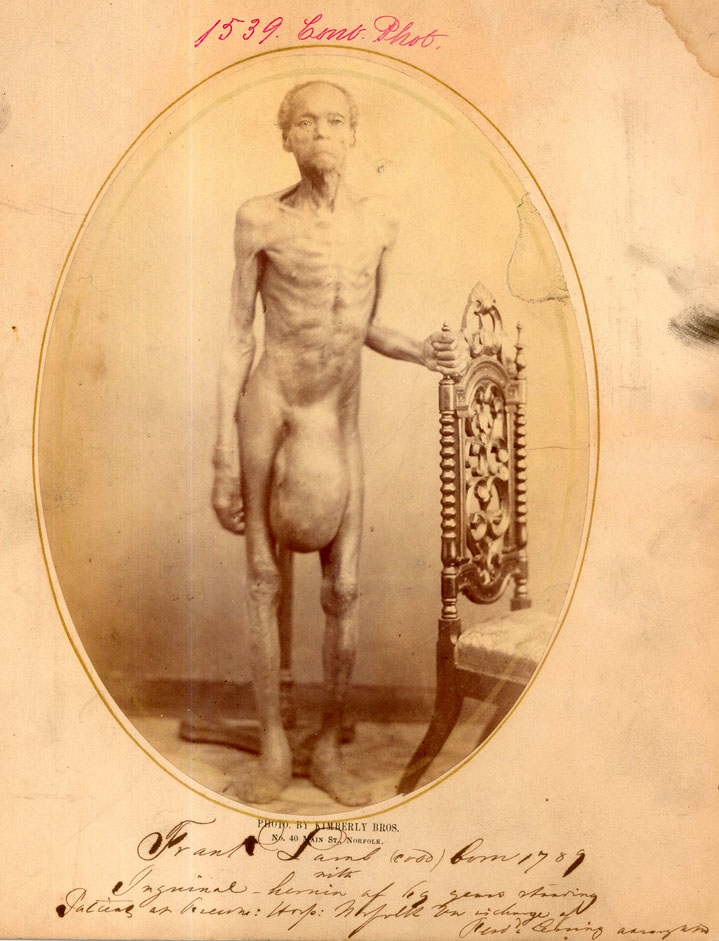 Constipation after hernia repair results in strain to evacuate the bowel causing pain, and fear that the sutures may rupture. Opioid analgesia makes constipation worse. Promoting an easy bowel motion is important post-operatively.
Surgical correction is always recommended for inguinal hernias in children.
Emergency surgery for incarceration and strangulation carry much higher risk than planned, "elective" procedures. However, the risk of incarceration is low, evaluated at 0.2% per year. On the other hand,
Constipation after hernia repair results in strain to evacuate the bowel causing pain, and fear that the sutures may rupture. Opioid analgesia makes constipation worse. Promoting an easy bowel motion is important post-operatively.
Surgical correction is always recommended for inguinal hernias in children.
Emergency surgery for incarceration and strangulation carry much higher risk than planned, "elective" procedures. However, the risk of incarceration is low, evaluated at 0.2% per year. On the other hand,
Indirect Inguinal Hernia - University of Connecticut Health Center
!-- - Rich Luzietti, MS 2005 - University of Connecticut Health Center - Lyman Maynard Stowe Library's Computer Education Center] --> * {{DEFAULTSORT:Inguinal Hernia Inguinal hernias Scrotum it:Ernia#Ernia inguinale
hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin herni ...
(protrusion) of abdominal-cavity contents through the inguinal canal
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. ...
. Symptoms, which may include pain or discomfort especially with or following coughing, exercise, or bowel movement
Defecation (or defaecation) follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus. The act has a variety of names ranging fro ...
s, are absent in about a third of patients. Symptoms often get worse throughout the day and improve when lying down. A bulging area may occur that becomes larger when bearing down. Inguinal hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the intestine is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness of the area.
Risk factors for the development of a hernia include: smoking, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops (gestation, gestates) inside a woman, woman's uterus (womb). A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Pregnancy usually occur ...
, peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis which uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte pro ...
, collagen vascular disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
, and previous open appendectomy
An appendectomy, also termed appendicectomy, is a Surgery, surgical operation in which the vermiform appendix (a portion of the intestine) is removed. Appendectomy is normally performed as an urgent or emergency procedure to treat complicated acu ...
