Indian Rivers Inter-link on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Indian Rivers Inter-link is a proposed large-scale civil engineering project that aims to effectively manage
The Interlinking of Indian Rivers: Some Questions on the Scientific, Economic and Environmental Dimensions of the Proposal
IIM Calcutta, IISWBM, Kolkata India accounts for 18% of the world population and about 4% of the world’s water resources. One of the solutions to solve the country’s water woes is to link rivers and lakes. The Inter-link project has been split into three parts: a northern Himalayan rivers inter-link component, a southern Peninsular component and starting 2005, an intrastate rivers linking component. The project is being managed by India's National Water Development Agency
Ministry of Water Resources, Govt of India (2014) However, the projects were not pursued. The river inter-linking idea was revived in 1999, after a new political alliance formed the central government, but this time with a major strategic shift. The proposal was modified to intra-basin development as opposed to inter-basin water transfer.Sharon Gourdji, Carrie Knowlton and Kobi Platt
Indian Inter-linking of Rivers: A Preliminary Evaluation
M.S. Thesis, University of Michigan (May 2005) ;21st century By 2004, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) led by Congress Party was in power, and it resurrected its opposition to the project concept and plans. Social activists campaigned that the project may be disastrous in terms of cost, potential environmental and ecological damage, water table and the dangers inherent with tinkering with nature. The central government of India, from 2005 through 2013, instituted a number of committees, rejected a number of reports, and financed a series of feasibility and impact studies, each with changing environmental law and standards.Koshy & Kanekal
By 2004, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) led by Congress Party was in power, and it resurrected its opposition to the project concept and plans. Social activists campaigned that the project may be disastrous in terms of cost, potential environmental and ecological damage, water table and the dangers inherent with tinkering with nature. The central government of India, from 2005 through 2013, instituted a number of committees, rejected a number of reports, and financed a series of feasibility and impact studies, each with changing environmental law and standards.Koshy & Kanekal
SC revives NDA dream to interlink rivers
LiveMint & The Wall Street Journal (28 February 2012) In February 2012, while disposing a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) lodged in the year 2002, Supreme Court (SC) refused to give any direction for implementation of Rivers Interlinking Project. SC stated that it involves policy decisions which are part of legislative competence of state and central governments. However, SC directed the Ministry of Water Resources to constitute an experts committee, the 'Special Committee on ILR' (SC ILR), to pursue the matter with the governments as no party had pleaded against the implementation of Rivers Interlinking Project.
 ;Drought, floods and shortage of drinking water
India receives about 4,000 cubic kilometers of rain annually, or about 1 million gallons of fresh water ''per person'' every year. However, the precipitation pattern in India varies dramatically across distance and over calendar months. Much of the precipitation in India, about 85%, is received during summer months through monsoons in the Himalayan catchments of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) basin. The northeastern region of the country receives heavy precipitation, in comparison with the northwestern, western and southern parts. The uncertainty of start date of monsoons, sometimes marked by prolonged dry spells and fluctuations in seasonal and annual rainfall is a serious problem for the country. The nation sees cycles of drought years and flood years, with large parts of west and south experiencing more deficits and large variations, resulting in immense hardship particularly the poorest farmers and rural populations. Lack of irrigation water regionally leads to crop failures and farmer suicides. Despite abundant rains during July–September, some regions in other seasons see shortages of drinking water. Some years, the problem temporarily becomes too much rainfall, and weeks of havoc from floods. This excess-scarcity regional disparity and flood-drought cycles have created the need for water resources management. Rivers inter-linking is one proposal to address that need.
;Population and food security
Population increase in India is the other driver of need for river inter-linking. India's population growth rate has been falling, but still continues to increase by about 10 to 15 million people every year. The resulting demand for food must be satisfied with higher yields and better crop security, both of which require adequate irrigation of about 140 million hectares of land. Currently, just a fraction of that land is irrigated, and most irrigation relies on monsoon. River inter-linking is claimed to be a possible means of assured and better irrigation for more farmers, and thus better
;Drought, floods and shortage of drinking water
India receives about 4,000 cubic kilometers of rain annually, or about 1 million gallons of fresh water ''per person'' every year. However, the precipitation pattern in India varies dramatically across distance and over calendar months. Much of the precipitation in India, about 85%, is received during summer months through monsoons in the Himalayan catchments of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) basin. The northeastern region of the country receives heavy precipitation, in comparison with the northwestern, western and southern parts. The uncertainty of start date of monsoons, sometimes marked by prolonged dry spells and fluctuations in seasonal and annual rainfall is a serious problem for the country. The nation sees cycles of drought years and flood years, with large parts of west and south experiencing more deficits and large variations, resulting in immense hardship particularly the poorest farmers and rural populations. Lack of irrigation water regionally leads to crop failures and farmer suicides. Despite abundant rains during July–September, some regions in other seasons see shortages of drinking water. Some years, the problem temporarily becomes too much rainfall, and weeks of havoc from floods. This excess-scarcity regional disparity and flood-drought cycles have created the need for water resources management. Rivers inter-linking is one proposal to address that need.
;Population and food security
Population increase in India is the other driver of need for river inter-linking. India's population growth rate has been falling, but still continues to increase by about 10 to 15 million people every year. The resulting demand for food must be satisfied with higher yields and better crop security, both of which require adequate irrigation of about 140 million hectares of land. Currently, just a fraction of that land is irrigated, and most irrigation relies on monsoon. River inter-linking is claimed to be a possible means of assured and better irrigation for more farmers, and thus better
Economic Impact of Interlinking of Rivers Programme
NCAER, India require significantly improve irrigation network than the current state. The average rainfall in India is about 4,000 billion cubic metre, of which annual surface water flow in India is estimated at 1,869 billion cubic metre. Of this, for topological and other reasons, only about 690 billion cubic metre of the available surface water can be utilised for irrigation, industrial, drinking and ground water replenishment purposes. In other words, about 1,100 billion cubic metre of water is available, on average, every year for irrigation in India. This amount of water is adequate for irrigating 140 million hectares. As of 2007, about 60% of this potential was realized through irrigation network or natural flow of Indian rivers, lakes and adoption of pumps to pull ground water for irrigation. 80% of the water India receives through its annual rains and surface water flow, happens over a 4-month period – June through September. This spatial and time variance in availability of natural water versus year round demand for irrigation, drinking and industrial water creates a demand-supply gap, that only worsens with India's rising population. Proponents claim the answers to India's water problem is to conserve the abundant monsoon water bounty, store it in reservoirs, and use this water in areas which have occasional inadequate rainfall, or are known to be drought-prone or in those times of the year when water supplies become scarce.
Proposed river-linking project of India: a boon or bane to nature
Environmental Geology, February 2007, Volume 51, Issue 8, pp 1361-1376 the authors claim inter-linking of rivers to initially appear to be a costly proposition in ecological, geological, hydrological and economical terms, but in the long run the net benefits coming from it will far outweigh these costs or losses. However, they suggest that there is a lack of an international legal framework for the projects India is proposing. In at least some inter-link projects, neighbouring countries such as Bangladesh may be affected, and international concerns for the project must be negotiated.
/ref> These storages and the interlinks will add nearly 170 million acre feet of water for beneficial uses in India, enabling irrigation over an additional area of 35 million hectares, generation of 40,000 MW capacity hydro power, flood control and other benefits. The total surface water available to India is nearly 1440 million acre feet (1776 billion cubic meters) of which only 220 million acre feet was being used in the year 1979. The rest is neither utilized nor managed, and it causes disastrous floods year after year. Up to 1979, India had built over 600 storage dams with an aggregate capacity of 171 billion cubic meters. These small storages hardly enable a seventh of the water available in the country to be utilized beneficially to its fullest potential. From India-wide perspective, at least 946 billion cubic meters of water flow annually could be utilized in India, power generation capacity added and perennial inland navigation could be provided. Also some benefits of flood control would be achieved. The project claims that the development of the rivers of the sub-continent, each state of India, as well as its international neighbours stand to gain by way of additional irrigation, hydro power generation, navigation and flood control. The project may also contribute to food security to the anticipated population peak of India. The Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna is a major international drainage basin which carries more than 1,000 million acre feet out of total 1440 million acre feet in India. Water is a scarce commodity and several basins such as Cauvery, Yamuna, Sutlej, Ravi and other smaller inter-State/intra-State rivers are short of water. 99 districts of the country are classified as drought prone, an area of about 40 million hectare is prone to recurring floods. The inter-link project is expected to help reduce the scale of this suffering and associated losses. The National Perspective Plan comprised, starting 1980s, of two main components: #Himalayan Rivers Development, and #Peninsular Rivers Development An intrastate component was added in 2005.
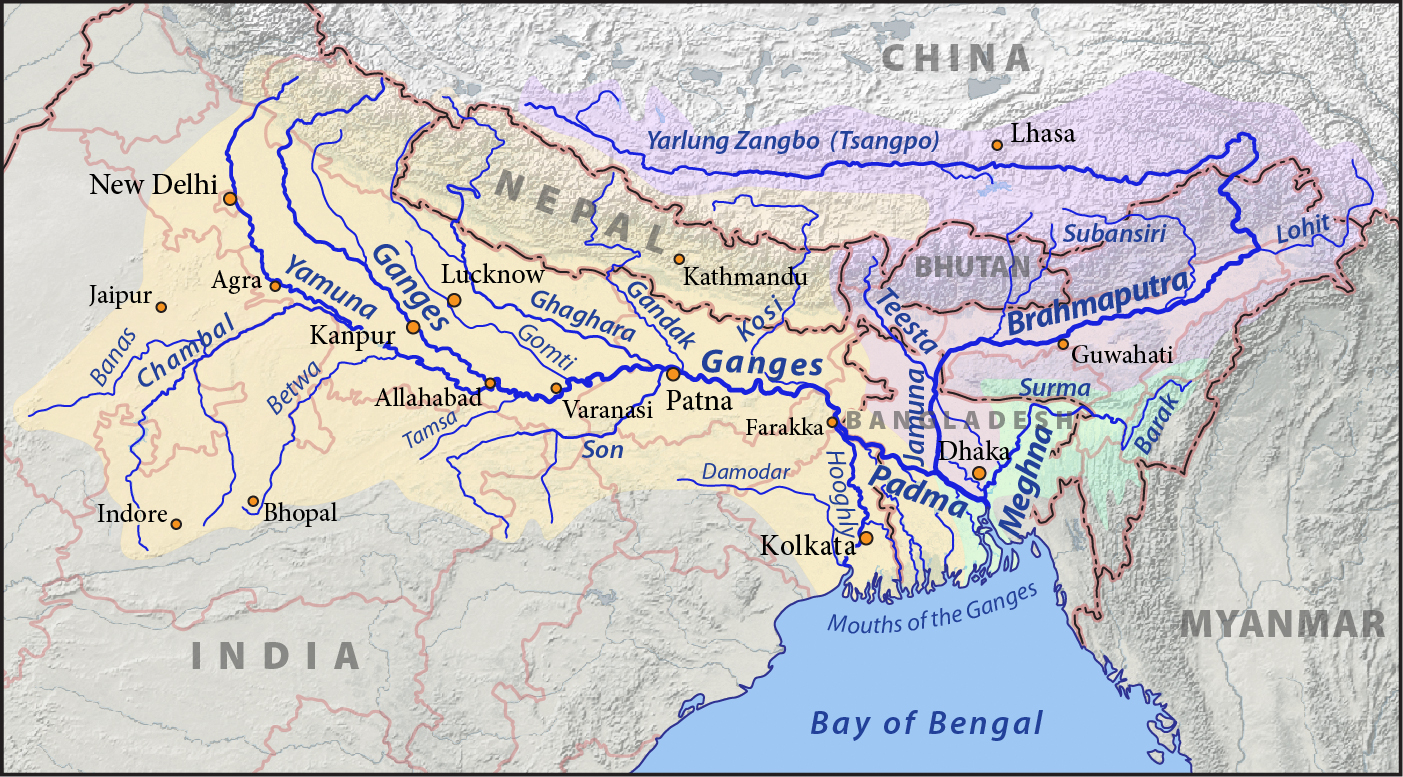 Himalayan Rivers Development envisages construction of storage reservoirs on the main Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their principal tributaries in India and Nepal along with inter-linking canal system to transfer surplus flows of the eastern tributaries of the Ganga to the West apart from linking of the main Brahmaputra with the Ganga. Apart from providing irrigation to an additional area of about 22 million hectares and generating about 30 million kilowatt of hydro-power, it will provide substantial flood control in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. The Scheme will benefit not only the States in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin, but also Nepal and Bangladesh, assuming river flow management treaties are successfully negotiated.
