Israel Hildreth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in
''Ancient Canaan and Israel: An Introduction,''
OUP, 2009 pp. 3–4. During the
 Under the British Mandate (1920–1948), the whole region was known as 'Palestine' (). Upon
Under the British Mandate (1920–1948), the whole region was known as 'Palestine' (). Upon
 The
The
''Canaan and Israel in Antiquity: A Textbook on History and Religion,''
A&C Black, 2012, rev.ed. pp. 137ff.
''Early History of the Israelite People: From the Written & Archaeological Sources,''
Brill, 2000 pp. 275–276: 'They are rather a very specific group among the population of Palestine which bears a name that occurs here for the first time that at a much later stage in Palestine's history bears a substantially different signification.' Ancestors of the Israelites are thought to have included There is debate about the earliest existence of the
There is debate about the earliest existence of the
"Saul and Highlands of Benjamin Update: The Role of Jerusalem"
in Joachim J. Krause, Omer Sergi, and Kristin Weingart (eds.), ''Saul, Benjamin, and the Emergence of Monarchy in Israel: Biblical and Archaeological Perspectives'', SBL Press, Atlanta, GA, p. 48, footnote 57: "...They became territorial kingdoms later, Israel in the first half of the ninth century BCE and Judah in its second half..."The Pitcher Is Broken: Memorial Essays for Gosta W. Ahlstrom, Steven W. Holloway, Lowell K. Handy, Continuum, 1 May 1995
Quote: "For Israel, the description of the battle of Qarqar in the Kurkh Monolith of Shalmaneser III (mid-ninth century) and for Judah, a Tiglath-pileser III text mentioning (Jeho-) Ahaz of Judah (IIR67 = K. 3751), dated 734–733, are the earliest published to date." The Kingdom of Israel was the more prosperous of the two kingdoms and soon developed into a regional power; during the days of the
"The Population of Palestine in Iron Age II"
''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', ''287''(1), 47–60. In 587/6 BCE, the
 With successive Persian rule, the autonomous province ''
With successive Persian rule, the autonomous province ''
 With the
With the  In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300
In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300  In 1470, Isaac b. Meir Latif arrived from Italy and counted 150 Jewish families in Jerusalem.
Thanks to
In 1470, Isaac b. Meir Latif arrived from Italy and counted 150 Jewish families in Jerusalem.
Thanks to
 After World War II, the UK found itself facing a Jewish Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine, guerrilla campaign over Jewish immigration restrictions, as well as continued conflict with the Arab community over limit levels. The Haganah joined Irgun and Lehi in an armed struggle against British rule. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of Jewish Holocaust survivors and refugees sought a new life far from their destroyed communities in Europe. The Haganah attempted to bring these refugees to Palestine in a programme called Aliyah Bet in which tens of thousands of Jewish refugees attempted to enter Palestine by ship. Most of the ships were intercepted by the Royal Navy and the refugees rounded up and placed in detention camps in Atlit detainee camp, Atlit and Cyprus internment camps, Cyprus by the British.
On 22 July 1946, Irgun King David Hotel bombing, bombed the British administrative headquarters for Palestine, which was housed in the southern wing of the King David Hotel in
After World War II, the UK found itself facing a Jewish Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine, guerrilla campaign over Jewish immigration restrictions, as well as continued conflict with the Arab community over limit levels. The Haganah joined Irgun and Lehi in an armed struggle against British rule. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of Jewish Holocaust survivors and refugees sought a new life far from their destroyed communities in Europe. The Haganah attempted to bring these refugees to Palestine in a programme called Aliyah Bet in which tens of thousands of Jewish refugees attempted to enter Palestine by ship. Most of the ships were intercepted by the Royal Navy and the refugees rounded up and placed in detention camps in Atlit detainee camp, Atlit and Cyprus internment camps, Cyprus by the British.
On 22 July 1946, Irgun King David Hotel bombing, bombed the British administrative headquarters for Palestine, which was housed in the southern wing of the King David Hotel in
article on the Irgun Zvai Leumi A total of 91 people of various nationalities were killed and 46 were injured.Thurston Clarke, Clarke, Thurston. ''By Blood and Fire'', G.P. Puttnam's Sons, New York, 1981 The hotel was the site of the Secretariat of the Government of Palestine and the Headquarters of the British Armed Forces in Mandatory Palestine and Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan. The attack initially had the approval of the Haganah. It was conceived as a response to Operation Agatha (a series of widespread raids, including one on the Jewish Agency for Israel, Jewish Agency, conducted by the British authorities) and was the deadliest directed at the British during the Mandate era. The Jewish insurgency continued throughout the rest of 1946 and 1947 despite concerted efforts by the British military and Palestine Police Force to suppress it. British efforts to mediate a negotiated solution with Jewish and Arab representatives also failed as the Jews were unwilling to accept any solution that did not involve a Jewish state and suggested a partition of Palestine into Jewish and Arab states, while the Arabs were adamant that a Jewish state in any part of Palestine was unacceptable and that the only solution was a unified Palestine under Arab rule. In February 1947, the British referred the Palestine issue to the newly formed
 Since 1964, Arab countries, concerned over Israeli plans to divert waters of the Jordan River into the
Since 1964, Arab countries, concerned over Israeli plans to divert waters of the Jordan River into the
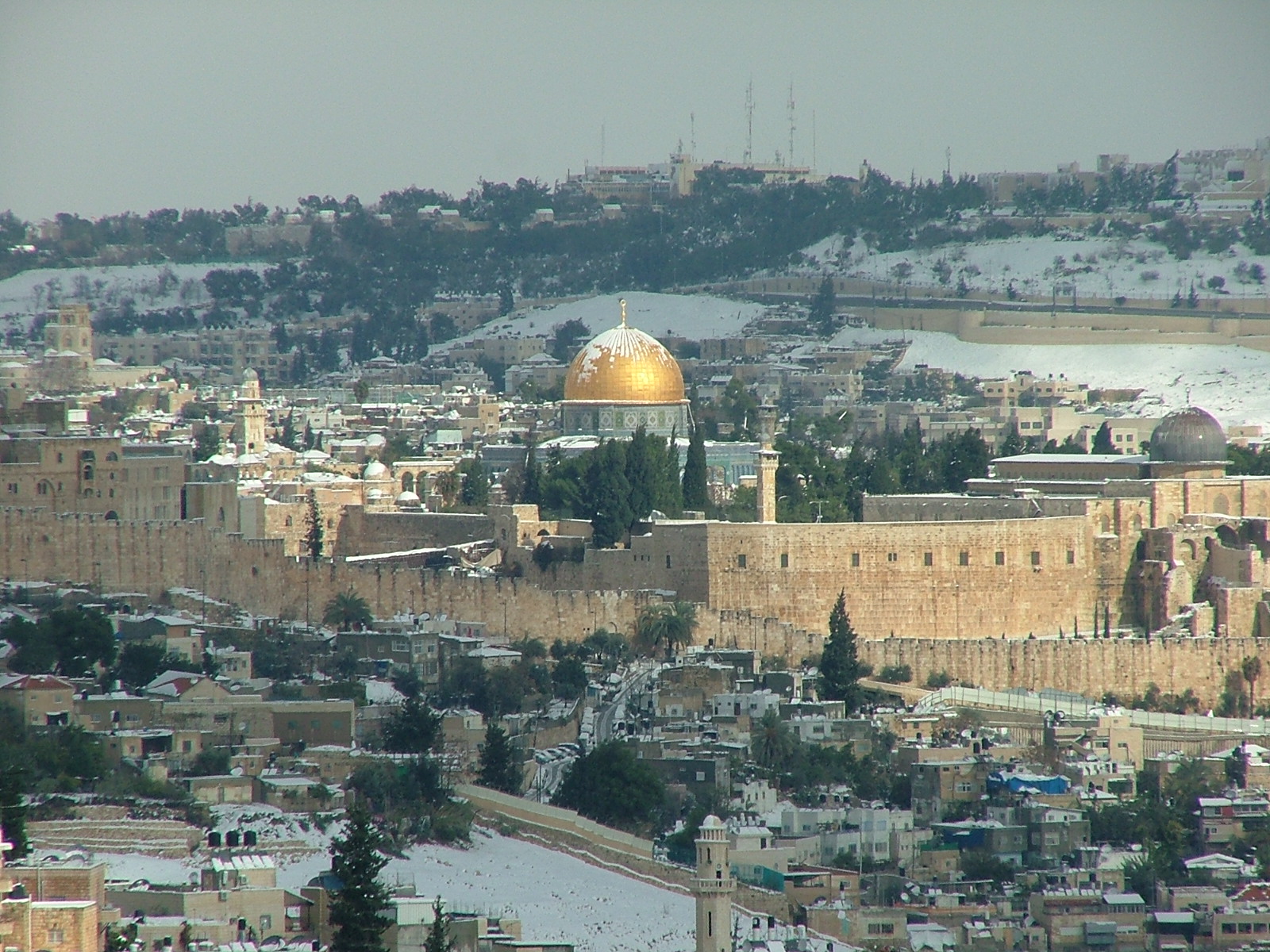 Meanwhile, Begin's government provided incentives for Israelis to Israeli settlements, settle in the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, occupied West Bank, increasing friction with the Palestinians in that area. The Jerusalem Law, Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel, passed in 1980, was believed by some to reaffirm Israel's 1967 annexation of Jerusalem by government decree, and UN Security Council Resolution 478, reignited international controversy over the Positions on Jerusalem, status of the city. No Israeli legislation has defined the territory of Israel and no act specifically included East Jerusalem therein. In 1981 Israel Golan Heights Law, effectively annexed the
Meanwhile, Begin's government provided incentives for Israelis to Israeli settlements, settle in the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, occupied West Bank, increasing friction with the Palestinians in that area. The Jerusalem Law, Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel, passed in 1980, was believed by some to reaffirm Israel's 1967 annexation of Jerusalem by government decree, and UN Security Council Resolution 478, reignited international controversy over the Positions on Jerusalem, status of the city. No Israeli legislation has defined the territory of Israel and no act specifically included East Jerusalem therein. In 1981 Israel Golan Heights Law, effectively annexed the  Under the leadership of Benjamin Netanyahu at the end of the 1990s, Israel Protocol Concerning the Redeployment in Hebron, withdrew from
Under the leadership of Benjamin Netanyahu at the end of the 1990s, Israel Protocol Concerning the Redeployment in Hebron, withdrew from
Escalation of hostilities in Lebanon and in Israel since Hizbollah's attack on Israel on 12 July 2006 On 6 September 2007, the Israeli Air Force Operation Orchard, destroyed a nuclear reactor in Syria. At the end of 2008, Israel entered another conflict as 2008 Israel–Hamas ceasefire, a ceasefire between Hamas and Israel collapsed. The Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War lasted three weeks and ended after Israel announced a unilateral ceasefire. Hamas announced its own ceasefire, with its own conditions of complete withdrawal and opening of Blockade of the Gaza Strip, border crossings. Despite neither the Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, rocket launchings nor Israeli List of Israeli attacks on the Gaza strip, retaliatory strikes having completely stopped, the fragile ceasefire remained in order. In what Israel described as a response to List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, 2012, more than a hundred Palestinian rocket attacks on southern Israeli cities, Israel began an Operation Pillar of Defense, operation in Gaza on 14 November 2012, lasting eight days. Israel started another Operation Protective Edge, operation in Gaza following an List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, 2014, escalation of rocket attacks by Hamas in July 2014. In May 2021, another Operation Guardian of the Walls, round of fighting took place in Gaza and Israel, lasting eleven days. In September 2010, Israel was invited to join the
Destructive earthquakes leading to serious loss of life strike about every 80 years.Zafrir Renat, ''Israel Is Due, and Ill Prepared, for Major Earthquake'', Haaretz, 15 January 2010. "On average, a destructive earthquake takes place in Israel once every 80 years, causing serious casualties and damage.
/ref> While stringent construction regulations are currently in place and recently built structures are earthquake-safe, the majority of the buildings in Israel were older than these regulations and many public buildings as well as 50,000 residential buildings did not meet the new standards and were "expected to collapse" if exposed to a strong earthquake.
 Temperatures in Israel vary widely, especially during the winter. Coastal areas, such as those of
Temperatures in Israel vary widely, especially during the winter. Coastal areas, such as those of
 , Israel's population was an estimated . In 2019, the civil government recorded 74.2% of the population as Israeli Jews, Jews, 20.9% of the population as Arab citizens of Israel, Arabs, and 4.8% as non-Arab Christians and people who have no religion listed. Over the last decade, large numbers of migrant workers from Romania, Thailand, China, Africa, and South America have settled in Israel. Exact figures are unknown, as many of them are living in the country illegally, but estimates run from 166,000 to 203,000.Adriana Kemp, "Labour migration and racialisation: labour market mechanisms and labour migration control policies in Israel", ''Social Identities'' 10:2, 267–292, 2004 By June 2012, approximately 60,000 Illegal immigration from Africa to Israel, African migrants had entered Israel. About 92% of Israelis live in urban areas. 90% of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinian Israelis reside in 139 densely populated towns and villages concentrated in the Galilee, Triangle (Israel), Triangle and Negev regions, with the remaining 10% in mixed cities and neighbourhoods. Data published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD in 2016 estimated the average life expectancy of Israelis at 82.5 years, making it the List of countries by life expectancy, 6th-highest in the world. Israeli Arab life expectancy lags behind by 3 to 4 years, still highest among Arabs or Muslims in the world.
, Israel's population was an estimated . In 2019, the civil government recorded 74.2% of the population as Israeli Jews, Jews, 20.9% of the population as Arab citizens of Israel, Arabs, and 4.8% as non-Arab Christians and people who have no religion listed. Over the last decade, large numbers of migrant workers from Romania, Thailand, China, Africa, and South America have settled in Israel. Exact figures are unknown, as many of them are living in the country illegally, but estimates run from 166,000 to 203,000.Adriana Kemp, "Labour migration and racialisation: labour market mechanisms and labour migration control policies in Israel", ''Social Identities'' 10:2, 267–292, 2004 By June 2012, approximately 60,000 Illegal immigration from Africa to Israel, African migrants had entered Israel. About 92% of Israelis live in urban areas. 90% of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinian Israelis reside in 139 densely populated towns and villages concentrated in the Galilee, Triangle (Israel), Triangle and Negev regions, with the remaining 10% in mixed cities and neighbourhoods. Data published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD in 2016 estimated the average life expectancy of Israelis at 82.5 years, making it the List of countries by life expectancy, 6th-highest in the world. Israeli Arab life expectancy lags behind by 3 to 4 years, still highest among Arabs or Muslims in the world.
 Israel was established as a homeland for the Jewish people and is often referred to as a Jewish state. The country's Law of Return grants all Jews and those of Jewish ancestry the right to Israeli nationality law, Israeli citizenship. Retention of Israel's population since 1948 is about even or greater, when compared to other countries with mass immigration. Jewish emigration from Israel (called ''yerida'' in Hebrew), primarily to the United States and Canada, is described by demographers as modest, but is often cited by Israeli government ministries as a major threat to Israel's future.
Three quarters of the population are Jews from a Jewish ethnic divisions, diversity of Jewish backgrounds. Approximately 75% of Israeli Jews are Sabra (person), born in Israel, 16% are immigrants from Europe and the Americas, and 7% are immigrants from Asia and Africa (including the
Israel was established as a homeland for the Jewish people and is often referred to as a Jewish state. The country's Law of Return grants all Jews and those of Jewish ancestry the right to Israeli nationality law, Israeli citizenship. Retention of Israel's population since 1948 is about even or greater, when compared to other countries with mass immigration. Jewish emigration from Israel (called ''yerida'' in Hebrew), primarily to the United States and Canada, is described by demographers as modest, but is often cited by Israeli government ministries as a major threat to Israel's future.
Three quarters of the population are Jews from a Jewish ethnic divisions, diversity of Jewish backgrounds. Approximately 75% of Israeli Jews are Sabra (person), born in Israel, 16% are immigrants from Europe and the Americas, and 7% are immigrants from Asia and Africa (including the
The Ethiopian Community in Israel
/ref> Russian language in Israel, Russian and Amharic are widely spoken. More than one million Russian-speaking immigrants 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, arrived in Israel from the post-Soviet states between 1990 and 2004. French is spoken by around 700,000 Israelis, mostly originating French Jews in Israel, from France and North Africa (see Maghrebi Jews). English was an official language during the Mandate period; it lost this status after the establishment of Israel, but retains a role comparable to that of an official language, as may be seen in Road signs in Israel, road signs and official documents. Many Israelis communicate reasonably well in English, as many television programmes are broadcast in English with subtitles and the language is taught from the early grades in elementary school. In addition, Israeli universities offer courses in the English language on various subjects.
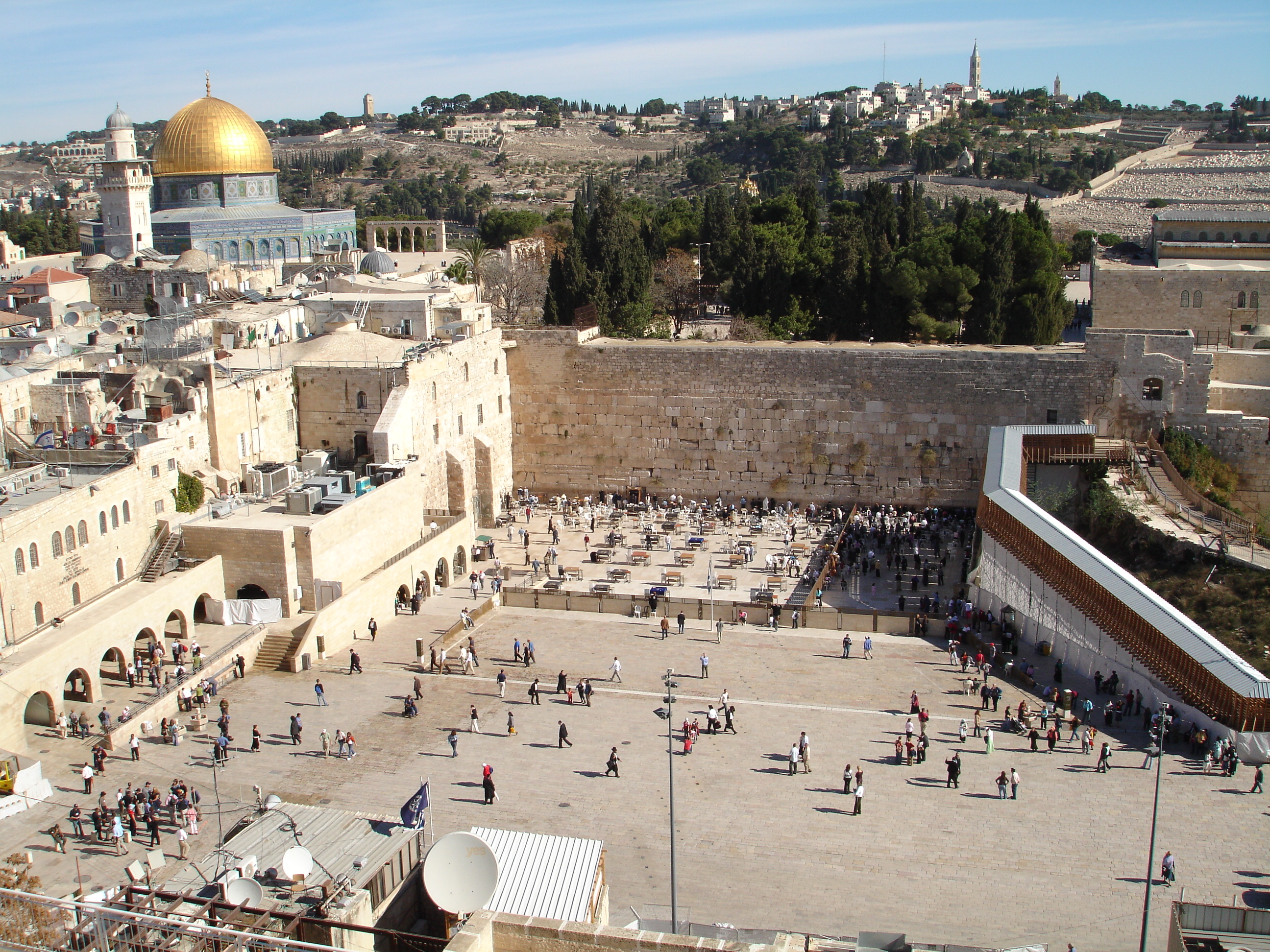 The city of
The city of
 Education is highly valued in the Israeli culture and was viewed as a History of education in ancient Israel and Judah, fundamental block of ancient Israelites. Jewish communities in the Levant were the first to introduce compulsory education for which the organized community, not less than the parents was responsible. Many international business leaders such as Microsoft founder Bill Gates have praised Israel for its high quality of education in helping spur Israel's economic development and technological boom. In 2015, the country List of countries by tertiary education attainment, ranked third among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD members (after Canada and Japan) for the percentage of 25–64 year-olds that have attained tertiary education with 49% compared with the OECD average of 35%. In 2012, the country ranked third in the world in the number of academic degrees per capita (20 percent of the population).
Israel has a school life expectancy of 16 years and a List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate of 97.8%. The State Education Law, passed in 1953, established five types of schools: state secular, state religious, ultra orthodox, communal settlement schools, and Arab schools. The public secular is the largest school group, and is attended by the majority of Jewish and non-Arab pupils in Israel. Most Arabs send their children to schools where Arabic is the language of instruction. Education is compulsory in Israel for children between the ages of three and eighteen. Schooling is divided into three tiers – primary school (grades 1–6), middle school (grades 7–9), and high school (grades 10–12) – culminating with ''Bagrut'' matriculation exams. Proficiency in core subjects such as mathematics, the
Education is highly valued in the Israeli culture and was viewed as a History of education in ancient Israel and Judah, fundamental block of ancient Israelites. Jewish communities in the Levant were the first to introduce compulsory education for which the organized community, not less than the parents was responsible. Many international business leaders such as Microsoft founder Bill Gates have praised Israel for its high quality of education in helping spur Israel's economic development and technological boom. In 2015, the country List of countries by tertiary education attainment, ranked third among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD members (after Canada and Japan) for the percentage of 25–64 year-olds that have attained tertiary education with 49% compared with the OECD average of 35%. In 2012, the country ranked third in the world in the number of academic degrees per capita (20 percent of the population).
Israel has a school life expectancy of 16 years and a List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate of 97.8%. The State Education Law, passed in 1953, established five types of schools: state secular, state religious, ultra orthodox, communal settlement schools, and Arab schools. The public secular is the largest school group, and is attended by the majority of Jewish and non-Arab pupils in Israel. Most Arabs send their children to schools where Arabic is the language of instruction. Education is compulsory in Israel for children between the ages of three and eighteen. Schooling is divided into three tiers – primary school (grades 1–6), middle school (grades 7–9), and high school (grades 10–12) – culminating with ''Bagrut'' matriculation exams. Proficiency in core subjects such as mathematics, the  Israel has a tradition of higher education where its quality university education has been largely responsible in spurring the nation's modern economic development. Israel has List of Israeli universities and colleges, nine public universities that are subsidized by the state and 49 private colleges. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel's second-oldest university after the Technion, houses the National Library of Israel, the world's largest repository of Judaica and Hebraica. The Technion and the Hebrew University consistently ranked among world's 100 top universities by the prestigious Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU academic ranking. Other major universities in the country include the Weizmann Institute of Science, Tel Aviv University, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Bar-Ilan University, the University of Haifa and the Open University of Israel. Ariel University, in the
Israel has a tradition of higher education where its quality university education has been largely responsible in spurring the nation's modern economic development. Israel has List of Israeli universities and colleges, nine public universities that are subsidized by the state and 49 private colleges. The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel's second-oldest university after the Technion, houses the National Library of Israel, the world's largest repository of Judaica and Hebraica. The Technion and the Hebrew University consistently ranked among world's 100 top universities by the prestigious Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU academic ranking. Other major universities in the country include the Weizmann Institute of Science, Tel Aviv University, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Bar-Ilan University, the University of Haifa and the Open University of Israel. Ariel University, in the
 Israel is a parliamentary democracy with
Israel is a parliamentary democracy with  The Basic Laws of Israel function as an uncodified constitution. In 2003, the Knesset began to draft an official Constitution of Israel, constitution based on these laws.
The president of Israel is head of state, with limited and largely ceremonial duties.
Israel has no official religion, but the definition of the state as "Jewish and democratic state, Jewish and democratic" creates a strong connection with Judaism, as well as a conflict between state law and religious law. Interaction between the political parties keeps Status quo (Israel), the balance between state and religion largely as it existed during the British Mandate.
On 19 July 2018, the Israeli Parliament passed a Basic Law that characterizes the State of Israel as principally a "Basic Law: Israel as the Nation-State of the Jewish People, Nation State of the Jewish People," and Hebrew as its official language. The bill ascribes "special status" to the Arabic language. The same bill gives Jews a unique right to national self-determination, and views the developing of Jewish settlement in the country as "a national interest," empowering the government to "take steps to encourage, advance and implement this interest."
The Basic Laws of Israel function as an uncodified constitution. In 2003, the Knesset began to draft an official Constitution of Israel, constitution based on these laws.
The president of Israel is head of state, with limited and largely ceremonial duties.
Israel has no official religion, but the definition of the state as "Jewish and democratic state, Jewish and democratic" creates a strong connection with Judaism, as well as a conflict between state law and religious law. Interaction between the political parties keeps Status quo (Israel), the balance between state and religion largely as it existed during the British Mandate.
On 19 July 2018, the Israeli Parliament passed a Basic Law that characterizes the State of Israel as principally a "Basic Law: Israel as the Nation-State of the Jewish People, Nation State of the Jewish People," and Hebrew as its official language. The bill ascribes "special status" to the Arabic language. The same bill gives Jews a unique right to national self-determination, and views the developing of Jewish settlement in the country as "a national interest," empowering the government to "take steps to encourage, advance and implement this interest."
 Israel has a Israeli judicial system, three-tier court system. At the lowest level are magistrate courts, situated in most cities across the country. Above them are district courts, serving as both appeal, appellate courts and trial court, courts of first instance; they are situated in five of Israel's six Districts of Israel, districts. The third and highest tier is the Supreme Court of Israel, Supreme Court, located in Jerusalem; it serves a dual role as the highest court of appeals and the High Court of Justice (Israel), High Court of Justice. In the latter role, the Supreme Court rules as a court of first instance, allowing individuals, both citizens and non-citizens, to petition against the decisions of state authorities. Although Israel supports the goals of the International Criminal Court, it has not ratified the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, Rome Statute, citing concerns about the ability of the court to remain free from political impartiality.
Israel's legal system combines three legal traditions: English law, English common law, civil law (legal system), civil law, and Halakha, Jewish law. It is based on the principle of ''stare decisis'' (precedent) and is an adversarial system, where the parties in the suit bring evidence before the court. Court cases are decided by professional judges with no role for juries. Marriage in Israel, Marriage and divorce are under the jurisdiction of the religious courts: Beth din, Jewish, Sharia, Muslim, Druze, and Christian. The election of judges is carried out by a Judicial Selection Committee (Israel), committee of two Knesset members, three Supreme Court justices, two Israel Bar Association, Israeli Bar members and two ministers (one of which, Israel's Ministry of Justice (Israel), justice minister, is the committee's chairman). The committee's members of the Knesset are Secret ballot, secretly elected by the Knesset, and one of them is traditionally a member of the opposition, the committee's Supreme Court justices are chosen by tradition from all Supreme Court justices by seniority, the Israeli Bar members are elected by the bar, and the second minister is appointed by the Israeli cabinet. The current justice minister and committee's chairman is Gideon Sa'ar. Administration of Israel's courts (both the "General" courts and the Labor Courts of Israel, Labor Courts) is carried by the Administration of Courts, situated in Jerusalem. Both General and Labor courts are paperless courts: the storage of court files, as well as court decisions, are conducted electronically. Israel's Basic Law: Human Dignity and Liberty seeks to defend Human rights in Israel, human rights and liberties in Israel. As a result of "Enclave law", large portions of Israeli Civil law (legal system), civil law are applied to Israeli settlements and Israeli residents in the occupied territories.
Israel has a Israeli judicial system, three-tier court system. At the lowest level are magistrate courts, situated in most cities across the country. Above them are district courts, serving as both appeal, appellate courts and trial court, courts of first instance; they are situated in five of Israel's six Districts of Israel, districts. The third and highest tier is the Supreme Court of Israel, Supreme Court, located in Jerusalem; it serves a dual role as the highest court of appeals and the High Court of Justice (Israel), High Court of Justice. In the latter role, the Supreme Court rules as a court of first instance, allowing individuals, both citizens and non-citizens, to petition against the decisions of state authorities. Although Israel supports the goals of the International Criminal Court, it has not ratified the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, Rome Statute, citing concerns about the ability of the court to remain free from political impartiality.
