
 In
In automotive engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software, and safety engineering as applied to the design, manufactu ...
, an inlet manifold or intake manifold (in American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
) is the part of an engine that supplies the fuel
A fuel is any material that can be made to react with other substances so that it releases energy as thermal energy or to be used for work. The concept was originally applied solely to those materials capable of releasing chemical energy but ...
/ air mixture to the cylinders. The word ''manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a n ...
'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' epeatedly and refers to the multiplying of one (pipe) into many.manifold, (adv.) "in the proportion of many to one, by many times". AD1526 ''Oxford English Dictionary'',
In contrast, an exhaust manifold
In automotive engineering, an exhaust manifold collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into one pipe. The word ''manifold'' comes from the Old English word ''manigfeald'' (from the Anglo-Saxon ''manig'' anyand ''feald'' old and refe ...
collects the exhaust gases from multiple cylinders into a smaller number of pipes – often down to one pipe.
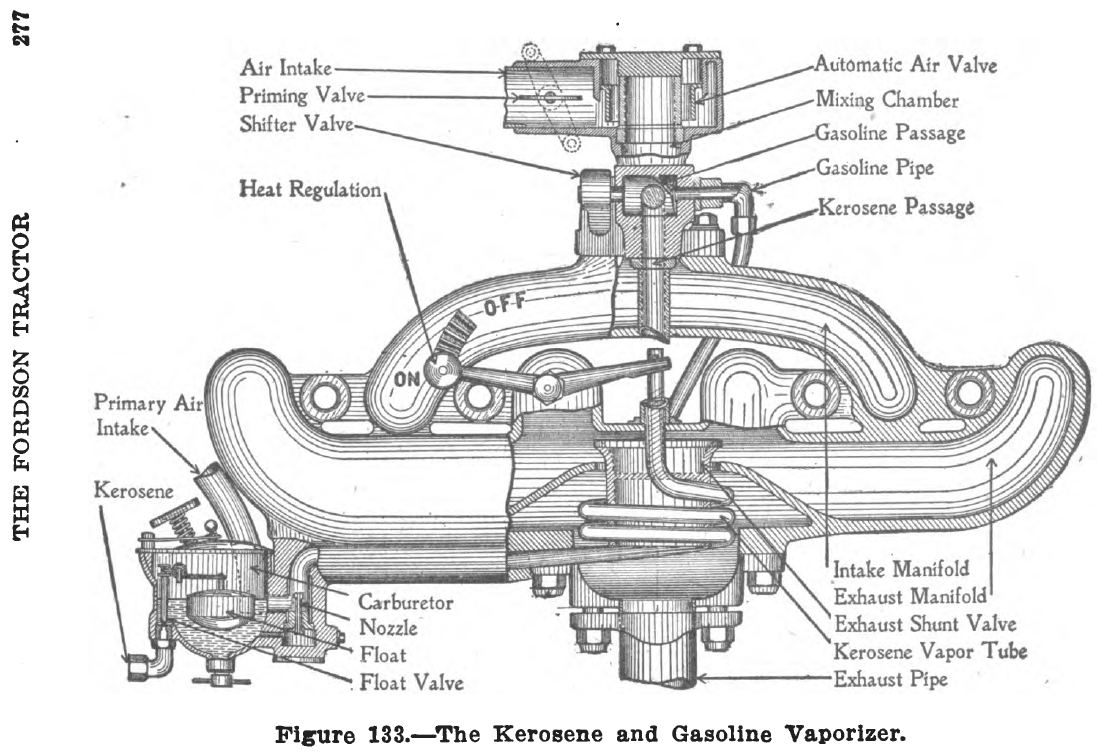
The primary function of the intake manifold is to ''evenly'' distribute the combustion mixture (or just air in a direct injection engine) to each intake port in the cylinder head(s). Even distribution is important to optimize the efficiency and performance of the engine. It may also serve as a mount for the carburetor, throttle body, fuel injectors and other components of the engine.
Due to the downward movement of the piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder and is made gas-tig ...
s and the restriction caused by the throttle valve, in a reciprocating spark ignition piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common featu ...
, a partial vacuum (lower than atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibar ...
) exists in the intake manifold. This manifold vacuum can be substantial, and can be used as a source of automobile ancillary power to drive auxiliary systems: power assisted brake
A brake is a mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of friction.