The Himalayan component would consist of a series of dams built along the
Himalayan Rivers Development envisages construction of storage reservoirs on the main Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their principal tributaries in India and Nepal along with inter-linking canal system to transfer surplus flows of the eastern tributaries of the Ganga to the West apart from linking of the main Brahmaputra with the Ganga. Apart from providing irrigation to an additional area of about 22 million hectares and generating about 30 million kilowatt of hydro-power, it will provide substantial flood control in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. The Scheme will benefit not only the States in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin, but also Nepal and Bangladesh, assuming river flow management treaties are successfully negotiated.
The Himalayan component would consist of a series of dams built along the
Govt of India (Accessdate=9 June 2014) Since 2005, NWDA completed feasibility studies on the projects, found 1 project infeasible, 20 projects as feasible, 1 project was withdrawn by Government of Maharashtra, and others are still under study.
Major and medium dams & barrages location map in India
The Guardian's Ravi S Jha writes on the project
BBC report on the Project
BBC Report on Bangladeshi objections
Economic Impact of Interlinking of Rivers Programme
National Water Development Agency official website, Ministry of Water Resources – Government of India
''Anatomy of Interlinking Rivers in India: A Decision in Doubt'', paper by A.C. Shukla and Vandana Asthana
அனைத்து மாநிலங்களும் வளம் பெற தேசிய அதி திறன் நீர்வழிச்சாலை வேண்டும்
தமிழக நதிகளை இணைத்தால் ஆண்டுக்கு ரூ.5,000 கோடி வருமானம்!
நீர்வழி திட்டத்திற்கு முன்னுரிமை கொடுப்போம்!
{{Government Schemes in India Inter-state disputes in India Water disputes in India Geography of India Water management Proposed infrastructure in India Flood control in Asia Environmental engineering Coastal construction Articles containing video clips Ministry of Water Resources (India)
water resources in India Water resources in India includes information on precipitation, surface and groundwater storage and hydropower potential. India experiences an average precipitation of per year, or about of rains annually or about of fresh water ''per person'' ev ...
by linking Indian rivers
This is a list of rivers of India, starting in the west and moving along the Indian coast southward, then northward. Tributary rivers are listed hierarchically in upstream order: the lower in the list, the more upstream.
The overall discharge of r ...
by a network of reservoirs and canals to enhance irrigation and groundwater recharge
Groundwater recharge or deep drainage or deep percolation is a hydrologic process, where water moves downward from surface water to groundwater. Recharge is the primary method through which water enters an aquifer. This process usually occurs in ...
, reduce persistent floods in some parts and water shortages in other parts of India.Jayanta Bandyopadhyay and Shama Perveen (2003)The Interlinking of Indian Rivers: Some Questions on the Scientific, Economic and Environmental Dimensions of the Proposal
IIM Calcutta, IISWBM, Kolkata India accounts for 18% of the world population and about 4% of the world’s water resources. One of the solutions to solve the country’s water woes is to link rivers and lakes. The Inter-link project has been split into three parts: a northern Himalayan rivers inter-link component, a southern Peninsular component and starting 2005, an intrastate rivers linking component. The project is being managed by India's National Water Development Agency
Ministry of Jal Shakti
Ministry of Jal Shakti () is a ministry under Government of India which was formed in May 2019 under the second Modi ministry. This was formed by merging of two ministries; Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation and Min ...
. NWDA has studied and prepared reports on 14 inter-link projects for Himalayan component, 16 inter-link projects for Peninsular component and 37 intrastate river linking projects.
The average rainfall in India is about 4,000 billion cubic metres, but most of India's rainfall comes over a 4-month period – June through September. Furthermore, the rain across the very large nation is not uniform, the east and north gets most of the rain, while the west and south get less. India also sees years of excess monsoons and floods, followed by below average or late monsoons with droughts. This geographical and time variance in availability of natural water versus the year round demand for irrigation, drinking and industrial water creates a demand-supply gap, that has been worsening with India's rising population.
Proponents of the rivers inter-linking projects claim the answers to India's water problem is to conserve the abundant monsoon water bounty, store it in reservoirs, and deliver this water – using rivers inter-linking project – to areas and over times when water becomes scarce. Beyond water security, the project is also seen to offer potential benefits to transport infrastructure through navigation, hydro power as well as to broadening income sources in rural areas through fish farming. Opponents are concerned about well-known environmental, ecological, social displacement impacts as well as unknown risks associated with tinkering with nature. Others are concerned that some projects create international impact and the rights of nations such as Bangladesh must be respected and negotiated.