Israel's legal system combines three legal traditions: English law, English common law, civil law (legal system), civil law, and Halakha, Jewish law. It is based on the principle of ''stare decisis'' (precedent) and is an adversarial system, where the parties in the suit bring evidence before the court. Court cases are decided by professional judges with no role for juries. Marriage in Israel, Marriage and divorce are under the jurisdiction of the religious courts: Beth din, Jewish, Sharia, Muslim, Druze, and Christian. The election of judges is carried out by a Judicial Selection Committee (Israel), committee of two Knesset members, three Supreme Court justices, two Israel Bar Association, Israeli Bar members and two ministers (one of which, Israel's Ministry of Justice (Israel), justice minister, is the committee's chairman). The committee's members of the Knesset are Secret ballot, secretly elected by the Knesset, and one of them is traditionally a member of the opposition, the committee's Supreme Court justices are chosen by tradition from all Supreme Court justices by seniority, the Israeli Bar members are elected by the bar, and the second minister is appointed by the Israeli cabinet. The current justice minister and committee's chairman is Gideon Sa'ar. Administration of Israel's courts (both the "General" courts and the Labor Courts of Israel, Labor Courts) is carried by the Administration of Courts, situated in Jerusalem. Both General and Labor courts are paperless courts: the storage of court files, as well as court decisions, are conducted electronically. Israel's Basic Law: Human Dignity and Liberty seeks to defend Human rights in Israel, human rights and liberties in Israel. As a result of "Enclave law", large portions of Israeli Civil law (legal system), civil law are applied to Israeli settlements and Israeli residents in the occupied territories.
 In 1967, as a result of the
In 1967, as a result of the  The West Bank excluding East Jerusalem is known in Israeli law as the Judea and Samaria Area; the almost 400,000 Israeli settlers residing in the area are considered part of Israel's population, have Knesset representation, a Enclave law, large part of Israel's civil and criminal laws applied to them, and their output is considered part of Israel's economy.Gilead Sher
The West Bank excluding East Jerusalem is known in Israeli law as the Judea and Samaria Area; the almost 400,000 Israeli settlers residing in the area are considered part of Israel's population, have Knesset representation, a Enclave law, large part of Israel's civil and criminal laws applied to them, and their output is considered part of Israel's economy.Gilead Sher
The Application of Israeli Law to the West Bank: De Facto Annexation?
INSS Insight No. 638, 4 December 2014 The land itself is not considered part of Israel under Israeli law, as Israel has consciously refrained from annexing the territory, without ever relinquishing its legal claim to the land or defining a border with the area. There is no border between Israel-proper and the West Bank for Israeli vehicles. Israeli political opposition to annexation is primarily due to the perceived "demographic threat" of incorporating the West Bank's Palestinian population into Israel. Outside of the Israeli settlements, the West Bank remains under direct Israeli military rule, and Palestinians in the area cannot become Israeli citizens. The international community maintains that Israel does not have sovereignty in the West Bank, and considers Israel's control of the area to be the longest military occupation is modern history.See for example:
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Azarova, Valentina. 2017
Israel's Unlawfully Prolonged Occupation: Consequences under an Integrated Legal Framework
European Council on Foreign Affairs Policy Brief: "June 2017 marks 50 years of Israel's belligerent occupation of Palestinian territory, making it the longest occupation in modern history." The West Bank Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, was occupied and annexed by Jordan in 1950, following the Arab rejection of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, UN decision to create two states in Palestine. Only Britain recognized this annexation and Jordan has since Jordanian disengagement from the West Bank, ceded its claim to the territory to the PLO. The Demographics of the Palestinian territories, population are mainly Palestinian people, Palestinians, including Palestinian refugee, refugees of the The Gaza Strip is considered to be a "foreign territory" under Israeli law; however, since Israel operates a land, air, and sea blockade of the Gaza Strip, together with Egypt, the international community considers Israel to be the occupying power. The Gaza Strip was Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, occupied by Egypt from 1948 to 1967 and then by Israel after 1967. In 2005, as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan, Israel removed all of its settlers and forces from the territory, however, it continues to maintain Blockade of the Gaza Strip, control of its airspace and waters. The international community, including numerous international humanitarian organizations and various bodies of the UN, consider Gaza to remain occupied. Following the Battle of Gaza (2007), 2007 Battle of Gaza, when Governance of the Gaza Strip, Hamas assumed power in the Gaza Strip, Israel tightened its control of the Gaza crossings along Israel–Gaza barrier, its border, as well as by sea and air, and prevented persons from entering and exiting the area except for isolated cases it deemed humanitarian. Gaza has a Gaza–Egypt border, border with Egypt, and an agreement between Israel, the European Union, and the PA governed how border crossing would take place (it was monitored by European observers). The application of democracy to its Palestinian citizens, and the selective application of Israeli democracy in the Israeli-controlled Palestinian territories, has been criticized.
The International Court of Justice, principal judicial organ of the UN, asserted, in its International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict#Ruling of the ICJ, 2004 advisory opinion on the legality of the construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier, that the lands captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, including East Jerusalem, are occupied territory. Most negotiations relating to the territories have been on the basis of United Nations Security Council Resolution 242, UN Security Council Resolution 242, which emphasizes "the inadmissibility of the acquisition of territory by war", and calls on Israel to withdraw from occupied territories in return for normalization of relations with Arab states, a principle known as "Land for peace". According to some observers, Israel has engaged in systematic and widespread violations of Human rights in the Israeli-occupied territories, human rights in the occupied territories, including the occupation itself and war crimes against civilians. The allegations include violations of international humanitarian law by the United Nations Human Rights Council, UN Human Rights Council, with local residents having "limited ability to hold governing authorities accountable for such abuses" by the U.S. State Department, mass arbitrary arrests, torture, unlawful killings, systemic abuses and impunity by Amnesty International and others and a denial of the right to Palestinian self-determination. In response to such allegations, Prime Minister Netanyahu has defended the country's security forces for protecting the innocent from terrorists and expressed contempt for what he describes as a lack of concern about the human rights violations committed by "criminal killers". Some observers, such as Israeli officials, scholars, United States Ambassador to the UN Nikki Haley and UN secretary-generals Ban Ki-moon and Kofi Annan, also assert that the UN is disproportionately concerned with Israeli misconduct.
The international community widely regards Israeli settlements in the occupied territories illegal under international law. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, passed on 23 December 2016 in a 14–0 vote by members of the United Nations Security Council, U.N. Security Council (UNSC) with the United States abstaining. The resolution states that Israel's settlement activity constitutes a "flagrant violation" of international law, has "no legal validity" and demands that Israel stop such activity and fulfill its obligations as an Military occupation#The occupying power, occupying power under the Fourth Geneva Convention.
Israel's treatment of the Palestinians within the occupied territories has drawn Israel and apartheid, accusations that it is guilty of the crime of apartheid by Israeli human rights groups Yesh Din and B'tselem, and other international organizations including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, with the criticism extending to its treatment of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinians within Israel as well. Amnesty's report was criticized by politicians and government representatives from Israel, the United States, the United Kingdom, Netherlands and Germany, while it was welcomed by Palestinians, representatives from other states, and organizations such as the Arab League. A 2021 survey of academic experts on the Middle East found an increase from 59% to 65% of these scholars describing Israel as a "one-state reality akin to apartheid".
The Gaza Strip is considered to be a "foreign territory" under Israeli law; however, since Israel operates a land, air, and sea blockade of the Gaza Strip, together with Egypt, the international community considers Israel to be the occupying power. The Gaza Strip was Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, occupied by Egypt from 1948 to 1967 and then by Israel after 1967. In 2005, as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan, Israel removed all of its settlers and forces from the territory, however, it continues to maintain Blockade of the Gaza Strip, control of its airspace and waters. The international community, including numerous international humanitarian organizations and various bodies of the UN, consider Gaza to remain occupied. Following the Battle of Gaza (2007), 2007 Battle of Gaza, when Governance of the Gaza Strip, Hamas assumed power in the Gaza Strip, Israel tightened its control of the Gaza crossings along Israel–Gaza barrier, its border, as well as by sea and air, and prevented persons from entering and exiting the area except for isolated cases it deemed humanitarian. Gaza has a Gaza–Egypt border, border with Egypt, and an agreement between Israel, the European Union, and the PA governed how border crossing would take place (it was monitored by European observers). The application of democracy to its Palestinian citizens, and the selective application of Israeli democracy in the Israeli-controlled Palestinian territories, has been criticized.
The International Court of Justice, principal judicial organ of the UN, asserted, in its International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict#Ruling of the ICJ, 2004 advisory opinion on the legality of the construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier, that the lands captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, including East Jerusalem, are occupied territory. Most negotiations relating to the territories have been on the basis of United Nations Security Council Resolution 242, UN Security Council Resolution 242, which emphasizes "the inadmissibility of the acquisition of territory by war", and calls on Israel to withdraw from occupied territories in return for normalization of relations with Arab states, a principle known as "Land for peace". According to some observers, Israel has engaged in systematic and widespread violations of Human rights in the Israeli-occupied territories, human rights in the occupied territories, including the occupation itself and war crimes against civilians. The allegations include violations of international humanitarian law by the United Nations Human Rights Council, UN Human Rights Council, with local residents having "limited ability to hold governing authorities accountable for such abuses" by the U.S. State Department, mass arbitrary arrests, torture, unlawful killings, systemic abuses and impunity by Amnesty International and others and a denial of the right to Palestinian self-determination. In response to such allegations, Prime Minister Netanyahu has defended the country's security forces for protecting the innocent from terrorists and expressed contempt for what he describes as a lack of concern about the human rights violations committed by "criminal killers". Some observers, such as Israeli officials, scholars, United States Ambassador to the UN Nikki Haley and UN secretary-generals Ban Ki-moon and Kofi Annan, also assert that the UN is disproportionately concerned with Israeli misconduct.
The international community widely regards Israeli settlements in the occupied territories illegal under international law. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, passed on 23 December 2016 in a 14–0 vote by members of the United Nations Security Council, U.N. Security Council (UNSC) with the United States abstaining. The resolution states that Israel's settlement activity constitutes a "flagrant violation" of international law, has "no legal validity" and demands that Israel stop such activity and fulfill its obligations as an Military occupation#The occupying power, occupying power under the Fourth Geneva Convention.
Israel's treatment of the Palestinians within the occupied territories has drawn Israel and apartheid, accusations that it is guilty of the crime of apartheid by Israeli human rights groups Yesh Din and B'tselem, and other international organizations including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, with the criticism extending to its treatment of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinians within Israel as well. Amnesty's report was criticized by politicians and government representatives from Israel, the United States, the United Kingdom, Netherlands and Germany, while it was welcomed by Palestinians, representatives from other states, and organizations such as the Arab League. A 2021 survey of academic experts on the Middle East found an increase from 59% to 65% of these scholars describing Israel as a "one-state reality akin to apartheid".
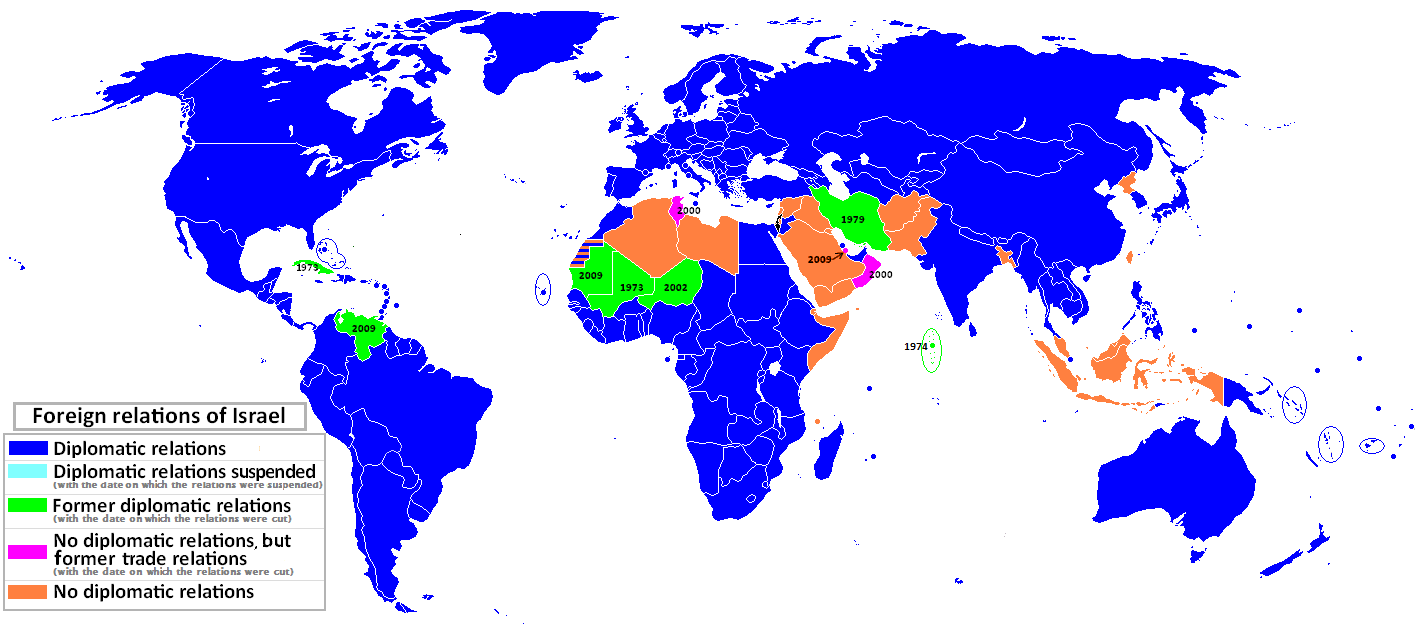 Israel maintains diplomatic relations , as well as with the Holy See, Kosovo, the Cook Islands and Niue. It has 107 List of diplomatic missions of Israel, diplomatic missions around the world; countries with whom they have no diplomatic relations include most Muslim countries. Six out of twenty-two nations in the Arab League have normalized relations with Israel. Egypt–Israel relations, Egypt and Israel–Jordan relations, Jordan signed peace treaties in Egypt–Israel peace treaty, 1979 and Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, 1994, respectively, but Israel remains formally in a Israel–Syria relations, state of war with Syria, a status that dates back uninterrupted to 1948. It has been in a similarly Israel–Lebanon relations, formal state of war with Lebanon since the end of the Lebanese Civil War in 2000, with the Israel–Lebanon border remaining unagreed by treaty.
In late 2020, Israel normalized relations with four more Arab countries: the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain in September (known as the Abraham Accords), Israel–Sudan normalization agreement, Sudan in October, and Israel–Morocco normalization agreement, Morocco in December. Despite the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, Israel is still widely considered an enemy country among Egyptians. Iran Iran–Israel relations, had diplomatic relations with Israel under the Pahlavi dynasty but withdrew its recognition of Israel during the Islamic Revolution. Israeli citizens may not visit Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen (countries Israel fought in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War that Israel does not have a peace treaty with) without permission from the Ministry of Interior (Israel), Ministry of the Interior. As a result of the Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War, Mauritania, Qatar, Bolivia, and Venezuela suspended political and economic ties with Israel, though Bolivia renewed ties in 2019. China–Israel relations, China maintains good ties with both Israel and the Arab world.
The Israel–United States relations, United States and the Israel–Russia relations, Soviet Union were the first two countries to recognize the State of Israel, having declared recognition roughly simultaneously. Diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union were broken in 1967, following the
Israel maintains diplomatic relations , as well as with the Holy See, Kosovo, the Cook Islands and Niue. It has 107 List of diplomatic missions of Israel, diplomatic missions around the world; countries with whom they have no diplomatic relations include most Muslim countries. Six out of twenty-two nations in the Arab League have normalized relations with Israel. Egypt–Israel relations, Egypt and Israel–Jordan relations, Jordan signed peace treaties in Egypt–Israel peace treaty, 1979 and Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, 1994, respectively, but Israel remains formally in a Israel–Syria relations, state of war with Syria, a status that dates back uninterrupted to 1948. It has been in a similarly Israel–Lebanon relations, formal state of war with Lebanon since the end of the Lebanese Civil War in 2000, with the Israel–Lebanon border remaining unagreed by treaty.
In late 2020, Israel normalized relations with four more Arab countries: the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain in September (known as the Abraham Accords), Israel–Sudan normalization agreement, Sudan in October, and Israel–Morocco normalization agreement, Morocco in December. Despite the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, Israel is still widely considered an enemy country among Egyptians. Iran Iran–Israel relations, had diplomatic relations with Israel under the Pahlavi dynasty but withdrew its recognition of Israel during the Islamic Revolution. Israeli citizens may not visit Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen (countries Israel fought in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War that Israel does not have a peace treaty with) without permission from the Ministry of Interior (Israel), Ministry of the Interior. As a result of the Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War, Mauritania, Qatar, Bolivia, and Venezuela suspended political and economic ties with Israel, though Bolivia renewed ties in 2019. China–Israel relations, China maintains good ties with both Israel and the Arab world.
The Israel–United States relations, United States and the Israel–Russia relations, Soviet Union were the first two countries to recognize the State of Israel, having declared recognition roughly simultaneously. Diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union were broken in 1967, following the  Although Turkey and Israel did not establish full diplomatic relations until 1991, Turkey has Israel–Turkey relations, cooperated with the Jewish state since its recognition of Israel in 1949. Turkey's ties to other Muslim-majority nations in the region have at times resulted in pressure from Arab and Muslim states to temper its relationship with Israel. Relations between Turkey and Israel took a downturn after the 2008–09 Gaza War and Israel's Gaza flotilla raid, raid of the Gaza flotilla. Greece–Israel relations, Relations between Greece and Israel have improved since 1995 due to the decline of Israeli–Turkish relations. The two countries have a defense cooperation agreement and in 2010, the Israeli Air Force hosted Greece's Hellenic Air Force in a joint exercise at the Ovda Airport, Uvda base. The joint Cyprus-Israel oil and gas explorations centered on the Leviathan gas field are an important factor for Greece, given its Cyprus–Greece relations, strong links with Cyprus. Cooperation in the world's longest Submarine power cable, subsea electric power cable, the EuroAsia Interconnector, has strengthened Cyprus–Israel relations, relations between Cyprus and Israel.
Azerbaijan is one of the few majority Muslim countries to develop strategic and economic Azerbaijan–Israel relations, relations with Israel. Azerbaijan supplies the country with a substantial amount of its oil needs, and Israel is a critical arms supplier for Azerbaijan. Kazakhstan also has an economic and strategic partnership with Israel. India established full India–Israel relations, diplomatic ties with Israel in 1992 and has fostered a strong military, technological and cultural partnership with the country since then. A 2009 survey done on behalf of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Israel), Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs listed India as more pro-Israel than 12 other countries surveyed. India is the largest customer of the Israeli military equipment and Israel is the second-largest military partner of India after Russia. Ethiopia–Israel relations, Ethiopia is Israel's main ally in Africa due to common political, religious and security interests. Israel provides expertise to Ethiopia on irrigation projects and thousands of Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopian Jews live in Israel.
Israel has a history of providing emergency aid and humanitarian response teams to disasters across the world. In 1955 Israel began its foreign aid programme in Burma. The programme's focus subsequently shifted to Africa. Israel's humanitarian efforts officially began in 1957, with the establishment of Mashav, the Israel's Agency for International Development Cooperation. In this early period, whilst Israel's aid represented only a small percentage of total aid to Africa, its programme was effective in creating goodwill throughout the continent; however, following the 1967 war relations soured. Israel's foreign aid programme subsequently shifted its focus to Latin America. Since the late 1970s Israel's foreign aid has gradually decreased, although in recent years Israel has tried to reestablish its aid to Africa. There are additional Israeli humanitarian and emergency response groups that work with the Israel government, including IsraAid, a joint programme run by 14 Israeli organizations and North American Jewish groups, ZAKA, The Fast Israeli Rescue and Search Team (FIRST), Israeli Flying Aid (IFA), Save a Child's Heart (SACH) and Latet. Between 1985 and 2015, Israel sent 24 delegations of IDF search and rescue unit, the Home Front Command, to 22 countries. Currently Israeli foreign aid List of development aid country donors, ranks low among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD nations, spending less than 0.1% of its Gross national income, GNI on development assistance. The UN has set a target of 0.7%. In 2015 six nations reached the UN target. The country ranked 38th in the 2018 World Giving Index.
Although Turkey and Israel did not establish full diplomatic relations until 1991, Turkey has Israel–Turkey relations, cooperated with the Jewish state since its recognition of Israel in 1949. Turkey's ties to other Muslim-majority nations in the region have at times resulted in pressure from Arab and Muslim states to temper its relationship with Israel. Relations between Turkey and Israel took a downturn after the 2008–09 Gaza War and Israel's Gaza flotilla raid, raid of the Gaza flotilla. Greece–Israel relations, Relations between Greece and Israel have improved since 1995 due to the decline of Israeli–Turkish relations. The two countries have a defense cooperation agreement and in 2010, the Israeli Air Force hosted Greece's Hellenic Air Force in a joint exercise at the Ovda Airport, Uvda base. The joint Cyprus-Israel oil and gas explorations centered on the Leviathan gas field are an important factor for Greece, given its Cyprus–Greece relations, strong links with Cyprus. Cooperation in the world's longest Submarine power cable, subsea electric power cable, the EuroAsia Interconnector, has strengthened Cyprus–Israel relations, relations between Cyprus and Israel.
Azerbaijan is one of the few majority Muslim countries to develop strategic and economic Azerbaijan–Israel relations, relations with Israel. Azerbaijan supplies the country with a substantial amount of its oil needs, and Israel is a critical arms supplier for Azerbaijan. Kazakhstan also has an economic and strategic partnership with Israel. India established full India–Israel relations, diplomatic ties with Israel in 1992 and has fostered a strong military, technological and cultural partnership with the country since then. A 2009 survey done on behalf of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Israel), Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs listed India as more pro-Israel than 12 other countries surveyed. India is the largest customer of the Israeli military equipment and Israel is the second-largest military partner of India after Russia. Ethiopia–Israel relations, Ethiopia is Israel's main ally in Africa due to common political, religious and security interests. Israel provides expertise to Ethiopia on irrigation projects and thousands of Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopian Jews live in Israel.
Israel has a history of providing emergency aid and humanitarian response teams to disasters across the world. In 1955 Israel began its foreign aid programme in Burma. The programme's focus subsequently shifted to Africa. Israel's humanitarian efforts officially began in 1957, with the establishment of Mashav, the Israel's Agency for International Development Cooperation. In this early period, whilst Israel's aid represented only a small percentage of total aid to Africa, its programme was effective in creating goodwill throughout the continent; however, following the 1967 war relations soured. Israel's foreign aid programme subsequently shifted its focus to Latin America. Since the late 1970s Israel's foreign aid has gradually decreased, although in recent years Israel has tried to reestablish its aid to Africa. There are additional Israeli humanitarian and emergency response groups that work with the Israel government, including IsraAid, a joint programme run by 14 Israeli organizations and North American Jewish groups, ZAKA, The Fast Israeli Rescue and Search Team (FIRST), Israeli Flying Aid (IFA), Save a Child's Heart (SACH) and Latet. Between 1985 and 2015, Israel sent 24 delegations of IDF search and rescue unit, the Home Front Command, to 22 countries. Currently Israeli foreign aid List of development aid country donors, ranks low among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD nations, spending less than 0.1% of its Gross national income, GNI on development assistance. The UN has set a target of 0.7%. In 2015 six nations reached the UN target. The country ranked 38th in the 2018 World Giving Index.
 The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and is headed by its Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff, the ''Ramatkal'', subordinate to the Cabinet of Israel, Cabinet. The IDF consists of the GOC Army Headquarters, army, Israeli Air Force, air force and Israeli Navy, navy. It was founded during the
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and is headed by its Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff, the ''Ramatkal'', subordinate to the Cabinet of Israel, Cabinet. The IDF consists of the GOC Army Headquarters, army, Israeli Air Force, air force and Israeli Navy, navy. It was founded during the

 Israel is considered the most advanced country in
Israel is considered the most advanced country in
 Israel's development of cutting-edge technologies in software, communications and the life sciences have Silicon Wadi, evoked comparisons with Silicon Valley. Israel is first in the world in List of countries by research and development spending, expenditure on research and development as a percentage of GDP. It is ranked sixteenth in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, down from tenth in 2019 and fifth in the 2019 Bloomberg Innovation Index. Israel has 140 scientists, technicians, and engineers per 10,000 employees, the highest number in the world, for comparison the U.S. has 85 per 100,000. Israel has produced six List of Israeli Nobel laureates, Nobel Prize-winning scientists since 2004 and has been frequently ranked as one of the countries with the highest ratios of scientific papers per capita in the world. Israel has led the world in stem cell, stem-cell research papers per capita since 2000. List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities are ranked among the top 50 world universities in computer science (Technion and Tel Aviv University), mathematics (Hebrew University of Jerusalem) and chemistry (Weizmann Institute of Science).
In 2012, Israel was ranked ninth in the world by the Futron's Space Competitiveness Index. The Israel Space Agency coordinates all Israeli space research programmes with scientific and commercial goals, and have indigenously designed and built at least 13 commercial, research and spy satellites. Some of Israel's satellites are ranked among the world's most advanced space systems. Shavit 2, Shavit is a space launch vehicle produced by Israel to launch small satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched in 1988, making Israel the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, eighth nation to have a space launch capability. In 2003, Ilan Ramon became Israel's first astronaut, serving as payload specialist of STS-107, the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, fatal mission of the Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''.
The ongoing shortage of Water supply and sanitation in Israel, water in the country has spurred innovation in water conservation techniques, and a substantial Agricultural research in Israel, agricultural modernization, drip irrigation, was List of Israeli inventions and discoveries, invented in Israel. Israel is also at the technological forefront of desalination and water recycling. The Sorek desalination plant is the largest seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) Desalination facilities, desalination facility in the world. By 2014, Israel's desalination programmes provided roughly 35% of Israel's drinking water and it is expected to supply 40% by 2015 and 70% by 2050. , more than 50 percent of the water for Israeli households, agriculture and industry is artificially produced. The country hosts an annual Water Technology and Environmental Control Exhibition & Conference (WATEC) that attracts thousands of people from across the world. In 2011, Israel's Water industry, water technology industry was worth around $2 billion a year with annual exports of products and services in the tens of millions of dollars. As a result of innovations in reverse osmosis technology, Israel is set to become a net Water export, exporter of water in the coming years.
Israel's development of cutting-edge technologies in software, communications and the life sciences have Silicon Wadi, evoked comparisons with Silicon Valley. Israel is first in the world in List of countries by research and development spending, expenditure on research and development as a percentage of GDP. It is ranked sixteenth in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, down from tenth in 2019 and fifth in the 2019 Bloomberg Innovation Index. Israel has 140 scientists, technicians, and engineers per 10,000 employees, the highest number in the world, for comparison the U.S. has 85 per 100,000. Israel has produced six List of Israeli Nobel laureates, Nobel Prize-winning scientists since 2004 and has been frequently ranked as one of the countries with the highest ratios of scientific papers per capita in the world. Israel has led the world in stem cell, stem-cell research papers per capita since 2000. List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities are ranked among the top 50 world universities in computer science (Technion and Tel Aviv University), mathematics (Hebrew University of Jerusalem) and chemistry (Weizmann Institute of Science).
In 2012, Israel was ranked ninth in the world by the Futron's Space Competitiveness Index. The Israel Space Agency coordinates all Israeli space research programmes with scientific and commercial goals, and have indigenously designed and built at least 13 commercial, research and spy satellites. Some of Israel's satellites are ranked among the world's most advanced space systems. Shavit 2, Shavit is a space launch vehicle produced by Israel to launch small satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched in 1988, making Israel the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, eighth nation to have a space launch capability. In 2003, Ilan Ramon became Israel's first astronaut, serving as payload specialist of STS-107, the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, fatal mission of the Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''.
The ongoing shortage of Water supply and sanitation in Israel, water in the country has spurred innovation in water conservation techniques, and a substantial Agricultural research in Israel, agricultural modernization, drip irrigation, was List of Israeli inventions and discoveries, invented in Israel. Israel is also at the technological forefront of desalination and water recycling. The Sorek desalination plant is the largest seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) Desalination facilities, desalination facility in the world. By 2014, Israel's desalination programmes provided roughly 35% of Israel's drinking water and it is expected to supply 40% by 2015 and 70% by 2050. , more than 50 percent of the water for Israeli households, agriculture and industry is artificially produced. The country hosts an annual Water Technology and Environmental Control Exhibition & Conference (WATEC) that attracts thousands of people from across the world. In 2011, Israel's Water industry, water technology industry was worth around $2 billion a year with annual exports of products and services in the tens of millions of dollars. As a result of innovations in reverse osmosis technology, Israel is set to become a net Water export, exporter of water in the coming years.
