|
Initiation
Initiation is a rite of passage marking entrance or acceptance into a group or society. It could also be a formal admission to adulthood in a community or one of its formal components. In an extended sense, it can also signify a transformation in which the initiate is 'reborn' into a new role. Examples of initiation ceremonies might include Christian baptism or confirmation, Jewish bar or bat mitzvah, acceptance into a fraternal organization, secret society or religious order, or graduation from school or recruit training. A person taking the initiation ceremony in traditional rites, such as those depicted in these pictures, is called an ''initiate''. Characteristics William Ian Miller notes the role of ritual humiliation in comic ordering and testing. Mircea Eliade discussed initiation as a principal religious act by classical or traditional societies. He defined initiation as "a basic change in existential condition", which liberates man from profane time and histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rite Of Passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of social status, status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite de passage'', a French term innovated by the Ethnography, ethnographer Arnold van Gennep in his work ''Les rites de passage'', ''The Rites of Passage''. The term is now fully adopted into anthropology as well as into the literature and popular cultures of many modern languages. Original conception In English, Van Gennep's first sentence of his first chapter begins: "Each larger society contains within it several distinctly separate groupings. ... In addition, all these groups break down into still smaller societies in subgroups." The population of a society belongs to multiple groups, some more important to the individual than others. Van Gennep uses the metaphor, "as a kind of house divided into rooms and corridors." A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baptism
Baptism (from ) is a Christians, Christian sacrament of initiation almost invariably with the use of water. It may be performed by aspersion, sprinkling or affusion, pouring water on the head, or by immersion baptism, immersing in water either partially or completely, traditionally three times, once for each person of the Trinity. The synoptic gospels recount that John the Baptist baptism of Jesus, baptized Jesus., , Baptism is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance (Christian), ordinance in others. Baptism according to the Trinitarian formula, which is done in most mainstream Christian denominations, is seen as being a basis for Christian ecumenism, the concept of unity amongst Christians. Baptism is also called christening, although some reserve the word "christening" for the Infant baptism, baptism of infants. In certain Christian denominations, such as the Catholic Churches, Eastern Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox Churches, Assyrian Church of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confirmation (Christian Sacrament)
In Christian denominations that practice infant baptism, confirmation is seen as the sealing of the covenant created in baptism. Those being confirmed are known as confirmands. The ceremony typically involves laying on of hands. Catholicism views Baptism as a sacrament. The sacrament is called chrismation in Eastern Christianity. In the East it takes place immediately after baptism; in the West, when a child reaches the age of reason or early adolescence, or in the case of adult baptism immediately afterwards in the same ceremony. Among those Christians who practise confirmation during their teenage years, the practice may be perceived, secondarily, as a coming of age rite. In many Protestant denominations, such as the Lutheran, Reformed, Anglican and Methodist traditions, confirmation is a rite that often includes a profession of faith by an already baptized person. Confirmation is required by Lutherans, Anglicans and other traditional Protestant denominations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleusinian Mysteries
The Eleusinian Mysteries () were initiations held every year for the Cult (religious practice), cult of Demeter and Persephone based at the Panhellenic Sanctuary of Eleusis in ancient Greece. They are considered the "most famous of the secret religious rites of ancient Greece". Their basis was a Bronze Age Agrarianism, agrarian cult, and there is some evidence that they were derived from the religious practices of the Mycenean Greece, Mycenean period.Dietrich (1975) ''The origins of Greek Religion''. Bristol Phoenix Press pp. 166, 167Walter Burkert. (1985)''Greek Religion''. Harvard University Press. p. 285 The Mysteries represented the myth of the Persephone#Abduction myth, abduction of Persephone from her mother Demeter by the king of the underworld Hades, in a cycle with three phases: the ''descent'' (loss), the ''search'', and the ''ascent'', with the main theme being the ''ascent'' () of Persephone and the reunion with her mother. It was a major festival during the Hellenistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as shamanic have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism. Terminology Etymology The Modern English word ''shamanism'' derives from the Russian word , , which itself comes from the word from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