Background ...
s, emission control devices, cruise control, ignition advance, windshield wipers, power windows, ventilation system valves, etc.
This vacuum can also be used to draw any piston blow-by gases from the engine's crankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block.
Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/a ...
. This is known as a positive crankcase ventilation system, in which the gases are burned with the fuel/air mixture.
The intake manifold has historically been manufactured from aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in AmE, American and CanE, Canadian English) is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately o ...
or cast iron, but use of composite plastic materials is gaining popularity (e.g. most Chrysler 4-cylinders, Ford Zetec 2.0, Duratec 2.0 and 2.3, and GM's Ecotec Ecotec (capitalized ECOTEC, from 'Emissions Control Optimization TEChnology') is a General Motors (GM) and Opel Automobile GmbH (Opel) trademark that refers to a series of emissions technologies that were implemented throughout a range of GM engines ...
series).
Turbulence
Thecarburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meteri ...
or the fuel injectors spray fuel droplets into the air in the manifold. Due to electrostatic forces and condensation from the boundary layer, some of the fuel will form into pools along the walls of the manifold, and due to surface tension of the fuel, small droplets may combine into larger droplets in the airstream. Both actions are undesirable because they create inconsistencies in the air-fuel ratio. Turbulence in the intake helps to break up fuel droplets, improving the degree of atomization. Better atomization allows for a more complete burn of all the fuel and helps reduce engine knock by enlarging the flame front. To achieve this turbulence it is a common practice to leave the surfaces of the intake and intake ports in the cylinder head rough and unpolished.
Only a certain degree of turbulence is useful in the intake. Once the fuel is sufficiently atomized additional turbulence causes unneeded pressure drops and a drop in engine performance.
Volumetric efficiency
 The design and orientation of the intake manifold is a major factor in the volumetric efficiency of an engine. Abrupt contour changes provoke pressure drops, resulting in less air (and/or fuel) entering the combustion chamber; high-performance manifolds have smooth contours and gradual transitions between adjacent segments.
Modern intake manifolds usually employ ''runners'', individual tubes extending to each intake port on the cylinder head which emanate from a central volume or "plenum" beneath the carburetor. The purpose of the runner is to take advantage of the
The design and orientation of the intake manifold is a major factor in the volumetric efficiency of an engine. Abrupt contour changes provoke pressure drops, resulting in less air (and/or fuel) entering the combustion chamber; high-performance manifolds have smooth contours and gradual transitions between adjacent segments.
Modern intake manifolds usually employ ''runners'', individual tubes extending to each intake port on the cylinder head which emanate from a central volume or "plenum" beneath the carburetor. The purpose of the runner is to take advantage of the Helmholtz resonance
Helmholtz resonance or wind throb is the phenomenon of air resonance in a cavity, such as when one blows across the top of an empty bottle. The name comes from a device created in the 1850s by Hermann von Helmholtz, the ''Helmholtz resonator'', wh ...
property of air. Air flows at considerable speed through the open valve. When the valve closes, the air that has not yet entered the valve still has a lot of momentum and compresses against the valve, creating a pocket of high pressure. This high-pressure air begins to equalize with lower-pressure air in the manifold. Due to the air's inertia, the equalization will tend to oscillate: At first the air in the runner will be at a lower pressure than the manifold. The air in the manifold then tries to equalize back into the runner, and the oscillation repeats. This process occurs at the speed of sound, and in most manifolds travels up and down the runner many times before the valve opens again.
The smaller the cross-sectional area of the runner, the higher the pressure changes on resonance for a given airflow. This aspect of Helmholtz resonance reproduces one result of the Venturi effect. When the piston accelerates downwards, the pressure at the output of the intake runner is reduced. This low pressure pulse runs to the input end, where it is converted into an over-pressure pulse. This pulse travels back through the runner and rams air through the valve. The valve then closes.
To harness the full power of the Helmholtz resonance effect, the opening of the intake valve must be timed correctly, otherwise the pulse could have a negative effect. This poses a very difficult problem for engines, since valve timing is dynamic and based on engine speed, whereas the pulse timing is static and dependent on the length of the intake runner and the speed of sound. The traditional solution has been to tune the length of the intake runner for a specific engine speed where maximum performance is desired. However, modern technology has given rise to a number of solutions involving electronically controlled valve timing (for example Valvetronic), and dynamic intake geometry (see below).
