Irian Ships 201 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
New Guinea (;
 The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from
The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from

 New Guinea is an island to the north of the
New Guinea is an island to the north of the  The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a
The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a  Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of
Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of
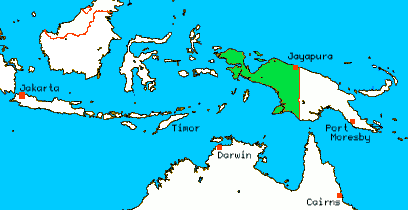
 The island of New Guinea is divided politically into roughly equal halves across a north–south line:
* The western portion of the island located west of 141°E longitude (except for a small section of territory to the east of the
The island of New Guinea is divided politically into roughly equal halves across a north–south line:
* The western portion of the island located west of 141°E longitude (except for a small section of territory to the east of the
 The current population of the island of New Guinea is about fifteen million. Many believe human habitation on the island dates to as early as 50,000 BC, and first settlement possibly dating back to 60,000 years ago has been proposed. The island is presently populated by almost a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world.
The current population of the island of New Guinea is about fifteen million. Many believe human habitation on the island dates to as early as 50,000 BC, and first settlement possibly dating back to 60,000 years ago has been proposed. The island is presently populated by almost a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world.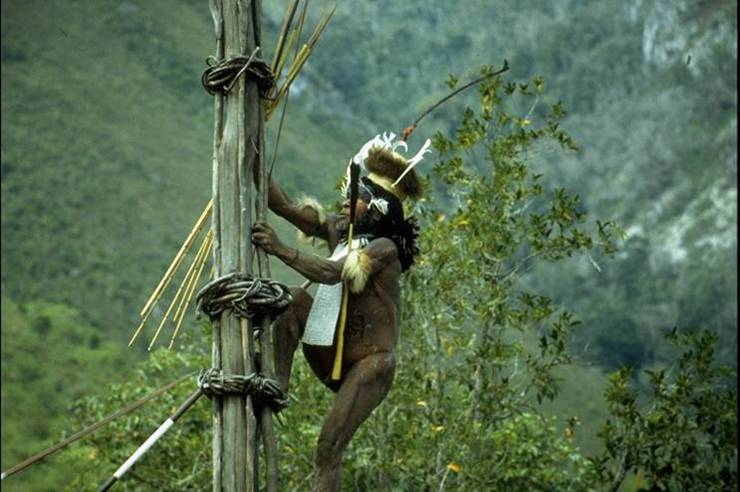  Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea at a time (either side of the
Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea at a time (either side of the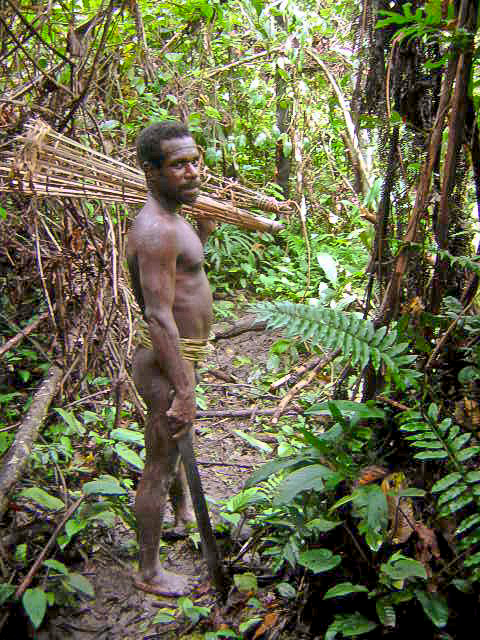  The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from
The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from


 As of 2020, the Western portion of New Guinea, Papua and West Papua, accounts for 54% of the island's primary forest and about 51% of the island's total tree cover, according to satellite data.
As of 2020, the Western portion of New Guinea, Papua and West Papua, accounts for 54% of the island's primary forest and about 51% of the island's total tree cover, according to satellite data.
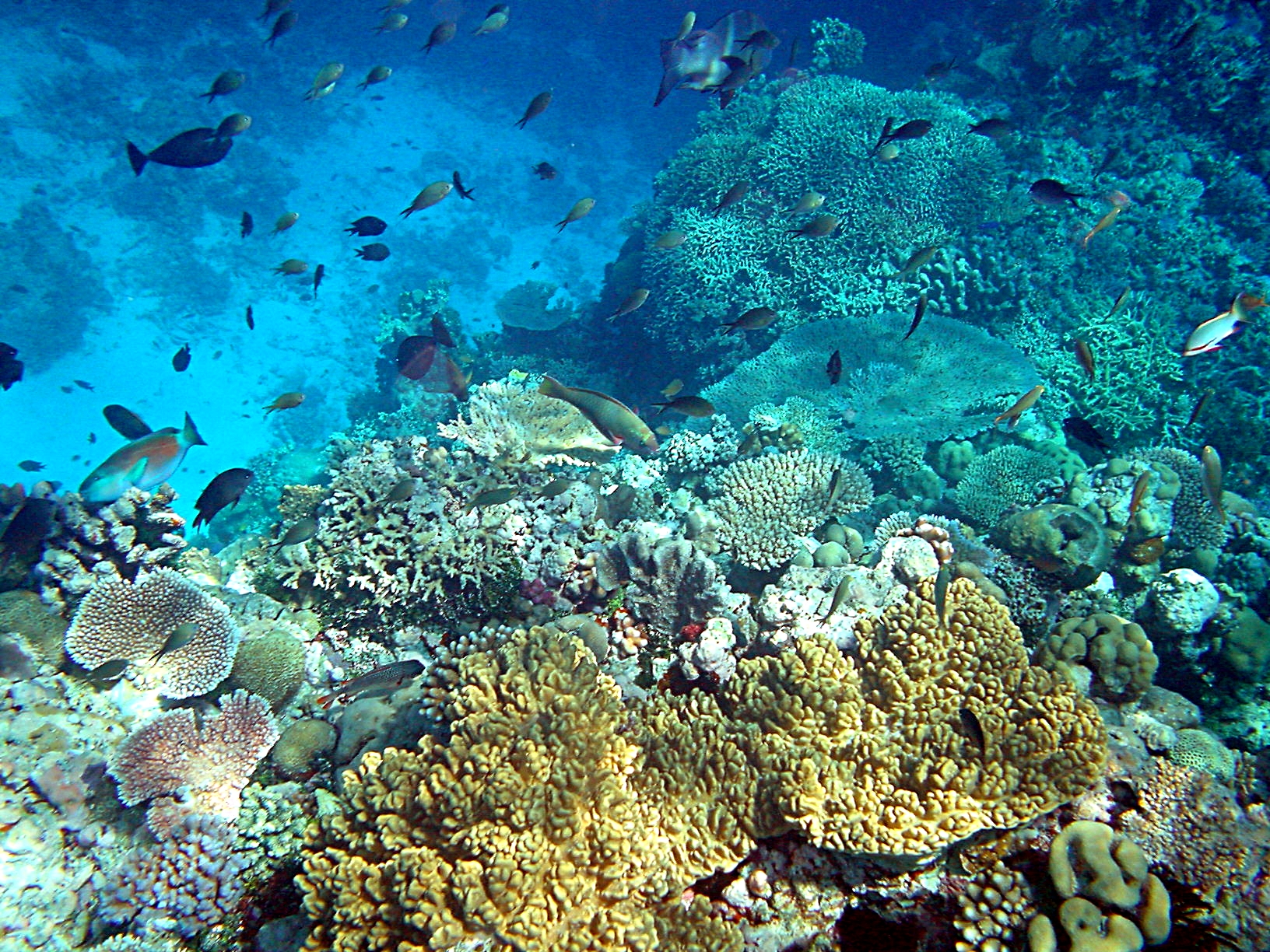

 The first inhabitants
The first inhabitants
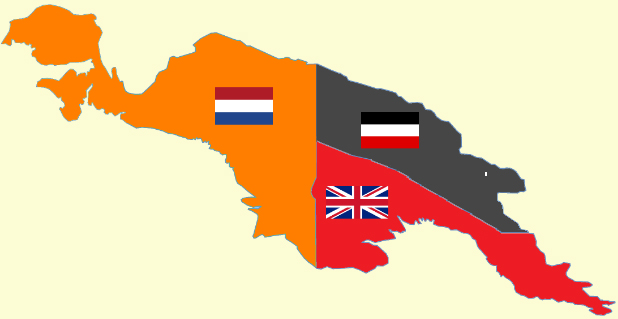 A successive European claim occurred in 1828, when the Netherlands formally claimed the western half of the island as
A successive European claim occurred in 1828, when the Netherlands formally claimed the western half of the island as 
 Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories were invaded in 1942 by the
Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories were invaded in 1942 by the
 During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the elected
During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the elected
Autonomy isn’t independence; Indonesian democracy stops in Papua
 From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a Papuan People's Assembly (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua;
From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a Papuan People's Assembly (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua;
Facsimile of material from "The Discovery of New Guinea" by George Collingridge
Scientists hail discovery of hundreds of new species in remote New Guinea
PapuaWeb official website
* {{Authority control Islands of the Pacific Ocean Divided regions International islands Melanesia Islands of Indonesia Islands of Papua New Guinea Former Spanish colonies
Hiri Motu
Hiri Motu, also known as Police Motu, Pidgin Motu, or just Hiri, is a language of Papua New Guinea, which is spoken in surrounding areas of Port Moresby (Capital of Papua New Guinea).