 Israel has embraced Solar power in Israel, solar energy; its engineers are on the cutting edge of solar energy technology and its solar companies work on projects around the world. Over 90% of Israeli homes use solar energy for hot water, the highest per capita in the world. According to government figures, the country saves 8% of its electricity consumption per year because of its solar energy use in heating. The high annual incident irradiance, solar irradiance at its geographic latitude creates ideal conditions for what is an internationally renowned solar research and development industry in the Negev Desert. Israel had a modern Electric vehicle network, electric car infrastructure involving a countrywide network of charging stations to facilitate the charging and exchange of car batteries. It was thought that this would have lowered Israel's oil dependency and lowered the fuel costs of hundreds of Israel's motorists that use cars powered only by electric batteries. The Israeli model was being studied by several countries and being implemented in Denmark and Australia. However, Israel's trailblazing electric car company Better Place (company), Better Place shut down in 2013.
Israel has embraced Solar power in Israel, solar energy; its engineers are on the cutting edge of solar energy technology and its solar companies work on projects around the world. Over 90% of Israeli homes use solar energy for hot water, the highest per capita in the world. According to government figures, the country saves 8% of its electricity consumption per year because of its solar energy use in heating. The high annual incident irradiance, solar irradiance at its geographic latitude creates ideal conditions for what is an internationally renowned solar research and development industry in the Negev Desert. Israel had a modern Electric vehicle network, electric car infrastructure involving a countrywide network of charging stations to facilitate the charging and exchange of car batteries. It was thought that this would have lowered Israel's oil dependency and lowered the fuel costs of hundreds of Israel's motorists that use cars powered only by electric batteries. The Israeli model was being studied by several countries and being implemented in Denmark and Australia. However, Israel's trailblazing electric car company Better Place (company), Better Place shut down in 2013.
 Israel has of paved Roads in Israel, roads, and 3 million motor vehicles. The List of countries by vehicles per capita, number of motor vehicles per 1,000 persons is 365, relatively low with respect to developed countries. Israel has 5,715 buses on scheduled routes, operated by several carriers, the largest and oldest of which is Egged (company), Egged, serving most of the country. Rail transport in Israel, Railways stretch across and are operated solely by government-owned Israel Railways. Following major investments beginning in the early to mid-1990s, the number of train passengers per year has grown from 2.5 million in 1990, to 53 million in 2015; railways are also transporting 7.5 million tons of cargo, per year.
Israel is served by two international List of airports in Israel, airports, Ben Gurion Airport, the country's main hub for international air travel near Tel Aviv, and Ramon Airport, which serves the southernmost port city of Eilat. Ben Gurion, Israel's largest airport, handled over 15 million passengers in 2015. The country has three main ports: the Port of Haifa, the country's oldest and largest, on the Mediterranean coast, Ashdod Port; and the smaller Port of Eilat on the
Israel has of paved Roads in Israel, roads, and 3 million motor vehicles. The List of countries by vehicles per capita, number of motor vehicles per 1,000 persons is 365, relatively low with respect to developed countries. Israel has 5,715 buses on scheduled routes, operated by several carriers, the largest and oldest of which is Egged (company), Egged, serving most of the country. Rail transport in Israel, Railways stretch across and are operated solely by government-owned Israel Railways. Following major investments beginning in the early to mid-1990s, the number of train passengers per year has grown from 2.5 million in 1990, to 53 million in 2015; railways are also transporting 7.5 million tons of cargo, per year.
Israel is served by two international List of airports in Israel, airports, Ben Gurion Airport, the country's main hub for international air travel near Tel Aviv, and Ramon Airport, which serves the southernmost port city of Eilat. Ben Gurion, Israel's largest airport, handled over 15 million passengers in 2015. The country has three main ports: the Port of Haifa, the country's oldest and largest, on the Mediterranean coast, Ashdod Port; and the smaller Port of Eilat on the
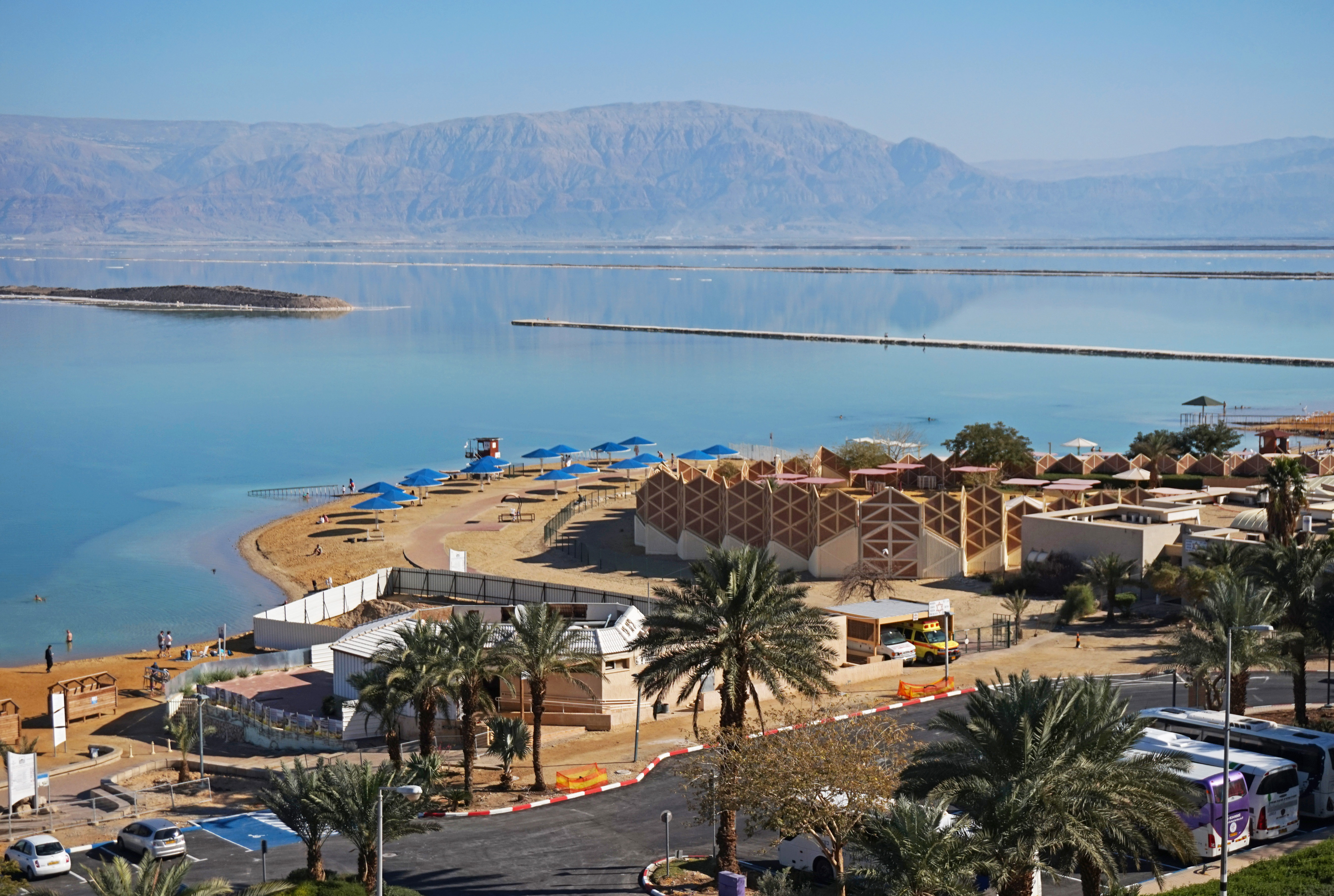 Tourism, especially religious tourism, is an important industry in Israel, with the country's temperate climate, List of beaches in Israel, beaches, Archaeology of Israel, archaeological, other List of World Heritage Sites in Israel, historical and List of biblical places, biblical sites, and unique geography also drawing tourists. Israel's security problems have taken their toll on the industry, but the number of incoming tourists is on the rebound. In 2017, a record of 3.6 million tourists visited Israel, yielding a 25 percent growth since 2016 and contributed NIS 20 billion to the Israeli economy.
Tourism, especially religious tourism, is an important industry in Israel, with the country's temperate climate, List of beaches in Israel, beaches, Archaeology of Israel, archaeological, other List of World Heritage Sites in Israel, historical and List of biblical places, biblical sites, and unique geography also drawing tourists. Israel's security problems have taken their toll on the industry, but the number of incoming tourists is on the rebound. In 2017, a record of 3.6 million tourists visited Israel, yielding a 25 percent growth since 2016 and contributed NIS 20 billion to the Israeli economy.
 Israeli literature is primarily Modern Hebrew poetry, poetry and prose written in Hebrew language, Hebrew, as part of the Revival of the Hebrew language, renaissance of Hebrew as a spoken language since the mid-19th century, although a small body of literature is published in other languages, such as English. By law, two copies of all printed matter published in Israel must be deposited in the National Library of Israel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. In 2001, the law was amended to include audio and video recordings, and other non-print media. In 2016, 89 percent of the 7,300 books transferred to the library were in Hebrew.
In 1966, Shmuel Yosef Agnon shared the Nobel Prize in Literature with German Jewish author Nelly Sachs. Leading Israeli poets have been Yehuda Amichai, Nathan Alterman, Leah Goldberg, and Rachel Bluwstein. Internationally famous contemporary Israeli novelists include Amos Oz, Etgar Keret and David Grossman. The Israeli-Arab satirist Sayed Kashua (who writes in Hebrew) is also internationally known. Israel has also been the home of Emile Habibi, whose novel ''The Secret Life of Saeed: The Pessoptimist'', and other writings, won him the Israel prize for Arabic literature.
Israeli literature is primarily Modern Hebrew poetry, poetry and prose written in Hebrew language, Hebrew, as part of the Revival of the Hebrew language, renaissance of Hebrew as a spoken language since the mid-19th century, although a small body of literature is published in other languages, such as English. By law, two copies of all printed matter published in Israel must be deposited in the National Library of Israel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. In 2001, the law was amended to include audio and video recordings, and other non-print media. In 2016, 89 percent of the 7,300 books transferred to the library were in Hebrew.
In 1966, Shmuel Yosef Agnon shared the Nobel Prize in Literature with German Jewish author Nelly Sachs. Leading Israeli poets have been Yehuda Amichai, Nathan Alterman, Leah Goldberg, and Rachel Bluwstein. Internationally famous contemporary Israeli novelists include Amos Oz, Etgar Keret and David Grossman. The Israeli-Arab satirist Sayed Kashua (who writes in Hebrew) is also internationally known. Israel has also been the home of Emile Habibi, whose novel ''The Secret Life of Saeed: The Pessoptimist'', and other writings, won him the Israel prize for Arabic literature.
 Music of Israel, Israeli music contains musical influences from all over the world; Mizrahi music, Mizrahi and Sephardic music, Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic melodies, Greek music in Israel, Greek music, jazz, and pop rock are all part of the music scene. Among Israel's world-renowned orchestras is the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra, which has been in operation for over seventy years and today performs more than two hundred concerts each year. Itzhak Perlman, Pinchas Zukerman and Ofra Haza are among the internationally acclaimed musicians born in Israel. Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest, Israel has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest nearly every year since 1973, winning the competition four times and hosting it twice. Eilat has hosted its own international music festival, the Red Sea Jazz Festival, every summer since 1987. The nation's canonical folk music, folk songs, known as "Songs of the Land of Israel," deal with the experiences of the pioneers in building the Jewish homeland.
Music of Israel, Israeli music contains musical influences from all over the world; Mizrahi music, Mizrahi and Sephardic music, Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic melodies, Greek music in Israel, Greek music, jazz, and pop rock are all part of the music scene. Among Israel's world-renowned orchestras is the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra, which has been in operation for over seventy years and today performs more than two hundred concerts each year. Itzhak Perlman, Pinchas Zukerman and Ofra Haza are among the internationally acclaimed musicians born in Israel. Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest, Israel has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest nearly every year since 1973, winning the competition four times and hosting it twice. Eilat has hosted its own international music festival, the Red Sea Jazz Festival, every summer since 1987. The nation's canonical folk music, folk songs, known as "Songs of the Land of Israel," deal with the experiences of the pioneers in building the Jewish homeland.
 The Israel Museum in Jerusalem is one of Israel's most important cultural institutions and houses the Dead Sea Scrolls, along with an extensive collection of Judaica and European art. Israel's national The Holocaust, Holocaust museum, Yad Vashem, is the world central archive of Holocaust-related information. ANU - Museum of the Jewish People on the campus of Tel Aviv University, is an interactive museum devoted to the history of Jewish communities around the world. Apart from the major museums in large cities, there are high-quality art spaces in many towns and kibbutzim. Mishkan LeOmanut in kibbutz Ein Harod (Meuhad), Ein Harod Meuhad is the largest art museum in the north of the country.
Israel has the highest number of museums per capita in the world. Several Israeli museums are devoted to Islamic culture, including the Rockefeller Museum and the L. A. Mayer Institute for Islamic Art, both in Jerusalem. The Rockefeller specializes in archaeological remains from the Ottoman and other periods of Middle East history. It is also the home of the first hominid fossil skull found in Western Asia, called Galilee Man. A cast of the skull is on display at the Israel Museum.
The Israel Museum in Jerusalem is one of Israel's most important cultural institutions and houses the Dead Sea Scrolls, along with an extensive collection of Judaica and European art. Israel's national The Holocaust, Holocaust museum, Yad Vashem, is the world central archive of Holocaust-related information. ANU - Museum of the Jewish People on the campus of Tel Aviv University, is an interactive museum devoted to the history of Jewish communities around the world. Apart from the major museums in large cities, there are high-quality art spaces in many towns and kibbutzim. Mishkan LeOmanut in kibbutz Ein Harod (Meuhad), Ein Harod Meuhad is the largest art museum in the north of the country.
Israel has the highest number of museums per capita in the world. Several Israeli museums are devoted to Islamic culture, including the Rockefeller Museum and the L. A. Mayer Institute for Islamic Art, both in Jerusalem. The Rockefeller specializes in archaeological remains from the Ottoman and other periods of Middle East history. It is also the home of the first hominid fossil skull found in Western Asia, called Galilee Man. A cast of the skull is on display at the Israel Museum.
 Israeli cuisine includes local dishes as well as Jewish cuisine brought to the country by immigrants from the Jewish diaspora, diaspora. Since the establishment of the state in 1948, and particularly since the late 1970s, an Israeli fusion cuisine has developed. Israeli cuisine has adopted, and continues to adapt, elements of the Cuisine of the Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi, Cuisine of the Sephardic Jews, Sephardi, and Ashkenazi cuisine, Ashkenazi styles of cooking. It incorporates many foods traditionally eaten in the Levantine cuisine, Levantine, Arab cuisine, Arab, Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines, such as falafel, hummus, shakshouka, couscous, and za'atar. Schnitzel, pizza, hamburgers, French fries, rice and salad are also common in Israel.
Roughly half of the Israeli-Jewish population attests to keeping kosher at home.Julia Bernstein
Israeli cuisine includes local dishes as well as Jewish cuisine brought to the country by immigrants from the Jewish diaspora, diaspora. Since the establishment of the state in 1948, and particularly since the late 1970s, an Israeli fusion cuisine has developed. Israeli cuisine has adopted, and continues to adapt, elements of the Cuisine of the Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi, Cuisine of the Sephardic Jews, Sephardi, and Ashkenazi cuisine, Ashkenazi styles of cooking. It incorporates many foods traditionally eaten in the Levantine cuisine, Levantine, Arab cuisine, Arab, Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines, such as falafel, hummus, shakshouka, couscous, and za'atar. Schnitzel, pizza, hamburgers, French fries, rice and salad are also common in Israel.
Roughly half of the Israeli-Jewish population attests to keeping kosher at home.Julia Bernstein
''Food for Thought: Transnational Contested Identities and Food Practices of Russian-Speaking Jewish Migrants in Israel and Germany,''
Campus Verlag, 2010 pp. 227, 233–234. Kosher restaurants, though rare in the 1960s, make up around a quarter of the total , perhaps reflecting the largely secular values of those who dine out.Yael Raviv
''Falafel Nation,''
University of Nebraska Press, 2015 Hotel restaurants are much more likely to serve kosher food. The non-kosher retail market was traditionally sparse, but grew rapidly and considerably following 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, the influx of immigrants from the post-Soviet states during the 1990s. Together with non-kosher fish, rabbits and ostriches, pork—often called "white meat" in IsraelBernstein
pp. 231–233
—is produced and consumed, though Religious restrictions on the consumption of pork, it is forbidden by both Judaism and Islam.
 The most popular spectator sports in Israel are association football and basketball. The Israeli Premier League is the country's premier football league, and the Israeli Basketball Premier League is the premier basketball league. Maccabi Haifa F.C., Maccabi Haifa, Maccabi Tel Aviv F.C., Maccabi Tel Aviv, Hapoel Tel Aviv F.C., Hapoel Tel Aviv and Beitar Jerusalem F.C., Beitar Jerusalem are the largest List of football clubs in Israel, football clubs. Maccabi Tel Aviv, Maccabi Haifa and Hapoel Tel Aviv have competed in the UEFA Champions League and Hapoel Tel Aviv reached the UEFA Cup quarter-finals. Israel hosted and won the 1964 AFC Asian Cup; in 1970 the Israel national football team qualified for the 1970 FIFA World Cup, FIFA World Cup, the only time it participated in the World Cup. The 1974 Asian Games, held in Tehran, were the last Asian Games in which Israel Israel at the Asian Games, participated, plagued by the Arab countries that Boycotts of Israel in sports, refused to compete with Israel. Israel was excluded from the 1978 Asian Games and since then has not competed in Asian sport events. In 1994, UEFA agreed to admit Israel, and its football teams now compete in Europe. Maccabi Tel Aviv B.C. has won the FIBA European Champions Cup and EuroLeague records and statistics, European championship in basketball six times. In 2016, the country was chosen as a host for the EuroBasket 2017.
Israel has won Israel at the Olympics, nine Olympic medals since its first win 1992 Summer Olympics, in 1992, including a gold medal in Sailing at the 2004 Summer Olympics – Men's Mistral One Design, windsurfing at the 2004 Summer Olympics. Israel has won Israel at the Paralympics, over 100 gold medals in the Paralympic Games and is ranked 20th in the All-time Paralympic Games medal table, all-time medal count. The 1968 Summer Paralympics were hosted by Israel. The Maccabiah Games, an Olympic-style event for List of Jews in sports, Jewish and Israeli athletes, was inaugurated in the 1930s, and has been held every four years since then. Israeli tennis champion Shahar Pe'er ranked 11th in the world on 31 January 2011. Krav Maga, a martial art developed by Jewish ghetto defenders during the struggle against fascism in Europe, is used by the Israeli security forces and police. Its effectiveness and practical approach to self-defense, have won it widespread admiration and adherence around the world.
The most popular spectator sports in Israel are association football and basketball. The Israeli Premier League is the country's premier football league, and the Israeli Basketball Premier League is the premier basketball league. Maccabi Haifa F.C., Maccabi Haifa, Maccabi Tel Aviv F.C., Maccabi Tel Aviv, Hapoel Tel Aviv F.C., Hapoel Tel Aviv and Beitar Jerusalem F.C., Beitar Jerusalem are the largest List of football clubs in Israel, football clubs. Maccabi Tel Aviv, Maccabi Haifa and Hapoel Tel Aviv have competed in the UEFA Champions League and Hapoel Tel Aviv reached the UEFA Cup quarter-finals. Israel hosted and won the 1964 AFC Asian Cup; in 1970 the Israel national football team qualified for the 1970 FIFA World Cup, FIFA World Cup, the only time it participated in the World Cup. The 1974 Asian Games, held in Tehran, were the last Asian Games in which Israel Israel at the Asian Games, participated, plagued by the Arab countries that Boycotts of Israel in sports, refused to compete with Israel. Israel was excluded from the 1978 Asian Games and since then has not competed in Asian sport events. In 1994, UEFA agreed to admit Israel, and its football teams now compete in Europe. Maccabi Tel Aviv B.C. has won the FIBA European Champions Cup and EuroLeague records and statistics, European championship in basketball six times. In 2016, the country was chosen as a host for the EuroBasket 2017.
Israel has won Israel at the Olympics, nine Olympic medals since its first win 1992 Summer Olympics, in 1992, including a gold medal in Sailing at the 2004 Summer Olympics – Men's Mistral One Design, windsurfing at the 2004 Summer Olympics. Israel has won Israel at the Paralympics, over 100 gold medals in the Paralympic Games and is ranked 20th in the All-time Paralympic Games medal table, all-time medal count. The 1968 Summer Paralympics were hosted by Israel. The Maccabiah Games, an Olympic-style event for List of Jews in sports, Jewish and Israeli athletes, was inaugurated in the 1930s, and has been held every four years since then. Israeli tennis champion Shahar Pe'er ranked 11th in the world on 31 January 2011. Krav Maga, a martial art developed by Jewish ghetto defenders during the struggle against fascism in Europe, is used by the Israeli security forces and police. Its effectiveness and practical approach to self-defense, have won it widespread admiration and adherence around the world.
 Chess is a leading sport in Israel and is enjoyed by people of all ages. There are many Israeli grandmasters and List of Israeli chess players, Israeli chess players have won a number of youth world championships. Israel stages an annual international Israeli Chess Championship, championship and hosted the World Team Chess Championship in 2005. The Ministry of Education and the FIDE, World Chess Federation agreed upon a project of teaching chess within Israeli schools, and it has been introduced into the curriculum of some schools. The city of Beersheba has become a national chess center, with the game being taught in the city's kindergartens. Owing partly to Soviet immigration, it is home to the largest number of Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmasters of any city in the world. The Israeli chess team won the silver medal at the 38th Chess Olympiad, 2008 Chess Olympiad and the bronze, coming in third among 148 teams, at the 39th Chess Olympiad, 2010 Olympiad. Israeli grandmaster Boris Gelfand won the Chess World Cup 2009 and the World Chess Championship 2012#Candidates tournament, 2011 Candidates Tournament for the right to challenge the world champion. He lost the World Chess Championship 2012 to reigning world champion Viswanathan Anand, Anand after a speed-chess tie breaker.
Chess is a leading sport in Israel and is enjoyed by people of all ages. There are many Israeli grandmasters and List of Israeli chess players, Israeli chess players have won a number of youth world championships. Israel stages an annual international Israeli Chess Championship, championship and hosted the World Team Chess Championship in 2005. The Ministry of Education and the FIDE, World Chess Federation agreed upon a project of teaching chess within Israeli schools, and it has been introduced into the curriculum of some schools. The city of Beersheba has become a national chess center, with the game being taught in the city's kindergartens. Owing partly to Soviet immigration, it is home to the largest number of Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmasters of any city in the world. The Israeli chess team won the silver medal at the 38th Chess Olympiad, 2008 Chess Olympiad and the bronze, coming in third among 148 teams, at the 39th Chess Olympiad, 2010 Olympiad. Israeli grandmaster Boris Gelfand won the Chess World Cup 2009 and the World Chess Championship 2012#Candidates tournament, 2011 Candidates Tournament for the right to challenge the world champion. He lost the World Chess Championship 2012 to reigning world champion Viswanathan Anand, Anand after a speed-chess tie breaker.
Israel
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. * * * * {{Portal bar, Israel, Judaism, Middle East, Asia Israel, 1948 establishments in Asia Arabic-speaking countries and territories Articles containing video clips Countries in Asia Eastern Mediterranean Jewish polities States and territories established in 1948 Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Middle Eastern countries Levant Western Asian countries Near Eastern countries Palestine (region), * Political entities in the Land of Israel Republics
Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
and the northern shore of the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
, and shares borders with Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
to the north, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
to the northeast, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
to the east, and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The I ...
of the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
and the Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
is the economic
An economy is an area of the Production (economics), production, Distribution (economics), distribution and trade, as well as Consumption (economics), consumption of Goods (economics), goods and Service (economics), services. In general, it is ...
and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally.
The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
ites during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
.Jonathan M Golde''Ancient Canaan and Israel: An Introduction,''
OUP, 2009 pp. 3–4. During the
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, the kingdoms of Israel and Judah
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscripti ...
emerged, and later fell, respectively, to the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
(c. 720 BCE) and Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ...
(586 BCE). During that period, much of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
was written. The region was then ruled by the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, Macedonian
Macedonian most often refers to someone or something from or related to Macedonia.
Macedonian(s) may specifically refer to:
People Modern
* Macedonians (ethnic group), a nation and a South Slavic ethnic group primarily associated with North M ...
, Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
, and Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
empires. A successful Maccabean revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
led to the rise of an independent Hasmonean kingdom
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, an ...
, but it was gradually incorporated into the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
. A series of large-scale Jewish revolts against Roman rule were unsuccessful, leading to wide-scale destruction, a high toll of life, and mass displacement. In the Middle Ages, the region was part of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate ( ar, اَلْخِلَافَةُ ٱلرَّاشِدَةُ, al-Khilāfah ar-Rāšidah) was the first caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was ruled by the first four successive caliphs of Muhammad after his ...
, Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
, Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, and Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
. With the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
, Crusader states
The Crusader States, also known as Outremer, were four Catholic realms in the Middle East that lasted from 1098 to 1291. These feudal polities were created by the Latin Catholic leaders of the First Crusade through conquest and political in ...
were established. The Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin h ...
pushed back the crusaders before Muslim rule was fully restored by the Mamluk Sultanate
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16th ...
, which ceded the territory to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
at the outset of the early modern period.
During the 19th century, the Zionist
Zionism ( he, צִיּוֹנוּת ''Tsiyyonut'' after ''Zion'') is a nationalist movement that espouses the establishment of, and support for a homeland for the Jewish people centered in the area roughly corresponding to what is known in Je ...
movement began promoting the creation of a Jewish homeland
A homeland for the Jewish people is an idea rooted in Jewish history, religion, and culture. The Jewish aspiration to return to Zion, generally associated with divine redemption, has suffused Jewish religious thought since the destruction ...
in Ottoman Syria
Ottoman Syria ( ar, سوريا العثمانية) refers to divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Syria, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south ...
. Following World War I, Britain was granted control of the region by the League of Nations mandate
A League of Nations mandate was a legal status for certain territories transferred from the control of one country to another following World War I, or the legal instruments that contained the internationally agreed-upon terms for administ ...
, in what became known as Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
. After World War II, the newly formed United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
adopted the Partition Plan for Palestine in 1947, recommending the creation of independent Arab and Jewish states, and an internationalized Jerusalem. Partition was accepted by the Jewish leadership, but rejected by Palestinian Arab leaders and the Arab states. Following a civil war within Mandatory Palestine between Yishuv
Yishuv ( he, ישוב, literally "settlement"), Ha-Yishuv ( he, הישוב, ''the Yishuv''), or Ha-Yishuv Ha-Ivri ( he, הישוב העברי, ''the Hebrew Yishuv''), is the body of Jewish residents in the Land of Israel (corresponding to the s ...
and Palestinian Arab forces, Israel declared independence at the termination of the British Mandate. A day later, several surrounding Arab countries intervened, leading to the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
, which concluded with the 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
and Gaza were held by Jordan and Egypt respectively. Over 700,000 Palestinian Arabs
Palestinians ( ar, الفلسطينيون, ; he, פָלַסְטִינִים, ) or Palestinian people ( ar, الشعب الفلسطيني, label=none, ), also referred to as Palestinian Arabs ( ar, الفلسطينيين العرب, label=non ...
, about half of the pre-war Arab population, were expelled from or fled the territory Israel would come to control. During and immediately after the war, around 260,000 Jews emigrated or fled from the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
to Israel.
Israel has since fought wars with several Arab countries, and since the 1967 Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
has occupied the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
and the Palestinian territories of the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip, though whether Gaza remains occupied following the Israeli disengagement is disputed. Israel has effectively annexed East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, though these actions have been rejected as illegal by the international community, and established settlements within the occupied territories, which are also considered illegal under international law. While Israel has signed peace treaties with Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
and Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, and has normalized relations with a number of other Arab countries, it remains formally at war with Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
and Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
, and efforts to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is one of the world's most enduring conflicts, beginning in the mid-20th century. Various attempts have been made to resolve the conflict as part of the Israeli–Palestinian peace process, alongside other ef ...
have thus far stalled.
In its Basic Laws, Israel defines itself as a Jewish and democratic state
"Jewish and democratic state" is the Israeli legal definition of the nature and character of the State of Israel. The "Jewish" nature was first defined within the Israeli Declaration of Independence in May 1948 (see Jewish state and Jewish homela ...
, and as the nation-state of the Jewish people. The country has a parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance of a state (or subordinate entity) where the executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the ...
, proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
, and universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
. The prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
serves as head of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
, while the Knesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with ...
is the unicameral legislature
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
. Israel is a highly developed country
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
and an OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
member, with a population of over nine million people . It has the world's 28th-largest economy by nominal GDP, and ranks twenty-two in the Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
.
Etymology
 Under the British Mandate (1920–1948), the whole region was known as 'Palestine' (). Upon
Under the British Mandate (1920–1948), the whole region was known as 'Palestine' (). Upon independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
in 1948, the country formally adopted the name 'State of Israel' ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, دَوْلَة إِسْرَائِيل, , ) after other proposed historical and religious names including 'Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
' (''Eretz Israel''), Ever (from ancestor Eber
Eber ( he, , ʿĒḇer; grc-x-biblical, Ἔβερ, Éber; ar, عٰابِر, ʿĀbir) is an ancestor of the Ishmaelites and the Israelites according to the "Table of Nations" in the Book of Genesis () and the Books of Chronicles ().
Lineage
...
), Zion
Zion ( he, צִיּוֹן ''Ṣīyyōn'', LXX , also variously transliterated ''Sion'', ''Tzion'', ''Tsion'', ''Tsiyyon'') is a placename in the Hebrew Bible used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole (see Names ...
, and Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous L ...
, were considered but rejected, while the name 'Israel' was suggested by Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; he, דָּוִד בֶּן-גּוּרִיּוֹן ; born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary national founder of the State of Israel and the first prime minister of Israel. Adopting the name ...
and passed by a vote of 6–3. In the early weeks of independence, the government chose the term "Israeli
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli ...
" to denote a citizen of Israel, with the formal announcement made by Minister of Foreign Affairs
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between cou ...
Moshe Sharett
Moshe Sharett ( he, משה שרת, born Moshe Chertok (Hebrew: ) 15 October 1894 – 7 July 1965) was a Russian-born Israeli politician who served as Israel's second prime minister from 1954 to 1955. A member of Mapai, Sharett's term was b ...
.
The names Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
and Children of Israel
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
have historically been used to refer to the biblical Kingdom of Israel and the entire Jewish people respectively. The name 'Israel' (Hebrew: ''Yisraʾel'', ''Isrāʾīl''; Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
el, Ἰσραήλ, ''Israēl'', 'El (God) persists/rules', though after often interpreted as 'struggle with God') in these phrases refers to the patriarch Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
who, according to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
, was given the name after he successfully wrestled with the angel of the Lord. Jacob's twelve sons became the ancestors of the ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. Hebrew: ''Tān ...
Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
, also known as the ''Twelve Tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( he, שִׁבְטֵי־יִשְׂרָאֵל, translit=Šīḇṭēy Yīsrāʾēl, lit=Tribes of Israel) are, according to Hebrew scriptures, the descendants of the biblical patriarch Jacob, also known as Israel, throu ...
'' or ''Children of Israel''. Jacob and his sons had lived in Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
but were forced by famine to go into Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
for four generations, lasting 430 years, until Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
, a great-great-grandson of Jacob, led the Israelites back into Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
during the "Exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* Ex ...
". The earliest known archaeological artefact to mention the word "Israel" as a collective is the Merneptah Stele
The Merneptah Stele, also known as the Israel Stele or the Victory Stele of Merneptah, is an inscription by Merneptah, a pharaoh in ancient Egypt who reigned from 1213–1203 BCE. Discovered by Flinders Petrie at Thebes in 1896, it is now hous ...
of ancient Egypt (dated to the late 13th century BCE).
History
Prehistory
TheSouthern Levant
The Southern Levant is a Region, geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southe ...
experienced human residence, agricultural communities, and civilization among the first in the globe. The oldest evidence of early humans
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus ''Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely related ...
in the territory of modern Israel, dating to 1.5 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
, was found in Ubeidiya Ubeidiya commonly refers to:
* Ubeidiya prehistoric site
* Ubeidiya, West Bank
* Ubeidiya, Tiberias
See also
* Abd (Arabic)
ʿAbd ( ar, عبد) is an Arabic word meaning one who is subordinated as a slave or a servant, and it means also to w ...
near the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest ...
. Other notable Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός ''palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone too ...
sites include the caves Tabun, Qesem and Manot. The oldest fossils of anatomically modern human
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
s found outside Africa are the Skhul and Qafzeh hominins
The Skhul/Qafzeh hominins or Qafzeh–Skhul early modern humans are hominin fossils discovered in Es-Skhul and Qafzeh caves in Israel. They are today classified as ''Homo sapiens'', among the earliest of their species in Eurasia. Skhul Cave i ...
, who lived in the area that is now northern Israel 120,000 years ago. Around the 10th millennium BCE, the Natufian culture
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction ...
existed in the area.
Antiquity
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
ites are archaeologically attested in the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(2100–1550 BCE). During the Late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
(1550–1200 BCE), large parts of Canaan formed vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
s paying tribute to the New Kingdom of Egypt
The New Kingdom, also referred to as the Egyptian Empire, is the period in ancient Egyptian history between the sixteenth century BC and the eleventh century BC, covering the Eighteenth, Nineteenth, and Twentieth dynasties of Egypt. Radioca ...
, whose administrative headquarters lay in Gaza. As a result of the Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East ...
, Canaan fell into chaos, and Egyptian control over the region collapsed completely. There is evidence that urban centers such as Hazor, Beit She'an
Beit She'an ( he, בֵּית שְׁאָן '), also Beth-shean, formerly Beisan ( ar, بيسان ), is a town in the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The town lies at the Beit She'an Valley about 120 m (394 feet) below se ...
, Megiddo Megiddo may refer to:
Places and sites in Israel
* Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley
* Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel
* Megiddo church (Israel)
* Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel
* Megiddo Junction, ...
, Ekron
Ekron (Philistine: 𐤏𐤒𐤓𐤍 ''*ʿAqārān'', he, עֶקְרוֹן, translit=ʿEqrōn, ar, عقرون), in the Hellenistic period known as Accaron ( grc-gre, Ακκαρων, Akkarōn}) was a Philistine city, one of the five cities o ...
, Ashdod
Ashdod ( he, ''ʾašdōḏ''; ar, أسدود or إسدود ''ʾisdūd'' or '' ʾasdūd'' ; Philistine: 𐤀𐤔𐤃𐤃 *''ʾašdūd'') is the sixth-largest city in Israel. Located in the country's Southern District, it lies on the Mediterran ...
and Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border with ...
were damaged or destroyed.
A people named Israel appear for the first time in the Merneptah Stele
The Merneptah Stele, also known as the Israel Stele or the Victory Stele of Merneptah, is an inscription by Merneptah, a pharaoh in ancient Egypt who reigned from 1213–1203 BCE. Discovered by Flinders Petrie at Thebes in 1896, it is now hous ...
, an ancient Egyptian inscription which dates to about 1200 BCE.K.L. Noll''Canaan and Israel in Antiquity: A Textbook on History and Religion,''
A&C Black, 2012, rev.ed. pp. 137ff.
Thomas L. Thompson
Thomas L. Thompson (born January 7, 1939 in Detroit, Michigan) is an American-born Danish biblical scholar and theologian. He was professor of theology at the University of Copenhagen from 1993 to 2009. He currently lives in Denmark.
Thompson is ...
''Early History of the Israelite People: From the Written & Archaeological Sources,''
Brill, 2000 pp. 275–276: 'They are rather a very specific group among the population of Palestine which bears a name that occurs here for the first time that at a much later stage in Palestine's history bears a substantially different signification.' Ancestors of the Israelites are thought to have included
ancient Semitic-speaking peoples
Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples or Proto-Semitic people were people who lived throughout the ancient Near East, including the Levant, Mesopotamia, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Horn of Africa from the 3rd millennium BC until the end of antiquit ...
native to this area. According to the modern archaeological account, the Israelites and their culture branched out of the Canaanite peoples and their cultures through the development of a distinct monolatristic
Monolatry ( grc, μόνος, monos, single, and grc, λατρεία, latreia, worship, label=none) is the belief in the existence of many gods, but with the consistent worship of only one deity. The term ''monolatry'' was perhaps first used by Ju ...
—and later monotheistic
Monotheism is the belief that there is only one deity, an all-supreme being that is universally referred to as God. Cross, F.L.; Livingstone, E.A., eds. (1974). "Monotheism". The Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (2 ed.). Oxford: Oxford ...
—religion centered on Yahweh
Yahweh *''Yahwe'', was the national god of ancient Israel and Judah. The origins of his worship reach at least to the early Iron Age, and likely to the Late Bronze Age if not somewhat earlier, and in the oldest biblical literature he posse ...
. They spoke an archaic form of the Hebrew language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, known as Biblical Hebrew
Biblical Hebrew (, or , ), also called Classical Hebrew, is an archaic form of the Hebrew language, a language in the Canaanite branch of Semitic languages spoken by the Israelites in the area known as the Land of Israel, roughly west of ...
. The archaeological evidence indicates a society of village-like centers, but with more limited resources and a small population. Villages had populations of up to 300 or 400, which lived by farming and herding, and were largely self-sufficient; economic interchange was prevalent. Writing was known and available for recording, even in small sites. Around the same time, the Philistines
The Philistines ( he, פְּלִשְׁתִּים, Pəlīštīm; Koine Greek (LXX): Φυλιστιείμ, romanized: ''Phulistieím'') were an ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan from the 12th century BC until 604 BC, when ...
settled on the southern coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
.
Modern archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
has largely discarded the historicity of the narrative in the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the s ...
concerning the patriarchs
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate (bishop), primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholicism, Independent Catholic Chur ...
, The Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yeẓi’at Miẓrayim'': ) is the founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four books of the Torah (or Pentateuch, corresponding to the first five books of the ...
, and the conquest of Canaan
''The Conquest of Canaan'' is a 1921 American silent drama film produced by Famous Players-Lasky and distributed by Paramount Pictures. It starred Thomas Meighan and Doris Kenyon and was directed by Roy William Neill. It was filmed in Ashevi ...
described in the Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua ( he, סֵפֶר יְהוֹשֻׁעַ ', Tiberian: ''Sēp̄er Yŏhōšūaʿ'') is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Isra ...
, and instead views the narrative as constituting the Israelites
The Israelites (; , , ) were a group of Semitic-speaking tribes in the ancient Near East who, during the Iron Age, inhabited a part of Canaan.
The earliest recorded evidence of a people by the name of Israel appears in the Merneptah Stele o ...
' national myth
A national myth is an inspiring narrative or anecdote about a nation's past. Such myths often serve as important national symbols and affirm a set of national values. A national myth may sometimes take the form of a national epic or be incorporate ...
. However, some elements of these traditions do appear to have historical roots.
Kingdoms of Israel and Judah
The history of ancient Israel and Judah begins in the Southern Levant during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. "Israel" as a people or tribal confederation (see Israelites) appears for the first time in the Merneptah Stele, an inscripti ...
and their extent and power. While it is unclear if there was ever a United Kingdom of Israel
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Re ...
, historians and archaeologists agree that the northern Kingdom of Israel existed by 900 BCE and that the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah ( he, , ''Yəhūdā''; akk, 𒅀𒌑𒁕𒀀𒀀 ''Ya'údâ'' 'ia-ú-da-a-a'' arc, 𐤁𐤉𐤕𐤃𐤅𐤃 ''Bēyt Dāwīḏ'', " House of David") was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Ce ...
existed by 850 BCE.Finkelstein, Israel, (2020)"Saul and Highlands of Benjamin Update: The Role of Jerusalem"
in Joachim J. Krause, Omer Sergi, and Kristin Weingart (eds.), ''Saul, Benjamin, and the Emergence of Monarchy in Israel: Biblical and Archaeological Perspectives'', SBL Press, Atlanta, GA, p. 48, footnote 57: "...They became territorial kingdoms later, Israel in the first half of the ninth century BCE and Judah in its second half..."The Pitcher Is Broken: Memorial Essays for Gosta W. Ahlstrom, Steven W. Holloway, Lowell K. Handy, Continuum, 1 May 1995
Quote: "For Israel, the description of the battle of Qarqar in the Kurkh Monolith of Shalmaneser III (mid-ninth century) and for Judah, a Tiglath-pileser III text mentioning (Jeho-) Ahaz of Judah (IIR67 = K. 3751), dated 734–733, are the earliest published to date." The Kingdom of Israel was the more prosperous of the two kingdoms and soon developed into a regional power; during the days of the
Omride dynasty
The Omrides, Omrids or House of Omri ( he, , translit=Bēt ʿOmrī; akk, 𒂍𒄷𒌝𒊑𒄿, translit=bīt-Ḫûmrî) were a ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) founded by King Omri. According to the Bible, the Omride rulers of ...
, it controlled Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first- ...
, Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galil ...
, the upper Jordan Valley
The Jordan Valley ( ar, غور الأردن, ''Ghor al-Urdun''; he, עֵמֶק הַיַרְדֵּן, ''Emek HaYarden'') forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. Unlike most other river valleys, the term "Jordan Valley" often applies just to ...
, the Sharon
Sharon ( he, שָׁרוֹן ''Šārôn'' "plain") is a given name as well as an Israeli surname.
In English-speaking areas, Sharon is now predominantly a feminine given name. However, historically it was also used as a masculine given name. In I ...
and large parts of the Transjordan Transjordan may refer to:
* Transjordan (region), an area to the east of the Jordan River
* Oultrejordain, a Crusader lordship (1118–1187), also called Transjordan
* Emirate of Transjordan, British protectorate (1921–1946)
* Hashemite Kingdom of ...
. Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first- ...
, the capital, was home to one of the largest Iron Age structures in the Levant. The kingdom was destroyed around 720 BCE, when it was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
. The Kingdom of Judah, with its capital in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, later became a client state
A client state, in international relations, is a state that is economically, politically, and/or militarily subordinate to another more powerful state (called the "controlling state"). A client state may variously be described as satellite state, ...
of first the Neo-Assyrian Empire and then the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ...
. It is estimated that the region's population was around 400,000 in the Iron Age II
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
.Broshi, M., & Finkelstein, I. (1992)"The Population of Palestine in Iron Age II"
''Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research'', ''287''(1), 47–60. In 587/6 BCE, the
Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. ...
conquered Judah. King Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
besieged and destroyed Jerusalem and Solomon's Temple, and exiled the Jews to Babylon
''Bābili(m)''
* sux, 𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠
* arc, 𐡁𐡁𐡋 ''Bāḇel''
* syc, ܒܒܠ ''Bāḇel''
* grc-gre, Βαβυλών ''Babylṓn''
* he, בָּבֶל ''Bāvel''
* peo, 𐎲𐎠𐎲𐎡𐎽𐎢 ''Bābiru''
* elx, 𒀸𒁀𒉿𒇷 ''Babi ...
. The defeat was also recorded in the Babylonian Chronicles
The Babylonian Chronicles are a series of tablets recording major events in Babylonian history. They are thus one of the first steps in the development of ancient historiography. The Babylonian Chronicles were written in Babylonian cuneiform, fr ...
. The Babylonian captivity
The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile is the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were captives in Babylon, the capital city of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, following their defeat ...
ended around 538 BCE under the rule of the Medo-Persian Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
after he captured Babylon. The Second Temple
The Second Temple (, , ), later known as Herod's Temple, was the reconstructed Temple in Jerusalem between and 70 CE. It replaced Solomon's Temple, which had been built at the same location in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited ...
was constructed around 520 BCE. As part of the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
, the former Kingdom of Judah became the province of Judah (''Yehud Medinata
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a Autonomy, self-governing region under its local Jews, Jewish po ...
'') with different borders, covering a smaller territory. The population of the province was greatly reduced from that of the kingdom, archaeological surveys showing a population of around 30,000 people in the 5th to 4th centuries BCE.
Classical period
 With successive Persian rule, the autonomous province ''
With successive Persian rule, the autonomous province ''Yehud Medinata
Yehud, also known as Yehud Medinata or Yehud Medinta (), was an administrative province of the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire in the region of Judea that functioned as a Autonomy, self-governing region under its local Jews, Jewish po ...
'' was gradually developing back into urban society, largely dominated by Judeans. The Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
conquests largely skipped the region without any resistance or interest; Jewish customs were mostly respected. Incorporated into the Ptolemaic Ptolemaic is the adjective formed from the name Ptolemy, and may refer to:
Pertaining to the Ptolemaic dynasty
* Ptolemaic dynasty, the Macedonian Greek dynasty that ruled Egypt founded in 305 BC by Ptolemy I Soter
* Ptolemaic Kingdom
Pertaining ...
and finally the Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
empires, the region was heavily hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in the ...
, building the tensions between Judeans and Greeks. Several centuries of tolerance came to an end when Antiochus IV
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his deat ...
forcibly imposed Hellenistic customs on the Jews, consecrated the temple, and forbade Jewish practices. In 167 BCE, the Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
erupted, and eventually succeeded in establishing an independent Hasmonean Kingdom
The Hasmonean dynasty (; he, ''Ḥašmōnaʾīm'') was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from BCE to 37 BCE. Between and BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, an ...
in Judah, which later expanded over much of modern Israel and parts of Jordan and Lebanon, as the Seleucids gradually lost control in the region.
The Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
invaded the region in 63 BCE, first taking control of Syria, and then intervening in the Hasmonean Civil War
The Hasmonean Civil War was a civil war between two claimants to the Hasmonean Jewish Crown. What began as an inter-Jewish conflict became a highly decisive conflict that included the Nabataean Kingdom and ended with Roman involvement. This conf ...
. The struggle
Struggle may refer to:
Film and TV
* ''Struggle'' (2003 film), an Austrian film
* Struggle (2013 film)
* ''Struggle'' (TV series), 2007 Chinese TV series
Music
* ''Struggle'' (Nonpoint album), 1999 release
* Struggle (Woody Guthrie album), 1 ...
between pro-Roman and pro-Parthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
factions in Judea eventually led to the installation of Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renov ...
by the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
and consolidation of the Herodian kingdom
The Herodian Kingdom of Judea was a client state of the Roman Republic from 37 BCE, when Herod the Great, who had been appointed "King of the Jews" by the Roman Senate in 40/39 BCE, took actual control over the country. When Herod died in 4 BCE, ...
as a vassal Judean state of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
. Herod undertook many colossal building projects, including fully rebuilding the Second Temple and expanding the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compoun ...
. He also built the great harbor of Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
. With the decline of the Herodian dynasty
The Herodian dynasty was a royal dynasty of Idumaean (Edomite) descent, ruling the Herodian Kingdom of Judea and later the Herodian Tetrarchy as a vassal state of the Roman Empire. The Herodian dynasty began with Herod the Great, who assumed the ...
, Judea transformed into a Roman province.
The first and second centuries CE saw a series of unsuccessful large-scale Jewish rebellions against Rome. The Roman suppression of these revolts led to wide-scale destruction, a high toll of life and enslavement. The First Jewish-Roman War
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
(66–73 CE) resulted in the destruction of Jerusalem and the Second Temple. Many died fighting and under siege during the revolt, and a sizable portion of the population was either expelled from the country or displaced. Judaism had to reshape itself for survival without a temple, resulting in the emergence of Rabbinic Judaism
Rabbinic Judaism ( he, יהדות רבנית, Yahadut Rabanit), also called Rabbinism, Rabbinicism, or Judaism espoused by the Rabbanites, has been the mainstream form of Judaism since the 6th century CE, after the codification of the Babylonian ...
, which eventually became the religion's mainstream form. Two generations later, the Bar Kokhba Revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''Mereḏ Bar Kōḵḇāʾ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Judea (Roman province), Roman province of Judea, led b ...
(132-136 CE) erupted. As a result, Judea's countryside was devastated and depopulated. Jerusalem was rebuilt as a Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Characteri ...
under the name of Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina (Traditional English Pronunciation: ; Latin in full: ) was a Roman colony founded during Emperor Hadrian's trip to Judah in 129/130, centered around Jerusalem, which had been almost totally razed after the siege of 70 CE. The f ...
, and the province of Judea was renamed Syria Palaestina
Syria Palaestina (literally, "Palestinian Syria";Trevor Bryce, 2009, ''The Routledge Handbook of the Peoples and Places of Ancient Western Asia''Roland de Vaux, 1978, ''The Early History of Israel'', Page 2: "After the revolt of Bar Cochba in 135 ...
.H.H. Ben-Sasson, ''A History of the Jewish People'', Harvard University Press, 1976, , page 334: "In an effort to wipe out all memory of the bond between the Jews and the land, Hadrian changed the name of the province from Judaea to Syria-Palestina, a name that became common in non-Jewish literature."Ariel Lewin. ''The archaeology of Ancient Judea and Palestine''. Getty Publications, 2005 p. 33. "It seems clear that by choosing a seemingly neutral name – one juxtaposing that of a neighboring province with the revived name of an ancient geographical entity (Palestine), already known from the writings of Herodotus – Hadrian was intending to suppress any connection between the Jewish people and that land."
Jewish presence in the region significantly dwindled after the failure of the Bar Kokhba revolt. Nevertheless, there was a continuous small Jewish presence and Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galil ...
became its religious center. Jewish communities continued to reside in the southern Hebron Hills
The Hebron Hills, also known as Mount Hebron ( ar, جبل الخليل, translit=Jabal al-Khalīl, he, הר חברון, translit=Har Hevron), are a mountain ridge, geographic region, and geologic formation, comprising the southern part of the J ...
and on the coastal plain. The Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah ...
and part of the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the cente ...
, central Jewish texts, were composed during the 2nd to 4th centuries CE in Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Fo ...
and Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. When the area stood under Byzantine rule, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
gradually evolved over Roman Paganism
Religion in ancient Rome consisted of varying imperial and provincial religious practices, which were followed both by the people of Rome as well as those who were brought under its rule.
The Romans thought of themselves as highly religious, ...
.
Medieval and modern period
 With the
With the conversion of Constantine
During the reign of the Roman Emperor Constantine the Great (AD 306–337), Christianity began to transition to the dominant religion of the Roman Empire. Historians remain uncertain about Constantine's reasons for favoring Christianity, and ...
in the 4th century, the situation for the Jewish majority in Palestine "became more difficult". Many Jews had emigrated to flourishing Diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of origin. Historically, the word was used first in reference to the dispersion of Greeks in the Hellenic world, and later Jews after ...
communities, while locally there was both Christian immigration and local conversion. Together, this led to the formation of a Christian majority by the middle of the 5th century. Towards the end of the 5th century, the Samaritan revolts
The Samaritan revolts (c. 484–573) were a series of insurrections in Palaestina Prima province, launched by the Samaritans against the Eastern Roman Empire. The revolts were marked by great violence on both sides, and their brutal suppression a ...
, which continued until the late 6th century, resulted in a large decrease in the Samaritan population, further increasing the Christian majority. After the Persian conquest and the installation of a short-lived Jewish Commonwealth in 614 CE, the Byzantine Empire reconquered the country in 628.
In 634–641 CE, the region, including Jerusalem, was conquered
Conquest is the act of military subjugation of an enemy by force of arms.
Military history provides many examples of conquest: the Roman conquest of Britain, the Mauryan conquest of Afghanistan and of vast areas of the Indian subcontinent, t ...
by the Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
who had recently adopted Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
. While the Arab conquerors mostly left the area and continued to other destinations, Arab tribes settled in the region before and after the conquest. These tribes helped accelerate the Islamization
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occur ...
of the region, which was predominantly Christian at the time. Throughout the next three centuries, control of the region transferred between the Rashidun
, image = تخطيط كلمة الخلفاء الراشدون.png
, caption = Calligraphic representation of Rashidun Caliphs
, birth_place = Mecca, Hejaz, Arabia present-day Saudi Arabia
, known_for = Companions of t ...
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s, Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
s, Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
, Fatimids
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the ea ...
, Seljuks
The Seljuk dynasty, or Seljukids ( ; fa, سلجوقیان ''Saljuqian'', alternatively spelled as Seljuqs or Saljuqs), also known as Seljuk Turks, Seljuk Turkomans "The defeat in August 1071 of the Byzantine emperor Romanos Diogenes
by the Turk ...
, Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
, and Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin h ...
.
During the siege of Jerusalem by the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic ru ...
in 1099, the Jewish inhabitants of the city fought side by side with the Fatimid garrison and the Muslim population who tried in vain to defend the city against the Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
. When the city fell, around 60,000 people were massacred, including 6,000 Jews seeking refuge in a synagogue. At this time, a full thousand years after the fall of the Jewish state, there were Jewish communities all over the country. Fifty of them are known and include Jerusalem, Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Fo ...
, Ramleh
Ramla or Ramle ( he, רַמְלָה, ''Ramlā''; ar, الرملة, ''ar-Ramleh'') is a city in the Central District of Israel. Today, Ramle is one of Israel's mixed cities, with both a significant Jewish and Arab populations.
The city was f ...
, Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border with ...
, Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
, and Gaza. According to Albert of Aachen Albert of Aix(-la-Chapelle) or Albert of Aachen; la, Albericus Aquensis; ''fl.'' c. 1100) was a historian of the First Crusade and the early Kingdom of Jerusalem. He was born during the later part of the 11th century, and afterwards became canon (p ...
, the Jewish residents of Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
were the main fighting force of the city, and "mixed with Saracen atimidtroops", they fought bravely for close to a month until forced into retreat by the Crusader fleet and land army.
In 1187, Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
, founder of the Ayyubid dynasty
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultan of Egypt, Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni ...
, defeated the Crusaders in the Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of t ...
and subsequently captured Jerusalem and almost all of Palestine. In time, Saladin issued a proclamation inviting Jews to return and settle in Jerusalem, and according to Judah al-Harizi
Yehuda Alharizi, also Judah ben Solomon Harizi or al-Harizi ( he, יהודה בן שלמה אלחריזי, ''Yehudah ben Shelomo al-Harizi'', ar, يحيا بن سليمان بن شاؤل أبو زكريا الحريزي اليهودي من أه� ...
, they did: "From the day the Arabs took Jerusalem, the Israelites inhabited it." Al-Harizi compared Saladin's decree allowing Jews to re-establish themselves in Jerusalem to the one issued by the Persian king Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
over 1,600 years earlier.
 In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300
In 1211, the Jewish community in the country was strengthened by the arrival of a group headed by over 300 rabbi
A rabbi () is a spiritual leader or religious teacher in Judaism. One becomes a rabbi by being ordained by another rabbi – known as ''semikha'' – following a course of study of Jewish history and texts such as the Talmud. The basic form of ...
s from France and England, among them Rabbi Samson ben Abraham of Sens Samson ben Abraham of Sens (שמשון בן אברהם משאנץ; c. 1150 – c. 1230),was one of the leading French Tosafists in the second half of the 12th and the beginning of the 13th centuries. He was the most outstanding student and the s ...
. Nachmanides
Moses ben Nachman ( he, מֹשֶׁה בֶּן־נָחְמָן ''Mōše ben-Nāḥmān'', "Moses son of Nachman"; 1194–1270), commonly known as Nachmanides (; el, Ναχμανίδης ''Nakhmanídēs''), and also referred to by the acronym Ra ...
(Ramban), the 13th-century Spanish rabbi and recognized leader of Jewry, greatly praised the Land of Israel and viewed its settlement as a positive commandment incumbent on all Jews. He wrote "If the gentile
Gentile () is a word that usually means "someone who is not a Jew". Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, sometimes use the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is generally used as a synonym for ...
s wish to make peace, we shall make peace and leave them on clear terms; but as for the land, we shall not leave it in their hands, nor in the hands of any nation, not in any generation."
In 1260, control passed to the Mamluk sultans of Egypt
The Mamluk Sultanate ( ar, سلطنة المماليك, translit=Salṭanat al-Mamālīk), also known as Mamluk Egypt or the Mamluk Empire, was a state that ruled Egypt, the Levant and the Hejaz (western Arabia) from the mid-13th to early 16t ...
. The country was located between the two centers of Mamluk power, Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
and Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, and only saw some development along the postal road connecting the two cities. Jerusalem, although left without the protection of any city walls
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
since 1219, also saw a flurry of new construction projects centered around the Haram al-Sharif
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew language, Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House
(the Temple Mount). In 1266, the Mamluk Sultan f the Holy
F, or f, is the sixth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Let ...
, also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al- ...Baybars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak ...
converted the Cave of the Patriarchs
, alternate_name = Tomb of the Patriarchs, Cave of Machpelah, Sanctuary of Abraham, Ibrahimi Mosque (Mosque of Abraham)
, image = Palestine Hebron Cave of the Patriarchs.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Southern view of the complex, 2009
, map ...
in Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
into an exclusive Islamic sanctuary and banned Christians and Jews from entering, who previously had been able to enter it for a fee. The ban remained in place until Israel took control of the building in 1967.
 In 1470, Isaac b. Meir Latif arrived from Italy and counted 150 Jewish families in Jerusalem.
Thanks to
In 1470, Isaac b. Meir Latif arrived from Italy and counted 150 Jewish families in Jerusalem.