, among others. Predisposition to hernias is genetic and they occur more often in certain families. Deleterious mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitos ...
s causing predisposition to hernias seem to have dominant inheritance (especially for men). It is unclear if inguinal hernias are associated with heavy lifting. Hernias can often be diagnosed based on signs and symptoms. Occasionally medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
is used to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other possible causes.
Groin hernias that do not cause symptoms in males do not need to be repaired. Repair, however, is generally recommended in females due to the higher rate of femoral hernia
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of ...
s which have more complications. If strangulation occurs immediate surgery is required. Repair may be done by open surgery or by laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medl ...
. Open surgery has the benefit of possibly being done under local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, that is, local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. It ...
rather than general anesthesia
General anaesthesia (UK) or general anesthesia (US) is a medically induced loss of consciousness that renders the patient unarousable even with painful stimuli. This effect is achieved by administering either intravenous or inhalational general ...
. Laparoscopic surgery generally has less pain following the procedure.
In 2015 inguinal, femoral and abdominal hernias affected about 18.5 million people. About 27% of males and 3% of females develop a groin hernia at some time in their life. Groin hernias occur most often before the age of one and after the age of fifty. Globally, inguinal, femoral and abdominal hernias resulted in 60,000 deaths in 2015 and 55,000 in 1990.
Signs and symptoms
 As the hernia progresses, contents of the abdominal cavity, such as the intestines, can descend into the hernia and run the risk of being pinched within the hernia, causing an
As the hernia progresses, contents of the abdominal cavity, such as the intestines, can descend into the hernia and run the risk of being pinched within the hernia, causing an intestinal obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or functional obstruction of the intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Either the small bowel or large bowel may be affected. Signs a ...
. Significant pain at the hernia site is suggestive of a more severe course, such as incarceration (the hernia cannot be reduced back into the abdomen) and subsequent ischemia and strangulation (when the hernia becomes deprived of blood supply). If the blood supply of the portion of the intestine caught in the hernia is compromised, the hernia is deemed "strangulated" and gut ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems wi ...
and gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
can result, with potentially fatal consequences. The timing of complications is not predictable.
Pathophysiology
In males, indirect hernias follow the same route as the descendingtestes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster ...
, which migrate from the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
into the scrotum during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs
The development of the urinary system begins during prenatal development, and relates to the development of the urogenital system – both the organs of the urinary system and the sex organs of the reproductive system. The development continues as ...
. The larger size of their inguinal canal
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. ...
, which transmitted the testicle and accommodates the structures of the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
, might be one reason why men are 25 times more likely to have an inguinal hernia than women. Although several mechanisms such as strength of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal and shutter mechanisms compensating for raised intra-abdominal pressure prevent hernia formation in normal individuals, the exact importance of each factor is still under debate. The physiological school of thought thinks that the risk of hernia is due to a physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
difference between patients who develop a hernia and those who do not, namely the presence of aponeurotic extensions from the transversus abdominis aponeurotic arch.
Inguinal hernias mostly contain the omentum or a part of the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
s, however, some unusual contents may be an appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. Symptoms commonly include right lower abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. However, approximately 40% of people do not have these typical symptoms. Severe complications of a rup ...
, diverticulitis, colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel mo ...
, urinary bladder
The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination. In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. Urine enters ...
, ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
, and rarely malignant lesions.
Diagnosis


 There are two types of inguinal
There are two types of inguinal hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin herni ...
, ''direct'' and ''indirect'', which are defined by their relationship to the inferior epigastric vessels. Direct inguinal hernias occur medial to the inferior epigastric vessels when abdominal contents herniate through a weak spot in the fascia of the posterior wall of the inguinal canal, which is formed by the transversalis fascia
The transversalis fascia (or transverse fascia) is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.
It forms part of the general layer of fascia lining ...
. Indirect inguinal hernias occur when abdominal contents protrude through the deep inguinal ring
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. ...
, lateral to the inferior epigastric vessels; this may be caused by failure of embryonic closure of the processus vaginalis
The vaginal process (or processus vaginalis) is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the parietal peritoneum. It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching.
Sex differences
In males, it prec ...
.