It is a simplified version of Motu, from the Austronesian l ...
: ''Niu Gini''; id, Papua, or , historically ) is the world's second-largest island with an area of . Located in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
in the southwestern Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, the island is separated from Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
by the wide Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island ...
. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the independent state of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
. The western half, known as Western New Guinea
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region ...
, forms a part of Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
and is organized as the provinces of Papua, Central Papua
Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Tengah) is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencie ...
, Highland Papua
Highland Papua ( id, Papua Pegunungan) is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official es ...
, South Papua
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Selatan), is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2 ...
, Southwest Papua
Southwest Papua ( id, Papua Barat Daya) is a province of Indonesia, and is a fraction of Western New Guinea. Despite being named southwest, it is a misnomer and this province is actually located in the northwest edge of Papua. The area that belo ...
, and West Papua. The largest cities on the island are Jayapura
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso ...
(capital of Papua, Indonesia) and Port Moresby
(; Tok Pisin: ''Pot Mosbi''), also referred to as Pom City or simply Moresby, is the capital and largest city of Papua New Guinea. It is one of the largest cities in the southwestern Pacific (along with Jayapura) outside of Australia and New Z ...
(capital of Papua New Guinea).
Names
 The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from
The island has been known by various names:
The name ''Papua'' was used to refer to parts of the island before contact with the West. Its etymology is unclear; one theory states that it derived from Tidore
Tidore ( id, Kota Tidore Kepulauan, lit. "City of Tidore Islands") is a city, island, and archipelago in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia, west of the larger island of Halmahera. Part of North Maluku Province, the city includes the island ...
, the language used by the Sultanate of Tidore
The Sultanate of Tidore (Indonesian: كسلطانن تيدوري, ''Kesultanan Tidore'', sometimes ''Kerajaan Tidore'') was a sultanate in Southeast Asia, centered on Tidore in the Maluku Islands (presently in North Maluku Province). It was also kn ...
. Expedition by Sultan of Tidore
The Sultanate of Tidore (Indonesian language, Indonesian: كسلطانن تيدوري, ''Kesultanan Tidore'', sometimes ''Kerajaan Tidore'') was a sultanate in Southeast Asia, centered on Tidore in the Maluku Islands (presently in North Maluku Prov ...
, with Sahmardan, ''Sangaji'' of Patani
Patani Darussalam ( Bahasa Malayu Arabic : , also sometimes Patani Raya or Patani Besar, "Greater Patani"; th, ปาตานี) is a historical region in the Malay peninsula. It includes the southern Thai provinces of Pattani, Yala (Ja ...
and Gurabesi Gurabesi was a legendary Papuan leader from Biak in West New Guinea, present-day Indonesia, who had a large role in tying part of the Papuans to the Islamic Sultanate of Tidore. He is commonly believed to have flourished in the 15th or early 16th c ...
managed to conquer some areas in New Guinea which was then reorganised to ''Korano Ngaruha'' ( "Four Kings") or Raja Ampat
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested fr ...
, ''Papo Ua Gamsio'' ( "The Papua Nine ''Negeri''"), and ''Mafor Soa Raha'' ( The Mafor "Four ''Soa''"). The name comes from the words ''papo'' ("to unite") and ''ua'' (negation), which means "not united" or, "territory that geographically is far away (and thus not fully integrated to Tidore proper)".
Anton Ploeg reports that the word ''papua'' is often said to be derived from the Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
word ''papua'' or ''pua-pua'', meaning "frizzly-haired", referring to the very curly hair of the inhabitants of these areas. Another possibility, put forward by Sollewijn Gelpke in 1993, is that it comes from the Biak
Biak is an island located in Cenderawasih Bay near the northern coast of Papua (province), Papua, an Indonesian province, and is just northwest of New Guinea. Biak is the largest island in its small archipelago, and has many atolls, reefs, and c ...
phrase ''sup i papwa'', which means "the land below he sunset
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
, and refers to the islands west of the Bird's Head
The Bird's Head Peninsula ( Indonesian: ''Kepala Burung'', nl, Vogelkop) or Doberai Peninsula (''Semenanjung Doberai''), is a large peninsula that makes up the northwest portion of the island of New Guinea, comprising the Indonesian provinces ...
, as far as Halmahera
Halmahera, formerly known as Jilolo, Gilolo, or Jailolo, is the largest island in the Maluku Islands. It is part of the North Maluku province of Indonesia, and Sofifi, the capital of the province, is located on the west coast of the island.
Hal ...
. The name ''Papua'' came to be associated with this area, and more especially with Halmahera, which was known to the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
by this name during the era of their colonization in this part of the world.
When Portuguese and Spanish explorers arrived on the island via the Spice Islands
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spices ar ...
, they also referred to the island as ''Papua''. However, Westerners, beginning with Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez Yñigo Ortiz de Retez ( ''fl.'' 1545) was a 16th-century Spanish maritime explorer of Basque origin, who navigated the northern coastline of the Pacific–Melanesian island of New Guinea, and is credited with bestowing the island's name (''"Nueva G ...
in 1545, used the name ''New Guinea'', referring to the similarities of the features of the indigenous peoples to those of native Africans of the Guinea region
Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the African coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.
Et ...
of the continent. The name is one of several toponyms
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of ''toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
sharing similar etymologies
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the form of words and ...
, ultimately meaning "land of the blacks" or similar meanings, in reference to the dark skin
Dark skin is a type of human skin color that is rich in melanin pigments. People with very dark skin are often referred to as "black people", although this usage can be ambiguous in some countries where it is also used to specifically refer to d ...
of the inhabitants.
The Dutch, who arrived later under Jacob Le Maire
Jacob Le Maire (c. 1585 – 22 December 1616) was a Dutch mariner who circumnavigated the earth in 1615 and 1616. The strait between Tierra del Fuego and Isla de los Estados was named the Le Maire Strait in his honour, though not without controvers ...
and Willem Schouten
Willem Cornelisz Schouten ( – 1625) was a Dutch navigator for the Dutch East India Company. He was the first to sail the Cape Horn route to the Pacific Ocean.
Biography
Willem Cornelisz Schouten was born in c. 1567 in Hoorn, Holland, Seven ...
, called it ''Schouten island''. They later used this name only to refer to islands off the north coast of Papua proper, the Schouten Islands
The Schouten Islands ( id, Kepulauan Biak, also Biak Islands or Geelvink Islands) are an island group of Papua province, eastern Indonesia in the Cenderawasih Bay (or Geelvink Bay) 50 km off the north-western coast of the island of New ...
or Biak Island. When the Dutch colonized this island as part of the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
, they called it ''Nieuw Guinea''.
The name ''Irian'' was used in the Indonesian language to refer to the island and Indonesian province, as ''Irian Barat'' (West Irian) Province and later ''Irian Jaya'' Province. The name Irian was suggested during a tribal committee meeting in Tobati, Jayapura, formed by Atmoprasojo under van Eechoed, to decide on a new name because of the negative association of ''Papua''. Frans Kaisiepo
Frans Kaisiepo (10 October 1921 – 10 April 1979) was a Papuan politician and Indonesian nationalist. He served as the fourth Governor of Papua Province. In 1993, Kaisiepo was posthumously declared a National Hero of Indonesia ( id, Pahlawan N ...
, the committee leader, suggested the name from Mansren Koreri myths, ''Iri-an'' from the Biak language
Biak (''wós Vyak'' or "Biak language"; ''wós kovedi'' or "our language"; Indonesian: ''bahasa Biak''), also known as Biak-Numfor, Noefoor, Mafoor, Mefoor, Nufoor, Mafoorsch, Myfoorsch and Noefoorsch, is an Austronesian language of the South H ...
of Biak Island
Biak is an island located in Cenderawasih Bay near the northern coast of Papua, an Indonesian province, and is just northwest of New Guinea. Biak is the largest island in its small archipelago, and has many atolls, reefs, and corals.
