Ireland International Men's Field Hockey Players on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ireland ( ; ga,
. ''
. ''
The Island of Ireland: Drowning the Myth of an Irish Land-bridge?
" Accessed 15 February 2013. Later, around 6100 BC, Great Britain became separated from continental Europe. Until recently, the earliest evidence of human activity in Ireland was dated at 12,500 years ago, demonstrated by a butchered bear bone found in a cave in
 The long-standing traditional view is that the Celtic language,
The long-standing traditional view is that the Celtic language,  In 2012, research showed that the occurrence of genetic markers for the earliest farmers was almost eliminated by Beaker-culture immigrants: they carried what was then a new Y-chromosome R1b marker, believed to have originated in Iberia about 2500 BC. The prevalence amongst modern Irish men of this mutation is a remarkable 84%, the highest in the world, and closely matched in other populations along the Atlantic fringes down to Spain. A similar genetic replacement happened with lineages in mitochondrial DNA. This conclusion is supported by recent research carried out by the geneticist David Reich, who says: "British and Irish skeletons from the Bronze Age that followed the Beaker period had at most 10 per cent ancestry from the first farmers of these islands, with other 90 per cent from people like those associated with the Bell Beaker culture in the Netherlands." He suggests that it was Beaker users who introduced an Indo-European language, represented here by Celtic (i.e. a new language and culture introduced directly by migration and genetic replacement).
In 2012, research showed that the occurrence of genetic markers for the earliest farmers was almost eliminated by Beaker-culture immigrants: they carried what was then a new Y-chromosome R1b marker, believed to have originated in Iberia about 2500 BC. The prevalence amongst modern Irish men of this mutation is a remarkable 84%, the highest in the world, and closely matched in other populations along the Atlantic fringes down to Spain. A similar genetic replacement happened with lineages in mitochondrial DNA. This conclusion is supported by recent research carried out by the geneticist David Reich, who says: "British and Irish skeletons from the Bronze Age that followed the Beaker period had at most 10 per cent ancestry from the first farmers of these islands, with other 90 per cent from people like those associated with the Bell Beaker culture in the Netherlands." He suggests that it was Beaker users who introduced an Indo-European language, represented here by Celtic (i.e. a new language and culture introduced directly by migration and genetic replacement).
 The earliest written records of Ireland come from classical
The earliest written records of Ireland come from classical  The arts of
The arts of
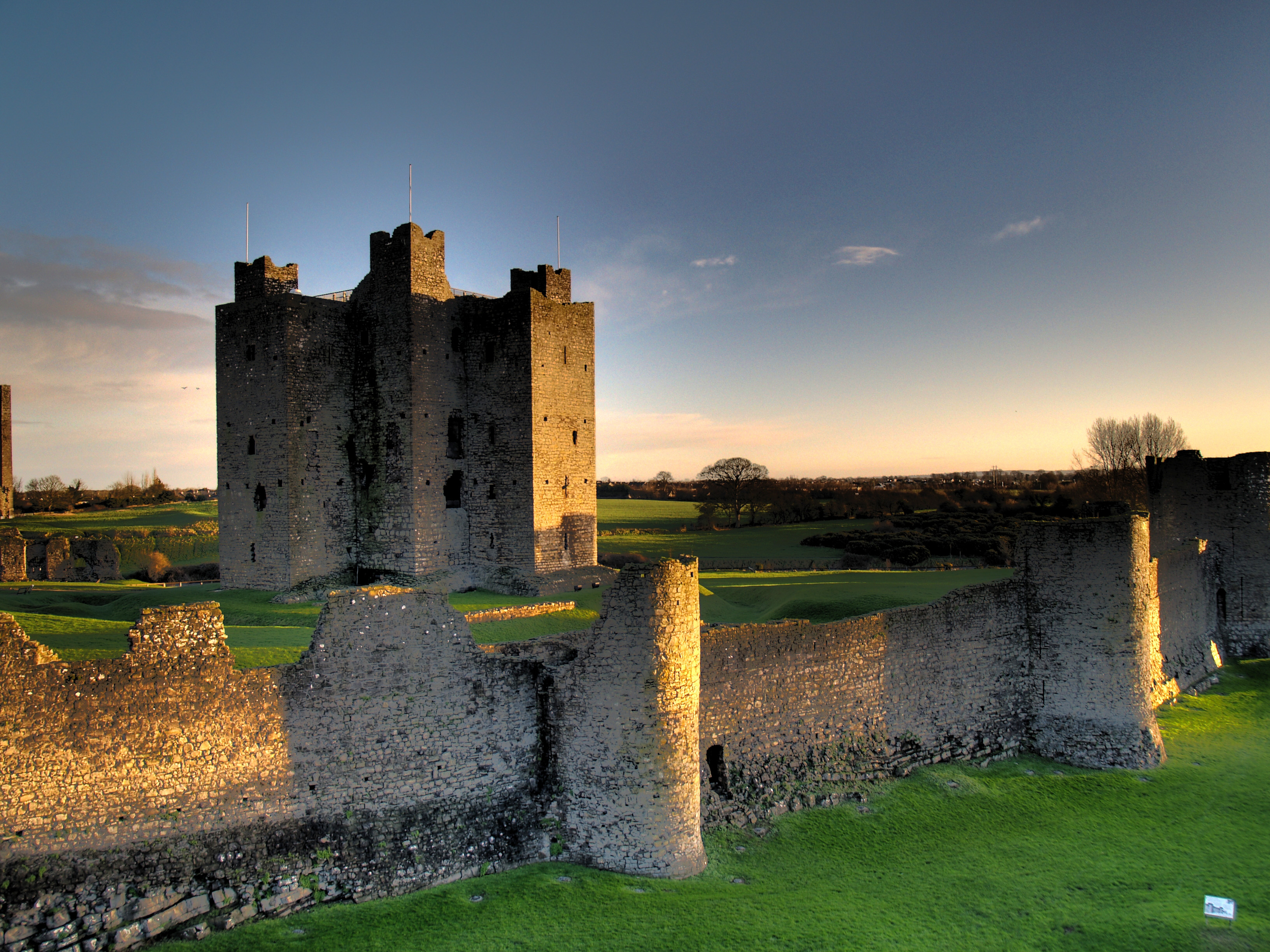 On 1 May 1169, an expedition of Cambro-
On 1 May 1169, an expedition of Cambro- In 1172, Pope Alexander III further encouraged Henry to advance the integration of the Irish Church with Rome. Henry was authorised to impose a tithe of one penny per hearth as an annual contribution. This church levy called
In 1172, Pope Alexander III further encouraged Henry to advance the integration of the Irish Church with Rome. Henry was authorised to impose a tithe of one penny per hearth as an annual contribution. This church levy called
 The title of
The title of  The "Irish Famine (1740–1741)#Cause, Great Frost" struck Ireland and the rest of Europe between December 1739 and September 1741, after a decade of relatively mild winters. The winters destroyed stored crops of potatoes and other staples, and the poor summers severely damaged harvests. This resulted in the Irish Famine (1740–1741), famine of 1740. An estimated 250,000 people (about one in eight of the population) died from the ensuing pestilence and disease. The Irish government halted export of corn and kept the army in quarters but did little more. Local gentry and charitable organisations provided relief but could do little to prevent the ensuing mortality.
In the aftermath of the famine, an increase in industrial production and a surge in trade brought a succession of construction booms. The population soared in the latter part of this century and the Georgian architecture, architectural legacy of Georgian Ireland was built. In 1782,
The "Irish Famine (1740–1741)#Cause, Great Frost" struck Ireland and the rest of Europe between December 1739 and September 1741, after a decade of relatively mild winters. The winters destroyed stored crops of potatoes and other staples, and the poor summers severely damaged harvests. This resulted in the Irish Famine (1740–1741), famine of 1740. An estimated 250,000 people (about one in eight of the population) died from the ensuing pestilence and disease. The Irish government halted export of corn and kept the army in quarters but did little more. Local gentry and charitable organisations provided relief but could do little to prevent the ensuing mortality.
In the aftermath of the famine, an increase in industrial production and a surge in trade brought a succession of construction booms. The population soared in the latter part of this century and the Georgian architecture, architectural legacy of Georgian Ireland was built. In 1782,
 The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845–1851 devastated Ireland, as in those years Ireland's population fell by one-third. More than one million people died from starvation and disease, with an additional million people emigrating during the famine, mostly to the United States and Canada. In the century that followed, an economic depression caused by the famine resulted in a further million people emigrating. By the end of the decade, half of all immigration to the United States was from Ireland. The period of civil unrest that followed until the end of the 19th century is referred to as the Land War. Mass emigration became deeply entrenched and the population continued to decline until the mid-20th century. Immediately prior to the famine the population was recorded as 8.2 million by the 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 census. The population has never returned to this level since. The population continued to fall until 1961; County Leitrim was the final Irish county to record a population increase post-famine, in 2006.
The 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of modern Irish nationalism, primarily among the Roman Catholic population. The pre-eminent Irish political figure after the Union was Daniel O'Connell. He was elected as Member of Parliament for Ennis (UK Parliament constituency), Ennis in a surprise result and despite being unable to take his seat The Test Act, as a Roman Catholic. O'Connell spearheaded a vigorous campaign that was taken up by the Prime Minister, the Irish-born soldier and statesman, the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. Steering the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, Catholic Relief Bill through Parliament, aided by future prime minister Robert Peel, Wellington prevailed upon a reluctant George IV of the United Kingdom, George IV to sign the Bill and proclaim it into law. George III, George's father had opposed the plan of the earlier Prime Minister, William Pitt the Younger, Pitt the Younger, to introduce such a bill following the Union of 1801, fearing Catholic Emancipation to be in conflict with the Act of Settlement 1701.
Daniel O'Connell led a subsequent campaign, for the repeal of the Act of Union, which failed. Later in the century, Charles Stewart Parnell and others campaigned for autonomy within the Union, or "Irish Home Rule Bills, Home Rule". Unionists, especially those located in Ulster, were strongly opposed to Home Rule, which they thought would be dominated by Catholic interests. After several attempts to pass a Home Rule bill through parliament, it looked certain that one would finally pass in 1914. To prevent this from happening, the Ulster Volunteers were formed in 1913 under the leadership of Edward Carson.
Their formation was followed in 1914 by the establishment of the Irish Volunteers, whose aim was to ensure that the Third Home Rule Act, Home Rule Bill was passed. The Act was passed but with the "temporary" exclusion of the six counties of Ulster, which later became Northern Ireland. Before it could be implemented, however, the Act was suspended for the duration of the World War I, First World War. The Irish Volunteers split into two groups. The majority, approximately 175,000 in number, under John Redmond, took the name National Volunteers and supported Ireland and World War I, Irish involvement in the war. A minority, approximately 13,000, retained the Irish Volunteers' name and opposed Ireland's involvement in the war.
The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845–1851 devastated Ireland, as in those years Ireland's population fell by one-third. More than one million people died from starvation and disease, with an additional million people emigrating during the famine, mostly to the United States and Canada. In the century that followed, an economic depression caused by the famine resulted in a further million people emigrating. By the end of the decade, half of all immigration to the United States was from Ireland. The period of civil unrest that followed until the end of the 19th century is referred to as the Land War. Mass emigration became deeply entrenched and the population continued to decline until the mid-20th century. Immediately prior to the famine the population was recorded as 8.2 million by the 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 census. The population has never returned to this level since. The population continued to fall until 1961; County Leitrim was the final Irish county to record a population increase post-famine, in 2006.
The 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of modern Irish nationalism, primarily among the Roman Catholic population. The pre-eminent Irish political figure after the Union was Daniel O'Connell. He was elected as Member of Parliament for Ennis (UK Parliament constituency), Ennis in a surprise result and despite being unable to take his seat The Test Act, as a Roman Catholic. O'Connell spearheaded a vigorous campaign that was taken up by the Prime Minister, the Irish-born soldier and statesman, the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. Steering the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, Catholic Relief Bill through Parliament, aided by future prime minister Robert Peel, Wellington prevailed upon a reluctant George IV of the United Kingdom, George IV to sign the Bill and proclaim it into law. George III, George's father had opposed the plan of the earlier Prime Minister, William Pitt the Younger, Pitt the Younger, to introduce such a bill following the Union of 1801, fearing Catholic Emancipation to be in conflict with the Act of Settlement 1701.
Daniel O'Connell led a subsequent campaign, for the repeal of the Act of Union, which failed. Later in the century, Charles Stewart Parnell and others campaigned for autonomy within the Union, or "Irish Home Rule Bills, Home Rule". Unionists, especially those located in Ulster, were strongly opposed to Home Rule, which they thought would be dominated by Catholic interests. After several attempts to pass a Home Rule bill through parliament, it looked certain that one would finally pass in 1914. To prevent this from happening, the Ulster Volunteers were formed in 1913 under the leadership of Edward Carson.
Their formation was followed in 1914 by the establishment of the Irish Volunteers, whose aim was to ensure that the Third Home Rule Act, Home Rule Bill was passed. The Act was passed but with the "temporary" exclusion of the six counties of Ulster, which later became Northern Ireland. Before it could be implemented, however, the Act was suspended for the duration of the World War I, First World War. The Irish Volunteers split into two groups. The majority, approximately 175,000 in number, under John Redmond, took the name National Volunteers and supported Ireland and World War I, Irish involvement in the war. A minority, approximately 13,000, retained the Irish Volunteers' name and opposed Ireland's involvement in the war.
 The Easter Rising of 1916 was carried out by the latter group together with a smaller socialist militia, the Irish Citizen Army. The British response, executing fifteen leaders of the Rising over a period of ten days and imprisoning or interning more than a thousand people, turned the mood of the country in favour of the rebels. Support for Physical force Irish republicanism, Irish republicanism increased further due to the ongoing war in Europe, as well as the Conscription Crisis of 1918.
The pro-independence republican party, Sinn Féin, received overwhelming endorsement in the 1918 Irish general election, general election of 1918, and in 1919 proclaimed an Irish Republic, setting up its own parliament () and government. Simultaneously the Volunteers, which became known as the Irish Republican Army (IRA), launched a Irish War of Independence, three-year guerrilla war, which ended in a truce in July 1921 (although violence continued until June 1922, mostly in Northern Ireland).
The Easter Rising of 1916 was carried out by the latter group together with a smaller socialist militia, the Irish Citizen Army. The British response, executing fifteen leaders of the Rising over a period of ten days and imprisoning or interning more than a thousand people, turned the mood of the country in favour of the rebels. Support for Physical force Irish republicanism, Irish republicanism increased further due to the ongoing war in Europe, as well as the Conscription Crisis of 1918.
The pro-independence republican party, Sinn Féin, received overwhelming endorsement in the 1918 Irish general election, general election of 1918, and in 1919 proclaimed an Irish Republic, setting up its own parliament () and government. Simultaneously the Volunteers, which became known as the Irish Republican Army (IRA), launched a Irish War of Independence, three-year guerrilla war, which ended in a truce in July 1921 (although violence continued until June 1922, mostly in Northern Ireland).
 During its first decade, the newly formed
During its first decade, the newly formed
 The island is divided between the Republic of Ireland, an independent Sovereign state, state, and Northern Ireland, a constituent country of the
The island is divided between the Republic of Ireland, an independent Sovereign state, state, and Northern Ireland, a constituent country of the
 The
The

 Ireland is located in the North-West Europe, north-west of Europe, between latitudes 51st parallel north, 51° and 56th parallel north, 56° N, and longitudes 11th meridian west, 11° and 5th meridian west, 5° W. It is separated from Great Britain by the
Ireland is located in the North-West Europe, north-west of Europe, between latitudes 51st parallel north, 51° and 56th parallel north, 56° N, and longitudes 11th meridian west, 11° and 5th meridian west, 5° W. It is separated from Great Britain by the
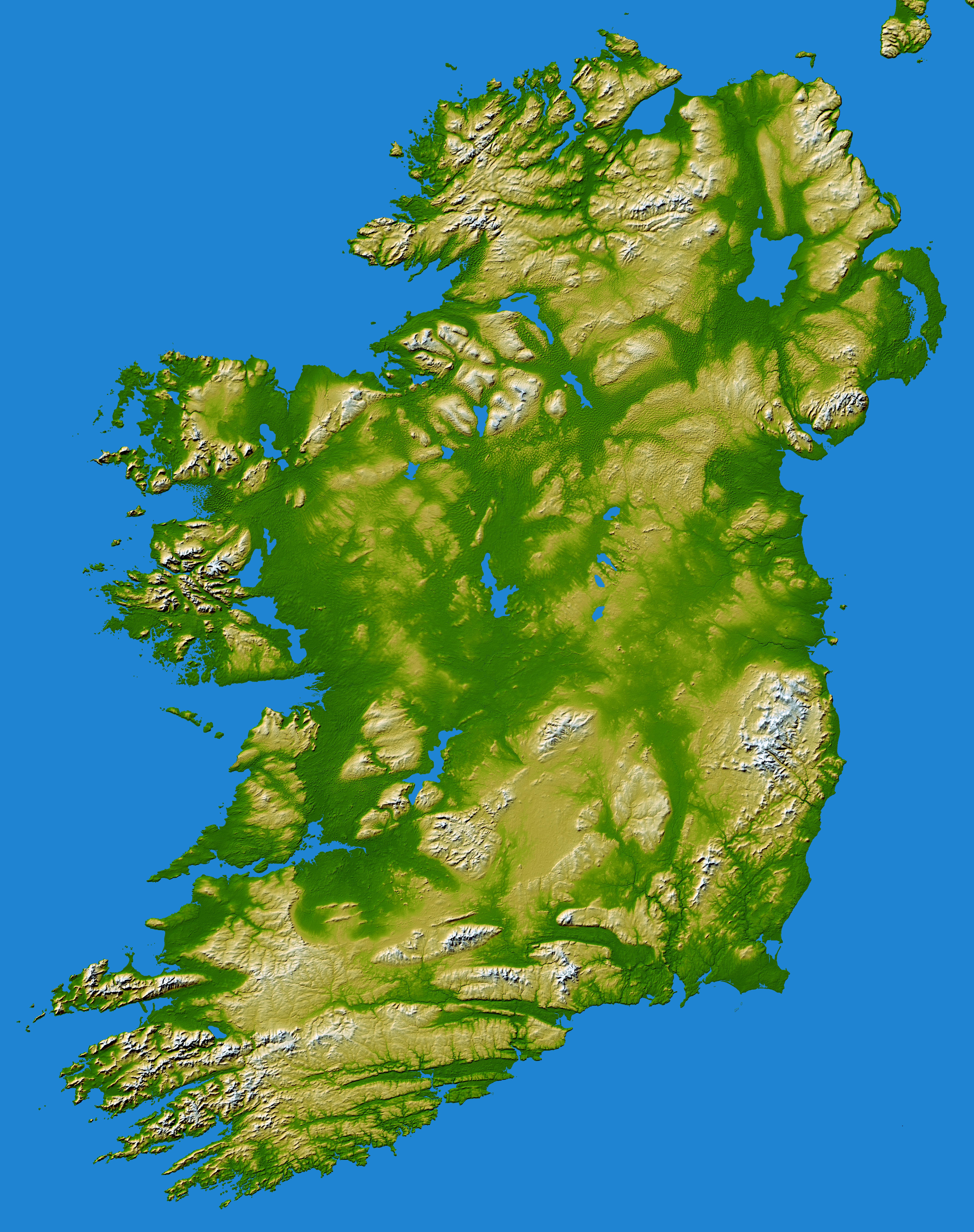 The island consists of varied geologic province, geological provinces. In the west, around County Galway and County Donegal, is a medium to high grade metamorphic and igneous complex of Caledonides, Caledonide affinity, similar to the Scottish Highlands. Across southeast Ulster and extending southwest to Longford and south to Navan is a province of Ordovician and Silurian rocks, with similarities to the Southern Uplands province of Scotland. Further south, along the
The island consists of varied geologic province, geological provinces. In the west, around County Galway and County Donegal, is a medium to high grade metamorphic and igneous complex of Caledonides, Caledonide affinity, similar to the Scottish Highlands. Across southeast Ulster and extending southwest to Longford and south to Navan is a province of Ordovician and Silurian rocks, with similarities to the Southern Uplands province of Scotland. Further south, along the
 Unlike Great Britain which had a
Unlike Great Britain which had a  Several different habitat types are found in Ireland, including farmland, open woodland, temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, conifer plantations, peat bogs and a variety of coastal habitats. However, agriculture drives current land use patterns in Ireland, limiting natural habitat preserves, particularly for larger wild mammals with greater territorial needs. With no large apex predators in Ireland other than humans and dogs, such populations of animals as semi-wild deer that cannot be controlled by smaller predators, such as the fox, are controlled by annual culling.
There are no snakes in Ireland, and only one species of reptile (the Viviparous lizard, common lizard) is native to the island. Extinct species include the Irish elk, the great auk, brown bear and the Wolves in Ireland, wolf. Some previously extinct birds, such as the golden eagle, have been reintroduced after decades of Local extinction, extirpation.
Ireland is now one of the least forested countries in Europe. Until the end of the Middle Ages, Ireland was heavily forested. Native species include deciduous trees such as oak, Fraxinus excelsior, ash, Corylus avellana, hazel, birch, Alnus glutinosa, alder, willow, Populus tremula, aspen, Sorbus aucuparia, rowan and Crataegus monogyna, hawthorn, as well as evergreen trees such Scots pine, Taxus baccata, yew, Ilex aquifolium, holly and Arbutus unedo, strawberry trees. Only about 10% of Ireland today is woodland; most of this is non-native conifer plantations, and only 2% is native woodland. The average woodland cover of European countries is over 33%. In the Republic, about is owned by the state, mainly by the forestry service Coillte. Remnants of native forest can be found scattered around the island, in particular in the Killarney National Park.
Several different habitat types are found in Ireland, including farmland, open woodland, temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, conifer plantations, peat bogs and a variety of coastal habitats. However, agriculture drives current land use patterns in Ireland, limiting natural habitat preserves, particularly for larger wild mammals with greater territorial needs. With no large apex predators in Ireland other than humans and dogs, such populations of animals as semi-wild deer that cannot be controlled by smaller predators, such as the fox, are controlled by annual culling.
There are no snakes in Ireland, and only one species of reptile (the Viviparous lizard, common lizard) is native to the island. Extinct species include the Irish elk, the great auk, brown bear and the Wolves in Ireland, wolf. Some previously extinct birds, such as the golden eagle, have been reintroduced after decades of Local extinction, extirpation.