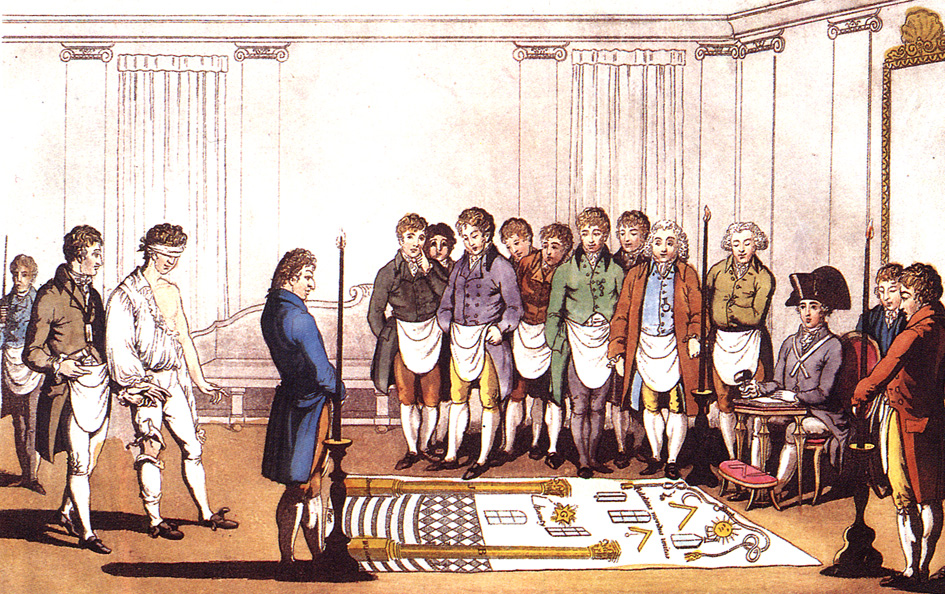
Freimaurer Initiation
Freemasonry (sometimes spelled Free-Masonry) consists of fraternal groups that trace their origins to the medieval guilds of stonemasons. Freemasonry is the oldest secular fraternity in the world and among the oldest still-existing organizations in history. Modern Freemasonry broadly consists of three main traditions: *Anglo-American Freemasonry, Anglo-American style Freemasonry, which insists that a "volume of sacred law", such as the Bible, Quran, or other religious text be open in a working Masonic lodge, lodge, that every member professes belief in a God, supreme being, that only men be admitted, and discussion of religion or politics does not take place within the lodge. *Continental Freemasonry or Liberal Freemasonry which has continued to evolve beyond these restrictions, particularly regarding religious belief and political discussion. *Co-Freemasonry, Women Freemasonry or Co-Freemasonry, which includes organizations that either admit women exclusively (such as the Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Dissonance
In the field of psychology, cognitive dissonance is described as a mental phenomenon in which people unknowingly hold fundamentally conflicting cognitions. Being confronted by situations that challenge this dissonance may ultimately result in some change in their cognitions or actions to cause greater alignment between them so as to reduce this dissonance. Relevant items of cognition include peoples' actions, feelings, ideas, beliefs, Value (ethics), values, and things in the Natural environment, environment. Cognitive dissonance exists without signs but surfaces through psychological stress when persons participate in an action that goes against one or more of conflicting things. According to this theory, when an action or idea is psychologically inconsistent with the other, people automatically try to resolve the conflict, usually by reframing a side to make the combination congruent. Discomfort is triggered by beliefs clashing with new information or by having to conceptually re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
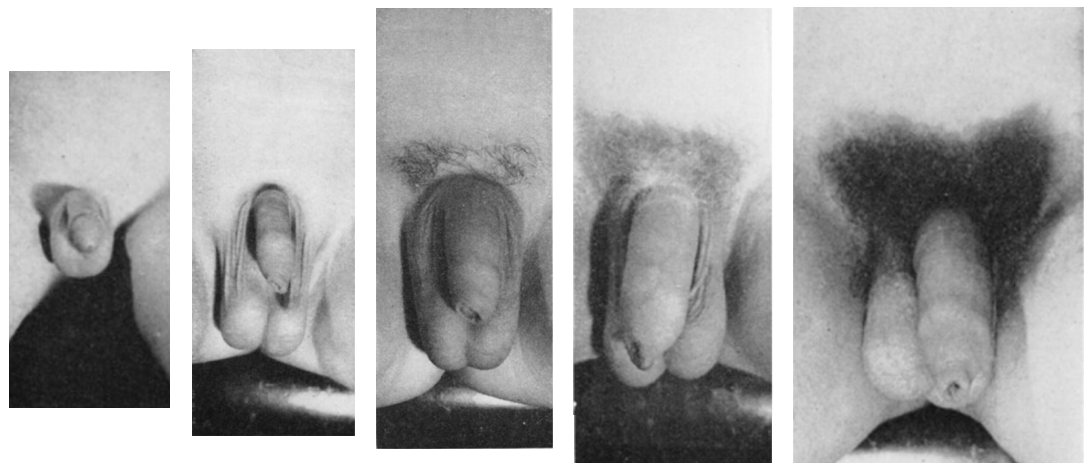
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirituality
The meaning of ''spirituality'' has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape of man", oriented at "the image of God" as exemplified by the List of founders of religious traditions, founders and sacred texts of the religions of the world. The term was used within early Christianity to refer to a life oriented toward Holy Spirit (Christianity), the Holy Spirit and broadened during the Late Middle Ages to include mind, mental aspects of life. In modern times, the term both spread to other religious traditions and broadened to refer to a wider range of experiences, including a range of Western esotericism, esoteric and religious traditions. Modern usages tend to refer to a subjective experience of a Sacredness, sacred dimension, and the "deepest values and meanings by which people live", often in a context separate from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monks Initiation (26392071260)
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many religions and in philosophy across numerous cultures. The Greek word for "monk" may be applied to men or women. In English, however, "monk" is applied mainly to men, while ''nun'' is typically used for female monastics. Although the term ''monachos'' is of Christianity, Christian origin, in the English language ''monk'' tends to be used loosely also for both male and female ascetics from other religious or philosophical backgrounds. However, being generic, it is not interchangeable with terms that denote particular kinds of monk, such as cenobite, hermit, anchorite, or Hesychasm, hesychast. Traditions of Christian monasticism exist in major Christian denominations, with religious orders being present in Catholicism, Lutheranism, Oriental Ort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpersonal Attraction
Interpersonal attraction, as a part of social psychology, is the study of the attraction between people which leads to the development of platonic or romantic relationships. It is distinct from perceptions such as physical attractiveness, and involves views of ''what is'' and ''what is not'' considered beautiful or attractive. Within the study of social psychology, interpersonal attraction is related to how much one likes or dislikes another person. It can be viewed as a force acting between two people that tends to draw them together and to resist their separation. When measuring interpersonal attraction, one must refer to the qualities of the attracted and those of the attractor to achieve predictive accuracy. It is suggested that to determine attraction, both the personalities and the situation must be taken into account. Measurement In social psychology, interpersonal attraction is most-frequently measured using the Interpersonal Attraction Judgment Scale developed by Donn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |