indigenous peoples of Canada on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In Canada, Indigenous groups comprise the First Nations,
/ref> National Indigenous Peoples Day recognizes the cultures and contributions of Indigenous peoples to the
 The term ''
The term ''
 According to
According to
Around 16,500 years ago, the glaciers began melting, allowing people to move south and east into Canada and beyond. The first inhabitants of North America arrived in Canada at least 14,000 years ago. It is believed the inhabitants entered the Americas pursuing Clovis sites dated at 13,500 years ago were discovered in western North America during the 1930s. Clovis peoples were regarded as the first widespread Paleo-Indian inhabitants of the
Clovis sites dated at 13,500 years ago were discovered in western North America during the 1930s. Clovis peoples were regarded as the first widespread Paleo-Indian inhabitants of the
 The vastness and variety of Canada's climates, ecology, vegetation, fauna, and landform separations have defined ancient peoples implicitly into cultural or Linguistics, linguistic divisions. Canada is surrounded north, east, and west with coastline and since the last ice age, Canada has consisted of distinct forest regions. Language contributes to the identity of a people by influencing social life ways and spiritual practices. Aboriginal religions developed from anthropomorphism and animism philosophies.
The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status. There is a continuous record of occupation of Stó:lō, S'ólh Téméxw by Aboriginal people dating from the early Holocene period, 10,000–9,000 years ago. Archaeological sites at Stave Lake, Coquitlam Lake, Fort Langley, British Columbia, Fort Langley and region uncovered early period artifacts. These early inhabitants were highly mobile hunter-gatherers, consisting of about 20 to 50 members of an extended family. The Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene people occupied much of the land area of northwest and central North America starting around 8,000 BCE. They were the earliest ancestors of the Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan-speaking peoples, including the Navajo people, Navajo and Apache. They had villages with large multi-family dwellings, used seasonally during the summer, from which they hunted, fished and gathered food supplies for the winter. The Wyandot people, Wendat peoples settled into Southern Ontario along the Eramosa River around 8,000–7,000 BCE (10,000–9,000 years ago). They were concentrated between Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay. Wendat hunted caribou to survive on the glacier-covered land. Many different First Nations cultures relied upon the buffalo starting by 6,000–5,000 BCE (8,000–7,000 years ago). They hunted buffalo by herding migrating buffalo off cliffs. Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump, near Lethbridge, Alberta, is a hunting grounds that was in use for about 5,000 years.
The vastness and variety of Canada's climates, ecology, vegetation, fauna, and landform separations have defined ancient peoples implicitly into cultural or Linguistics, linguistic divisions. Canada is surrounded north, east, and west with coastline and since the last ice age, Canada has consisted of distinct forest regions. Language contributes to the identity of a people by influencing social life ways and spiritual practices. Aboriginal religions developed from anthropomorphism and animism philosophies.
The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status. There is a continuous record of occupation of Stó:lō, S'ólh Téméxw by Aboriginal people dating from the early Holocene period, 10,000–9,000 years ago. Archaeological sites at Stave Lake, Coquitlam Lake, Fort Langley, British Columbia, Fort Langley and region uncovered early period artifacts. These early inhabitants were highly mobile hunter-gatherers, consisting of about 20 to 50 members of an extended family. The Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene people occupied much of the land area of northwest and central North America starting around 8,000 BCE. They were the earliest ancestors of the Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan-speaking peoples, including the Navajo people, Navajo and Apache. They had villages with large multi-family dwellings, used seasonally during the summer, from which they hunted, fished and gathered food supplies for the winter. The Wyandot people, Wendat peoples settled into Southern Ontario along the Eramosa River around 8,000–7,000 BCE (10,000–9,000 years ago). They were concentrated between Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay. Wendat hunted caribou to survive on the glacier-covered land. Many different First Nations cultures relied upon the buffalo starting by 6,000–5,000 BCE (8,000–7,000 years ago). They hunted buffalo by herding migrating buffalo off cliffs. Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump, near Lethbridge, Alberta, is a hunting grounds that was in use for about 5,000 years.
 The west coast of Canada by 7,000–5000 BCE (9,000–7,000 years ago) saw various cultures who organized themselves around salmon fishing. The Nuu-chah-nulth people, Nuu-chah-nulth of Vancouver Island began whaling with advanced long spears at about this time. The Maritime Archaic is one group of North America's Archaic stage, Archaic culture of sea-mammal hunters in the subarctic. They prospered from approximately 7,000 BCE–1,500 BCE (9,000–3,500 years ago) along the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Coast of North America. Their settlements included longhouses and boat-topped temporary or seasonal houses. They engaged in long-distance trade, using as currency white chert, a rock quarried from northern Labrador to Maine. The Pre-Columbian culture, whose members were called Red Paint People, is indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America. The culture flourished between 3,000 BCE – 1,000 BCE (5,000–3,000 years ago) and was named after their burial ceremonies, which used large quantities of red ochre to cover bodies and grave goods.
The Arctic small tool tradition is a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2,500 BCE (4,500 years ago). These Paleo-Arctic tradition, Paleo-Arctic peoples had a highly distinctive toolkit of small blades (Microblade technology, microblades) that were pointed at both ends and used as side- or end-barbs on arrows or spears made of other materials, such as bone or antler. Scraper (archaeology), Scrapers, engraving tools and adze blades were also included in their toolkits. The Arctic small tool tradition branches off into two cultural variants, including the Pre-Dorset, and the Independence II culture, Independence traditions. These two groups, ancestors of Thule people, were displaced by the Inuit by 1000 CE.
The west coast of Canada by 7,000–5000 BCE (9,000–7,000 years ago) saw various cultures who organized themselves around salmon fishing. The Nuu-chah-nulth people, Nuu-chah-nulth of Vancouver Island began whaling with advanced long spears at about this time. The Maritime Archaic is one group of North America's Archaic stage, Archaic culture of sea-mammal hunters in the subarctic. They prospered from approximately 7,000 BCE–1,500 BCE (9,000–3,500 years ago) along the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Coast of North America. Their settlements included longhouses and boat-topped temporary or seasonal houses. They engaged in long-distance trade, using as currency white chert, a rock quarried from northern Labrador to Maine. The Pre-Columbian culture, whose members were called Red Paint People, is indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America. The culture flourished between 3,000 BCE – 1,000 BCE (5,000–3,000 years ago) and was named after their burial ceremonies, which used large quantities of red ochre to cover bodies and grave goods.
The Arctic small tool tradition is a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2,500 BCE (4,500 years ago). These Paleo-Arctic tradition, Paleo-Arctic peoples had a highly distinctive toolkit of small blades (Microblade technology, microblades) that were pointed at both ends and used as side- or end-barbs on arrows or spears made of other materials, such as bone or antler. Scraper (archaeology), Scrapers, engraving tools and adze blades were also included in their toolkits. The Arctic small tool tradition branches off into two cultural variants, including the Pre-Dorset, and the Independence II culture, Independence traditions. These two groups, ancestors of Thule people, were displaced by the Inuit by 1000 CE.
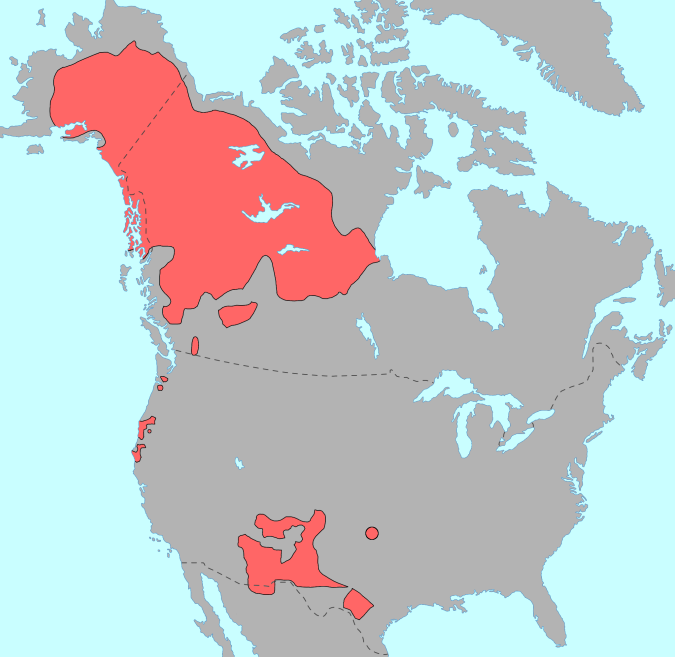
 First Nations peoples had settled and established trade routes across what is now Canada by 500 BCE – 1,000 CE. Communities developed each with its own culture, customs, and character. In the northwest were the Athapaskan, Slavey people, Slavey, Dogrib people, Dogrib, Northern Tutchone, Tutchone, and Tlingit people, Tlingit. Along the Pacific coast were the Tsimshian; Haida; Coast Salish peoples, Salish; Kwakiutl; Heiltsuk; Nuu-chah-nulth, Nootka; Nisga'a; Senakw and Gitxsan. In the plains were the Blackfoot Confederacy, Niisitapi; Kainai Nation, Káínawa; Tsuutʼina Nation, Tsuutʼina; and Piikani Nation, Piikáni. In the northern woodlands were the Cree, Nēhiyawak and Chipewyan. Around the Great Lakes were the Anishinaabe; Algonquin people, Algonquin; Iroquois, Haudenosaunee and Wendat. Along the Atlantic coast were the Beothuk, Maliseet, Wəlastəkwewiyik, Innu, Abenaki and Mi'kmaq.
Many First Nations civilizations established characteristics and hallmarks that included permanent urban settlements or cities, agriculture, civic and Mound builder (people), monumental architecture, and complex society, complex societal hierarchies. These cultures had evolved and changed by the time of the first permanent European arrivals (c. late 15th–early 16th centuries), and have been brought forward through archaeological investigations.
There are indications of contact made before Christopher Columbus between the first peoples and those from other continents. Aboriginal people in Canada first interacted with Europeans around 1000 CE, but prolonged contact came after Europeans established permanent settlements in the 17th and 18th centuries. European written accounts generally recorded friendliness of the First Nations, who profited in trade with Europeans. Such trade generally strengthened the more organized political entities such as the Iroquois Confederation. Throughout the 16th century, European fleets made almost annual visits to the eastern shores of Canada to cultivate the fishing opportunities. A sideline industry emerged in the un-organized Fur trade, traffic of furs overseen by the Indian Department.
Prominent First Nations people include Joe Capilano, who met with King of the United Kingdom, Edward VII, to speak of the need to settle land claims and Ovide Mercredi, a leader at both the Meech Lake Accord constitutional reform discussions and Oka Crisis.
First Nations peoples had settled and established trade routes across what is now Canada by 500 BCE – 1,000 CE. Communities developed each with its own culture, customs, and character. In the northwest were the Athapaskan, Slavey people, Slavey, Dogrib people, Dogrib, Northern Tutchone, Tutchone, and Tlingit people, Tlingit. Along the Pacific coast were the Tsimshian; Haida; Coast Salish peoples, Salish; Kwakiutl; Heiltsuk; Nuu-chah-nulth, Nootka; Nisga'a; Senakw and Gitxsan. In the plains were the Blackfoot Confederacy, Niisitapi; Kainai Nation, Káínawa; Tsuutʼina Nation, Tsuutʼina; and Piikani Nation, Piikáni. In the northern woodlands were the Cree, Nēhiyawak and Chipewyan. Around the Great Lakes were the Anishinaabe; Algonquin people, Algonquin; Iroquois, Haudenosaunee and Wendat. Along the Atlantic coast were the Beothuk, Maliseet, Wəlastəkwewiyik, Innu, Abenaki and Mi'kmaq.
Many First Nations civilizations established characteristics and hallmarks that included permanent urban settlements or cities, agriculture, civic and Mound builder (people), monumental architecture, and complex society, complex societal hierarchies. These cultures had evolved and changed by the time of the first permanent European arrivals (c. late 15th–early 16th centuries), and have been brought forward through archaeological investigations.
There are indications of contact made before Christopher Columbus between the first peoples and those from other continents. Aboriginal people in Canada first interacted with Europeans around 1000 CE, but prolonged contact came after Europeans established permanent settlements in the 17th and 18th centuries. European written accounts generally recorded friendliness of the First Nations, who profited in trade with Europeans. Such trade generally strengthened the more organized political entities such as the Iroquois Confederation. Throughout the 16th century, European fleets made almost annual visits to the eastern shores of Canada to cultivate the fishing opportunities. A sideline industry emerged in the un-organized Fur trade, traffic of furs overseen by the Indian Department.