Thanks to Joseph Saragossi
Joseph Saragossi, ( he, יוסף סרגוסי) (1460 – 1507) was a Spanish-born rabbi and kabbalist of the 15th and 16th centuries. He is credited with developing Safed into an important Jewish and Kabbalah, kabbalistic centre. Due to a legend h ...
who had arrived in the closing years of the 15th century, Safed
Safed (known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as Tzfat; Sephardi Hebrew, Sephardic Hebrew & Modern Hebrew: צְפַת ''Tsfat'', Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation, Ashkenazi Hebrew: ''Tzfas'', Biblical Hebrew: ''Ṣǝp̄aṯ''; ar, صفد, ''Ṣafad''), i ...
and its environs had developed into the largest concentration of Jews in Palestine. With the help of the Sephardic
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), ...
immigration from Spain, the Jewish population had increased to 10,000 by the early 16th century.
In 1516, the region was conquered by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
; it remained under Turkish rule until the end of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, when Britain defeated the Ottoman forces and set up a military administration
Military administration identifies both the techniques and systems used by military departments, agencies, and armed services involved in managing the armed forces. It describes the processes that take place within military organisations outsid ...
across the former Ottoman Syria
Ottoman Syria ( ar, سوريا العثمانية) refers to divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Syria, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south ...
. In 1660, a Druze revolt led to the destruction of Safed
Safed (known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as Tzfat; Sephardi Hebrew, Sephardic Hebrew & Modern Hebrew: צְפַת ''Tsfat'', Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation, Ashkenazi Hebrew: ''Tzfas'', Biblical Hebrew: ''Ṣǝp̄aṯ''; ar, صفد, ''Ṣafad''), i ...
and 1660 destruction of Tiberias, Tiberias. In the late 18th century, local Arab Sheikh Zahir al-Umar created a de facto independent Emirate in the Galilee. Ottoman attempts to subdue the Sheikh failed, but after Zahir's death the Ottomans regained control of the area. In 1799 governor Jazzar Pasha successfully repelled an Siege of Acre (1799), assault on Acre by troops of Napoleon, prompting the French to abandon the Syrian campaign. In 1834, a Peasants' revolt in Palestine, revolt by Palestinian Arab peasants broke out against Egyptian conscription and taxation policies under Muhammad Ali of Egypt, Muhammad Ali. Although the revolt was suppressed, Muhammad Ali's army retreated and Ottoman rule was restored with British support in 1840. Shortly after, the Tanzimat reforms were implemented across the Ottoman Empire. In 1920, after the Allies of World War I, Allies Sinai and Palestine Campaign, conquered the Levant during World War I, the territory was divided between Britain and France under the League of Nations mandate, mandate system, and the British-administered area which included modern day Israel was named Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 ...
.
Zionism and British Mandate
Since the existence of the earliest Jewish diaspora, many Jews have aspired to Aliyah, return to "Zion" and the "Land of Israel", though the amount of effort that should be spent towards such an aim was a matter of dispute. After the Jews were Alhambra Decree, expelled from Spain in 1492, some communities settled in Palestine. During the 16th century, Jewish communities struck roots in the Four Holy Cities—Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Fo ...
, Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
, and Safed
Safed (known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as Tzfat; Sephardi Hebrew, Sephardic Hebrew & Modern Hebrew: צְפַת ''Tsfat'', Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation, Ashkenazi Hebrew: ''Tzfas'', Biblical Hebrew: ''Ṣǝp̄aṯ''; ar, صفد, ''Ṣafad''), i ...
—and in 1697, Rabbi Yehuda Hachasid led a group of 1,500 Jews to Jerusalem. In the second half of the 18th century, Eastern European Misnagdim, opponents of Hasidic Judaism, Hasidism, known as the Perushim, settled in Palestine.
The first wave of modern Jewish migration to Southern Syria, Ottoman-ruled Palestine, known as the First Aliyah, began in 1881, as Jews fled Pogrom#Pogroms against Jews, pogroms in Eastern Europe. Although the Zionist movement already existed in practice, Austro-Hungarian journalist Theodor Herzl is credited with founding political Zionism, a movement that sought to establish a Jewish state in the Land of Israel, thus offering a solution to the so-called Jewish question of the European states, in conformity with the goals and achievements of other national projects of the time. In 1896, Herzl published ''Der Judenstaat'' (''The Jewish State''), offering his vision of a future Jewish state; the following year he presided over the First Zionist Congress in Basel, Switzerland. The Second Aliyah (1904–14) began after the Kishinev pogrom; some 40,000 Jews settled in Palestine, although nearly half of them left eventually. Both the first and second waves of migrants were mainly Orthodox Jews, although the Second Aliyah included Labor Zionism, socialist groups who established the ''kibbutz'' movement. Though the immigrants of the Second Aliyah largely sought to create communal agricultural settlements, the period also saw the establishment of Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
in 1909 as the "first Hebrew city." This period also saw the appearance of Jewish armed self-defense organizations as a means of defense for Jewish settlements. The first such organization was Bar-Giora (organization), Bar-Giora, a small secret guard founded in 1907. Two years later, larger Hashomer organization was founded as its replacement. During World War I, British Foreign Secretary Arthur Balfour sent the Balfour Declaration to Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Lord Rothschild (Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild), a leader of the British Jewish community, that stated that Britain intended for the creation of a Jewish "Homeland for the Jewish people, national home" in Palestine.
In 1918, the Jewish Legion, a group primarily of Zionist volunteers, assisted in the British Sinai and Palestine Campaign, conquest of Palestine. Arab opposition to British rule and Jewish immigration led to the 1920 Palestine riots and the formation of a Jewish militia known as the Haganah (meaning "The Defense" in Hebrew) in 1920 as an outgrowth of Hashomer, from which the Irgun and Lehi (group), Lehi (or the Stern Gang) paramilitaries later split off. In 1922, the League of Nations granted Britain the Mandate for Palestine under terms which included the Balfour Declaration with its promise to the Jews, and with similar provisions regarding the Arab Palestinians. The Demographic history of Palestine (region), population of the area at this time was predominantly Arab and Muslim, with Jews accounting for about 11%, and Arab Christians about 9.5% of the population.
The Third Aliyah, Third (1919–23) and Fourth Aliyahs (1924–29) brought an additional 100,000 Jews to Palestine. The Hitler's rise to power, rise of Nazism and the increasing persecution of Jews in 1930s Europe led to the Fifth Aliyah, with an influx of a quarter of a million Jews. This was a major cause of the 1936–39 Arab revolt in Palestine, Arab revolt of 1936–39, which was launched as a reaction to continued Jewish immigration and land purchases. Several hundred Jews and British security personnel were killed, while the British Mandate authorities alongside the Zionist militias of the Haganah and Irgun killed 5,032 Arabs and wounded 14,760, resulting in over ten percent of the adult male Palestinian Arab population killed, wounded, imprisoned or exiled. The British introduced restrictions on Jewish immigration to Palestine with the White Paper of 1939. With countries around the world turning away Jewish refugees fleeing the Holocaust, a clandestine movement known as Aliyah Bet was organized to bring Jews to Palestine. By the end of World War II, the Jewish population of Palestine had increased to 31% of the total population.
After World War II
 After World War II, the UK found itself facing a Jewish Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine, guerrilla campaign over Jewish immigration restrictions, as well as continued conflict with the Arab community over limit levels. The Haganah joined Irgun and Lehi in an armed struggle against British rule. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of Jewish Holocaust survivors and refugees sought a new life far from their destroyed communities in Europe. The Haganah attempted to bring these refugees to Palestine in a programme called Aliyah Bet in which tens of thousands of Jewish refugees attempted to enter Palestine by ship. Most of the ships were intercepted by the Royal Navy and the refugees rounded up and placed in detention camps in Atlit detainee camp, Atlit and Cyprus internment camps, Cyprus by the British.
On 22 July 1946, Irgun King David Hotel bombing, bombed the British administrative headquarters for Palestine, which was housed in the southern wing of the King David Hotel in
After World War II, the UK found itself facing a Jewish Jewish insurgency in Mandatory Palestine, guerrilla campaign over Jewish immigration restrictions, as well as continued conflict with the Arab community over limit levels. The Haganah joined Irgun and Lehi in an armed struggle against British rule. At the same time, hundreds of thousands of Jewish Holocaust survivors and refugees sought a new life far from their destroyed communities in Europe. The Haganah attempted to bring these refugees to Palestine in a programme called Aliyah Bet in which tens of thousands of Jewish refugees attempted to enter Palestine by ship. Most of the ships were intercepted by the Royal Navy and the refugees rounded up and placed in detention camps in Atlit detainee camp, Atlit and Cyprus internment camps, Cyprus by the British.
On 22 July 1946, Irgun King David Hotel bombing, bombed the British administrative headquarters for Palestine, which was housed in the southern wing of the King David Hotel in Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
.Encyclopædia Britannicaarticle on the Irgun Zvai Leumi A total of 91 people of various nationalities were killed and 46 were injured.Thurston Clarke, Clarke, Thurston. ''By Blood and Fire'', G.P. Puttnam's Sons, New York, 1981 The hotel was the site of the Secretariat of the Government of Palestine and the Headquarters of the British Armed Forces in Mandatory Palestine and Emirate of Transjordan, Transjordan. The attack initially had the approval of the Haganah. It was conceived as a response to Operation Agatha (a series of widespread raids, including one on the Jewish Agency for Israel, Jewish Agency, conducted by the British authorities) and was the deadliest directed at the British during the Mandate era. The Jewish insurgency continued throughout the rest of 1946 and 1947 despite concerted efforts by the British military and Palestine Police Force to suppress it. British efforts to mediate a negotiated solution with Jewish and Arab representatives also failed as the Jews were unwilling to accept any solution that did not involve a Jewish state and suggested a partition of Palestine into Jewish and Arab states, while the Arabs were adamant that a Jewish state in any part of Palestine was unacceptable and that the only solution was a unified Palestine under Arab rule. In February 1947, the British referred the Palestine issue to the newly formed
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
. On 15 May 1947, the General Assembly of the United Nations, General Assembly of the United Nations resolved that the United Nations Special Committee on Palestine be created "to prepare for consideration at the next regular session of the Assembly a report on the question of Palestine." In the Report of the Committee dated 3 September 1947 to the General Assembly, the majority of the Committee in Chapter VI United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, proposed a plan to replace the British Mandate with "an independent Arab State, an independent Jewish State, and the City of Jerusalem [...] the last to be under an International Trusteeship System." Meanwhile, the Jewish insurgency continued and peaked in July 1947, with a series of widespread guerrilla raids culminating in the Sergeants affair. After three Irgun fighters had been sentenced to death for their role in the Acre Prison break, a May 1947 Irgun raid on Acre Prison in which 27 Irgun and Lehi militants were freed, the Irgun captured two British sergeants and held them hostage, threatening to kill them if the three men were executed. When the British carried out the executions, the Irgun responded by killing both hostages and hanged their bodies from eucalyptus trees, booby-trapping one of them with a mine which injured a British officer as he cut the body down. The hangings caused widespread outrage in Britain and were a major factor in the consensus forming in Britain that it was time to evacuate Palestine.
In September 1947, the British cabinet decided that the Mandate was no longer tenable, and to evacuate Palestine. According to Colonial Secretary Arthur Creech Jones, four major factors led to the decision to evacuate Palestine: the inflexibility of Jewish and Arab negotiators who were unwilling to compromise on their core positions over the question of a Jewish state in Palestine, the economic pressure that stationing a large garrison in Palestine to deal with the Jewish insurgency and the possibility of a wider Jewish rebellion and the possibility of an Arab rebellion put on a British economy already strained by World War II, the "deadly blow to British patience and pride" caused by the hangings of the sergeants, and the mounting criticism the government faced in failing to find a new policy for Palestine in place of the White Paper of 1939.
On 29 November 1947, the General Assembly adopted United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, Resolution 181 (II) recommending the adoption and implementation of the ''Plan of Partition with Economic Union''. The plan attached to the resolution was essentially that proposed by the majority of the Committee in the report of 3 September. The Jewish Agency, which was the recognized representative of the Jewish community, accepted the plan, which assigned to Jews – a third of the population owning less than 7% of the land – 55–56% of Mandatory Palestine. The Arab League and Arab Higher Committee of Palestine rejected it, and indicated that they would reject any other plan of partition. On the following day, 1 December 1947, the Arab Higher Committee proclaimed a three-day strike, and 1947 Jerusalem riots, riots broke out in Jerusalem. The situation spiraled into a 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine, civil war; just two weeks after the UN vote, Colonial Secretary Arthur Creech Jones announced that the British Mandate would end on 15 May 1948, at which point the British would evacuate. As Arab militias and gangs attacked Jewish areas, they were faced mainly by the Haganah, as well as the smaller Irgun and Lehi. In April 1948, the Haganah moved onto the offensive. During this period 250,000 Palestinian Arabs fled or were expelled, due to Causes of the 1948 Palestinian exodus, a number of factors.
On 14 May 1948, the day before the expiration of the British Mandate, David Ben-Gurion, the head of the Jewish Agency, Israeli Declaration of Independence, declared "the establishment of a Jewish state in Eretz-Israel, to be known as the State of Israel." The only reference in the text of the Declaration to the borders of the new state is the use of the term ''Eretz-Israel'' ("Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
"). The following day, the armies of four Arab countries—Kingdom of Egypt, Egypt, Syrian Republic (1946–63), Syria, Jordan, Transjordan and Kingdom of Iraq, Iraq—entered into parts of what had been British Mandatory Palestine, launching the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
; contingents from Yemen, Morocco, Saudi Arabia and Sudan joined the war. The apparent purpose of the invasion was to prevent the establishment of the Jewish state at inception, and some Arab leaders talked about "driving the Jews into the sea". According to Benny Morris, Jews were worried that the invading Arab armies held the intent to slaughter them. The Arab league stated the invasion was to restore law and order and to prevent further bloodshed.
After a year of fighting, a 1949 Armistice Agreements, ceasefire was declared and temporary borders, known as the Green Line (Israel), Green Line, were established. Jordan Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, annexed what became known as the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, including East Jerusalem, and Egypt Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, occupied the Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
. The UN estimated that more than 700,000 Palestinians were 1948 Palestinian exodus, expelled by or fled from advancing Israel Defense Forces, Israeli forces during the conflict—what would become known in Arabic as the ''Nakba'' ("catastrophe"). Some 156,000 remained and became Arab citizens of Israel.
Early years of the State of Israel
Israel United Nations General Assembly Resolution 273, was admitted as a member of the UN by majority vote on 11 May 1949. An Israeli-Jordanian attempt at negotiating a peace agreement broke down after the British government, fearful of the Egyptian reaction to such a treaty, expressed their opposition to the Government of Jordan, Jordanian government. In the early years of the state, the Labor Zionism, Labor Zionist movement led by Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion dominated Politics of Israel, Israeli politics. Immigration to Israel during the late 1940s and early 1950s was aided by the Israeli Immigration Department and the non-government sponsored Mossad LeAliyah Bet ( "Institute for Aliyah Bet, Immigration B") which organized illegal and clandestine immigration. Both groups facilitated regular immigration logistics like arranging transportation, but the latter also engaged in clandestine operations in countries, particularly in the Middle East and Eastern Europe, where the lives of Jews were believed to be in danger and exit from those places was difficult. Mossad LeAliyah Bet was disbanded in 1953. The immigration was in accordance with the One Million Plan. The immigrants came for differing reasons: some held Zionist beliefs or came for the promise of a better life in Israel, while others moved to escape persecution or were expelled. An Aliyah#Early statehood (1948–1960), influx of Holocaust survivors and Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries, Jews from Arab and Muslim countries to Israel during the first three years increased the number of Jews from 700,000 to 1,400,000. By 1958, the population of Israel rose to two million. Between 1948 and 1970, approximately 1,150,000 Jewish refugees relocated to Israel. Some new immigrants arrived as refugees with no possessions and were housed in temporary camps known as ''ma'abarot''; by 1952, over 200,000 people were living in these tent cities. Ashkenazi Jews, Jews of European background were often treated more favorably than Jews from Mizrahi Jews, Middle Eastern and Sephardi Jews, North African countries—housing units reserved for the latter were often re-designated for the former, with the result that Jews newly arrived from Arab lands generally ended up staying in transit camps for longer. During this period, food, clothes and furniture had to be rationed in what became known as the Austerity in Israel, austerity period. The need to solve the crisis led Ben-Gurion to sign a Reparations Agreement between Israel and West Germany, reparations agreement with West Germany that triggered mass protests by Jews angered at the idea that Israel could accept monetary compensation for the Holocaust. During the 1950s, Israel was frequently List of attacks against Israeli civilians before 1967, attacked by Palestinian fedayeen, nearly always against civilians, mainly from the Egyptian-occupied Gaza Strip, leading to several Israeli reprisal operations. In 1956, the United Kingdom and France aimed at regaining control of the Suez Canal, which the Egyptians had nationalized. The continued blockade of the Suez Canal and Straits of Tiran to Israeli shipping, together with the growing amount of Fedayeen attacks against Israel's southern population, and recent Arab grave and threatening statements, prompted Israel to attack Egypt. Israel joined Protocol of Sèvres, a secret alliance with the United Kingdom and France and overran the Sinai Peninsula but was pressured to withdraw by the UN in return for guarantees of Israeli shipping rights in theRed Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
via the Straits of Tiran and the Canal. The war, known as the Suez Crisis, resulted in significant reduction of Israeli border infiltration. In the early 1960s, Israel captured Nazi war criminal Adolf Eichmann in Argentina and brought him to Israel for Eichmann trial, trial. The trial had a major impact on public awareness of the Holocaust. Eichmann remains the only person executed in Israel by conviction in an Israeli judicial system, Israeli civilian court. During the spring and summer of 1963 Israel was engaged in a diplomatic standoff with the United States due to the Israeli Nuclear weapons and Israel, nuclear programme.
coastal plain
A coastal plain is flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and a piedmont area. Some of the largest coastal plains are in Alaska and the southeastern United States. The Gulf Coa ...
, had been trying to divert the headwaters to deprive Israel of water resources, provoking War over Water (Jordan river), tensions between Israel on the one hand, and Syria and Lebanon on the other. Arab nationalists led by Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser refused to recognize Israel and called for its destruction. By 1966, Israeli-Arab relations had deteriorated to the point of actual battles taking place between Israeli and Arab forces. In May 1967, Egypt massed its army near the border with Israel, expelled United Nations Emergency Force, UN peacekeepers, stationed in the Sinai Peninsula since 1957, and blocked Israel's access to the Red Sea. Other Arab states mobilized their forces. Israel reiterated that these actions were a ''casus belli'' and, on 5 June, launched a Operation Focus, pre-emptive strike against Egypt. Jordan, Syria and Iraq responded and attacked Israel. In a Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
, Israel captured and occupied the West Bank from Jordan, the Gaza Strip and Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
from Syria. Jerusalem's boundaries were enlarged, incorporating East Jerusalem, and the 1949 Green Line (Israel), Green Line became the administrative boundary between Israel and the Israeli-occupied territories, occupied territories.
Following the 1967 war and the "Three Nos" resolution of the Arab League, Israel faced attacks from the Egyptians in the Sinai Peninsula during the 1967–1970 War of Attrition, and from Palestinian groups targeting Israelis in the occupied territories, in Israel proper, and around the world. Most important among the various Palestinian and Arab groups was the Palestinian Liberation Organization (PLO), established in 1964, which initially committed itself to "armed struggle as the only way to liberate the homeland". In the late 1960s and early 1970s, Palestinian groups launched a Palestinian political violence, wave of attacks against Israeli and Jewish targets around the world, including Munich massacre, a massacre of Israeli athletes at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich. The Israeli government responded with an Operation Wrath of God, assassination campaign against the organizers of the massacre, a 1972 Israeli air raid in Syria and Lebanon, bombing and a 1973 Israeli raid on Lebanon, raid on the PLO headquarters in Lebanon.
On 6 October 1973, as Jews were observing Yom Kippur, the Egyptian and Syrian armies launched Operation Badr (1973), a surprise attack against Israeli forces in the Sinai Peninsula and Golan Heights, that opened the Yom Kippur War. The war ended on 25 October with Israel successfully repelling Egyptian and Syrian forces but having suffered over 2,500 soldiers killed in a war which collectively took 10–35,000 lives in about 20 days. An Agranat Commission, internal inquiry exonerated Fifteenth government of Israel, the government of responsibility for failures before and during the war, but public anger forced Prime Minister Golda Meir to resign. In July 1976, an airliner was hijacked during its flight from Israel to France by Palestinian guerrillas and landed at Entebbe International Airport, Uganda. Israeli commandos carried out Operation Entebbe, an operation in which 102 out of 106 Israeli hostages were successfully rescued.
Further conflict and peace process
The 1977 Israeli legislative election, 1977 Knesset elections marked a major turning point in Israeli political history as Menachem Begin's Likud party took control from the Labor Party (Israel), Labor Party. Later that year, Egyptian President Anwar El Sadat made a trip to Israel and spoke before theKnesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with ...
in what was the first recognition of Israel by an Arab head of state. In the two years that followed, Sadat and Begin signed the Camp David Accords (1978) and the Egypt–Israel peace treaty (1979). In return, Israel withdrew from the Sinai Peninsula and agreed to enter negotiations over an autonomy for Palestinians in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip.
On 11 March 1978, a PLO guerilla raid from Lebanon led to the Coastal Road massacre. Israel responded by launching an 1978 South Lebanon conflict, invasion of southern Lebanon to destroy the PLO bases south of the Litani River. Most PLO fighters withdrew, but Israel was able to secure southern Lebanon until a United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, UN force and the Lebanese army could take over. The PLO soon resumed its Palestinian insurgency in South Lebanon, policy of attacks against Israel. In the next few years, the PLO infiltrated the south and kept up a sporadic shelling across the border. Israel carried out numerous retaliatory attacks by air and on the ground.
 Meanwhile, Begin's government provided incentives for Israelis to Israeli settlements, settle in the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, occupied West Bank, increasing friction with the Palestinians in that area. The Jerusalem Law, Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel, passed in 1980, was believed by some to reaffirm Israel's 1967 annexation of Jerusalem by government decree, and UN Security Council Resolution 478, reignited international controversy over the Positions on Jerusalem, status of the city. No Israeli legislation has defined the territory of Israel and no act specifically included East Jerusalem therein. In 1981 Israel Golan Heights Law, effectively annexed the
Meanwhile, Begin's government provided incentives for Israelis to Israeli settlements, settle in the Israeli occupation of the West Bank, occupied West Bank, increasing friction with the Palestinians in that area. The Jerusalem Law, Basic Law: Jerusalem, Capital of Israel, passed in 1980, was believed by some to reaffirm Israel's 1967 annexation of Jerusalem by government decree, and UN Security Council Resolution 478, reignited international controversy over the Positions on Jerusalem, status of the city. No Israeli legislation has defined the territory of Israel and no act specifically included East Jerusalem therein. In 1981 Israel Golan Heights Law, effectively annexed the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, although annexation was not recognized internationally. The international community largely rejected these moves, with the UN Security Council declaring both the Jerusalem Law and the Golan Heights Law null and void. Israel's population diversity expanded in the 1980s and 1990s. Several waves of Ethiopian Jews Aliyah from Ethiopia, immigrated to Israel since the 1980s, while between 1990 and 1994, 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, immigration from the post-Soviet states increased Israel's population by twelve percent.
On 7 June 1981, during the Iran–Iraq War, the Israeli air force Operation Opera, destroyed Iraq's sole Osirak, nuclear reactor under construction just outside Baghdad, in order to impede Iraq's nuclear weapons programme. Following a series of PLO attacks in 1982, Israel 1982 Lebanon War, invaded Lebanon that year to destroy the bases from which the PLO launched attacks and missiles into northern Israel. In the first six days of fighting, the Israelis destroyed the military forces of the PLO in Lebanon and decisively defeated the Syrians. An Israeli government inquiry—the Kahan Commission—would later hold Begin and several Israeli generals as indirectly responsible for the Sabra and Shatila massacre and hold Defense Minister of Israel, Defense minister Ariel Sharon as bearing "personal responsibility" for the massacre. Sharon was forced to resign as Defense Minister. In 1985, Israel responded to a Palestinian Larnaca yacht killings, terrorist attack in Cyprus by Operation Wooden Leg, bombing the PLO headquarters in Tunisia. Israel withdrew from most of Lebanon in 1986, but maintained a Israeli occupation of Southern Lebanon, borderland buffer zone in southern Lebanon until 2000, from where Israeli forces South Lebanon conflict (1985–2000), engaged in conflict with Hezbollah. The First Intifada, a Palestinian uprising against Israeli rule, broke out in 1987, with waves of uncoordinated demonstrations and violence occurring in the occupied West Bank and Gaza. Over the following six years, the Intifada became more organized and included economic and cultural measures aimed at disrupting the Israeli occupation. More than a thousand people were killed in the violence. During the 1991 Gulf War, the PLO supported Saddam Hussein and Iraqi Scud missile Iraqi rocket attacks on Israel, attacks against Israel. Despite public outrage, Israel heeded American calls to refrain from hitting back and did not participate in that war.
In 1992, Yitzhak Rabin became prime minister following 1992 Israeli legislative election, an election in which his party called for compromise with Israel's neighbours. The following year, Shimon Peres on behalf of Israel, and Mahmoud Abbas for the PLO, signed the Oslo Accords, which gave the Palestinian National Authority the right to govern West Bank Areas in the Oslo II Accord, parts of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. The PLO also Israel–Palestine Liberation Organization letters of recognition, recognized Israel's right to exist and pledged an end to terrorism. In 1994, the Israel–Jordan peace treaty was signed, making Jordan the second Arab country to normalize relations with Israel. Arab public support for the Accords was damaged by the continuation of Israeli settlements and Israeli checkpoint, checkpoints, and the deterioration of economic conditions. Israeli public support for the Accords waned as Israel was struck by List of Palestinian suicide attacks, Palestinian suicide attacks. In November 1995, Yitzhak Rabin assassination of Yitzhak Rabin, was assassinated as he left a peace rally by Yigal Amir, a far-right Jew who opposed the Accords.
Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
, and signed the Wye River Memorandum, giving greater control to the Palestinian National Authority. Ehud Barak, 1999 Israeli general election, elected Prime Minister in 1999, began the new millennium by withdrawing forces from Southern Lebanon and conducting negotiations with Palestinian Authority Chairman Yasser Arafat and U.S. President Bill Clinton at the 2000 Camp David Summit. During the summit, Barak offered a plan for the establishment of a Palestinian state. The proposed state included the entirety of the Gaza Strip and over 90% of the West Bank with Jerusalem as a shared capital. Each side blamed the other for the failure of the talks. After a controversial visit by Likud leader Ariel Sharon to the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compoun ...
, the Second Intifada began. Palestinian suicide attacks, Suicide bombings have been a recurring feature of the Intifada, causing Israeli civilian life to become a battlefield. Some commentators contend that the Intifada was pre-planned by Arafat due to the collapse of peace talks. Sharon became prime minister in a 2001 Israeli prime ministerial election, 2001 special election. During his tenure, Sharon carried out his plan to Israeli disengagement from Gaza, unilaterally withdraw from the Gaza Strip and also spearheaded the construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier, ending the Intifada. Between 2000 and 2008, 1,063 Israelis, 5,517 Palestinians and 64 foreign citizens had been killed.
In July 2006, a Hezbollah artillery assault on Israel's northern border communities and a 2006 Hezbollah cross-border raid, cross-border abduction of two Israeli soldiers precipitated the month-long Second Lebanon War.Escalation of hostilities in Lebanon and in Israel since Hizbollah's attack on Israel on 12 July 2006 On 6 September 2007, the Israeli Air Force Operation Orchard, destroyed a nuclear reactor in Syria. At the end of 2008, Israel entered another conflict as 2008 Israel–Hamas ceasefire, a ceasefire between Hamas and Israel collapsed. The Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War lasted three weeks and ended after Israel announced a unilateral ceasefire. Hamas announced its own ceasefire, with its own conditions of complete withdrawal and opening of Blockade of the Gaza Strip, border crossings. Despite neither the Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, rocket launchings nor Israeli List of Israeli attacks on the Gaza strip, retaliatory strikes having completely stopped, the fragile ceasefire remained in order. In what Israel described as a response to List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, 2012, more than a hundred Palestinian rocket attacks on southern Israeli cities, Israel began an Operation Pillar of Defense, operation in Gaza on 14 November 2012, lasting eight days. Israel started another Operation Protective Edge, operation in Gaza following an List of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, 2014, escalation of rocket attacks by Hamas in July 2014. In May 2021, another Operation Guardian of the Walls, round of fighting took place in Gaza and Israel, lasting eleven days. In September 2010, Israel was invited to join the
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
. Israel has also signed free trade agreements with the European Union, the Israel–United States Free Trade Agreement, United States, the European Free Trade Association, Turkey, Mexico, Canada–Israel Free Trade Agreement, Canada, Jordan, and Egypt, and in 2007, it became the first non-Latin-American country to sign a free trade agreement with the Mercosur trade bloc. By the 2010s, the Arab states–Israeli alliance against Iran, increasing regional cooperation between Israel and Arab League countries, with many of whom peace agreements (Jordan, Egypt) diplomatic relations (UAE, Palestine) and unofficial relations (Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Morocco, Tunisia), have been established, the Israeli security situation shifted from the traditional Arab–Israeli conflict, Arab–Israeli hostility towards regional rivalry with Iran and its proxies. The Iran–Israel proxy conflict gradually emerged from the declared hostility of post-revolutionary Islamic Republic of Iran towards Israel since the 1979 Revolution, into covert Iranian support of Hezbollah during the South Lebanon conflict (1985–2000) and essentially developed into a proxy regional conflict from 2005. With increasing Iranian involvement in the Syrian Civil War from 2011 the conflict shifted from proxy warfare into direct confrontation by early 2018.