Ireland is now one of the least forested countries in Europe. Until the end of the Middle Ages, Ireland was heavily forested. Native species include deciduous trees such as oak, Fraxinus excelsior, ash, Corylus avellana, hazel, birch, Alnus glutinosa, alder, willow, Populus tremula, aspen, Sorbus aucuparia, rowan and Crataegus monogyna, hawthorn, as well as evergreen trees such Scots pine, Taxus baccata, yew, Ilex aquifolium, holly and Arbutus unedo, strawberry trees. Only about 10% of Ireland today is woodland; most of this is non-native conifer plantations, and only 2% is native woodland. The average woodland cover of European countries is over 33%. In the Republic, about is owned by the state, mainly by the forestry service Coillte. Remnants of native forest can be found scattered around the island, in particular in the Killarney National Park.
 Much of the land is now covered with pasture and there are many species of wild-flower. Gorse (''Ulex europaeus''), a wild furze, is commonly found growing in the uplands and ferns are plentiful in the more moist regions, especially in the western parts. It is home to hundreds of plant species, some of them unique to the island, and has been "invaded" by some grasses, such as ''Spartina anglica''.
The algal and seaweed flora is that of the cold-temperate variety. The total number of species is 574 The island has been invaded by some algae, some of which are now well established.
Because of its mild climate, many species, including subtropics, sub-tropical species such as Arecaceae, palm trees, are grown in Ireland. Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Ireland belongs to the Atlantic European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The island can be subdivided into two ecoregions: the Celtic broadleaf forests and North Atlantic moist mixed forests.
Much of the land is now covered with pasture and there are many species of wild-flower. Gorse (''Ulex europaeus''), a wild furze, is commonly found growing in the uplands and ferns are plentiful in the more moist regions, especially in the western parts. It is home to hundreds of plant species, some of them unique to the island, and has been "invaded" by some grasses, such as ''Spartina anglica''.
The algal and seaweed flora is that of the cold-temperate variety. The total number of species is 574 The island has been invaded by some algae, some of which are now well established.
Because of its mild climate, many species, including subtropics, sub-tropical species such as Arecaceae, palm trees, are grown in Ireland. Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Ireland belongs to the Atlantic European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The island can be subdivided into two ecoregions: the Celtic broadleaf forests and North Atlantic moist mixed forests.
 The long history of agricultural production, coupled with modern intensive agricultural methods such as pesticide and fertiliser use and runoff from contaminants into streams, rivers and lakes, has placed pressure on biodiversity in Ireland. A land of green fields for crop cultivation and cattle rearing limits the space available for the establishment of native wild species. Hedgerows, however, traditionally used for maintaining and demarcating land boundaries, act as a refuge for native wild flora. This ecosystem stretches across the countryside and acts as a network of connections to preserve remnants of the ecosystem that once covered the island. Subsidies under the Common Agricultural Policy, which supported agricultural practices that preserved hedgerow environments, are undergoing reforms. The Common Agricultural Policy had in the past subsidised potentially destructive agricultural practices, for example by emphasising production without placing limits on indiscriminate use of fertilisers and pesticides; but reforms have gradually decoupled subsidies from production levels and introduced environmental and other requirements. 32% of Ireland's greenhouse gas emissions are correlated to agriculture. Forested areas typically consist of monoculture plantations of non-native species, which may result in habitats that are not suitable for supporting native species of invertebrates. Natural areas require fencing to prevent over-grazing by Deer of Ireland, deer and sheep that roam over uncultivated areas. Grazing in this manner is one of the main factors preventing the natural regeneration of forests across many regions of the country.
The long history of agricultural production, coupled with modern intensive agricultural methods such as pesticide and fertiliser use and runoff from contaminants into streams, rivers and lakes, has placed pressure on biodiversity in Ireland. A land of green fields for crop cultivation and cattle rearing limits the space available for the establishment of native wild species. Hedgerows, however, traditionally used for maintaining and demarcating land boundaries, act as a refuge for native wild flora. This ecosystem stretches across the countryside and acts as a network of connections to preserve remnants of the ecosystem that once covered the island. Subsidies under the Common Agricultural Policy, which supported agricultural practices that preserved hedgerow environments, are undergoing reforms. The Common Agricultural Policy had in the past subsidised potentially destructive agricultural practices, for example by emphasising production without placing limits on indiscriminate use of fertilisers and pesticides; but reforms have gradually decoupled subsidies from production levels and introduced environmental and other requirements. 32% of Ireland's greenhouse gas emissions are correlated to agriculture. Forested areas typically consist of monoculture plantations of non-native species, which may result in habitats that are not suitable for supporting native species of invertebrates. Natural areas require fencing to prevent over-grazing by Deer of Ireland, deer and sheep that roam over uncultivated areas. Grazing in this manner is one of the main factors preventing the natural regeneration of forests across many regions of the country.
 The population of Ireland is just over 7 million, of which approximately 5.1 million reside in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million reside in Northern Ireland.
People have lived in Ireland for over 9,000 years. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of major groups such as the , , , , , , , , . Later major groups included the , , . Smaller groups included the (see ), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , . Many survived into late medieval times, others vanished as they became politically unimportant. Over the past 1,200 years, Vikings, Normans, Welsh people, Welsh, Flemings, Scottish people, Scots, English people, English, African diaspora, Africans and Eastern Europeans have all added to the population and have had significant influences on Irish culture.
The population of Ireland rose rapidly from the 16th century until the mid-19th century, interrupted briefly by the Irish Famine (1740–41), Famine of 1740–41, which killed roughly two-fifths of the island's population. The population rebounded and multiplied over the next century, but the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of the 1840s caused one million deaths and forced over one million more to emigrate in its immediate wake. Over the following century, the population was reduced by over half, at a time when the general trend in European countries was for populations to rise by an average of three-fold.
Ireland's largest religious group is Christianity. The largest denomination is Roman Catholicism, representing over 73% of the island (and about 87% of the Republic of Ireland). Most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations (about 48% of Northern Ireland). The largest is the Anglicanism, Anglican Church of Ireland. The Islam in Ireland, Muslim community is growing in Ireland, mostly through increased immigration, with a 50% increase in the republic between the 2006 and 2011 census. The island has a small History of the Jews in Ireland, Jewish community. About 4% of the Republic's population and about 14% of the Northern Ireland population describe themselves as of no religion. In a 2010 survey conducted on behalf of the Irish Times, 32% of respondents said they went to a religious service more than once per week.
The population of Ireland is just over 7 million, of which approximately 5.1 million reside in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million reside in Northern Ireland.
People have lived in Ireland for over 9,000 years. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of major groups such as the , , , , , , , , . Later major groups included the , , . Smaller groups included the (see ), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , . Many survived into late medieval times, others vanished as they became politically unimportant. Over the past 1,200 years, Vikings, Normans, Welsh people, Welsh, Flemings, Scottish people, Scots, English people, English, African diaspora, Africans and Eastern Europeans have all added to the population and have had significant influences on Irish culture.
The population of Ireland rose rapidly from the 16th century until the mid-19th century, interrupted briefly by the Irish Famine (1740–41), Famine of 1740–41, which killed roughly two-fifths of the island's population. The population rebounded and multiplied over the next century, but the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of the 1840s caused one million deaths and forced over one million more to emigrate in its immediate wake. Over the following century, the population was reduced by over half, at a time when the general trend in European countries was for populations to rise by an average of three-fold.
Ireland's largest religious group is Christianity. The largest denomination is Roman Catholicism, representing over 73% of the island (and about 87% of the Republic of Ireland). Most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations (about 48% of Northern Ireland). The largest is the Anglicanism, Anglican Church of Ireland. The Islam in Ireland, Muslim community is growing in Ireland, mostly through increased immigration, with a 50% increase in the republic between the 2006 and 2011 census. The island has a small History of the Jews in Ireland, Jewish community. About 4% of the Republic's population and about 14% of the Northern Ireland population describe themselves as of no religion. In a 2010 survey conducted on behalf of the Irish Times, 32% of respondents said they went to a religious service more than once per week.
 The population of Ireland collapsed dramatically during the second half of the 19th century. A population of over 8 million in 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 was reduced to slightly over 4 million by 1921. In part, the fall in population was caused by death from the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845 to 1852, which took roughly 1 million lives. The remaining decline of around 3 million was due to the entrenched culture of emigration caused by the dire economic state of the country, lasting until the 21st century.
Emigration from Ireland in the 19th century contributed to the populations of England, the United States, Canada and Australia, in all of which a large Irish diaspora lives. , 4.3 million Canadians, or 14% of the population, were of Irish descent, while around one-third of the Australian population had an element of Irish descent. , there were 40 million Irish-Americans and 33 million Americans who claimed Irish ancestry.
With growing prosperity since the last decade of the 20th century, Ireland became a destination for immigrants. Since the European Union expanded to include Poland in 2004, Polish people have comprised the largest number of immigrants (over 150,000) from Central Europe. There has also been significant immigration from Lithuania, Czech Republic and Latvia.
Demographics of the Republic of Ireland#Immigration, The Republic of Ireland in particular has seen large-scale immigration, with 420,000 foreign nationals as of 2006, about 10% of the population. Nearly a quarter of births (24 percent) in 2009 were to mothers born outside of Ireland. Up to 50,000 eastern and central European migrant workers left Ireland in response to the Irish financial crisis.
The population of Ireland collapsed dramatically during the second half of the 19th century. A population of over 8 million in 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 was reduced to slightly over 4 million by 1921. In part, the fall in population was caused by death from the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845 to 1852, which took roughly 1 million lives. The remaining decline of around 3 million was due to the entrenched culture of emigration caused by the dire economic state of the country, lasting until the 21st century.
Emigration from Ireland in the 19th century contributed to the populations of England, the United States, Canada and Australia, in all of which a large Irish diaspora lives. , 4.3 million Canadians, or 14% of the population, were of Irish descent, while around one-third of the Australian population had an element of Irish descent. , there were 40 million Irish-Americans and 33 million Americans who claimed Irish ancestry.
With growing prosperity since the last decade of the 20th century, Ireland became a destination for immigrants. Since the European Union expanded to include Poland in 2004, Polish people have comprised the largest number of immigrants (over 150,000) from Central Europe. There has also been significant immigration from Lithuania, Czech Republic and Latvia.
Demographics of the Republic of Ireland#Immigration, The Republic of Ireland in particular has seen large-scale immigration, with 420,000 foreign nationals as of 2006, about 10% of the population. Nearly a quarter of births (24 percent) in 2009 were to mothers born outside of Ireland. Up to 50,000 eastern and central European migrant workers left Ireland in response to the Irish financial crisis.
 The two official languages of the Republic of Ireland are Irish and English. Each language has produced noteworthy literature. Irish, though now only the language of a minority, was the vernacular of the Irish people for thousands of years and was possibly introduced during the Iron Age. It began to be written down after Christianisation in the 5th century and spread to Scotland and the Isle of Man, where it evolved into the Scottish Gaelic and Manx Language, Manx languages respectively.
The Irish language has a vast treasury of written texts from many centuries and is divided by linguists into
The two official languages of the Republic of Ireland are Irish and English. Each language has produced noteworthy literature. Irish, though now only the language of a minority, was the vernacular of the Irish people for thousands of years and was possibly introduced during the Iron Age. It began to be written down after Christianisation in the 5th century and spread to Scotland and the Isle of Man, where it evolved into the Scottish Gaelic and Manx Language, Manx languages respectively.
The Irish language has a vast treasury of written texts from many centuries and is divided by linguists into
 Ireland's culture comprises elements of the culture of ancient peoples, later immigrant and broadcast cultural influences (chiefly Gaels, Gaelic culture, Anglicisation, Americanisation and aspects of broader European culture). In broad terms, Ireland is regarded as one of the Celtic nations of Europe, alongside Scotland, Wales, Cornwall, Isle of Man and Brittany. This combination of cultural influences is visible in the intricate designs termed ''Irish Interlace (visual arts), interlace'' or ''Celtic knotwork.'' These can be seen in the ornamentation of medieval religious and secular works. The style is still popular today in jewellery and graphic art, as is the distinctive style of traditional Irish music and dance, and has become indicative of modern "Celtic" culture in general.
Religion in Ireland, Religion has played a significant role in the cultural life of the island since ancient times (and since the 17th century Plantations of Ireland, plantations, has been the focus of political identity and divisions on the island). Ireland's pre-Christian heritage fused with the Celtic Church following the missions of
Ireland's culture comprises elements of the culture of ancient peoples, later immigrant and broadcast cultural influences (chiefly Gaels, Gaelic culture, Anglicisation, Americanisation and aspects of broader European culture). In broad terms, Ireland is regarded as one of the Celtic nations of Europe, alongside Scotland, Wales, Cornwall, Isle of Man and Brittany. This combination of cultural influences is visible in the intricate designs termed ''Irish Interlace (visual arts), interlace'' or ''Celtic knotwork.'' These can be seen in the ornamentation of medieval religious and secular works. The style is still popular today in jewellery and graphic art, as is the distinctive style of traditional Irish music and dance, and has become indicative of modern "Celtic" culture in general.
Religion in Ireland, Religion has played a significant role in the cultural life of the island since ancient times (and since the 17th century Plantations of Ireland, plantations, has been the focus of political identity and divisions on the island). Ireland's pre-Christian heritage fused with the Celtic Church following the missions of


 The Irish philosopher and theologian Johannes Scotus Eriugena was considered one of the leading intellectuals of the early Middle Ages. Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton, an Irish explorer, was one of the principal figures of Antarctic exploration. He, along with his expedition, made the first ascent of Mount Erebus and the discovery of the approximate location of the South Magnetic Pole. Robert Boyle was a 17th-century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, inventor and early gentleman scientist. He is largely regarded as one of the founders of modern chemistry and is best known for the formulation of Boyle's law.
19th-century physicist, John Tyndall, discovered the Tyndall effect. Father Nicholas Joseph Callan, Professor of Natural Philosophy in Maynooth College, is best known for his invention of the induction coil, transformer and he discovered an early method of galvanisation in the 19th century.
Other notable Irish physicists include Ernest Walton, winner of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Physics. With Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, he was the first to split the nucleus of the atom by artificial means and made contributions to the development of a new theory of wave equation. William Thomson, or Lord Kelvin, is the person whom the absolute temperature unit, the kelvin, is named after. Sir Joseph Larmor, a physicist and mathematician, made innovations in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics and the electron theory of matter. His most influential work was Aether and Matter, a book on theoretical physics published in 1900.
George Johnstone Stoney introduced the term ''electron'' in 1891. John Stewart Bell was the originator of Bell's Theorem and a paper concerning the discovery of the Chiral anomaly, Bell-Jackiw-Adler anomaly and was nominated for a Nobel prize. The astronomer Jocelyn Bell Burnell, from Lurgan, County Armagh, discovered pulsars in 1967. Notable mathematicians include Sir William Rowan Hamilton, famous for work in Hamiltonian mechanics, classical mechanics and the invention of quaternions. Francis Ysidro Edgeworth's contribution, the Edgeworth Box. remains influential in neo-classical microeconomic theory to this day; while Richard Cantillon inspired Adam Smith, among others. John B. Cosgrave was a specialist in number theory and discovered a 2000-digit prime number in 1999 and a record composite Fermat number in 2003. John Lighton Synge made progress in different fields of science, including mechanics and geometrical methods in general relativity. He had mathematician John Forbes Nash Jr., John Nash as one of his students. Kathleen Lonsdale, born in Ireland and most known for her work with X-ray crystallography, crystallography, became the first female president of the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
Ireland has nine universities, seven in the Republic of Ireland and two in Northern Ireland, including Trinity College Dublin and the University College Dublin, as well as numerous third-level colleges and institutes and a branch of the Open University, the Open University in Ireland. Ireland was ranked 19th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 12th in 2019.
The Irish philosopher and theologian Johannes Scotus Eriugena was considered one of the leading intellectuals of the early Middle Ages. Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton, an Irish explorer, was one of the principal figures of Antarctic exploration. He, along with his expedition, made the first ascent of Mount Erebus and the discovery of the approximate location of the South Magnetic Pole. Robert Boyle was a 17th-century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, inventor and early gentleman scientist. He is largely regarded as one of the founders of modern chemistry and is best known for the formulation of Boyle's law.
19th-century physicist, John Tyndall, discovered the Tyndall effect. Father Nicholas Joseph Callan, Professor of Natural Philosophy in Maynooth College, is best known for his invention of the induction coil, transformer and he discovered an early method of galvanisation in the 19th century.
Other notable Irish physicists include Ernest Walton, winner of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Physics. With Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, he was the first to split the nucleus of the atom by artificial means and made contributions to the development of a new theory of wave equation. William Thomson, or Lord Kelvin, is the person whom the absolute temperature unit, the kelvin, is named after. Sir Joseph Larmor, a physicist and mathematician, made innovations in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics and the electron theory of matter. His most influential work was Aether and Matter, a book on theoretical physics published in 1900.
George Johnstone Stoney introduced the term ''electron'' in 1891. John Stewart Bell was the originator of Bell's Theorem and a paper concerning the discovery of the Chiral anomaly, Bell-Jackiw-Adler anomaly and was nominated for a Nobel prize. The astronomer Jocelyn Bell Burnell, from Lurgan, County Armagh, discovered pulsars in 1967. Notable mathematicians include Sir William Rowan Hamilton, famous for work in Hamiltonian mechanics, classical mechanics and the invention of quaternions. Francis Ysidro Edgeworth's contribution, the Edgeworth Box. remains influential in neo-classical microeconomic theory to this day; while Richard Cantillon inspired Adam Smith, among others. John B. Cosgrave was a specialist in number theory and discovered a 2000-digit prime number in 1999 and a record composite Fermat number in 2003. John Lighton Synge made progress in different fields of science, including mechanics and geometrical methods in general relativity. He had mathematician John Forbes Nash Jr., John Nash as one of his students. Kathleen Lonsdale, born in Ireland and most known for her work with X-ray crystallography, crystallography, became the first female president of the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
Ireland has nine universities, seven in the Republic of Ireland and two in Northern Ireland, including Trinity College Dublin and the University College Dublin, as well as numerous third-level colleges and institutes and a branch of the Open University, the Open University in Ireland. Ireland was ranked 19th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 12th in 2019.
 Gaelic football, hurling and Gaelic handball, handball are the best-known Irish traditional sports, collectively known as
Gaelic football, hurling and Gaelic handball, handball are the best-known Irish traditional sports, collectively known as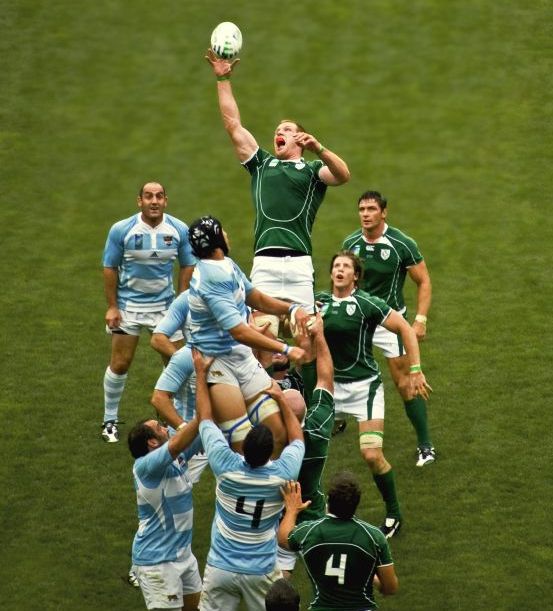  In 1950, FIFA directed the associations only to select players from within their respective territories and, in 1953, directed that the FAI's team be known only as "Republic of Ireland national football team, Republic of Ireland" and that the IFA's team be known as "Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland" (with certain exceptions). Northern Ireland qualified for the FIFA World Cup, World Cup finals in 1958 FIFA World Cup, 1958 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982 and 1986 FIFA World Cup, 1986 and the UEFA European Championship, European Championship in UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. The Republic qualified for the World Cup finals in 1990 FIFA World Cup, 1990 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 and the European Championship in UEFA Euro 1988, 1988, UEFA Euro 2012, 2012 and UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. Across Ireland, there is significant interest in the Premier League, English and, to a lesser extent, Scottish Premier League, Scottish soccer leagues.
Ireland fields a single Ireland national rugby union team, national rugby team and a single association, the Irish Rugby Football Union, governs the sport across the island. The Irish rugby team have played in every Rugby World Cup, making the quarter-finals in six of them. Ireland also hosted games during the 1991 Rugby World Cup, 1991 and the 1999 Rugby World Cups (including a quarter-final). There are four professional Irish teams; all four play in the Pro14 and at least three compete for the Heineken Cup. Irish rugby has become increasingly competitive at both the international and provincial levels since the sport went professional in 1994. During that time, Ulster Rugby, Ulster (1998–99 Heineken Cup, 1999), Munster Rugby, Munster (2005–06 Heineken Cup, 2006 and 2007–08 Heineken Cup, 2008) and Leinster Rugby, Leinster (2008–09 Heineken Cup, 2009, 2010–11 Heineken Cup, 2011 and 2011–12 Heineken Cup, 2012) have won the Heineken Cup. In addition to this, the Irish International side has had increased success in the Six Nations Championship against the other European elite sides. This success, including Triple Crown (rugby union), Triple Crowns in 2004, 2006 and 2007, culminated with a clean sweep of victories, known as a Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slam, in 2009 and 2018.
In 1950, FIFA directed the associations only to select players from within their respective territories and, in 1953, directed that the FAI's team be known only as "Republic of Ireland national football team, Republic of Ireland" and that the IFA's team be known as "Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland" (with certain exceptions). Northern Ireland qualified for the FIFA World Cup, World Cup finals in 1958 FIFA World Cup, 1958 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982 and 1986 FIFA World Cup, 1986 and the UEFA European Championship, European Championship in UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. The Republic qualified for the World Cup finals in 1990 FIFA World Cup, 1990 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 and the European Championship in UEFA Euro 1988, 1988, UEFA Euro 2012, 2012 and UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. Across Ireland, there is significant interest in the Premier League, English and, to a lesser extent, Scottish Premier League, Scottish soccer leagues.
Ireland fields a single Ireland national rugby union team, national rugby team and a single association, the Irish Rugby Football Union, governs the sport across the island. The Irish rugby team have played in every Rugby World Cup, making the quarter-finals in six of them. Ireland also hosted games during the 1991 Rugby World Cup, 1991 and the 1999 Rugby World Cups (including a quarter-final). There are four professional Irish teams; all four play in the Pro14 and at least three compete for the Heineken Cup. Irish rugby has become increasingly competitive at both the international and provincial levels since the sport went professional in 1994. During that time, Ulster Rugby, Ulster (1998–99 Heineken Cup, 1999), Munster Rugby, Munster (2005–06 Heineken Cup, 2006 and 2007–08 Heineken Cup, 2008) and Leinster Rugby, Leinster (2008–09 Heineken Cup, 2009, 2010–11 Heineken Cup, 2011 and 2011–12 Heineken Cup, 2012) have won the Heineken Cup. In addition to this, the Irish International side has had increased success in the Six Nations Championship against the other European elite sides. This success, including Triple Crown (rugby union), Triple Crowns in 2004, 2006 and 2007, culminated with a clean sweep of victories, known as a Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slam, in 2009 and 2018.
