Islamic archaeology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Islamic archaeology involves the recovery and scientific investigation of the material remains of past cultures that can illuminate the periods and descriptions in the Quran, and early Islam. The science of archaeology grew out of the older multi-disciplinary study known as
Islamic archaeology involves the recovery and scientific investigation of the material remains of past cultures that can illuminate the periods and descriptions in the Quran, and early Islam. The science of archaeology grew out of the older multi-disciplinary study known as
 Islamic archaeology involves the recovery and scientific investigation of the material remains of past cultures that can illuminate the periods and descriptions in the Quran, and early Islam. The science of archaeology grew out of the older multi-disciplinary study known as
Islamic archaeology involves the recovery and scientific investigation of the material remains of past cultures that can illuminate the periods and descriptions in the Quran, and early Islam. The science of archaeology grew out of the older multi-disciplinary study known as antiquarianism
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifacts, archaeological and historic sit ...
. The Egyptian "Antiquities Authority
A Department of Antiquities is a government department with responsibility for cultural heritage management, archaeological research and regulating antiquities trading in some countries. Many were established by British and French colonial adminis ...
" was established in 1858 and remains a government organization which serves to protect and preserve the heritage and ancient history of Egypt.
Early pioneers in Islamic archaeology included Eduard Glaser
Eduard Glaser (15 March 1855 ã 7 May 1908) was an Austrian Arabist and archaeologist. He was one of the first Europeans to explore South Arabia. He collected thousands of inscriptions in Yemen that are today held by the Kunsthistorisches Museu ...
and Alois Musil. Khaled al-Asaad was principal custodian of the Palmyra site from 1963, overseeing its elevation to a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Some of the earliest areas investigated in Saudi Arabia include Al Faw Village and Madain Saleh
Hegra ( grc, Ã¥ö°üöÝ), known to Muslims as Al-Hijr (), also known as Madaãin Salih ( ar, ì
ìÄ₤ìÄÏÄÎìì ÄçìÄÏììÄÙ, madáò¥in ÿÂáliáË, lit=Cities of Salih), is an archaeological site located in the area of Al-'Ula within Medina Provin ...
. Jodi Magness has covered the archaeology of early Islamic settlement in Palestine. The Museum of Islamic Archaeology and Art of Iran was opened in 1972. It houses tools dating back 30,000 to 35,000 years and crafted by Mousterian Neanderthals in Yafteh. Among the oldest human artifacts are 9,000-year-old and animal figurines from the Sarab mound in Kermanshah Province. The Gaza Museum of Archaeology was opened in 2008. Objects protected from display include Aphrodite in revealing gown, images of ancient deities and oil lamps featuring menorahs. Since 2016 the Al-Qasimi Professor of African and Islamic Archaeology at the University of Exeter, Timothy Insoll, has directed the Centre for Islamic Archaeology. Insoll is on the editorial board of the ''Journal of Islamic Archaeology''.