In the case of the female, the opening of the superficial inguinal ring is smaller than that of the male. As a result, the possibility for hernias through the inguinal canal in males is much greater because they have a larger opening and therefore a much weaker wall through which the intestines may protrude.
Inguinal hernias, in turn, belong to groin hernias, which also includes femoral hernia
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of ...
s. A femoral hernia is not via the inguinal canal, but via the femoral canal
The femoral canal is the medial (and smallest) compartment of the three compartments of the femoral sheath. It is conical in shape. The femoral canal contains lymphatic vessels, and adipose and loose connective tissue, as well as - sometimes - a ...
, which normally allows passage of the common femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the fem ...
and vein from the pelvis to the leg.
In Amyand's hernia, the content of the hernial sac is the vermiform appendix
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal r caecalappendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large i ...
.
 In Littre's hernia, the content of the hernial sac contains a
In Littre's hernia, the content of the hernial sac contains a Meckel's diverticulum
A Meckel's diverticulum, a true congenital diverticulum, is a slight bulge in the small intestine present at birth and a vestigial remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct (also called the vitelline duct or yolk stalk). It is the most common malformat ...
.
Clinical classification of hernia is also important according to which hernia is classified into
# Reducible hernia: is one which can be pushed back into the abdomen by putting manual pressure to it.
# Irreducible/Incarcerated hernia: is one which cannot be pushed back into the abdomen by applying manual pressure.
Irreducible hernias are further classified into
# Obstructed hernia: is one in which the lumen of the herniated part of intestine is obstructed.
# Strangulated hernia: is one in which the blood supply of the hernia contents is cut off, thus, leading to ischemia. The lumen of the intestine may be patent or not.
Direct inguinal hernia
The direct inguinal hernia enters through a weak point in thefascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. ...
of the abdominal wall
In anatomy, the abdominal wall represents the boundaries of the abdominal cavity. The abdominal wall is split into the anterolateral and posterior walls.
There is a common set of layers covering and forming all the walls: the deepest being the v ...
, and its sac is noted to be medial to the inferior epigastric vessels. Direct inguinal hernias may occur in males or females, but males are ten times more likely to get a direct inguinal hernia.
A direct inguinal hernia protrudes through a weakened area in the transversalis fascia
The transversalis fascia (or transverse fascia) is a thin aponeurotic membrane of the abdomen. It lies between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle and the parietal peritoneum.
It forms part of the general layer of fascia lining ...
near the medial inguinal fossa
The medial inguinal fossa is a depression located within the inguinal triangle on the peritoneal surface of the anterior abdominal wall between the ridges formed by the lateral umbilical fold and the medial umbilical ligament, corresponding to the ...
within an anatomic region known as the inguinal or Hesselbach's triangle
In human anatomy, the inguinal triangle is a region of the abdominal wall. It is also known by the eponym Hesselbach's triangle, after Franz Kaspar Hesselbach.
Structure
It is defined by the following structures:
* Medial border: Lateral margin ...
, an area defined by the edge of the rectus abdominis muscle
The rectus abdominis muscle, ( la, straight abdominal) also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply the "abs", is a paired straight muscle. It is a paired muscle, separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the linea alba. It exte ...
, the inguinal ligament
The inguinal ligament (), also known as Poupart's ligament or groin ligament, is a band running from the pubic tubercle to the anterior superior iliac spine. It forms the base of the inguinal canal through which an indirect inguinal hernia may dev ...
and the inferior epigastric artery. These hernias are capable of exiting via the superficial inguinal ring and are unable to extend into the scrotum
The scrotum or scrotal sac is an anatomical male reproductive structure located at the base of the penis that consists of a suspended dual-chambered sac of skin and smooth muscle. It is present in most terrestrial male mammals. The scrotum cont ...
.
When a patient develops a simultaneous direct and indirect hernia on the same side, it is called a pantaloon hernia or saddlebag hernia because it resembles a pair of pants with the epigastric vessels in the crotch, and the defects can be repaired separately or together. Another term for pantaloon hernia is Romberg's hernia.
Since the abdominal walls weaken with age, direct hernias tend to occur in the middle-aged and elderly. This is in contrast to indirect hernias which can occur at any age including the young, since their etiology includes a congenital component where the inguinal canal is left more patent (compared to individuals less susceptible to indirect hernias).James Harmon M.D. Lecture 13. Human Gross Anatomy. University of Minnesota. September 4, 2008. Additional risk factors include chronic constipation, being overweight or obese, chronic cough, family history and prior episodes of direct inguinal hernias.