The large ...
, meaning "hot land" referring to the local hot climate, but also from ''Iryan'' which means heated process as a metaphor for a land that is entering a new era. In Serui ''Iri-an'' ( "land-nation") means "pillar of nation", while in Merauke ''Iri-an'' ( "placed higher-nation") means "rising spirit" or "to rise". The name was promoted in 1945 by Marcus Kaisiepo, brother of Frans Kaisiepo
Frans Kaisiepo (10 October 1921 – 10 April 1979) was a Papuan politician and Indonesian nationalist. He served as the fourth Governor of Papua Province. In 1993, Kaisiepo was posthumously declared a National Hero of Indonesia ( id, Pahlawan N ...
. The name was politicized later by Marthin Indey, Silas Papare, and others with the Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
backronym
A backronym is an acronym formed from an already existing word by expanding its letters into the words of a phrase. Backronyms may be invented with either serious or humorous intent, or they may be a type of false etymology or folk etymology. The ...
''Ikut Republik Indonesia Anti Nederland'' ("Join the Republic of Indonesia Oppose the Netherlands"). The name was used until 2001, when ''Papua'' was again used for the island and the province. The name ''Irian'', which was originally favored by natives, is now considered to be a name imposed by the authority of Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
.
Geography
Australian mainland
Mainland Australia is the main landmass of the Australian continent, excluding the Aru Islands, New Guinea, Tasmania, and other Australian offshore islands. The landmass also constitutes the mainland of the territory governed by the Commonwealt ...
, south of the equator. It is isolated by the Arafura Sea
The Arafura Sea (or Arafuru Sea) lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea (also called Papua), which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.
Geography
The Arafura Sea is ...
to the west, and the Torres Strait
The Torres Strait (), also known as Zenadh Kes, is a strait between Australia and the Melanesian island of New Guinea. It is wide at its narrowest extent. To the south is Cape York Peninsula, the northernmost extremity of the Australian mai ...
and Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down the Australian northeast coast. Most of it is protected by the Fre ...
to the east. Sometimes considered to be the easternmost island of the Indonesian archipelago
The islands of Indonesia, also known as the Indonesian Archipelago ( id, Kepulauan Indonesia) or Nusantara, may refer either to the islands comprising the country of Indonesia or to the geographical groups which include its islands.
History ...
, it lies north of Australia's Top End
The Top End of Australia's Northern Territory is a geographical region encompassing the northernmost section of the Northern Territory, which aside from the Cape York Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Australian continent. It covers a ra ...
, the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria (, ) is a large, shallow sea enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea (the body of water that lies between Australia and New Guinea). The northern boundary is ...
and Cape York Peninsula
Cape York Peninsula is a large peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest unspoiled wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth’s last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación ...
, and west of the Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
and the Solomon Islands archipelago
The Solomon Islands (archipelago) is an island group in the western South Pacific Ocean, north-east of Australia. The archipelago is in the Melanesian subregion and bioregion of Oceania and forms the eastern boundary of the Solomon Sea. The ...
.
Politically, the western half of the island comprises five provinces of Indonesia
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''Roman province, provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire ...
: Papua, Central Papua
Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Tengah) is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencie ...
, Highland Papua
Highland Papua ( id, Papua Pegunungan) is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official es ...
, South Papua
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Selatan), is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2 ...
, and West Papua. The eastern half forms the mainland of the country of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
.
 The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a
The shape of New Guinea is often compared to that of a bird-of-paradise
The birds-of-paradise are members of the family Paradisaeidae of the order Passeriformes. The majority of species are found in eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia. The family has 44 species in 17 genera. The members of thi ...
(indigenous to the island), and this results in the usual names for the two extremes of the island: the Bird's Head Peninsula
The Bird's Head Peninsula ( Indonesian: ''Kepala Burung'', nl, Vogelkop) or Doberai Peninsula (''Semenanjung Doberai''), is a large peninsula that makes up the northwest portion of the island of New Guinea, comprising the Indonesian provinces o ...
in the northwest (''Vogelkop'' in Dutch, ''Kepala Burung'' in Indonesian; also known as the Doberai Peninsula), and the Bird's Tail Peninsula in the southeast (also known as the Papuan Peninsula
The Papuan Peninsula, also known as the Bird's Tail Peninsula, is a large peninsula in Papua New Guinea, southeast of the city of Lae, that makes up the southeastern portion of the island of New Guinea. The peninsula is the easternmost extent of t ...
).
A spine of east–west mountains, the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya , the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home ...
, dominates the geography of New Guinea, stretching over across the island, with many mountains over . The western half of the island contains the highest mountains in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
, with its highest point, Puncak Jaya
Puncak Jaya (; literally "Glorious Peak") or Carstensz Pyramid, Mount Jayawijaya or Mount Carstensz () on the island of New Guinea, with an elevation of , is the list of islands by highest point, highest mountain peak of an island on Earth. Th ...
, reaching an elevation of 4,884 m (16,023 ft). The tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snowp ...
is around elevation, and the tallest peaks contain equatorial glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s—which have been retreating since at least 1936. Various other smaller mountain ranges occur both north and west of the central ranges. Except in high elevations, most areas possess a warm humid climate throughout the year, with some seasonal variation associated with the northeast monsoon season.
 Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of
Another major habitat feature is the vast southern and northern lowlands. Stretching for hundreds of kilometres, these include lowland rainforests, extensive wetlands, savanna grasslands, and some of the largest expanses of mangrove forest in the world. The southern lowlands are the site of Lorentz National Park
Lorentz National Park is a national park located in Central Papua, Indonesia, in the southwest of western New Guinea. With an area of 25,056 km2 (9,674 mi2), it is the largest national park in Southeast Asia. In 1999 Lorentz was declare ...
, a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
. The northern lowlands are drained principally by the Mamberamo River
The Mamberamo (''Indonesian: Sungai Mamberamo'') is the second longest river on the island of New Guinea, after Sepik River (1,146 km) and third largest in Oceania by discharge (5,500 m3/s) volume after Fly River (7,500 m3/s) and Sepik (7,000 m3/ ...
and its tributaries on the western side, and by the Sepik
The Sepik () is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun (formerly West Sepi ...
on the eastern side. The more extensive southern lowlands are drained by a larger number of rivers, principally the Digul
The Digul River () is a major river in southern Papua (province), Papua province, Indonesia, on the island of New Guinea. It is the fourth longest river in New Guinea after Sepik River, Mamberamo River and Fly River. With a total length of and ...
in the west and the Fly
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwing ...
in the east. The largest island offshore, Dolak
Pulau Yos Sudarso or Pulau Dolok is an island separated only by the narrow Muli Strait from the main island of New Guinea. It is part of the Merauke Regency, in the Indonesian province of South Papua. The island is leaf-shaped, about long with a ...
, lies near the Digul estuary, separated by a strait so narrow it has been named a "creek".
New Guinea contains many of the world's ecosystem types: glacial, alpine tundra
Alpine tundra is a type of natural region or biome that does not contain trees because it is at high elevation, with an associated alpine climate, harsh climate. As the latitude of a location approaches the poles, the threshold elevation for alp ...
, savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
, montane
Montane ecosystems are found on the slopes of mountains. The alpine climate in these regions strongly affects the ecosystem because temperatures fall as elevation increases, causing the ecosystem to stratify. This stratification is a crucial f ...
and lowland rainforest, mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evoluti ...
s, wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s, lake and river ecosystem
River ecosystems are flowing waters that drain the landscape, and include the biotic (living) interactions amongst plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (nonliving) physical and chemical interactions of its many parts.Angelier, ...
s, seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the orde ...
es, and some of the richest coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
Co ...
s on the planet.
The entire length of the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya , the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home ...
system passes through New Guinea as a vast watershed. The northern rivers flow into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
, the southern rivers into the Arafura Sea
The Arafura Sea (or Arafuru Sea) lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea (also called Papua), which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.
Geography
The Arafura Sea is ...
and the Gulf of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of .
Geography
Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow i ...
. On the north side, the largest rivers are the Mamberamo, Sepik and Ramu.