Prominent First Nations people include Joe Capilano, who met with King of the United Kingdom, Edward VII, to speak of the need to settle land claims and Ovide Mercredi, a leader at both the Meech Lake Accord constitutional reform discussions and Oka Crisis.
 Warfare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut (Uummarmiut) who inhabited the Mackenzie River delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, :is:Ívar Bárðarson, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts relate that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling.
After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, the Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid-16th century, Basque people, Basque fishers were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as those excavated at Red Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Red Bay. The Inuit appear not to have interfered with their operations, but they did raid the stations in winter for tools, and particularly worked iron, which they adapted to native needs.
Notable among the Inuit are Abraham Ulrikab and family who became a zoo exhibit in Hamburg, Germany, and Tanya Tagaq, a traditional Inuit throat singing, throat singer. Abe Okpik was instrumental in helping Inuit obtain surnames rather than disc numbers and Kiviaq (person), Kiviaq (David Ward) won the legal right to use his single-word Inuktituk name.
Warfare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut (Uummarmiut) who inhabited the Mackenzie River delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, :is:Ívar Bárðarson, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts relate that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling.
After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, the Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid-16th century, Basque people, Basque fishers were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as those excavated at Red Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Red Bay. The Inuit appear not to have interfered with their operations, but they did raid the stations in winter for tools, and particularly worked iron, which they adapted to native needs.
Notable among the Inuit are Abraham Ulrikab and family who became a zoo exhibit in Hamburg, Germany, and Tanya Tagaq, a traditional Inuit throat singing, throat singer. Abe Okpik was instrumental in helping Inuit obtain surnames rather than disc numbers and Kiviaq (person), Kiviaq (David Ward) won the legal right to use his single-word Inuktituk name.
 The Métis are people descended from marriages between Europeans (mainly French) and Cree, Ojibway, Algonquin, Saulteaux, Menominee, Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and other First Nations.
Their history dates to the mid-17th century.
When Europeans first arrived to Canada they relied on Aboriginal peoples for fur trading skills and survival. To ensure alliances, relationships between European fur traders and Aboriginal women were often consolidated through marriage. The Métis homeland consists of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario, as well as the Northwest Territories (NWT).
Amongst notable Métis people are singer and actor Tom Jackson (actor), Tom Jackson, Commissioner of the Northwest Territories Tony Whitford, and Louis Riel who led two resistance movements: the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870 and the North-West Rebellion of 1885, which ended in his Trial of Louis Riel, trial and subsequent execution.
The languages inherently Métis are either Métis French or a mixed language called Michif language, Michif. Michif, Mechif or Métchif is a Pronunciation spelling, phonetic spelling of Métif, a variant of Métis. The Métis today predominantly speak Canadian English, English, with Canadian French, French a strong second language, as well as numerous Indigenous languages of the Americas, Aboriginal tongues. A 19th-century community of the Métis people, the Anglo-Métis, were referred to as Countryborn. They were children of Rupert's Land fur trade typically of Orcadian, Scottish, or English paternal descent and Aboriginal maternal descent. Their first languages would have been Aboriginal (Cree language, Cree, Saulteaux language, Saulteaux, Assiniboine language, Assiniboine, etc.) and English. Their fathers spoke Canadian Gaelic, Gaelic, thus leading to the development of an English dialect referred to as "Bungee language, Bungee".
S.35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' mentions the Métis yet there has long been debate over legally defining the term Métis, but on September 23, 2003, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Métis are a distinct people with significant rights (Powley ruling).
Unlike First Nations people, there has been no distinction between status and non-status Métis; the Métis, their heritage and Aboriginal ancestry have often been absorbed and assimilated into their surrounding populations.
The Métis are people descended from marriages between Europeans (mainly French) and Cree, Ojibway, Algonquin, Saulteaux, Menominee, Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and other First Nations.
Their history dates to the mid-17th century.
When Europeans first arrived to Canada they relied on Aboriginal peoples for fur trading skills and survival. To ensure alliances, relationships between European fur traders and Aboriginal women were often consolidated through marriage. The Métis homeland consists of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario, as well as the Northwest Territories (NWT).
Amongst notable Métis people are singer and actor Tom Jackson (actor), Tom Jackson, Commissioner of the Northwest Territories Tony Whitford, and Louis Riel who led two resistance movements: the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870 and the North-West Rebellion of 1885, which ended in his Trial of Louis Riel, trial and subsequent execution.
The languages inherently Métis are either Métis French or a mixed language called Michif language, Michif. Michif, Mechif or Métchif is a Pronunciation spelling, phonetic spelling of Métif, a variant of Métis. The Métis today predominantly speak Canadian English, English, with Canadian French, French a strong second language, as well as numerous Indigenous languages of the Americas, Aboriginal tongues. A 19th-century community of the Métis people, the Anglo-Métis, were referred to as Countryborn. They were children of Rupert's Land fur trade typically of Orcadian, Scottish, or English paternal descent and Aboriginal maternal descent. Their first languages would have been Aboriginal (Cree language, Cree, Saulteaux language, Saulteaux, Assiniboine language, Assiniboine, etc.) and English. Their fathers spoke Canadian Gaelic, Gaelic, thus leading to the development of an English dialect referred to as "Bungee language, Bungee".
S.35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' mentions the Métis yet there has long been debate over legally defining the term Métis, but on September 23, 2003, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Métis are a distinct people with significant rights (Powley ruling).
Unlike First Nations people, there has been no distinction between status and non-status Métis; the Métis, their heritage and Aboriginal ancestry have often been absorbed and assimilated into their surrounding populations.
 Missionary, Missionary work directed at the Aboriginal people of Canada had been ongoing since the first missionaries arrived in the 1600s, generally from France, some of whom were martyred (Jesuit saints called the Canadian Martyrs). Christianization as government policy became more systematic with the ''Indian Act'' in 1876, which would bring new sanctions for those who did not Conversion to Christianity, convert to Christianity. For example, the new laws would prevent non-Christian Aboriginal people from testifying or having their cases heard in court, and ban alcohol consumption. When the ''Indian Act'' was amended in 1884, traditional religious and social practices, such as the Potlatch, would be banned, and further amendments in 1920 would prevent "status Indians" (as defined in the ''Act'') from wearing traditional dress or performing traditional dances in an attempt to stop all non-Christian practices.
Missionary, Missionary work directed at the Aboriginal people of Canada had been ongoing since the first missionaries arrived in the 1600s, generally from France, some of whom were martyred (Jesuit saints called the Canadian Martyrs). Christianization as government policy became more systematic with the ''Indian Act'' in 1876, which would bring new sanctions for those who did not Conversion to Christianity, convert to Christianity. For example, the new laws would prevent non-Christian Aboriginal people from testifying or having their cases heard in court, and ban alcohol consumption. When the ''Indian Act'' was amended in 1884, traditional religious and social practices, such as the Potlatch, would be banned, and further amendments in 1920 would prevent "status Indians" (as defined in the ''Act'') from wearing traditional dress or performing traditional dances in an attempt to stop all non-Christian practices.
 The final government strategy of assimilation, made possible by the ''Indian Act'' was the Canadian Indian residential school system, Canadian residential school system:
Beginning in 1847 and lasting until 1996, the Canadian government, in partnership with the dominant Christian Churches, ran 130 residential boarding schools across Canada for Aboriginal children, who were forcibly taken from their homes. While the schools provided some education, they were plagued by under-funding, disease, and abuse.
According to some scholars, the Canadian government's laws and policies, including the residential school system, that encouraged or required Indigenous peoples to Cultural imperialism, assimilate into a Eurocentrism, Eurocentric society, violated the United Nations Genocide Convention that Canada signed in 1949 and passed through Parliament in 1952. Therefore, these scholars believe that Canada could be tried in international court for genocide.
A legal case resulted in settlement of in 2006 and the 2008 establishment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Canada), Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which confirmed the injurious effect on children of this system and turmoil created between Indigenous peoples and non-Indigenous peoples.
In 2008, Prime Minister Stephen Harper issued an apology on behalf of the Canadian government and its citizens for the residential school system.
The final government strategy of assimilation, made possible by the ''Indian Act'' was the Canadian Indian residential school system, Canadian residential school system:
Beginning in 1847 and lasting until 1996, the Canadian government, in partnership with the dominant Christian Churches, ran 130 residential boarding schools across Canada for Aboriginal children, who were forcibly taken from their homes. While the schools provided some education, they were plagued by under-funding, disease, and abuse.
According to some scholars, the Canadian government's laws and policies, including the residential school system, that encouraged or required Indigenous peoples to Cultural imperialism, assimilate into a Eurocentrism, Eurocentric society, violated the United Nations Genocide Convention that Canada signed in 1949 and passed through Parliament in 1952. Therefore, these scholars believe that Canada could be tried in international court for genocide.
A legal case resulted in settlement of in 2006 and the 2008 establishment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Canada), Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which confirmed the injurious effect on children of this system and turmoil created between Indigenous peoples and non-Indigenous peoples.
In 2008, Prime Minister Stephen Harper issued an apology on behalf of the Canadian government and its citizens for the residential school system.
 The Canadian Crown and Indigenous peoples began Timeline of colonization of North America, interactions during the European colonization period. Many agreements signed before the Confederation of Canada are recognized in Canadian law, such as the Peace and Friendship Treaties, the Robinson Treaties, the Douglas Treaties, and many others. After Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory in 1870, the eleven Numbered treaties were signed between First Nations and Canadian crown, the Crown from 1871 to 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Crown administered by Canadian Aboriginal law and overseen by the Minister of Crown–Indigenous Relations.
In 1973, Canada re-started signing new treaties and agreements with Indigenous peoples to address Indigenous land claims in Canada, their land claims. The first Comprehensive land claim, modern treaty implemented under the new framework was the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement in 1970. The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement of 1993 lead to the creation of the
The Canadian Crown and Indigenous peoples began Timeline of colonization of North America, interactions during the European colonization period. Many agreements signed before the Confederation of Canada are recognized in Canadian law, such as the Peace and Friendship Treaties, the Robinson Treaties, the Douglas Treaties, and many others. After Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory in 1870, the eleven Numbered treaties were signed between First Nations and Canadian crown, the Crown from 1871 to 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Crown administered by Canadian Aboriginal law and overseen by the Minister of Crown–Indigenous Relations.
In 1973, Canada re-started signing new treaties and agreements with Indigenous peoples to address Indigenous land claims in Canada, their land claims. The first Comprehensive land claim, modern treaty implemented under the new framework was the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement in 1970. The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement of 1993 lead to the creation of the
 The ''Indian Act'' is federal legislation that dates from 1876. There have been over 20 major changes made to the act since then, the last time being in 1951; amended in 1985 with Bill C-31. The ''Indian Act'' indicates how reserves and bands can operate and defines who is recognized as an "Indian."
In 1985, the Canadian Parliament passed Bill C-31, ''An Act to Amend the Indian Act''. Because of a constitutional requirement, the bill took effect on 17 April 1985.
* It ends discriminatory provisions of the ''Indian Act'', especially those that discriminated against women.
* It changes the meaning of ''status'' and for the first time allows for limited reinstatement of Indians who were denied or lost status or band membership.
* It allows bands to define their own membership rules.
Those people accepted into band membership under band rules may not be status Indians. C-31 clarified that various sections of the ''Indian Act'' apply to band members. The sections under debate concern community life and land holdings. Sections pertaining to Indians (First Nations peoples) as individuals (in this case, wills and taxation of personal property) were not included.
The ''Indian Act'' is federal legislation that dates from 1876. There have been over 20 major changes made to the act since then, the last time being in 1951; amended in 1985 with Bill C-31. The ''Indian Act'' indicates how reserves and bands can operate and defines who is recognized as an "Indian."
In 1985, the Canadian Parliament passed Bill C-31, ''An Act to Amend the Indian Act''. Because of a constitutional requirement, the bill took effect on 17 April 1985.
* It ends discriminatory provisions of the ''Indian Act'', especially those that discriminated against women.
* It changes the meaning of ''status'' and for the first time allows for limited reinstatement of Indians who were denied or lost status or band membership.
* It allows bands to define their own membership rules.
Those people accepted into band membership under band rules may not be status Indians. C-31 clarified that various sections of the ''Indian Act'' apply to band members. The sections under debate concern community life and land holdings. Sections pertaining to Indians (First Nations peoples) as individuals (in this case, wills and taxation of personal property) were not included.