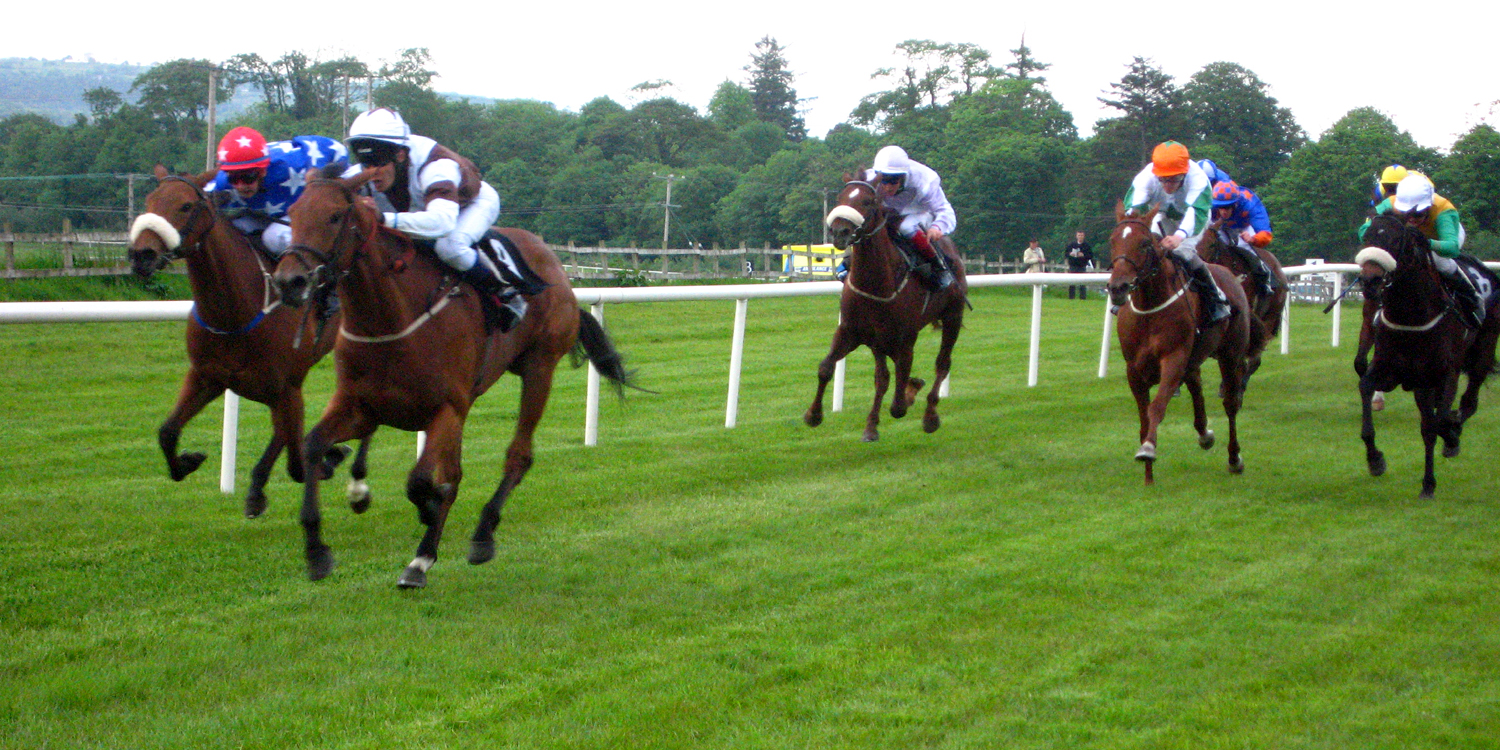 Horse racing and greyhound racing are both popular in Ireland. There are frequent horse race meetings and greyhound stadiums are well-attended. The island is noted for the breeding and training of race horses and is also a large exporter of racing dogs. The horse racing sector is largely concentrated in the County Kildare.
Irish athletics is an all-Ireland sport governed by Athletics Ireland. Sonia O'Sullivan won two medals at 5,000 metres on the track; gold at the 1995 IAAF World Championships in Athletics, World Championships and silver at the 2000 Summer Olympics, 2000 Sydney Olympics. Gillian O'Sullivan won silver in the 20k walk at the 2003 World Championships, while sprint hurdler Derval O'Rourke won gold at the 2006 World Indoor Championship in Moscow. Olive Loughnane won a silver medal in the 20k walk at the World Athletics Championships in Berlin in 2009.
Golf is very popular, and golf tourism is a major industry attracting more than 240,000 golfing visitors annually. The 2006 Ryder Cup was held at The Kildare Hotel and Golf Club, The K Club in County Kildare. Pádraig Harrington became the first Irishman since Fred Daly (golfer), Fred Daly in 1947 to win the The Open Championship, British Open at Carnoustie in July 2007. He successfully defended his title in July 2008 before going on to win the PGA Championship in August. Harrington became the first European to win the PGA Championship in 78 years and was the first winner from Ireland. Three golfers from Northern Ireland have been particularly successful. In 2010, Graeme McDowell became the first Irish golfer to win the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, and the first European to win that tournament since 1970. Rory McIlroy, at the age of 22, won the 2011 U.S. Open, while Darren Clarke's latest victory was the 2011 Open Championship at Royal St. George's. In August 2012, McIlroy won his 2nd major championship by winning the USPGA Championship by a record margin of 8 shots.
Horse racing and greyhound racing are both popular in Ireland. There are frequent horse race meetings and greyhound stadiums are well-attended. The island is noted for the breeding and training of race horses and is also a large exporter of racing dogs. The horse racing sector is largely concentrated in the County Kildare.
Irish athletics is an all-Ireland sport governed by Athletics Ireland. Sonia O'Sullivan won two medals at 5,000 metres on the track; gold at the 1995 IAAF World Championships in Athletics, World Championships and silver at the 2000 Summer Olympics, 2000 Sydney Olympics. Gillian O'Sullivan won silver in the 20k walk at the 2003 World Championships, while sprint hurdler Derval O'Rourke won gold at the 2006 World Indoor Championship in Moscow. Olive Loughnane won a silver medal in the 20k walk at the World Athletics Championships in Berlin in 2009.
Golf is very popular, and golf tourism is a major industry attracting more than 240,000 golfing visitors annually. The 2006 Ryder Cup was held at The Kildare Hotel and Golf Club, The K Club in County Kildare. Pádraig Harrington became the first Irishman since Fred Daly (golfer), Fred Daly in 1947 to win the The Open Championship, British Open at Carnoustie in July 2007. He successfully defended his title in July 2008 before going on to win the PGA Championship in August. Harrington became the first European to win the PGA Championship in 78 years and was the first winner from Ireland. Three golfers from Northern Ireland have been particularly successful. In 2010, Graeme McDowell became the first Irish golfer to win the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, and the first European to win that tournament since 1970. Rory McIlroy, at the age of 22, won the 2011 U.S. Open, while Darren Clarke's latest victory was the 2011 Open Championship at Royal St. George's. In August 2012, McIlroy won his 2nd major championship by winning the USPGA Championship by a record margin of 8 shots.
 Food and cuisine in Ireland take their influence from the crops grown and animals farmed in the island's temperate climate and from the social and political circumstances of Irish history. For example, whilst from the Middle Ages until the arrival of the potato in the 16th century the dominant feature of the Irish economy was the herding of cattle, the number of cattle a person owned was equated to their social standing. Thus herders would avoid slaughtering a milk-producing cow.
For this reason, pork and white meat were more common than beef, and thick fatty strips of salted bacon (known as rashers) and the eating of salted butter (i.e. a dairy product rather than beef itself) have been a central feature of the diet in Ireland since the Middle Ages. The practice of bleeding cattle and mixing the blood with milk and butter (not unlike the practice of the Maasai people, Maasai) was common and black pudding, made from blood, grain (usually barley) and seasoning, remains a breakfast staple in Ireland. All of these influences can be seen today in the phenomenon of the "breakfast roll".
The introduction of the potato in the second half of the 16th century heavily influenced cuisine thereafter. Great poverty encouraged a subsistence approach to food, and by the mid-19th century, the vast majority of the population sufficed with a diet of potatoes and milk. A typical family, consisting of a man, a woman and four children, would eat of potatoes per week. Consequently, dishes that are considered as national dishes represent a fundamental simplicity to cooking, such as the Irish stew, bacon and cabbage, boxty, a type of potato pancake, or colcannon, a dish of mashed potatoes and kale or cabbage.
Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a "New Irish Cuisine" based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made List of Irish cheeses, cheeses that are now being produced across the country. An example of this new cuisine is "Dublin Lawyer": lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to
Food and cuisine in Ireland take their influence from the crops grown and animals farmed in the island's temperate climate and from the social and political circumstances of Irish history. For example, whilst from the Middle Ages until the arrival of the potato in the 16th century the dominant feature of the Irish economy was the herding of cattle, the number of cattle a person owned was equated to their social standing. Thus herders would avoid slaughtering a milk-producing cow.
For this reason, pork and white meat were more common than beef, and thick fatty strips of salted bacon (known as rashers) and the eating of salted butter (i.e. a dairy product rather than beef itself) have been a central feature of the diet in Ireland since the Middle Ages. The practice of bleeding cattle and mixing the blood with milk and butter (not unlike the practice of the Maasai people, Maasai) was common and black pudding, made from blood, grain (usually barley) and seasoning, remains a breakfast staple in Ireland. All of these influences can be seen today in the phenomenon of the "breakfast roll".
The introduction of the potato in the second half of the 16th century heavily influenced cuisine thereafter. Great poverty encouraged a subsistence approach to food, and by the mid-19th century, the vast majority of the population sufficed with a diet of potatoes and milk. A typical family, consisting of a man, a woman and four children, would eat of potatoes per week. Consequently, dishes that are considered as national dishes represent a fundamental simplicity to cooking, such as the Irish stew, bacon and cabbage, boxty, a type of potato pancake, or colcannon, a dish of mashed potatoes and kale or cabbage.
Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a "New Irish Cuisine" based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made List of Irish cheeses, cheeses that are now being produced across the country. An example of this new cuisine is "Dublin Lawyer": lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to  Ireland once dominated the world's market for whiskey, producing 90% of the world's whiskey at the start of the 20th century. However, as a consequence of bootleggers during the prohibition in the United States (who sold poor-quality whiskey bearing Irish-sounding names thus eroding the pre-prohibition popularity for Irish brands) and tariffs on Irish whiskey across the British Empire during the Anglo-Irish Trade War of the 1930s, sales of Irish whiskey worldwide fell to a mere 2% by the mid-20th century. In 1953, an Irish government survey, found that 50% of whiskey drinkers in the United States had never heard of Irish whiskey.
Irish whiskey, as researched in 2009 by the CNBC American broadcaster, remains popular domestically and has grown in international sales steadily over a few decades. Typically CNBC states Irish whiskey is not as smoky as a Scotch whisky, but not as sweet as American whiskey, American or Canadian whiskey, Canadian whiskies. Whiskey forms the basis of Irish Cream, cream liqueurs, such as Baileys Irish Cream, Baileys, and the "Irish coffee" (a cocktail of coffee and whiskey reputedly invented at Foynes, Foynes flying-boat station) is probably the best-known Irish cocktail.
Porter (beer), Stout, a kind of porter beer, particularly Guinness, is typically associated with Ireland, although historically it was more closely associated with London. Porter remains very popular, although it has lost sales since the mid-20th century to lager. Cider, particularly ''Magners'' (marketed in the
Ireland once dominated the world's market for whiskey, producing 90% of the world's whiskey at the start of the 20th century. However, as a consequence of bootleggers during the prohibition in the United States (who sold poor-quality whiskey bearing Irish-sounding names thus eroding the pre-prohibition popularity for Irish brands) and tariffs on Irish whiskey across the British Empire during the Anglo-Irish Trade War of the 1930s, sales of Irish whiskey worldwide fell to a mere 2% by the mid-20th century. In 1953, an Irish government survey, found that 50% of whiskey drinkers in the United States had never heard of Irish whiskey.
Irish whiskey, as researched in 2009 by the CNBC American broadcaster, remains popular domestically and has grown in international sales steadily over a few decades. Typically CNBC states Irish whiskey is not as smoky as a Scotch whisky, but not as sweet as American whiskey, American or Canadian whiskey, Canadian whiskies. Whiskey forms the basis of Irish Cream, cream liqueurs, such as Baileys Irish Cream, Baileys, and the "Irish coffee" (a cocktail of coffee and whiskey reputedly invented at Foynes, Foynes flying-boat station) is probably the best-known Irish cocktail.
Porter (beer), Stout, a kind of porter beer, particularly Guinness, is typically associated with Ireland, although historically it was more closely associated with London. Porter remains very popular, although it has lost sales since the mid-20th century to lager. Cider, particularly ''Magners'' (marketed in the
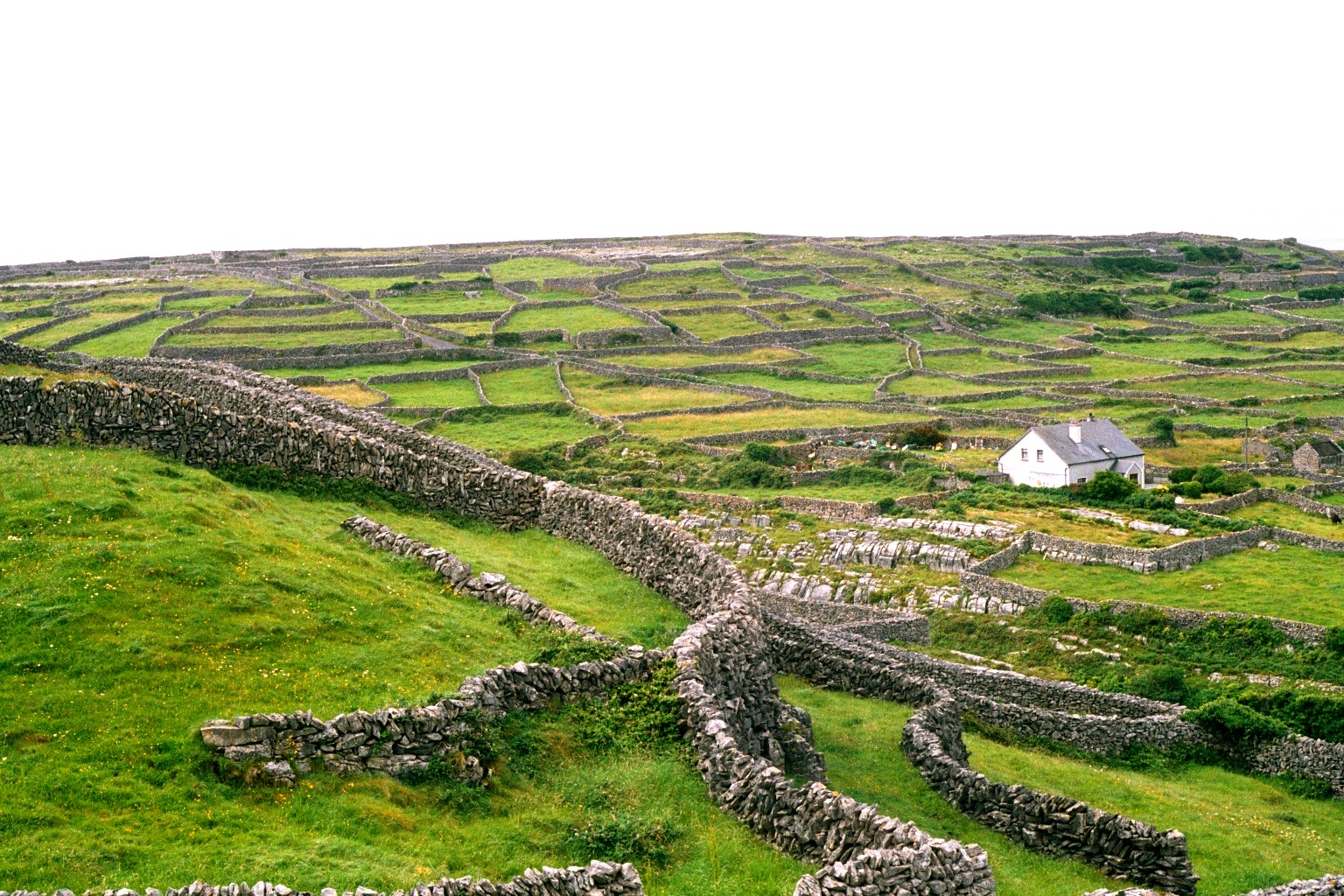
 There are three World Heritage Sites on the island: the complex, Skellig Michael and the Giant's Causeway. Several other places are on the tentative list, for example the Burren, the Ceide Fields and Mount Stewart.
Some of the most visited sites in Ireland include Bunratty Castle, the Rock of Cashel, the Cliffs of Moher, Holy Cross Abbey and Blarney Castle. Historically important monastic sites include Glendalough and Clonmacnoise, which are maintained as National Monument (Ireland), national monuments in the Republic of Ireland.
The Dublin region receives the most tourists and is home to several of the most popular attractions such as the Guinness Storehouse and
There are three World Heritage Sites on the island: the complex, Skellig Michael and the Giant's Causeway. Several other places are on the tentative list, for example the Burren, the Ceide Fields and Mount Stewart.
Some of the most visited sites in Ireland include Bunratty Castle, the Rock of Cashel, the Cliffs of Moher, Holy Cross Abbey and Blarney Castle. Historically important monastic sites include Glendalough and Clonmacnoise, which are maintained as National Monument (Ireland), national monuments in the Republic of Ireland.
The Dublin region receives the most tourists and is home to several of the most popular attractions such as the Guinness Storehouse and
 Ireland has an ancient industry based on peat (known locally as "turf") as a source of energy for home fires. A form of biomass energy, this source of heat is still widely used in rural areas. However, because of the ecological importance of peatlands in storing carbon and their rarity, the EU is attempting to protect this habitat by fining Ireland for digging up peat. In cities, heat is generally supplied by natural gas or heating oil, although some urban suppliers distribute sods of turf as "smokeless fuel" for domestic use.
The Republic has a strong commitment to renewable energy and ranks as one of the top 10 markets for clean technology, clean-technology investment in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index. Research and development in renewable energy (such as wind power) has increased since 2004. Large List of wind farms in the Republic of Ireland, wind farms have been constructed in Cork, Donegal, Mayo and Antrim. The construction of wind farms has in some cases been delayed by opposition from local communities, some of whom regard the wind turbines as unsightly. The Republic is hindered by an ageing network that was not designed to handle the varying availability of power that comes from wind farms. The ESB's Turlough Hill facility is the only power-storage facility in the state.
Ireland has an ancient industry based on peat (known locally as "turf") as a source of energy for home fires. A form of biomass energy, this source of heat is still widely used in rural areas. However, because of the ecological importance of peatlands in storing carbon and their rarity, the EU is attempting to protect this habitat by fining Ireland for digging up peat. In cities, heat is generally supplied by natural gas or heating oil, although some urban suppliers distribute sods of turf as "smokeless fuel" for domestic use.
The Republic has a strong commitment to renewable energy and ranks as one of the top 10 markets for clean technology, clean-technology investment in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index. Research and development in renewable energy (such as wind power) has increased since 2004. Large List of wind farms in the Republic of Ireland, wind farms have been constructed in Cork, Donegal, Mayo and Antrim. The construction of wind farms has in some cases been delayed by opposition from local communities, some of whom regard the wind turbines as unsightly. The Republic is hindered by an ageing network that was not designed to handle the varying availability of power that comes from wind farms. The ESB's Turlough Hill facility is the only power-storage facility in the state.
excerpt
* * * * * * *
Government of Ireland
Northern Ireland Executive
{{Authority control Ireland, British Isles Celtic nations Divided regions International islands
Éire
() is Irish for "Ireland", the name of both an island in the North Atlantic and the sovereign state of the Republic of Ireland which governs 84% of the island's landmass. The latter is distinct from Northern Ireland, which covers the remainde ...
; Ulster-Scots Ulster Scots, may refer to:
* Ulster Scots people
The Ulster Scots ( Ulster-Scots: ''Ulstèr-Scotch''; ga, Albanaigh Ultach), also called Ulster Scots people (''Ulstèr-Scotch fowk'') or (in North America) Scotch-Irish (''Scotch-Airisch'') ...
: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
, in north-western Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern Europe, Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnography, ethnographically.
Geographic defini ...
. It is separated from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
to its east by the North Channel North Channel may refer to:
*North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland)
*North Channel (Ontario), body of water along the north shore of Lake Huron, Canada
*North Channel, Hong Kong
*Canal du Nord, France
{{geodis ...
, the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
, and St George's Channel
St George's Channel ( cy, Sianel San Siôr, ga, Muir Bhreatan) is a sea channel connecting the Irish Sea to the north and the Celtic Sea to the southwest.
Historically, the name "St George's Channel" was used interchangeably with "Irish Sea" ...
. Ireland is the second-largest island of the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
, the third-largest in Europe, and the twentieth-largest on Earth.
Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
(officially named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
, which is part of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. As of 2022, the population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the second-most populous island in Europe after Great Britain.The 2022 population of the Republic of Ireland was 5,123,536 and that of Northern Ireland in 2021 was 1,903,100. These are Census data from the official governmental statistics agencies in the respective jurisdictions:
*
*
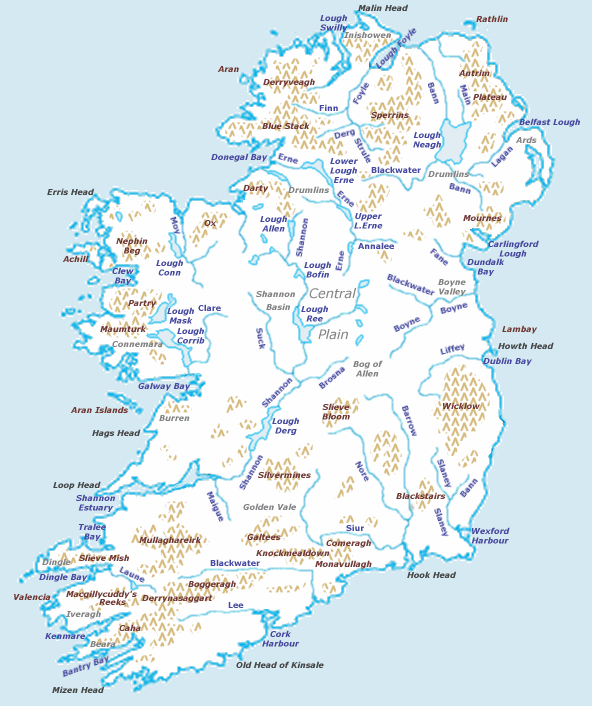
The geography of Ireland
:Ireland is an island in Northwestern Europe in the north Atlantic Ocean. The island lies on the European continental shelf, part of the Eurasian Plate. The island's main geographical features include low central plains surrounded by coasta ...
comprises relatively low-lying mountains surrounding a central plain, with several navigable rivers extending inland. Its lush vegetation is a product of its mild but changeable climate which is free of extremes in temperature. Much of Ireland was woodland until the end of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Today, woodland makes up about 10% of the island, compared with a European average of over 33%, with most of it being non-native conifer plantations."Native trees cover just 2% of Ireland. How can this be increased?". ''
The Irish Times
''The Irish Times'' is an Irish daily broadsheet newspaper and online digital publication. It launched on 29 March 1859. The editor is Ruadhán Mac Cormaic. It is published every day except Sundays. ''The Irish Times'' is considered a newspaper ...