Mamberamo
The Mamberamo (''Indonesian: Sungai Mamberamo'') is the second longest river on the island of New Guinea, after Sepik River (1,146 km) and third largest in Oceania by discharge (5,500 m3/s) volume after Fly River (7,500 m3/s) and Sepik (7,000 m3/ ...
was born from the confluence of two large inland rivers. Tariku comes from the west to the east and Taritatu from the east. These rivers meander through swamps with huge internal descents and then merge. The Mamberamo thus formed reaches the ocean by breaking through the Coastal Mountains. Mamberamo River is navigable to Marine Falls. The Sepik
The Sepik () is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun (formerly West Sepi ...
is a much more important river. Similarly, it collects water from a spacious pool. It is 1,100 kilometers from the Victor Emanuel Range
The Victor Emanuel Range is a limestone mountain range in the New Guinea Highlands of western Papua New Guinea. It was named after the King of Italy by the Italian naturalist Luigi D'Albertis while he was charting the course of the Fly River, whic ...
to the estuary, making it the longest river in New Guinea. The winding, muddy, sluggish river can be navigated for 500 km. Ramu
The Ramu River is a major river in northern Papua New Guinea. The headwaters of the river are formed in the Kratke Range from where it then travels about northwest to the Bismarck Sea.
Along the Ramu's course, it receives numerous tributaries ...
is a 650 km long river. Its lower section is navigable, but its upper flow is high-falling, fast-flowing. The energy of the river is used by a power plant near the city of Kainantu
Kainantu is a town in the Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea. It had some historical significance as an airstrip town during WWII. It functions primarily as a market town for local produce growers and cash croppers. It is located on the " Hig ...
. On the south side, the most significant rivers are Pulau, Digul, Fly, Kikori
Kikori is a small town in the Gulf Province of Papua New Guinea.
Kikori lies in the delta of the Kikori River at the head of the Gulf of Papua. This area is particularly biologically rich with a diversity of ecosystems and densely forested, with ...
and Purari. The largest river in the western part of the island is Digul
The Digul River () is a major river in southern Papua (province), Papua province, Indonesia, on the island of New Guinea. It is the fourth longest river in New Guinea after Sepik River, Mamberamo River and Fly River. With a total length of and ...
. It originates from the Star Mountains
The Star Mountains (Dutch (colonial)'': Sterrengebergte''; Indonesian'': Pegunungan Bintang'') are a mountain range in western Papua New Guinea and the eastern end of Highland Papua, Indonesia, stretching from the eastern end of Indonesia to the ...
, which rise to an altitude of 4,700 m. The coastal plain is bordered by a swamp world hundreds of kilometers wide. Digul is the main transport route to the fertile hills and mountains within the island.
The river Fly
Flies are insects of the Order (biology), order Diptera, the name being derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwing ...
is born near the eastern branches of the Digul. It is named after one of the ships of the English Royal Fleet, which first sailed into the mouth of the river in 1845. The total length of the river is 1,050 km. Smaller boats can sail 900 km on the river. The estuary section, which decomposes into islands, is 70 km wide. The tide of the sea can have an effect of up to 300 kilometers. Strickland, a tributary of the Fly, reaches the Papuan Plain through wild gorges. Fly and Strickland together form the largest river in New Guinea. The many rivers flowing into the Gulf of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of .
Geography
Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow i ...
form a single delta complex. The rivers of the island are extremely rich in water due to the annual rainfall of 2,000–10,000 mm. According to a modest calculation, the New Guinea River carries about of water into the sea. Fly alone carries more water than all the rivers in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
combined.
Relation to surroundings
The island of New Guinea lies to the east of theMalay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago (Indonesian/Malay: , tgl, Kapuluang Malay) is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the " Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies", Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Archipe ...
, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago. Geologically it is a part of the same tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
as Australia. When world sea levels were low, the two shared shorelines (which now lie 100 to 140 metres below sea level), and combined with lands now inundated into the tectonic continent of Sahul
__NOTOC__
Sahul (), also called Sahul-land, Meganesia, Papualand and Greater Australia, was a paleocontinent that encompassed the modern-day landmasses of mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and the Aru Islands.
Sahul was in the south-we ...
, also known as Greater Australia. The two landmasses became separated when the area now known as the Torres Strait flooded after the end of the last glacial period.
Anthropologically, New Guinea is considered part of Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
.
New Guinea is differentiated from its drier, flatter, and less fertile southern counterpart, Australia, by its much higher rainfall and its active volcanic geology. Yet the two land masses share a similar animal fauna, with marsupials, including wallabies
A wallaby () is a small or middle-sized macropod native to Australia and New Guinea, with introduced populations in New Zealand, Hawaii, the United Kingdom and other countries. They belong to the same taxonomic family as kangaroos and so ...
and possums
Possum may refer to:
Animals
* Phalangeriformes, or possums, any of a number of arboreal marsupial species native to Australia, New Guinea, and Sulawesi
** Common brushtail possum (''Trichosurus vulpecula''), a common possum in Australian urban a ...
, and the egg-laying monotreme, the echidna
Echidnas (), sometimes known as spiny anteaters, are quill-covered monotremes (egg-laying mammals) belonging to the family Tachyglossidae . The four extant species of echidnas and the platypus are the only living mammals that lay eggs and the ...
. Other than bats and some two dozen indigenous rodent genera, there are no pre-human indigenous placental mammals
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguishe ...
. Pigs, several additional species of rats, and the ancestor of the New Guinea singing dog
The New Guinea singing dog or New Guinea Highland dog is an ancient ( basal) lineage of dog found in the New Guinea Highlands, on the island of New Guinea. Once considered to be a separate species in its own right, under the name ''Canis hallstr ...
were introduced with human colonization.
Prior to the 1970s, archaeologists called the single Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
landmass by the name ''Australasia'', although this word is most often used for a wider region that includes lands, such as New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, which are not on the same continental shelf. In the early 1970s, they introduced the term ''Greater Australia'' for the Pleistocene continent. Then, at a 1975 conference and consequent publication, they extended the name ''Sahul'' from its previous use for just the Sahul Shelf to cover the continent.
Political divisions
Fly River
The Fly River is the third longest river in the island of New Guinea, after the Sepik River and Mamberamo River, with a total length of and the largest by volume of discharge in Oceania, the largest in the world without a single dam in its catc ...
which belongs to Papua New Guinea) was formerly a Dutch colony, part of the Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
. After the West New Guinea dispute
The West New Guinea dispute (1950–1962), also known as the West Irian dispute, was a diplomatic and political conflict between the Netherlands and Indonesia over the territory of Dutch New Guinea. While the Netherlands had ceded sovereignty ov ...
it is now five Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
n provinces:
** West Papua with Manokwari
Manokwari is a coastal town and the capital of the Indonesian province of West Papua. It is one of only seven provincial capitals of Indonesia without a city status. It is also the administrative seat of Manokwari Regency. However, under pro ...
as its capital.
** Papua with the city of Jayapura
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso ...
as its capital.
** Highland Papua
Highland Papua ( id, Papua Pegunungan) is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official es ...
with Wamena
Wamena is a town and the capital of the Indonesian province of Highland Papua. It also serves as the seat of Jayawijaya Regency. It is the largest town in Indonesian Papua's highlands, in the Baliem Valley and had a population of 64,967 at the ...
as its capital.
** Central Papua
Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Tengah) is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencie ...
with Nabire
Nabire is a town in the Indonesian province of Central Papua, at the western end of New Guinea. The town is the administrative seat of the Nabire Regency, and has been designated to be the administrative capital of the new province. It is served by ...
as its capital.
** South Papua
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Selatan), is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2 ...
with Merauke
Merauke is a large town and the capital of the South Papua province, Indonesia. It is also the administrative centre of Merauke Regency in South Papua. It is considered the easternmost city in Indonesia. The town was originally called Ermasoe. It ...
as its capital.
* The eastern part forms the mainland of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
, which has been an independent country since 1975. It was formerly the Territory of Papua and New Guinea
The Territory of Papua and New Guinea, officially the Administrative Union of the Territory of Papua and the Territory of New Guinea, was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New G ...
governed by Australia, consisting of the Trust Territory of New Guinea (northeastern quarter, formerly German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
), and the Territory of Papua
The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the a ...
(southeastern quarter). Three of Papua New Guinea's four regions are parts of New Guinea island:
** Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
, consisting of Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
, Gulf
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodie ...
, Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
, Oro (Northern) and Milne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range to t ...
provinces.
** Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
*Sou ...
, consisting of Southern Highlands, Hela Province
Hela is a province of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital is Tari. The province covers an area of 10,498 km², and there are 249,449 inhabitants (2011 census figures). Hela province officially came into being on 17 May 2012, comprising t ...
, Jiwaka Province
Jiwaka is a province of Papua New Guinea. The provincial capital is temporarily located in Kurumul. Mostly all provincial matters are handled in Kurumul while few are handled in Banz and Minj.
The province covers an area of 4,798 km², and ...
, Enga Province
Enga is one of the provinces in Papua New Guinea (PNG). It is located in the north most region of the highlands of PNG, having been divided from the Western Highlands to become a separate province when the provinces were created at the time of in ...
