Initiation Fee on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Initiation is a
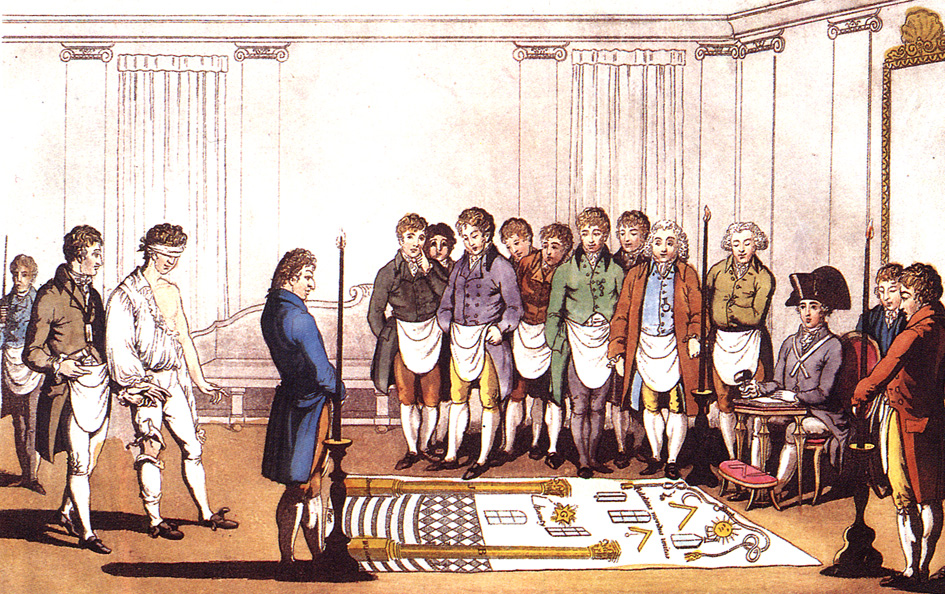 A spiritual initiation rite normally implies a shepherding process where those who are at a higher level guide the initiate through a process of greater exposure of knowledge. This may include the revelation of secrets, hence the term secret society for such organizations, usually reserved for those at the higher level of understanding. One famous historical example is the
A spiritual initiation rite normally implies a shepherding process where those who are at a higher level guide the initiate through a process of greater exposure of knowledge. This may include the revelation of secrets, hence the term secret society for such organizations, usually reserved for those at the higher level of understanding. One famous historical example is the
 Some communities on board a military vessel and also of military soldiers tend to form a closed 'family' which absorbs in members, who are often formally accepted, generally after a form of trial or
Some communities on board a military vessel and also of military soldiers tend to form a closed 'family' which absorbs in members, who are often formally accepted, generally after a form of trial or
Associated Gangs in this county
. New members may be physically beaten by fellow gang members to demonstrate their courage, also known as "beat-in" or "jump-in", which occasionally results in a fatality. One study indicates that young people are more likely to be hurt in gang initiation than they are by refusing to join. Female members may be required to have sex with male members as a form of initiation, also known as "sex in", though they may also be "jumped-in" like their male counterparts. One study shows that female members who were “sexed-in” as part of gang initiation were thereafter viewed with lower respect than those that were "jumped-in", even when promised they would become full-fledged members. Another study found that sexed-in members face greater risks of sexual exploitation and
 Tribes often have initiations. The initiation done in the Bapedi tribe of South Africa is normally regarded as a stage where a boy is to be taught manhood and a girl to be taught womanhood. In many African tribes, initiation involves
Tribes often have initiations. The initiation done in the Bapedi tribe of South Africa is normally regarded as a stage where a boy is to be taught manhood and a girl to be taught womanhood. In many African tribes, initiation involves  In some African tribes, boys take about 3–4 months participating in initiation rites and girls take about 1–2 months.
Australian Aboriginal tribes usually had long periods of time to help prepare adolescent boys, teaching them traditional lore before they were ready to attend large elaborate ceremonies at the time of initiation when they were finally recognized as full-fledged men in their society. Most tribes had circumcision and scarification as part of the male initiation rituals, while many
In some African tribes, boys take about 3–4 months participating in initiation rites and girls take about 1–2 months.
Australian Aboriginal tribes usually had long periods of time to help prepare adolescent boys, teaching them traditional lore before they were ready to attend large elaborate ceremonies at the time of initiation when they were finally recognized as full-fledged men in their society. Most tribes had circumcision and scarification as part of the male initiation rituals, while many
rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
marking entrance or acceptance into a group or society. It could also be a formal admission to adulthood in a community or one of its formal components. In an extended sense, it can also signify a transformation in which the initiate is 'reborn' into a new role. Examples of initiation ceremonies might include Christian baptism
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
or confirmation
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. For adults, it is an affirmation of belief. It involves laying on ...