'', 6 July 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2019."Ireland’s native woodlands are quietly disappearing". ''
The Irish Times
''The Irish Times'' is an Irish daily broadsheet newspaper and online digital publication. It launched on 29 March 1859. The editor is Ruadhán Mac Cormaic. It is published every day except Sundays. ''The Irish Times'' is considered a newspaper ...
'', 19 June 2018. Retrieved 29 January 2019. The Irish climate is influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and thus very moderate, and winters are milder than expected for such a northerly area, although summers are cooler than those in continental Europe. Rainfall and cloud cover are abundant.
Gaelic Ireland
Gaelic Ireland ( ga, Éire Ghaelach) was the Gaelic political and social order, and associated culture, that existed in Ireland from the late prehistoric era until the early 17th century. It comprised the whole island before Anglo-Normans co ...
had emerged by the 1st century AD. The island was Christianised from the 5th century onwards. Following the 12th century Anglo-Norman invasion, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
claimed sovereignty. However, English rule did not extend over the whole island until the 16th–17th century Tudor conquest, which led to colonisation by settlers from Britain. In the 1690s, a system of Protestant English rule was designed to materially disadvantage the Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
majority and Protestant dissenter
A dissenter (from the Latin ''dissentire'', "to disagree") is one who dissents (disagrees) in matters of opinion, belief, etc.
Usage in Christianity
Dissent from the Anglican church
In the social and religious history of England and Wales, and ...
s, and was extended during the 18th century. With the Acts of Union in 1801, Ireland became a part of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. A war of independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of o ...
in the early 20th century was followed by the partition of the island, thus creating the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
, which became increasingly sovereign over the following decades, and Northern Ireland, which remained a part of the United Kingdom. Northern Ireland saw much civil unrest from the late 1960s until the 1990s. This subsided following the Good Friday Agreement
The Good Friday Agreement (GFA), or Belfast Agreement ( ga, Comhaontú Aoine an Chéasta or ; Ulster-Scots: or ), is a pair of agreements signed on 10 April 1998 that ended most of the violence of The Troubles, a political conflict in No ...
in 1998. In 1973, the Republic of Ireland joined the European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
while the United Kingdom, and Northern Ireland as part of it, did the same. In 2020, the United Kingdom, Northern Ireland included, left what was by then the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
(EU).
Irish culture
The culture of Ireland includes language, literature, music, art, folklore, cuisine, and sport associated with Ireland and the Irish people. For most of its recorded history, Irish culture has been primarily Gaelic (see Gaelic Ireland). It has ...
has had a significant influence on other cultures, especially in the field of literature
Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction, drama, and poetry. In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include ...
. Alongside mainstream Western culture
Leonardo da Vinci's ''Vitruvian Man''. Based on the correlations of ideal Body proportions">human proportions with geometry described by the ancient Roman architect Vitruvius in Book III of his treatise ''De architectura''.
image:Plato Pio-Cle ...
, a strong indigenous culture exists, as expressed through Gaelic games
Gaelic games ( ga, Cluichí Gaelacha) are a set of sports played worldwide, though they are particularly popular in Ireland, where they originated. They include Gaelic football, hurling, Gaelic handball and rounders. Football and hurling, the ...
, Irish music
Irish music is music that has been created in various genres on the island of Ireland.
The indigenous music of the island is termed Irish traditional music. It has remained vibrant through the 20th and into the 21st century, despite globalis ...
, Irish language
Irish ( Standard Irish: ), also known as Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Insular Celtic branch of the Celtic language family, which is a part of the Indo-European language family. Irish is indigenous to the island of Ireland and was ...
, and Irish dance
Irish dance refers to a group of traditional dance forms that originate in Ireland, encompassing dancing both solo and in groups, and dancing for social, competitive, and performance purposes. Irish dance in its current form developed from vario ...
. The island's culture shares many features with that of Great Britain, including the English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the is ...
, and sports such as association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 players who primarily use their feet to propel the ball around a rectangular field called a pitch. The objective of the game is ...
, rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
, horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
, golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
, and boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
.
Etymology
The names ''Ireland'' and derive fromOld Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
''Ériu
In Irish mythology, Ériu (; modern ga, Éire ), daughter of Delbáeth and Ernmas of the Tuatha Dé Danann, was the eponymous matron goddess of Ireland.
The English name for Ireland comes from the name Ériu and the Germanic languages, Germani ...
'', a goddess in Irish mythology
Irish mythology is the body of myths native to the island of Ireland. It was originally passed down orally in the prehistoric era, being part of ancient Celtic religion. Many myths were later written down in the early medieval era by C ...
first recorded in the ninth century. The etymology of Ériu is disputed but may derive from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
root *', referring to flowing water.
History
Prehistoric Ireland
During the last glacial period, and until about 16,000 BC, much of Ireland was periodically covered in ice. Therelative sea level Relative sea level (abbreviated as RSL) is defined as the sea level that is observed with respect to a land-based reference frame. It is often contrasted with eustatic sea level, which is a measure of the total mass or volume of the oceans. Relative ...
was less than 50m lower resulting in an ice bridge
An ice bridge is a frozen natural structure formed over seas, bays, rivers or lake surfaces. They facilitate migration of animals or people over a water body that was previously uncrossable by terrestrial animals, including humans. The most sign ...
(but not a land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and Colonisation (biology), colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regre ...
) forming between Ireland and Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
. By 14,000 BC this ice bridge existed only between Northern Ireland and Scotland and by 12,000 BC Ireland was completely separated from Great Britain.Edwards, Robin & al.The Island of Ireland: Drowning the Myth of an Irish Land-bridge?
" Accessed 15 February 2013. Later, around 6100 BC, Great Britain became separated from continental Europe. Until recently, the earliest evidence of human activity in Ireland was dated at 12,500 years ago, demonstrated by a butchered bear bone found in a cave in
County Clare
County Clare ( ga, Contae an Chláir) is a county in Ireland, in the Southern Region and the province of Munster, bordered on the west by the Atlantic Ocean. Clare County Council is the local authority. The county had a population of 118,817 ...
. Since 2021, the earliest evidence of human activity in Ireland is dated to 33,000 years ago.
By about 8000 BC, more sustained occupation of the island has been shown, with evidence for Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
communities around the island.
Some time before 4000 BC, Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
settlers introduced cereal cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, ...
s, domesticated animals such as cattle and sheep, built large timber buildings, and stone monuments. The earliest evidence for farming in Ireland or Great Britain is from Ferriter's Cove
Ferriter's Cove ( gle, Cuan an Chaoil) is a small bay located at the westernmost point of Dingle Peninsula, in County Kerry, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, Nor ...
, County Kerry
County Kerry ( gle, Contae Chiarraí) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and forms part of the province of Munster. It is named after the Ciarraige who lived in part of the present county. The population of the co ...
, where a flint knife, cattle bones and a sheep's tooth were carbon-dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was dev ...
to c. 4350 BC. Field systems were developed in different parts of Ireland, including at the , that has been preserved beneath a blanket of peat in present-day Tyrawley. An extensive field system The study of field systems (collections of fields) in landscape history is concerned with the size, shape and orientation of a number of fields. These are often adjacent, but may be separated by a later feature.
Field systems by region Czech Republ ...
, arguably the oldest in the world, consisted of small divisions separated by dry-stone wall
Dry stone, sometimes called drystack or, in Scotland, drystane, is a building method by which structures are constructed from stones without any mortar to bind them together. Dry stone structures are stable because of their construction me ...
s. The fields were farmed for several centuries between 3500 BC and 3000 BC. Wheat and barley were the principal crops.
The Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
began around 2500 BC, with technology changing people's everyday lives during this period through innovations such as the wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction wi ...
; harnessing oxen
An ox ( : oxen, ), also known as a bullock (in BrE
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Oxford Dictionaries, "English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer spec ...
; weaving textiles; brewing alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
; and skilful metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale ...
, which produced new weapons and tools, along with fine gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
decoration and jewellery, such as brooch
A brooch (, also ) is a decorative jewelry item designed to be attached to garments, often to fasten them together. It is usually made of metal, often silver or gold or some other material. Brooches are frequently decorated with vitreous enamel, ...
es and torc
A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some had hook and ring closures and a few had ...
s.
Emergence of Celtic Ireland
How and when the island became Celtic has been debated for close to a century, with the migrations of the Celts being one of the more enduring themes of archaeological and linguistic studies. The most recent genetic research strongly associates the spread of Indo-European languages (including Celtic) through Western Europe with a people bringing a compositeBeaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the Inverted bell, inverted-bell beaker (archaeology), beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the E ...
, with its arrival in Britain and Ireland dated to around the middle of the third millennium BC. According to John T. Koch
John T. Koch is an American academic, historian and linguist who specializes in Celtic studies, especially prehistory and the early Middle Ages. He is the editor of the five-volume ''Celtic Culture. A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2006, ABC Clio). He ...
and others, Ireland in the Late Bronze Age was part of a maritime trading-network culture called the Atlantic Bronze Age
The Atlantic Bronze Age is a cultural complex of the Bronze Age period in Prehistoric Europe of approximately 1300–700 BC that includes different cultures in Britain, France, Ireland, Portugal, and Spain.
Trade
The Atlantic Bronze Age ...
that also included Britain, western France and Iberia, and that this is where Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
developed. This contrasts with the traditional view that their origin lies in mainland Europe with the Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
.
 The long-standing traditional view is that the Celtic language,
The long-standing traditional view is that the Celtic language, Ogham
Ogham (Modern Irish: ; mga, ogum, ogom, later mga, ogam, label=none ) is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the early Irish language (in the "orthodox" inscriptions, 4th to 6th centuries AD), and later the Old Irish langua ...
script and culture were brought to Ireland by waves of invading or migrating Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
from mainland Europe. This theory draws on the ''Lebor Gabála Érenn
''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' (literally "The Book of the Taking of Ireland"), known in English as ''The Book of Invasions'', is a collection of poems and prose narratives in the Irish language intended to be a history of Ireland and the Irish fro ...
'', a medieval Christian pseudo-history of Ireland, along with the presence of Celtic culture, language and artefacts found in Ireland such as Celtic bronze spears, shields, torcs and other finely crafted Celtic associated possessions. The theory holds that there were four separate Celtic invasions of Ireland. The Priteni
The Cruthin (; mga, Cruithnig or ; ga, label= Modern Irish, Cruithne ) were a people of early medieval Ireland. Their heartland was in Ulster and included parts of the present-day counties of Antrim, Down and Londonderry. They are also said ...
were said to be the first, followed by the Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
from northern Gaul and Britain. Later, Laighin tribes from Armorica (present-day Brittany) were said to have invaded Ireland and Britain more or less simultaneously. Lastly, the Milesians (Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langu ...
) were said to have reached Ireland from either northern Iberia or southern Gaul. It was claimed that a second wave named the Euerni, belonging to the Belgae people of northern Gaul, began arriving about the sixth century BC. They were said to have given their name to the island.
The theory was advanced in part because of the lack of archaeological evidence for large-scale Celtic immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
, though it is accepted that such movements are notoriously difficult to identify. Historical linguists are skeptical that this method alone could account for the absorption of Celtic language, with some saying that an assumed processual view of Celtic linguistic formation is 'an especially hazardous exercise'. Genetic lineage investigation into the area of Celtic migration to Ireland has led to findings that showed no significant differences in mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
between Ireland and large areas of continental Europe, in contrast to parts of the Y-chromosome pattern. When taking both into account, a study concluded that modern Celtic speakers in Ireland could be thought of as European "Atlantic Celts" showing a shared ancestry throughout the Atlantic zone from northern Iberia to western Scandinavia rather than substantially central European.
 In 2012, research showed that the occurrence of genetic markers for the earliest farmers was almost eliminated by Beaker-culture immigrants: they carried what was then a new Y-chromosome R1b marker, believed to have originated in Iberia about 2500 BC. The prevalence amongst modern Irish men of this mutation is a remarkable 84%, the highest in the world, and closely matched in other populations along the Atlantic fringes down to Spain. A similar genetic replacement happened with lineages in mitochondrial DNA. This conclusion is supported by recent research carried out by the geneticist David Reich, who says: "British and Irish skeletons from the Bronze Age that followed the Beaker period had at most 10 per cent ancestry from the first farmers of these islands, with other 90 per cent from people like those associated with the Bell Beaker culture in the Netherlands." He suggests that it was Beaker users who introduced an Indo-European language, represented here by Celtic (i.e. a new language and culture introduced directly by migration and genetic replacement).
In 2012, research showed that the occurrence of genetic markers for the earliest farmers was almost eliminated by Beaker-culture immigrants: they carried what was then a new Y-chromosome R1b marker, believed to have originated in Iberia about 2500 BC. The prevalence amongst modern Irish men of this mutation is a remarkable 84%, the highest in the world, and closely matched in other populations along the Atlantic fringes down to Spain. A similar genetic replacement happened with lineages in mitochondrial DNA. This conclusion is supported by recent research carried out by the geneticist David Reich, who says: "British and Irish skeletons from the Bronze Age that followed the Beaker period had at most 10 per cent ancestry from the first farmers of these islands, with other 90 per cent from people like those associated with the Bell Beaker culture in the Netherlands." He suggests that it was Beaker users who introduced an Indo-European language, represented here by Celtic (i.e. a new language and culture introduced directly by migration and genetic replacement).
Late antiquity and early medieval times
 The earliest written records of Ireland come from classical
The earliest written records of Ireland come from classical Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
geographers. Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
in his ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'' refers to Ireland as ''Mikra Brettania'' ("Little Britain"), in contrast to the larger island, which he called ''Megale Brettania'' ("Great Britain"). In his later work, ''Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and ...
'', Ptolemy refers to Ireland as '' Iouernia'' and to Great Britain as ''Albion''. These 'new' names were likely to have been the local names for the islands at the time. The earlier names, in contrast, were likely to have been coined before direct contact with local peoples was made.
The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
referred to Ireland by this name too in its Latinised form, ''Hibernia'', or Scotia
Scotia is a Latin placename derived from ''Scoti'', a Latin name for the Gaels, first attested in the late 3rd century.Duffy, Seán. ''Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia''. Routledge, 2005. p.698 The Romans referred to Ireland as "Scotia" around ...
. Ptolemy records sixteen nations inhabiting every part of Ireland in 100 AD. The relationship between the Roman Empire and the kingdoms of ancient Ireland is unclear. However, a number of finds of Roman coins have been made, for example at the Iron Age settlement of Freestone Hill near Gowran
Gowran (; ) is a town located on the eastern side of County Kilkenny, Ireland. The historic St. Mary's Collegiate Church is located in the centre of Gowran close to Gowran Castle. Gowran Park race course and Golf Course is located one km from t ...
and Newgrange
Newgrange ( ga, Sí an Bhrú) is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, located on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3200 BC, ...
.
Ireland continued as a patchwork of rival kingdoms; however, beginning in the 7th century, a concept of national kingship gradually became articulated through the concept of a High King of Ireland
High King of Ireland ( ga, Ardrí na hÉireann ) was a royal title in Gaelic Ireland held by those who had, or who are claimed to have had, lordship over all of Ireland. The title was held by historical kings and later sometimes assigned ana ...
. Medieval Irish literature
Early Irish literature is one of the oldest vernacular literatures in Western Europe, though inscriptions utilising Irish and Latin are found on Ogham stones dating from the 4th century, indicating simultaneous usage of both languages by this per ...
portrays an almost unbroken sequence of high kings stretching back thousands of years, but modern historians believe the scheme was constructed in the 8th century to justify the status of powerful political groupings by projecting the origins of their rule into the remote past., "Ireland, 400–800", in (ed.), ''A New History of Ireland 1: Prehistoric and Early Ireland'', Oxford University Press, 2005, pp. 182–234.
All of the Irish kingdoms had their own kings but were nominally subject to the high king. The high king was drawn from the ranks of the provincial kings and ruled also the royal kingdom of Meath
Meath (; Old Irish: ''Mide'' ; spelt ''Mí'' in Modern Irish) was a kingdom in Ireland from the 1st to the 12th century AD. Its name means "middle," denoting its location in the middle of the island.
At its greatest extent, it included all of ...
, with a ceremonial capital at the Hill of Tara
The Hill of Tara ( ga, Teamhair or ) is a hill and ancient ceremonial and burial site near Skryne in County Meath, Ireland. Tradition identifies the hill as the inauguration place and seat of the High Kings of Ireland; it also appears in Iri ...
. The concept did not become a political reality until the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period and the Ger ...
and even then was not a consistent one. Ireland did have a culturally unifying rule of law: the early written judicial system, the Brehon Laws
Early Irish law, historically referred to as (English: Freeman-ism) or (English: Law of Freemen), also called Brehon law, comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norma ...
, administered by a professional class of jurists known as the ''brehons''.
''The Chronicle of Ireland
The Chronicle of Ireland ( ga, Croinic na hÉireann) is the modern name for a hypothesized collection of ecclesiastical annals recording events in Ireland from 432 to 911 AD.
Several surviving annals share events in the same sequence and wordin ...
'' records that in 431, Bishop Palladius arrived in Ireland on a mission from Pope Celestine I
Pope Celestine I ( la, Caelestinus I) (c. 376 – 1 August 432) was the bishop of Rome from 10 September 422 to his death on 1 August 432. Celestine's tenure was largely spent combatting various ideologies deemed heretical. He supported the missi ...
to minister to the Irish "already believing in Christ". The same chronicle records that Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick ( la, Patricius; ga, Pádraig ; cy, Padrig) was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints be ...
, Ireland's best known patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, or Eastern Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or perso ...
, arrived the following year. There is continued debate over the missions of Palladius and Patrick, but the consensus is that they both took place and that the older druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. Whi ...
tradition collapsed in the face of the new religion. Irish Christian scholars excelled in the study of Latin and Greek learning and Christian theology. In the monastic culture that followed the Christianisation of Ireland, Latin and Greek learning was preserved in Ireland during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
in contrast to elsewhere in Western Europe, where the Dark Ages followed the Fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Ancient Rome, Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rul ...
.
 The arts of
The arts of manuscript illumination
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
, metalworking and sculpture flourished and produced treasures such as the ''Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New ...
'', ornate jewellery and the many carved stone crosses that still dot the island today. A mission founded in 563 on Iona
Iona (; gd, Ì Chaluim Chille (IPA: �iːˈxaɫ̪ɯimˈçiʎə, sometimes simply ''Ì''; sco, Iona) is a small island in the Inner Hebrides, off the Ross of Mull on the western coast of Scotland. It is mainly known for Iona Abbey, though there ...
by the Irish monk Saint Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
began a tradition of Irish missionary work that spread Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
and learning to Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
on continental Europe after the fall of Rome. These missions continued until the late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur ...
, establishing monasteries and centres of learning, producing scholars such as Sedulius Scottus
Sedulius Scotus or Scottus ( fl. 840–860) was an Irish teacher, Latin grammarian, and scriptural commentator who lived in the 9th century. During the reign of the Emperor Lothair (840–855), he was one of a colony of Irish teachers at Liège. ...
and Johannes Eriugena
John Scotus Eriugena, also known as Johannes Scotus Erigena, John the Scot, or John the Irish-born ( – c. 877) was an Irish Neoplatonist philosopher, theologian and poet of the Early Middle Ages. Bertrand Russell dubbed him "the most ...
and exerting much influence in Europe.
From the 9th century, waves of Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raiders plundered Irish monasteries and towns. These raids added to a pattern of raiding and endemic warfare
__NOTOC__
Ritual warfare (sometimes called endemic warfare) is a state of continual or frequent warfare, such as is found in some tribal societies (but is not limited to tribal societies).
Description
Ritual fighting (or ritual battle or ritual ...
that was already deep-seated in Ireland. The Vikings were involved in establishing most of the major coastal settlements in Ireland: Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
, Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
, Cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
, Wexford
Wexford () is the county town of County Wexford, Ireland. Wexford lies on the south side of Wexford Harbour, the estuary of the River Slaney near the southeastern corner of the island of Ireland. The town is linked to Dublin by the M11/N11 N ...
, Waterford
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
, as well as other smaller settlements.
Norman and English invasions
 On 1 May 1169, an expedition of Cambro-
On 1 May 1169, an expedition of Cambro-Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
knights, with an army of about 600 men, landed at Bannow Strand in present-day County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''Uí Ceinns ...
. It was led by Richard de Clare
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Old Frankish and is a compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'stron ...
, known as 'Strongbow' owing to his prowess as an archer. The invasion, which coincided with a period of renewed Norman expansion, was at the invitation of Dermot Mac Murrough
Diarmait Mac Murchada (Modern Irish: Diarmaid Mac Murchadha), anglicised as Dermot MacMurrough, Dermod MacMurrough, or Dermot MacMorrogh (c. 1110 – c. 1 May 1171), was a King of Leinster in Ireland. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King ...
, King of Leinster
The kings of Leinster ( ga, Rí Laighín), ruled from the establishment of Kingdom of Leinster, Leinster during the Irish Iron Age, until the 17th century Early Modern Ireland. According to Gaelic traditional history, laid out in works such as th ...
.
In 1166, Mac Murrough had fled to Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
, France, following a war involving Tighearnán Ua Ruairc, of Breifne, and sought the assistance of the Angevin
Angevin or House of Anjou may refer to:
*County of Anjou or Duchy of Anjou, a historical county, and later Duchy, in France
**Angevin (language), the traditional langue d'oïl spoken in Anjou
**Counts and Dukes of Anjou
* House of Ingelger, a Frank ...