 The Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples was a Royal Commission undertaken by the Government of Canada in 1991 to address issues of the Aboriginal peoples of Canada. It assessed past government policies toward Aboriginal people, such as residential schools, and provided policy recommendations to the government. The Commission issued its final report in November 1996. The five-volume, 4,000-page report covered a vast range of issues; its 440 recommendations called for sweeping changes to the interaction between Aboriginal, non-Aboriginal people and the governments in Canada. The report "set out a 20-year agenda for change."
The Royal Commission on Aboriginal Peoples was a Royal Commission undertaken by the Government of Canada in 1991 to address issues of the Aboriginal peoples of Canada. It assessed past government policies toward Aboriginal people, such as residential schools, and provided policy recommendations to the government. The Commission issued its final report in November 1996. The five-volume, 4,000-page report covered a vast range of issues; its 440 recommendations called for sweeping changes to the interaction between Aboriginal, non-Aboriginal people and the governments in Canada. The report "set out a 20-year agenda for change."
 Countless Indigenous words, inventions and games have become an everyday part of Spoken languages of Canada, Canadian language and use. The canoe, snowshoes, the toboggan, lacrosse, tug of war, maple syrup and tobacco are just a few of the products, inventions and games. Some of the words include the barbecue, Reindeer, caribou, chipmunk, Groundhog, woodchuck, hammock, skunk, and moose.
List of place names in Canada of aboriginal origin, Many places in Canada, both natural features and human habitations, use Indigenous names. The word ''Canada'' itself derives from the Laurentian language, St. Lawrence Iroquoian word meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. The province of Saskatchewan derives its name from the Saskatchewan River, which in the Cree language is called ''Kisiskatchewani Sipi'', meaning 'swift-flowing river'. ''Ottawa'', the name of Canada's capital city, comes from the Algonquin language term ''adawe'', meaning 'to trade'.
Modern youth groups, such as Scouts Canada and the Girl Guides of Canada, include programs based largely on Indigenous lore, arts and crafts, character building and outdoor camp craft and living.
Aboriginal cultural areas depend upon their ancestors' primary Types of societies, lifeway, or occupation, at the time of European contact. These culture areas correspond closely with geography of Canada, physical and ecological List of regions of Canada, regions of Canada. The Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast were centred around ocean and river fishing; in the interior of British Columbia, hunter-gatherer and river fishing. In both of these areas, the salmon was of chief importance. For the people of the plains, bison hunting was the primary activity. In the taiga, subarctic forest, other species such as the moose were more important. For peoples near the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, Shifting cultivation, shifting agriculture was practised, including the raising of maize, beans, and Squash (plant), squash. While for the Inuit, hunting was the primary source of food with Pinniped, seals the primary component of their diet.
The caribou, fish, other marine mammals and to a lesser extent plants, berries and seaweed are part of the Inuit cuisine, Inuit diet. One of the most noticeable symbols of Inuit culture, the inuksuk is the emblem of the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. ''Inuksuit'' are rock sculptures made by stacking stones; in the shape of a human figure, they are called ''inunnguaq''.
Countless Indigenous words, inventions and games have become an everyday part of Spoken languages of Canada, Canadian language and use. The canoe, snowshoes, the toboggan, lacrosse, tug of war, maple syrup and tobacco are just a few of the products, inventions and games. Some of the words include the barbecue, Reindeer, caribou, chipmunk, Groundhog, woodchuck, hammock, skunk, and moose.
List of place names in Canada of aboriginal origin, Many places in Canada, both natural features and human habitations, use Indigenous names. The word ''Canada'' itself derives from the Laurentian language, St. Lawrence Iroquoian word meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. The province of Saskatchewan derives its name from the Saskatchewan River, which in the Cree language is called ''Kisiskatchewani Sipi'', meaning 'swift-flowing river'. ''Ottawa'', the name of Canada's capital city, comes from the Algonquin language term ''adawe'', meaning 'to trade'.
Modern youth groups, such as Scouts Canada and the Girl Guides of Canada, include programs based largely on Indigenous lore, arts and crafts, character building and outdoor camp craft and living.
Aboriginal cultural areas depend upon their ancestors' primary Types of societies, lifeway, or occupation, at the time of European contact. These culture areas correspond closely with geography of Canada, physical and ecological List of regions of Canada, regions of Canada. The Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast were centred around ocean and river fishing; in the interior of British Columbia, hunter-gatherer and river fishing. In both of these areas, the salmon was of chief importance. For the people of the plains, bison hunting was the primary activity. In the taiga, subarctic forest, other species such as the moose were more important. For peoples near the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, Shifting cultivation, shifting agriculture was practised, including the raising of maize, beans, and Squash (plant), squash. While for the Inuit, hunting was the primary source of food with Pinniped, seals the primary component of their diet.
The caribou, fish, other marine mammals and to a lesser extent plants, berries and seaweed are part of the Inuit cuisine, Inuit diet. One of the most noticeable symbols of Inuit culture, the inuksuk is the emblem of the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. ''Inuksuit'' are rock sculptures made by stacking stones; in the shape of a human figure, they are called ''inunnguaq''.
 Indian reserves, established in Law of Canada, Canadian law by treaties such as Treaty 7, are lands of First Nations recognized by non-Indigenous governments. Some reserves are within cities, such as the Opawikoscikan Reserve in Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Wendake, Quebec, Wendake in Quebec City or Enoch Cree Nation 135 in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region. There are more reserves in Canada than there are First Nations, which were ceded multiple reserves by treaty. Aboriginal people currently work in a variety of occupations and may live outside their ancestral homes. The traditional cultures of their ancestors, shaped by nature, still exert a strong influence on them, from spirituality to political attitudes. National Indigenous Peoples Day is a day of recognition of the cultures and contributions of the First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples of Canada. The day was first celebrated in 1996, after it was proclaimed that year, by then Governor General of Canada Roméo LeBlanc, to be celebrated on June 21 annually. Most provincial jurisdictions do not recognize it as a Public holidays in Canada, statutory holiday.
Indian reserves, established in Law of Canada, Canadian law by treaties such as Treaty 7, are lands of First Nations recognized by non-Indigenous governments. Some reserves are within cities, such as the Opawikoscikan Reserve in Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Wendake, Quebec, Wendake in Quebec City or Enoch Cree Nation 135 in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region. There are more reserves in Canada than there are First Nations, which were ceded multiple reserves by treaty. Aboriginal people currently work in a variety of occupations and may live outside their ancestral homes. The traditional cultures of their ancestors, shaped by nature, still exert a strong influence on them, from spirituality to political attitudes. National Indigenous Peoples Day is a day of recognition of the cultures and contributions of the First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples of Canada. The day was first celebrated in 1996, after it was proclaimed that year, by then Governor General of Canada Roméo LeBlanc, to be celebrated on June 21 annually. Most provincial jurisdictions do not recognize it as a Public holidays in Canada, statutory holiday.
 Indigenous peoples were producing art for thousands of years before the arrival of European Settler colonialism, settler colonists and the eventual establishment of Canada as a nation state. Like the peoples who produced them, Indigenous art traditions spanned territories across North America. Indigenous art traditions are organized by art historians according to cultural, linguistic or regional groups: Northwest Coast, Plateau First Nations, Plateau, Plains Indians, Plains, Eastern Woodlands tribes, Eastern Woodlands, Subarctic, and Arctic.
Art traditions vary enormously amongst and within these diverse groups. Indigenous art with a focus on portability and the body is distinguished from European traditions and its focus on architecture. Indigenous visual art may be used in conjunction with other arts. Shamanism among Eskimo peoples, Shamans' Masks among Eskimo peoples, masks and rattles are used ceremoniously in dance, storytelling and music. Artworks preserved in museum collections date from the period after European contact and show evidence of the creative adoption and adaptation of European trade goods such as metal and glass beads. The distinct Métis cultures that have arisen from inter-cultural relationships with Europeans contribute culturally hybrid art forms. During the 19th and the first half of the 20th century the Canadian government pursued an active policy of Forced assimilation, forced and cultural assimilation toward Indigenous peoples. The ''Indian Act'' banned manifestations of the Sun Dance, the Potlatch, and works of art depicting them.
It was not until the 1950s and 1960s that Indigenous artists such as Mungo Martin, Bill Reid and Norval Morrisseau began to publicly renew and re-invent Indigenous art traditions. Currently, there are Indigenous artists practising in all media in Canada and two Indigenous artists, Edward Poitras and Rebecca Belmore, have represented Canada at the Venice Biennale in 1995 and 2005 respectively.
Indigenous peoples were producing art for thousands of years before the arrival of European Settler colonialism, settler colonists and the eventual establishment of Canada as a nation state. Like the peoples who produced them, Indigenous art traditions spanned territories across North America. Indigenous art traditions are organized by art historians according to cultural, linguistic or regional groups: Northwest Coast, Plateau First Nations, Plateau, Plains Indians, Plains, Eastern Woodlands tribes, Eastern Woodlands, Subarctic, and Arctic.
Art traditions vary enormously amongst and within these diverse groups. Indigenous art with a focus on portability and the body is distinguished from European traditions and its focus on architecture. Indigenous visual art may be used in conjunction with other arts. Shamanism among Eskimo peoples, Shamans' Masks among Eskimo peoples, masks and rattles are used ceremoniously in dance, storytelling and music. Artworks preserved in museum collections date from the period after European contact and show evidence of the creative adoption and adaptation of European trade goods such as metal and glass beads. The distinct Métis cultures that have arisen from inter-cultural relationships with Europeans contribute culturally hybrid art forms. During the 19th and the first half of the 20th century the Canadian government pursued an active policy of Forced assimilation, forced and cultural assimilation toward Indigenous peoples. The ''Indian Act'' banned manifestations of the Sun Dance, the Potlatch, and works of art depicting them.
It was not until the 1950s and 1960s that Indigenous artists such as Mungo Martin, Bill Reid and Norval Morrisseau began to publicly renew and re-invent Indigenous art traditions. Currently, there are Indigenous artists practising in all media in Canada and two Indigenous artists, Edward Poitras and Rebecca Belmore, have represented Canada at the Venice Biennale in 1995 and 2005 respectively.

 There are three (First Nations, Inuit and Métis people (Canada), Métis) distinctive groups of Indigenous peoples that are recognized in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section Twenty-five of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, sections 25 and 35. Under the ''Employment equity (Canada), Employment Equity Act'', Aboriginal people are a designated group along with women, visible minorities, and persons with disabilities; as such, they are neither a visible minority under the ''Act'' or in the view of Statistics Canada.
The Canada 2016 Census, 2016 Canadian Census enumerated 1,673,780 Aboriginal people in Canada, 4.9% of the country's total population.[Aboriginal peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census] This total includes 977,230 First Nations people, 587,545 Métis, and 65,025 Inuit. National representative bodies of Aboriginal people in Canada include the Assembly of First Nations, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, the Métis National Council, the Native Women's Association of Canada, the National Association of Native Friendship Centres, and the Congress of Aboriginal Peoples.
In 2016, Indigenous children ages zero to four accounted for 7.7% of those aged zero to four in Canada, and made up 51.2% of children in this age group living in foster care.
In the 20th century the Aboriginal population of Canada increased tenfold. Between 1900 and 1950 the population grew by 29%. After the 1960s the infant mortality level on reserves dropped dramatically and the population grew by 161%. Since the 1980s the number of First Nations babies more than doubled and currently almost half of the First Nations population is under the age of 25.
Indigenous people assert that their Sovereignty, sovereign rights are valid, and point to the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which is mentioned in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section 25, the ''British North America Acts'' and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, 1969 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (to which Canada is a signatory) in support of this claim.
There are three (First Nations, Inuit and Métis people (Canada), Métis) distinctive groups of Indigenous peoples that are recognized in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section Twenty-five of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, sections 25 and 35. Under the ''Employment equity (Canada), Employment Equity Act'', Aboriginal people are a designated group along with women, visible minorities, and persons with disabilities; as such, they are neither a visible minority under the ''Act'' or in the view of Statistics Canada.
The Canada 2016 Census, 2016 Canadian Census enumerated 1,673,780 Aboriginal people in Canada, 4.9% of the country's total population.[Aboriginal peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census] This total includes 977,230 First Nations people, 587,545 Métis, and 65,025 Inuit. National representative bodies of Aboriginal people in Canada include the Assembly of First Nations, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, the Métis National Council, the Native Women's Association of Canada, the National Association of Native Friendship Centres, and the Congress of Aboriginal Peoples.