, Jewish bar or bat mitzvah, acceptance into a fraternal organization
A fraternity (from Latin ''frater'': "brother"; whence, "brotherhood") or fraternal organization is an organization, society, club or fraternal order traditionally of men associated together for various religious or secular aims. Fraternity in ...
, secret society
A secret society is a club or an organization whose activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
or religious order
A religious order is a lineage of communities and organizations of people who live in some way set apart from society in accordance with their specific religious devotion, usually characterized by the principles of its founder's religious practi ...
, or graduation
Graduation is the awarding of a diploma to a student by an educational institution. It may also refer to the ceremony that is associated with it. The date of the graduation ceremony is often called graduation day. The graduation ceremony is a ...
from school or recruit training. A person taking the initiation ceremony in traditional rites, such as those depicted in these pictures, is called an ''initiate''.
See also rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
.
Characteristics
William Ian Miller William Ian Miller (born March 30, 1946) is the Thomas G. Long Professor of Law at the University of Michigan
, mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth"
, former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817 ...
notes the role of ritual humiliation in comic ordering and testing.
Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanians, Romanian History of religion, historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. He was a leading interpreter of religious experience, who establ ...
discussed initiation as a principal religious act by classical or traditional societies. He defined initiation as "a basic change in existential condition", which liberates man from profane time and history. "Initiation recapitulates the sacred history of the world. And through this recapitulation, the whole world is sanctified anew... he initiand
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
can perceive the world as a sacred work, a creation of the Gods."
Eliade differentiates between types of initiations in two ways: types and functions.
Reasons for and functions
* "this real valuation of ritual death finally led to conquest of the fear of real death." * " nitiation'sfunction is to reveal the deep meaning of existence to the new generations and to help them assume the responsibility of being truly men and hence of participating in culture." * "it reveals a world open to the trans-human, a world that, in our philosophical terminology, we should call transcendental." * "to makehe initiand
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
open to spiritual values."
Types
*Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
rites: "collective rituals whose function is to effect the transition from childhood or adolescence to adulthood." They represent "above all the revelation of the sacred."
* Entering into a Secret Society
A secret society is a club or an organization whose activities, events, inner functioning, or membership are concealed. The society may or may not attempt to conceal its existence. The term usually excludes covert groups, such as intelligence a ...
* Mystical vocation: "the vocation of a medicine man or a shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritu ...
." This is limited to the few who are "destined to participate in a more intense religious experience than is accessible to the rest of the community."
These can be broken into two types:
* puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy. ...
rites, "by virtue of which adolescents gain access to the sacred, to knowledge, and to sexuality-- by which, in short, they become human beings."
* specialized initiations, which certain individuals undergo in order to transcend their human condition and become protégés of the Supernatural Beings or even their equals."
Psychological
In the study of certain social forms of initiation, such as hazing in college fraternities and sororities, laboratory experiments in psychology suggest that severe initiations produce cognitive dissonance. Dissonance is then thought to produce feelings of strong group attraction among initiates after the experience, because they want to justify the effort used.Rewards
Reward may refer to:
Places
* Reward (Shelltown, Maryland), a historic home in Shelltown Maryland
* Reward, California (disambiguation)
* Reward-Tilden's Farm, a historic home in Chestertown Maryland
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Reward" ...
during initiations have important consequences in that initiates who feel more rewarded express stronger group identity. As well as group attraction, initiations can also produce conformity
Conformity is the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to group norms, politics or being like-minded. Norms are implicit, specific rules, shared by a group of individuals, that guide their interactions with others. People often choo ...
among new members. Psychology experiments have also shown that initiations increase feelings of affiliation
Affiliation or affiliate may refer to:
* Affiliate (commerce), a legal form of entity relationship used in Business Law
* Affiliation (family law), a legal form of family relationship
* Affiliate marketing
* Affiliate network or affiliation platfo ...
.
Examples
Religious and spiritual
 A spiritual initiation rite normally implies a shepherding process where those who are at a higher level guide the initiate through a process of greater exposure of knowledge. This may include the revelation of secrets, hence the term secret society for such organizations, usually reserved for those at the higher level of understanding. One famous historical example is the
A spiritual initiation rite normally implies a shepherding process where those who are at a higher level guide the initiate through a process of greater exposure of knowledge. This may include the revelation of secrets, hence the term secret society for such organizations, usually reserved for those at the higher level of understanding. One famous historical example is the Eleusinian Mysteries
The Eleusinian Mysteries ( el, Ἐλευσίνια Μυστήρια, Eleusínia Mystḗria) were initiations held every year for the cult of Demeter and Persephone based at the Panhellenic Sanctuary of Elefsina in ancient Greece. They are the " ...
of ancient Greece, thought to go back to at least the Mycenaean period or "Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
".