King Henry II, in recapturing his kingdom. In 1171, Henry arrived in Ireland in order to review the general progress of the expedition. He wanted to re-exert royal authority over the invasion which was expanding beyond his control. Henry successfully re-imposed his authority over Strongbow and the Cambro-Norman warlords and persuaded many of the Irish kings to accept him as their overlord, an arrangement confirmed in the 1175 Treaty of Windsor.
The invasion was legitimised by reference to provisions of the alleged Papal Bull ''Laudabiliter
''Laudabiliter'' was a bull issued in 1155 by Pope Adrian IV, the only Englishman to have served in that office. Existence of the bull has been disputed by scholars over the centuries; no copy is extant but scholars cite the many references to ...
'', issued by an Englishman, Adrian IV
Pope Adrian IV ( la, Adrianus IV; born Nicholas Breakspear (or Brekespear); 1 September 1159, also Hadrian IV), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 4 December 1154 to his death in 1159. He is the only Englishman ...
, in 1155. The document apparently encouraged Henry to take control in Ireland in order to oversee the financial and administrative reorganisation of the Irish Church and its integration into the Roman Church system. Some restructuring had already begun at the ecclesiastical level following the Synod of Kells
The Synod of Kells (, ) took place in 1152, under the presidency of Giovanni Cardinal Paparoni, and continued the process begun at the Synod of Ráth Breasail (1111) of reforming the Irish church. The sessions were divided between the abbeys of ...
in 1152. There has been significant controversy regarding the authenticity of ''Laudabiliter'', and there is no general agreement as to whether the bull was genuine or a forgery. Further, it had no standing in the Irish legal system.
 In 1172, Pope Alexander III further encouraged Henry to advance the integration of the Irish Church with Rome. Henry was authorised to impose a tithe of one penny per hearth as an annual contribution. This church levy called
In 1172, Pope Alexander III further encouraged Henry to advance the integration of the Irish Church with Rome. Henry was authorised to impose a tithe of one penny per hearth as an annual contribution. This church levy called Peter's Pence
Peter's Pence (or ''Denarii Sancti Petri'' and "Alms of St Peter") are donations or payments made directly to the Holy See of the Catholic Church. The practice began under the Saxons in England and spread through Europe. Both before and after the ...
, is extant in Ireland as a voluntary donation. In turn, Henry assumed the title of Lord of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between ...
which Henry conferred on his younger son, John Lackland
John (24 December 1166 – 19 October 1216) was King of England from 1199 until his death in 1216. He lost the Duchy of Normandy and most of his other French lands to King Philip II of France, resulting in the collapse of the Angevin Empi ...
, in 1185. This defined the Anglo-Norman administration in Ireland as the Lordship of Ireland
The Lordship of Ireland ( ga, Tiarnas na hÉireann), sometimes referred to retroactively as Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England (styled as "Lord of Ireland") and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman lords between ...
. When Henry's successor died unexpectedly in 1199, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
inherited the crown of England and retained the Lordship of Ireland. Over the century that followed, Norman feudal law gradually replaced the Gaelic Brehon Law across large areas, so that by the late 13th century the Norman-Irish
From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales and Anglo-Normans from ...
had established a feudal system throughout much of Ireland. Norman settlements were characterised by the establishment of baronies, manors, towns and the seeds of the modern county system. A version of the Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
(the Great Charter of Ireland
(or the Great Charter of Ireland) is an issue of the English ''Magna Carta'' (or Great Charter of Liberties) in Ireland. King Henry III of England's Charter of 1216 was issued for Ireland on 12 November 1216 but not transmitted to Ireland until ...
), substituting ''Dublin'' for ''London'' and the ''Irish Church'' for, the English church at the time, the ''Catholic Church'', was published in 1216 and the Parliament of Ireland
The Parliament of Ireland ( ga, Parlaimint na hÉireann) was the legislature of the Lordship of Ireland, and later the Kingdom of Ireland, from 1297 until 1800. It was modelled on the Parliament of England and from 1537 comprised two chamb ...
was founded in 1297.
Gaelicisation
From the mid-14th century, after theBlack Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, Norman settlements in Ireland went into a period of decline. The Norman rulers and the Gaelic Irish elites intermarried and the areas under Norman rule became Gaelicised
Gaelicisation, or Gaelicization, is the act or process of making something Gaelic, or gaining characteristics of the ''Gaels'', a sub-branch of celticisation. The Gaels are an ethno-linguistic group, traditionally viewed as having spread from Irel ...
. In some parts, a hybrid Hiberno-Norman culture emerged. In response, the Irish parliament passed the Statutes of Kilkenny
The Statutes of Kilkenny were a series of thirty-five acts enacted by the Parliament of Ireland at Kilkenny in 1366, aiming to curb the decline of the Hiberno-Norman Lordship of Ireland.
Background to the Statutes
By the middle decades of the ...
in 1367. These were a set of laws designed to prevent the assimilation of the Normans into Irish society by requiring English subjects in Ireland to speak English, follow English customs and abide by English law.
By the end of the 15th century, central English authority in Ireland had all but disappeared, and a renewed Irish culture and language, albeit with Norman influences, was dominant again. English Crown control remained relatively unshaken in an amorphous foothold around Dublin known as The Pale
The Pale (Irish: ''An Pháil'') or the English Pale (' or ') was the part of Ireland directly under the control of the English government in the Late Middle Ages. It had been reduced by the late 15th century to an area along the east coast st ...
, and under the provisions of Poynings' Law Poynings' Law or the Statute of Drogheda may refer to the following acts of the Parliament of Ireland:
* The acts of Poynings' Parliament, summoned to Drogheda in 1494–5 by Edward Poynings; or more specifically
** Poynings' Law (on certification ...
of 1494, Irish Parliamentary legislation was subject to the approval of the English Privy Council
The Privy Council of England, also known as His (or Her) Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council (), was a body of advisers to the sovereign of the Kingdom of England. Its members were often senior members of the House of Lords and the House of ...
.
The Kingdom of Ireland
 The title of
The title of King of Ireland
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the tit ...
was re-created in 1542 by Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
, the then King of England
The monarchy of the United Kingdom, commonly referred to as the British monarchy, is the constitutional form of government by which a hereditary sovereign reigns as the head of state of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies (the Bailiw ...
, of the Tudor dynasty. English rule was reinforced and expanded in Ireland during the latter part of the 16th century, leading to the Tudor conquest of Ireland. A near-complete conquest was achieved by the turn of the 17th century, following the Nine Years' War (Ireland), Nine Years' War and the Flight of the Earls.
This control was consolidated during the wars and conflicts of the 17th century, including the English and Scottish colonisation in the Plantations of Ireland, the Wars of the Three Kingdoms and the Williamite War in Ireland, Williamite War. Irish losses during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms (which, in Ireland, included the Irish Confederacy and the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland) are estimated to include 20,000 battlefield casualties. 200,000 civilians are estimated to have died as a result of a combination of war-related famine, displacement, guerrilla activity and pestilence throughout the war. A further 50,000 were sent into indentured servitude in the West Indies. Physician-general William Petty estimated that 504,000 Catholic Irish and 112,000 Protestant settlers died, and 100,000 people were transported, as a result of the war. If a prewar population of 1.5 million is assumed, this would mean that the population was reduced by almost half.
The religious struggles of the 17th century left a deep sectarian division in Ireland. Religious allegiance now determined the perception in law of loyalty to the Irish King and Parliament. After the passing of Test Act#Test Act of 1673, the Test Act 1672, and the victory of the forces of the dual monarchy of William III of England, William and Mary II of England, Mary over the Jacobitism, Jacobites, Roman Catholics and nonconforming Protestant Dissenters were barred from sitting as members in the Parliament of Ireland, Irish Parliament. Under the emerging Penal Laws (Ireland), Penal Laws, Irish Roman Catholics and Dissenters were increasingly deprived of various civil rights, even the ownership of hereditary property. Additional regressive punitive legislation followed in 1703, 1709 and 1728. This completed a comprehensive systemic effort to materially disadvantage Roman Catholics and Protestant Dissenters while enriching a new ruling class of Anglican conformists. The new Anglo-Irish ruling class became known as the Protestant Ascendancy.
 The "Irish Famine (1740–1741)#Cause, Great Frost" struck Ireland and the rest of Europe between December 1739 and September 1741, after a decade of relatively mild winters. The winters destroyed stored crops of potatoes and other staples, and the poor summers severely damaged harvests. This resulted in the Irish Famine (1740–1741), famine of 1740. An estimated 250,000 people (about one in eight of the population) died from the ensuing pestilence and disease. The Irish government halted export of corn and kept the army in quarters but did little more. Local gentry and charitable organisations provided relief but could do little to prevent the ensuing mortality.
In the aftermath of the famine, an increase in industrial production and a surge in trade brought a succession of construction booms. The population soared in the latter part of this century and the Georgian architecture, architectural legacy of Georgian Ireland was built. In 1782,
The "Irish Famine (1740–1741)#Cause, Great Frost" struck Ireland and the rest of Europe between December 1739 and September 1741, after a decade of relatively mild winters. The winters destroyed stored crops of potatoes and other staples, and the poor summers severely damaged harvests. This resulted in the Irish Famine (1740–1741), famine of 1740. An estimated 250,000 people (about one in eight of the population) died from the ensuing pestilence and disease. The Irish government halted export of corn and kept the army in quarters but did little more. Local gentry and charitable organisations provided relief but could do little to prevent the ensuing mortality.
In the aftermath of the famine, an increase in industrial production and a surge in trade brought a succession of construction booms. The population soared in the latter part of this century and the Georgian architecture, architectural legacy of Georgian Ireland was built. In 1782, Poynings' Law Poynings' Law or the Statute of Drogheda may refer to the following acts of the Parliament of Ireland:
* The acts of Poynings' Parliament, summoned to Drogheda in 1494–5 by Edward Poynings; or more specifically
** Poynings' Law (on certification ...
was repealed, giving Ireland legislative independence from Great Britain for the first time since 1495. The British government, however, still retained the right to nominate the government of Ireland without the consent of the Irish parliament.
Union with Great Britain
In 1798, members of the Protestant Dissenter tradition (mainly Presbyterianism, Presbyterian) made common cause with Roman Catholics in a republican rebellion inspired and led by the Society of United Irishmen, with the aim of creating an independent Ireland. Despite assistance from France the Irish Rebellion of 1798, rebellion was put down by British and Irish government and yeomanry forces. In 1800, the British and Irish parliaments both passed Acts of Union that, with effect from 1 January 1801, merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of Great Britain to create a United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The passage of the Act in the Irish Parliament was ultimately achieved with substantial majorities, having failed on the first attempt in 1799. According to contemporary documents and historical analysis, this was achieved through a considerable degree of bribery, with funding provided by the British Secret Service Office, and the awarding of peerages, places and honours to secure votes. Thus, the parliament in Ireland was abolished and replaced by a Parliament of the United Kingdom, united parliament at Westminster in London, though resistance remained, as evidenced by Robert Emmet's failed Irish Rebellion of 1803. Aside from the development of the linen industry, Ireland was largely passed over by the industrial revolution, partly because it lacked coal and iron resources and partly because of the impact of the sudden union with the structurally superior economy of England, which saw Ireland as a source of agricultural produce and capital. The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845–1851 devastated Ireland, as in those years Ireland's population fell by one-third. More than one million people died from starvation and disease, with an additional million people emigrating during the famine, mostly to the United States and Canada. In the century that followed, an economic depression caused by the famine resulted in a further million people emigrating. By the end of the decade, half of all immigration to the United States was from Ireland. The period of civil unrest that followed until the end of the 19th century is referred to as the Land War. Mass emigration became deeply entrenched and the population continued to decline until the mid-20th century. Immediately prior to the famine the population was recorded as 8.2 million by the 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 census. The population has never returned to this level since. The population continued to fall until 1961; County Leitrim was the final Irish county to record a population increase post-famine, in 2006.
The 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of modern Irish nationalism, primarily among the Roman Catholic population. The pre-eminent Irish political figure after the Union was Daniel O'Connell. He was elected as Member of Parliament for Ennis (UK Parliament constituency), Ennis in a surprise result and despite being unable to take his seat The Test Act, as a Roman Catholic. O'Connell spearheaded a vigorous campaign that was taken up by the Prime Minister, the Irish-born soldier and statesman, the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. Steering the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, Catholic Relief Bill through Parliament, aided by future prime minister Robert Peel, Wellington prevailed upon a reluctant George IV of the United Kingdom, George IV to sign the Bill and proclaim it into law. George III, George's father had opposed the plan of the earlier Prime Minister, William Pitt the Younger, Pitt the Younger, to introduce such a bill following the Union of 1801, fearing Catholic Emancipation to be in conflict with the Act of Settlement 1701.
Daniel O'Connell led a subsequent campaign, for the repeal of the Act of Union, which failed. Later in the century, Charles Stewart Parnell and others campaigned for autonomy within the Union, or "Irish Home Rule Bills, Home Rule". Unionists, especially those located in Ulster, were strongly opposed to Home Rule, which they thought would be dominated by Catholic interests. After several attempts to pass a Home Rule bill through parliament, it looked certain that one would finally pass in 1914. To prevent this from happening, the Ulster Volunteers were formed in 1913 under the leadership of Edward Carson.
Their formation was followed in 1914 by the establishment of the Irish Volunteers, whose aim was to ensure that the Third Home Rule Act, Home Rule Bill was passed. The Act was passed but with the "temporary" exclusion of the six counties of Ulster, which later became Northern Ireland. Before it could be implemented, however, the Act was suspended for the duration of the World War I, First World War. The Irish Volunteers split into two groups. The majority, approximately 175,000 in number, under John Redmond, took the name National Volunteers and supported Ireland and World War I, Irish involvement in the war. A minority, approximately 13,000, retained the Irish Volunteers' name and opposed Ireland's involvement in the war.
The Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845–1851 devastated Ireland, as in those years Ireland's population fell by one-third. More than one million people died from starvation and disease, with an additional million people emigrating during the famine, mostly to the United States and Canada. In the century that followed, an economic depression caused by the famine resulted in a further million people emigrating. By the end of the decade, half of all immigration to the United States was from Ireland. The period of civil unrest that followed until the end of the 19th century is referred to as the Land War. Mass emigration became deeply entrenched and the population continued to decline until the mid-20th century. Immediately prior to the famine the population was recorded as 8.2 million by the 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 census. The population has never returned to this level since. The population continued to fall until 1961; County Leitrim was the final Irish county to record a population increase post-famine, in 2006.
The 19th and early 20th centuries saw the rise of modern Irish nationalism, primarily among the Roman Catholic population. The pre-eminent Irish political figure after the Union was Daniel O'Connell. He was elected as Member of Parliament for Ennis (UK Parliament constituency), Ennis in a surprise result and despite being unable to take his seat The Test Act, as a Roman Catholic. O'Connell spearheaded a vigorous campaign that was taken up by the Prime Minister, the Irish-born soldier and statesman, the Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, Duke of Wellington. Steering the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, Catholic Relief Bill through Parliament, aided by future prime minister Robert Peel, Wellington prevailed upon a reluctant George IV of the United Kingdom, George IV to sign the Bill and proclaim it into law. George III, George's father had opposed the plan of the earlier Prime Minister, William Pitt the Younger, Pitt the Younger, to introduce such a bill following the Union of 1801, fearing Catholic Emancipation to be in conflict with the Act of Settlement 1701.
Daniel O'Connell led a subsequent campaign, for the repeal of the Act of Union, which failed. Later in the century, Charles Stewart Parnell and others campaigned for autonomy within the Union, or "Irish Home Rule Bills, Home Rule". Unionists, especially those located in Ulster, were strongly opposed to Home Rule, which they thought would be dominated by Catholic interests. After several attempts to pass a Home Rule bill through parliament, it looked certain that one would finally pass in 1914. To prevent this from happening, the Ulster Volunteers were formed in 1913 under the leadership of Edward Carson.
Their formation was followed in 1914 by the establishment of the Irish Volunteers, whose aim was to ensure that the Third Home Rule Act, Home Rule Bill was passed. The Act was passed but with the "temporary" exclusion of the six counties of Ulster, which later became Northern Ireland. Before it could be implemented, however, the Act was suspended for the duration of the World War I, First World War. The Irish Volunteers split into two groups. The majority, approximately 175,000 in number, under John Redmond, took the name National Volunteers and supported Ireland and World War I, Irish involvement in the war. A minority, approximately 13,000, retained the Irish Volunteers' name and opposed Ireland's involvement in the war.
Partition
In December 1921, the Anglo-Irish Treaty was concluded between the British government and representatives of the Second Dáil. It gave Ireland complete independence in its home affairs and practical independence for foreign policy, but an opt-out clause allowedNorthern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
to remain within the United Kingdom, which it immediately exercised. Additionally, Members of the Third Dáil, Free State Parliament were required to swear Oath of Allegiance (Ireland), an oath of allegiance to the Constitution of the Irish Free State and make a statement of faithfulness to the king. Disagreements over these provisions led to a split in the nationalist movement and a subsequent Irish Civil War between the new government of the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
and those opposed to the treaty, led by Éamon de Valera. The civil war officially ended in May 1923 when de Valera issued a cease-fire order.
Independence
 During its first decade, the newly formed
During its first decade, the newly formed Irish Free State
The Irish Free State ( ga, Saorstát Éireann, , ; 6 December 192229 December 1937) was a state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between th ...
was governed by the victors of the civil war. When de Valera achieved power, he took advantage of the Statute of Westminster 1931, Statute of Westminster and Edward VIII abdication crisis, political circumstances to build upon inroads to greater sovereignty made by the previous government. The oath was abolished and in 1937 a new constitution was adopted. This completed a process of gradual separation from the British Empire that governments had pursued since independence. However, it was not until 1949 that the state was declared, officially, to be the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
.
Irish neutrality, The state was neutral during The Emergency (Ireland), World War II, but offered Irish neutrality during World War II, clandestine assistance to the Allies, particularly in the potential defence of Northern Ireland. Despite their country's neutrality, approximately 50,000 volunteers from independent Ireland joined the British forces during the war, four being awarded Victoria Crosses.
The Abwehr, German intelligence was also active in Ireland.Hull, Mark: "The Irish Interlude: German Intelligence in Ireland, 1939–1943", ''Journal of Military History'', Vol. 66, No. 3 (July 2002), pp. 695–717 Its operations ended in September 1941 when Garda Síochána, police made arrests based on surveillance carried out on the key diplomatic legations in Dublin. To the authorities, counterintelligence was a fundamental line of defence. With a regular army of only slightly over seven thousand men at the start of the war, and with limited supplies of modern weapons, the state would have had great difficulty in defending itself from invasion from either side in the conflict.
Large-scale emigration marked most of the post-WWII period (particularly during the 1950s and 1980s), but beginning in 1987 the economy improved, and the 1990s saw the beginning of substantial economic growth. This period of growth became known as the Celtic Tiger. The Republic's real GDP grew by an average of 9.6% per annum between 1995 and 1999, in which year the Republic joined the euro. In 2000, it was the sixth-richest country in the world in terms of GDP per capita. Historian R. F. Foster (historian), R. F. Foster argues the cause was a combination of a new sense of initiative and the entry of American corporations. He concludes the chief factors were low taxation, pro-business regulatory policies, and a young, tech-savvy workforce. For many multinationals, the decision to do business in Ireland was made easier still by generous incentives from the IDA Ireland, Industrial Development Authority. In addition European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
membership was helpful, giving the country lucrative access to markets that it had previously reached only through the United Kingdom, and pumping huge subsidies and investment capital into the Irish economy.
Modernisation brought secularisation in its wake. The traditionally high levels of religiosity have sharply declined. Foster points to three factors: First, Irish feminism, largely imported from America with liberal stances on contraception, abortion and divorce, undermined the authority of bishops and priests. Second, the mishandling of the paedophile scandals humiliated the Church, whose bishops seemed less concerned with the victims and more concerned with covering up for errant priests. Third, prosperity brought hedonism and materialism that undercut the ideals of saintly poverty.
The Post-2008 Irish economic downturn, financial crisis that began in 2008 dramatically ended this period of boom. GDP fell by 3% in 2008 and by 7.1% in 2009, the worst year since records began (although earnings by foreign-owned businesses continued to grow). The state has since experienced deep recession, with unemployment, which doubled during 2009, remaining above 14% in 2012.
Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland resulted from the division of the United Kingdom by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, and until 1972 was a self-governing jurisdiction within the United Kingdom with its own parliament and prime minister. Northern Ireland, as part of the United Kingdom, was not neutral during the Second World War, and Belfast Blitz, Belfast suffered four bombing raids in 1941. Conscription was not extended to Northern Ireland, and roughly an equal number volunteered from Northern Ireland as volunteered from the Republic of Ireland. Although Northern Ireland was largely spared the strife of the civil war, in the decades that followed partition there were sporadic episodes of inter-communal violence. Nationalists, mainly Roman Catholic, wanted to unite Ireland as an independent republic, whereas unionists, mainly Protestant, wanted Northern Ireland to remain in the United Kingdom. The Protestant and Catholic communities in Northern Ireland voted largely along sectarian lines, meaning that the government of Northern Ireland (elected by Plurality electoral system, "first-past-the-post" from 1929) was controlled by the Ulster Unionist Party. Over time, the minority Catholic community felt increasingly alienated with further disaffection fuelled by practices such as gerrymandering and discrimination in housing and employment. In the late 1960s, nationalist grievances were aired publicly in mass civil rights protests, which were often confronted by Ulster loyalism, loyalist counter-protests. The government's reaction to confrontations was seen to be one-sided and heavy-handed in favour of unionists. Law and order broke down as unrest and inter-communal violence increased. The Northern Ireland government requested the British Army to aid the police and protect the Irish Nationalist population. In 1969, the paramilitary Provisional Irish Republican Army, Provisional IRA, which favoured the creation of a united Ireland, emerged from a split in the Irish Republican Army (1922–1969), Irish Republican Army and began a campaign against what it called the "British occupation of the six counties". Other groups, both the unionist and nationalist participated in violence, and a period known as "the Troubles" began. Over 3,600 deaths resulted over the subsequent three decades of conflict. Owing to the civil unrest during the Troubles, the British government suspended home rule in 1972 and imposed Direct rule over Northern Ireland, direct rule. There were several unsuccessful attempts to end the Troubles politically, such as the Sunningdale Agreement of 1973. In 1998, following a ceasefire by the Provisional IRA and multi-party talks, theGood Friday Agreement
The Good Friday Agreement (GFA), or Belfast Agreement ( ga, Comhaontú Aoine an Chéasta or ; Ulster-Scots: or ), is a pair of agreements signed on 10 April 1998 that ended most of the violence of The Troubles, a political conflict in No ...
was concluded as a treaty between the British and Irish governments, annexing the text agreed in the multi-party talks.