As a result of "resonance tuning", some naturally aspirated intake systems operate at a volumetric efficiency above 100%: the air pressure in the combustion chamber before the compression stroke is greater than the atmospheric pressure. In combination with this intake manifold design feature, the exhaust manifold design, as well as the exhaust valve opening time can be so calibrated as to achieve greater evacuation of the cylinder. The exhaust manifolds achieve a vacuum in the cylinder just before the piston reaches top dead center. The opening inlet valve can then—at typical compression ratios—fill 10% of the cylinder before beginning downward travel. Instead of achieving higher pressure in the cylinder, the inlet valve can stay open after the piston reaches bottom dead center while the air still flows in.
In some engines the intake runners are straight for minimal resistance. In most engines, however, the runners have curves, some very convoluted to achieve desired runner length. These turns allow for a more compact manifold, with denser packaging of the whole engine, as a result. Also, these "snaked" runners are needed for some variable length/ split runner designs, and allow the size of the plenum to be reduced. In an engine with at least six cylinders the averaged intake flow is nearly constant and the plenum volume can be smaller. To avoid standing waves within the plenum it is made as compact as possible. The intake runners each use a smaller part of the plenum surface than the inlet, which supplies air to the plenum, for aerodynamic reasons. Each runner is placed to have nearly the same distance to the main inlet. Runners whose cylinders fire close after each other, are not placed as neighbors.
In 180-degree intake manifolds, originally designed for carburetor V8 engines, the two plane, the split plenum intake manifold separates the intake pulses which the manifold experiences by 180 degrees in the firing order. This minimizes interference of one cylinder's pressure waves with those of another, giving better torque from smooth mid-range flow. Such manifolds may have been originally designed for either two- or four-barrel carburetors, but now are used with both throttle-body and multi-point fuel injection. An example of the latter is the Honda J engine
The J-series is Honda's fourth production V6 engine family introduced in 1996, after the Honda C engine, C-series, which consisted of three dissimilar versions. The J-series engine was designed in the United States by Honda engineers. It is built ...
which converts to a single plane manifold around 3500 rpm for greater peak flow and horsepower.
Older heat riser manifolds with 'wet runners' for carbureted engines used exhaust gas diversion through the intake manifold to provide vaporizing heat. The amount of exhaust gas flow diversion was controlled by a heat riser valve in the exhaust manifold, and employed a bi-metallic spring which changed tension according to the heat in the manifold. Today's fuel-injected engines do not require such devices.
Variable-length intake manifold
A variable-length intake manifold (VLIM) is an internal combustion engine manifold technology. Four common implementations exist. First, two discrete intake runners with different length are employed, and a butterfly valve can close the short path. Second the intake runners can be bent around a common plenum, and a sliding valve separates them from the plenum with a variable length. Straight high-speed runners can receive plugs, which contain small long runner extensions. The plenum of a 6- or 8-cylinder engine can be parted into halves, with the even firing cylinders in one half and the odd firing cylinders in the other part. Both sub-plenums and the air intake are connected to an Y (sort of main plenum). The air oscillates between both sub-plenums, with a large pressure oscillation there, but a constant pressure at the main plenum. Each runner from a sub plenum to the main plenum can be changed in length. For V engines this can be implemented by parting a single large plenum at high engine speed by means of sliding valves into it when speed is reduced. As the name implies, VLIM can vary the length of the intake tract in order to optimize power and torque, as well as provide betterfuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, wh ...
.
There are two main effects of variable intake geometry:
* Venturi effect: At low rpm, the speed of the airflow is increased by directing the air through a path with limited capacity (cross-sectional area). The larger path opens when the load increases so that a greater amount of air can enter the chamber. In dual overhead cam (DOHC) designs, the air paths are often connected to separate intake valves so the shorter path can be excluded by deactivating the intake valve itself.