History
;British colonial era The Inter-linking of Rivers in India proposal has a long history. During the British colonial rule, for example, the 19th century engineerArthur Cotton
General Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton (15 May 1803 – 24 July 1899) was a British general and irrigation engineer.
Cotton devoted his life to the construction of irrigation and navigation canals throughout British India. He helped many people by b ...
proposed the plan to interlink major Indian rivers in order to hasten import and export of goods from its colony in South Asia, as well as to address water shortages and droughts in southeastern India, now Andhra Pradesh and Orissa.
;Post independence
In the 1970s, Dr. K.L. Rao, a dams designer and former irrigation minister proposed "National Water Grid". He was concerned about the severe shortages of water in the South and repetitive flooding in the North every year. He suggested that the Brahmaputra and Ganga basins are water surplus areas, and central and south India as water deficit areas. He proposed that surplus water be diverted to areas of deficit. When Rao made the proposal, several inter-basin transfer projects had already been successfully implemented in India, and Rao suggested that the success be scaled up.A.K. Singh (2003), Interlinking of Rivers in India: A Preliminary Assessment, New Delhi
In 1980, India’s Ministry of Water Resources came out with a report entitled "National Perspectives for Water Resources Development". This report split the water development project in two parts – the Himalayan and Peninsular components. Congress Party came to power and it abandoned the plan. In 1982, India financed and set up a committee of nominated experts, through National Water Development Agency (NWDA) to complete detailed studies, surveys and investigations in respect of reservoirs, canals and all aspects of feasibility of inter-linking Peninsular rivers and related water resource management. NWDA has produced many reports over 30 years, from 1982 through 2013.National Water Development AgencyMinistry of Water Resources, Govt of India (2014) However, the projects were not pursued. The river inter-linking idea was revived in 1999, after a new political alliance formed the central government, but this time with a major strategic shift. The proposal was modified to intra-basin development as opposed to inter-basin water transfer.Sharon Gourdji, Carrie Knowlton and Kobi Platt
Indian Inter-linking of Rivers: A Preliminary Evaluation
M.S. Thesis, University of Michigan (May 2005) ;21st century
 By 2004, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) led by Congress Party was in power, and it resurrected its opposition to the project concept and plans. Social activists campaigned that the project may be disastrous in terms of cost, potential environmental and ecological damage, water table and the dangers inherent with tinkering with nature. The central government of India, from 2005 through 2013, instituted a number of committees, rejected a number of reports, and financed a series of feasibility and impact studies, each with changing environmental law and standards.Koshy & Kanekal
By 2004, the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) led by Congress Party was in power, and it resurrected its opposition to the project concept and plans. Social activists campaigned that the project may be disastrous in terms of cost, potential environmental and ecological damage, water table and the dangers inherent with tinkering with nature. The central government of India, from 2005 through 2013, instituted a number of committees, rejected a number of reports, and financed a series of feasibility and impact studies, each with changing environmental law and standards.Koshy & KanekalSC revives NDA dream to interlink rivers
LiveMint & The Wall Street Journal (28 February 2012) In February 2012, while disposing a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) lodged in the year 2002, Supreme Court (SC) refused to give any direction for implementation of Rivers Interlinking Project. SC stated that it involves policy decisions which are part of legislative competence of state and central governments. However, SC directed the Ministry of Water Resources to constitute an experts committee, the 'Special Committee on ILR' (SC ILR), to pursue the matter with the governments as no party had pleaded against the implementation of Rivers Interlinking Project.
The need
food security
Food security speaks to the availability of food in a country (or geography) and the ability of individuals within that country (geography) to access, afford, and source adequate foodstuffs. According to the United Nations' Committee on World F ...
for a growing population. In a tropical country like India with high evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpi ...
, food security can be achieved with water security which in turn is achieved with energy security to pump water to uplands from water surplus lower elevation river points up to sea level.
;Salt export needs
When sufficient salt export is not taking place from a river basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the ...
to the sea in an attempt to harness the river water fully, it leads to river basin closure, and the available water in downstream area of the river basin closer to the sea becomes saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
and/ or alkaline water
A water ionizer (also known as an alkaline ionizer) is a home appliance which claims to raise the pH of drinking water by using electrolysis to separate the incoming water stream into acidic and alkaline components. The alkaline stream of the trea ...
. Land irrigated with saline or alkaline water gradually turns in to saline
Saline may refer to:
* Saline (medicine), a liquid with salt content to match the human body
* Saline water, non-medicinal salt water
* Saline, a historical term (especially US) for a salt works or saltern
Places
* Saline, Calvados, a commune in ...
or alkali soils. The water percolation in alkali soils is very poor leading to waterlogging problems. Proliferation of alkali soils would compel the farmers to cultivate rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
or grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns and ...
only as the soil productivity is poor with other crops and tree plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. The ...
s. Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
is the preferred crop in saline soils compared to many other crops. Interlinking water surplus rivers with water deficit rivers is needed for the long term sustainable productivity of the river basins and for mitigating the anthropogenic influences on the rivers by allowing adequate salt export to the sea in the form of environmental flow
Environmental flows describe the quantity, timing, and quality of water flows required to sustain freshwater and estuarine ecosystems and the human livelihoods and well being that depend on these ecosystems. In the Indian context river flows requir ...
s.
;Navigation
India needs infrastructure for logistics and movement of freight. Using connected rivers as navigation is a cleaner, low carbon footprint form of transport infrastructure, particularly for ores and food grains.