Indirect inguinal hernia

 An indirect inguinal hernia results from the failure of embryonic closure of the
An indirect inguinal hernia results from the failure of embryonic closure of the deep inguinal ring
The inguinal canals are the two passages in the anterior abdominal wall of humans and animals which in males convey the spermatic cords and in females the round ligament of the uterus. The inguinal canals are larger and more prominent in males. ...
after the testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testostero ...
has passed through it. It is the most common cause of groin hernia. A double indirect inguinal hernia has two sacs.
In the male fetus, the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesoth ...
gives a coat to the testicle as it passes through this ring, forming a temporary connection called the processus vaginalis
The vaginal process (or processus vaginalis) is an embryonic developmental outpouching of the parietal peritoneum. It is present from around the 12th week of gestation, and commences as a peritoneal outpouching.
Sex differences
In males, it prec ...
. In normal development, the processus is obliterated once the testicle is completely descended. The permanent coat of peritoneum that remains around the testicle is called the tunica vaginalis
The tunica vaginalis is the pouch of serous membrane that covers the testes. It is derived from the vaginal process of the peritoneum, which in the fetus precedes the descent of the testes from the abdomen into the scrotum.
After its descent, ...
. The testicle remains connected to its blood vessels and the vas deferens, which make up the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
and descend through the inguinal canal to the scrotum.
The deep inguinal ring, which is the beginning of the inguinal canal, remains as an opening in the fascia transversalis, which forms the fascial inner wall of the spermatic cord. When the opening is larger than necessary for passage of the spermatic cord, the stage is set for an indirect inguinal hernia. The protrusion of peritoneum through the internal inguinal ring can be considered an incomplete obliteration of the processus.
In an indirect inguinal hernia, the protrusion passes through the deep inguinal ring and is located lateral to the inferior epigastric artery. Hence, the conjoint tendon is not weakened.
There are three main types
*Bubonocele: in this case the hernia is limited in inguinal canal.
*Funicular: here the processus vaginalis is closed at its lower end just above the epididymis. The content of the hernial sac can be felt separately from the testis which lies below the hernia.
*Complete (or scrotal): here the processus vaginalis is patent throughout. The hernial sac is continuous with the tunica vaginalis of the testis. The hernia descends down to the bottom of the scrotum and it is difficult to differentiate the testis from hernia.
In the female, groin hernias are only 4% as common as in males. ''Indirect inguinal hernia'' is still the most common groin hernia for females. If a woman has an indirect inguinal hernia, her internal inguinal ring is patent, which is abnormal for females. The protrusion of peritoneum is not called "processus vaginalis" in women, as this structure is related to the migration of the testicle to the scrotum. It is simply a hernia sac. The eventual destination of the hernia contents for a woman is the labium majus
The labia majora (singular: ''labium majus'') are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal Skin, cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora they form the ...
on the same side, and hernias can enlarge one labium dramatically if they are allowed to progress.
Medical imaging
A physician may diagnose an inguinal hernia, as well as the type, frommedical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other peo ...
and physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patien ...