* Pressurization: A tuned intake path can have a light pressurizing effect similar to a low-pressure supercharger
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
The current categorisation is that a supercharger is a form of forced induct ...
due to Helmholtz resonance. However, this effect occurs only over a narrow engine speed range which is directly influenced by intake length. A variable intake can create two or more pressurized "hot spots." When the intake air speed is higher, the dynamic pressure pushing the air (and/or mixture) inside the engine is increased. The dynamic pressure is proportional to the square of the inlet air speed, so by making the passage narrower or longer the speed/dynamic pressure is increased.
Many automobile manufacturers use similar technology with different names. Another common term for this technology is variable resonance induction system (VRIS).
* Audi: 2.8-liter V6 gas engine (1991–98); 3.6- and 4.2-liter V8 engines, 1987–present
* Alfa Romeo: 2.0 TwinSpark 16v - 155 ps(114 kW)
* BMW: DISA and DIVA systems
*Dodge
Dodge is an American brand of automobiles and a division of Stellantis, based in Auburn Hills, Michigan. Dodge vehicles have historically included performance cars, and for much of its existence Dodge was Chrysler's mid-priced brand above P ...
: 2.0 A588 – ECH (2001–2005) used in the 2001–2005 model year Dodge Neon R/T
* Ferrari
Ferrari S.p.A. (; ) is an Italian luxury sports car manufacturer based in Maranello, Italy. Founded by Enzo Ferrari (1898–1988) in 1939 from the Alfa Romeo racing division as ''Auto Avio Costruzioni'', the company built its first car in ...
: 360 Modena, 550 Maranello
* Ford VIS (Variable-resonance Intake System): on their 2.9-liter 24V Cosworth (BOB) based on the Ford Cologne V6 engine in the later model Ford Scorpio
* Ford DSI (dual-stage intake): on their Duratec 2.5- and 3.0-liter V6s and it was also found on the Yamaha V6 in the Taurus SHO
*Ford: The Ford Modular V8 engines sport either the Intake Manifold Runner Control (IMRC) for 4V engines, or the Charge Motion Control Valve (CMCV) for 3V engines.
*Ford: The 2.0L Split Port engine in the Ford Escort and Mercury Tracer feature an Intake Manifold Runner Control variable geometry intake manifold.
* General Motors
The General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. It is the largest automaker in the United States and ...
: 3.9L LZ8/LZ9 V6, 3.2L LA3 V6, and the 4.3L LF4 V6 in some second generation S10s and Sonomas
* GM Daewoo: DOHC versions of E-TEC II
The Family 1 is a straight-four piston engine that was developed by Opel, a former subsidiary of General Motors and now a subsidiary of PSA Group, to replace the Opel cam-in-head engines for use on mid-range cars from Opel/Vauxhall. Originally p ...
engines
* Holden
Holden, formerly known as General Motors-Holden, was an Australian subsidiary company of General Motors. It was an Australian automobile manufacturer, importer, and exporter which sold cars under its own marque in Australia. In its last thre ...
: Alloytec
The GM High Feature engine (also known as the HFV6, and including the 3600 LY7 and derivative LP1) is a family of modern General Motors DOHC V6 engines. The series was introduced in 2004 with the Cadillac CTS and the Holden Commodore (VZ).
It is ...
* Honda: Integra, Legend, NSX, Prelude
Prelude may refer to:
Music
*Prelude (music), a musical form
*Prelude (band), an English-based folk band
*Prelude Records (record label), a former New York-based dance independent record label
*Chorale prelude, a short liturgical composition for ...
* Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate ("chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai As ...
: XG V6
* Isuzu: Isuzu Rodeo, used in the second generation V6, 3.2L (6VD1) Rodeos
* Jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus '' Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the th ...
: AJ-V6
* Lancia
Lancia () is an Italian car manufacturer and a subsidiary of FCA Italy S.p.A., which is currently a Stellantis division. The present legal entity of Lancia was formed in January 2007 when its corporate parent reorganised its businesses, but it ...
: VIS
* Mazda: VICS (variable inertia charging system) is used on the Mazda FE-DOHC engine and Mazda B engine family of straight-4
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
s, and VRIS (variable resistance induction system) in the Mazda K engine family of V6 engines. An updated version of this technology is employed on the new Mazda Z engine, which is also used by Ford as the Duratec.
* Mercedes-Benz
* MG: MG ZS 180
The MG ZS was a sports family car that was built by MG Rover from 2001 until 2005. The ZS is essentially a tuned version of the Rover 45 (which was launched in 1999). The 45 in turn is a facelifted version of the Rover 400 which was launched ...