In 2016, Indigenous children ages zero to four accounted for 7.7% of those aged zero to four in Canada, and made up 51.2% of children in this age group living in foster care.
In the 20th century the Aboriginal population of Canada increased tenfold. Between 1900 and 1950 the population grew by 29%. After the 1960s the infant mortality level on reserves dropped dramatically and the population grew by 161%. Since the 1980s the number of First Nations babies more than doubled and currently almost half of the First Nations population is under the age of 25.
Indigenous people assert that their Sovereignty, sovereign rights are valid, and point to the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which is mentioned in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section 25, the ''British North America Acts'' and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, 1969 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (to which Canada is a signatory) in support of this claim.
The Dawn of Canadian History: A Chronicle of Aboriginal Canada
', Dodo Press * * *
Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada Portal
– Government of Canada
Aboriginal Peoples and Communities
– Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada
Aboriginal Heritage Resources and Services
– Library and Archives Canada
Aboriginal Virtual Exhibits
– Virtual Museum of Canada
Battle for Aboriginal Treaty Rights
– Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (Digital Archives)
First Peoples of Canada
– The Canadian Museum of Civilization
– Department of Canadian Heritage
Map of historical territory treaties
– Natural Resources Canada {{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous Peoples In Canada Indigenous peoples in Canada, Social history of Canada History of indigenous peoples of North America, Canada Hunter-gatherers of Canada
Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
and Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Canadian Prairies, Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United State ...
. Although ''Indian'' is a term still commonly used in legal documents, the descriptors ''Indian'' and ''Eskimo
Eskimo () is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Greenlandic Inuit, and the Canadian Inuit) and the Yupik (or Yuit) of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related ...
'' have fallen into disuse in Canada, and most consider them to be pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
. ''Aboriginal peoples'' as a collective noun
In linguistics, a collective noun is a word referring to a collection of things taken as a whole. Most collective nouns in everyday speech are not specific to one kind of thing. For example, the collective noun "group" can be applied to people (" ...
is a specific term of art
Jargon is the specialized terminology associated with a particular field or area of activity. Jargon is normally employed in a particular communicative context and may not be well understood outside that context. The context is usually a partic ...
used in some legal documents, including the ''Constitution Act, 1982
The ''Constitution Act, 1982'' (french: link=no, Loi constitutionnelle de 1982) is a part of the Constitution of Canada.Formally enacted as Schedule B of the ''Canada Act 1982'', enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Section 60 of t ...
'', though in most Indigenous circles ''Aboriginal'' has also fallen into disfavour.
Old Crow Flats and Bluefish Caves are some of the earliest known sites of human habitation in Canada. The Paleo-Indian Clovis, Plano and Pre-Dorset
The Pre-Dorset is a loosely defined term for a Paleo-Eskimo culture or group of cultures that existed in the Eastern Canadian Arctic from c. 3200 to 850 cal BC, and preceded the Dorset culture.
Due to its vast geographical expanse and to history ...
cultures pre-date the current Indigenous peoples of the Americas. Projectile point
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have ...
tools, spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fastene ...
s, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and ...
, bangle
Bangles are traditionally rigid bracelets which are usually made of metal, wood, glass or plastic. These ornament are worn mostly by women in the Indian subcontinent, Southeastern Asia, Arabian Peninsula, and Africa. It is common to see a brid ...
s, chisels
A chisel is a tool with a characteristically shaped cutting edge (such that wood chisels have lent part of their name to a particular grind) of blade on its end, for carving or cutting a hard material such as wood, stone, or metal by hand, s ...
and scrapers mark archaeological sites, thus distinguishing cultural periods, traditions, and lithic reduction
In archaeology, in particular of the Stone Age, lithic reduction is the process of fashioning stones or rocks from their natural state into tools or weapons by removing some parts. It has been intensely studied and many archaeological industrie ...
styles.
The characteristics of Indigenous culture in Canada includes a long history of permanent settlements, agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
, civic and ceremonial architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
, complex societal hierarchies, and trading network
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
An early form of trade, barter, saw the direct excha ...
s. Métis of mixed ancestry originated in the mid-17th century when First Nations and Inuit married European fur traders, primarily the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
. The Inuit had more limited interaction with European settlers during that early period. Various laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vari ...
, treaties
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
, and legislation have been enacted between European immigrants and First Nations across Canada. Today, it is a common perception that Aboriginal peoples in Canada have the right to self-government to provide an opportunity to manage historical, cultural, political, health care and economic control aspects within First Nation's communities. However, some Canadian legislation may contradict this, for example the Indian act states 35 (3), ''"the Governor in Council may, in lieu of the province, authority or corporation taking or using the lands without the consent of the owner, authorize a transfer or grant of the lands to the province, authority or corporation, subject to any terms that may be prescribed by the Governor in Council."''
As of the 2021 census, Indigenous peoples in Canada totaled 1,807,250 people, or 5.0% of the national population, with 1,048,405 First Nations people, 624,220 Métis, and 70,540 Inuit. 7.7% of the population under the age of 14 are of Indigenous descent. ndigenous peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census/ref> There are over 600 recognized First Nations governments
In Canada, an Indian band or band (french: bande indienne, link=no), sometimes referred to as a First Nation band (french: bande de la Première Nation, link=no) or simply a First Nation, is the basic unit of government for those peoples subjec ...
or bands with distinctive cultures, languages, art, and music.2011 National Household Survey: Indigenous Peoples in Canada: First Nations People, Métis and Inuit/ref> National Indigenous Peoples Day recognizes the cultures and contributions of Indigenous peoples to the
history of Canada
The history of Canada covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Indians to North America thousands of years ago to the present day. Prior to European colonization, the lands encompassing present-day Canada were inhabited for millennia by ...
. First Nations, Inuit, and Métis peoples of all backgrounds have become prominent figures and have served as role models in the Indigenous community and help to shape the Canadian cultural identity.
Terminology
In Section 35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982
The ''Constitution Act, 1982'' (french: link=no, Loi constitutionnelle de 1982) is a part of the Constitution of Canada.Formally enacted as Schedule B of the ''Canada Act 1982'', enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Section 60 of t ...
'', "Aboriginal peoples of Canada" includes First Nations, Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
, and Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives ...
peoples. ''Aboriginal peoples'' is a legal term encompassing all Indigenous peoples living in Canada. ''Aboriginal peoples'' has begun to be considered outdated and is slowly being replaced by the term ''Indigenous peoples''. There is also an effort to recognize each Indigenous group as a distinct nation, much as there are distinct European, African, and Asian cultures in their respective places.
''First Nations'' (most often used in the plural) has come into general use since the 1970s replacing ''Indians'' and ''Indian bands'' in everyday vocabulary. However, on reserves, '' First Nations'' is being supplanted by members of various nations referring to themselves by their group or ethnic identity. In conversation, this would be "I am Haida
Haida may refer to:
Places
* Haida, an old name for Nový Bor
* Haida Gwaii, meaning "Islands of the People", formerly called the Queen Charlotte Islands
* Haida Islands, a different archipelago near Bella Bella, British Columbia
Ships
* , a 1 ...
," or "we are Kwantlens," in recognition of their First Nations ethnicities. Also coming into general use since the 1970s, First Peoples refers to all Indigenous groups, i.e. First Nations, Inuit, and Métis.
Native
Notwithstanding Canada's location within theAmericas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
, the term ''Native American'' is not used in Canada as it is typically used solely to describe the Indigenous peoples within the boundaries of the present-day United States. ''Native Canadians'' was often used in Canada to differentiate this American term until the 1980s.
In contrast to the more-specific ''Aboriginal'', one of the issues with the term is its general applicability: in certain contexts, it could be used in reference to non-Indigenous peoples in regards to an individual place of origin/birth. For instance, people who were born or grew up in Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
may call themselves "Calgary natives", as in they are ''native'' to that city. With this in mind, even the term ''native American'', as another example, may very well indicate someone who is ''native to America'' rather than a person who is ethnically Indigenous to the boundaries of the present-day United States. In this sense, ''native'' may encompass a broad range of populations and is therefore not recommended.
Indian
The ''Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' (, long name ''An Act to amend and consolidate the laws respecting Indians'') is a Canadian act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still ...
'' ( R.S.C., 1985, c. I-5) sets the legal term ''Indian'', designating that "a person who pursuant to this Act is registered as an Indian or is entitled to be registered as an Indian." Section 5 of the act states that a registry shall be maintained "in which shall be recorded the name of every person who is entitled to be registered as an Indian under this Act." No other term is legally recognized for the purpose of registration and the term ''Indian'' specifically excludes reference to Inuit as per section 4 of the act.
''Indian'' remains in place as the legal term used in the Canadian Constitution
The Constitution of Canada (french: Constitution du Canada) is the supreme law in Canada. It outlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in Canada. Its contents a ...
; however, its usage outside such situations can be considered offensive.
Eskimo
Eskimo
Eskimo () is an exonym used to refer to two closely related Indigenous peoples: the Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Greenlandic Inuit, and the Canadian Inuit) and the Yupik (or Yuit) of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related ...
'' has pejorative
A pejorative or slur is a word or grammatical form expressing a negative or a disrespectful connotation, a low opinion, or a lack of respect toward someone or something. It is also used to express criticism, hostility, or disregard. Sometimes, a ...
connotations in Canada and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
. Indigenous peoples in those areas have replaced the term ''Eskimo'' with ''Inuit'', though the Yupik Yupik may refer to:
* Yupik peoples, a group of indigenous peoples of Alaska and the Russian Far East
* Yupik languages, a group of Eskimo-Aleut languages
Yupꞌik (with the apostrophe) may refer to:
* Yup'ik people
The Yup'ik or Yupiaq (sg ...
of Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
do not consider themselves Inuit, and ethnographers
Ethnography (from Greek ''ethnos'' "folk, people, nation" and ''grapho'' "I write") is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. Ethnography explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject o ...
agree they are a distinct people. They prefer the terminology Yupik, Yupiit, or Eskimo. The Yupik languages
The Yupik languages () are a family of languages spoken by the Yupik peoples of western and south-central Alaska and Chukotka. The Yupik languages differ enough from one another that they are not mutually intelligible, although speakers of one ...
are linguistically distinct from the Inuit languages
The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and adjacent subarctic, reaching farthest south in Labrador. The related Yupik languages (spoken in western ...
, but are related to each other. Linguistic groups
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hist ...
of Arctic people have no universal replacement term for ''Eskimo'', inclusive of all Inuit and Yupik across the geographical area inhabited by them.
Legal categories
Besides these ethnic descriptors, Aboriginal peoples are often divided into legal categories based on their relationship withthe Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different ...
(i.e. the state). Section 91(24) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867
The ''Constitution Act, 1867'' (french: Loi constitutionnelle de 1867),''The Constitution Act, 1867'', 30 & 31 Victoria (U.K.), c. 3, http://canlii.ca/t/ldsw retrieved on 2019-03-14. originally enacted as the ''British North America Act, 186 ...
'' gives the federal government (as opposed to the provinces) the sole responsibility for "Indians, and Lands reserved for the Indians." The government inherited treaty obligations from the British colonial authorities in Eastern Canada
Eastern Canada (also the Eastern provinces or the East) is generally considered to be the region of Canada south of the Hudson Bay/Strait and east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces (from east to west): Newfoundland and Labrador, ...
and signed treaties itself with First Nations in Western Canada
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West or the Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada� ...
(the Numbered Treaties
The Numbered Treaties (or Post-Confederation Treaties) are a series of eleven treaties signed between the First Nations, one of three groups of Indigenous peoples in Canada, and the reigning monarch of Canada (Victoria, Edward VII or George V) ...
). It also passed the ''Indian Act'' in 1876 which governed its interactions with all treaty and non-treaty peoples.
Members of First Nations bands who are subject to the ''Indian Act'' are compiled on a list called the Indian Register
The Indian Register is the official record of people registered under the ''Indian Act'' in Canada, called status Indians or ''registered Indians''. People registered under the ''Indian Act'' have rights and benefits that are not granted to othe ...
, and such people are designated as status Indians. Many non-treaty First Nations and all Inuit and Métis peoples are not subject to the ''Indian Act''. However, two court cases have clarified that Inuit, Métis, and non-status First Nations people, all are covered by the term ''Indians'' in the ''Constitution Act, 1867''. The first was ''Re Eskimos
is a decision by the Supreme Court of Canada regarding the constitutional status of Canada's Inuit, then called " Eskimos." The case concerned section 91(24) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', then the ''British North America Act, 1867'', which a ...