The substance of the Agreement (formally referred to as the Belfast Agreement) was later endorsed by referendums in both parts of Ireland. The Agreement restored self-government to Northern Ireland on the basis of power-sharing in a regional Northern Ireland Executive, Executive drawn from the major parties in a new Northern Ireland Assembly, with entrenched protections for the two main communities. The Executive is jointly headed by a First Minister and deputy First Minister drawn from the unionist and nationalist parties. Violence had decreased greatly after the Provisional IRA and loyalist ceasefires in 1994 and in 2005 the Provisional IRA announced the end of its armed campaign and an Independent International Commission on Decommissioning, independent commission supervised its disarmament and that of other nationalist and unionist paramilitary organisations.
The Assembly and power-sharing Executive were suspended several times but were restored again in 2007. In that year the British government officially ended its military support of the police in Northern Ireland (Operation Banner) and began withdrawing troops. On 27 June 2012, Northern Ireland's deputy first minister and former IRA commander, Martin McGuinness, shook hands with Queen Elizabeth II in Belfast, symbolising reconciliation between the two sides.
Politics
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. They share an Irish border, open border and both are part of the Common Travel Area and as a consequence, there is internal market, free movement of people, goods, services and capital across the border.
The Republic of Ireland is a member state of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
while the United Kingdom is a former member state, having both acceded to its precursor entity, the European Economic Community (EEC), in 1973 but the UK Brexit, left the European Union in 2020 after a 2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, referendum on EU membership was held in 2016 which resulted in 51.9% of UK voters choosing to leave the bloc.
Republic of Ireland
 The
The Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
is a parliamentary democracy based on the Westminster system, with a Constitution of Ireland, written constitution and a popularly elected President of Ireland, president whose role is mostly ceremonial. The Oireachtas is a bicameral parliament, composed of (the Dáil), a house of representatives, and (the Seanad), an upper house. The Government of Ireland, government is headed by a prime minister, the , who is appointed by the president on the nomination of the . Its capital is Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
.
The Republic of Ireland today ranks among the wealthiest countries in the world in terms of GDP per capita and in 2015 was ranked the sixth most developed nation in the world by the United Nations' Human Development Index. A period of rapid economic expansion from 1995 onwards became known as the Celtic Tiger period, was brought to an end in 2008 with an unprecedented Post-2008 Irish economic downturn, financial crisis and an economic depression in 2009.
Northern Ireland

Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is variously described as a country, province or region. Nort ...
is a part of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
with a local Northern Ireland Executive, executive and Northern Ireland Assembly, assembly which exercise devolved powers. The executive is jointly headed by the first and deputy first minister, with the ministries being allocated in proportion to each party's representation in the assembly. Its capital is Belfast.
Ultimately political power is held by the UK government, from which Northern Ireland has gone through intermittent periods of direct rule during which devolved powers have been suspended. Northern Ireland elects 18 of the UK House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons' 650 MPs. The Northern Ireland Secretary is a cabinet-level post in the British government.
Along with England and Wales and with Scotland, Northern Ireland forms one of the three separate legal jurisdictions of the UK, all of which share the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom as their court of final appeal.
All-island institutions
As part of the Good Friday Agreement, the British and Irish governments agreed on the creation of all-island institutions and areas of cooperation. The North/South Ministerial Council is an institution through which ministers from the Government of Ireland and the Northern Ireland Executive agree all-island policies. At least six of these policy areas must have an associated all-island "implementation body," and at least six others must be implemented separately in each jurisdiction. The implementation bodies are: Waterways Ireland, the Food Safety Promotion Board, InterTradeIreland, the Special European Union Programmes Body, the North/South Language Body and the Commissioners of Irish Lights, Foyle, Carlingford and Irish Lights Commission. The British–Irish Intergovernmental Conference provides for co-operation between the Government of Ireland and the Government of the United Kingdom on all matters of mutual interest, especially Northern Ireland. In light of the Republic's particular interest in the governance of Northern Ireland, "regular and frequent" meetings co-chaired by the ROI Minister for Foreign Affairs and the UK Secretary of State for Northern Ireland, dealing with non-devolved matters to do with Northern Ireland and non-devolved all-Ireland issues, are required to take place under the establishing treaty. The North/South Inter-Parliamentary Association is a joint parliamentary forum for the island of Ireland. It has no formal powers but operates as a forum for discussing matters of common concern between the respective legislatures.Geography
 Ireland is located in the North-West Europe, north-west of Europe, between latitudes 51st parallel north, 51° and 56th parallel north, 56° N, and longitudes 11th meridian west, 11° and 5th meridian west, 5° W. It is separated from Great Britain by the
Ireland is located in the North-West Europe, north-west of Europe, between latitudes 51st parallel north, 51° and 56th parallel north, 56° N, and longitudes 11th meridian west, 11° and 5th meridian west, 5° W. It is separated from Great Britain by the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Ce ...
and the North Channel North Channel may refer to:
*North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland)
*North Channel (Ontario), body of water along the north shore of Lake Huron, Canada
*North Channel, Hong Kong
*Canal du Nord, France
{{geodis ...
, which has a width of at its narrowest point. To the west is the northern Atlantic Ocean and to the south is the Celtic Sea, which lies between Ireland and Brittany, in France. Ireland has a total area of , of which the Republic of Ireland occupies 83 percent. Ireland and Great Britain, together with many nearby smaller islands, are known collectively as the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
. As British Isles naming dispute, the term British Isles is controversial in relation to Ireland, the alternate term ''Britain and Ireland'' is often used as a neutral term for the islands.
A ring of coastal mountains surrounds low plains at the centre of the island. The highest of these is Carrauntoohil ( ga, Corrán Tuathail) in County Kerry
County Kerry ( gle, Contae Chiarraí) is a county in Ireland. It is located in the South-West Region and forms part of the province of Munster. It is named after the Ciarraige who lived in part of the present county. The population of the co ...
, which rises to above sea level. The most arable land lies in the province of Leinster. Western areas are mainly mountainous and rocky with green panoramic vistas. River Shannon, the island's longest river at long, rises in County Cavan in the north-west and flows through Limerick
Limerick ( ; ga, Luimneach ) is a western city in Ireland situated within County Limerick. It is in the province of Munster and is located in the Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region. With a population of 94,192 at the 2016 ...
in the midwest.
Geology
 The island consists of varied geologic province, geological provinces. In the west, around County Galway and County Donegal, is a medium to high grade metamorphic and igneous complex of Caledonides, Caledonide affinity, similar to the Scottish Highlands. Across southeast Ulster and extending southwest to Longford and south to Navan is a province of Ordovician and Silurian rocks, with similarities to the Southern Uplands province of Scotland. Further south, along the
The island consists of varied geologic province, geological provinces. In the west, around County Galway and County Donegal, is a medium to high grade metamorphic and igneous complex of Caledonides, Caledonide affinity, similar to the Scottish Highlands. Across southeast Ulster and extending southwest to Longford and south to Navan is a province of Ordovician and Silurian rocks, with similarities to the Southern Uplands province of Scotland. Further south, along the County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''Uí Ceinns ...
coastline, is an area of granite intrusion, intrusives into more Ordovician and Silurian rocks, like that found in Wales.
In the southwest, around Bantry Bay and the mountains of MacGillycuddy's Reeks, is an area of substantially deformed, lightly metamorphic rock, metamorphosed Devonian-aged rocks. This partial ring of "hard rock" geology is covered by a blanket of Carboniferous limestone over the centre of the country, giving rise to a comparatively fertile and lush landscape. The west-coast district of the Burren around Lisdoonvarna has well-developed karst features. Significant stratiform lead-zinc mineralisation is found in the limestones around Silvermines and Tynagh.
Hydrocarbon exploration is ongoing following the first major find at the Kinsale Head gas field off Cork (city), Cork in the mid-1970s. In 1999, economically significant finds of natural gas were made in the Corrib Gas Field off the County Mayo coast. This has increased activity off the west coast in parallel with the "North Sea oil#West of Shetland, West of Shetland" step-out development from the North Sea oil, North Sea hydrocarbon province. In 2000, the Helvick oil field was discovered, which was estimated to contain over of oil.
Climate
The island's lush vegetation, a product of its mild climate and frequent rainfall, earns it the sobriquet ''the Emerald Isle''. Overall, Ireland has a mild but changeable oceanic climate with few extremes. The climate is typically insular and Temperate climate, temperate, avoiding the extremes in temperature of many other areas in the world at similar latitudes. This is a result of the moist winds which ordinarily prevail from the southwestern Atlantic. Precipitation falls throughout the year but is light overall, particularly in the east. The west tends to be wetter on average and prone to Atlantic storms, especially in the late autumn and winter months. These occasionally bring destructive winds and higher total rainfall to these areas, as well as sometimes snow and hail. The regions of north County Galway and east County Mayo have the highest incidents of recorded lightning annually for the island, with lightning occurring approximately five to ten days per year in these areas. Munster, in the south, records the least snow whereas Ulster, in the north, records the most. Inland areas are warmer in summer and colder in winter. Usually around 40 days of the year are below freezing at inland weather stations, compared to 10 days at coastal stations. Ireland is sometimes affected by heat waves, most recently in 1995, 2003 European heat wave, 2003, 2006 European heat wave#Ireland, 2006, 2013 and 2018 British Isles heat wave, 2018. In common with the rest of Europe, Ireland experienced unusually cold weather during Winter of 2010–11 in Great Britain and Ireland, the winter of 2010–11. Temperatures fell as low as −17.2 °C (1 °F) in County Mayo on 20 December and up to a metre (3 ft) of snow fell in mountainous areas.Flora and fauna
 Unlike Great Britain which had a
Unlike Great Britain which had a land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and Colonisation (biology), colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regre ...
with mainland Europe, Ireland only had an ice bridge
An ice bridge is a frozen natural structure formed over seas, bays, rivers or lake surfaces. They facilitate migration of animals or people over a water body that was previously uncrossable by terrestrial animals, including humans. The most sign ...
ending around 14,000 years ago at the end of the Last Glacial Period, last ice age and as a result, it has fewer land animal and plant species than Great Britain or mainland Europe. There are List of mammals of Ireland, 55 mammal species in Ireland, and of them, only 26 land mammal species are considered native to Ireland.Costello, M.J. and Kelly, K.S., 1993 ''Biogeography of Ireland: past, present and future'' Irish Biogeographic Society Occasional Publications Number 2 Some species, such as, the red fox, European hedgehog, hedgehog and European badger, badger, are very common, whereas others, like the Mountain hare, Irish hare, red deer and pine marten are less so. Aquatic wildlife, such as species of sea turtle, shark, seal, whale, and dolphin, are common off the coast. About 400 species of birds have been recorded in Ireland. Many of these are migratory, including the barn swallow.
 Several different habitat types are found in Ireland, including farmland, open woodland, temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, conifer plantations, peat bogs and a variety of coastal habitats. However, agriculture drives current land use patterns in Ireland, limiting natural habitat preserves, particularly for larger wild mammals with greater territorial needs. With no large apex predators in Ireland other than humans and dogs, such populations of animals as semi-wild deer that cannot be controlled by smaller predators, such as the fox, are controlled by annual culling.
There are no snakes in Ireland, and only one species of reptile (the Viviparous lizard, common lizard) is native to the island. Extinct species include the Irish elk, the great auk, brown bear and the Wolves in Ireland, wolf. Some previously extinct birds, such as the golden eagle, have been reintroduced after decades of Local extinction, extirpation.
Ireland is now one of the least forested countries in Europe. Until the end of the Middle Ages, Ireland was heavily forested. Native species include deciduous trees such as oak, Fraxinus excelsior, ash, Corylus avellana, hazel, birch, Alnus glutinosa, alder, willow, Populus tremula, aspen, Sorbus aucuparia, rowan and Crataegus monogyna, hawthorn, as well as evergreen trees such Scots pine, Taxus baccata, yew, Ilex aquifolium, holly and Arbutus unedo, strawberry trees. Only about 10% of Ireland today is woodland; most of this is non-native conifer plantations, and only 2% is native woodland. The average woodland cover of European countries is over 33%. In the Republic, about is owned by the state, mainly by the forestry service Coillte. Remnants of native forest can be found scattered around the island, in particular in the Killarney National Park.
Several different habitat types are found in Ireland, including farmland, open woodland, temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, conifer plantations, peat bogs and a variety of coastal habitats. However, agriculture drives current land use patterns in Ireland, limiting natural habitat preserves, particularly for larger wild mammals with greater territorial needs. With no large apex predators in Ireland other than humans and dogs, such populations of animals as semi-wild deer that cannot be controlled by smaller predators, such as the fox, are controlled by annual culling.
There are no snakes in Ireland, and only one species of reptile (the Viviparous lizard, common lizard) is native to the island. Extinct species include the Irish elk, the great auk, brown bear and the Wolves in Ireland, wolf. Some previously extinct birds, such as the golden eagle, have been reintroduced after decades of Local extinction, extirpation.
Ireland is now one of the least forested countries in Europe. Until the end of the Middle Ages, Ireland was heavily forested. Native species include deciduous trees such as oak, Fraxinus excelsior, ash, Corylus avellana, hazel, birch, Alnus glutinosa, alder, willow, Populus tremula, aspen, Sorbus aucuparia, rowan and Crataegus monogyna, hawthorn, as well as evergreen trees such Scots pine, Taxus baccata, yew, Ilex aquifolium, holly and Arbutus unedo, strawberry trees. Only about 10% of Ireland today is woodland; most of this is non-native conifer plantations, and only 2% is native woodland. The average woodland cover of European countries is over 33%. In the Republic, about is owned by the state, mainly by the forestry service Coillte. Remnants of native forest can be found scattered around the island, in particular in the Killarney National Park.
 Much of the land is now covered with pasture and there are many species of wild-flower. Gorse (''Ulex europaeus''), a wild furze, is commonly found growing in the uplands and ferns are plentiful in the more moist regions, especially in the western parts. It is home to hundreds of plant species, some of them unique to the island, and has been "invaded" by some grasses, such as ''Spartina anglica''.
The algal and seaweed flora is that of the cold-temperate variety. The total number of species is 574 The island has been invaded by some algae, some of which are now well established.
Because of its mild climate, many species, including subtropics, sub-tropical species such as Arecaceae, palm trees, are grown in Ireland. Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Ireland belongs to the Atlantic European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The island can be subdivided into two ecoregions: the Celtic broadleaf forests and North Atlantic moist mixed forests.
Much of the land is now covered with pasture and there are many species of wild-flower. Gorse (''Ulex europaeus''), a wild furze, is commonly found growing in the uplands and ferns are plentiful in the more moist regions, especially in the western parts. It is home to hundreds of plant species, some of them unique to the island, and has been "invaded" by some grasses, such as ''Spartina anglica''.
The algal and seaweed flora is that of the cold-temperate variety. The total number of species is 574 The island has been invaded by some algae, some of which are now well established.
Because of its mild climate, many species, including subtropics, sub-tropical species such as Arecaceae, palm trees, are grown in Ireland. Phytogeography, Phytogeographically, Ireland belongs to the Atlantic European province of the Circumboreal Region within the Boreal Kingdom. The island can be subdivided into two ecoregions: the Celtic broadleaf forests and North Atlantic moist mixed forests.
Impact of agriculture
 The long history of agricultural production, coupled with modern intensive agricultural methods such as pesticide and fertiliser use and runoff from contaminants into streams, rivers and lakes, has placed pressure on biodiversity in Ireland. A land of green fields for crop cultivation and cattle rearing limits the space available for the establishment of native wild species. Hedgerows, however, traditionally used for maintaining and demarcating land boundaries, act as a refuge for native wild flora. This ecosystem stretches across the countryside and acts as a network of connections to preserve remnants of the ecosystem that once covered the island. Subsidies under the Common Agricultural Policy, which supported agricultural practices that preserved hedgerow environments, are undergoing reforms. The Common Agricultural Policy had in the past subsidised potentially destructive agricultural practices, for example by emphasising production without placing limits on indiscriminate use of fertilisers and pesticides; but reforms have gradually decoupled subsidies from production levels and introduced environmental and other requirements. 32% of Ireland's greenhouse gas emissions are correlated to agriculture. Forested areas typically consist of monoculture plantations of non-native species, which may result in habitats that are not suitable for supporting native species of invertebrates. Natural areas require fencing to prevent over-grazing by Deer of Ireland, deer and sheep that roam over uncultivated areas. Grazing in this manner is one of the main factors preventing the natural regeneration of forests across many regions of the country.
The long history of agricultural production, coupled with modern intensive agricultural methods such as pesticide and fertiliser use and runoff from contaminants into streams, rivers and lakes, has placed pressure on biodiversity in Ireland. A land of green fields for crop cultivation and cattle rearing limits the space available for the establishment of native wild species. Hedgerows, however, traditionally used for maintaining and demarcating land boundaries, act as a refuge for native wild flora. This ecosystem stretches across the countryside and acts as a network of connections to preserve remnants of the ecosystem that once covered the island. Subsidies under the Common Agricultural Policy, which supported agricultural practices that preserved hedgerow environments, are undergoing reforms. The Common Agricultural Policy had in the past subsidised potentially destructive agricultural practices, for example by emphasising production without placing limits on indiscriminate use of fertilisers and pesticides; but reforms have gradually decoupled subsidies from production levels and introduced environmental and other requirements. 32% of Ireland's greenhouse gas emissions are correlated to agriculture. Forested areas typically consist of monoculture plantations of non-native species, which may result in habitats that are not suitable for supporting native species of invertebrates. Natural areas require fencing to prevent over-grazing by Deer of Ireland, deer and sheep that roam over uncultivated areas. Grazing in this manner is one of the main factors preventing the natural regeneration of forests across many regions of the country.
Demographics
 The population of Ireland is just over 7 million, of which approximately 5.1 million reside in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million reside in Northern Ireland.
People have lived in Ireland for over 9,000 years. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of major groups such as the , , , , , , , , . Later major groups included the , , . Smaller groups included the (see ), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , . Many survived into late medieval times, others vanished as they became politically unimportant. Over the past 1,200 years, Vikings, Normans, Welsh people, Welsh, Flemings, Scottish people, Scots, English people, English, African diaspora, Africans and Eastern Europeans have all added to the population and have had significant influences on Irish culture.
The population of Ireland rose rapidly from the 16th century until the mid-19th century, interrupted briefly by the Irish Famine (1740–41), Famine of 1740–41, which killed roughly two-fifths of the island's population. The population rebounded and multiplied over the next century, but the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of the 1840s caused one million deaths and forced over one million more to emigrate in its immediate wake. Over the following century, the population was reduced by over half, at a time when the general trend in European countries was for populations to rise by an average of three-fold.
Ireland's largest religious group is Christianity. The largest denomination is Roman Catholicism, representing over 73% of the island (and about 87% of the Republic of Ireland). Most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations (about 48% of Northern Ireland). The largest is the Anglicanism, Anglican Church of Ireland. The Islam in Ireland, Muslim community is growing in Ireland, mostly through increased immigration, with a 50% increase in the republic between the 2006 and 2011 census. The island has a small History of the Jews in Ireland, Jewish community. About 4% of the Republic's population and about 14% of the Northern Ireland population describe themselves as of no religion. In a 2010 survey conducted on behalf of the Irish Times, 32% of respondents said they went to a religious service more than once per week.
The population of Ireland is just over 7 million, of which approximately 5.1 million reside in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million reside in Northern Ireland.
People have lived in Ireland for over 9,000 years. Early historical and genealogical records note the existence of major groups such as the , , , , , , , , . Later major groups included the , , . Smaller groups included the (see ), , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , . Many survived into late medieval times, others vanished as they became politically unimportant. Over the past 1,200 years, Vikings, Normans, Welsh people, Welsh, Flemings, Scottish people, Scots, English people, English, African diaspora, Africans and Eastern Europeans have all added to the population and have had significant influences on Irish culture.
The population of Ireland rose rapidly from the 16th century until the mid-19th century, interrupted briefly by the Irish Famine (1740–41), Famine of 1740–41, which killed roughly two-fifths of the island's population. The population rebounded and multiplied over the next century, but the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of the 1840s caused one million deaths and forced over one million more to emigrate in its immediate wake. Over the following century, the population was reduced by over half, at a time when the general trend in European countries was for populations to rise by an average of three-fold.
Ireland's largest religious group is Christianity. The largest denomination is Roman Catholicism, representing over 73% of the island (and about 87% of the Republic of Ireland). Most of the rest of the population adhere to one of the various Protestant denominations (about 48% of Northern Ireland). The largest is the Anglicanism, Anglican Church of Ireland. The Islam in Ireland, Muslim community is growing in Ireland, mostly through increased immigration, with a 50% increase in the republic between the 2006 and 2011 census. The island has a small History of the Jews in Ireland, Jewish community. About 4% of the Republic's population and about 14% of the Northern Ireland population describe themselves as of no religion. In a 2010 survey conducted on behalf of the Irish Times, 32% of respondents said they went to a religious service more than once per week.
Divisions and settlements
Traditionally, Ireland is subdivided into Provinces of Ireland, four provinces: Connacht (west), Leinster (east), Munster (south), and Ulster (north). In a system that developed between the 13th and 17th centuries, Ireland has Counties of Ireland, 32 traditional counties. Twenty-six of these counties are in the Republic of Ireland, and Counties of Northern Ireland, six are in Northern Ireland. The six counties that constitute Northern Ireland are all in the province of Ulster (which has nine counties in total). As such, ''Ulster'' is often used as a synonym for Northern Ireland, although the two are not coterminous. In the Republic of Ireland, counties form the basis of the system of local government. Counties County Dublin, Dublin,Cork
Cork or CORK may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Cork (plug), a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
***Wine cork
Places Ireland
* Cork (city)
** Metropolitan Cork, also known as G ...
, County Limerick, Limerick, County Galway, Galway, County Waterford, Waterford and County Tipperary, Tipperary have been broken up into smaller administrative areas. However, they are still treated as counties for cultural and some official purposes, for example, postal addresses and by the Ordnance Survey Ireland. Counties in Northern Ireland are Local government in Northern Ireland, no longer used for local governmental purposes, but, as in the Republic, their traditional boundaries are still used for informal purposes such as sports leagues and in cultural or tourism contexts.
City status in Ireland is decided by legislation, legislative or royal charter. Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
, with over 1 million residents in the Greater Dublin Area, is the largest city on the island. Belfast, with 579,726 residents, is the largest city in Northern Ireland. City status does not directly equate with population size. For example, Armagh, with 14,590 is the seat of the Church of Ireland and the Roman Catholic Primate of All Ireland and was re-granted City status in the United Kingdom#Northern Ireland, city status by Queen Elizabeth II in 1994 (having lost that status in Municipal Corporations (Ireland) Act 1840, local government reforms of 1840). In the Republic of Ireland, Kilkenny, the seat of the Butler dynasty, while no longer a city for administrative purposes (since the 2001 Local Government Act 2001, Local Government Act), is entitled by law to continue to use the description.