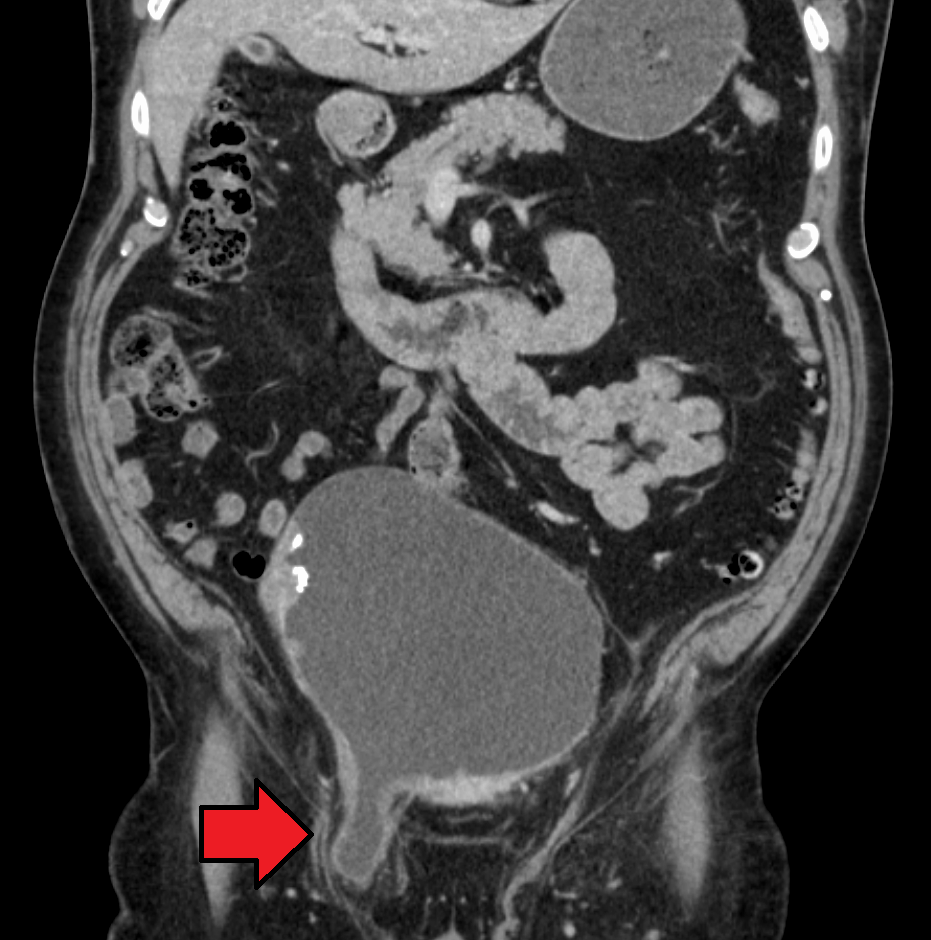
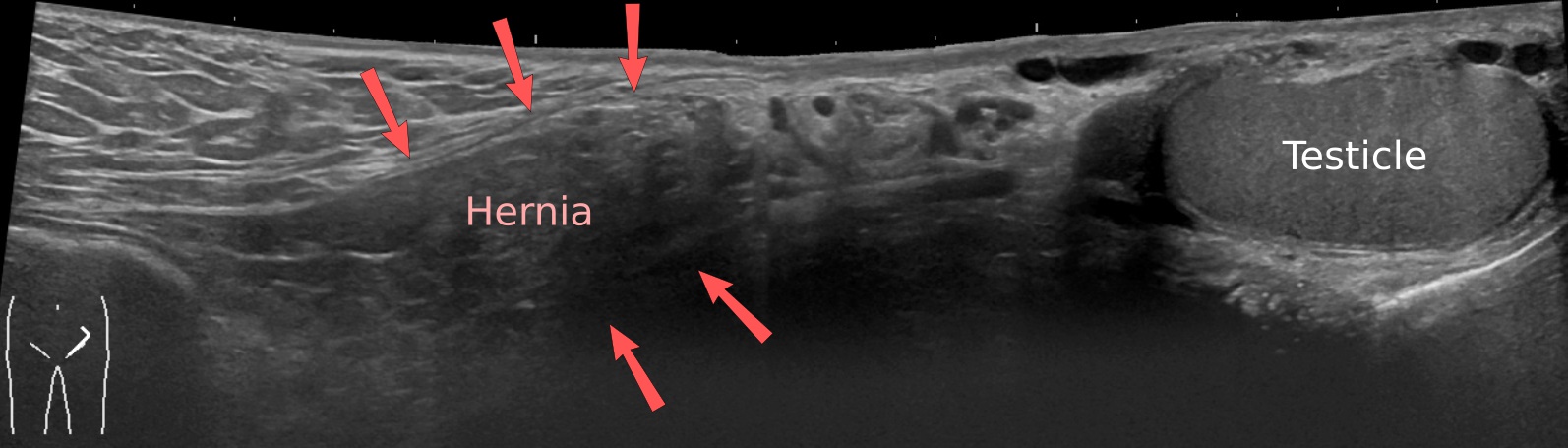
. For confirmation or in uncertain cases, medical ultrasonography
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal ...
is the first choice of imaging, because it can both detect the hernia and evaluate its changes with for example pressure, standing and Valsalva maneuver
The Valsalva maneuver is performed by a forceful attempt of exhalation against a closed airway, usually done by closing one's mouth and pinching one's nose shut while expelling air out as if blowing up a balloon. Variations of the maneuver can ...