'' in 1939 covering the Inuit, the second being ''Daniels v. Canada
is a case of the Supreme Court of Canada, which ruled that Métis and non-status Indians are "Indians" for the purpose of s 91(24) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867''.
Parties
The plaintiffs were Harry Daniels, a Métis activist from Saskatch ...
'' in 2013 which applies to Métis and non-status First Nations.
History
Paleo-Indian period
archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
and genetic evidence, North and South America
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
were the last continents in the world with human habitation
Habitability refers to the adequacy of an environment for human living. Where housing is concerned, there are generally local ordinances which define habitability. If a residence complies with those laws it is said to be habitable. In extreme e ...
.
During the Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
, 50,000–17,000 years ago, falling sea levels allowed people to move across the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
that joined Siberia to northwest North America (Alaska).
Alaska was ice-free because of low snowfall, allowing a small population to exist. The Laurentide Ice Sheet
The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years a ...
covered most of Canada, blocking nomadic
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the popu ...
inhabitants and confining them to Alaska (East Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
) for thousands of years.
Aboriginal genetic studies suggest that the first inhabitants of the Americas share a single ancestral population, one that developed in isolation, conjectured to be Beringia. The isolation of these peoples in Beringia might have lasted 10,000–20,000 years.
page 2Around 16,500 years ago, the glaciers began melting, allowing people to move south and east into Canada and beyond. The first inhabitants of North America arrived in Canada at least 14,000 years ago. It is believed the inhabitants entered the Americas pursuing
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fina ...
mammals such as the giant beaver, steppe wisent
The steppe bisonSeveral literatures address the species as ''primeval bison''. or steppe wisent (''Bison'' ''priscus'')
– Y ...
, – Y ...
musk ox
Musk (Persian: مشک, ''Mushk'') is a class of aromatic substances commonly used as base notes in perfumery. They include glandular secretions from animals such as the musk deer, numerous plants emitting similar fragrances, and artificial sub ...
, mastodons
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of th ...
, woolly mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived during the Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with '' Mammuthus subp ...
s and ancient reindeer (early caribou). One route hypothesized is that people walked south by way of an ice-free corridor on the east side of the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, and then fanned out across North America before continuing on to South America. The other conjectured route is that they migrated, either on foot or using primitive boats, down the Pacific Coast
Pacific coast may be used to reference any coastline that borders the Pacific Ocean.
Geography Americas
Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western or southwestern border, except for Panama, where the Pac ...
to the tip of South America, and then crossed the Rockies and Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
. Evidence of the latter has been covered by a sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cry ...
of hundreds of metres following the last ice age.
The Old Crow Flats and basin was one of the areas in Canada untouched by glaciations during the Pleistocene Ice ages, thus it served as a pathway and refuge for ice age plants and animals. The area holds evidence of early human habitation in Canada dating from about 12,000. Fossils from the area include some never accounted for in North America, such as hyena
Hyenas, or hyaenas (from Ancient Greek , ), are feliform carnivoran mammals of the family Hyaenidae . With only four extant species (each in its own genus), it is the fifth-smallest family in the Carnivora and one of the smallest in the clas ...
s and large camel
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. C ...
s. Bluefish Caves is an archaeological site in Yukon
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
, Canada from which a specimen of apparently human-worked mammoth bone has been radiocarbon dated to 12,000 years ago.
 Clovis sites dated at 13,500 years ago were discovered in western North America during the 1930s. Clovis peoples were regarded as the first widespread Paleo-Indian inhabitants of the
Clovis sites dated at 13,500 years ago were discovered in western North America during the 1930s. Clovis peoples were regarded as the first widespread Paleo-Indian inhabitants of the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 3 ...
and ancestors to all Indigenous peoples in the Americas. Archaeological discoveries in the past thirty years have brought forward other distinctive knapping
Knapping is the shaping of flint, chert, obsidian, or other conchoidal fracturing stone through the process of lithic reduction to manufacture stone tools, strikers for flintlock firearms, or to produce flat-faced stones for building or facing ...
cultures who occupied the Americas from the lower Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
to the shores of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
.
Localized regional cultures developed from the time of the Younger Dryas
The Younger Dryas (c. 12,900 to 11,700 years BP) was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, c. 27,000 to 20,000 years BP). The Younger Dryas was the last stage ...
cold climate period from 12,900 to 11,500 years ago. The Folsom tradition
The Folsom Complex is a Paleo-Indian archaeological culture that occupied much of central North America from c. 8500 BCE to c. 4000 BCE. The term was first used in 1927 by Jesse Dade Figgins, director of the Colorado Museum of Natural History.
...
are characterized by their use of Folsom point
Folsom points are projectile points associated with the Folsom tradition of North America. The style of tool-making was named after the Folsom site located in Folsom, New Mexico, where the first sample was found in 1908 by George McJunkin within ...
s as projectile tips at archaeological sites. These tools assisted activities at kill sites that marked the slaughter and butchering of bison.
The land bridge existed until 13,000–11,000 years ago, long after the oldest proven human settlements in the New World began. Lower sea levels in the Queen Charlotte sound and Hecate Strait
, image = HecateStrait(PittIsland).JPG
, image_size = 260px
, alt =
, caption = Hecate Strait and Pitt Island
, image_bathymetry = Loc-QCS-Hecate-Dixon.png
, alt_bathymetry =
, caption ...
produced great grass lands called ''archipelago of Haida Gwaii
Haida Gwaii (; hai, X̱aaydag̱a Gwaay.yaay / , literally "Islands of the Haida people") is an archipelago located between off the northern Pacific coast of Canada. The islands are separated from the mainland to the east by the shallow Hecat ...
''.
Hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s of the area left distinctive lithic technology
In archaeology, lithic technology includes a broad array of techniques used to produce usable tools from various types of stone. The earliest stone tools were recovered from modern Ethiopia and were dated to between two-million and three-million ...
tools and the remains of large butchered mammals, occupying the area from 13,000– 9,000 years ago. In July 1992, the Government of Canada officially designated X̱á:ytem (near Mission, British Columbia) as a National Historic Site, one of the first Indigenous spiritual sites in Canada to be formally recognized in this manner.
The Plano cultures
The Plano cultures is a name given by archaeologists to a group of disparate hunter-gatherer communities that occupied the Great Plains area of North America during the Paleo-Indian or Archaic period.
Distinguishing characteristics
The Plano cu ...
was a group of hunter-gatherer communities that occupied the Great Plains area of North America between 12,000 and 10,000 years ago. The Paleo-Indians moved into new territory as it emerged from under the glaciers. Big game flourished in this new environment. The Plano culture are characterized by a range of projectile point tools collectively called Plano point
In archaeology, Plano point is flaked stone projectile points and tools created by the various Plano cultures of the North American Great Plains between 9000 BC and 6000 BC for hunting, and possibly to kill other humans.
They are bifacially worked ...
s, which were used to hunt bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North Ame ...
. Their diets also included pronghorn
The pronghorn (, ) (''Antilocapra americana'') is a species of artiodactyl (even-toed, hoofed) mammal indigenous to interior western and central North America. Though not an antelope, it is known colloquially in North America as the American a ...
, elk
The elk (''Cervus canadensis''), also known as the wapiti, is one of the largest species within the deer family, Cervidae, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central and East Asia. The common ...
, deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the reindeer ...
, raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
and coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecologica ...
. At the beginning of the Archaic Era, they began to adopt a sedentary
Sedentary lifestyle is a lifestyle type, in which one is physically inactive and does little or no physical movement and or exercise. A person living a sedentary lifestyle is often sitting or lying down while engaged in an activity like soci ...
approach to subsistence. Sites in and around Belmont, Nova Scotia
Belmont is a community in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scoti ...
have evidence of Plano-Indians, indicating small seasonal hunting camps, perhaps re-visited over generations from around 11,000–10,000 years ago. Seasonal large and smaller game fish and fowl were food and raw material sources. Adaptation to the harsh environment included tailored clothing and skin-covered tents on wooden frames.
Archaic period
The North American climate stabilized by 8000 Common Era, BCE (10,000 years ago); climatic conditions were very similar to today's. This led to widespread migration, Plant cultivation, cultivation and later a dramatic rise in population all over the Americas. Over the course of thousands of years, Indigenous peoples of the Americas domesticated, bred and cultivated a large array of plant species. These species now constitute 50–60% of all crops in cultivation worldwide. The vastness and variety of Canada's climates, ecology, vegetation, fauna, and landform separations have defined ancient peoples implicitly into cultural or Linguistics, linguistic divisions. Canada is surrounded north, east, and west with coastline and since the last ice age, Canada has consisted of distinct forest regions. Language contributes to the identity of a people by influencing social life ways and spiritual practices. Aboriginal religions developed from anthropomorphism and animism philosophies.
The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status. There is a continuous record of occupation of Stó:lō, S'ólh Téméxw by Aboriginal people dating from the early Holocene period, 10,000–9,000 years ago. Archaeological sites at Stave Lake, Coquitlam Lake, Fort Langley, British Columbia, Fort Langley and region uncovered early period artifacts. These early inhabitants were highly mobile hunter-gatherers, consisting of about 20 to 50 members of an extended family. The Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene people occupied much of the land area of northwest and central North America starting around 8,000 BCE. They were the earliest ancestors of the Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan-speaking peoples, including the Navajo people, Navajo and Apache. They had villages with large multi-family dwellings, used seasonally during the summer, from which they hunted, fished and gathered food supplies for the winter. The Wyandot people, Wendat peoples settled into Southern Ontario along the Eramosa River around 8,000–7,000 BCE (10,000–9,000 years ago). They were concentrated between Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay. Wendat hunted caribou to survive on the glacier-covered land. Many different First Nations cultures relied upon the buffalo starting by 6,000–5,000 BCE (8,000–7,000 years ago). They hunted buffalo by herding migrating buffalo off cliffs. Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump, near Lethbridge, Alberta, is a hunting grounds that was in use for about 5,000 years.
The vastness and variety of Canada's climates, ecology, vegetation, fauna, and landform separations have defined ancient peoples implicitly into cultural or Linguistics, linguistic divisions. Canada is surrounded north, east, and west with coastline and since the last ice age, Canada has consisted of distinct forest regions. Language contributes to the identity of a people by influencing social life ways and spiritual practices. Aboriginal religions developed from anthropomorphism and animism philosophies.
The placement of artifacts and materials within an Archaic burial site indicated social differentiation based upon status. There is a continuous record of occupation of Stó:lō, S'ólh Téméxw by Aboriginal people dating from the early Holocene period, 10,000–9,000 years ago. Archaeological sites at Stave Lake, Coquitlam Lake, Fort Langley, British Columbia, Fort Langley and region uncovered early period artifacts. These early inhabitants were highly mobile hunter-gatherers, consisting of about 20 to 50 members of an extended family. The Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene people occupied much of the land area of northwest and central North America starting around 8,000 BCE. They were the earliest ancestors of the Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan-speaking peoples, including the Navajo people, Navajo and Apache. They had villages with large multi-family dwellings, used seasonally during the summer, from which they hunted, fished and gathered food supplies for the winter. The Wyandot people, Wendat peoples settled into Southern Ontario along the Eramosa River around 8,000–7,000 BCE (10,000–9,000 years ago). They were concentrated between Lake Simcoe and Georgian Bay. Wendat hunted caribou to survive on the glacier-covered land. Many different First Nations cultures relied upon the buffalo starting by 6,000–5,000 BCE (8,000–7,000 years ago). They hunted buffalo by herding migrating buffalo off cliffs. Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump, near Lethbridge, Alberta, is a hunting grounds that was in use for about 5,000 years.
 The west coast of Canada by 7,000–5000 BCE (9,000–7,000 years ago) saw various cultures who organized themselves around salmon fishing. The Nuu-chah-nulth people, Nuu-chah-nulth of Vancouver Island began whaling with advanced long spears at about this time. The Maritime Archaic is one group of North America's Archaic stage, Archaic culture of sea-mammal hunters in the subarctic. They prospered from approximately 7,000 BCE–1,500 BCE (9,000–3,500 years ago) along the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Coast of North America. Their settlements included longhouses and boat-topped temporary or seasonal houses. They engaged in long-distance trade, using as currency white chert, a rock quarried from northern Labrador to Maine. The Pre-Columbian culture, whose members were called Red Paint People, is indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America. The culture flourished between 3,000 BCE – 1,000 BCE (5,000–3,000 years ago) and was named after their burial ceremonies, which used large quantities of red ochre to cover bodies and grave goods.