, Western Highlands, Simbu and Eastern Highlands
:''"Eastern Highlands" also refers to Eastern Highlands Province in Papua New Guinea, and part of the Great Dividing Range, Australia.''
The Eastern Highlands, also known as the Manica Highlands, is a mountain range on the border of Zimbabwe ...
provinces.
** Momase, consisting of Morobe, Madang
Madang (old German name: ''Friedrich-Wilhelmshafen'') is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 (in 2005) on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.
Histor ...
, East Sepik
East Sepik is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Wewak. East Sepik has an estimated population of 433,481 people (2010 census) and is 43,426 km square in size.
History
Cherubim Dambui was appointed as East Sepik's first premier b ...
and Sandaun
Sandaun Province (formerly West Sepik Province) is the northwesternmost mainland province of Papua New Guinea. It covers an area of 35,920 km2 (13868 m2) and has a population of 248,411 (2011 census). The capital is Vanimo. In July 1998 the a ...
(West Sepik) provinces.
People
 The current population of the island of New Guinea is about fifteen million. Many believe human habitation on the island dates to as early as 50,000 BC, and first settlement possibly dating back to 60,000 years ago has been proposed. The island is presently populated by almost a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world.
The current population of the island of New Guinea is about fifteen million. Many believe human habitation on the island dates to as early as 50,000 BC, and first settlement possibly dating back to 60,000 years ago has been proposed. The island is presently populated by almost a thousand different tribal groups and a near-equivalent number of separate languages, which makes New Guinea the most linguistically diverse area in the world. Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensiv ...
's 14th edition lists 826 languages of Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
and 257 languages of Western New Guinea
Western New Guinea, also known as Papua, Indonesian New Guinea, or Indonesian Papua, is the western half of the Melanesian island of New Guinea which is administered by Indonesia. Since the island is alternatively named as Papua, the region ...
, total 1073 languages, with 12 languages overlapping. They can be divided into two groups, the Austronesian languages, and all the others, called Papuan languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geogra ...
for convenience. The term ''Papuan languages'' refers to an areal grouping, rather than a linguistic one, since so-called Papuan languages comprise hundreds of different languages, most of which are not related.
The separation is not merely linguistic; warfare
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular ...
among societies was a factor in the evolution of the ''men's house'': separate housing of groups of adult men, from the single-family houses of the women and children, for mutual protection from other tribal groups. Pig-based trade between the groups and pig-based feasts are a common theme with the other peoples of southeast Asia and Oceania. Most societies practice agriculture, supplemented by hunting and gathering.
 Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea at a time (either side of the
Current evidence indicates that the Papuans (who constitute the majority of the island's peoples) are descended from the earliest human inhabitants of New Guinea. These original inhabitants first arrived in New Guinea at a time (either side of the Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
, approx 21,000 years ago) when the island was connected to the Australian continent via a land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and Colonisation (biology), colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regre ...
, forming the landmass of Sahul
__NOTOC__
Sahul (), also called Sahul-land, Meganesia, Papualand and Greater Australia, was a paleocontinent that encompassed the modern-day landmasses of mainland Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and the Aru Islands.
Sahul was in the south-we ...
. These peoples had made the (shortened) sea-crossing from the islands of Wallacea
Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lo ...
and Sundaland
Sundaland (also called Sundaica or the Sundaic region) is a biogeographical region of South-eastern Asia corresponding to a larger landmass that was exposed throughout the last 2.6 million years during periods when sea levels were lower. It ...
(the present Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago (Indonesian/Malay: , tgl, Kapuluang Malay) is the archipelago between mainland Indochina and Australia. It has also been called the " Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies", Indo-Australian Archipelago, Spices Archipe ...
) by at least 40,000 years ago.
 The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from
The ancestral Austronesian peoples are believed to have arrived considerably later, approximately 3,500 years ago, as part of a gradual seafaring migration from Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, south-eastern region of Asia, consistin ...
, possibly originating in Taiwan. Austronesian-speaking peoples colonized many of the offshore islands to the north and east of New Guinea, such as New Ireland and New Britain
New Britain ( tpi, Niu Briten) is the largest island in the Bismarck Archipelago, part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. It is separated from New Guinea by a northwest corner of the Solomon Sea (or with an island hop of Umboi the Dam ...
, with settlements also on the coastal fringes of the main island in places. Human habitation of New Guinea over tens of thousands of years has led to a great deal of diversity, which was further increased by the later arrival of the Austronesians and the more recent history of European and Asian settlement through events like transmigration.
Large areas of New Guinea are yet to be explored by scientists and anthropologists. The Indonesian province of West Papua is home to an estimated 44 uncontacted tribal groups.
Biodiversity and ecology
With some 786,000 km2 of tropical land—less than one-half of one percent (0.5%) of the Earth's surface—New Guinea has an immensebiodiversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic (''genetic variability''), species (''species diversity''), and ecosystem (''ecosystem diversity'') l ...
, containing between 5 and 10 percent of the total species on the planet. This percentage is about the same amount as that found in the United States or Australia. A high percentage of New Guinea's species are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
, and thousands are still unknown to science: probably well over 200,000 species of insect, between 11,000 and 20,000 plant species, and over 650 resident bird species. Most of these species are shared, at least in their origin, with the continent of Australia, which was until fairly recent geological times part of the same landmass (see Australia-New Guinea
The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul (), Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, Meganesia, or Papualand to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and East ...
for an overview). The island is so large that it is considered 'nearly a continent' in terms of its biological distinctiveness.
In the period from 1998 to 2008, conservationists identified 1,060 new species in New Guinea, including 218 plants, 43 reptiles, 12 mammals, 580 invertebrates, 134 amphibians, 2 birds and 71 fish. Between 2011 and 2017, researchers described 465 previously undocumented plant species in New Guinea. As of 2019, the Indonesian portion of New Guinea and the Maluku Islands is estimated to have 9,518 species of vascular plants, of which 4,380 are endemic. In 2020, an international study conducted by a team of 99 experts cataloged 13,634 species representing 1,742 genera and 264 families of vascular plants for New Guinea and its associated islands (Aru Islands
The Aru Islands Regency ( id, Kabupaten Kepulauan Aru) is a group of about 95 low-lying islands in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia. It also forms a regency of Maluku Province, with a land area of . At the 2011 Census the Regency had a po ...
, Bismarck Archipelago
The Bismarck Archipelago (, ) is a group of islands off the northeastern coast of New Guinea in the western Pacific Ocean and is part of the Islands Region of Papua New Guinea. Its area is about 50,000 square km.
History
The first inhabitants o ...
, D'Entrecasteaux Islands
D'Entrecasteaux Islands () are situated near the eastern tip of New Guinea in the Solomon Sea in Milne Bay Province of Papua New Guinea. The group spans a distance of , has a total land area of approximately and is separated from the Papua New G ...
, Louisiade Archipelago
The Louisiade Archipelago is a string of ten larger volcanic islands frequently fringed by coral reefs, and 90 smaller coral islands in Papua New Guinea.
It is located 200 km southeast of New Guinea, stretching over more than and spread ...
), making it the world's most floristically diverse island, surpassing Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
(11,488), Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
(11,165), Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
(4,598), and the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
(9,432).


Biogeographically
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities of ...
, New Guinea is part of Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologica ...
rather than the Indomalaya
The Indomalayan realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms. It extends across most of South and Southeast Asia and into the southern parts of East Asia.
Also called the Oriental realm by biogeographers, Indomalaya spreads all over the Indi ...
n realm, although New Guinea's flora has many more affinities with Asia than its fauna, which is overwhelmingly Australian. Botanically, New Guinea is considered part of Malesia
Malesia is a biogeographical region straddling the Equator and the boundaries of the Indomalayan and Australasian realms, and also a phytogeographical floristic region in the Paleotropical Kingdom. It has been given different definitions. The ...
, a floristic region that extends from the Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula (Malay: ''Semenanjung Tanah Melayu'') is a peninsula in Mainland Southeast Asia. The landmass runs approximately north–south, and at its terminus, it is the southernmost point of the Asian continental mainland. The area ...
across Indonesia to New Guinea and the East Melanesian Islands The East Melanesian Islands, also known as the Solomons-Vanuatu-Bismarck moist forests, is a biogeographic region in the Melanesia subregion of Oceania. Biogeographically, the East Melanesian Islands are part of the Australasian realm.
It is notabl ...
. The flora of New Guinea is a mixture of many tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equatori ...
species with origins in Asia, together with typically Australasian flora. Typical Southern Hemisphere flora include the conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s ''Podocarpus
''Podocarpus'' () is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family, the Podocarpaceae. The name comes from Greek πούς (poús, “foot”) + καρπός (karpós, “fruit”). ''Podocarpus'' species ...
