IBM Monochrome Display Adapter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Monochrome Display Adapter (MDA, also MDA card, Monochrome Display and Printer Adapter, MDPA) is IBM's standard video display card and computer display standard for the IBM PC introduced in 1981. The MDA does not have any pixel-addressable graphics modes, only a single
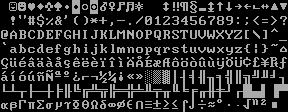
 The MDA was based on the IBM System/23 Datamaster's display system, and was intended to support business and word processing use with its sharp, high-resolution characters. Each character is rendered in a box of 9×14 pixels, of which 7×11 depicts the character itself and the other pixels provide space between character columns and lines. Some characters, such as the lowercase "m", are rendered eight pixels across.
The theoretical total screen display resolution of the MDA is 720×350 pixels, if the dimensions of all character cells are added up, but the MDA cannot address individual pixels to take full advantage of this resolution. Each character cell can be set to one of 256 bitmap characters stored in ROM on the card, and this character set cannot be altered from the built-in
The MDA was based on the IBM System/23 Datamaster's display system, and was intended to support business and word processing use with its sharp, high-resolution characters. Each character is rendered in a box of 9×14 pixels, of which 7×11 depicts the character itself and the other pixels provide space between character columns and lines. Some characters, such as the lowercase "m", are rendered eight pixels across.
The theoretical total screen display resolution of the MDA is 720×350 pixels, if the dimensions of all character cells are added up, but the MDA cannot address individual pixels to take full advantage of this resolution. Each character cell can be set to one of 256 bitmap characters stored in ROM on the card, and this character set cannot be altered from the built-in

monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochr ...
text mode which can display 80 columns by 25 lines of high resolution text characters or symbols useful for drawing forms.
Hardware design
The original IBM MDA was an 8-bitISA card
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 808 ...
with a Motorola 6845 display controller, 4 KB of RAM, a DE-9 output port intended for use with an IBM monochrome monitor, and a parallel port for attachment of a printer, avoiding the need to purchase a separate card.
Capabilities

 The MDA was based on the IBM System/23 Datamaster's display system, and was intended to support business and word processing use with its sharp, high-resolution characters. Each character is rendered in a box of 9×14 pixels, of which 7×11 depicts the character itself and the other pixels provide space between character columns and lines. Some characters, such as the lowercase "m", are rendered eight pixels across.
The theoretical total screen display resolution of the MDA is 720×350 pixels, if the dimensions of all character cells are added up, but the MDA cannot address individual pixels to take full advantage of this resolution. Each character cell can be set to one of 256 bitmap characters stored in ROM on the card, and this character set cannot be altered from the built-in
The MDA was based on the IBM System/23 Datamaster's display system, and was intended to support business and word processing use with its sharp, high-resolution characters. Each character is rendered in a box of 9×14 pixels, of which 7×11 depicts the character itself and the other pixels provide space between character columns and lines. Some characters, such as the lowercase "m", are rendered eight pixels across.
The theoretical total screen display resolution of the MDA is 720×350 pixels, if the dimensions of all character cells are added up, but the MDA cannot address individual pixels to take full advantage of this resolution. Each character cell can be set to one of 256 bitmap characters stored in ROM on the card, and this character set cannot be altered from the built-in hardware code page
In computing, a hardware code page (HWCP) refers to a code page supported natively by a hardware device such as a display adapter or printer. The glyphs to present the characters are stored in the alphanumeric character generator's resident read ...
437
__NOTOC__
Year 437 ( CDXXXVII) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aetius and Sigisvultus (or, less frequently, year 1190 ...
. The only way to simulate "graphics" is through ASCII art.
Code page 437 has 256 characters (0-255), including the standard 95 printable ASCII
ASCII ( ), abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because ...
characters from (32-126), and the 33 ASCII control codes (0-31 and 127) are replaced with printable graphic symbols. It also includes another 128 characters (128-255) like the aforementioned characters for drawing forms. Some of these shapes appear in Unicode as box-drawing characters.
There are several attribute values - bit flags that can be set on each character on the screen. These are ''invisible, underline, normal, bright (bold), reverse video,'' and ''blinking''. Reverse video swaps the foreground and background colors, while blinking causes text to flash periodically. Some of these attributes can be combined, so that e.g. bright, underlined text can be rendered.
Early versions of the MDA board have hardware capable of outputting red, green and blue TTL signals on the normally unconnected DE-9 video connector pins, theoretically allowing an 8-color display with a suitable monitor. The registers also allow the monochrome mode to be set on and off. No (widely) published software exists to actually control the feature.