Geography and environment
Israel is located in the Levant area of the Fertile Crescent region. The country is at the Eastern Mediterranean, eastern end of theMediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
, bounded by Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan and the West Bank to the east, and Egypt and the Gaza Strip to the southwest. It lies between latitudes 29th parallel north, 29° and 34th parallel north, 34° N, and longitudes 34th meridian east, 34° and 36th meridian east, 36° E.
The sovereign territory of Israel (according to the demarcation lines of the 1949 Armistice Agreements
The 1949 Armistice Agreements were signed between Israel and Egypt,Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
) is approximately in area, of which two percent is water. However Israel is so narrow (100 km at its widest, compared to 400 km from north to south) that the exclusive economic zone in the Mediterranean is double the land area of the country. The total area under Israeli law, including East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
, is , and the total area under Israeli control, including the military-controlled and partially Palestinian National Authority, Palestinian-governed territory of the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, is .
Despite its small size, Israel is home to a variety of geographic features, from the Negev desert in the south to the inland fertile Jezreel Valley, mountain ranges of the Galilee
Galilee (; he, הַגָּלִיל, hagGālīl; ar, الجليل, al-jalīl) is a region located in northern Israel and southern Lebanon. Galilee traditionally refers to the mountainous part, divided into Upper Galilee (, ; , ) and Lower Galil ...
, Mount Carmel, Carmel and toward the Golan Heights, Golan in the north. The Israeli coastal plain on the shores of the Mediterranean is home to most of the nation's population. East of the central highlands lies the Jordan Rift Valley, which forms a small part of the Great Rift Valley. The Jordan River runs along the Jordan Rift Valley, from Mount Hermon through the Hulah Valley and the Sea of Galilee
The Sea of Galilee ( he, יָם כִּנֶּרֶת, Judeo-Aramaic: יַמּא דטבריא, גִּנֵּיסַר, ar, بحيرة طبريا), also called Lake Tiberias, Kinneret or Kinnereth, is a freshwater lake in Israel. It is the lowest ...
to the Dead Sea, the Extreme points of Earth, lowest point on the surface of the Earth. Further south is the Arabah, ending with the Gulf of Aqaba, Gulf of Eilat, part of the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
. Makhtesh, or "erosion cirques" are unique to the Negev and the Sinai Peninsula, the largest being the Makhtesh Ramon at 38 km in length. A report on the environmental status of the Mediterranean Basin states that Israel has the largest number of plant species per square meter of all the countries in the basin. Israel contains four terrestrial ecoregions: Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests, Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests, Arabian Desert, and Mesopotamian shrub desert. It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 4.14/10, ranking it 135th globally out of 172 countries.
Tectonics and seismicity
The Jordan Rift Valley is the result of tectonic movements within the Dead Sea Transform (DSF) fault system. The DSF forms the transform fault, transform boundary between the African Plate to the west and the Arabian Plate to the east. The Golan Heights and all ofJordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
are part of the Arabian Plate, while the Galilee, West Bank, Coastal Plain, and Negev along with the Sinai Peninsula are on the African Plate. This tectonic disposition leads to a relatively high List of earthquakes in the Levant, seismic activity in the region. The entire Jordan Valley segment is thought to have ruptured repeatedly, for instance during the last two major Geography of Israel#Seismic activity, earthquakes along this structure in 749 Galilee earthquake, 749 and 1033 Jordan Rift Valley earthquake, 1033. The deficit in Fault (geology)#Slip, heave, throw, slip that has built up since the 1033 event is sufficient to cause an earthquake of ~7.4.
The most catastrophic known earthquakes occurred in 31 BCE, Galilee earthquake of 363, 363, 749, and 1033 CE, that is every 400 years on average.American Friends of the Tel Aviv University, ''Earthquake Experts at Tel Aviv University Turn to History for Guidance'' (4 October 2007). Quote: The major ones were recorded along the Jordan Valley in the years 31 B.C.E., 363 C.E., 749 C.E., and 1033 C.E. "So roughly, we are talking about an interval of every 400 years. If we follow the patterns of nature, a major quake should be expected any time because almost a whole millennium has passed since the last strong earthquake of 1033." (Tel Aviv University Associate Professor Dr. Shmuel (Shmulik) Marco)Destructive earthquakes leading to serious loss of life strike about every 80 years.Zafrir Renat, ''Israel Is Due, and Ill Prepared, for Major Earthquake'', Haaretz, 15 January 2010. "On average, a destructive earthquake takes place in Israel once every 80 years, causing serious casualties and damage.
/ref> While stringent construction regulations are currently in place and recently built structures are earthquake-safe, the majority of the buildings in Israel were older than these regulations and many public buildings as well as 50,000 residential buildings did not meet the new standards and were "expected to collapse" if exposed to a strong earthquake.
Climate
Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
and Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, have a typical Mediterranean climate with cool, rainy winters and long, hot summers. The area of Beersheba and the Northern Negev have a semi-arid climate with hot summers, cool winters, and fewer rainy days than the Mediterranean climate. The Southern Negev and the Arava areas have a desert climate with very hot, dry summers, and mild winters with few days of rain. The highest temperature in the world outside Africa and North America , 54 °C (129 °F), was recorded in 1942 in the Tirat Zvi kibbutz in the northern Jordan River valley.
At the other extreme, mountainous regions can be windy and cold, and areas at elevation of or more (same elevation as Jerusalem) will usually receive at least one Snow in Israel, snowfall each year. From May to September, rain in Israel is rare. With scarce water resources, Israel has developed various water-saving technologies, including drip irrigation. Israelis also take advantage of the considerable sunlight available for solar energy, making Solar power in Israel, Israel the leading nation in solar energy use per capita—practically every house uses solar panels for water heating.
There are four different phytogeographic regions in Israel, due to the country's location between the temperate and tropical zones, bordering the Mediterranean Sea in the west and the desert in the east. For this reason, the flora and fauna of Israel are extremely diverse. There are 2,867 known List of endemic flora of Israel, species of plants found in Israel. Of these, at least 253 species are List of adventive wild plants in Israel, introduced and non-native. There are 380 National parks and nature reserves of Israel, Israeli nature reserves.
The Israeli Ministry of Environmental Protection (Israel), Ministry of Environmental Protection has reported that Climate change in Israel, climate change "will have a decisive impact on all areas of life, including: water, public health, agriculture, energy, biodiversity, coastal infrastructure, economics, nature, national security, and geostrategy", and will have the greatest effect on vulnerable populations such as the poor, the elderly, and the chronically ill.
Demographics
 Israel was established as a homeland for the Jewish people and is often referred to as a Jewish state. The country's Law of Return grants all Jews and those of Jewish ancestry the right to Israeli nationality law, Israeli citizenship. Retention of Israel's population since 1948 is about even or greater, when compared to other countries with mass immigration. Jewish emigration from Israel (called ''yerida'' in Hebrew), primarily to the United States and Canada, is described by demographers as modest, but is often cited by Israeli government ministries as a major threat to Israel's future.
Three quarters of the population are Jews from a Jewish ethnic divisions, diversity of Jewish backgrounds. Approximately 75% of Israeli Jews are Sabra (person), born in Israel, 16% are immigrants from Europe and the Americas, and 7% are immigrants from Asia and Africa (including the
Israel was established as a homeland for the Jewish people and is often referred to as a Jewish state. The country's Law of Return grants all Jews and those of Jewish ancestry the right to Israeli nationality law, Israeli citizenship. Retention of Israel's population since 1948 is about even or greater, when compared to other countries with mass immigration. Jewish emigration from Israel (called ''yerida'' in Hebrew), primarily to the United States and Canada, is described by demographers as modest, but is often cited by Israeli government ministries as a major threat to Israel's future.
Three quarters of the population are Jews from a Jewish ethnic divisions, diversity of Jewish backgrounds. Approximately 75% of Israeli Jews are Sabra (person), born in Israel, 16% are immigrants from Europe and the Americas, and 7% are immigrants from Asia and Africa (including the Arab world
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western A ...
). Jews from Europe and the former Soviet Union and their descendants born in Israel, including Ashkenazi Jews, constitute approximately 50% of Jewish Israelis. Jewish exodus from Arab and Muslim countries, Jews who left or fled Arab and Muslim countries and their descendants, including both Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi and Sephardi Jews, Sephardi Jews, form most of the rest of the Jewish population. Jewish intermarriage rates run at over 35% and recent studies suggest that the percentage of Israelis descended from both Sephardi and Ashkenazi Jews increases by 0.5 percent every year, with over 25% of school children now originating from both communities. Around 4% of Israelis (300,000), ethnically defined as "others", are 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, Russian descendants of Jewish origin or family who are not Jewish according to rabbinical law, but were eligible for Israeli citizenship under the Law of Return.
The total number of Israeli settlement, Israeli settlers beyond the Green Line (Israel), Green Line is over 600,000 (≈10% of the Jewish Israeli population). , 399,300 Israelis Population statistics for Israeli settlements in the West Bank, lived in West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
settlements, including those that predated the establishment of the State of Israel and which were re-established after the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
, in cities such as Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
and Gush Etzion bloc. In addition to the West Bank settlements, there were more than 200,000 Jews living in East Jerusalem, and 22,000 in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. Approximately 7,800 Israelis Population statistics for Israeli Gaza Strip settlements, lived in settlements in the Gaza Strip, known as Gush Katif, until they were evacuated by the government as part of its 2005 Israel's unilateral disengagement plan, disengagement plan.
Israeli Arabs (including the Arab population of East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights) comprise 21.1% of the population or 1,995,000 people. In a 2017 telephone poll, 40% of Arab citizens of Israel identified as "Arab in Israel" or "Arab citizen of Israel", 15% identified as "Palestinian", 8.9% as "Palestinian in Israel" or "Palestinian citizen of Israel", and 8.7% as "Arab"; 60% of Israeli Arabs have a positive view of the state. According to Sammy Smooha, "The identity of 83.0% of the Arabs in 2019 (up from 75.5% in 2017) has an Israeli component and 61.9% (unchanged from 60.3%) has a Palestinian component. However, when these two components were presented as competitors, 69.0% of the Arabs in 2019 chose exclusive or primary Palestinian identity, compared with 29.8% who chose exclusive or primary Israeli Arab identity."
Major urban areas
Israel has four major metropolitan areas: Gush Dan (Tel Aviv metropolitan area; population 3,854,000), Jerusalem metropolitan area (population 1,253,900), Haifa metropolitan area (population 924,400), and Beersheba metropolitan area (population 377,100). Israel's largest municipality, in population and area, isJerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
with residents in an area of . Israeli government statistics on Jerusalem include the population and area of East Jerusalem, which is widely recognized as part of the Palestinian territories
The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The I ...
under Israeli-occupied territories, Israeli occupation. Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the G ...
and Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
rank as Israel's next most populous cities, with populations of and , respectively.
The (mainly Haredi) city of Bnei Brak is the most densely populated city in Israel and one of the List of cities proper by population density, 10 most densely populated cities in the world.
Israel has 16 List of cities in Israel, cities with populations over 100,000. In all, there are 77 Israeli localities granted City council (Israel), "municipalities" (or "city") status by the Ministry of the Interior, List of Israeli settlements with city status in the West Bank, four of which are in the West Bank. Two more cities are planned: Kasif, Israel, Kasif, a planned city to be built in the Negev, and Harish, Israel, Harish, originally a small town that is being built into a large city since 2015.
Language
Israel has one official language, Hebrew language, Hebrew. Until 2018, Arabic language in Israel, Arabic was also one of two official languages of the State of Israel; in 2018 Basic Law: Israel as the Nation-State of the Jewish People, it was downgraded to having a 'special status in the state' with its use by state institutions to be set in law. Hebrew is the primary language of the state and is spoken every day by the majority of the population. Arabic is spoken by the Arab minority, with Hebrew taught in Arab schools. As a country of aliyah, immigrants, many languages can be heard on the streets. Due to mass immigration from the former Soviet Union and Aliyah from Ethiopia, Ethiopia (some 130,000 Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopian Jews live in Israel),Israel Central Bureau of StatisticsThe Ethiopian Community in Israel
/ref> Russian language in Israel, Russian and Amharic are widely spoken. More than one million Russian-speaking immigrants 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, arrived in Israel from the post-Soviet states between 1990 and 2004. French is spoken by around 700,000 Israelis, mostly originating French Jews in Israel, from France and North Africa (see Maghrebi Jews). English was an official language during the Mandate period; it lost this status after the establishment of Israel, but retains a role comparable to that of an official language, as may be seen in Road signs in Israel, road signs and official documents. Many Israelis communicate reasonably well in English, as many television programmes are broadcast in English with subtitles and the language is taught from the early grades in elementary school. In addition, Israeli universities offer courses in the English language on various subjects.
Religion
Israel comprises a major part of the Holy Land, a region of significant importance to all Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity,Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, Samaritanism, the Druze, Druze Faith and the Baháʼí Faith.
The Jewish religious movements, religious affiliation of Israeli Jews varies widely: a social survey from 2016 made by Pew Research indicates that 49% self-identify as Hiloni (secular), 29% as Masortim, Masorti (traditional), 13% as Dati (religious) and 9% as Haredi Judaism, Haredi (ultra-Orthodox). Haredi Jews are expected to represent more than 20% of Israel's Jewish population by 2028.
Islam in Israel, Muslims constitute Israel's largest religious minority, making up about 17.6% of the population. About 2% of the population is Christianity in Israel, Christian and 1.6% is Druze in Israel, Druze. The Christian population is composed primarily of Arab Christians and Arameans in Israel, Aramean Christians, but also includes post-Soviet immigrants, the foreign laborers of multinational origins, and followers of Messianic Judaism, considered by most Christians and Jews to be a form of Christianity. Members of many other religious groups, including Buddhism, Buddhists and Hinduism in Israel, Hindus, maintain a presence in Israel, albeit in small numbers. Out of more than one million 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, immigrants from the former Soviet Union, about 300,000 are considered not Jewish by the Chief Rabbinate of Israel.
 The city of
The city of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
is of Religious significance of Jerusalem, special importance to Jews, Muslims, and Christians, as it is the home of List of places in Jerusalem, sites that are pivotal to their religious beliefs, such as the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City that incorporates the Western Wall and the Temple Mount
The Temple Mount ( hbo, הַר הַבַּיִת, translit=Har haBayīt, label=Hebrew, lit=Mount of the House f the Holy}), also known as al-Ḥaram al-Sharīf (Arabic: الحرم الشريف, lit. 'The Noble Sanctuary'), al-Aqsa Mosque compoun ...
(Al-Aqsa Mosque compound) and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. Other locations of religious importance in Israel are Nazareth (holy in Christianity as the site of the Annunciation of Mary (mother of Jesus), Mary), Tiberias
Tiberias ( ; he, טְבֶרְיָה, ; ar, طبريا, Ṭabariyyā) is an Israeli city on the western shore of the Sea of Galilee. A major Jewish center during Late Antiquity, it has been considered since the 16th century one of Judaism's Fo ...
and Safed
Safed (known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as Tzfat; Sephardi Hebrew, Sephardic Hebrew & Modern Hebrew: צְפַת ''Tsfat'', Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation, Ashkenazi Hebrew: ''Tzfas'', Biblical Hebrew: ''Ṣǝp̄aṯ''; ar, صفد, ''Ṣafad''), i ...
(two of the Four Holy Cities in Judaism), the White Mosque, Ramla, White Mosque in Ramla (holy in Islam as the shrine of the prophet Salih, Saleh), and the Church of Saint George, Lod, Church of Saint George in Lod (holy in Christianity and Islam as the tomb of Saint George or Al Khidr). A number of other religious landmarks are located in the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, among them Joseph's Tomb in Nablus, the Church of the Nativity, birthplace of Jesus and Rachel's Tomb in Bethlehem, and the Cave of the Patriarchs
, alternate_name = Tomb of the Patriarchs, Cave of Machpelah, Sanctuary of Abraham, Ibrahimi Mosque (Mosque of Abraham)
, image = Palestine Hebron Cave of the Patriarchs.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Southern view of the complex, 2009
, map ...
in Hebron
Hebron ( ar, الخليل or ; he, חֶבְרוֹן ) is a Palestinian. city in the southern West Bank, south of Jerusalem. Nestled in the Judaean Mountains, it lies above sea level. The second-largest city in the West Bank (after East J ...
. The Arc (Baháʼí), administrative center of the Baháʼí Faith and the Shrine of the Báb are located at the Baháʼí World Centre in Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
; the leader of the faith is Shrine of Bahá'u'lláh, buried in Acre, Israel, Acre. A few kilometres south of the Baháʼí World Centre is Mahmood Mosque, Haifa, Mahmood Mosque affiliated with the reformist Ahmadiyya in Israel, Ahmadiyya movement. Kababir, Haifa's mixed neighbourhood of Jews and Ahmadi Arabs is one of a few of its kind in the country, others being Jaffa, Acre, Israel, Acre, other Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
neighbourhoods, Harish, Israel, Harish and Upper Nazareth.
Education
 Education is highly valued in the Israeli culture and was viewed as a History of education in ancient Israel and Judah, fundamental block of ancient Israelites. Jewish communities in the Levant were the first to introduce compulsory education for which the organized community, not less than the parents was responsible. Many international business leaders such as Microsoft founder Bill Gates have praised Israel for its high quality of education in helping spur Israel's economic development and technological boom. In 2015, the country List of countries by tertiary education attainment, ranked third among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD members (after Canada and Japan) for the percentage of 25–64 year-olds that have attained tertiary education with 49% compared with the OECD average of 35%. In 2012, the country ranked third in the world in the number of academic degrees per capita (20 percent of the population).
Israel has a school life expectancy of 16 years and a List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate of 97.8%. The State Education Law, passed in 1953, established five types of schools: state secular, state religious, ultra orthodox, communal settlement schools, and Arab schools. The public secular is the largest school group, and is attended by the majority of Jewish and non-Arab pupils in Israel. Most Arabs send their children to schools where Arabic is the language of instruction. Education is compulsory in Israel for children between the ages of three and eighteen. Schooling is divided into three tiers – primary school (grades 1–6), middle school (grades 7–9), and high school (grades 10–12) – culminating with ''Bagrut'' matriculation exams. Proficiency in core subjects such as mathematics, the
Education is highly valued in the Israeli culture and was viewed as a History of education in ancient Israel and Judah, fundamental block of ancient Israelites. Jewish communities in the Levant were the first to introduce compulsory education for which the organized community, not less than the parents was responsible. Many international business leaders such as Microsoft founder Bill Gates have praised Israel for its high quality of education in helping spur Israel's economic development and technological boom. In 2015, the country List of countries by tertiary education attainment, ranked third among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD members (after Canada and Japan) for the percentage of 25–64 year-olds that have attained tertiary education with 49% compared with the OECD average of 35%. In 2012, the country ranked third in the world in the number of academic degrees per capita (20 percent of the population).
Israel has a school life expectancy of 16 years and a List of countries by literacy rate, literacy rate of 97.8%. The State Education Law, passed in 1953, established five types of schools: state secular, state religious, ultra orthodox, communal settlement schools, and Arab schools. The public secular is the largest school group, and is attended by the majority of Jewish and non-Arab pupils in Israel. Most Arabs send their children to schools where Arabic is the language of instruction. Education is compulsory in Israel for children between the ages of three and eighteen. Schooling is divided into three tiers – primary school (grades 1–6), middle school (grades 7–9), and high school (grades 10–12) – culminating with ''Bagrut'' matriculation exams. Proficiency in core subjects such as mathematics, the Hebrew language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, Hebrew and general literature, the English language, history, Biblical scripture and civics is necessary to receive a Bagrut certificate.
Israel's Jewish population maintains a relatively high level of educational attainment where just under half of all Israeli Jews (46%) hold post-secondary degrees. This figure has remained stable in their already high levels of educational attainment over recent generations. Israeli Jews (among those ages 25 and older) have average of 11.6 years of schooling making them one of the most highly educated of all major religious groups in the world. In Arab, Christian and Druze schools, the exam on Biblical studies is replaced by an exam on Muslim, Christian or Druze heritage. ''Maariv (newspaper), Maariv'' described the Christian Arabs sectors as "the most successful in education system", since Christians fared the best in terms of education in comparison to any other religion in Israel. Israeli children from Russian-speaking families have a higher bagrut pass rate at high-school level. Amongst immigrant children born in the former Soviet Union, the bagrut pass rate is higher amongst those families from European FSU states at 62.6% and lower amongst those from Central Asian and Caucasian FSU states. In 2014, 61.5% of all Israeli twelfth graders earned a matriculation certificate.
West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, is the newest university institution, upgraded from college status, and the first in over thirty years.
Government and politics
 Israel is a parliamentary democracy with
Israel is a parliamentary democracy with universal suffrage
Universal suffrage (also called universal franchise, general suffrage, and common suffrage of the common man) gives the right to vote to all adult citizens, regardless of wealth, income, gender, social status, race, ethnicity, or political stanc ...
. A member of parliament supported by a parliamentary majority becomes the prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
—usually this is the chair of the largest party. The prime minister is the head of government and head of the Cabinet of Israel, cabinet.
Israel is governed by a 120-member parliament, known as the Knesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with ...
. Membership of the Knesset is based on proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
of List of political parties in Israel, political parties, with a 3.25% electoral threshold, which in practice has resulted in coalition governments. Residents of Israeli settlements in the West Bank are eligible to vote and after the 2015 Israeli legislative election, 2015 election, 10 of the 120 MKs () were settlers. Parliamentary Elections in Israel, elections are scheduled every four years, but unstable coalitions or a motion of no confidence, no-confidence vote by the Knesset can dissolve a government earlier. The first Arab-led party was established in 1988 and the main Arab bloc, the Joint List, holds about 10% of the parliament's seats.
Legal system
 Israel has a Israeli judicial system, three-tier court system. At the lowest level are magistrate courts, situated in most cities across the country. Above them are district courts, serving as both appeal, appellate courts and trial court, courts of first instance; they are situated in five of Israel's six Districts of Israel, districts. The third and highest tier is the Supreme Court of Israel, Supreme Court, located in Jerusalem; it serves a dual role as the highest court of appeals and the High Court of Justice (Israel), High Court of Justice. In the latter role, the Supreme Court rules as a court of first instance, allowing individuals, both citizens and non-citizens, to petition against the decisions of state authorities. Although Israel supports the goals of the International Criminal Court, it has not ratified the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, Rome Statute, citing concerns about the ability of the court to remain free from political impartiality.
Israel's legal system combines three legal traditions: English law, English common law, civil law (legal system), civil law, and Halakha, Jewish law. It is based on the principle of ''stare decisis'' (precedent) and is an adversarial system, where the parties in the suit bring evidence before the court. Court cases are decided by professional judges with no role for juries. Marriage in Israel, Marriage and divorce are under the jurisdiction of the religious courts: Beth din, Jewish, Sharia, Muslim, Druze, and Christian. The election of judges is carried out by a Judicial Selection Committee (Israel), committee of two Knesset members, three Supreme Court justices, two Israel Bar Association, Israeli Bar members and two ministers (one of which, Israel's Ministry of Justice (Israel), justice minister, is the committee's chairman). The committee's members of the Knesset are Secret ballot, secretly elected by the Knesset, and one of them is traditionally a member of the opposition, the committee's Supreme Court justices are chosen by tradition from all Supreme Court justices by seniority, the Israeli Bar members are elected by the bar, and the second minister is appointed by the Israeli cabinet. The current justice minister and committee's chairman is Gideon Sa'ar. Administration of Israel's courts (both the "General" courts and the Labor Courts of Israel, Labor Courts) is carried by the Administration of Courts, situated in Jerusalem. Both General and Labor courts are paperless courts: the storage of court files, as well as court decisions, are conducted electronically. Israel's Basic Law: Human Dignity and Liberty seeks to defend Human rights in Israel, human rights and liberties in Israel. As a result of "Enclave law", large portions of Israeli Civil law (legal system), civil law are applied to Israeli settlements and Israeli residents in the occupied territories.
Israel has a Israeli judicial system, three-tier court system. At the lowest level are magistrate courts, situated in most cities across the country. Above them are district courts, serving as both appeal, appellate courts and trial court, courts of first instance; they are situated in five of Israel's six Districts of Israel, districts. The third and highest tier is the Supreme Court of Israel, Supreme Court, located in Jerusalem; it serves a dual role as the highest court of appeals and the High Court of Justice (Israel), High Court of Justice. In the latter role, the Supreme Court rules as a court of first instance, allowing individuals, both citizens and non-citizens, to petition against the decisions of state authorities. Although Israel supports the goals of the International Criminal Court, it has not ratified the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court, Rome Statute, citing concerns about the ability of the court to remain free from political impartiality.
Israel's legal system combines three legal traditions: English law, English common law, civil law (legal system), civil law, and Halakha, Jewish law. It is based on the principle of ''stare decisis'' (precedent) and is an adversarial system, where the parties in the suit bring evidence before the court. Court cases are decided by professional judges with no role for juries. Marriage in Israel, Marriage and divorce are under the jurisdiction of the religious courts: Beth din, Jewish, Sharia, Muslim, Druze, and Christian. The election of judges is carried out by a Judicial Selection Committee (Israel), committee of two Knesset members, three Supreme Court justices, two Israel Bar Association, Israeli Bar members and two ministers (one of which, Israel's Ministry of Justice (Israel), justice minister, is the committee's chairman). The committee's members of the Knesset are Secret ballot, secretly elected by the Knesset, and one of them is traditionally a member of the opposition, the committee's Supreme Court justices are chosen by tradition from all Supreme Court justices by seniority, the Israeli Bar members are elected by the bar, and the second minister is appointed by the Israeli cabinet. The current justice minister and committee's chairman is Gideon Sa'ar. Administration of Israel's courts (both the "General" courts and the Labor Courts of Israel, Labor Courts) is carried by the Administration of Courts, situated in Jerusalem. Both General and Labor courts are paperless courts: the storage of court files, as well as court decisions, are conducted electronically. Israel's Basic Law: Human Dignity and Liberty seeks to defend Human rights in Israel, human rights and liberties in Israel. As a result of "Enclave law", large portions of Israeli Civil law (legal system), civil law are applied to Israeli settlements and Israeli residents in the occupied territories.
Administrative divisions
The State of Israel is divided into six main administrative Districts of Israel, districts, known as ''mehozot'' (; singular: ''mahoz'') – Central District (Israel), Center, Haifa District, Haifa, Jerusalem District, Jerusalem, Northern District (Israel), North, Southern District (Israel), South, and Tel Aviv District, Tel Aviv districts, as well as the Judea and Samaria Area in theWest Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
. All of the Judea and Samaria Area and parts of the Jerusalem and Northern districts are not recognized internationally as part of Israel. Districts are further divided into fifteen sub-districts known as ''nafot'' (; singular: ''nafa''), which are themselves partitioned into fifty natural regions.
: Including over 200,000 Jews and 300,000 Arabs in East Jerusalem.
: Israeli citizens only.
Israeli-occupied territories
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
, Israel captured and Israeli-occupied territories, occupied the West Bank
The West Bank ( ar, الضفة الغربية, translit=aḍ-Ḍiffah al-Ġarbiyyah; he, הגדה המערבית, translit=HaGadah HaMaʽaravit, also referred to by some Israelis as ) is a landlocked territory near the coast of the Mediter ...
, including East Jerusalem, the Gaza Strip
The Gaza Strip (;The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p.761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory under the control of the Palestinian National Authority and Hamas, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza.. ...
and the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. Israel also captured the Sinai Peninsula, but returned it to Egypt as part of the 1979 Egypt–Israel peace treaty. Between 1982 and 2000, Israel occupied Israeli occupation of Southern Lebanon, part of southern Lebanon, in what was known as the South Lebanon Security Belt, Security Belt. Since Israel's capture of these territories, Israeli settlements and military installations have been built within each of them, except Lebanon.