.
When assessed by ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
or cross sectional imaging with CT or MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves ...
, the major differential in diagnosing indirect inguinal hernias is differentiation from spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (''ductus deferens'') and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal ring down to each testicle. Its serosal covering, the tunica vaginalis, is an exten ...
lipomas
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than in size. Common locations include upper back, ...
, as both can contain only fat and extend along the inguinal canal into the scrotum.
On axial CT, lipomas originate inferior or lateral to the cord, and are located inside the cremaster muscle
The cremaster muscle is a paired structure made of thin layers of striated and smooth muscle that covers the testis and the spermatic cord in human males. It consists of the lateral and medial parts. Cremaster is an involuntary muscle, responsibl ...
, while inguinal hernias lie anteromedial to the cord and are not intramuscular. Large lipomas may appear nearly indistinguishable as the fat engulfs anatomic boundaries, but they do not change position with coughing or straining.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
In healthcare, a differential diagnosis (abbreviated DDx) is a method of analysis of a patient's history and physical examination to arrive at the correct diagnosis. It involves distinguishing a particular disease or condition from others that p ...
of the symptoms of inguinal hernia mainly includes the following potential conditions:
* Femoral hernia
Femoral hernias occur just below the inguinal ligament, when abdominal contents pass through a naturally occurring weakness in the abdominal wall called the femoral canal. Femoral hernias are a relatively uncommon type, accounting for only 3% of ...
* Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the epididymis, a curved structure at the back of the testicle. Onset of pain is typically over a day or two. The pain may improve with raising the testicle. Other symptoms may ...
* Testicular torsion
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. The testicle may be higher than ...
* Lipoma
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than in size. Common locations include upper back, ...
s
* Inguinal adenopathy
Lymphadenopathy or adenopathy is a disease of the lymph nodes, in which they are abnormal in size or consistency. Lymphadenopathy of an inflammation, inflammatory type (the most common type) is lymphadenitis, producing swelling (medical), swolle ...
(Lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
Swelling)
* Groin abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
* Saphenous vein dilation, called Saphena varix A saphena varix, or saphenous varix, is a dilation of the saphenous vein at its junction with the femoral vein in the groin. It is a common surgical problem, and patients may present with groin swelling.
Clinical features
It displays a cough impu ...
* Vascular aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus (s ...
or pseudoaneurysm
A pseudoaneurysm, also known as a false aneurysm, is a locally contained hematoma outside an artery or heart due to damage to the vessel wall. The injury goes through all the three layers of the arterial wall causing a leak, which is contained b ...
* Hydrocele
A hydrocele is an accumulation of serous fluid in a body cavity. A hydrocele testis, the most common form of hydrocele, is the accumulation of fluids around a testicle. It is often caused by fluid collecting within a layer wrapped around the testi ...
* Varicocele
varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum. This plexus of veins drains blood from the testicles back to the heart. The vessels originate in the abdomen and course down through the inguinal canal as part ...
* Cryptorchidism
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tract. About 3% of ...
(Undescended testes
Cryptorchidism, also known as undescended testis, is the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotum. The word is from Greek language, Greek () 'hidden' and () 'testicle'. It is the most common birth defect of the male genital tra ...
)
Management
Conservative
There is currently no medical recommendation about how to manage an inguinal hernia condition in adults, due to the fact that, until recently,elective surgery
Elective surgery or elective procedure (from the la, eligere, meaning to choose) is surgery that is scheduled in advance because it does not involve a medical emergency. Semi-elective surgery is a surgery that must be done to preserve the patien ...
used to be recommended. The hernia truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so that the assembl ...