Migration
 The population of Ireland collapsed dramatically during the second half of the 19th century. A population of over 8 million in 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 was reduced to slightly over 4 million by 1921. In part, the fall in population was caused by death from the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845 to 1852, which took roughly 1 million lives. The remaining decline of around 3 million was due to the entrenched culture of emigration caused by the dire economic state of the country, lasting until the 21st century.
Emigration from Ireland in the 19th century contributed to the populations of England, the United States, Canada and Australia, in all of which a large Irish diaspora lives. , 4.3 million Canadians, or 14% of the population, were of Irish descent, while around one-third of the Australian population had an element of Irish descent. , there were 40 million Irish-Americans and 33 million Americans who claimed Irish ancestry.
With growing prosperity since the last decade of the 20th century, Ireland became a destination for immigrants. Since the European Union expanded to include Poland in 2004, Polish people have comprised the largest number of immigrants (over 150,000) from Central Europe. There has also been significant immigration from Lithuania, Czech Republic and Latvia.
Demographics of the Republic of Ireland#Immigration, The Republic of Ireland in particular has seen large-scale immigration, with 420,000 foreign nationals as of 2006, about 10% of the population. Nearly a quarter of births (24 percent) in 2009 were to mothers born outside of Ireland. Up to 50,000 eastern and central European migrant workers left Ireland in response to the Irish financial crisis.
The population of Ireland collapsed dramatically during the second half of the 19th century. A population of over 8 million in 1841 census of Ireland, 1841 was reduced to slightly over 4 million by 1921. In part, the fall in population was caused by death from the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine of 1845 to 1852, which took roughly 1 million lives. The remaining decline of around 3 million was due to the entrenched culture of emigration caused by the dire economic state of the country, lasting until the 21st century.
Emigration from Ireland in the 19th century contributed to the populations of England, the United States, Canada and Australia, in all of which a large Irish diaspora lives. , 4.3 million Canadians, or 14% of the population, were of Irish descent, while around one-third of the Australian population had an element of Irish descent. , there were 40 million Irish-Americans and 33 million Americans who claimed Irish ancestry.
With growing prosperity since the last decade of the 20th century, Ireland became a destination for immigrants. Since the European Union expanded to include Poland in 2004, Polish people have comprised the largest number of immigrants (over 150,000) from Central Europe. There has also been significant immigration from Lithuania, Czech Republic and Latvia.
Demographics of the Republic of Ireland#Immigration, The Republic of Ireland in particular has seen large-scale immigration, with 420,000 foreign nationals as of 2006, about 10% of the population. Nearly a quarter of births (24 percent) in 2009 were to mothers born outside of Ireland. Up to 50,000 eastern and central European migrant workers left Ireland in response to the Irish financial crisis.
Languages
 The two official languages of the Republic of Ireland are Irish and English. Each language has produced noteworthy literature. Irish, though now only the language of a minority, was the vernacular of the Irish people for thousands of years and was possibly introduced during the Iron Age. It began to be written down after Christianisation in the 5th century and spread to Scotland and the Isle of Man, where it evolved into the Scottish Gaelic and Manx Language, Manx languages respectively.
The Irish language has a vast treasury of written texts from many centuries and is divided by linguists into
The two official languages of the Republic of Ireland are Irish and English. Each language has produced noteworthy literature. Irish, though now only the language of a minority, was the vernacular of the Irish people for thousands of years and was possibly introduced during the Iron Age. It began to be written down after Christianisation in the 5th century and spread to Scotland and the Isle of Man, where it evolved into the Scottish Gaelic and Manx Language, Manx languages respectively.
The Irish language has a vast treasury of written texts from many centuries and is divided by linguists into Old Irish
Old Irish, also called Old Gaelic ( sga, Goídelc, Ogham script: ᚌᚑᚔᚇᚓᚂᚉ; ga, Sean-Ghaeilge; gd, Seann-Ghàidhlig; gv, Shenn Yernish or ), is the oldest form of the Goidelic/Gaelic language for which there are extensive writt ...
from the 6th to 10th century, Middle Irish from the 10th to 13th century, Early Modern Irish until the 17th century, and the Modern Irish spoken today. It remained the dominant language of Ireland for most of those periods, having influences from Latin Language, Latin, Old Norse, Anglo-Norman language, French and English. It declined under British rule but remained the majority tongue until the early 19th century, and since then has been a minority language.
The Gaelic Revival of the late 19th and early 20th centuries had a long-term influence. Irish is taught in mainstream Irish schools as a compulsory subject, but teaching methods have been criticised for their ineffectiveness, with most students showing little evidence of fluency even after fourteen years of instruction.
There is now a growing population of urban Irish speakers in both the Republic and Northern Ireland, especially in Dublin and Belfast, with the children of such Irish speakers sometimes attending Irish-medium schools (). It has been argued that they tend to be more highly educated than monolingual English speakers. Recent research suggests that urban Irish is developing in a direction of its own, both in pronunciation and grammar.
Traditional rural Irish-speaking areas, known collectively as the , are in linguistic decline. The main areas are in the west, south-west and north-west, in Galway, Mayo, Donegal, western Cork and Kerry with smaller areas near Dungarvan in Waterford and in Meath.
Hiberno-English, English in Ireland was first introduced during the Norman invasion. It was spoken by a few peasants and merchants brought over from England and was largely replaced by Irish before the Tudor conquest of Ireland. It was introduced as the official language during the Tudor and Cromwellian conquests. The Ulster plantations gave it a permanent foothold in Ulster, and it remained the official and upper-class language elsewhere, the Irish-speaking chieftains and nobility having been deposed. Language shift during the 19th century replaced Irish with English as the first language for a vast majority of the population.
Fewer than 2% of the population of the Republic of Ireland today speak Irish on a daily basis, and under 10% regularly, outside of the education system and 38% of those over 15 years are classified as "Irish speakers". In Northern Ireland, English is the de facto official language, but official recognition is afforded to Irish, including specific protective measures under Part III of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. A lesser status (including recognition under Part II of the Charter) is given to Ulster Scots dialects, which are spoken by roughly 2% of Northern Ireland residents, and also spoken by some in the Republic of Ireland. Since the 1960s with the increase in immigration, many more languages have been introduced, particularly deriving from Asia and Eastern Europe.
Also native to Ireland are Shelta language, Shelta, the language of the nomadic Irish Travellers, Irish Sign Language, and Northern Ireland Sign Language.
Culture
 Ireland's culture comprises elements of the culture of ancient peoples, later immigrant and broadcast cultural influences (chiefly Gaels, Gaelic culture, Anglicisation, Americanisation and aspects of broader European culture). In broad terms, Ireland is regarded as one of the Celtic nations of Europe, alongside Scotland, Wales, Cornwall, Isle of Man and Brittany. This combination of cultural influences is visible in the intricate designs termed ''Irish Interlace (visual arts), interlace'' or ''Celtic knotwork.'' These can be seen in the ornamentation of medieval religious and secular works. The style is still popular today in jewellery and graphic art, as is the distinctive style of traditional Irish music and dance, and has become indicative of modern "Celtic" culture in general.
Religion in Ireland, Religion has played a significant role in the cultural life of the island since ancient times (and since the 17th century Plantations of Ireland, plantations, has been the focus of political identity and divisions on the island). Ireland's pre-Christian heritage fused with the Celtic Church following the missions of
Ireland's culture comprises elements of the culture of ancient peoples, later immigrant and broadcast cultural influences (chiefly Gaels, Gaelic culture, Anglicisation, Americanisation and aspects of broader European culture). In broad terms, Ireland is regarded as one of the Celtic nations of Europe, alongside Scotland, Wales, Cornwall, Isle of Man and Brittany. This combination of cultural influences is visible in the intricate designs termed ''Irish Interlace (visual arts), interlace'' or ''Celtic knotwork.'' These can be seen in the ornamentation of medieval religious and secular works. The style is still popular today in jewellery and graphic art, as is the distinctive style of traditional Irish music and dance, and has become indicative of modern "Celtic" culture in general.
Religion in Ireland, Religion has played a significant role in the cultural life of the island since ancient times (and since the 17th century Plantations of Ireland, plantations, has been the focus of political identity and divisions on the island). Ireland's pre-Christian heritage fused with the Celtic Church following the missions of Saint Patrick
Saint Patrick ( la, Patricius; ga, Pádraig ; cy, Padrig) was a fifth-century Romano-British Christian missionary and bishop in Ireland. Known as the "Apostle of Ireland", he is the primary patron saint of Ireland, the other patron saints be ...
in the 5th century. The Hiberno-Scottish missions, begun by the Irish monk Saint Columba
Columba or Colmcille; gd, Calum Cille; gv, Colum Keeilley; non, Kolban or at least partly reinterpreted as (7 December 521 – 9 June 597 AD) was an Irish abbot and missionary evangelist credited with spreading Christianity in what is toda ...
, spread the Celtic Christianity, Irish vision of Christianity to pagan England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
. These missions brought written language to an illiterate population of Europe during the Dark Ages that followed the fall of Rome, earning Ireland the sobriquet, "the island of saints and scholars".
Since the 20th century Irish pubs worldwide have become outposts of Irish culture, especially those with a full range of cultural and gastronomic offerings.
The Republic of Ireland's national theatre is the Abbey Theatre, which was founded in 1904, and the national Irish-language theatre is , which was established in 1928 in Galway. Playwrights such as Seán O'Casey, Brian Friel, Sebastian Barry, Conor McPherson and Billy Roche are internationally renowned.
Arts

Literature
Ireland has made a substantial contribution to world literature in all its branches, both in Irish and English. Poetry in Irish is among the oldest vernacular literature, vernacular poetry in Europe, with the earliest examples dating from the 6th century. Irish remained the dominant literary language down to the nineteenth century, despite the spread of English from the seventeenth century on. Prominent names from the medieval period and later include (fourteenth century), (seventeenth century) and Aogán Ó Rathaille (eighteenth century). (c. 1743 – c. 1800) was an outstanding poet in the oral tradition. The latter part of the nineteenth century saw a rapid replacement of Irish by English. By 1900, however, cultural nationalists had begun the Gaelic revival, which saw the beginnings of modern literature in Irish. This was to produce a number of notable writers, including , and others. Irish-language publishers such as and continue to produce scores of titles every year. In English, Jonathan Swift, often called the foremost satirist in the English language, gained fame for works such as ''Gulliver's Travels'' and ''A Modest Proposal''. Other notable 18th-century writers of Irish origin included Oliver Goldsmith and Richard Brinsley Sheridan, though they spent most of their lives in England. The Anglo-Irish novel came to the fore in the nineteenth century, featuring such writers as Charles Kickham, William Carleton, and (in collaboration) Edith Somerville and Violet Florence Martin. The playwright and poet Oscar Wilde, noted for his epigrams, was born in Ireland. In the 20th century, Ireland produced four winners of the Nobel Prize for Literature: George Bernard Shaw, William Butler Yeats, Samuel Beckett and Seamus Heaney. Although not a Nobel Prize winner, James Joyce is widely considered to be one of the most significant writers of the 20th century. Joyce's 1922 novel ''Ulysses (novel), Ulysses'' is considered one of the most important works of Modernist literature and his life is celebrated annually on 16 June in Dublin as "Bloomsday". A comparable writer in Irish is , whose novel is regarded as a modernist masterpiece and has been translated into several languages. Modern Irish literature is often connected with its rural heritage through English-language writers such as John McGahern and Seamus Heaney and Irish-language writers such as and others from the .
Music
Music has been in evidence in Ireland since prehistoric times. Although in the early Middle Ages the church was "quite unlike its counterpart in continental Europe", there was a considerable interchange between monastic settlements in Ireland and the rest of Europe that contributed to what is known as Gregorian chant. Outside religious establishments, musical genres in early Gaelic Ireland are referred to as a triad of weeping music (''goltraige''), laughing music (''geantraige'') and sleeping music (''suantraige''). Vocal and instrumental music (e.g. for the harp, pipes, and various string instruments) was transmitted orally, but the Irish harp, in particular, was of such significance that it became Ireland's national symbol. Classical music following European models first developed in urban areas, in establishments of Anglo-Irish rule such as Dublin Castle, St Patrick's Cathedral, Dublin, St Patrick's Cathedral and Christ Church Cathedral, Dublin, Christ Church as well as the country houses of the Anglo-Irish ascendancy, with the first performance of George Frideric Handel, Handel's ''Messiah (Handel), Messiah'' (1742) being among the highlights of the baroque era. In the 19th century, public concerts provided access to classical music to all classes of society. Yet, for political and financial reasons Ireland has been too small to provide a living to many musicians, so the names of the better-known List of Irish classical composers, Irish composers of this time belong to emigrants. Irish folk music, traditional music and dance have seen a surge in popularity and global coverage since the 1960s. In the middle years of the 20th century, as Irish society was modernising, traditional music had fallen out of favour, especially in urban areas. However during the 1960s, there was a revival of interest in Irish traditional music led by groups such as The Dubliners, The Chieftains, The Wolfe Tones, the Clancy Brothers, Sweeney's Men and individuals like and Christy Moore. Groups and musicians including Horslips, Van Morrison and Thin Lizzy incorporated elements of Irish traditional music into contemporary rock music and, during the 1970s and 1980s, the distinction between traditional and rock musicians became blurred, with many individuals regularly crossing over between these styles of playing. This trend can be seen more recently in the work of artists like Enya, The Saw Doctors, The Corrs, Sinéad O'Connor, Clannad (musical group), Clannad, The Cranberries and The Pogues among others.Art
The earliest known Irish graphic art and sculpture are Neolithic carvings found at sites such asNewgrange
Newgrange ( ga, Sí an Bhrú) is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, located on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3200 BC, ...
and is traced through Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
artefacts and the religious carvings and illuminated manuscripts of the medieval period. During the course of the 19th and 20th centuries, a strong tradition of painting emerged, including such figures as John Butler Yeats, William Orpen, Jack Yeats and Louis le Brocquy. Contemporary Irish visual artists of note include Sean Scully, Kevin Abosch, and Alice Maher.
Science
 The Irish philosopher and theologian Johannes Scotus Eriugena was considered one of the leading intellectuals of the early Middle Ages. Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton, an Irish explorer, was one of the principal figures of Antarctic exploration. He, along with his expedition, made the first ascent of Mount Erebus and the discovery of the approximate location of the South Magnetic Pole. Robert Boyle was a 17th-century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, inventor and early gentleman scientist. He is largely regarded as one of the founders of modern chemistry and is best known for the formulation of Boyle's law.
19th-century physicist, John Tyndall, discovered the Tyndall effect. Father Nicholas Joseph Callan, Professor of Natural Philosophy in Maynooth College, is best known for his invention of the induction coil, transformer and he discovered an early method of galvanisation in the 19th century.
Other notable Irish physicists include Ernest Walton, winner of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Physics. With Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, he was the first to split the nucleus of the atom by artificial means and made contributions to the development of a new theory of wave equation. William Thomson, or Lord Kelvin, is the person whom the absolute temperature unit, the kelvin, is named after. Sir Joseph Larmor, a physicist and mathematician, made innovations in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics and the electron theory of matter. His most influential work was Aether and Matter, a book on theoretical physics published in 1900.
George Johnstone Stoney introduced the term ''electron'' in 1891. John Stewart Bell was the originator of Bell's Theorem and a paper concerning the discovery of the Chiral anomaly, Bell-Jackiw-Adler anomaly and was nominated for a Nobel prize. The astronomer Jocelyn Bell Burnell, from Lurgan, County Armagh, discovered pulsars in 1967. Notable mathematicians include Sir William Rowan Hamilton, famous for work in Hamiltonian mechanics, classical mechanics and the invention of quaternions. Francis Ysidro Edgeworth's contribution, the Edgeworth Box. remains influential in neo-classical microeconomic theory to this day; while Richard Cantillon inspired Adam Smith, among others. John B. Cosgrave was a specialist in number theory and discovered a 2000-digit prime number in 1999 and a record composite Fermat number in 2003. John Lighton Synge made progress in different fields of science, including mechanics and geometrical methods in general relativity. He had mathematician John Forbes Nash Jr., John Nash as one of his students. Kathleen Lonsdale, born in Ireland and most known for her work with X-ray crystallography, crystallography, became the first female president of the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
Ireland has nine universities, seven in the Republic of Ireland and two in Northern Ireland, including Trinity College Dublin and the University College Dublin, as well as numerous third-level colleges and institutes and a branch of the Open University, the Open University in Ireland. Ireland was ranked 19th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 12th in 2019.
The Irish philosopher and theologian Johannes Scotus Eriugena was considered one of the leading intellectuals of the early Middle Ages. Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton, an Irish explorer, was one of the principal figures of Antarctic exploration. He, along with his expedition, made the first ascent of Mount Erebus and the discovery of the approximate location of the South Magnetic Pole. Robert Boyle was a 17th-century natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, inventor and early gentleman scientist. He is largely regarded as one of the founders of modern chemistry and is best known for the formulation of Boyle's law.
19th-century physicist, John Tyndall, discovered the Tyndall effect. Father Nicholas Joseph Callan, Professor of Natural Philosophy in Maynooth College, is best known for his invention of the induction coil, transformer and he discovered an early method of galvanisation in the 19th century.
Other notable Irish physicists include Ernest Walton, winner of the 1951 Nobel Prize in Physics. With Sir John Douglas Cockcroft, he was the first to split the nucleus of the atom by artificial means and made contributions to the development of a new theory of wave equation. William Thomson, or Lord Kelvin, is the person whom the absolute temperature unit, the kelvin, is named after. Sir Joseph Larmor, a physicist and mathematician, made innovations in the understanding of electricity, dynamics, thermodynamics and the electron theory of matter. His most influential work was Aether and Matter, a book on theoretical physics published in 1900.
George Johnstone Stoney introduced the term ''electron'' in 1891. John Stewart Bell was the originator of Bell's Theorem and a paper concerning the discovery of the Chiral anomaly, Bell-Jackiw-Adler anomaly and was nominated for a Nobel prize. The astronomer Jocelyn Bell Burnell, from Lurgan, County Armagh, discovered pulsars in 1967. Notable mathematicians include Sir William Rowan Hamilton, famous for work in Hamiltonian mechanics, classical mechanics and the invention of quaternions. Francis Ysidro Edgeworth's contribution, the Edgeworth Box. remains influential in neo-classical microeconomic theory to this day; while Richard Cantillon inspired Adam Smith, among others. John B. Cosgrave was a specialist in number theory and discovered a 2000-digit prime number in 1999 and a record composite Fermat number in 2003. John Lighton Synge made progress in different fields of science, including mechanics and geometrical methods in general relativity. He had mathematician John Forbes Nash Jr., John Nash as one of his students. Kathleen Lonsdale, born in Ireland and most known for her work with X-ray crystallography, crystallography, became the first female president of the British Association for the Advancement of Science.
Ireland has nine universities, seven in the Republic of Ireland and two in Northern Ireland, including Trinity College Dublin and the University College Dublin, as well as numerous third-level colleges and institutes and a branch of the Open University, the Open University in Ireland. Ireland was ranked 19th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, down from 12th in 2019.
Sports
Gaelic football is the most popular sport in Ireland in terms of match attendance and community involvement, with about 2,600 clubs on the island. In 2003 it represented 34% of total sports attendances at events in Ireland and abroad, followed by hurling at 23%, soccer at 16% and rugby football, rugby at 8%. The All-Ireland Football Final is the most watched event in the sporting calendar. Soccer is the most widely played team game on the island and the most popular in Northern Ireland. Other sporting activities with the highest levels of playing participation include swimming, golf, aerobics, cycling, and billiards/snooker. Many other sports are also played and followed, includingboxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
, cricket, fishing, greyhound racing, Gaelic handball, handball, field hockey, hockey, horse racing, motor sport, show jumping and tennis.
The island fields a single international team in most sports. One notable exception to this is association football, although both associations continued to field international teams under the name "Ireland" until the 1950s. The sport is also the most notable exception where the Republic of Ireland national football team, Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland field separate international teams. Northern Ireland has produced two World Snooker Champions.
Field sports
 Gaelic football, hurling and Gaelic handball, handball are the best-known Irish traditional sports, collectively known as
Gaelic football, hurling and Gaelic handball, handball are the best-known Irish traditional sports, collectively known as Gaelic games
Gaelic games ( ga, Cluichí Gaelacha) are a set of sports played worldwide, though they are particularly popular in Ireland, where they originated. They include Gaelic football, hurling, Gaelic handball and rounders. Football and hurling, the ...
. Gaelic games are governed by the Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA), with the exception of women's Gaelic football and camogie (women's variant of hurling), which are governed by separate organisations. The headquarters of the GAA (and the main stadium) is located at Croke Park in north Dublin and has a capacity of 82,500. Many major GAA games are played there, including the semi-finals and finals of the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship and All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship. During the redevelopment of the Lansdowne Road, Lansdowne Road stadium in 2007–2010, international rugby and soccer were played there. All GAA players, even at the highest level, are amateurs, receiving no wages, although they are permitted to receive a limited amount of sport-related income from commercial sponsorship.
The Irish Football Association (IFA) was originally the governing body for soccer across the island. The game has been played in an organised fashion in Ireland since the 1870s, with Cliftonville F.C. in Belfast being Ireland's oldest club. It was most popular, especially in its first decades, around Belfast and in Ulster. However, some clubs based outside Belfast thought that the IFA largely favoured Ulster-based clubs in such matters as selection for the national team. In 1921, following an incident in which, despite an earlier promise, the IFA moved an Irish Cup semi-final replay from Dublin to Belfast, Dublin-based clubs broke away to form the Football Association of the Irish Free State. Today the southern association is known as the Football Association of Ireland (FAI). Despite being initially blacklisted by the Home Nations' associations, the FAI was recognised by FIFA in 1923 and organised its first international fixture in 1926 (against Italy national football team, Italy). However, both the IFA and FAI continued to select their teams from the whole of Ireland, with some players earning international caps for matches with both teams. Both also referred to their respective teams as ''Ireland''.
 In 1950, FIFA directed the associations only to select players from within their respective territories and, in 1953, directed that the FAI's team be known only as "Republic of Ireland national football team, Republic of Ireland" and that the IFA's team be known as "Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland" (with certain exceptions). Northern Ireland qualified for the FIFA World Cup, World Cup finals in 1958 FIFA World Cup, 1958 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982 and 1986 FIFA World Cup, 1986 and the UEFA European Championship, European Championship in UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. The Republic qualified for the World Cup finals in 1990 FIFA World Cup, 1990 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 and the European Championship in UEFA Euro 1988, 1988, UEFA Euro 2012, 2012 and UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. Across Ireland, there is significant interest in the Premier League, English and, to a lesser extent, Scottish Premier League, Scottish soccer leagues.