It is also possible to combine the values of output pins 6 (''Video)'' and 7 (''Intensity),'' to generate four brightness levels. ''Video'' corresponds to 2/3 luminance and ''Intensity'' to 1/3 luminance), but the actual display of these levels is monitor dependent:
Use
The MDA was released alongside the IBM Color Graphics Adapter, and in fact could be installed alongside the CGA in the same computer. A command included with PC DOS permitted switching the primary display between the CGA and MDA cards. Because of the lack of pixel-addressable graphics, MDA owners were unable to play PC games released with graphics support. However, textmode games were released for the PC (includingtext adventures
''
Interactive fiction, often abbreviated IF, is software simulating environments in which players use text commands to control characters and influence the environment. Works in this form can be understood as literary narratives, either in the f ...
) and at least one game, IBM's ''One Hundred And One Monochrome Mazes'', requires MDA. Box-drawing characters made the production of rudimentary graphics practical for early PC game titles, including BBS door games or titles such as '' Castle Adventure''.
Another use for the MDA was as a secondary display for debugging. Applications like SoftICE
SoftICE is a kernel mode debugger for DOS and Windows up to Windows XP. It is designed to run underneath Windows, so that the operating system is unaware of its presence. Unlike an application debugger, SoftICE is capable of suspending all ...
and the Windows debugger permitted the simultaneous use of an MDA and another graphics card, with the MDA displaying a debugger interface while the other card was showing the primary display.
Disadvantage
A typical 8-bit monochrome card could turn the 16-bit 8 MHz ISA bus into an 8-bit 4 MHz PC bus, which resulted in having the bus bandwidth cut by up to 75%. If the monochrome card was added to the PC as a second card besides a normalVGA
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the PC industry within three years. The term can now ...
card for debugging purposes, this resulted in slow VGA performance. Microsoft recommended in its "Writing HOT Games for Microsoft® Windows™ The Microsoft Game Developers’ Handbook" to remove the monochrome card in such a setup for maximum speed of the VGA card.
Reception
The author of an internal IBM publication stated in October 1981 that he had planned to purchase the CGA adapter but changed his mind after seeing its poor display quality. Describing MDA as beautiful, he observed that "you stare at text a whole lot more than you stare at color graphics". MDA was more popular than CGA for business applications. The higher resolution of MDA's text and inclusion of a printer port made it more appealing for the business applications that were the focus of the original PC. However, dissatisfaction with its limitations quickly led to third parties releasing competing hardware. A well known example was the Hercules Graphics Card. Introduced in 1982, it offered both an MDA-compatible high resolution text mode and a monochrome graphics mode. The founder of Hercules Computer Technology, Van Suwannukul, created the Hercules Graphics Card so that he could work on his doctoral thesis on an IBM PC using the Thai alphabet, which was impossible at the low resolution of CGA or the fixed character set of MDA. It could address individual pixels, and displayed a black and white picture of 720×348 pixels. This resolution was superior to the CGA card, yet offered pixel-addressable graphics, so despite lacking color capability, the Hercules adapter's offer of high resolution bitmap graphics combined with MDA-grade text quality made it a popular choice, which was even shipped with many clones.Specifications
Connector
Signal
Clone boards
Other boards offer MDAcompatibility
Compatibility may refer to:
Computing
* Backward compatibility, in which newer devices can understand data generated by older devices
* Compatibility card, an expansion card for hardware emulation of another device
* Compatibility layer, compon ...
, although with differences on how attributes are displayed or the font used.
*3270 PC
*Amstrad PPC / PC20
*Control Systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial c ...
Artist 1
*Tamarack Microelectronics Tamarack Microelectronics was a designer and manufacturer of mixed-signal integrated circuits, primarily Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan are ...
TD3088A3
See also
* Hercules Graphics Card * Color Graphics Adapter *Orchid Graphics Adapter
The Orchid Graphics Adapter is a graphics board for IBM PC compatible computers, released in 1982 by Orchid Technology.
It was intended to provide high resolution (at the time) monochrome graphic abilities to computers limited to text displays ...
* Green-screen display
A monochrome monitor is a type of computer monitor in which computer text and images are displayed in varying tones of only one color, as opposed to a color monitor that can display text and images in multiple colors. They were very common in t ...
* List of video connectors
This is a list of physical RF and video connectors and related video signal standards.
By signal standard
Physical connectors
D-subminiature family
DVI-related
DIN/ Mini-DIN
Others
See also
*Computer display standard
Computer di ...
* List of defunct graphics chips and card companies
References
{{Computer display standard Monochrome Display Adapter Monochrome Display Adapter Computer display standards Graphics cards Computer-related introductions in 1981