;Current reserves and loss in groundwater level
India currently stores only 30 days of rainfall, while developed nations strategically store 900 days worth of water demand in arid areas river basins and reservoirs. India’s dam reservoirs store only 200 cubic meters per person. India also relies excessively on groundwater, which accounts for over 50 percent of irrigated area with 20 million tube wells installed. About 15 percent of India’s food is being produced using rapidly depleting groundwater. The end of the era of massive expansion in groundwater use is going to demand greater reliance on surface water supply systems. Proponents of the project suggest India's water situation is already critical, and it needs sustainable development and management of surface water and groundwater usage. Some proponents feel that India is not running out of water but water is running out of India.
Discussion
Costs
The rivers inter-linking feasibility reports completed by 2013, suggest the following investment needs and potential economic impact: #The cost conversion in US $ is at latest conversion price on the historical cost estimates in Indian rupeesEcological and environmental issues
Some activists and scholars have, between 2002 and 2008, questioned the merits of Indian rivers inter-link projects, and questioned if appropriate study of benefits and risks to environment and ecology has been completed so far. Bandyopadhyay et al. claim there are knowledge gaps between the claimed benefits and potential threats from environment and ecological impact. They also question whether the inter-linking project will deliver the benefits offlood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
. Vaidyanathan claimed, in 2003, that there are uncertainty and unknowns about operations, how much water will be shifted and when, whether this may cause water logging, salinity/alkalinity and the resulting desertification in the command areas of these projects. Other scholars have asked whether there are other technologies to address the cycle of droughts and flood havoc's, with less uncertainties about potential environmental and ecological impact. Rivers may change their courses every (approximately) 100 years, so the interlinking may not be useful after 100 years. Interlinking may also lead to deforestation and cause ecological imbalances, widely expected to alter fish communities.
Displacement of people and fisheries profession
Water storage and distributed reservoirs are likely to displace people – a rehabilitation process that has attracted concern of sociologists and political groups. Further, the inter-link would create a path for aquatic ecosystems to be affected by movement of species from one river to another, which in turn may affect the livelihoods of people who rely on specific aquatic species for their income. Lakra et al., in their 2011 study, claim large dams, interbasin transfers and water withdrawal from rivers is likely to have negative as well as positive impacts on freshwater aquatic ecosystem. As regards to the impact on fish and aquatic biodiversity, there could be positive as well as negative impacts.Poverty and population issues
India has a growing population, and large impoverished rural population that relies on monsoon-irrigated agriculture. Weather uncertainties, and potential climate change induced weather volatilities, raise concerns of social stability and impact of floods and droughts on rural poverty. The population of India is expected to grow further at a decelerating pace and stabilize around 1.5 billion by 2050, or another 300 million people – the size of United States – compared to the 2011 census. This will increase demand for reliable sources of food and improved agriculture yields – both of which, claims India's National Council of Applied Economic Research,Suman BeryEconomic Impact of Interlinking of Rivers Programme
NCAER, India require significantly improve irrigation network than the current state. The average rainfall in India is about 4,000 billion cubic metre, of which annual surface water flow in India is estimated at 1,869 billion cubic metre. Of this, for topological and other reasons, only about 690 billion cubic metre of the available surface water can be utilised for irrigation, industrial, drinking and ground water replenishment purposes. In other words, about 1,100 billion cubic metre of water is available, on average, every year for irrigation in India. This amount of water is adequate for irrigating 140 million hectares. As of 2007, about 60% of this potential was realized through irrigation network or natural flow of Indian rivers, lakes and adoption of pumps to pull ground water for irrigation. 80% of the water India receives through its annual rains and surface water flow, happens over a 4-month period – June through September. This spatial and time variance in availability of natural water versus year round demand for irrigation, drinking and industrial water creates a demand-supply gap, that only worsens with India's rising population. Proponents claim the answers to India's water problem is to conserve the abundant monsoon water bounty, store it in reservoirs, and use this water in areas which have occasional inadequate rainfall, or are known to be drought-prone or in those times of the year when water supplies become scarce.
International issues
In a 2007 articleMisra et al.Proposed river-linking project of India: a boon or bane to nature
Environmental Geology, February 2007, Volume 51, Issue 8, pp 1361-1376 the authors claim inter-linking of rivers to initially appear to be a costly proposition in ecological, geological, hydrological and economical terms, but in the long run the net benefits coming from it will far outweigh these costs or losses. However, they suggest that there is a lack of an international legal framework for the projects India is proposing. In at least some inter-link projects, neighbouring countries such as Bangladesh may be affected, and international concerns for the project must be negotiated.
Technological developments
Cost of power generation by solar power projects would be below Rs. 1.0 per Kwh in few years. Availability of cheaper, clean and perennial/renewable power would favour more water lifting/pumping and tunnels in the river link projects rather than purely gravity links to economize on cost, reduce construction time and reduce land submergence by optimum use of existing reservoirs/less storage, etc. Tunnelling technology/methodology has also undergone drastic improvements to make them alternate choice to the gravity open canal links with shortest distance and cost effective manner.Political views
BJP-ledNDA
NDA may stand for:
Military
* National Defence Academy (India), a military academy in India
* National Defence Act, legislation for organizing and funding Canada's military
* National Defense Academy of Japan, a military academy in Japan
* Nig ...
government of Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Atal Bihari Vajpayee (; 25 December 1924 – 16 August 2018) was an Indian politician who served three terms as the 10th prime minister of India, first for a term of 13 days in 1996, then for a period of 13 months fr ...
had propagated the idea of interlinking of rivers to deal with the problem of drought and different parts of the country at the same time.
The Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of a ...
general secretary Rahul Gandhi said in 2009 that the entire idea of interlinking of rivers was dangerous and that he was opposed to interlinking of rivers as it would have "severe" environmental implications. Jairam Ramesh
Jairam Ramesh (born 9 April 1954) is an Indian politician belonging to Indian National Congress. He is a Member of Parliament representing Karnataka state in the Rajya Sabha. In July 2011, Jairam was elevated to the Union Council of Ministers o ...
, a cabinet minister in former UPA government, said the idea of interlinking India's rivers was a "disaster", putting a question mark on the future of the ambitious project.
Karunanidhi
Muthuvel Karunanidhi (3 June 1924 – 7 August 2018) was an Indian writer and politician who served as Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu for almost two decades over five terms between 1969 and 2011. He was popularly referred to as Kalaignar (Art ...
, whose DMK has been a key ally of the Congress-led UPA at the Centre, wrote that linking rivers at the national level perhaps is the only permanent solution to the water scarcity problem in the country. Karunanidhi said the government should make an assessment of the project's feasibility starting with the south-bound rivers. DMK for 2014 general elections added Nationalisation and inter-linking of rivers to its manifesto.
Kalpasar Project
The Kalpasar Project or the Gulf of Khambhat Development Project envisages building a 30 km dam across the Gulf of Khambat in India for establishing a huge fresh water coastal reservoir for irrigation, drinking and industrial purposes. T ...
is an irrigation project which envisages storing Narmada River water in an off-shore fresh water reservoir located in Gulf of Khambhat
The Gulf of Khambhat, historically known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about long, about wide in the north and u ...
sea for further pumping to arid Sourashtra
Saurashtra (Saurashtra script: , Tamil script: சௌராட்டிர மொழி, Devanagari script: सौराष्ट्र भाषा) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken primarily by the Saurashtrians of Southern India who migrated ...
region for irrigation use.
Plan
The National perspective plan envisions about 150 million acre feet (MAF) (185 billion cubic metres) of water storage along with building inter-links.National perspectives for water resources development (accessdate 12 June 2014)/ref> These storages and the interlinks will add nearly 170 million acre feet of water for beneficial uses in India, enabling irrigation over an additional area of 35 million hectares, generation of 40,000 MW capacity hydro power, flood control and other benefits. The total surface water available to India is nearly 1440 million acre feet (1776 billion cubic meters) of which only 220 million acre feet was being used in the year 1979. The rest is neither utilized nor managed, and it causes disastrous floods year after year. Up to 1979, India had built over 600 storage dams with an aggregate capacity of 171 billion cubic meters. These small storages hardly enable a seventh of the water available in the country to be utilized beneficially to its fullest potential. From India-wide perspective, at least 946 billion cubic meters of water flow annually could be utilized in India, power generation capacity added and perennial inland navigation could be provided. Also some benefits of flood control would be achieved. The project claims that the development of the rivers of the sub-continent, each state of India, as well as its international neighbours stand to gain by way of additional irrigation, hydro power generation, navigation and flood control. The project may also contribute to food security to the anticipated population peak of India. The Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna is a major international drainage basin which carries more than 1,000 million acre feet out of total 1440 million acre feet in India. Water is a scarce commodity and several basins such as Cauvery, Yamuna, Sutlej, Ravi and other smaller inter-State/intra-State rivers are short of water. 99 districts of the country are classified as drought prone, an area of about 40 million hectare is prone to recurring floods. The inter-link project is expected to help reduce the scale of this suffering and associated losses. The National Perspective Plan comprised, starting 1980s, of two main components: #Himalayan Rivers Development, and #Peninsular Rivers Development An intrastate component was added in 2005.
Himalayan component
 Himalayan Rivers Development envisages construction of storage reservoirs on the main Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their principal tributaries in India and Nepal along with inter-linking canal system to transfer surplus flows of the eastern tributaries of the Ganga to the West apart from linking of the main Brahmaputra with the Ganga. Apart from providing irrigation to an additional area of about 22 million hectares and generating about 30 million kilowatt of hydro-power, it will provide substantial flood control in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. The Scheme will benefit not only the States in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin, but also Nepal and Bangladesh, assuming river flow management treaties are successfully negotiated.
The Himalayan component would consist of a series of dams built along the
Himalayan Rivers Development envisages construction of storage reservoirs on the main Ganga and the Brahmaputra and their principal tributaries in India and Nepal along with inter-linking canal system to transfer surplus flows of the eastern tributaries of the Ganga to the West apart from linking of the main Brahmaputra with the Ganga. Apart from providing irrigation to an additional area of about 22 million hectares and generating about 30 million kilowatt of hydro-power, it will provide substantial flood control in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. The Scheme will benefit not only the States in the Ganga-Brahmaputra Basin, but also Nepal and Bangladesh, assuming river flow management treaties are successfully negotiated.
The Himalayan component would consist of a series of dams built along the Ganga
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
and Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Tibet, northeast India, and Bangladesh. It is also known as the Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, Luit in Assamese, and Jamuna River in Bangla. It ...
rivers in India, Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne,
सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mai ...
and Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
for the purposes of storage. Canals would be built to transfer surplus water from the eastern tributaries of the Ganga to the west. This is expected to contribute to flood control measures in the Ganga and Brahmaputra river basins. It could also provide excess water for the Farakka Barrage to flush out the silt at the port of Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
.
By 2015, fourteen inter-links under consideration for Himalayan component are as follows, with feasibility study status identified:
Peninsular Component
This Scheme is divided in four major parts. #Interlinking of Mahanadi-Godavari-Krishna-Palar-Pennar-Kaveri, #Interlinking of West Flowing Rivers, North of Mumbai and South of Tapi, #Inter-linking of Ken with Chambal and #Diversion of some water from West Flowing Rivers This component will irrigate an additional 25 million hectares by surface waters, 10 million hectares by increased use of ground waters and generate hydro power, apart from benefits of improved flood control and regional navigation. The main part of the project would send water from the eastern part of India to the south and west. The southern development project (Phase I) would consist of four main parts. First, theMahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay o ...
, Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
. Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery, the anglicized name) is one of the major Indian rivers flowing through the states of Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. The Kaveri river rises at Talakaveri in the Brahmagiri range in the Western Ghats, Kodagu dis ...
rivers would all be inter-linked by canals. Reservoirs and dams would be built along the course of these rivers. These would be used to transfer surplus water from the Mahanadi and Godavari rivers to the south of India. Under Phase II, some rivers that flow west to the north of Mumbai
Mumbai (, ; also known as Bombay — the official name until 1995) is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra and the ''de facto'' financial centre of India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Mumbai is the second- ...
and the south of Tapi would be inter-linked. The water would supply additional drinking water needs of Mumbai and provide irrigation in the coastal areas of Maharashtra
Maharashtra (; , abbr. MH or Maha) is a states and union territories of India, state in the western India, western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. Maharashtra is the List of states and union te ...
. In Phase 3, the Ken and Chambal rivers would be inter-linked to serve regional water needs of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
. Over Phase 4, a number of west-flowing rivers in the Western Ghats, would be inter-linked for irrigation purposes to east flowing rivers such as Kaveri and Krishna.
The 800-km long Mahanadi
The Mahanadi is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around and has a total length of . Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha and finally merged with Bay o ...
-Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
interlinking project would link River Sankosh originating from Bhutan
Bhutan (; dz, འབྲུག་ཡུལ་, Druk Yul ), officially the Kingdom of Bhutan,), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is situated in the Eastern Himalayas, between China in the north and India in the south. A mountainous ...
to the Godavari in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
through rivers like Teesta
Teesta River is a long river that rises in the Pauhunri Mountain of eastern Himalayas, flows through the Indian states of Sikkim and West Bengal through Rangpur, and enters the Bay of Bengal. It drains an area of . In India, it flows through ...
- Mahananda- Subarnarekha and Mahanadi.
The inter-links under consideration for Peninsular component are as follows, with respective status of feasibility studies:
Intra-state inter-linking of rivers
India approved and commissioned NWDA in June 2005 to identify and complete feasibility studies of intra-State projects that would inter-link rivers within that state. The Governments of Nagaland, Meghalaya, Kerala, Punjab, Delhi, Sikkim, Haryana, Union Territories of Puducherry, Andaman & Nicobar islands, Daman & Diu and Lakshadweep responded that they have no intrastate river connecting proposals. Govt. of Puducherry proposed Pennaiyar – Sankarabarani link (even though it is not an intrastate project). The States Government of Bihar proposed 6 inter-linking projects, Maharashtra 20 projects, Gujarat 1 project, Orissa 3 projects, Rajasthan 2 projects, Jharkhand 3 projects and Tamil Nadu proposed 1 inter-linking proposal between rivers inside their respective territories.National water Development Agency (NWDA) StudiesGovt of India (Accessdate=9 June 2014) Since 2005, NWDA completed feasibility studies on the projects, found 1 project infeasible, 20 projects as feasible, 1 project was withdrawn by Government of Maharashtra, and others are still under study.
Progress
On 16 September 2015, first linking was completed of riversKrishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and Godavari
The Godavari ( IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakesh ...
. It is still under review. But it isn't considered as a true river interlinking as it is just a small lift irrigation with few lines of pipes.
Current status
NWDA had drafted Detailed Project Report (DPR) of Godavari-Cauvery link project consisting of three links; Godavari (Inchampalli/Janampet) – Krishna (Nagarjunasagar), Krishna (Nagarjunasagar) – Pennar (Somasila), Pennar (Somasila)-Cauvery (Grand Anicut) link projects which was circulated to involved States in March 2019. The concerns of involved states had been attended in September 2020. ;Key * PFR- Pre Feasibility Report * FR- Feasibility Report * DPR- Detailed Project ReportInternational comparisons
The Indian Rivers Inter-link project is similar in scope and technical challenges as other major global river inter-link projects, such as: # Rhine–Main–Danube Canal – completed in 1992, and also called the Europa Canal, it inter-links theMain
Main may refer to:
Geography
* Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*"Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries
...
river to the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
river, thus connecting North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
and Atlantic Ocean to the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Roma ...
. It provides a navigable artery between the Rhine delta at Rotterdam in the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
to the Danube Delta in eastern Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
. It is 171 km long, has the summit altitude (between the Hilpoltstein and Bachhausen locks) is 406 m above sea level, the highest point on Earth reachable by ships from the sea. In 2010, the inter-link provided navigation for 5.2 million tonnes of goods, mostly food, agriculture, ores and fertilizers, reducing the need for 250,000 truck trips per year. The canal is also a source for irrigation, industrial water and power generation plants.
# Illinois Waterway system consists of 541 kilometres of interlink that connects a system of rivers, lakes, and canals to provide a shipping connection from the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
via the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. It provides a navigation route; primary cargoes are coal to powerplants, chemicals and petroleum upstream, and agriculture produce downstream primarily for export. The Illinois waterway is the principal source of industrial and municipal services water needs along its way; it serves the petroleum refining, pulp and paper processing, metal works, fermentation and distillation, and agricultural products industries.