(or hernia belt) is intended to contain a reducible inguinal hernia within the abdomen. It is not considered to provide a cure, and if the pads are hard and intrude into the hernia aperture they may cause scarring and enlargement of the aperture. In addition, most trusses with older designs are not able effectively to contain the hernia at all times, because their pads do not remain permanently in contact with the hernia. The more modern variety of truss is made with non-intrusive flat pads and comes with a guarantee to hold the hernia securely during all activities. They have been described by users as providing greater confidence and comfort when carrying out physically demanding tasks. However, their use is controversial, as data to determine whether they help prevent hernia complications are lacking. A truss also increases the probability of complications, which include strangulation of the hernia, atrophy of the spermatic cord, and atrophy of the fascial margins. This allows the defect to enlarge and makes subsequent repair more difficult. Their popularity is nonetheless likely to increase, as many individuals with small, painless hernias are now delaying hernia surgery due to the risk of post-herniorrhaphy pain syndrome. Elasticated pants used by athletes may also provide useful support for the smaller hernia.
Surgical
 Surgical correction of inguinal hernias is called a
Surgical correction of inguinal hernias is called a hernia repair
Hernia repair refers to a surgical operation for the correction of a hernia—a bulging of internal organs or tissues through the wall that contains it. It can be of two different types: herniorrhaphy; or hernioplasty. This operation may be pe ...
. It is not recommended in minimally symptomatic hernias, for which watchful waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed.
Related terms include ''expec ...
is advised, due to the risk of post herniorraphy pain syndrome. Surgery is commonly performed as outpatient surgery
Outpatient surgery, also known as ambulatory surgery, day surgery, day case surgery, or same-day surgery, is surgery that does not require an overnight hospital stay.The International Association for Ambulatory Surgery (IAAS) would not consider a ...
. There are various surgical strategies which may be considered in the planning of inguinal hernia repair. These include the consideration of mesh use (e.g. synthetic or biologic), open repair, use of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.Medli ...
, type of anesthesia (general or local), appropriateness of bilateral repair, etc. Mesh or non mesh repairs have both benefits in different areas, but mesh repairs may reduce the rate of hernia reappearance, visceral or neurovascular injuries, length of hospital stay and time to return to activities of daily living. Laparoscopy is most commonly used for non-emergency cases; however, a minimally invasive open repair may have a lower incidence of post-operative nausea and mesh associated pain. During surgery conducted under local anaesthesia, the patient will be asked to cough and strain during the procedure to help in demonstrating that the repair is without tension and sound.
 Constipation after hernia repair results in strain to evacuate the bowel causing pain, and fear that the sutures may rupture. Opioid analgesia makes constipation worse. Promoting an easy bowel motion is important post-operatively.
Surgical correction is always recommended for inguinal hernias in children.
Emergency surgery for incarceration and strangulation carry much higher risk than planned, "elective" procedures. However, the risk of incarceration is low, evaluated at 0.2% per year. On the other hand,
Constipation after hernia repair results in strain to evacuate the bowel causing pain, and fear that the sutures may rupture. Opioid analgesia makes constipation worse. Promoting an easy bowel motion is important post-operatively.
Surgical correction is always recommended for inguinal hernias in children.
Emergency surgery for incarceration and strangulation carry much higher risk than planned, "elective" procedures. However, the risk of incarceration is low, evaluated at 0.2% per year. On the other hand, surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
has a risk of inguinodynia Post herniorrhaphy pain syndrome, or inguinodynia is pain or discomfort lasting greater than 3 months after surgery of inguinal hernia. Randomized trials of laparoscopic vs open inguinal hernia repair have demonstrated similar recurrence rates wi ...
(10-12%), and this is why males with minimal symptoms are advised to watchful waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed.
Related terms include ''expec ...
. However, if they experience discomfort while doing physical activities or they routinely avoid them for fear of pain, they should seek surgical evaluation. For female patients, surgery is recommended even for asymptomatic patients.
Epidemiology
A direct inguinal hernia is less common (~25–30% of inguinal hernias) and usually occurs in men over 40 years of age. Men have an 8 times higher incidence of inguinal hernia than women.See also
*Birkett hernia
John Birkett, F.R.C.S. F.L.S. (1815–1904) was an English surgeon and member of the Linnean Society of London who was an early specialist on breast disease, including breast cancer, and an early advocate of histology. He published a book on brea ...
References
External links
Indirect Inguinal Hernia - University of Connecticut Health Center
!-- - Rich Luzietti, MS 2005 - University of Connecticut Health Center - Lyman Maynard Stowe Library's Computer Education Center] --> * {{DEFAULTSORT:Inguinal Hernia Inguinal hernias Scrotum it:Ernia#Ernia inguinale