Ireland fields a single Ireland national rugby union team, national rugby team and a single association, the Irish Rugby Football Union, governs the sport across the island. The Irish rugby team have played in every Rugby World Cup, making the quarter-finals in six of them. Ireland also hosted games during the 1991 Rugby World Cup, 1991 and the 1999 Rugby World Cups (including a quarter-final). There are four professional Irish teams; all four play in the Pro14 and at least three compete for the Heineken Cup. Irish rugby has become increasingly competitive at both the international and provincial levels since the sport went professional in 1994. During that time, Ulster Rugby, Ulster (1998–99 Heineken Cup, 1999), Munster Rugby, Munster (2005–06 Heineken Cup, 2006 and 2007–08 Heineken Cup, 2008) and Leinster Rugby, Leinster (2008–09 Heineken Cup, 2009, 2010–11 Heineken Cup, 2011 and 2011–12 Heineken Cup, 2012) have won the Heineken Cup. In addition to this, the Irish International side has had increased success in the Six Nations Championship against the other European elite sides. This success, including Triple Crown (rugby union), Triple Crowns in 2004, 2006 and 2007, culminated with a clean sweep of victories, known as a Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slam, in 2009 and 2018.
In 1950, FIFA directed the associations only to select players from within their respective territories and, in 1953, directed that the FAI's team be known only as "Republic of Ireland national football team, Republic of Ireland" and that the IFA's team be known as "Northern Ireland national football team, Northern Ireland" (with certain exceptions). Northern Ireland qualified for the FIFA World Cup, World Cup finals in 1958 FIFA World Cup, 1958 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982 and 1986 FIFA World Cup, 1986 and the UEFA European Championship, European Championship in UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. The Republic qualified for the World Cup finals in 1990 FIFA World Cup, 1990 (reaching the quarter-finals), 1994 FIFA World Cup, 1994, 2002 FIFA World Cup, 2002 and the European Championship in UEFA Euro 1988, 1988, UEFA Euro 2012, 2012 and UEFA Euro 2016, 2016. Across Ireland, there is significant interest in the Premier League, English and, to a lesser extent, Scottish Premier League, Scottish soccer leagues.
Ireland fields a single Ireland national rugby union team, national rugby team and a single association, the Irish Rugby Football Union, governs the sport across the island. The Irish rugby team have played in every Rugby World Cup, making the quarter-finals in six of them. Ireland also hosted games during the 1991 Rugby World Cup, 1991 and the 1999 Rugby World Cups (including a quarter-final). There are four professional Irish teams; all four play in the Pro14 and at least three compete for the Heineken Cup. Irish rugby has become increasingly competitive at both the international and provincial levels since the sport went professional in 1994. During that time, Ulster Rugby, Ulster (1998–99 Heineken Cup, 1999), Munster Rugby, Munster (2005–06 Heineken Cup, 2006 and 2007–08 Heineken Cup, 2008) and Leinster Rugby, Leinster (2008–09 Heineken Cup, 2009, 2010–11 Heineken Cup, 2011 and 2011–12 Heineken Cup, 2012) have won the Heineken Cup. In addition to this, the Irish International side has had increased success in the Six Nations Championship against the other European elite sides. This success, including Triple Crown (rugby union), Triple Crowns in 2004, 2006 and 2007, culminated with a clean sweep of victories, known as a Grand Slam (rugby union), Grand Slam, in 2009 and 2018.
Boxing
Amateur boxing on the island of Ireland is governed by the Irish Athletic Boxing Association. Ireland has won more medals in boxing than in any other Olympic sport. Michael Carruth won a gold medal and Wayne McCullough won a silver medal in the 1992 Summer Olympics, Barcelona Olympic Games. In 2008 Kenneth Egan won a silver medal in the Beijing Games. Paddy Barnes secured bronze in those games and gold in the 2010 European Amateur Boxing Championships (where Ireland came 2nd in the overall medal table) and 2010 Commonwealth Games. Katie Taylor has won gold in every European and World championship since 2005. In August 2012 at the Olympic Games in London, Taylor created history by becoming the first Irish woman to win a gold medal in boxing in the 60 kg lightweight. More recently, Kellie Harrington won a gold medal at the 2020 Tokyo Olympics.Other sports
 Horse racing and greyhound racing are both popular in Ireland. There are frequent horse race meetings and greyhound stadiums are well-attended. The island is noted for the breeding and training of race horses and is also a large exporter of racing dogs. The horse racing sector is largely concentrated in the County Kildare.
Irish athletics is an all-Ireland sport governed by Athletics Ireland. Sonia O'Sullivan won two medals at 5,000 metres on the track; gold at the 1995 IAAF World Championships in Athletics, World Championships and silver at the 2000 Summer Olympics, 2000 Sydney Olympics. Gillian O'Sullivan won silver in the 20k walk at the 2003 World Championships, while sprint hurdler Derval O'Rourke won gold at the 2006 World Indoor Championship in Moscow. Olive Loughnane won a silver medal in the 20k walk at the World Athletics Championships in Berlin in 2009.
Golf is very popular, and golf tourism is a major industry attracting more than 240,000 golfing visitors annually. The 2006 Ryder Cup was held at The Kildare Hotel and Golf Club, The K Club in County Kildare. Pádraig Harrington became the first Irishman since Fred Daly (golfer), Fred Daly in 1947 to win the The Open Championship, British Open at Carnoustie in July 2007. He successfully defended his title in July 2008 before going on to win the PGA Championship in August. Harrington became the first European to win the PGA Championship in 78 years and was the first winner from Ireland. Three golfers from Northern Ireland have been particularly successful. In 2010, Graeme McDowell became the first Irish golfer to win the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, and the first European to win that tournament since 1970. Rory McIlroy, at the age of 22, won the 2011 U.S. Open, while Darren Clarke's latest victory was the 2011 Open Championship at Royal St. George's. In August 2012, McIlroy won his 2nd major championship by winning the USPGA Championship by a record margin of 8 shots.
Horse racing and greyhound racing are both popular in Ireland. There are frequent horse race meetings and greyhound stadiums are well-attended. The island is noted for the breeding and training of race horses and is also a large exporter of racing dogs. The horse racing sector is largely concentrated in the County Kildare.
Irish athletics is an all-Ireland sport governed by Athletics Ireland. Sonia O'Sullivan won two medals at 5,000 metres on the track; gold at the 1995 IAAF World Championships in Athletics, World Championships and silver at the 2000 Summer Olympics, 2000 Sydney Olympics. Gillian O'Sullivan won silver in the 20k walk at the 2003 World Championships, while sprint hurdler Derval O'Rourke won gold at the 2006 World Indoor Championship in Moscow. Olive Loughnane won a silver medal in the 20k walk at the World Athletics Championships in Berlin in 2009.
Golf is very popular, and golf tourism is a major industry attracting more than 240,000 golfing visitors annually. The 2006 Ryder Cup was held at The Kildare Hotel and Golf Club, The K Club in County Kildare. Pádraig Harrington became the first Irishman since Fred Daly (golfer), Fred Daly in 1947 to win the The Open Championship, British Open at Carnoustie in July 2007. He successfully defended his title in July 2008 before going on to win the PGA Championship in August. Harrington became the first European to win the PGA Championship in 78 years and was the first winner from Ireland. Three golfers from Northern Ireland have been particularly successful. In 2010, Graeme McDowell became the first Irish golfer to win the U.S. Open (golf), U.S. Open, and the first European to win that tournament since 1970. Rory McIlroy, at the age of 22, won the 2011 U.S. Open, while Darren Clarke's latest victory was the 2011 Open Championship at Royal St. George's. In August 2012, McIlroy won his 2nd major championship by winning the USPGA Championship by a record margin of 8 shots.
Recreation
The west coast of Ireland, Lahinch and Donegal Bay in particular, have popular surfing beaches, being fully exposed to the Atlantic Ocean. Donegal Bay is shaped like a funnel and catches west/south-west Atlantic winds, creating good surf, especially in winter. Since just before the year 2010, Bundoran has hosted European championship surfing. Scuba diving is increasingly popular in Ireland with clear waters and large populations of sea life, particularly along the western seaboard. There are also many shipwrecks along the coast of Ireland, with some of the best wreck dives being in Malin Head and off the County Cork coast. With thousands of lakes, over of fish-bearing rivers and over of List of Irish counties by coastline, coastline, Ireland is a popular angling destination. The temperate Irish climate is suited to sport angling. While salmon and trout fishing remain popular with anglers, salmon fishing, in particular, received a boost in 2006 with the closing of the salmon driftnet fishery. Coarse fishing continues to increase its profile. Sea angling is developed with many beaches mapped and signposted, and the range of sea angling species is around 80.Food and drink
 Food and cuisine in Ireland take their influence from the crops grown and animals farmed in the island's temperate climate and from the social and political circumstances of Irish history. For example, whilst from the Middle Ages until the arrival of the potato in the 16th century the dominant feature of the Irish economy was the herding of cattle, the number of cattle a person owned was equated to their social standing. Thus herders would avoid slaughtering a milk-producing cow.
For this reason, pork and white meat were more common than beef, and thick fatty strips of salted bacon (known as rashers) and the eating of salted butter (i.e. a dairy product rather than beef itself) have been a central feature of the diet in Ireland since the Middle Ages. The practice of bleeding cattle and mixing the blood with milk and butter (not unlike the practice of the Maasai people, Maasai) was common and black pudding, made from blood, grain (usually barley) and seasoning, remains a breakfast staple in Ireland. All of these influences can be seen today in the phenomenon of the "breakfast roll".
The introduction of the potato in the second half of the 16th century heavily influenced cuisine thereafter. Great poverty encouraged a subsistence approach to food, and by the mid-19th century, the vast majority of the population sufficed with a diet of potatoes and milk. A typical family, consisting of a man, a woman and four children, would eat of potatoes per week. Consequently, dishes that are considered as national dishes represent a fundamental simplicity to cooking, such as the Irish stew, bacon and cabbage, boxty, a type of potato pancake, or colcannon, a dish of mashed potatoes and kale or cabbage.
Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a "New Irish Cuisine" based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made List of Irish cheeses, cheeses that are now being produced across the country. An example of this new cuisine is "Dublin Lawyer": lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to
Food and cuisine in Ireland take their influence from the crops grown and animals farmed in the island's temperate climate and from the social and political circumstances of Irish history. For example, whilst from the Middle Ages until the arrival of the potato in the 16th century the dominant feature of the Irish economy was the herding of cattle, the number of cattle a person owned was equated to their social standing. Thus herders would avoid slaughtering a milk-producing cow.
For this reason, pork and white meat were more common than beef, and thick fatty strips of salted bacon (known as rashers) and the eating of salted butter (i.e. a dairy product rather than beef itself) have been a central feature of the diet in Ireland since the Middle Ages. The practice of bleeding cattle and mixing the blood with milk and butter (not unlike the practice of the Maasai people, Maasai) was common and black pudding, made from blood, grain (usually barley) and seasoning, remains a breakfast staple in Ireland. All of these influences can be seen today in the phenomenon of the "breakfast roll".
The introduction of the potato in the second half of the 16th century heavily influenced cuisine thereafter. Great poverty encouraged a subsistence approach to food, and by the mid-19th century, the vast majority of the population sufficed with a diet of potatoes and milk. A typical family, consisting of a man, a woman and four children, would eat of potatoes per week. Consequently, dishes that are considered as national dishes represent a fundamental simplicity to cooking, such as the Irish stew, bacon and cabbage, boxty, a type of potato pancake, or colcannon, a dish of mashed potatoes and kale or cabbage.
Since the last quarter of the 20th century, with a re-emergence of wealth in Ireland, a "New Irish Cuisine" based on traditional ingredients incorporating international influences has emerged. This cuisine is based on fresh vegetables, fish (especially salmon, trout, oysters, mussels and other shellfish), as well as traditional soda breads and the wide range of hand-made List of Irish cheeses, cheeses that are now being produced across the country. An example of this new cuisine is "Dublin Lawyer": lobster cooked in whiskey and cream. The potato remains however a fundamental feature of this cuisine and the Irish remain the highest per capita consumers of potatoes in Europe. Traditional regional foods can be found throughout the country, for example coddle in Dublin or drisheen in Cork, both a type of sausage, or blaa, a doughy white bread particular to Waterford
"Waterford remains the untaken city"
, mapsize = 220px
, pushpin_map = Ireland#Europe
, pushpin_map_caption = Location within Ireland##Location within Europe
, pushpin_relief = 1
, coordinates ...
.
 Ireland once dominated the world's market for whiskey, producing 90% of the world's whiskey at the start of the 20th century. However, as a consequence of bootleggers during the prohibition in the United States (who sold poor-quality whiskey bearing Irish-sounding names thus eroding the pre-prohibition popularity for Irish brands) and tariffs on Irish whiskey across the British Empire during the Anglo-Irish Trade War of the 1930s, sales of Irish whiskey worldwide fell to a mere 2% by the mid-20th century. In 1953, an Irish government survey, found that 50% of whiskey drinkers in the United States had never heard of Irish whiskey.
Irish whiskey, as researched in 2009 by the CNBC American broadcaster, remains popular domestically and has grown in international sales steadily over a few decades. Typically CNBC states Irish whiskey is not as smoky as a Scotch whisky, but not as sweet as American whiskey, American or Canadian whiskey, Canadian whiskies. Whiskey forms the basis of Irish Cream, cream liqueurs, such as Baileys Irish Cream, Baileys, and the "Irish coffee" (a cocktail of coffee and whiskey reputedly invented at Foynes, Foynes flying-boat station) is probably the best-known Irish cocktail.
Porter (beer), Stout, a kind of porter beer, particularly Guinness, is typically associated with Ireland, although historically it was more closely associated with London. Porter remains very popular, although it has lost sales since the mid-20th century to lager. Cider, particularly ''Magners'' (marketed in the
Ireland once dominated the world's market for whiskey, producing 90% of the world's whiskey at the start of the 20th century. However, as a consequence of bootleggers during the prohibition in the United States (who sold poor-quality whiskey bearing Irish-sounding names thus eroding the pre-prohibition popularity for Irish brands) and tariffs on Irish whiskey across the British Empire during the Anglo-Irish Trade War of the 1930s, sales of Irish whiskey worldwide fell to a mere 2% by the mid-20th century. In 1953, an Irish government survey, found that 50% of whiskey drinkers in the United States had never heard of Irish whiskey.
Irish whiskey, as researched in 2009 by the CNBC American broadcaster, remains popular domestically and has grown in international sales steadily over a few decades. Typically CNBC states Irish whiskey is not as smoky as a Scotch whisky, but not as sweet as American whiskey, American or Canadian whiskey, Canadian whiskies. Whiskey forms the basis of Irish Cream, cream liqueurs, such as Baileys Irish Cream, Baileys, and the "Irish coffee" (a cocktail of coffee and whiskey reputedly invented at Foynes, Foynes flying-boat station) is probably the best-known Irish cocktail.
Porter (beer), Stout, a kind of porter beer, particularly Guinness, is typically associated with Ireland, although historically it was more closely associated with London. Porter remains very popular, although it has lost sales since the mid-20th century to lager. Cider, particularly ''Magners'' (marketed in the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. A ...
as ''Bulmers''), is also a popular drink. Red lemonade, a soft-drink, is consumed on its own and as a mixer, particularly with whiskey.
Economy
Overview and GDP
The GDP of the Republic of Ireland as of 2018 was $382.754 billion (nominal), and in Northern Ireland as of 2016 it was €43 billion (nominal). The GDP per capita in the Republic of Ireland was $78,335 (nominal) as of 2018, and in Northern Ireland (as of 2016) was €23,700. Despite the two jurisdictions using two distinct currencies (the euro and pound sterling), a growing amount of commercial activity is carried out on an all-Ireland basis. This has been facilitated by the two jurisdictions' former shared membership of the European Union, and there have been calls from members of the business community and policymakers for the creation of an "all-Ireland economy" to take advantage of economies of scale and boost competitiveness.Regional economics
Below is a comparison of the regional GDP on the island of Ireland.Economic history
Prior to partition in 1921, Ireland had a long history as an economic colony – first, partially, of the Norse, via their cities (9th to 10th centuries CE), and later of England. Though the climate and soil favoured certain forms of agriculture, trade barriers frequently hobbled its development. Repeated invasions and plantations of Ireland, "plantations" disrupted land tenure, land-ownership, and Irish Rebellion (disambiguation), multiple failed uprisings also contributed to repeated phases of penal transportation, deportation and of Irish emigrant, emigration. Salient events in the economic history of Ireland include: * 16th and 17th centuries: confiscation and redistribution of land in the Plantations of Ireland * 1845-1849: Great Famine (Ireland), The Great Famine occasioned depopulation and mass emigration * 1846: Westminster's repeal of the Corn Laws disrupted Irish agricultureMajor industries
Tourism
 There are three World Heritage Sites on the island: the complex, Skellig Michael and the Giant's Causeway. Several other places are on the tentative list, for example the Burren, the Ceide Fields and Mount Stewart.
Some of the most visited sites in Ireland include Bunratty Castle, the Rock of Cashel, the Cliffs of Moher, Holy Cross Abbey and Blarney Castle. Historically important monastic sites include Glendalough and Clonmacnoise, which are maintained as National Monument (Ireland), national monuments in the Republic of Ireland.
The Dublin region receives the most tourists and is home to several of the most popular attractions such as the Guinness Storehouse and
There are three World Heritage Sites on the island: the complex, Skellig Michael and the Giant's Causeway. Several other places are on the tentative list, for example the Burren, the Ceide Fields and Mount Stewart.
Some of the most visited sites in Ireland include Bunratty Castle, the Rock of Cashel, the Cliffs of Moher, Holy Cross Abbey and Blarney Castle. Historically important monastic sites include Glendalough and Clonmacnoise, which are maintained as National Monument (Ireland), national monuments in the Republic of Ireland.
The Dublin region receives the most tourists and is home to several of the most popular attractions such as the Guinness Storehouse and Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New ...
. The west and south west, which includes the Lakes of Killarney and the Dingle peninsula in County Kerry and Connemara and the Aran Islands in County Galway, are also popular tourist destinations.
Achill Island lies off the coast of County Mayo and is Ireland's largest island. It is a popular tourist destination for surfing and contains 5 Blue Flag beaches and Croaghaun one of the world's highest sea cliffs. Stately homes, built during the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries in Palladian, Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical and neo-Gothic styles, such as Castle Ward, Castletown House, Bantry House, Strokestown Park and Glenveagh Castle are also of interest to tourists. Some have been converted into hotels, such as Ashford Castle, Castle Leslie and Dromoland Castle.
Energy
Although for most of their existence electricity networks in the Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland were entirely separate, the island has operated for some time as a single market for electricity. Both networks were designed and constructed independently post-partition but they are now connected with three interlinks and are also connected through Great Britain to mainland Europe. The situation in Northern Ireland is complicated by the issue of private companies not supplying Northern Ireland Electricity with enough power. In the Republic of Ireland, the ESB Group, ESB has failed to modernise its power stations, and the availability of power plants has recently averaged only 66%, one of the worst such rates in Western Europe. EirGrid has started building a High-voltage direct current, HVDC transmission line between Ireland and Great Britain with a capacity of 500 MW, about 10% of Ireland's peak demand. As with electricity, the natural gas distribution network is also now all-island, with a pipeline linking Gormanston, County Meath, and Ballyclare, County Antrim. Most of Ireland's gas comes through interconnectors between Twynholm in Scotland and Ballylumford power station, Ballylumford, County Antrim and Loughshinny, County Dublin. Supplies come from the Corrib Gas Field, off the coast of County Mayo, with a supply previously also coming from the Kinsale gas field off the County Cork coast. The County Mayo field faces some localised opposition over Corrib gas controversy, a controversial decision to refine the gas onshore. Ireland has an ancient industry based on peat (known locally as "turf") as a source of energy for home fires. A form of biomass energy, this source of heat is still widely used in rural areas. However, because of the ecological importance of peatlands in storing carbon and their rarity, the EU is attempting to protect this habitat by fining Ireland for digging up peat. In cities, heat is generally supplied by natural gas or heating oil, although some urban suppliers distribute sods of turf as "smokeless fuel" for domestic use.
The Republic has a strong commitment to renewable energy and ranks as one of the top 10 markets for clean technology, clean-technology investment in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index. Research and development in renewable energy (such as wind power) has increased since 2004. Large List of wind farms in the Republic of Ireland, wind farms have been constructed in Cork, Donegal, Mayo and Antrim. The construction of wind farms has in some cases been delayed by opposition from local communities, some of whom regard the wind turbines as unsightly. The Republic is hindered by an ageing network that was not designed to handle the varying availability of power that comes from wind farms. The ESB's Turlough Hill facility is the only power-storage facility in the state.
Ireland has an ancient industry based on peat (known locally as "turf") as a source of energy for home fires. A form of biomass energy, this source of heat is still widely used in rural areas. However, because of the ecological importance of peatlands in storing carbon and their rarity, the EU is attempting to protect this habitat by fining Ireland for digging up peat. In cities, heat is generally supplied by natural gas or heating oil, although some urban suppliers distribute sods of turf as "smokeless fuel" for domestic use.
The Republic has a strong commitment to renewable energy and ranks as one of the top 10 markets for clean technology, clean-technology investment in the 2014 Global Green Economy Index. Research and development in renewable energy (such as wind power) has increased since 2004. Large List of wind farms in the Republic of Ireland, wind farms have been constructed in Cork, Donegal, Mayo and Antrim. The construction of wind farms has in some cases been delayed by opposition from local communities, some of whom regard the wind turbines as unsightly. The Republic is hindered by an ageing network that was not designed to handle the varying availability of power that comes from wind farms. The ESB's Turlough Hill facility is the only power-storage facility in the state.
Explanatory notes
References
Bibliography
* * Beckett, J.C. ''The making of Modern Ireland 1603-1923'' (1971) * * Bew, Paul. ''Ireland: The Politics of Enmity 1789-2006'' (2007). * * Daly, Mary E. ''Sixties Ireland: reshaping the economy, state and society, 1957–1973'' (Cambridge University Press, 2016). * * * * Ferriter, Diarmaid. "Women and political change in Ireland since 1960." ''Éire-Ireland'' 43.1 (2008): 179-204. * * Foster, R. F. ''Luck and the Irish: A Brief History of Change 1970-2000'' (2007excerpt
* * * * * * *
External links
*Government of Ireland
Northern Ireland Executive
{{Authority control Ireland, British Isles Celtic nations Divided regions International islands