#Tennessee–Tombigbee Waterway
The Tennessee–Tombigbee Waterway (popularly known as the Tenn-Tom) is a artificial U.S. waterway built in the 20th century from the Tennessee River to the junction of the Black Warrior-Tombigbee River system near Demopolis, Alabama. The Tenn ...
is a 377 kilometre man-made waterway that interlinks the Tennessee River to the Black Warrior-Tombigbee River in the United States. The Tennessee–Tombigbee Waterway links major coal producing regions to coal consuming regions, and serves as commercial navigation for coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
and timber products. Industries that utilize these natural resources have found the Waterway to be their most cost-efficient mode of transportation. The water from the Tenn-Tom Waterway is a major source of industrial water supply, public drinking water supply, and irrigation along its way.
# Gulf Intracoastal Waterway, completed in 1949, interlinks 8 rivers, and is located along the Gulf Coast of the United States. It is a navigable inland waterway running approximately 1700 kilometres from Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
to Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. It is the third busiest waterway in the United States, handling 70 million tonnes of cargo per year, and a major low cost, ecologically friendly and low carbon footprint way to import, export and transport raw materials and products for industrial, chemical and petrochemical industries in the United States. It has also become a significant source for fishing industry as well as for harvesting and shipping shellfish along the coast line of the United States.
#The Central Yunnan Water Diversion Project is a water diversion project from the Jinsha River with 63 tunnels of total length 600 km to the Dianchi Lake in Yunnan province of China. Once this project is completed, it would be world's longest tunnel relegating Delaware Aqueduct
The Delaware Aqueduct is an aqueduct in the New York City water supply system. It takes water from the Rondout, Cannonsville, Neversink, and Pepacton reservoirs on the west bank of the Hudson River through the Chelsea Pump Station, then into ...
tunnel of 137 km to second place.
# Murray–Darling basin, this region in southern Australia with two rivers and associated watercourses was engineered for agriculture and a number of flows were altered over decades with the earliest alterations beginning in 1890. Among the results were changes in seasonal flows causing numerous ecological problems including cyanobacteria blooms killing off fishes, high salinity, acidification, and decline in numerous species of plants and animals. A study of attempts to repair the ecology that began in 2012 were reported as failing in 2017.
Other completed rivers inter-linking projects include the Marne-Rhine Canal in France, the All-American Canal and California State Water Project in the United States, South–North Water Transfer Project
The South–North Water Transfer Project, also translated as the South-to-North Water Diversion Project () is a multi-decade infrastructure mega-project in China. Ultimately it aims to channel 44.8 billion cubic meters of fresh water annually fro ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, etc.
See also
*Environment of India
The environment of India comprises some of the world's most biodiverse
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), ...
** List of rivers by dissolved load
** Pollution of the Ganges
Pollution of the Ganges, the largest river in India, poses significant threats to human health and the larger environment. The river, which is severely polluted with human waste and industrial contaminants, provides water to about 40% of In ...
** Water pollution in India
Water pollution is a major environmental issue in India. The largest source of water pollution in India is untreated
sewage. Other sources of pollution include agricultural runoff and unregulated small-scale industry. Most rivers, lakes and surfa ...
* Irrigation in India
** Ground water in India
** Interstate River Water Disputes Act
** Kalpasar Project
The Kalpasar Project or the Gulf of Khambhat Development Project envisages building a 30 km dam across the Gulf of Khambat in India for establishing a huge fresh water coastal reservoir for irrigation, drinking and industrial purposes. T ...
** Polavaram Project
* List of drainage basins by area
The list of drainage basins by area identifies basins (also known as "catchments" or, in North American usage, "watersheds"), sorted by area, which drain to oceans, mediterranean seas, rivers, lakes and other water bodies. All basins larger than ...
** List of rivers of India by discharge
** List of rivers by discharge
This is a list of rivers by their average discharge (that is, their water flow rate). Here, only those rivers whose discharge is more than are shown, as this list does not concern itself with rivers having a water flow rate of less than .
For c ...
** List of dams and reservoirs in India
* National Water Policy National Water Policy is formulated by the Ministry of Water Resources of the Government of India to govern the planning and development of water resources and their optimum utilization. The first National Water Policy was adopted in September, 198 ...
** Water supply and sanitation in India
India faces challenges ranging from sourcing water for its megacities to its distribution network which is largely intermittent with continuous distribution networks just beginning to emerge. Non-revenue water is a challenge.
The share of Ind ...
** Water scarcity in India
Water scarcity in India is an ongoing water crisis that affects nearly hundreds of million of people each year. In addition to affecting the huge rural and urban population, the water scarcity in India also extensively affects the ecosystem and a ...
* Waterways in India
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary ...
** RORO ferries in India RORO ferry services in India include the following, many others are under implementation or planning phases.
List
Assam
* Majuli island in Brahmaputra River: 2 vessels operate on National Waterway 2 (NW2) by Inland Waterways Authority of Indi ...
** Sagar Mala project
Notes
References
External links
Major and medium dams & barrages location map in India
The Guardian's Ravi S Jha writes on the project
BBC report on the Project
BBC Report on Bangladeshi objections
Economic Impact of Interlinking of Rivers Programme
National Water Development Agency official website, Ministry of Water Resources – Government of India
''Anatomy of Interlinking Rivers in India: A Decision in Doubt'', paper by A.C. Shukla and Vandana Asthana
அனைத்து மாநிலங்களும் வளம் பெற தேசிய அதி திறன் நீர்வழிச்சாலை வேண்டும்
தமிழக நதிகளை இணைத்தால் ஆண்டுக்கு ரூ.5,000 கோடி வருமானம்!
நீர்வழி திட்டத்திற்கு முன்னுரிமை கொடுப்போம்!
{{Government Schemes in India Inter-state disputes in India Water disputes in India Geography of India Water management Proposed infrastructure in India Flood control in Asia Environmental engineering Coastal construction Articles containing video clips Ministry of Water Resources (India)