In the context of ritual magic
Ceremonial magic (ritual magic, high magic or learned magic) encompasses a wide variety of rituals of magic. The works included are characterized by ceremony and numerous requisite accessories to aid the practitioner. It can be seen as an e ...
and esotericism, an initiation is considered to cause a fundamental process of change to begin within the person being initiated and its "evolution operates within both the material world and the spiritual world". The person conducting the initiation (the ''initiator''), being in possession of a certain power or state of being, transfers this power or state to the person being initiated. Thus the concept of initiation is similar to that of apostolic succession
Apostolic succession is the method whereby the ministry of the Christian Church is held to be derived from the apostles by a continuous succession, which has usually been associated with a claim that the succession is through a series of bish ...
. The initiation process is often likened to a simultaneous death and rebirth, because as well as being a beginning it also implies an ending as existence on one level drops away in an ascension to the next.
Initiation is a key component of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, r ...
and Shiism, Vaishnavism
Vaishnavism ( sa, वैष्णवसम्प्रदायः, Vaiṣṇavasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu denominations along with Shaivism, Shaktism, and Smartism. It is also called Vishnuism since it considers Vishnu as the ...
, Sant Mat
Sant Mat was a spiritual movement on the Indian subcontinent during the 13th–17th centuries CE. The name literally means "teachings of sants", i.e. mystic Hindu saints. Through association and seeking truth by following ''sants'' and their teac ...
, Surat Shabd Yoga, Vajrayana Buddhism
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
, Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and was ...
, and similar religious gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
traditions. It denotes acceptance by the Guru
Guru ( sa, गुरु, IAST: ''guru;'' Pali'': garu'') is a Sanskrit term for a "mentor, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field. In pan-Indian traditions, a guru is more than a teacher: traditionally, the guru is a reverentia ...
and also implies that the Chela (student or disciple) agrees to the requirements (such as living an ethical lifestyle, meditating, etc.)
Trade union
In unionisedorganization
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
s, the "initiation" is typically no more than a brief familiarization with basic procedures and the provision of a copy of the appropriate collective bargaining
Collective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employers and a group of employees aimed at agreements to regulate working salaries, working conditions, benefits, and other aspects of workers' compensation and rights for workers. The i ...
agreement Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus, a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of law
** Meeting o ...
that governs the work performed by members of the union. Some unions also charge a one-time initiation fee, after which the joining person
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, ...
is officially deemed to be a member in good standing.
Naval and military
 Some communities on board a military vessel and also of military soldiers tend to form a closed 'family' which absorbs in members, who are often formally accepted, generally after a form of trial or
Some communities on board a military vessel and also of military soldiers tend to form a closed 'family' which absorbs in members, who are often formally accepted, generally after a form of trial or hazing
Hazing (American English), initiation, beasting (British English), bastardisation (Australian English), ragging (South Asian English) or deposition refers to any activity expected of someone in joining or participating in a group that humiliates, ...
.
In addition, there can be similar rites of passages associated with parts of naval and military life, which do not constitute true initiations as the participants are already and remain members of the same community. One such rite is associated with crossing the equator
The line-crossing ceremony is an initiation rite that commemorates a person's first crossing of the Equator. The tradition may have originated with ceremonies when passing headlands, and become a "folly" sanctioned as a boost to morale,Robert Fit ...
on board a naval ship, but it can even be taken by passengers on board a cruise liner, who are not and do not become members of anything but the so-called "equator crossing club". Another form, “Kissing the Royal Belly” or “Royal Baby”, calls for initiates to kneel before a senior member of the crew, who wears a mock diaper. This “Baby” usually has a huge stomach covered with greasy materials ranging from cooking oil to mustard, shaving cream, eggs, and oysters. Junior sailors must lick the Baby's navel area, while the "baby" grabs and shakes their head to better smear the goo onto their faces.
Gang
Gangs often require new members to commit crimes before accepting them as part of the gang.Maryland gangAssociated Gangs in this county
. New members may be physically beaten by fellow gang members to demonstrate their courage, also known as "beat-in" or "jump-in", which occasionally results in a fatality. One study indicates that young people are more likely to be hurt in gang initiation than they are by refusing to join. Female members may be required to have sex with male members as a form of initiation, also known as "sex in", though they may also be "jumped-in" like their male counterparts. One study shows that female members who were “sexed-in” as part of gang initiation were thereafter viewed with lower respect than those that were "jumped-in", even when promised they would become full-fledged members. Another study found that sexed-in members face greater risks of sexual exploitation and
abuse
Abuse is the improper usage or treatment of a thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, crimes, or other t ...
by fellow male members.Miller, J. (2002). Young Women in Street Gangs: Risk Factors, Delinquency, and Victimization Risk. National Crime Journal, Ch.3>
Tribal
 Tribes often have initiations. The initiation done in the Bapedi tribe of South Africa is normally regarded as a stage where a boy is to be taught manhood and a girl to be taught womanhood. In many African tribes, initiation involves
Tribes often have initiations. The initiation done in the Bapedi tribe of South Africa is normally regarded as a stage where a boy is to be taught manhood and a girl to be taught womanhood. In many African tribes, initiation involves circumcision
Circumcision is a surgical procedure, procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin ...