'' and the rainforest emergents ''Araucaria
''Araucaria'' (; original pronunciation: .ɾawˈka. ɾja is a genus of evergreen Conifer, coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. There are 20 extant taxon, extant species in New Caledonia (where 14 species are endemism, ende ...
'' and ''Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of 22 species of evergreen tree. The genus is part of the ancient conifer family Araucariaceae, a group once widespread during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, but now largely re ...
,'' as well as tree fern
The tree ferns are arborescent (tree-like) ferns that grow with a trunk elevating the fronds above ground level, making them trees. Many extant tree ferns are members of the order Cyatheales, to which belong the families Cyatheaceae (scaly tree ...
s and several species of ''Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as euca ...
''.
New Guinea has 284 species and six orders of mammals: monotremes
Monotremes () are prototherian mammals of the order Monotremata. They are one of the three groups of living mammals, along with placentals (Eutheria), and marsupials (Metatheria). Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, ...
, three orders of marsupials
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
, rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are na ...
s and bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most bi ...
s; 195 of the mammal species (69%) are endemic. New Guinea has 578 species of breeding birds, of which 324 species are endemic. The island's frogs are one of the most poorly known vertebrate groups, totalling 282 species, but this number is expected to double or even triple when all species have been documented. New Guinea has a rich diversity of coral life and 1,200 species of fish have been found. Also about 600 species of reef-building coral—the latter equal to 75 percent of the world's known total. The entire coral area covers 18 million hectares off a peninsula in northwest New Guinea.
Ecoregions
Terrestrial
According to the WWF, New Guinea can be divided into twelveterrestrial ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
s:
* Central Range montane rain forests
The Central Range montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion on the island of New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the Central Range of the New Guinea Highlands, which extends along the spine of the island. The montane rain forests of ...
* Central Range sub-alpine grasslands
The Central Range sub-alpine grasslands is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion on the island of New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the highest-elevation portions of the New Guinea Highlands, which extend along the spine of the island. The ...
* Huon Peninsula montane rain forests
The Huon Peninsula montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountains of northeastern New Guinea's Huon Peninsula.
Geography
The ecoregion is made up of montane rain forests on the Huon Pen ...
* New Guinea mangroves
The New Guinea mangroves is a mangrove ecoregion that covers extensive areas of the coastline New Guinea, the large island in the western Pacific Ocean north of Australia.
Location and description
The New Guinea mangroves cover an area of , ...
* Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests
The Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of northern New Guinea.
Setting
The Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests extend across the northern lowl ...
* Northern New Guinea montane rain forests
The Northern New Guinea montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in northern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers several separate mountain ranges lying north of New Guinea's Central Range and south of the Pacific Ocean.
Geogra ...
* Southeastern Papuan rain forests
* Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests
The Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southern New Guinea. The ecoregion includes the extensive swamp forests of southern and western New Guinea.
Geography
New Guinea is home to extensive swa ...
* Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests
The Southern New Guinea lowland rain forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical moist forest ecoregion in southeastern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers portions of New Guinea's southern lowlands.
Geography
The eco ...
* Trans-Fly savanna and grasslands
The Trans Fly savanna and grasslands are a lowland ecoregion on the south coast of the island of New Guinea in both the Indonesian and Papua New Guinean sides of the island. With their monsoon and dry season climate these grasslands are quite di ...
* Vogelkop montane rain forests
The Vogelkop montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in western New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountains of western New Guinea's Bird's Head and Bomberai peninsulas.
Geography
The ecoregion includes the montane forest ...
* Vogelkop-Aru lowland rain forests
Freshwater
The WWF andNature Conservancy
The Nature Conservancy (TNC) is a global environmental organization headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. it works via affiliates or branches in 79 countries and territories, as well as across every state in the US.
Founded in 1951, The Natu ...
divide New Guinea into five freshwater ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of l ...
s:
* Vogelkop–Bomberai
* New Guinea North Coast
New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created.
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
Albums and EPs
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ...
* New Guinea Central Mountains
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya , the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home ...
* Southwest New Guinea–Trans-Fly Lowland
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east ...
* Papuan Peninsula
The Papuan Peninsula, also known as the Bird's Tail Peninsula, is a large peninsula in Papua New Guinea, southeast of the city of Lae, that makes up the southeastern portion of the island of New Guinea. The peninsula is the easternmost extent of t ...
Marine
The WWF and Nature Conservancy identify severalmarine ecoregion
A marine ecoregion is an ecoregion, or ecological region, of the oceans and seas identified and defined based on biogeography, biogeographic characteristics.
Introduction
A more complete definition describes them as “Areas of relatively homogen ...
s in the seas bordering New Guinea:
* Papua
* Bismarck Sea
The Bismarck Sea (, ) lies in the southwestern Pacific Ocean within the nation of Papua New Guinea. It is located northeast of the island of New Guinea and south of the Bismarck Archipelago. It has coastlines in districts of the Islands Region, ...
* Solomon Sea
The Solomon Sea is a sea located within the Pacific Ocean. It lies between Papua New Guinea and Solomon Islands. Many major battles were fought there during World War II.
Extent
The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of ...
* Southeast Papua New Guinea
* Gulf of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of .
Geography
Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow i ...
* Arafura Sea
The Arafura Sea (or Arafuru Sea) lies west of the Pacific Ocean, overlying the continental shelf between Australia and Western New Guinea (also called Papua), which is the Indonesian part of the Island of New Guinea.
Geography
The Arafura Sea is ...
History
Early history
 The first inhabitants
The first inhabitants Indigenous people of New Guinea
The indigenous peoples of West Papua in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Arch ...
, from whom the Papuan people are probably descended, adapted to the range of ecologies and, in time, developed one of the earliest known agricultures. Remains of this agricultural system, in the form of ancient irrigation systems in the highlands of Papua New Guinea, are being studied by archaeologists. Research indicates that the highlands were an early and independent center of agriculture, with evidence of irrigation going back at least 10,000 years. Sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
was cultivated for the first time in New Guinea around 6000 BC.
The gardens of the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya , the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home ...
are ancient, intensive permaculture
Permaculture is an approach to land management and settlement design that adopts arrangements observed in flourishing natural ecosystems. It includes a set of design principles derived using whole-systems thinking. It applies these principle ...
s, adapted to high population densities, very high rainfalls (as high as 10,000 mm per year (400 in/yr)), earthquakes, hilly land, and occasional frost. Complex mulches, crop rotations and tillages are used in rotation on terraces with complex irrigation systems. Western agronomists still do not understand all of the practices, and it has been noted that native gardeners are as, or even more, successful than most scientific farmers in raising certain crops. There is evidence that New Guinea gardeners invented crop rotation well before western Europeans. A unique feature of New Guinea permaculture is the silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and wo ...
of ''Casuarina oligodon'', a tall, sturdy native ironwood
Ironwood is a common name for many woods or plants that have a reputation for hardness, or specifically a wood density that is heavier than water (approximately 1000 kg/m3, or 62 pounds per cubic foot), although usage of the name ironwood in E ...
tree, suited to use for timber and fuel, with root nodules that fix nitrogen. Pollen studies show that it was adopted during an ancient period of extreme deforestation.
In more recent millennia, another wave of people arrived on the shores of New Guinea. These were the Austronesian people
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austrones ...
, who had spread down from Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, through the South-east Asian archipelago, colonising many of the islands on the way. The Austronesian people had technology and skills extremely well adapted to ocean voyaging and Austronesian language speaking people are present along much of the coastal areas and islands of New Guinea. They also introduced pigs and dogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relative. Do ...
. These Austronesian migrants are considered the ancestors of most people in insular Southeast Asia, from Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
and Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List ...
to Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and eas ...
and Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
, as well as coastal new Guinea.
Precolonial history
The western part of the island was in contact with kingdoms in other parts of modern-day Indonesia. The ''Negarakertagama
The ''Nagarakretagama'' or ''Nagarakṛtāgama'', also known as ''Desawarnana'' or ''Deśavarṇana'', is an Old Javanese eulogy to Hayam Wuruk, a Javanese king of the Majapahit Empire. It was written on lontar as a ''kakawin'' by Mpu Prapan ...