MG ZT 160, 180 and 190
* Mitsubishi
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries.
Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 1870 ...
: Cyclone is used on the 2.0L I4 4G63 engine family.
* Nissan
, trade name, trading as Nissan Motor Corporation and often shortened to Nissan, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan. The company sells ...
: I4, V6, V8
* Opel
Opel Automobile GmbH (), usually shortened to Opel, is a German automobile manufacturer which has been a subsidiary of Stellantis since 16 January 2021. It was owned by the American automaker General Motors from 1929 until 2017 and the PSA Grou ...
(or Vauxhall): TwinPort – modern versions of Ecotec Family 1 and Ecotec Family 0
The Family 0 is a family of inline piston engines that was developed by Opel, at the time a subsidiary of General Motors, as a low-displacement engine for use on entry-level subcompact cars from Opel/Vauxhall.
These engines feature a light-w ...
straight-4 engines; a similar technology is used in 3.2 L 54° V6 engine
* Peugeot: 2.2 L I4, 3.0 L V6
* Porsche
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see #Pronunciation, below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany ...
: VarioRam – 964
Year 964 ( CMLXIV) was a leap year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
Byzantine Empire
* Arab–Byzantine War: Emperor Nikephoros II continues the reconquest of south-eastern Anatoli ...
, 993, 996, Boxster
The Porsche Boxster and Cayman are mid-engine two-seater sports cars manufactured and marketed by German automobile manufacturer Porsche across four generations—as a two-door, two-seater roadster (Boxster) and a three-door, two-seater fastba ...
* Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
: Campro CPS and VIM – Proton Gen-2 CPS and Proton Waja CPS; Proton Campro IAFM – 2008 Proton Saga 1.3
* Renault: Clio 2.0RS
* Rover: Rover 623
The Rover 600 Series was a compact executive car range that was produced by the British manufacturer Rover (marque), Rover from 1993 to 1999.
The exterior of the Rover 600 was designed by Rover, a reskin of the European Honda Accord#European A ...
, Rover 825
The Rover 800 series is an executive car (E-segment in Europe) range manufactured by the Austin Rover Group subsidiary of British Leyland, and its successor the Rover Group from 1986 to 1999. It was also marketed as the Sterling in the United St ...
, Rover 75 v6, Rover 45 v6
* Subaru Legacy 1989–1994 JDM EJ20 2.0-liter naturally aspirated DOHC 16-valve flat-4
* Subaru SVX
The Subaru Alcyone SVX, marketed outside Japan as the Subaru SVX, is a two-door, front-engine, all- or front-wheel drive coupé manufactured and marketed by Subaru from 1991 to 1996 over a single generation.
Superseding the company's aviation-i ...
1992–1997 EG33 3.3-liter naturally aspirated DOHC 24-valve flat-6
* Subaru Legacy and Subaru Impreza 1999–2001 JDM EJ20 2.0-liter naturally aspirated DOHC 16-valve flat-4
* Toyota: T-VIS – (Toyota Variable Induction System) used in the early versions of the 3S-GE
The Toyota S Series engines are a family of straight-4 petrol or CNG engines with displacement from 1.8 L to 2.2 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation from January 1980 to August 2007. The series has cast iron engine blocks and alloy cy ...
, 7M-GE, and 4A-GE
The Toyota A Series engines are a family of inline-four internal combustion engines with displacement from 1.3 L to 1.8 L produced by Toyota Motor Corporation. The series has cast iron engine blocks and aluminum cylind ...
engines, and ACIS (acoustic control induction system)
* Volkswagen: 1.6 L I4, VR6, W8
* Volvo: VVIS (Volvo variable induction system) – Volvo B5254S and B5204S engines as found on the Volvo 850 vehicles. Longer inlet ducts used between 1500 and 4100 rpm at 80% load or higher.Volvoclub UK: 850GLT Engine Info/ref>
See also
*Cylinder head porting
Cylinder head porting refers to the process of modifying the intake and exhaust ports of an internal combustion engine to improve their air flow. Cylinder heads, as manufactured, are usually suboptimal for racing applications due to being design ...
* Fusible core injection molding
References
{{Automotive engine Engine technology Auto parts