/ genital mutilation of males and sometimes circumcision
Circumcision is a surgical procedure, procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin ...
/ genital mutilation of females as well. Initiation is considered necessary for the individual to be regarded as a full member of the tribe. Otherwise, the individual may not be allowed to participate in ceremonies or even in social rituals such as marriage. A man will not be allowed to marry or have any special relationship with a woman who did not go to an initiation, because she is not considered to be a woman.
Initiation may be thought of as an event which may help teens prepare themselves to be good husbands and wives. Where modernization is occurring, initiation is not taken so seriously as before, although there are still certain areas which still perform initiations.
 In some African tribes, boys take about 3–4 months participating in initiation rites and girls take about 1–2 months.
Australian Aboriginal tribes usually had long periods of time to help prepare adolescent boys, teaching them traditional lore before they were ready to attend large elaborate ceremonies at the time of initiation when they were finally recognized as full-fledged men in their society. Most tribes had circumcision and scarification as part of the male initiation rituals, while many
In some African tribes, boys take about 3–4 months participating in initiation rites and girls take about 1–2 months.
Australian Aboriginal tribes usually had long periods of time to help prepare adolescent boys, teaching them traditional lore before they were ready to attend large elaborate ceremonies at the time of initiation when they were finally recognized as full-fledged men in their society. Most tribes had circumcision and scarification as part of the male initiation rituals, while many Central Australian
Central Australia, also sometimes referred to as the Red Centre, is an inexactly defined region associated with the geographic centre of Australia. In its narrowest sense it describes a region that is limited to the town of Alice Springs and ...
tribes also practiced subincision.
A salient shared cultural feature of the Min peoples of the New Guinea Highlands is initiation into a secret male religious cult. For example, the Urapmin people
The Urapmin people are an ethnic group numbering about 375 people in the Telefomin District of the West Sepik Province of Papua New Guinea. One of the Min peoples who inhabit this area, the Urapmin share the common Min practices of hunter-gather ...
used to practice a type of male initiation known in Urap
''Urap'' (sometimes spelled ''urab'' or in its plural form ''urap-urap'') is a salad dish of steamed vegetables mixed with seasoned and spiced grated coconut for dressing. It is commonly found in Indonesian cuisine, more precisely Javanese cui ...
as ''ban''. These elaborate rituals were a central part of Urapmin social life. The ''ban'' was a multistage process which involved beatings and manipulation of various objects. At each stage, the initiate was offered revelations of secret knowledge (Urap: ''weng awem''), but at the next stage these would be shown to be false (Urap: ''famoul''). These initiations were abandoned with the adoption of Christianity, and the Urap have expressed relief at no longer having to administer the beatings which were involved.
The Sateré-Mawé people of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
use intentional bullet ant stings as part of their initiation rites to become warriors.
Historical China
Chinese boys, under theRites of Zhou
The ''Rites of Zhou'' (), originally known as "Officers of Zhou" () is a work on bureaucracy and organizational theory. It was renamed by Liu Xin to differentiate it from a chapter in the ''Book of History'' by the same name. To replace a lost ...
, initiate their adulthood when they are 20 years old (加冠) and girls when they are 15 (及笄). Yili (儀禮), a text in the chapter of the rites(?) (士冠禮) describes various details of the ceremonies involved.
Nearing the late parts of the ceremony, the initiate gains an alias, or a "Courtesy name
A courtesy name (), also known as a style name, is a name bestowed upon one at adulthood in addition to one's given name. This practice is a tradition in the East Asian cultural sphere, including China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Ulrich Theobald ...
"; thereafter use of their personal name is strictly prohibited except before parents and rulers.
See also
*Hazing
Hazing (American English), initiation, beasting (British English), bastardisation (Australian English), ragging (South Asian English) or deposition refers to any activity expected of someone in joining or participating in a group that humiliates, ...
* Ulwaluko
References
Bibliography
* * * * *Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanians, Romanian History of religion, historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. He was a leading interpreter of religious experience, who establ ...
, ''Rites and Symbols of Initiation
Rail India Technical and Economic Service Limited, abbreviated as RITES Ltd, is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India. It is an engineering consultancy corporation, specializing in the field ...
'', first edition, New York, NY Harper and Row, 1958.
External links
{{Authority control Rites of passage Majority–minority relations