'' mentioned the region of Wanin and Sran, in eastern Nusantara
Nusantara most commonly refers to:
*Nusantara (archipelago), an Old Javanese term which initially referred to the conquered territories of the Majapahit empire, corresponding to present-day Indonesia
*Nusantara (planned city), the future capital ci ...
as part of Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
's tributary. This 'Wanin' has been identified with the Onin Peninsula, part of the Bomberai Peninsula
Bomberai Peninsula ( id, Semenanjung Bomberai), otherwise known as the Bird's Beak Peninsula ( id, Semenanjung Paruh Burung), is located in the Western New Guinea region, opposite to and to the south of the Bird's Head Peninsula. To the west lies ...
near the city of Fakfak
Fakfak () is a town in West Papua and seat of the Fakfak Regency. It had a population of 12,566 at the 2010 Census, which rose to 18,900 at the 2020 Census.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. It is served by Fakfak Airport. It is the only town i ...
., while ' Sran' had been identified as region of Kowiai, just south of Onin peninsula. The sultans of Tidore
Tidore ( id, Kota Tidore Kepulauan, lit. "City of Tidore Islands") is a city, island, and archipelago in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia, west of the larger island of Halmahera. Part of North Maluku Province, the city includes the island ...
, in the Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands (; Indonesian: ''Kepulauan Maluku'') or the Moluccas () are an archipelago in the east of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located eas ...
, claimed sovereignty over various coastal parts of the island. During Tidore's rule, the main exports of the island during this period were resins, spices, slaves and the highly priced feathers of the bird-of-paradise
The birds-of-paradise are members of the family Paradisaeidae of the order Passeriformes. The majority of species are found in eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and eastern Australia. The family has 44 species in 17 genera. The members of thi ...
. In a period of constant conflict called 'hongi wars', in which rival villages or kingdoms would invoke the name of Tidore Sultan, rightly, for punitive expeditions for not fulfilling their tributary obligations, or opportunitively for competitions over resources and prestige. Sultan Nuku, one of the most famous Tidore sultans who rebelled against Dutch colonization, called himself "Sultan of Tidore and Papua", during his revolt in 1780s. He commanded loyalty from both Moluccan and Papuan chiefs, especially those of Raja Ampat
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested fr ...
Islands, from his base in Gebe
Gebe is an island in Maluku Islands, Indonesia. Administratively it is part of Central Halmahera, North Maluku.
The island is part of a small island group which also include Fau island, Yoi, Uta, and Sain.
Gebe is part of the Halmahera rain f ...
. Following Tidore's subjugation as Dutch tributary, much of the territory it claimed in western part of New Guinea came under Dutch rule as part of Dutch East Indies.
European contact
The first European contact with New Guinea was by Portuguese and Spanish sailors in the 16th century. In 1526–27, Portuguese explorerJorge de Meneses
Jorge de Menezes (c. 1498 – 1537) was a Portuguese explorer, who in 1526–27 landed on the islands of Biak (Cenderawasih Bay), whilst he awaited the passing of the monsoon season, and on the northern coasts of the Bird's Head Peninsula, calling ...
saw the western tip of New Guinea and named it ''ilhas dos Papuas''. In 1528, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Saavedra also recorded its sighting when trying to return from Tidore
Tidore ( id, Kota Tidore Kepulauan, lit. "City of Tidore Islands") is a city, island, and archipelago in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia, west of the larger island of Halmahera. Part of North Maluku Province, the city includes the island ...
to New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
. In 1545, Spaniard Íñigo Ortíz de Retes sailed along the north coast of New Guinea as far as the Mamberamo River
The Mamberamo (''Indonesian: Sungai Mamberamo'') is the second longest river on the island of New Guinea, after Sepik River (1,146 km) and third largest in Oceania by discharge (5,500 m3/s) volume after Fly River (7,500 m3/s) and Sepik (7,000 m3/ ...
, near which he landed on 20 June, naming the island 'Nueva Guinea'. The first map showing the whole island (as an island) was published in 1600 and shows it as 'Nova Guinea'. In 1606, Luís Vaz de Torres
Luís Vaz de Torres ( Galician and Portuguese), or Luis Váez de Torres in the Spanish spelling (born c. 1565; fl. 1607), was a 16th- and 17th-century maritime explorer of a Spanish expedition noted for the first recorded European navigation of ...
explored the southern coast of New Guinea from Milne Bay
Milne Bay is a large bay in Milne Bay Province, south-eastern Papua New Guinea. More than long and over wide, Milne Bay is a sheltered deep-water harbor accessible via Ward Hunt Strait. It is surrounded by the heavily wooded Stirling Range to t ...
to the Gulf of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of .
Geography
Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow i ...
including Orangerie Bay
An orangery or orangerie was a room or a dedicated building on the grounds of fashionable residences of Northern Europe from the 17th to the 19th centuries where orange and other fruit trees were protected during the winter, as a very large ...
, which he named ''Bahía de San Lorenzo''. His expedition also discovered Basilaki Island
Basilaki Island (Moresby Island) is an island in the Louisiade Archipelago in Milne Bay Province, Papua New Guinea. It is located at the eastern end of the New Guinea mainland.
History
First recorded sighting by Europeans was by the Spanish exp ...
naming it ''Tierra de San Buenaventura'', which he claimed for Spain in July 1606.Translation of Torres’ report to the king in Collingridge, G. (1895) ''Discovery of Australia'' p.229-237. Golden Press Edition 1983, Gladesville, NSW. On 18 October, his expedition reached the western part of the island in present-day Indonesia, and also claimed the territory for the King of Spain.
 A successive European claim occurred in 1828, when the Netherlands formally claimed the western half of the island as
A successive European claim occurred in 1828, when the Netherlands formally claimed the western half of the island as Netherlands New Guinea
Dutch New Guinea or Netherlands New Guinea ( nl, Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea, id, Nugini Belanda) was the western half of the island of New Guinea that was a part of the Dutch East Indies until 1949, later an overseas territory of the Kingdo ...
. Dutch colonial authority built Fort Du Bus
Fort Du Bus was a Dutch administrative and trading post established in 1828 on Triton Bay on the southwest coast of New Guinea, in the current Indonesian regency of Kaimana Regency, Kaimana, West Papua (province), West Papua. Intended to counter ...
an administrative and trading post established near Lobo, Triton Bay, but by 1835 had been abandoned. Considering that New Guinea had little economic value for them, the Dutch promoted Tidore as suzerain of Papua. By 1849, Tidore's borders had been extended to the proximity of the current international border between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country i ...
, as it formed extensive trade pact and custom of ''Uli-Siwa'' ( federation of nine ).
In 1883, following a short-lived French annexation of New Ireland, the British colony of Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
annexed south-eastern New Guinea. However, the Queensland government's superiors in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
revoked the claim, and (formally) assumed direct responsibility in 1884, when Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
claimed north-eastern New Guinea as the protectorate of German New Guinea
German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neu-Guinea) consisted of the northeastern part of the island of New Guinea and several nearby island groups and was the first part of the German colonial empire. The mainland part of the territory, called , ...
(also called Kaiser-Wilhelmsland
Kaiser-Wilhelmsland ("Emperor William's Land") formed part of German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neuguinea), the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor () from 1871 to 1888, i ...
).
The first Dutch government posts were established in 1898 and in 1902: Manokwari on the north coast, Fak-Fak in the west and Merauke in the south at the border with British New Guinea
The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the a ...
. The German, Dutch and British colonial administrators each attempted to suppress the still-widespread practices of inter-village warfare and headhunting
Headhunting is the practice of hunting a human and collecting the severed head after killing the victim, although sometimes more portable body parts (such as ear, nose or scalp) are taken instead as trophies. Headhunting was practiced in hi ...
within their respective territories.
In 1905, the British government transferred some administrative responsibility over southeast New Guinea to Australia (which renamed the area "Territory of Papua
The Territory of Papua comprised the southeastern quarter of the island of New Guinea from 1883 to 1975. In 1883, the Government of Queensland annexed this territory for the British Empire. The United Kingdom Government refused to ratify the a ...
"); and, in 1906, transferred all remaining responsibility to Australia. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Australian forces seized German New Guinea, which in 1920 became the Territory of New Guinea
The Territory of New Guinea was an Australian-administered United Nations trust territory on the island of New Guinea from 1914 until 1975. In 1949, the Territory and the Territory of Papua were established in an administrative union by the nam ...
, to be administered by Australia under a League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
mandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also ...
. The territories under Australian administration became collectively known as The Territories of Papua and New Guinea (until February 1942).
Before about 1930, European maps showed the highlands as uninhabited forests. When first flown over by aircraft, numerous settlements with agricultural terraces and stockades were observed. The most startling discovery took place on 4 August 1938, when Richard Archbold
Richard Archbold (April 9, 1907 – August 1, 1976) was an American zoologist and philanthropist. He was independently wealthy, being the grandson of the capitalist John Dustin Archbold. He was educated at private schools, and later attended cla ...
discovered the Grand Valley of the Baliem River, which had 50,000 yet-undiscovered Stone Age farmers living in orderly villages. The people, known as the Dani, were the last society of its size to make first contact with the rest of the world. A 1930 expedition led by the prospector Michael Lehay also encountered an indigenous group in the highlands. The inhabitants, believing themselves to be the only people in the world and, having never seen Europeans before, initially believed the explorers to be spirits of the dead due to the local belief that a person's skin turned white when they died and crossed into the land of the dead.