The Arctic small tool tradition is a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2,500 BCE (4,500 years ago). These Paleo-Arctic tradition, Paleo-Arctic peoples had a highly distinctive toolkit of small blades (Microblade technology, microblades) that were pointed at both ends and used as side- or end-barbs on arrows or spears made of other materials, such as bone or antler. Scraper (archaeology), Scrapers, engraving tools and adze blades were also included in their toolkits. The Arctic small tool tradition branches off into two cultural variants, including the Pre-Dorset, and the Independence II culture, Independence traditions. These two groups, ancestors of Thule people, were displaced by the Inuit by 1000 CE.
The west coast of Canada by 7,000–5000 BCE (9,000–7,000 years ago) saw various cultures who organized themselves around salmon fishing. The Nuu-chah-nulth people, Nuu-chah-nulth of Vancouver Island began whaling with advanced long spears at about this time. The Maritime Archaic is one group of North America's Archaic stage, Archaic culture of sea-mammal hunters in the subarctic. They prospered from approximately 7,000 BCE–1,500 BCE (9,000–3,500 years ago) along the Arctic Ocean, Atlantic Coast of North America. Their settlements included longhouses and boat-topped temporary or seasonal houses. They engaged in long-distance trade, using as currency white chert, a rock quarried from northern Labrador to Maine. The Pre-Columbian culture, whose members were called Red Paint People, is indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America. The culture flourished between 3,000 BCE – 1,000 BCE (5,000–3,000 years ago) and was named after their burial ceremonies, which used large quantities of red ochre to cover bodies and grave goods.
The Arctic small tool tradition is a broad cultural entity that developed along the Alaska Peninsula, around Bristol Bay, and on the eastern shores of the Bering Strait around 2,500 BCE (4,500 years ago). These Paleo-Arctic tradition, Paleo-Arctic peoples had a highly distinctive toolkit of small blades (Microblade technology, microblades) that were pointed at both ends and used as side- or end-barbs on arrows or spears made of other materials, such as bone or antler. Scraper (archaeology), Scrapers, engraving tools and adze blades were also included in their toolkits. The Arctic small tool tradition branches off into two cultural variants, including the Pre-Dorset, and the Independence II culture, Independence traditions. These two groups, ancestors of Thule people, were displaced by the Inuit by 1000 CE.
Post-Archaic periods
The Old Copper complex societies dating from 3,000 BCE – 500 BCE (5,000–2,500 years ago) are a manifestation of the Woodland period, Woodland Culture, and are pre-pottery in nature. Evidence found in the northern Great Lakes regions indicates that they extracted copper from local glacial deposits and used it in its natural form to manufacture tools and implements. The Woodland cultural period dates from about 2,000 BCE – 1,000 CE, and has locales in Ontario, Quebec, and Maritime regions. The introduction of pottery distinguishes the Woodland culture from the earlier Archaic stage inhabitants. Laurentides, Laurentian people of southern Ontario manufactured the oldest pottery excavated to date in Canada. They created pointed-bottom beakers decorated by a cord marking technique that involved impressing tooth implements into wet clay. Woodland technology included items such as beaver incisor knives, bangles, and chisels. The population practising sedentary agricultural life ways continued to increase on a diet of squash, corn, and bean crops. The Hopewell tradition is an Aboriginal culture that flourished along American rivers from 300 BCE – 500 CE. At its greatest extent, the Hopewell Exchange System networked cultures and societies with the peoples on the Canadian shores of Lake Ontario. Canadian expression of the Hopewellian peoples encompasses the Point Peninsula complex, Point Peninsula, Saugeen complex, Saugeen, and Laurel complexes.First Nations
 First Nations peoples had settled and established trade routes across what is now Canada by 500 BCE – 1,000 CE. Communities developed each with its own culture, customs, and character. In the northwest were the Athapaskan, Slavey people, Slavey, Dogrib people, Dogrib, Northern Tutchone, Tutchone, and Tlingit people, Tlingit. Along the Pacific coast were the Tsimshian; Haida; Coast Salish peoples, Salish; Kwakiutl; Heiltsuk; Nuu-chah-nulth, Nootka; Nisga'a; Senakw and Gitxsan. In the plains were the Blackfoot Confederacy, Niisitapi; Kainai Nation, Káínawa; Tsuutʼina Nation, Tsuutʼina; and Piikani Nation, Piikáni. In the northern woodlands were the Cree, Nēhiyawak and Chipewyan. Around the Great Lakes were the Anishinaabe; Algonquin people, Algonquin; Iroquois, Haudenosaunee and Wendat. Along the Atlantic coast were the Beothuk, Maliseet, Wəlastəkwewiyik, Innu, Abenaki and Mi'kmaq.
Many First Nations civilizations established characteristics and hallmarks that included permanent urban settlements or cities, agriculture, civic and Mound builder (people), monumental architecture, and complex society, complex societal hierarchies. These cultures had evolved and changed by the time of the first permanent European arrivals (c. late 15th–early 16th centuries), and have been brought forward through archaeological investigations.
There are indications of contact made before Christopher Columbus between the first peoples and those from other continents. Aboriginal people in Canada first interacted with Europeans around 1000 CE, but prolonged contact came after Europeans established permanent settlements in the 17th and 18th centuries. European written accounts generally recorded friendliness of the First Nations, who profited in trade with Europeans. Such trade generally strengthened the more organized political entities such as the Iroquois Confederation. Throughout the 16th century, European fleets made almost annual visits to the eastern shores of Canada to cultivate the fishing opportunities. A sideline industry emerged in the un-organized Fur trade, traffic of furs overseen by the Indian Department.
Prominent First Nations people include Joe Capilano, who met with King of the United Kingdom, Edward VII, to speak of the need to settle land claims and Ovide Mercredi, a leader at both the Meech Lake Accord constitutional reform discussions and Oka Crisis.
First Nations peoples had settled and established trade routes across what is now Canada by 500 BCE – 1,000 CE. Communities developed each with its own culture, customs, and character. In the northwest were the Athapaskan, Slavey people, Slavey, Dogrib people, Dogrib, Northern Tutchone, Tutchone, and Tlingit people, Tlingit. Along the Pacific coast were the Tsimshian; Haida; Coast Salish peoples, Salish; Kwakiutl; Heiltsuk; Nuu-chah-nulth, Nootka; Nisga'a; Senakw and Gitxsan. In the plains were the Blackfoot Confederacy, Niisitapi; Kainai Nation, Káínawa; Tsuutʼina Nation, Tsuutʼina; and Piikani Nation, Piikáni. In the northern woodlands were the Cree, Nēhiyawak and Chipewyan. Around the Great Lakes were the Anishinaabe; Algonquin people, Algonquin; Iroquois, Haudenosaunee and Wendat. Along the Atlantic coast were the Beothuk, Maliseet, Wəlastəkwewiyik, Innu, Abenaki and Mi'kmaq.
Many First Nations civilizations established characteristics and hallmarks that included permanent urban settlements or cities, agriculture, civic and Mound builder (people), monumental architecture, and complex society, complex societal hierarchies. These cultures had evolved and changed by the time of the first permanent European arrivals (c. late 15th–early 16th centuries), and have been brought forward through archaeological investigations.
There are indications of contact made before Christopher Columbus between the first peoples and those from other continents. Aboriginal people in Canada first interacted with Europeans around 1000 CE, but prolonged contact came after Europeans established permanent settlements in the 17th and 18th centuries. European written accounts generally recorded friendliness of the First Nations, who profited in trade with Europeans. Such trade generally strengthened the more organized political entities such as the Iroquois Confederation. Throughout the 16th century, European fleets made almost annual visits to the eastern shores of Canada to cultivate the fishing opportunities. A sideline industry emerged in the un-organized Fur trade, traffic of furs overseen by the Indian Department.
Prominent First Nations people include Joe Capilano, who met with King of the United Kingdom, Edward VII, to speak of the need to settle land claims and Ovide Mercredi, a leader at both the Meech Lake Accord constitutional reform discussions and Oka Crisis.
Inuit
Inuit are the descendants of what Anthropology, anthropologists call the Thule culture, which emerged from western Alaska around 1,000 CE and spread eastward across the Arctic, displacing the Dorset culture (in Inuktitut, the Tuniit). Inuit historically referred to the Tuniit as "giants", who were taller and stronger than the Inuit. Researchers hypothesize that the Dorset culture lacked dogs, larger weapons and other technologies used by the expanding Inuit society. By 1300, the Inuit had settled in west Greenland, and finally moved into east Greenland over the following century. The Inuit had trade routes with more southern cultures. Boundary disputes were common and led to aggressive actions. Warfare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut (Uummarmiut) who inhabited the Mackenzie River delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, :is:Ívar Bárðarson, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts relate that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling.
After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, the Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid-16th century, Basque people, Basque fishers were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as those excavated at Red Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Red Bay. The Inuit appear not to have interfered with their operations, but they did raid the stations in winter for tools, and particularly worked iron, which they adapted to native needs.
Notable among the Inuit are Abraham Ulrikab and family who became a zoo exhibit in Hamburg, Germany, and Tanya Tagaq, a traditional Inuit throat singing, throat singer. Abe Okpik was instrumental in helping Inuit obtain surnames rather than disc numbers and Kiviaq (person), Kiviaq (David Ward) won the legal right to use his single-word Inuktituk name.
Warfare was common among Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit, such as the Nunatamiut (Uummarmiut) who inhabited the Mackenzie River delta area, often engaged in common warfare. The Central Arctic Inuit lacked the population density to engage in warfare. In the 13th century, the Thule culture began arriving in Greenland from what is now Canada. Norse accounts are scant. Norse-made items from Inuit campsites in Greenland were obtained by either trade or plunder. One account, :is:Ívar Bárðarson, Ívar Bárðarson, speaks of "small people" with whom the Norsemen fought. 14th-century accounts relate that a western settlement, one of the two Norse settlements, was taken over by the Skræling.
After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, the Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid-16th century, Basque people, Basque fishers were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as those excavated at Red Bay, Newfoundland and Labrador, Red Bay. The Inuit appear not to have interfered with their operations, but they did raid the stations in winter for tools, and particularly worked iron, which they adapted to native needs.
Notable among the Inuit are Abraham Ulrikab and family who became a zoo exhibit in Hamburg, Germany, and Tanya Tagaq, a traditional Inuit throat singing, throat singer. Abe Okpik was instrumental in helping Inuit obtain surnames rather than disc numbers and Kiviaq (person), Kiviaq (David Ward) won the legal right to use his single-word Inuktituk name.
Métis
 The Métis are people descended from marriages between Europeans (mainly French) and Cree, Ojibway, Algonquin, Saulteaux, Menominee, Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and other First Nations.
Their history dates to the mid-17th century.
When Europeans first arrived to Canada they relied on Aboriginal peoples for fur trading skills and survival. To ensure alliances, relationships between European fur traders and Aboriginal women were often consolidated through marriage. The Métis homeland consists of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario, as well as the Northwest Territories (NWT).
Amongst notable Métis people are singer and actor Tom Jackson (actor), Tom Jackson, Commissioner of the Northwest Territories Tony Whitford, and Louis Riel who led two resistance movements: the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870 and the North-West Rebellion of 1885, which ended in his Trial of Louis Riel, trial and subsequent execution.
The languages inherently Métis are either Métis French or a mixed language called Michif language, Michif. Michif, Mechif or Métchif is a Pronunciation spelling, phonetic spelling of Métif, a variant of Métis. The Métis today predominantly speak Canadian English, English, with Canadian French, French a strong second language, as well as numerous Indigenous languages of the Americas, Aboriginal tongues. A 19th-century community of the Métis people, the Anglo-Métis, were referred to as Countryborn. They were children of Rupert's Land fur trade typically of Orcadian, Scottish, or English paternal descent and Aboriginal maternal descent. Their first languages would have been Aboriginal (Cree language, Cree, Saulteaux language, Saulteaux, Assiniboine language, Assiniboine, etc.) and English. Their fathers spoke Canadian Gaelic, Gaelic, thus leading to the development of an English dialect referred to as "Bungee language, Bungee".
S.35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' mentions the Métis yet there has long been debate over legally defining the term Métis, but on September 23, 2003, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Métis are a distinct people with significant rights (Powley ruling).
Unlike First Nations people, there has been no distinction between status and non-status Métis; the Métis, their heritage and Aboriginal ancestry have often been absorbed and assimilated into their surrounding populations.