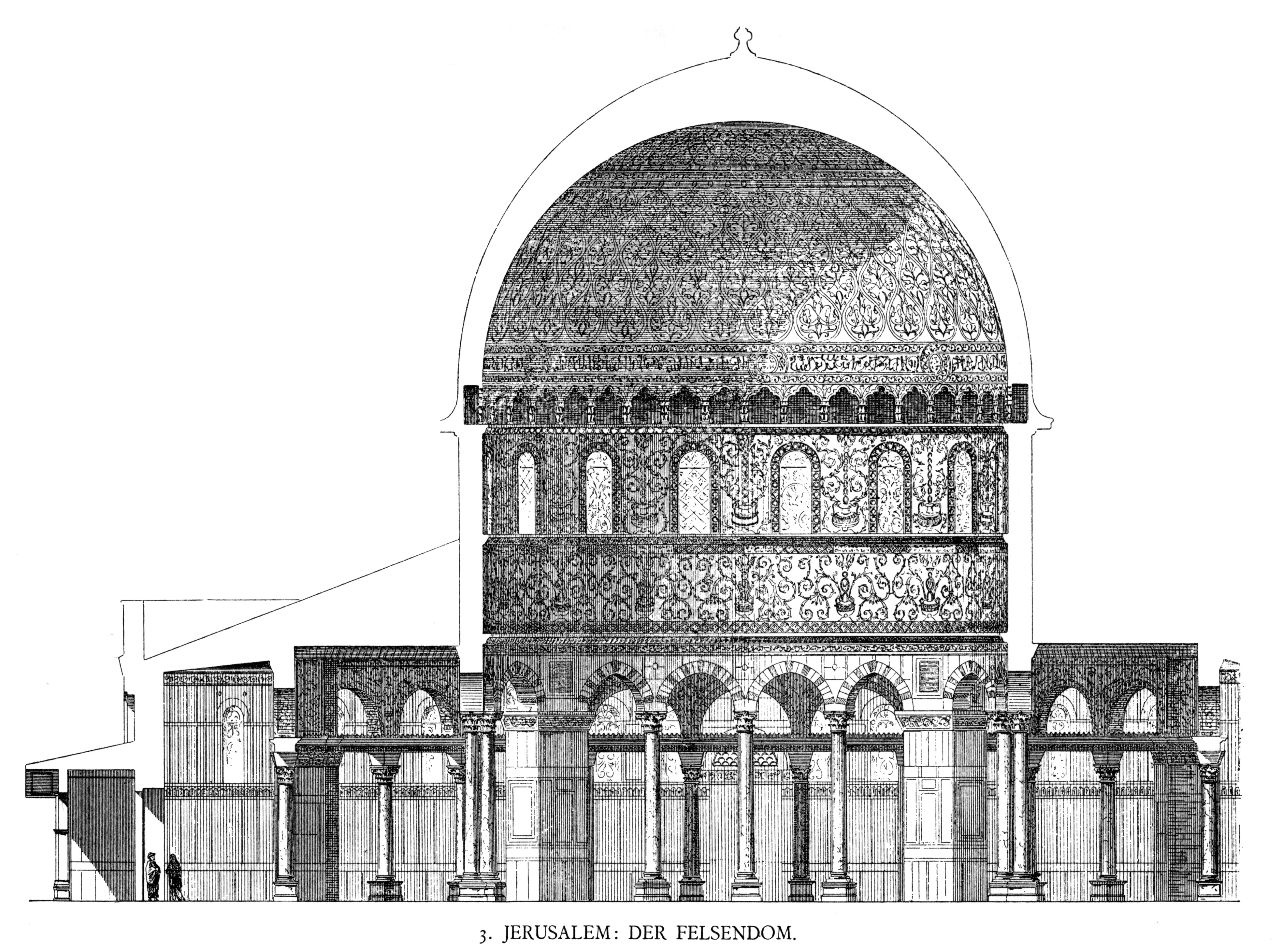
The oldest extant Islamic monument is The Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, ìÄ´Äˋ ÄÏìÄçÄÛÄÝÄˋ, Qubbat aÿÈ-ÿÂakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
in Jerusalem which contains some of the earliest extant quránic text, dated to 692CE. They vary from today's standard text (mainly changes from the first to the third person) and are mixed with pious inscriptions absent from the Quran. During a six-week period in 1833, Frederick Catherwood produced the first known detailed survey. Pre-Islamic In-situ archaeology includes south Arabian 4th CE rock inscriptions that evidence fewer pagan expressions and the start in use of the monotheistic " rahmán".Robert Schick, ''Archaeology and the Quran'', Encyclopaedia of the Qur'an Fewer archaeological surveys have taken place in the Arabian peninsula and are considered taboo in Mecca (''The Noble
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in ...
'') and Medina (''The Enlightened City
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Mû¥nevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madá¨nah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
''). There is no architecture from the time of Mohammed in either city and the battlefields of the Quran have not been unearthed. Known settlements from the time, such as Khaybar, remain uninvestigated. Archaeologial evidence for Quranic narratives yet to be uncovered include that for the ò¢ád who built monuments and strongholds at every high point and their fate ''evident from the remains of their dwellings.''Quran 46
Al-Ahqaf ( ar, ÄÏìÄÈÄÙìÄÏì, ; "the sand dunes" or "the winding sand tracts") is the 46th chapter (''surah'') of the Qur'an with 35 verses (''ayat''). This is the seventh and last chapter starting with the Muqattaò¢at letters ''He (letter), H ...
A political dispute in the Uttar Pradesh city of Ayodhya, as noted by academic, K. K. Muhammed, has revolved around archaeological Issues: whether an archaeological plot, believed the temple birthplace of the Hindu deity Rama was demolished or modified to create the Babri Masjid
Babri Masjid (IAST: BábarᨠMasjid; meaning ''Mosque of Babur'') was a mosque in Ayodhya, India, at a site believed by many Hindus to be the birthplace of Hindu deity Rama. It has been a focus of dispute between the Hindu and Muslim communi ...
mosque.; ;
See also
*Archaeology of Afghanistan
Located on the strategic crossroads of Iran, India, China and Central Asia, Afghanistan boasts a diverse cultural and religious history. The soil is rich with archaeological treasures and art that have for decades come under threat of destruction ...
*Archaeology of Qatar
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes ...
*Archaeology of Iran The Archaeology of Iran encompasses the following subjects:
Archaeological discoveries in Iran
Archaeological sites in Iran:
*Rock art in Iran
*Great Wall of Gorgan
*Hasanlu Lovers
* Islamic ceramics from the Susa site
* Achaemenid inscription in t ...
* Archaeology of Saudi Arabia
References
{{reflist Archaeological sub-disciplines