World War II
 Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories were invaded in 1942 by the
Netherlands New Guinea and the Australian territories were invaded in 1942 by the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
. The Australian territories were put under military administration and were known simply as New Guinea. The highlands, northern and eastern parts of the island became key battlefields in the South West Pacific Theatre
The South West Pacific theatre, during World War II, was a major theatre of the war between the Allies and the Axis. It included the Philippines, the Dutch East Indies (except for Sumatra), Borneo, Australia and its mandate Territory of ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Papuans often gave vital assistance to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, fighting alongside Australian troops, and carrying equipment and injured men across New Guinea. Approximately 216,000 Japanese, Australian and U.S. soldiers, sailors and airmen died during the New Guinea Campaign.
Since World War II
Following the return to civil administration after World War II, the Australian section was known as the Territory of Papua-New Guinea from 1945 to 1949 and then asTerritory of Papua and New Guinea
The Territory of Papua and New Guinea, officially the Administrative Union of the Territory of Papua and the Territory of New Guinea, was established by an administrative union between the Australian-administered territories of Papua and New G ...
. Although the rest of the Dutch East Indies achieved independence as Indonesia on 27 December 1949, the Netherlands regained control of western New Guinea.
 During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the elected
During the 1950s, the Dutch government began to prepare Netherlands New Guinea for full independence and allowed elections in 1959; the elected New Guinea Council
The New Guinea Council ( nl, Nieuw-Guinea Raad) was a unicameral representative body formed in the Dutch colony of Netherlands New Guinea in 1961.
History
Prior to the formation of the New Guinea Council, there existed a Council of Directors, w ...
took office on 5 April 1961. The Council decided on the name of West Papua (''Papua Barat'') for the territory, along with an emblem, flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
, and anthem
An anthem is a musical composition of celebration, usually used as a symbol for a distinct group, particularly the national anthems of countries. Originally, and in music theory and religious contexts, it also refers more particularly to short ...
to complement those of the Netherlands. On 1 October 1962, after some military interventions and negotiations, the Dutch handed over the territory to the United Nations Temporary Executive Authority
The United Nations Temporary Executive Authority (UNTEA) and the United Nations Security Force (UNSF) in West New Guinea was established during October 1962 in accord with General Assembly Resolution 1752 as requested in Article two of the New ...
, until 1 May 1963, when Indonesia took control. The territory was renamed West Irian (''Irian Barat'') and then Irian Jaya. In 1969, Indonesia, under the 1962 New York Agreement
The New York Agreement is an agreement signed by the Netherlands and Indonesia regarding the administration of the territory of Western New Guinea. The first part of the agreement proposes that the United Nations assume administration of the terr ...
, organised a referendum named the Act of Free Choice
The Act of Free Choice ( id, Penentuan Pendapat Rakyat, PEPERA, Determination of the People's Opinion) was a controversial plebiscite held between 14 July and 2 August 1969 in which 1,025 people selected by the Indonesian military in Western New ...
, in which the military hand picked Papuan tribal elders to vote for integration with Indonesia.
There has been significant reported resistance to Indonesian integration and occupation,Philippe Pataud CelerierAutonomy isn’t independence; Indonesian democracy stops in Papua
Le Monde Diplomatique
''Le Monde diplomatique'' (meaning "The Diplomatic World" in French) is a French monthly newspaper offering analysis and opinion on politics, culture, and current affairs.
The publication is owned by Le Monde diplomatique SA, a subsidiary com ...
, June 2010 both through civil disobedience (such as publicly raising the Morning Star flag) and via the formation of the Organisasi Papua Merdeka (OPM, or Free Papua Movement) in 1965. Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and sup ...
has estimated more than 100,000 Papuans, one-sixth of the population, have died as a result of government-sponsored violence against West Papuans. Reports published by TRT World
TRT World is a Turkish public broadcaster international news channel which broadcasts in English 24 hours a day, operated by the TRT and based in Taksim Square, Istıklal Avenue, Beyoğlu, Istanbul. It provides worldwide news and current affair ...
and De Gruyter Oldenbourg have put the number of killed Papuans since the start of the conflict at roughly 500,000.
 From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a Papuan People's Assembly (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua;
From 1971, the name Papua New Guinea was used for the Australian territory. On 16 September 1975, Australia granted full independence to Papua New Guinea. In 2000, Irian Jaya was formally renamed "The Province of Papua" and a Law on Special Autonomy was passed in 2001. The Law established a Papuan People's Assembly (MRP) with representatives of the different indigenous cultures of Papua. The MRP was empowered to protect the rights of Papuans, raise the status of women in Papua, and to ease religious tensions in Papua; block grants
A block grant is a grant-in-aid of a specified amount from a larger government to a smaller regional government body. Block grants have less oversight from the larger government and provide flexibility to each subsidiary government body in terms ...
were given for the implementation of the Law as much as $266 million in 2004. The Indonesian courts' enforcement of the Law on Special Autonomy blocked further creation of subdivisions of Papua: although President Megawati Sukarnoputri
Diah Permata Megawati Setiawati Sukarnoputri (; born 23 January 1947) is an Indonesian politician who served as the fifth president of Indonesia from 2001 to 2004. She previously served as the eighth Vice President of Indonesia, vice president f ...
was able to create a separate West Papua province in 2003 as a fait accompli
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman Conquest, before the language settled into what became Modern Engli ...
, plans for a third province on western New Guinea were blocked by the courts. Critics argue that the Indonesian government has been reluctant to establish or issue various government implementing regulations so that the legal provisions of special autonomy could be put into practice, and as a result special autonomy in Papua has "failed".
In 2022, the Indonesian Government split Papuan Province into 4 provinces. In addition to Papua Province
Papua is a province of Indonesia, comprising the northern coast of Western New Guinea together with island groups in Cenderawasih Bay to the west. It roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Tabi Saireri. It is bordered by the ...
proper (capital Jayapura
Jayapura (formerly Dutch: ''Hollandia'') is the capital and largest city of the Indonesian province of Papua. It is situated on the northern coast of New Guinea island and covers an area of . The city borders the Pacific Ocean and Yos Sudarso ...
), the three new provinces are South Papua
South Papua, officially the South Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Selatan), is an Indonesian province located in the southern portion of Papua, following the borders of Papuan customary region of Anim Ha. Formally established on 11 November 2 ...
(capital Merauke
Merauke is a large town and the capital of the South Papua province, Indonesia. It is also the administrative centre of Merauke Regency in South Papua. It is considered the easternmost city in Indonesia. The town was originally called Ermasoe. It ...
), Central Papua
Central Papua, officially the Central Papua Province ( id, Provinsi Papua Tengah) is an Indonesian province located in the central region of Western New Guinea. It was formally established on 11 November 2022 from the former eight western regencie ...
(capital Nabire
Nabire is a town in the Indonesian province of Central Papua, at the western end of New Guinea. The town is the administrative seat of the Nabire Regency, and has been designated to be the administrative capital of the new province. It is served by ...
) and Highland Papua
Highland Papua ( id, Papua Pegunungan) is a province of Indonesia, which roughly follows the borders of Papuan customary region of Lano-Pago, shortened to La Pago. It covers an area of and had a population of 1,408,641 according to the official es ...
(capital Wamena
Wamena is a town and the capital of the Indonesian province of Highland Papua. It also serves as the seat of Jayawijaya Regency. It is the largest town in Indonesian Papua's highlands, in the Baliem Valley and had a population of 64,967 at the ...
).
The culture of inter-tribal warfare and animosity between the neighboring tribes are still present in New Guinea.
Notes
References
Further reading
*Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American geographer, historian, ornithologist, and author best known for his popular science books ''The Third Chimpanzee'' (1991); ''Guns, Germs, and Steel'' (1997, awarded a Pulitzer Prize); ...
, '' Guns, Germs and Steel: A Short History of Everybody for the last 13,000 Years'', 1997.
External links
Facsimile of material from "The Discovery of New Guinea" by George Collingridge
Scientists hail discovery of hundreds of new species in remote New Guinea
PapuaWeb official website
* {{Authority control Islands of the Pacific Ocean Divided regions International islands Melanesia Islands of Indonesia Islands of Papua New Guinea Former Spanish colonies