The Métis are people descended from marriages between Europeans (mainly French) and Cree, Ojibway, Algonquin, Saulteaux, Menominee, Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and other First Nations.
Their history dates to the mid-17th century.
When Europeans first arrived to Canada they relied on Aboriginal peoples for fur trading skills and survival. To ensure alliances, relationships between European fur traders and Aboriginal women were often consolidated through marriage. The Métis homeland consists of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario, as well as the Northwest Territories (NWT).
Amongst notable Métis people are singer and actor Tom Jackson (actor), Tom Jackson, Commissioner of the Northwest Territories Tony Whitford, and Louis Riel who led two resistance movements: the Red River Rebellion of 1869–1870 and the North-West Rebellion of 1885, which ended in his Trial of Louis Riel, trial and subsequent execution.
The languages inherently Métis are either Métis French or a mixed language called Michif language, Michif. Michif, Mechif or Métchif is a Pronunciation spelling, phonetic spelling of Métif, a variant of Métis. The Métis today predominantly speak Canadian English, English, with Canadian French, French a strong second language, as well as numerous Indigenous languages of the Americas, Aboriginal tongues. A 19th-century community of the Métis people, the Anglo-Métis, were referred to as Countryborn. They were children of Rupert's Land fur trade typically of Orcadian, Scottish, or English paternal descent and Aboriginal maternal descent. Their first languages would have been Aboriginal (Cree language, Cree, Saulteaux language, Saulteaux, Assiniboine language, Assiniboine, etc.) and English. Their fathers spoke Canadian Gaelic, Gaelic, thus leading to the development of an English dialect referred to as "Bungee language, Bungee".
S.35 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' mentions the Métis yet there has long been debate over legally defining the term Métis, but on September 23, 2003, the Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Métis are a distinct people with significant rights (Powley ruling).
Unlike First Nations people, there has been no distinction between status and non-status Métis; the Métis, their heritage and Aboriginal ancestry have often been absorbed and assimilated into their surrounding populations.
Forced assimilation
From the late 18th century, European Canadians (and the Canadian government) encouraged Cultural assimilation, assimilation of Aboriginal culture into what was referred to as "Culture of Canada, Canadian culture." These attempts reached a climax in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with a series of initiatives that aimed at complete assimilation and subjugation of the Aboriginal peoples. These policies, which were made possible by legislation such as the ''Gradual Civilization Act'' and the ''Indian Act'', focused on European ideals of Christianity, sedentary living, agriculture, and education.Christianization
 Missionary, Missionary work directed at the Aboriginal people of Canada had been ongoing since the first missionaries arrived in the 1600s, generally from France, some of whom were martyred (Jesuit saints called the Canadian Martyrs). Christianization as government policy became more systematic with the ''Indian Act'' in 1876, which would bring new sanctions for those who did not Conversion to Christianity, convert to Christianity. For example, the new laws would prevent non-Christian Aboriginal people from testifying or having their cases heard in court, and ban alcohol consumption. When the ''Indian Act'' was amended in 1884, traditional religious and social practices, such as the Potlatch, would be banned, and further amendments in 1920 would prevent "status Indians" (as defined in the ''Act'') from wearing traditional dress or performing traditional dances in an attempt to stop all non-Christian practices.
Missionary, Missionary work directed at the Aboriginal people of Canada had been ongoing since the first missionaries arrived in the 1600s, generally from France, some of whom were martyred (Jesuit saints called the Canadian Martyrs). Christianization as government policy became more systematic with the ''Indian Act'' in 1876, which would bring new sanctions for those who did not Conversion to Christianity, convert to Christianity. For example, the new laws would prevent non-Christian Aboriginal people from testifying or having their cases heard in court, and ban alcohol consumption. When the ''Indian Act'' was amended in 1884, traditional religious and social practices, such as the Potlatch, would be banned, and further amendments in 1920 would prevent "status Indians" (as defined in the ''Act'') from wearing traditional dress or performing traditional dances in an attempt to stop all non-Christian practices.
Sedentary living, reserves, and 'gradual civilization'
Another focus of the Canadian government was to make the Aboriginal groups of Canada sedentary, as they thought that this would make them easier to assimilate. In the 19th century, the government began to support the creation of model farming villages, which were meant to encourage non-sedentary Aboriginal groups to settle in an area and begin to cultivate agriculture. When most of these model farming villages failed, the government turned instead to the creation of Indian reserves with the ''Indian Act'' of 1876. With the creation of these reserves came many restricting laws, such as further bans on all intoxicants, restrictions on eligibility to vote in band elections, decreased hunting and fishing areas, and inability for status Indians to visit other groups on their reservations. Through the ''Gradual Civilization Act'' in 1857, the government would encourage Indians (i.e., First Nations) to ''enfranchise'' – to ''remove all legal distinctions between [Indians] and Her Majesty's other Canadian Subjects''. If an Aboriginal chose to enfranchise, it would strip them and their family of Aboriginal title, with the idea that they would become "less savage" and "more civilized," thus become assimilated into Canadian society. However, they were often still defined as ''non-citizens'' by Europeans, and those few who did enfranchise were often met with disappointment.Residential system
 The final government strategy of assimilation, made possible by the ''Indian Act'' was the Canadian Indian residential school system, Canadian residential school system:
Beginning in 1847 and lasting until 1996, the Canadian government, in partnership with the dominant Christian Churches, ran 130 residential boarding schools across Canada for Aboriginal children, who were forcibly taken from their homes. While the schools provided some education, they were plagued by under-funding, disease, and abuse.
According to some scholars, the Canadian government's laws and policies, including the residential school system, that encouraged or required Indigenous peoples to Cultural imperialism, assimilate into a Eurocentrism, Eurocentric society, violated the United Nations Genocide Convention that Canada signed in 1949 and passed through Parliament in 1952. Therefore, these scholars believe that Canada could be tried in international court for genocide.
A legal case resulted in settlement of in 2006 and the 2008 establishment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Canada), Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which confirmed the injurious effect on children of this system and turmoil created between Indigenous peoples and non-Indigenous peoples.
In 2008, Prime Minister Stephen Harper issued an apology on behalf of the Canadian government and its citizens for the residential school system.
The final government strategy of assimilation, made possible by the ''Indian Act'' was the Canadian Indian residential school system, Canadian residential school system:
Beginning in 1847 and lasting until 1996, the Canadian government, in partnership with the dominant Christian Churches, ran 130 residential boarding schools across Canada for Aboriginal children, who were forcibly taken from their homes. While the schools provided some education, they were plagued by under-funding, disease, and abuse.
According to some scholars, the Canadian government's laws and policies, including the residential school system, that encouraged or required Indigenous peoples to Cultural imperialism, assimilate into a Eurocentrism, Eurocentric society, violated the United Nations Genocide Convention that Canada signed in 1949 and passed through Parliament in 1952. Therefore, these scholars believe that Canada could be tried in international court for genocide.
A legal case resulted in settlement of in 2006 and the 2008 establishment of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (Canada), Truth and Reconciliation Commission, which confirmed the injurious effect on children of this system and turmoil created between Indigenous peoples and non-Indigenous peoples.
In 2008, Prime Minister Stephen Harper issued an apology on behalf of the Canadian government and its citizens for the residential school system.
Politics, law, and legislation
Indigenous law vs. Aboriginal law
Canadian Indigenous law refers to Indigenous peoples' own legal systems. This includes the laws and legal processes developed by Indigenous groups to govern their relationships, manage their natural resources, and manage conflicts. Indigenous law is developed from a variety of sources and institutions, which differ across legal traditions. Canadian aboriginal law is the area of law related to the Canadian Government's relationship with its Indigenous peoples. Section 91(24) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867'' gives the federal parliament exclusive power to legislate in matters related to Aboriginals, which includes groups governed by the ''Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' (, long name ''An Act to amend and consolidate the laws respecting Indians'') is a Canadian act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still ...
'', different Numbered Treaties
The Numbered Treaties (or Post-Confederation Treaties) are a series of eleven treaties signed between the First Nations, one of three groups of Indigenous peoples in Canada, and the reigning monarch of Canada (Victoria, Edward VII or George V) ...
and outside of those Acts.
Treaties
 The Canadian Crown and Indigenous peoples began Timeline of colonization of North America, interactions during the European colonization period. Many agreements signed before the Confederation of Canada are recognized in Canadian law, such as the Peace and Friendship Treaties, the Robinson Treaties, the Douglas Treaties, and many others. After Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory in 1870, the eleven Numbered treaties were signed between First Nations and Canadian crown, the Crown from 1871 to 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Crown administered by Canadian Aboriginal law and overseen by the Minister of Crown–Indigenous Relations.
In 1973, Canada re-started signing new treaties and agreements with Indigenous peoples to address Indigenous land claims in Canada, their land claims. The first Comprehensive land claim, modern treaty implemented under the new framework was the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement in 1970. The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement of 1993 lead to the creation of the
The Canadian Crown and Indigenous peoples began Timeline of colonization of North America, interactions during the European colonization period. Many agreements signed before the Confederation of Canada are recognized in Canadian law, such as the Peace and Friendship Treaties, the Robinson Treaties, the Douglas Treaties, and many others. After Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land and the North-Western Territory in 1870, the eleven Numbered treaties were signed between First Nations and Canadian crown, the Crown from 1871 to 1921. These treaties are agreements with the Crown administered by Canadian Aboriginal law and overseen by the Minister of Crown–Indigenous Relations.
In 1973, Canada re-started signing new treaties and agreements with Indigenous peoples to address Indigenous land claims in Canada, their land claims. The first Comprehensive land claim, modern treaty implemented under the new framework was the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement in 1970. The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement of 1993 lead to the creation of the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territorie ...
-majority territory of Nunavut later that decade. The Canadian Crown continues to sign new treaties with Indigenous peoples, notably though the British Columbia Treaty Process.
According to the ''First Nations–Federal Crown Political Accord'', "cooperation will be a cornerstone for partnership between Canada and First Nations, wherein ''Canada'' is the short-form reference to Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada. The Supreme Court of Canada argued that treaties "served to reconcile pre-existing Aboriginal sovereignty with assumed Crown sovereignty, and to define Aboriginal rights." First Nations interpreted agreements covered in treaty 8 to last "as long as the sun shines, grass grows and rivers flow." However, the Canadian government has frequently breached the Crown's treaty obligations over the years, and tries to address these issues by negotiating Indigenous specific land claims in Canada, specific land claim.
''Indian Act''
 The ''Indian Act'' is federal legislation that dates from 1876. There have been over 20 major changes made to the act since then, the last time being in 1951; amended in 1985 with Bill C-31. The ''Indian Act'' indicates how reserves and bands can operate and defines who is recognized as an "Indian."
In 1985, the Canadian Parliament passed Bill C-31, ''An Act to Amend the Indian Act''. Because of a constitutional requirement, the bill took effect on 17 April 1985.
* It ends discriminatory provisions of the ''Indian Act'', especially those that discriminated against women.
* It changes the meaning of ''status'' and for the first time allows for limited reinstatement of Indians who were denied or lost status or band membership.
* It allows bands to define their own membership rules.
Those people accepted into band membership under band rules may not be status Indians. C-31 clarified that various sections of the ''Indian Act'' apply to band members. The sections under debate concern community life and land holdings. Sections pertaining to Indians (First Nations peoples) as individuals (in this case, wills and taxation of personal property) were not included.
The ''Indian Act'' is federal legislation that dates from 1876. There have been over 20 major changes made to the act since then, the last time being in 1951; amended in 1985 with Bill C-31. The ''Indian Act'' indicates how reserves and bands can operate and defines who is recognized as an "Indian."
In 1985, the Canadian Parliament passed Bill C-31, ''An Act to Amend the Indian Act''. Because of a constitutional requirement, the bill took effect on 17 April 1985.
* It ends discriminatory provisions of the ''Indian Act'', especially those that discriminated against women.
* It changes the meaning of ''status'' and for the first time allows for limited reinstatement of Indians who were denied or lost status or band membership.
* It allows bands to define their own membership rules.
Those people accepted into band membership under band rules may not be status Indians. C-31 clarified that various sections of the ''Indian Act'' apply to band members. The sections under debate concern community life and land holdings. Sections pertaining to Indians (First Nations peoples) as individuals (in this case, wills and taxation of personal property) were not included.