The Golan Heights Law, Golan Heights and Jerusalem Law, East Jerusalem have been fully incorporated into Israel under Israeli law, but not under international law. Israel has applied civilian law to both areas and granted their inhabitants permanent residency status and the ability to Israeli nationality law, apply for citizenship. The UN Security Council has declared the annexation of the Golan Heights and East Jerusalem to be "null and void" and continues to view the territories as occupied. The Positions on Jerusalem, status of East Jerusalem in any future peace settlement has at times been a difficult issue in Israeli–Palestinian peace process, negotiations between Israeli governments and representatives of the Palestinians, as Israel views it as its sovereign territory, as well as part of its capital.
The Application of Israeli Law to the West Bank: De Facto Annexation?
INSS Insight No. 638, 4 December 2014 The land itself is not considered part of Israel under Israeli law, as Israel has consciously refrained from annexing the territory, without ever relinquishing its legal claim to the land or defining a border with the area. There is no border between Israel-proper and the West Bank for Israeli vehicles. Israeli political opposition to annexation is primarily due to the perceived "demographic threat" of incorporating the West Bank's Palestinian population into Israel. Outside of the Israeli settlements, the West Bank remains under direct Israeli military rule, and Palestinians in the area cannot become Israeli citizens. The international community maintains that Israel does not have sovereignty in the West Bank, and considers Israel's control of the area to be the longest military occupation is modern history.See for example:
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Azarova, Valentina. 2017
Israel's Unlawfully Prolonged Occupation: Consequences under an Integrated Legal Framework
European Council on Foreign Affairs Policy Brief: "June 2017 marks 50 years of Israel's belligerent occupation of Palestinian territory, making it the longest occupation in modern history." The West Bank Jordanian annexation of the West Bank, was occupied and annexed by Jordan in 1950, following the Arab rejection of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine, UN decision to create two states in Palestine. Only Britain recognized this annexation and Jordan has since Jordanian disengagement from the West Bank, ceded its claim to the territory to the PLO. The Demographics of the Palestinian territories, population are mainly Palestinian people, Palestinians, including Palestinian refugee, refugees of the
1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
. From their occupation in 1967 until 1993, the Palestinians living in these territories were under Coordinator of Government Activities in the Territories, Israeli military administration. Since the Israel–Palestine Liberation Organization letters of recognition, Israel–PLO letters of recognition, most of the Palestinian population and List of cities administered by the State of Palestine, cities have been under the internal jurisdiction of the Palestinian National Authority, Palestinian Authority, and only partial Israeli military control, although Israel has on several occasions redeployed its Israel Defense Forces, troops and reinstated full military administration during periods of unrest. In response to increasing attacks during the Second Intifada, the Israeli government started to construct the Israeli West Bank barrier. When completed, approximately 13% of the barrier will be constructed on the Green Line (Israel), Green Line or in Israel with 87% inside the West Bank.
 The Gaza Strip is considered to be a "foreign territory" under Israeli law; however, since Israel operates a land, air, and sea blockade of the Gaza Strip, together with Egypt, the international community considers Israel to be the occupying power. The Gaza Strip was Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, occupied by Egypt from 1948 to 1967 and then by Israel after 1967. In 2005, as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan, Israel removed all of its settlers and forces from the territory, however, it continues to maintain Blockade of the Gaza Strip, control of its airspace and waters. The international community, including numerous international humanitarian organizations and various bodies of the UN, consider Gaza to remain occupied. Following the Battle of Gaza (2007), 2007 Battle of Gaza, when Governance of the Gaza Strip, Hamas assumed power in the Gaza Strip, Israel tightened its control of the Gaza crossings along Israel–Gaza barrier, its border, as well as by sea and air, and prevented persons from entering and exiting the area except for isolated cases it deemed humanitarian. Gaza has a Gaza–Egypt border, border with Egypt, and an agreement between Israel, the European Union, and the PA governed how border crossing would take place (it was monitored by European observers). The application of democracy to its Palestinian citizens, and the selective application of Israeli democracy in the Israeli-controlled Palestinian territories, has been criticized.
The International Court of Justice, principal judicial organ of the UN, asserted, in its International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict#Ruling of the ICJ, 2004 advisory opinion on the legality of the construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier, that the lands captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, including East Jerusalem, are occupied territory. Most negotiations relating to the territories have been on the basis of United Nations Security Council Resolution 242, UN Security Council Resolution 242, which emphasizes "the inadmissibility of the acquisition of territory by war", and calls on Israel to withdraw from occupied territories in return for normalization of relations with Arab states, a principle known as "Land for peace". According to some observers, Israel has engaged in systematic and widespread violations of Human rights in the Israeli-occupied territories, human rights in the occupied territories, including the occupation itself and war crimes against civilians. The allegations include violations of international humanitarian law by the United Nations Human Rights Council, UN Human Rights Council, with local residents having "limited ability to hold governing authorities accountable for such abuses" by the U.S. State Department, mass arbitrary arrests, torture, unlawful killings, systemic abuses and impunity by Amnesty International and others and a denial of the right to Palestinian self-determination. In response to such allegations, Prime Minister Netanyahu has defended the country's security forces for protecting the innocent from terrorists and expressed contempt for what he describes as a lack of concern about the human rights violations committed by "criminal killers". Some observers, such as Israeli officials, scholars, United States Ambassador to the UN Nikki Haley and UN secretary-generals Ban Ki-moon and Kofi Annan, also assert that the UN is disproportionately concerned with Israeli misconduct.
The international community widely regards Israeli settlements in the occupied territories illegal under international law. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, passed on 23 December 2016 in a 14–0 vote by members of the United Nations Security Council, U.N. Security Council (UNSC) with the United States abstaining. The resolution states that Israel's settlement activity constitutes a "flagrant violation" of international law, has "no legal validity" and demands that Israel stop such activity and fulfill its obligations as an Military occupation#The occupying power, occupying power under the Fourth Geneva Convention.
Israel's treatment of the Palestinians within the occupied territories has drawn Israel and apartheid, accusations that it is guilty of the crime of apartheid by Israeli human rights groups Yesh Din and B'tselem, and other international organizations including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, with the criticism extending to its treatment of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinians within Israel as well. Amnesty's report was criticized by politicians and government representatives from Israel, the United States, the United Kingdom, Netherlands and Germany, while it was welcomed by Palestinians, representatives from other states, and organizations such as the Arab League. A 2021 survey of academic experts on the Middle East found an increase from 59% to 65% of these scholars describing Israel as a "one-state reality akin to apartheid".
The Gaza Strip is considered to be a "foreign territory" under Israeli law; however, since Israel operates a land, air, and sea blockade of the Gaza Strip, together with Egypt, the international community considers Israel to be the occupying power. The Gaza Strip was Occupation of the Gaza Strip by Egypt, occupied by Egypt from 1948 to 1967 and then by Israel after 1967. In 2005, as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan, Israel removed all of its settlers and forces from the territory, however, it continues to maintain Blockade of the Gaza Strip, control of its airspace and waters. The international community, including numerous international humanitarian organizations and various bodies of the UN, consider Gaza to remain occupied. Following the Battle of Gaza (2007), 2007 Battle of Gaza, when Governance of the Gaza Strip, Hamas assumed power in the Gaza Strip, Israel tightened its control of the Gaza crossings along Israel–Gaza barrier, its border, as well as by sea and air, and prevented persons from entering and exiting the area except for isolated cases it deemed humanitarian. Gaza has a Gaza–Egypt border, border with Egypt, and an agreement between Israel, the European Union, and the PA governed how border crossing would take place (it was monitored by European observers). The application of democracy to its Palestinian citizens, and the selective application of Israeli democracy in the Israeli-controlled Palestinian territories, has been criticized.
The International Court of Justice, principal judicial organ of the UN, asserted, in its International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict#Ruling of the ICJ, 2004 advisory opinion on the legality of the construction of the Israeli West Bank barrier, that the lands captured by Israel in the Six-Day War, including East Jerusalem, are occupied territory. Most negotiations relating to the territories have been on the basis of United Nations Security Council Resolution 242, UN Security Council Resolution 242, which emphasizes "the inadmissibility of the acquisition of territory by war", and calls on Israel to withdraw from occupied territories in return for normalization of relations with Arab states, a principle known as "Land for peace". According to some observers, Israel has engaged in systematic and widespread violations of Human rights in the Israeli-occupied territories, human rights in the occupied territories, including the occupation itself and war crimes against civilians. The allegations include violations of international humanitarian law by the United Nations Human Rights Council, UN Human Rights Council, with local residents having "limited ability to hold governing authorities accountable for such abuses" by the U.S. State Department, mass arbitrary arrests, torture, unlawful killings, systemic abuses and impunity by Amnesty International and others and a denial of the right to Palestinian self-determination. In response to such allegations, Prime Minister Netanyahu has defended the country's security forces for protecting the innocent from terrorists and expressed contempt for what he describes as a lack of concern about the human rights violations committed by "criminal killers". Some observers, such as Israeli officials, scholars, United States Ambassador to the UN Nikki Haley and UN secretary-generals Ban Ki-moon and Kofi Annan, also assert that the UN is disproportionately concerned with Israeli misconduct.
The international community widely regards Israeli settlements in the occupied territories illegal under international law. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, passed on 23 December 2016 in a 14–0 vote by members of the United Nations Security Council, U.N. Security Council (UNSC) with the United States abstaining. The resolution states that Israel's settlement activity constitutes a "flagrant violation" of international law, has "no legal validity" and demands that Israel stop such activity and fulfill its obligations as an Military occupation#The occupying power, occupying power under the Fourth Geneva Convention.
Israel's treatment of the Palestinians within the occupied territories has drawn Israel and apartheid, accusations that it is guilty of the crime of apartheid by Israeli human rights groups Yesh Din and B'tselem, and other international organizations including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, with the criticism extending to its treatment of Palestinian citizens of Israel, Palestinians within Israel as well. Amnesty's report was criticized by politicians and government representatives from Israel, the United States, the United Kingdom, Netherlands and Germany, while it was welcomed by Palestinians, representatives from other states, and organizations such as the Arab League. A 2021 survey of academic experts on the Middle East found an increase from 59% to 65% of these scholars describing Israel as a "one-state reality akin to apartheid".
Foreign relations
 Israel maintains diplomatic relations , as well as with the Holy See, Kosovo, the Cook Islands and Niue. It has 107 List of diplomatic missions of Israel, diplomatic missions around the world; countries with whom they have no diplomatic relations include most Muslim countries. Six out of twenty-two nations in the Arab League have normalized relations with Israel. Egypt–Israel relations, Egypt and Israel–Jordan relations, Jordan signed peace treaties in Egypt–Israel peace treaty, 1979 and Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, 1994, respectively, but Israel remains formally in a Israel–Syria relations, state of war with Syria, a status that dates back uninterrupted to 1948. It has been in a similarly Israel–Lebanon relations, formal state of war with Lebanon since the end of the Lebanese Civil War in 2000, with the Israel–Lebanon border remaining unagreed by treaty.
In late 2020, Israel normalized relations with four more Arab countries: the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain in September (known as the Abraham Accords), Israel–Sudan normalization agreement, Sudan in October, and Israel–Morocco normalization agreement, Morocco in December. Despite the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, Israel is still widely considered an enemy country among Egyptians. Iran Iran–Israel relations, had diplomatic relations with Israel under the Pahlavi dynasty but withdrew its recognition of Israel during the Islamic Revolution. Israeli citizens may not visit Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen (countries Israel fought in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War that Israel does not have a peace treaty with) without permission from the Ministry of Interior (Israel), Ministry of the Interior. As a result of the Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War, Mauritania, Qatar, Bolivia, and Venezuela suspended political and economic ties with Israel, though Bolivia renewed ties in 2019. China–Israel relations, China maintains good ties with both Israel and the Arab world.
The Israel–United States relations, United States and the Israel–Russia relations, Soviet Union were the first two countries to recognize the State of Israel, having declared recognition roughly simultaneously. Diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union were broken in 1967, following the
Israel maintains diplomatic relations , as well as with the Holy See, Kosovo, the Cook Islands and Niue. It has 107 List of diplomatic missions of Israel, diplomatic missions around the world; countries with whom they have no diplomatic relations include most Muslim countries. Six out of twenty-two nations in the Arab League have normalized relations with Israel. Egypt–Israel relations, Egypt and Israel–Jordan relations, Jordan signed peace treaties in Egypt–Israel peace treaty, 1979 and Israel–Jordan Treaty of Peace, 1994, respectively, but Israel remains formally in a Israel–Syria relations, state of war with Syria, a status that dates back uninterrupted to 1948. It has been in a similarly Israel–Lebanon relations, formal state of war with Lebanon since the end of the Lebanese Civil War in 2000, with the Israel–Lebanon border remaining unagreed by treaty.
In late 2020, Israel normalized relations with four more Arab countries: the United Arab Emirates and Bahrain in September (known as the Abraham Accords), Israel–Sudan normalization agreement, Sudan in October, and Israel–Morocco normalization agreement, Morocco in December. Despite the peace treaty between Israel and Egypt, Israel is still widely considered an enemy country among Egyptians. Iran Iran–Israel relations, had diplomatic relations with Israel under the Pahlavi dynasty but withdrew its recognition of Israel during the Islamic Revolution. Israeli citizens may not visit Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and Yemen (countries Israel fought in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War that Israel does not have a peace treaty with) without permission from the Ministry of Interior (Israel), Ministry of the Interior. As a result of the Gaza War (2008–09), 2008–09 Gaza War, Mauritania, Qatar, Bolivia, and Venezuela suspended political and economic ties with Israel, though Bolivia renewed ties in 2019. China–Israel relations, China maintains good ties with both Israel and the Arab world.
The Israel–United States relations, United States and the Israel–Russia relations, Soviet Union were the first two countries to recognize the State of Israel, having declared recognition roughly simultaneously. Diplomatic relations with the Soviet Union were broken in 1967, following the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
, and renewed in October 1991. The United States regards Israel as its "most reliable partner in the Middle East," based on "common democratic values, religious affinities, and security interests". The United States has provided $68 billion in Israel–United States military relations, military assistance and $32 billion in grants to Israel since 1967, under the Foreign Assistance Act (period beginning 1962), more than any other country for that period until 2003. Most surveyed Americans have also held consistently favorable views of Israel. The United Kingdom is seen as having a "natural" Israel–United Kingdom relations, relationship with Israel on account of the Mandate for Palestine. Relations between the two countries were also made stronger by former prime minister Tony Blair's efforts for a two state resolution. , Germany–Israel relations, Germany had paid 25 billion euros in Reparations Agreement between Israel and West Germany, reparations to the Israeli state and individual Israeli Holocaust survivors. Israel is included in the European Union's European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), which aims at bringing the EU and its neighbours closer.
 Although Turkey and Israel did not establish full diplomatic relations until 1991, Turkey has Israel–Turkey relations, cooperated with the Jewish state since its recognition of Israel in 1949. Turkey's ties to other Muslim-majority nations in the region have at times resulted in pressure from Arab and Muslim states to temper its relationship with Israel. Relations between Turkey and Israel took a downturn after the 2008–09 Gaza War and Israel's Gaza flotilla raid, raid of the Gaza flotilla. Greece–Israel relations, Relations between Greece and Israel have improved since 1995 due to the decline of Israeli–Turkish relations. The two countries have a defense cooperation agreement and in 2010, the Israeli Air Force hosted Greece's Hellenic Air Force in a joint exercise at the Ovda Airport, Uvda base. The joint Cyprus-Israel oil and gas explorations centered on the Leviathan gas field are an important factor for Greece, given its Cyprus–Greece relations, strong links with Cyprus. Cooperation in the world's longest Submarine power cable, subsea electric power cable, the EuroAsia Interconnector, has strengthened Cyprus–Israel relations, relations between Cyprus and Israel.
Azerbaijan is one of the few majority Muslim countries to develop strategic and economic Azerbaijan–Israel relations, relations with Israel. Azerbaijan supplies the country with a substantial amount of its oil needs, and Israel is a critical arms supplier for Azerbaijan. Kazakhstan also has an economic and strategic partnership with Israel. India established full India–Israel relations, diplomatic ties with Israel in 1992 and has fostered a strong military, technological and cultural partnership with the country since then. A 2009 survey done on behalf of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Israel), Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs listed India as more pro-Israel than 12 other countries surveyed. India is the largest customer of the Israeli military equipment and Israel is the second-largest military partner of India after Russia. Ethiopia–Israel relations, Ethiopia is Israel's main ally in Africa due to common political, religious and security interests. Israel provides expertise to Ethiopia on irrigation projects and thousands of Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopian Jews live in Israel.
Israel has a history of providing emergency aid and humanitarian response teams to disasters across the world. In 1955 Israel began its foreign aid programme in Burma. The programme's focus subsequently shifted to Africa. Israel's humanitarian efforts officially began in 1957, with the establishment of Mashav, the Israel's Agency for International Development Cooperation. In this early period, whilst Israel's aid represented only a small percentage of total aid to Africa, its programme was effective in creating goodwill throughout the continent; however, following the 1967 war relations soured. Israel's foreign aid programme subsequently shifted its focus to Latin America. Since the late 1970s Israel's foreign aid has gradually decreased, although in recent years Israel has tried to reestablish its aid to Africa. There are additional Israeli humanitarian and emergency response groups that work with the Israel government, including IsraAid, a joint programme run by 14 Israeli organizations and North American Jewish groups, ZAKA, The Fast Israeli Rescue and Search Team (FIRST), Israeli Flying Aid (IFA), Save a Child's Heart (SACH) and Latet. Between 1985 and 2015, Israel sent 24 delegations of IDF search and rescue unit, the Home Front Command, to 22 countries. Currently Israeli foreign aid List of development aid country donors, ranks low among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD nations, spending less than 0.1% of its Gross national income, GNI on development assistance. The UN has set a target of 0.7%. In 2015 six nations reached the UN target. The country ranked 38th in the 2018 World Giving Index.
Although Turkey and Israel did not establish full diplomatic relations until 1991, Turkey has Israel–Turkey relations, cooperated with the Jewish state since its recognition of Israel in 1949. Turkey's ties to other Muslim-majority nations in the region have at times resulted in pressure from Arab and Muslim states to temper its relationship with Israel. Relations between Turkey and Israel took a downturn after the 2008–09 Gaza War and Israel's Gaza flotilla raid, raid of the Gaza flotilla. Greece–Israel relations, Relations between Greece and Israel have improved since 1995 due to the decline of Israeli–Turkish relations. The two countries have a defense cooperation agreement and in 2010, the Israeli Air Force hosted Greece's Hellenic Air Force in a joint exercise at the Ovda Airport, Uvda base. The joint Cyprus-Israel oil and gas explorations centered on the Leviathan gas field are an important factor for Greece, given its Cyprus–Greece relations, strong links with Cyprus. Cooperation in the world's longest Submarine power cable, subsea electric power cable, the EuroAsia Interconnector, has strengthened Cyprus–Israel relations, relations between Cyprus and Israel.
Azerbaijan is one of the few majority Muslim countries to develop strategic and economic Azerbaijan–Israel relations, relations with Israel. Azerbaijan supplies the country with a substantial amount of its oil needs, and Israel is a critical arms supplier for Azerbaijan. Kazakhstan also has an economic and strategic partnership with Israel. India established full India–Israel relations, diplomatic ties with Israel in 1992 and has fostered a strong military, technological and cultural partnership with the country since then. A 2009 survey done on behalf of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Israel), Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs listed India as more pro-Israel than 12 other countries surveyed. India is the largest customer of the Israeli military equipment and Israel is the second-largest military partner of India after Russia. Ethiopia–Israel relations, Ethiopia is Israel's main ally in Africa due to common political, religious and security interests. Israel provides expertise to Ethiopia on irrigation projects and thousands of Ethiopian Jews in Israel, Ethiopian Jews live in Israel.
Israel has a history of providing emergency aid and humanitarian response teams to disasters across the world. In 1955 Israel began its foreign aid programme in Burma. The programme's focus subsequently shifted to Africa. Israel's humanitarian efforts officially began in 1957, with the establishment of Mashav, the Israel's Agency for International Development Cooperation. In this early period, whilst Israel's aid represented only a small percentage of total aid to Africa, its programme was effective in creating goodwill throughout the continent; however, following the 1967 war relations soured. Israel's foreign aid programme subsequently shifted its focus to Latin America. Since the late 1970s Israel's foreign aid has gradually decreased, although in recent years Israel has tried to reestablish its aid to Africa. There are additional Israeli humanitarian and emergency response groups that work with the Israel government, including IsraAid, a joint programme run by 14 Israeli organizations and North American Jewish groups, ZAKA, The Fast Israeli Rescue and Search Team (FIRST), Israeli Flying Aid (IFA), Save a Child's Heart (SACH) and Latet. Between 1985 and 2015, Israel sent 24 delegations of IDF search and rescue unit, the Home Front Command, to 22 countries. Currently Israeli foreign aid List of development aid country donors, ranks low among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, OECD nations, spending less than 0.1% of its Gross national income, GNI on development assistance. The UN has set a target of 0.7%. In 2015 six nations reached the UN target. The country ranked 38th in the 2018 World Giving Index.
Military
 The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and is headed by its Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff, the ''Ramatkal'', subordinate to the Cabinet of Israel, Cabinet. The IDF consists of the GOC Army Headquarters, army, Israeli Air Force, air force and Israeli Navy, navy. It was founded during the
The Israel Defense Forces (IDF) is the sole military wing of the Israeli security forces, and is headed by its Chief of General Staff (Israel), Chief of General Staff, the ''Ramatkal'', subordinate to the Cabinet of Israel, Cabinet. The IDF consists of the GOC Army Headquarters, army, Israeli Air Force, air force and Israeli Navy, navy. It was founded during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War
The 1948 (or First) Arab–Israeli War was the second and final stage of the 1948 Palestine war. It formally began following the end of the British Mandate for Palestine at midnight on 14 May 1948; the Israeli Declaration of Independence had ...
by consolidating paramilitary organizations—chiefly the Haganah—that preceded the establishment of the state. The IDF also draws upon the resources of the Military Intelligence Directorate (Israel), Military Intelligence Directorate (''Aman''), which works with Mossad and Shin Bet, Shabak. The Israel Defense Forces have been involved in several List of wars involving Israel, major wars and border conflicts in its short history, making it one of the most battle-trained armed forces in the world.
Most Israelis are Conscription in Israel, drafted into the military at the age of 18. Men serve two years and eight months and Women in the Israel Defense Forces, women two years. Following mandatory service, Israeli men join the reserve forces and usually do up to several weeks of Reserve duty (Israel), reserve duty every year until their forties. Most women are exempt from reserve duty. Arab citizens of Israel (except the Druze in Israel, Druze) and those engaged in full-time religious studies are Exemption from military service in Israel, exempt from military service, although the Tal committee, exemption of yeshiva students has been a source of contention in Israeli society for many years. An alternative for those who receive exemptions on various grounds is ''Sherut Leumi'', or national service, which involves a programme of service in hospitals, schools and other social welfare frameworks. A small minority of Israeli Arabs also volunteer to serve in the army. As a result of its conscription programme, the IDF maintains approximately 176,500 active troops and an additional 465,000 reservists, giving Israel one of the world's highest List of countries by number of military and paramilitary personnel, percentage of citizens with military training.#IISS2018, IISS 2018, pp. 339–340
The nation's military relies heavily on high-tech Military equipment of Israel, weapons systems Defense industry of Israel, designed and manufactured in Israel as well as some foreign imports. The Arrow (Israeli missile), Arrow missile is one of the world's few operational anti-ballistic missile systems. The Python (missile), Python air-to-air missile series is often considered one of the most crucial weapons in its military history. Israel's Spike (missile), Spike missile is one of the most widely exported anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs) in the world. Israel's Iron Dome anti-missile air defense system gained worldwide acclaim after intercepting hundreds of Qassam rocket, Qassam, BM-21 Grad, 122 mm Grad and Fajr-5 artillery Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel, rockets fire by Palestinian militants from the Gaza Strip. Since the Yom Kippur War, Israel has developed a network of reconnaissance satellites. The success of the ''Ofeq'' programme has made Israel Timeline of first orbital launches by country, one of seven countries capable of launching such satellites.
Israel is widely believed to Nuclear weapons and Israel, possess nuclear weapons and per a 1993 report, chemical and biological Israel and weapons of mass destruction, weapons of mass destruction. Israel has not signed the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and maintains a policy of deliberate ambiguity toward its nuclear capabilities. The Israeli Navy's Dolphin-class submarine, Dolphin submarines are believed to be armed with nuclear Popeye Turbo missiles, offering second strike, second-strike capability. Since the Gulf War in 1991, when Israel was attacked by Al Hussein (missile), Iraqi Scud missiles, all homes in Israel are required to have a reinforced security room, Merkhav Mugan, impermeable to chemical and biological substances.
Since Israel's establishment, military expenditure constituted a significant portion of the country's gross domestic product, with peak of 30.3% of GDP spent on defense in 1975. In 2016, Israel ranked sixth in the world by List of countries by military expenditure share of GDP, defense spending as a percentage of GDP, with 5.7%, and 15th List of countries by military expenditures, by total military expenditure, with $18 billion. Since 1974, the United States has been a particularly notable contributor of Israel–United States military relations#Military aid and procurement, military aid to Israel. Under a memorandum of understanding signed in 2016, the U.S. is expected to provide the country with $3.8 billion per year, or around 20% of Israel's defense budget, from 2018 to 2028. Israel ranked fifth globally for Arms industry, arms exports in 2017. The majority of Israel's arms exports are unreported for security reasons. Israel is consistently rated low in the Global Peace Index, ranking 141st out of 163 nations for peacefulness in 2021.
Economy

 Israel is considered the most advanced country in
Israel is considered the most advanced country in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
and the Middle East in economic and industrial development. Israel's quality List of universities and colleges in Israel, university education and the establishment of a highly motivated and educated populace is largely responsible for spurring the country's high technology boom and rapid economic development. In 2010, it joined the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
. The country is ranked 20th in the World Economic Forum's ''Global Competitiveness Report'' and 35th on the World Bank's Ease of doing business index, ''Ease of Doing Business'' index. Israel was also ranked fifth in the world by share of people in high-skilled employment. Israeli economic data covers the economic territory of Israel, including the Golan Heights, East Jerusalem and Israeli settlements in the West Bank.
Despite limited natural resources, intensive development of the Agriculture in Israel, agricultural and industrial sectors over the past decades has made Israel largely self-sufficient in food production, apart from grains and beef. Imports to Israel, totaling $96.5 billion in 2020, include raw materials, military equipment, investment goods, rough diamonds, fuels, grain, and consumer goods. Leading exports include machinery and equipment, software, Diamond industry in Israel, cut diamonds, agricultural products, chemicals, and textiles and apparel; in 2020, Israeli exports reached $114 billion. The Bank of Israel holds $173 billion of foreign-exchange reserves. Since the 1970s, Israel has received Israel–United States military relations, military aid from the United States, as well as economic assistance in the form of loan guarantees, which now account for roughly half of Israel's external debt. Israel has List of countries by external debt, one of the lowest external debts in the developed world, and is a lender in terms of net external debt (Net international investment position, assets vs. liabilities abroad), which stood at a surplus of $69 billion.
Israel has the second-largest number of startup company, startup companies in the world after the United States, and the third-largest number of List of Israeli companies quoted on the Nasdaq, NASDAQ-listed companies after the U.S. and China. Intel and Microsoft built their first overseas research and development facilities in Israel, and other high-tech multi-national corporations, such as IBM, Google, Apple Inc., Apple, Hewlett-Packard, Cisco Systems, Facebook and Motorola have opened List of multinational companies with research and development centres in Israel, research and development centres in the country. In 2007, American investor Warren Buffett's holding company Berkshire Hathaway bought an Israeli company, Iscar, its first List of assets owned by Berkshire Hathaway, acquisition outside the United States, for $4 billion.
Days of working time in Israel are Sunday through Thursday (for a five-day workweek), or Friday (for a six-day workweek). In observance of ''Shabbat'', in places where Friday is a work day and the majority of population is Jewish, Friday is a "short day", usually lasting until 14:00 in the winter, or 16:00 in the summer. Several proposals have been raised to adjust the work week with the majority of the world, and make Sunday a non-working day, while extending working time of other days or replacing Friday with Sunday as a work day.
Science and technology
 Israel's development of cutting-edge technologies in software, communications and the life sciences have Silicon Wadi, evoked comparisons with Silicon Valley. Israel is first in the world in List of countries by research and development spending, expenditure on research and development as a percentage of GDP. It is ranked sixteenth in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, down from tenth in 2019 and fifth in the 2019 Bloomberg Innovation Index. Israel has 140 scientists, technicians, and engineers per 10,000 employees, the highest number in the world, for comparison the U.S. has 85 per 100,000. Israel has produced six List of Israeli Nobel laureates, Nobel Prize-winning scientists since 2004 and has been frequently ranked as one of the countries with the highest ratios of scientific papers per capita in the world. Israel has led the world in stem cell, stem-cell research papers per capita since 2000. List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities are ranked among the top 50 world universities in computer science (Technion and Tel Aviv University), mathematics (Hebrew University of Jerusalem) and chemistry (Weizmann Institute of Science).
In 2012, Israel was ranked ninth in the world by the Futron's Space Competitiveness Index. The Israel Space Agency coordinates all Israeli space research programmes with scientific and commercial goals, and have indigenously designed and built at least 13 commercial, research and spy satellites. Some of Israel's satellites are ranked among the world's most advanced space systems. Shavit 2, Shavit is a space launch vehicle produced by Israel to launch small satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched in 1988, making Israel the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, eighth nation to have a space launch capability. In 2003, Ilan Ramon became Israel's first astronaut, serving as payload specialist of STS-107, the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, fatal mission of the Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''.
The ongoing shortage of Water supply and sanitation in Israel, water in the country has spurred innovation in water conservation techniques, and a substantial Agricultural research in Israel, agricultural modernization, drip irrigation, was List of Israeli inventions and discoveries, invented in Israel. Israel is also at the technological forefront of desalination and water recycling. The Sorek desalination plant is the largest seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) Desalination facilities, desalination facility in the world. By 2014, Israel's desalination programmes provided roughly 35% of Israel's drinking water and it is expected to supply 40% by 2015 and 70% by 2050. , more than 50 percent of the water for Israeli households, agriculture and industry is artificially produced. The country hosts an annual Water Technology and Environmental Control Exhibition & Conference (WATEC) that attracts thousands of people from across the world. In 2011, Israel's Water industry, water technology industry was worth around $2 billion a year with annual exports of products and services in the tens of millions of dollars. As a result of innovations in reverse osmosis technology, Israel is set to become a net Water export, exporter of water in the coming years.
Israel's development of cutting-edge technologies in software, communications and the life sciences have Silicon Wadi, evoked comparisons with Silicon Valley. Israel is first in the world in List of countries by research and development spending, expenditure on research and development as a percentage of GDP. It is ranked sixteenth in the Global Innovation Index in 2022, down from tenth in 2019 and fifth in the 2019 Bloomberg Innovation Index. Israel has 140 scientists, technicians, and engineers per 10,000 employees, the highest number in the world, for comparison the U.S. has 85 per 100,000. Israel has produced six List of Israeli Nobel laureates, Nobel Prize-winning scientists since 2004 and has been frequently ranked as one of the countries with the highest ratios of scientific papers per capita in the world. Israel has led the world in stem cell, stem-cell research papers per capita since 2000. List of Israeli universities and colleges, Israeli universities are ranked among the top 50 world universities in computer science (Technion and Tel Aviv University), mathematics (Hebrew University of Jerusalem) and chemistry (Weizmann Institute of Science).
In 2012, Israel was ranked ninth in the world by the Futron's Space Competitiveness Index. The Israel Space Agency coordinates all Israeli space research programmes with scientific and commercial goals, and have indigenously designed and built at least 13 commercial, research and spy satellites. Some of Israel's satellites are ranked among the world's most advanced space systems. Shavit 2, Shavit is a space launch vehicle produced by Israel to launch small satellites into low Earth orbit. It was first launched in 1988, making Israel the Timeline of first orbital launches by country, eighth nation to have a space launch capability. In 2003, Ilan Ramon became Israel's first astronaut, serving as payload specialist of STS-107, the Space Shuttle Columbia disaster, fatal mission of the Space Shuttle Columbia, Space Shuttle ''Columbia''.
The ongoing shortage of Water supply and sanitation in Israel, water in the country has spurred innovation in water conservation techniques, and a substantial Agricultural research in Israel, agricultural modernization, drip irrigation, was List of Israeli inventions and discoveries, invented in Israel. Israel is also at the technological forefront of desalination and water recycling. The Sorek desalination plant is the largest seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) Desalination facilities, desalination facility in the world. By 2014, Israel's desalination programmes provided roughly 35% of Israel's drinking water and it is expected to supply 40% by 2015 and 70% by 2050. , more than 50 percent of the water for Israeli households, agriculture and industry is artificially produced. The country hosts an annual Water Technology and Environmental Control Exhibition & Conference (WATEC) that attracts thousands of people from across the world. In 2011, Israel's Water industry, water technology industry was worth around $2 billion a year with annual exports of products and services in the tens of millions of dollars. As a result of innovations in reverse osmosis technology, Israel is set to become a net Water export, exporter of water in the coming years.
 Israel has embraced Solar power in Israel, solar energy; its engineers are on the cutting edge of solar energy technology and its solar companies work on projects around the world. Over 90% of Israeli homes use solar energy for hot water, the highest per capita in the world. According to government figures, the country saves 8% of its electricity consumption per year because of its solar energy use in heating. The high annual incident irradiance, solar irradiance at its geographic latitude creates ideal conditions for what is an internationally renowned solar research and development industry in the Negev Desert. Israel had a modern Electric vehicle network, electric car infrastructure involving a countrywide network of charging stations to facilitate the charging and exchange of car batteries. It was thought that this would have lowered Israel's oil dependency and lowered the fuel costs of hundreds of Israel's motorists that use cars powered only by electric batteries. The Israeli model was being studied by several countries and being implemented in Denmark and Australia. However, Israel's trailblazing electric car company Better Place (company), Better Place shut down in 2013.
Israel has embraced Solar power in Israel, solar energy; its engineers are on the cutting edge of solar energy technology and its solar companies work on projects around the world. Over 90% of Israeli homes use solar energy for hot water, the highest per capita in the world. According to government figures, the country saves 8% of its electricity consumption per year because of its solar energy use in heating. The high annual incident irradiance, solar irradiance at its geographic latitude creates ideal conditions for what is an internationally renowned solar research and development industry in the Negev Desert. Israel had a modern Electric vehicle network, electric car infrastructure involving a countrywide network of charging stations to facilitate the charging and exchange of car batteries. It was thought that this would have lowered Israel's oil dependency and lowered the fuel costs of hundreds of Israel's motorists that use cars powered only by electric batteries. The Israeli model was being studied by several countries and being implemented in Denmark and Australia. However, Israel's trailblazing electric car company Better Place (company), Better Place shut down in 2013.
Transportation
 Israel has of paved Roads in Israel, roads, and 3 million motor vehicles. The List of countries by vehicles per capita, number of motor vehicles per 1,000 persons is 365, relatively low with respect to developed countries. Israel has 5,715 buses on scheduled routes, operated by several carriers, the largest and oldest of which is Egged (company), Egged, serving most of the country. Rail transport in Israel, Railways stretch across and are operated solely by government-owned Israel Railways. Following major investments beginning in the early to mid-1990s, the number of train passengers per year has grown from 2.5 million in 1990, to 53 million in 2015; railways are also transporting 7.5 million tons of cargo, per year.
Israel is served by two international List of airports in Israel, airports, Ben Gurion Airport, the country's main hub for international air travel near Tel Aviv, and Ramon Airport, which serves the southernmost port city of Eilat. Ben Gurion, Israel's largest airport, handled over 15 million passengers in 2015. The country has three main ports: the Port of Haifa, the country's oldest and largest, on the Mediterranean coast, Ashdod Port; and the smaller Port of Eilat on the
Israel has of paved Roads in Israel, roads, and 3 million motor vehicles. The List of countries by vehicles per capita, number of motor vehicles per 1,000 persons is 365, relatively low with respect to developed countries. Israel has 5,715 buses on scheduled routes, operated by several carriers, the largest and oldest of which is Egged (company), Egged, serving most of the country. Rail transport in Israel, Railways stretch across and are operated solely by government-owned Israel Railways. Following major investments beginning in the early to mid-1990s, the number of train passengers per year has grown from 2.5 million in 1990, to 53 million in 2015; railways are also transporting 7.5 million tons of cargo, per year.
Israel is served by two international List of airports in Israel, airports, Ben Gurion Airport, the country's main hub for international air travel near Tel Aviv, and Ramon Airport, which serves the southernmost port city of Eilat. Ben Gurion, Israel's largest airport, handled over 15 million passengers in 2015. The country has three main ports: the Port of Haifa, the country's oldest and largest, on the Mediterranean coast, Ashdod Port; and the smaller Port of Eilat on the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
.
Tourism
 Tourism, especially religious tourism, is an important industry in Israel, with the country's temperate climate, List of beaches in Israel, beaches, Archaeology of Israel, archaeological, other List of World Heritage Sites in Israel, historical and List of biblical places, biblical sites, and unique geography also drawing tourists. Israel's security problems have taken their toll on the industry, but the number of incoming tourists is on the rebound. In 2017, a record of 3.6 million tourists visited Israel, yielding a 25 percent growth since 2016 and contributed NIS 20 billion to the Israeli economy.
Tourism, especially religious tourism, is an important industry in Israel, with the country's temperate climate, List of beaches in Israel, beaches, Archaeology of Israel, archaeological, other List of World Heritage Sites in Israel, historical and List of biblical places, biblical sites, and unique geography also drawing tourists. Israel's security problems have taken their toll on the industry, but the number of incoming tourists is on the rebound. In 2017, a record of 3.6 million tourists visited Israel, yielding a 25 percent growth since 2016 and contributed NIS 20 billion to the Israeli economy.
Energy
Israel began producing natural gas from its own offshore gas fields in 2004. Between 2005 and 2012, Israel had imported gas from Egypt via the al-Arish–Ashkelon pipeline, which was terminated due to Egyptian crisis (2011–14), Egyptian Crisis of 2011–14. In 2009, a Natural gas in Israel, natural gas reserve, Tamar gas field, Tamar, was found near the coast of Israel. A second natural gas reserve, Leviathan gas field, Leviathan, was discovered in 2010. The natural gas reserves in these two fields (Leviathan has around 19 trillion cubic feet) could make Israel energy secure for more than 50 years. In 2013, Israel began commercial production of natural gas from the Tamar field. , Israel produced over 7.5 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas a year. Israel had 199 billion cubic meters (bcm) of proven reserves of natural gas as of the start of 2016. The Leviathan gas field started production in 2019. Ketura Sun is Israel's first commercial solar field. Built in early 2011 by the Arava Power Company on Ketura, Israel, Kibbutz Ketura, Ketura Sun covers twenty acres and is expected to produce green energy amounting to 4.95 megawatts (MW). The field consists of 18,500 Photovoltaics, photovoltaic panels made by Suntech Power, Suntech, which will produce about 9 gigawatt-hours (GWh) of electricity per year. In the next twenty years, the field will spare the production of some 125,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide. The field was inaugurated on 15 June 2011. On 22 May 2012 Arava Power Company announced that it had reached financial close on an additional 58.5 MW for 8 projects to be built in the Arava and the Negev valued at 780 million NIS or approximately $204 million.Real estate
Housing prices in Israel are listed in the top third, with an average of 150 salaries required to buy an apartment. As of 2022, there are about 2.7 million properties in Israel, with an annual increase of more than 50,000. However, the demand for housing exceeds supply, with a shortage of about 200,000 apartments as of 2021, and thus rising house prices. As a result, by 2021 housing prices rose by 5.6%. High prices do not stop Israelis from buying properties. In 2021, Israelis took a record of NIS 116.1 billion in mortgages, an increase of 50% from 2020.Culture
Israel's diverse culture stems from the diversity of its population. Jews from diaspora communities around the world brought their cultural and religious traditions back with them, creating a melting pot of Jewish customs and beliefs. Arab influences are present in many cultural spheres, such as Architecture of Israel, architecture, Music of Israel, music, and Israeli cuisine, cuisine. Israel is the only country in the world where life revolves around the Hebrew calendar. Public holidays in Israel, Work and school holidays are determined by the Jewish holidays, and the official day of rest is Saturday, the Shabbat, Jewish Sabbath.Literature
 Israeli literature is primarily Modern Hebrew poetry, poetry and prose written in Hebrew language, Hebrew, as part of the Revival of the Hebrew language, renaissance of Hebrew as a spoken language since the mid-19th century, although a small body of literature is published in other languages, such as English. By law, two copies of all printed matter published in Israel must be deposited in the National Library of Israel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. In 2001, the law was amended to include audio and video recordings, and other non-print media. In 2016, 89 percent of the 7,300 books transferred to the library were in Hebrew.
In 1966, Shmuel Yosef Agnon shared the Nobel Prize in Literature with German Jewish author Nelly Sachs. Leading Israeli poets have been Yehuda Amichai, Nathan Alterman, Leah Goldberg, and Rachel Bluwstein. Internationally famous contemporary Israeli novelists include Amos Oz, Etgar Keret and David Grossman. The Israeli-Arab satirist Sayed Kashua (who writes in Hebrew) is also internationally known. Israel has also been the home of Emile Habibi, whose novel ''The Secret Life of Saeed: The Pessoptimist'', and other writings, won him the Israel prize for Arabic literature.
Israeli literature is primarily Modern Hebrew poetry, poetry and prose written in Hebrew language, Hebrew, as part of the Revival of the Hebrew language, renaissance of Hebrew as a spoken language since the mid-19th century, although a small body of literature is published in other languages, such as English. By law, two copies of all printed matter published in Israel must be deposited in the National Library of Israel at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. In 2001, the law was amended to include audio and video recordings, and other non-print media. In 2016, 89 percent of the 7,300 books transferred to the library were in Hebrew.
In 1966, Shmuel Yosef Agnon shared the Nobel Prize in Literature with German Jewish author Nelly Sachs. Leading Israeli poets have been Yehuda Amichai, Nathan Alterman, Leah Goldberg, and Rachel Bluwstein. Internationally famous contemporary Israeli novelists include Amos Oz, Etgar Keret and David Grossman. The Israeli-Arab satirist Sayed Kashua (who writes in Hebrew) is also internationally known. Israel has also been the home of Emile Habibi, whose novel ''The Secret Life of Saeed: The Pessoptimist'', and other writings, won him the Israel prize for Arabic literature.
Music and dance
 Music of Israel, Israeli music contains musical influences from all over the world; Mizrahi music, Mizrahi and Sephardic music, Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic melodies, Greek music in Israel, Greek music, jazz, and pop rock are all part of the music scene. Among Israel's world-renowned orchestras is the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra, which has been in operation for over seventy years and today performs more than two hundred concerts each year. Itzhak Perlman, Pinchas Zukerman and Ofra Haza are among the internationally acclaimed musicians born in Israel. Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest, Israel has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest nearly every year since 1973, winning the competition four times and hosting it twice. Eilat has hosted its own international music festival, the Red Sea Jazz Festival, every summer since 1987. The nation's canonical folk music, folk songs, known as "Songs of the Land of Israel," deal with the experiences of the pioneers in building the Jewish homeland.
Music of Israel, Israeli music contains musical influences from all over the world; Mizrahi music, Mizrahi and Sephardic music, Hasidic Judaism, Hasidic melodies, Greek music in Israel, Greek music, jazz, and pop rock are all part of the music scene. Among Israel's world-renowned orchestras is the Israel Philharmonic Orchestra, which has been in operation for over seventy years and today performs more than two hundred concerts each year. Itzhak Perlman, Pinchas Zukerman and Ofra Haza are among the internationally acclaimed musicians born in Israel. Israel in the Eurovision Song Contest, Israel has participated in the Eurovision Song Contest nearly every year since 1973, winning the competition four times and hosting it twice. Eilat has hosted its own international music festival, the Red Sea Jazz Festival, every summer since 1987. The nation's canonical folk music, folk songs, known as "Songs of the Land of Israel," deal with the experiences of the pioneers in building the Jewish homeland.
Cinema and theatre
Ten Israeli films List of Israeli submissions for the Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, have been final nominees for Academy Award for Best Foreign Language Film, Best Foreign Language Film at the Academy Awards since the establishment of Israel. The 2009 movie ''Ajami (film), Ajami'' was the third consecutive nomination of an Israeli film. Palestinian Israeli filmmakers have made a number of films dealing with the Arab-Israeli conflict and the status of Palestinians within Israel, such as Mohammed Bakri's 2002 film ''Jenin, Jenin'' and ''The Syrian Bride''. Continuing the strong theatrical traditions of the Yiddish theatre in Eastern Europe, Israel maintains a vibrant theatre scene. Founded in 1918, Habima Theatre in Tel Aviv is Israel's oldest repertory theater company and national theater.Media
The 2017 ''Freedom of the Press (report), Freedom of the Press'' annual report by Freedom House ranked Israel as the MENA, Middle East and North Africa's most free country, and 64th globally. In the 2017 Press Freedom Index by Reporters Without Borders, Israel (including "Israel extraterritorial" since 2013 ranking) was placed 91st of 180 countries, first in the Middle East and North Africa region. Reporters Without Borders noted that "Palestinian journalists are systematically subjected to violence as a result of their coverage of events in the West Bank". More than fifty Palestinian journalists have been killed by Israel since 2001.Museums
 The Israel Museum in Jerusalem is one of Israel's most important cultural institutions and houses the Dead Sea Scrolls, along with an extensive collection of Judaica and European art. Israel's national The Holocaust, Holocaust museum, Yad Vashem, is the world central archive of Holocaust-related information. ANU - Museum of the Jewish People on the campus of Tel Aviv University, is an interactive museum devoted to the history of Jewish communities around the world. Apart from the major museums in large cities, there are high-quality art spaces in many towns and kibbutzim. Mishkan LeOmanut in kibbutz Ein Harod (Meuhad), Ein Harod Meuhad is the largest art museum in the north of the country.
Israel has the highest number of museums per capita in the world. Several Israeli museums are devoted to Islamic culture, including the Rockefeller Museum and the L. A. Mayer Institute for Islamic Art, both in Jerusalem. The Rockefeller specializes in archaeological remains from the Ottoman and other periods of Middle East history. It is also the home of the first hominid fossil skull found in Western Asia, called Galilee Man. A cast of the skull is on display at the Israel Museum.
The Israel Museum in Jerusalem is one of Israel's most important cultural institutions and houses the Dead Sea Scrolls, along with an extensive collection of Judaica and European art. Israel's national The Holocaust, Holocaust museum, Yad Vashem, is the world central archive of Holocaust-related information. ANU - Museum of the Jewish People on the campus of Tel Aviv University, is an interactive museum devoted to the history of Jewish communities around the world. Apart from the major museums in large cities, there are high-quality art spaces in many towns and kibbutzim. Mishkan LeOmanut in kibbutz Ein Harod (Meuhad), Ein Harod Meuhad is the largest art museum in the north of the country.
Israel has the highest number of museums per capita in the world. Several Israeli museums are devoted to Islamic culture, including the Rockefeller Museum and the L. A. Mayer Institute for Islamic Art, both in Jerusalem. The Rockefeller specializes in archaeological remains from the Ottoman and other periods of Middle East history. It is also the home of the first hominid fossil skull found in Western Asia, called Galilee Man. A cast of the skull is on display at the Israel Museum.
Cuisine
 Israeli cuisine includes local dishes as well as Jewish cuisine brought to the country by immigrants from the Jewish diaspora, diaspora. Since the establishment of the state in 1948, and particularly since the late 1970s, an Israeli fusion cuisine has developed. Israeli cuisine has adopted, and continues to adapt, elements of the Cuisine of the Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi, Cuisine of the Sephardic Jews, Sephardi, and Ashkenazi cuisine, Ashkenazi styles of cooking. It incorporates many foods traditionally eaten in the Levantine cuisine, Levantine, Arab cuisine, Arab, Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines, such as falafel, hummus, shakshouka, couscous, and za'atar. Schnitzel, pizza, hamburgers, French fries, rice and salad are also common in Israel.
Roughly half of the Israeli-Jewish population attests to keeping kosher at home.Julia Bernstein
Israeli cuisine includes local dishes as well as Jewish cuisine brought to the country by immigrants from the Jewish diaspora, diaspora. Since the establishment of the state in 1948, and particularly since the late 1970s, an Israeli fusion cuisine has developed. Israeli cuisine has adopted, and continues to adapt, elements of the Cuisine of the Mizrahi Jews, Mizrahi, Cuisine of the Sephardic Jews, Sephardi, and Ashkenazi cuisine, Ashkenazi styles of cooking. It incorporates many foods traditionally eaten in the Levantine cuisine, Levantine, Arab cuisine, Arab, Middle Eastern cuisine, Middle Eastern and Mediterranean cuisine, Mediterranean cuisines, such as falafel, hummus, shakshouka, couscous, and za'atar. Schnitzel, pizza, hamburgers, French fries, rice and salad are also common in Israel.
Roughly half of the Israeli-Jewish population attests to keeping kosher at home.Julia Bernstein''Food for Thought: Transnational Contested Identities and Food Practices of Russian-Speaking Jewish Migrants in Israel and Germany,''
Campus Verlag, 2010 pp. 227, 233–234. Kosher restaurants, though rare in the 1960s, make up around a quarter of the total , perhaps reflecting the largely secular values of those who dine out.Yael Raviv
''Falafel Nation,''
University of Nebraska Press, 2015 Hotel restaurants are much more likely to serve kosher food. The non-kosher retail market was traditionally sparse, but grew rapidly and considerably following 1990s Post-Soviet aliyah, the influx of immigrants from the post-Soviet states during the 1990s. Together with non-kosher fish, rabbits and ostriches, pork—often called "white meat" in IsraelBernstein
pp. 231–233
—is produced and consumed, though Religious restrictions on the consumption of pork, it is forbidden by both Judaism and Islam.
Sports
 The most popular spectator sports in Israel are association football and basketball. The Israeli Premier League is the country's premier football league, and the Israeli Basketball Premier League is the premier basketball league. Maccabi Haifa F.C., Maccabi Haifa, Maccabi Tel Aviv F.C., Maccabi Tel Aviv, Hapoel Tel Aviv F.C., Hapoel Tel Aviv and Beitar Jerusalem F.C., Beitar Jerusalem are the largest List of football clubs in Israel, football clubs. Maccabi Tel Aviv, Maccabi Haifa and Hapoel Tel Aviv have competed in the UEFA Champions League and Hapoel Tel Aviv reached the UEFA Cup quarter-finals. Israel hosted and won the 1964 AFC Asian Cup; in 1970 the Israel national football team qualified for the 1970 FIFA World Cup, FIFA World Cup, the only time it participated in the World Cup. The 1974 Asian Games, held in Tehran, were the last Asian Games in which Israel Israel at the Asian Games, participated, plagued by the Arab countries that Boycotts of Israel in sports, refused to compete with Israel. Israel was excluded from the 1978 Asian Games and since then has not competed in Asian sport events. In 1994, UEFA agreed to admit Israel, and its football teams now compete in Europe. Maccabi Tel Aviv B.C. has won the FIBA European Champions Cup and EuroLeague records and statistics, European championship in basketball six times. In 2016, the country was chosen as a host for the EuroBasket 2017.
Israel has won Israel at the Olympics, nine Olympic medals since its first win 1992 Summer Olympics, in 1992, including a gold medal in Sailing at the 2004 Summer Olympics – Men's Mistral One Design, windsurfing at the 2004 Summer Olympics. Israel has won Israel at the Paralympics, over 100 gold medals in the Paralympic Games and is ranked 20th in the All-time Paralympic Games medal table, all-time medal count. The 1968 Summer Paralympics were hosted by Israel. The Maccabiah Games, an Olympic-style event for List of Jews in sports, Jewish and Israeli athletes, was inaugurated in the 1930s, and has been held every four years since then. Israeli tennis champion Shahar Pe'er ranked 11th in the world on 31 January 2011. Krav Maga, a martial art developed by Jewish ghetto defenders during the struggle against fascism in Europe, is used by the Israeli security forces and police. Its effectiveness and practical approach to self-defense, have won it widespread admiration and adherence around the world.
The most popular spectator sports in Israel are association football and basketball. The Israeli Premier League is the country's premier football league, and the Israeli Basketball Premier League is the premier basketball league. Maccabi Haifa F.C., Maccabi Haifa, Maccabi Tel Aviv F.C., Maccabi Tel Aviv, Hapoel Tel Aviv F.C., Hapoel Tel Aviv and Beitar Jerusalem F.C., Beitar Jerusalem are the largest List of football clubs in Israel, football clubs. Maccabi Tel Aviv, Maccabi Haifa and Hapoel Tel Aviv have competed in the UEFA Champions League and Hapoel Tel Aviv reached the UEFA Cup quarter-finals. Israel hosted and won the 1964 AFC Asian Cup; in 1970 the Israel national football team qualified for the 1970 FIFA World Cup, FIFA World Cup, the only time it participated in the World Cup. The 1974 Asian Games, held in Tehran, were the last Asian Games in which Israel Israel at the Asian Games, participated, plagued by the Arab countries that Boycotts of Israel in sports, refused to compete with Israel. Israel was excluded from the 1978 Asian Games and since then has not competed in Asian sport events. In 1994, UEFA agreed to admit Israel, and its football teams now compete in Europe. Maccabi Tel Aviv B.C. has won the FIBA European Champions Cup and EuroLeague records and statistics, European championship in basketball six times. In 2016, the country was chosen as a host for the EuroBasket 2017.
Israel has won Israel at the Olympics, nine Olympic medals since its first win 1992 Summer Olympics, in 1992, including a gold medal in Sailing at the 2004 Summer Olympics – Men's Mistral One Design, windsurfing at the 2004 Summer Olympics. Israel has won Israel at the Paralympics, over 100 gold medals in the Paralympic Games and is ranked 20th in the All-time Paralympic Games medal table, all-time medal count. The 1968 Summer Paralympics were hosted by Israel. The Maccabiah Games, an Olympic-style event for List of Jews in sports, Jewish and Israeli athletes, was inaugurated in the 1930s, and has been held every four years since then. Israeli tennis champion Shahar Pe'er ranked 11th in the world on 31 January 2011. Krav Maga, a martial art developed by Jewish ghetto defenders during the struggle against fascism in Europe, is used by the Israeli security forces and police. Its effectiveness and practical approach to self-defense, have won it widespread admiration and adherence around the world.
Chess
 Chess is a leading sport in Israel and is enjoyed by people of all ages. There are many Israeli grandmasters and List of Israeli chess players, Israeli chess players have won a number of youth world championships. Israel stages an annual international Israeli Chess Championship, championship and hosted the World Team Chess Championship in 2005. The Ministry of Education and the FIDE, World Chess Federation agreed upon a project of teaching chess within Israeli schools, and it has been introduced into the curriculum of some schools. The city of Beersheba has become a national chess center, with the game being taught in the city's kindergartens. Owing partly to Soviet immigration, it is home to the largest number of Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmasters of any city in the world. The Israeli chess team won the silver medal at the 38th Chess Olympiad, 2008 Chess Olympiad and the bronze, coming in third among 148 teams, at the 39th Chess Olympiad, 2010 Olympiad. Israeli grandmaster Boris Gelfand won the Chess World Cup 2009 and the World Chess Championship 2012#Candidates tournament, 2011 Candidates Tournament for the right to challenge the world champion. He lost the World Chess Championship 2012 to reigning world champion Viswanathan Anand, Anand after a speed-chess tie breaker.
Chess is a leading sport in Israel and is enjoyed by people of all ages. There are many Israeli grandmasters and List of Israeli chess players, Israeli chess players have won a number of youth world championships. Israel stages an annual international Israeli Chess Championship, championship and hosted the World Team Chess Championship in 2005. The Ministry of Education and the FIDE, World Chess Federation agreed upon a project of teaching chess within Israeli schools, and it has been introduced into the curriculum of some schools. The city of Beersheba has become a national chess center, with the game being taught in the city's kindergartens. Owing partly to Soviet immigration, it is home to the largest number of Grandmaster (chess), chess grandmasters of any city in the world. The Israeli chess team won the silver medal at the 38th Chess Olympiad, 2008 Chess Olympiad and the bronze, coming in third among 148 teams, at the 39th Chess Olympiad, 2010 Olympiad. Israeli grandmaster Boris Gelfand won the Chess World Cup 2009 and the World Chess Championship 2012#Candidates tournament, 2011 Candidates Tournament for the right to challenge the world champion. He lost the World Chess Championship 2012 to reigning world champion Viswanathan Anand, Anand after a speed-chess tie breaker.
See also
* Index of Israel-related articles * Outline of IsraelReferences
Notes
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Israel
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency. * * * * {{Portal bar, Israel, Judaism, Middle East, Asia Israel, 1948 establishments in Asia Arabic-speaking countries and territories Articles containing video clips Countries in Asia Eastern Mediterranean Jewish polities States and territories established in 1948 Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Middle Eastern countries Levant Western Asian countries Near Eastern countries Palestine (region), * Political entities in the Land of Israel Republics