Royal Commission
Health policy
In 1995, the Government of Canada announced the Aboriginal Right to Self-Government Policy. This policy recognizes that First Nations and Inuit have the constitutional right to shape their own forms of government to suit their particular historical, cultural, political and economic circumstances. The Indian Health Transfer Policy (Canada), Indian Health Transfer Policy provided a framework for the assumption of control of health services by Aboriginal peoples, and set forth a developmental approach to transfer centred on self-determination in health. Through this process, the decision to enter transfer discussions with Health Canada rests with each community. Once involved in transfer, communities can take control of health programme responsibilities at a pace determined by their individual circumstances and health management capabilities. The National Aboriginal Health Organization (NAHO) incorporated in 2000, was an Aboriginal-designed and-controlled not-for-profit body in Canada that worked to influence and advance the health and well-being of Aboriginal Peoples. Its funding was discontinued in 2012.Political organization
First Nations and Inuit organizations ranged in size from Band society, band societies of a few people to multi-nation confederacies like the Iroquois. First Nations leaders from across the country formed the Assembly of First Nations, which began as the National Indian Brotherhood in 1968. The Métis and the Inuit are represented nationally by the Métis National Council and Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami respectively. Today's political organizations have resulted from interaction with European-style methods of government through the Federal Interlocutor for Métis and Non-Status Indians. Indigenous political organizations throughout Canada vary in political standing, viewpoints, and reasons for forming. First Nations, Métis and Inuit negotiate with the Government of Canada through Indian and Northern Affairs Canada in all affairs concerning land, entitlement, and rights. The First Nation groups that operate independently do not belong to these groups.Culture
 Countless Indigenous words, inventions and games have become an everyday part of Spoken languages of Canada, Canadian language and use. The canoe, snowshoes, the toboggan, lacrosse, tug of war, maple syrup and tobacco are just a few of the products, inventions and games. Some of the words include the barbecue, Reindeer, caribou, chipmunk, Groundhog, woodchuck, hammock, skunk, and moose.
List of place names in Canada of aboriginal origin, Many places in Canada, both natural features and human habitations, use Indigenous names. The word ''Canada'' itself derives from the Laurentian language, St. Lawrence Iroquoian word meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. The province of Saskatchewan derives its name from the Saskatchewan River, which in the Cree language is called ''Kisiskatchewani Sipi'', meaning 'swift-flowing river'. ''Ottawa'', the name of Canada's capital city, comes from the Algonquin language term ''adawe'', meaning 'to trade'.
Modern youth groups, such as Scouts Canada and the Girl Guides of Canada, include programs based largely on Indigenous lore, arts and crafts, character building and outdoor camp craft and living.
Aboriginal cultural areas depend upon their ancestors' primary Types of societies, lifeway, or occupation, at the time of European contact. These culture areas correspond closely with geography of Canada, physical and ecological List of regions of Canada, regions of Canada. The Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast were centred around ocean and river fishing; in the interior of British Columbia, hunter-gatherer and river fishing. In both of these areas, the salmon was of chief importance. For the people of the plains, bison hunting was the primary activity. In the taiga, subarctic forest, other species such as the moose were more important. For peoples near the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, Shifting cultivation, shifting agriculture was practised, including the raising of maize, beans, and Squash (plant), squash. While for the Inuit, hunting was the primary source of food with Pinniped, seals the primary component of their diet.
The caribou, fish, other marine mammals and to a lesser extent plants, berries and seaweed are part of the Inuit cuisine, Inuit diet. One of the most noticeable symbols of Inuit culture, the inuksuk is the emblem of the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. ''Inuksuit'' are rock sculptures made by stacking stones; in the shape of a human figure, they are called ''inunnguaq''.
Countless Indigenous words, inventions and games have become an everyday part of Spoken languages of Canada, Canadian language and use. The canoe, snowshoes, the toboggan, lacrosse, tug of war, maple syrup and tobacco are just a few of the products, inventions and games. Some of the words include the barbecue, Reindeer, caribou, chipmunk, Groundhog, woodchuck, hammock, skunk, and moose.
List of place names in Canada of aboriginal origin, Many places in Canada, both natural features and human habitations, use Indigenous names. The word ''Canada'' itself derives from the Laurentian language, St. Lawrence Iroquoian word meaning 'village' or 'settlement'. The province of Saskatchewan derives its name from the Saskatchewan River, which in the Cree language is called ''Kisiskatchewani Sipi'', meaning 'swift-flowing river'. ''Ottawa'', the name of Canada's capital city, comes from the Algonquin language term ''adawe'', meaning 'to trade'.
Modern youth groups, such as Scouts Canada and the Girl Guides of Canada, include programs based largely on Indigenous lore, arts and crafts, character building and outdoor camp craft and living.
Aboriginal cultural areas depend upon their ancestors' primary Types of societies, lifeway, or occupation, at the time of European contact. These culture areas correspond closely with geography of Canada, physical and ecological List of regions of Canada, regions of Canada. The Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast were centred around ocean and river fishing; in the interior of British Columbia, hunter-gatherer and river fishing. In both of these areas, the salmon was of chief importance. For the people of the plains, bison hunting was the primary activity. In the taiga, subarctic forest, other species such as the moose were more important. For peoples near the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, Shifting cultivation, shifting agriculture was practised, including the raising of maize, beans, and Squash (plant), squash. While for the Inuit, hunting was the primary source of food with Pinniped, seals the primary component of their diet.
The caribou, fish, other marine mammals and to a lesser extent plants, berries and seaweed are part of the Inuit cuisine, Inuit diet. One of the most noticeable symbols of Inuit culture, the inuksuk is the emblem of the Vancouver 2010 Winter Olympics. ''Inuksuit'' are rock sculptures made by stacking stones; in the shape of a human figure, they are called ''inunnguaq''.
Languages
There are 13 Spoken languages of Canada#Indigenous languages, Aboriginal language groups, 11 oral and 2 sign language, sign, in Canada, made up of more than 65 distinct dialects. Of these, only Cree, Inuktitut, and Ojibwe language, Ojibwe have a large enough population of fluent speakers to be considered viable to survive in the long term. Two of Canada's territories give official status to native languages. In Nunavut, Inuktitut and Inuinnaqtun are official languages alongside the national languages of English and French, and Inuktitut is a common vehicular language in territorial government. In the Northwest Territories, the ''Official Languages Act (Northwest Territories), Official Languages Act'' declares that there are 11 different languages: Dene Suline language, Chipewyan, Cree, English, French, Gwichʼin language, Gwichʼin, Inuinnaqtun, Inuktitut, Inuvialuktun, North Slavey language, Slavey, South Slavey, and Dogrib language, Tłįchǫ. Besides English and French, these languages are not vehicular in government; official status entitles citizens to receive services in them on request and to deal with the government in them.Visual art

Music
The Aboriginal peoples of Canada encompass diverse ethnic groups with their individual musical traditions. Music is usually social (public) or ceremonial (private). Public, social music may be dance music accompanied by rattle (percussion instrument), rattles and drums. Private, ceremonial music includes vocal songs with accompaniment on percussion, used to mark occasions like Midewivin ceremonies and Sun Dances. Traditionally, Indigenous peoples used the materials at hand to make their instruments for centuries before Europeans immigrated to Canada. First Nations people made gourds and animal Horn (anatomy), horns into rattles, which were elaborately carved and brightly painted. In woodland areas, they made horns of birch bark and Percussion mallet, drumsticks of carved antlers and wood. Traditional percussion instruments such as drums were generally made of carved wood and animal Hide (skin), hides. These musical instruments provide the background for songs, and songs the background for dances. Traditional First Nations people consider song and dance to be sacred. For years after Europeans came to Canada, First Nations people were forbidden to practice their ceremonies.Demography
 There are three (First Nations, Inuit and Métis people (Canada), Métis) distinctive groups of Indigenous peoples that are recognized in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section Twenty-five of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, sections 25 and 35. Under the ''Employment equity (Canada), Employment Equity Act'', Aboriginal people are a designated group along with women, visible minorities, and persons with disabilities; as such, they are neither a visible minority under the ''Act'' or in the view of Statistics Canada.
The Canada 2016 Census, 2016 Canadian Census enumerated 1,673,780 Aboriginal people in Canada, 4.9% of the country's total population.[Aboriginal peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census] This total includes 977,230 First Nations people, 587,545 Métis, and 65,025 Inuit. National representative bodies of Aboriginal people in Canada include the Assembly of First Nations, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, the Métis National Council, the Native Women's Association of Canada, the National Association of Native Friendship Centres, and the Congress of Aboriginal Peoples.
In 2016, Indigenous children ages zero to four accounted for 7.7% of those aged zero to four in Canada, and made up 51.2% of children in this age group living in foster care.
In the 20th century the Aboriginal population of Canada increased tenfold. Between 1900 and 1950 the population grew by 29%. After the 1960s the infant mortality level on reserves dropped dramatically and the population grew by 161%. Since the 1980s the number of First Nations babies more than doubled and currently almost half of the First Nations population is under the age of 25.
Indigenous people assert that their Sovereignty, sovereign rights are valid, and point to the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which is mentioned in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section 25, the ''British North America Acts'' and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, 1969 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (to which Canada is a signatory) in support of this claim.
There are three (First Nations, Inuit and Métis people (Canada), Métis) distinctive groups of Indigenous peoples that are recognized in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section Twenty-five of the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, sections 25 and 35. Under the ''Employment equity (Canada), Employment Equity Act'', Aboriginal people are a designated group along with women, visible minorities, and persons with disabilities; as such, they are neither a visible minority under the ''Act'' or in the view of Statistics Canada.
The Canada 2016 Census, 2016 Canadian Census enumerated 1,673,780 Aboriginal people in Canada, 4.9% of the country's total population.[Aboriginal peoples in Canada: Key results from the 2016 Census] This total includes 977,230 First Nations people, 587,545 Métis, and 65,025 Inuit. National representative bodies of Aboriginal people in Canada include the Assembly of First Nations, the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, the Métis National Council, the Native Women's Association of Canada, the National Association of Native Friendship Centres, and the Congress of Aboriginal Peoples.
In 2016, Indigenous children ages zero to four accounted for 7.7% of those aged zero to four in Canada, and made up 51.2% of children in this age group living in foster care.
In the 20th century the Aboriginal population of Canada increased tenfold. Between 1900 and 1950 the population grew by 29%. After the 1960s the infant mortality level on reserves dropped dramatically and the population grew by 161%. Since the 1980s the number of First Nations babies more than doubled and currently almost half of the First Nations population is under the age of 25.
Indigenous people assert that their Sovereignty, sovereign rights are valid, and point to the Royal Proclamation of 1763, which is mentioned in the Canadian ''Constitution Act, 1982'', Section 25, the ''British North America Acts'' and the Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, 1969 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (to which Canada is a signatory) in support of this claim.
Geographical distribution
Provinces & territories
Ethnography, Ethnographers commonly classify Indigenous peoples of the Americas in the United States and Canada into ten geographical regions, Classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas, cultural areas, with shared cultural traits. The Canadian regions are: *Inuit, Arctic cultural area (Eskimo–Aleut languages) * Subarctic peoples, Subarctic culture area (Na-Dene languages and Algic languages) *Indigenous peoples of the Eastern Woodlands, Eastern Woodlands (Northeast) cultural area (Algic languages and Iroquoian languages) *Plains Indians, Plains cultural area (Siouan–Catawban languages) *Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau, Northwest Plateau cultural area (Salishan languages) *Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, Northwest Coast cultural area (Penutian languages, Tsimshianic languages and Wakashan languages)Urban population
Across Canada, 56% of Indigenous peoples live in urban areas. The urban Indigenous population is the fastest-growing population segment in Canada.See also
* Index of articles related to Indigenous Canadians, Index of articles related to Indigenous peoples living in Canada *Native Americans in the United States * Aboriginal land title in Canada * Settler Colonialism in Canada *Indigenous education in CanadaReferences
Sources
* * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * Leacock, Stephen (2009),The Dawn of Canadian History: A Chronicle of Aboriginal Canada
', Dodo Press * * *
Notes on terminology
External links
Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada Portal
– Government of Canada
Aboriginal Peoples and Communities
– Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada
Aboriginal Heritage Resources and Services
– Library and Archives Canada
Aboriginal Virtual Exhibits
– Virtual Museum of Canada
Battle for Aboriginal Treaty Rights
– Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (Digital Archives)
First Peoples of Canada
– The Canadian Museum of Civilization
– Department of Canadian Heritage
Map of historical territory treaties
– Natural Resources Canada {{DEFAULTSORT:Indigenous Peoples In Canada Indigenous peoples in Canada, Social history of Canada History of indigenous peoples of North America, Canada Hunter-gatherers of Canada